Abstract
Maintaining sustainable development in semi-arid regions is a complex task due to scarce precipitation, with notable temporal and spatial variations that complicate planning and proper management of water resources. Most of the water extractions from the aquifers in southeast Spain are carried out to supply a growing agricultural sector and increasingly successful tourism, which is the case of the Sierra de Gador-Campo de Dalias system. Savings, reutilization and awareness among water users are essential elements in any sustainable water policy. Some of the possible solutions proposed that offer low environmental impacts include certain infrastructure works, such as dams, ditches or recharge in gravel pits. Also, desalinization plants constitute a technical alternative in theory but involve high costs. The integration of all these resources, together with their proper management, is necessary to ensure the future water supply and economic growth in the region, safeguarding the state of its aquifers that are currently intensely overexploited.
1. Introduction
Arid and semi-arid regions account for 10% of the world’s population, despite representing 30% of the world’s land area [1,2]. This is owing to scarce, and frequently overexploited, water resources that limit socioeconomic development in these regions. Human-made infrastructure attempting to manage surface water resources in response to water scarcity proves ineffective most years due to a lack of precipitation. In these regions, agriculture is the greatest consumer of water, surpassing in some cases 80% of the total demand [3]. For this reason, aquifers have become the main water sources.
Semi-arid regions pose a great deal of uncertainty with respect to the recharge of their aquifers due to the irregularity of precipitation, which tends to be torrential [4,5]. Most conventional infrastructure works, such as surface reservoirs and other storage systems, prove inefficient against the natural evaporation power of the atmosphere, making them unsuitable for satisfying water demands during strong periods of drought. Scarce precipitation, an interannual dry period and considerable intra-annual variation are aspects that influence the hydrology of a region, the organization of flow, and the drainage network. Riverbeds are frequently dry and are commonly used as paths or roads. However, they eventually receive very high peak flows that can be especially destructive, above all in those areas lacking suitable spatial planning. For this and other reasons, exploiting these sporadic flows to recharge aquifers would be of great interest [6].
Both droughts and floods are among the characteristics of semi-arid regions, presenting inherent difficulties for the tasks of planning and management. Droughts favor the practice of indiscriminate drilling and the intensive exploitation of aquifers. During the driest years, infiltration in aquifers is practically non-existent. During wet years and/or heavy rainfall, infiltration can be very high, especially if specific measures are taken.
Water planning in Spain represented a pioneering initiative in the world, creating a model system for managing rivers, with infrastructure dating back to the times of Moorish rule [7] and improved over the centuries. The same cannot be said for groundwater, as this was systematically ignored. From the outset, planning for the exploitation the large basins in semiarid regions in Spain was disastrous, given the immense spatial and temporal variation of river flow volumes. The criteria that dictated water planning throughout most of the 20th century, possibly due to the absence of suitable legislation, were very different from what exists today. Nonetheless, numerous infrastructure constructions made survival and development possible in an environment that is particularly hostile for its dryness.
The Spanish southeast is now far removed from the traditional systems of water supply (e.g., cisterns, waterwheels and galleries), albeit the practice of diverting water from the headwaters of the few existing rivers with continuous water flow and the systems for rainwater harvesting remain throughout the area. The introduction of the technology of mechanical drilling allowed considerable development in the agricultural and tourism sectors, which in turn led to substantial socioeconomic improvement in a traditionally poor region.
Quite often, those in charge of water planning ignored or misinterpreted the role of aquifers and their behavior, or applied principles that were either not respectful towards the environment or not relevant to the hydrological conditions of the southeast. The intensive exploitation of groundwater throughout southeast Spain over the last 60 years has resulted in a general decrease in groundwater levels, the drying of springs, the abandonment of numerous wells and the salinization of soils and water [8,9,10,11]. In the province of Almeria, perennial water flows in its low basin are very scarce, with river mouths remaining dry most of the year and only on few occasions is water discharged to the sea. For these reasons, groundwater has become the main resource to exploit.
The objective of this work is to demonstrate the difficulty of sustainably exploiting the aquifers in semi-arid southeast Spain (Figure 1). For this purpose, we focus on an emblematic example, the Sierra de Gador-Campo de Dalias system, to show the complexity of managing water resources. This system represents the main source of water supply for the most productive fruit and vegetable sector in Europe [12].
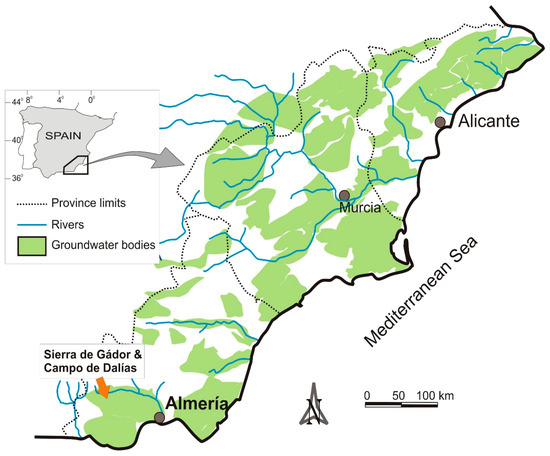
Figure 1.
Schematic map of southeast Spain locating the main rivers and groundwater bodies (modified from [18]).
2. Estimation of Aquifer Recharge
The low availability of water in semi-arid regions is the result of scarce and variable precipitation. The precise calculation of infiltration in aquifers is complex. Without knowing how much water is available, it is difficult to plan its usage with reliable guarantees. There are numerous possible methods for quantifying the recharge in these regions, yet all carry a degree of uncertainty [13,14,15,16]. The classic method applies water balance equation to a specific area and quantifies or estimates the precipitation, the real evapotranspiration (using empirical methods) and the runoff, ultimately obtaining the fraction that infiltrates. It is the most traditionally used method and has been applied as a standard practice working directly with precipitation percentages as estimated recharge, frequently as the only value, without quantifying the uncertainties associated with the method. The mean value assigned to the recharge could have little real significance. In contrast, there are empirical methods, which are more rigorous, using local parameters that are both easy to apply and apparently highly accurate [15,17].
The most sophisticated methods are the ecohydrological models based on satellite images that allow estimating potential recharge, although the real evapotranspiration is what these methods actually estimate [4,19]. The chloride mass balance to estimate potential recharge in transit is another very useful method, applicable in a Geographic Information System (GIS) environment. Numerical simulation models are also widely used as they facilitate determining real recharge in specific cases. In addition, isotopic studies constitute a reliable tool that helps to identify recharge sources and their altitudes, among other aspects [20,21,22]. There are also other highly useful methods that consider land use, vegetation and simulated surface processes through the utilization of remote sensors [23,24].
The potential recharge in mountainous areas in southeast Spain reaches a mean value of 40 ± 15% of measured precipitation, with considerable variation in extreme years (1% to 75%; [25]). This implies that the recharge is negligible in dry years and can be especially significant in wet to very wet years [26]. When outcrop materials in carbonated aquifers include sections with low permeability, most of the runoff tends to infiltrate at the edges whenever a permeable piedmont exists [27]. Such circumstances complicate the application of methods that calculate potential recharge to estimate real recharge. The recharge values obtained through the ERAS code—a unicellular model based on the response of groundwater level versus exploitation and rainfall recharge of overexploited aquifers [28]—are indicative of the problem’s complexity, as values vary between 0% and 45% of the precipitation in small isolated karst aquifers. Therefore, calculating and estimating the hydric balance in aquifers in semi-arid regions involves certain difficulties, yet it is also the basis for sustainable groundwater management.
3. Demand and Availability
Groundwater has been the fundamental pillar of the economic development in southeast Spain. Featuring the climate conditions previously detailed, agricultural activity in this region was traditionally limited to certain privileged locations with access to water by means of the traditional system of diversion channels that directed water from rivers or other sources to specific areas for irrigation purposes.
The demand for agricultural produce and the growth of tourism resulted in an increased need for water, which required the drilling of numerous wells, funded either privately or by government subsidies. This practice of drilling was carried out rather haphazardly at first, without the guidance of any sustainability studies. The most immediate effect was the depletion of the smaller aquifers and the intensive exploitation of the majority of those that remained [29,30]. Following the various problems caused by the depletion of aquifers, timid efforts to conduct studies began with the aim of finding solutions to water scarcity. In general, all these studies were based on satisfying demands by any means necessary, without any concern by planners for the sustainability of the processes to be adopted.
Once the smaller aquifers had been depleted, the solutions that followed involved the importation of external resources (transfers from rivers with “surplus” water). In the mid-1980s and in the 1990s, planners obtained figures that quantified water needs; a portion of water was allocated that would successively recharge overexploited aquifers, requiring the implementation of artificial recharge systems. According to the last edition of the Hydrological Basin Plans for southeast Spain, water demands vastly surpass the natural supply, implying not only issues of quantity but also water quality [31]. These problems are more severe and urgent during dry periods when water transfers cannot be carried out due to a lack of water at the origin and because rainfall contributions are negligible.
Some of the direct negative consequences associated with overexploitation have already been identified: decrease in groundwater levels; subsidence and induced compaction of terrain [32]; aquifer compartmentalization; increased costs of exploitation; deterioration in water quality; well abandonment; induced modifications of river regime; wet regions either dried or adversely affected [33]; and legal problems due to infringement of rights of third parties. Similarly, indirect negative consequences can also be linked to this particular area: damage to infrastructure; salinization of soils [34]; progressive desertification; collapse [35]; and, changes in physical properties of aquifers.
4. The Case of Sierra de Gador-Campo de Dalias
The present work focuses on the emblematic aquifer in the semi-arid region of southeast Spain: the Sierra de Gador-Campo de Dalias system (Figure 2). It is one of the main aquifers in the region and the necessary water resources extracted from it supply one of the most productive horticultural areas in Europe.
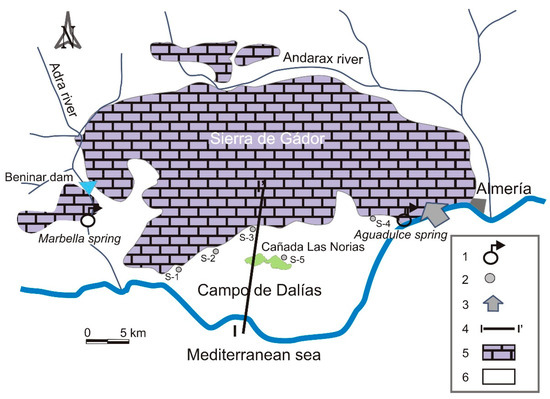
Figure 2.
Hydrogeological schematic map. 1: main springs; 2: boreholes; 3: marine influence; 4: cross-sections (Figure 3); 5: carbonate deposits; 6: Pliocene-Quaternary deposits.
The Sierra de Gador-Campo de Dalias system occupies a land area over 1100 km2. The main aquifer materials in this system are dolomites and dolomitic limestones from the Triassic age, with a thickness that can surpass 1000 m and outcroppings to the North that form the Sierra de Gador [36]. These materials progressively deepen below Neogene and Quartenary deposits in the Campo de Dalias area. The impermeable Neogene materials confine the carbonate aquifer and separate it from a detritic Pliocene-Quatenary aquifer (Figure 3).
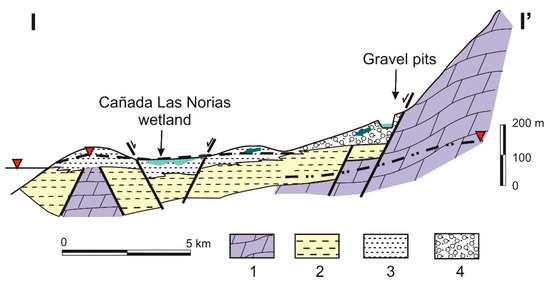
Figure 3.
Schematic cross-section. 1: Carbonate deposits (limestone and dolostone); 2: impermeable materials (marl and silt); Pliocene-Quaternary deposits (3: calcarenite; 4: gravel).
This aquifer originally had two main discharge points. The first, in the interior, the so-called “fuentes de Marbella” (Marbella spring) beside the Adra River to the south of Beninar reservoir. The other one corresponds to a submarine groundwater discharge located in the Aguadulce area, where the carbonate aquifer intersects with the coastline (Figure 2). The intensive exploitation, which began in the 1970s, practically eliminated the freshwater discharges and even generated the inland movement in freshwater-saltwater contact [20]. Consequently, the submarine groundwater discharge in Aguadulce is currently a seawater entry point, constituting one of the greatest risks to water quality in the system [37,38]. On the other hand, the Marbella spring has maintained its water flow, which has even increased considerably as a result of a severe leakage in the Beninar reservoir located upstream from this spring, as a consequence of its permeable base [39].
The annual precipitation values in the Campo de Dalias coastal plain are 280 mm, with maximum values of 600 mm and minimum values of 140 mm. The intra-annual variability is also significant, with values of 0 mm during the dry season and torrential rains that can reach 100 mm/day on occasional rainfall events in autumn. There are inter-annual cycles of 5–6 years, as well as dry and wet cycles. At the height of one of these wet cycles, in the year 2009–2010, despite heavy groundwater pumping in the area, the groundwater levels rose in general [40].
However, the evolution of the groundwater level in this carbonate aquifer has registered changes from −10 m a.s.l. to −40 m a.s.l. in the westernmost sector, as can be observed in the evolution of the groundwater level for sample S-1 (Figure 4). The trends are similar in the central sector but the absolute decrease values are lower (S-2 and S-3), while in the eastern sector (S-4) a recovery of the groundwater level is observed. This is due to less exploitation in the area as a result of salinization—the proximity to the coastline has favored the seawater intrusion in areas like Aguadulce [38] and Balerma [41]. Thus, although the largest decreases took place in the western sector, the eastern area suffers the greatest salinization problem given its better connection to the sea.
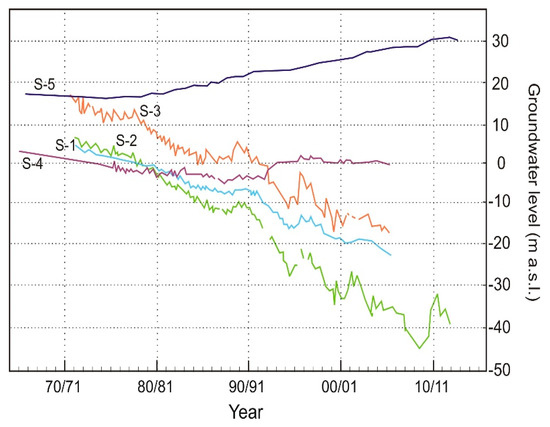
Figure 4.
Hydrographs in some wells in the Campo de Dalías (see location in Figure 2). The selected wells are representatives of different sectors in the study area, allowing to know the groundwater level trends in each sector.
The evolution of the groundwater level in the upper-detritic aquifer displays a slight decrease during the initial decades of exploitation, followed by a progressive increase up to present times (S-5, Figure 4). This trend reflects a deterioration of the water quality in this aquifer, resulting in a considerable reduction in the amounts extracted from it.
Groundwater extractions by means of drilling have rapidly increased from the 1960s to the present. Initially, the upper-detritic aquifer was exploited mainly for its easier accessibility. Thus, the evolution of extractions rose from 10 · 106 m3/year in the 1970s to 45 · 106 m3/year in the 1980s (Figure 5). In the 1990s, the extraction volume in this aquifer fell by 20 · 106–25 · 106 m3/year due to the salinization of its waters as a result of irrigation return flows and soil salinization. This situation led to the search for other water resources, and the lower carbonate aquifer began to be heavily exploited by deep drilling, reaching extraction volumes of up to 120 · 106 m3/year (Figure 5).
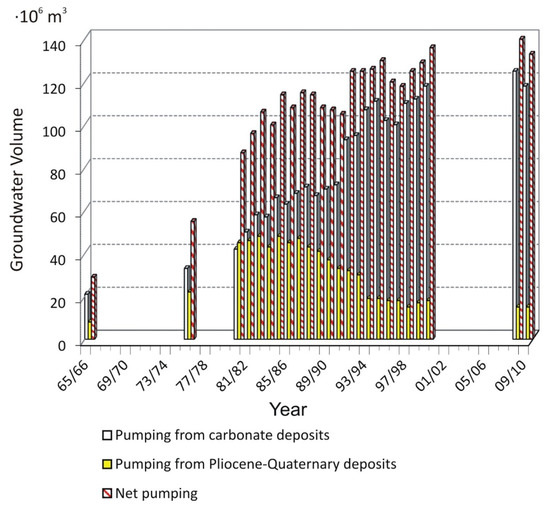
Figure 5.
Evolution of groundwater exploitation (m3) in carbonate and detritic aquifers from 1965 to 2010 (in blank: there is no data).
4.1. La Cañada de las Norias, a Hydrological Uniqueness in a Heavily Exploited Environment
Within this context, a particular wetland of human-made origin proves quite interesting—it is known as La Cañada de las Norias (Figure 2 and Figure 3). This water body is located on what was originally an old clay extraction area that supplied greenhouse construction. The resulting depression in the land from this extraction began to flood at the beginning of the 1990s due to a gradual increase in the groundwater level of the detritic aquifer. Currently, La Cañada de las Norias has become a wetland with a total area of more than 1 km2. It has also flooded a large number of greenhouses, creating a serious problem in the area; the heavy precipitation of 2009–2010 even endangered the homes of the nearby population.
There is a clear relationship between the level of this wetland, which mirrors the local groundwater level, and the rainfall (Figure 6). It is paradoxical that the general increase in the phreatic level is in a heavily exploited area. The reason for this anomalous behavior lies in the suspension of groundwater extraction in the detritic aquifer as a result of the water salinization due to the irrigation return flows from the greenhouse area. These are saline waters rich in nitrates with an average conductivity of 4 mS/cm [42,43]. However, the original formation of this human-made wetland would also be linked to the irrigation return flow of pumping water from the lower carbonate aquifer, which is heavily overexploited and displays levels clearly in decline.
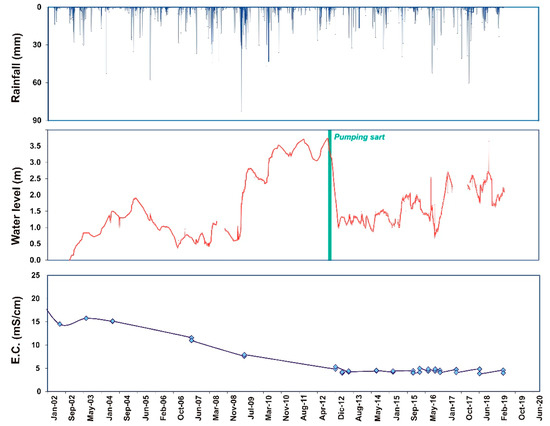
Figure 6.
Evolution of rainfall (mm), water level (m) and electrical conductivity (E.C. in mS/cm) in La Cañada de Las Norias wetland from 2002 to 2019.
This wetland’s water surface gradually rose, with stronger increases in years with greater precipitation, as occurred in the year 2009–2010. This increase posed a risk to infrastructure surrounding the wetland as the water level rose over 3.5 m (Figure 6). Pumping was chosen as the option to mitigate this risk, applying water volumes of up to 690 L/s. These volumes have fluctuated over time according to the need to lower the wetland level. This water is drained directly into the sea. Given the connection between the wetland and the upper aquifer, the volume needed to lower the water surface and eliminate the risk is enormous. As a result, extraction volumes of 6.43 · 106 m3 have been required over four months [42].
Considering the study area is located in a region with low precipitation, subjected to intensive water exploitation, it would seem sensible to attempt to adequately take advantage of this water by mixing it with higher quality water or by means of desalination. Either method could be applied to an amount of water that eliminates the risk of flooding in the area without increasing the maximum storage level, while also guaranteeing and respecting the ecosystem developed around this human-made wetland. Different alternatives have been proposed by ACUAMED, the state agency for water from the Mediterranean Basin, as the construction of a tunnel to evacuate part of the water from the wetland to the sea by gravity [44]. However, the most suitable option is the construction of a desalination plant that reduces the salinity of the water, with the objective of using them for irrigation rather than dumping them into the sea. The alternation between dry and wet periods means water resources are limited to specific periods, which must be taken into account in the sustainable management planning of this area.
4.2. Recharge Induced by Engineering Systems
4.2.1. Check Dams
The southern slope of Sierra de Gador is the main source of water supply for the Campo de Dalias. It comprises 55 small basins with a surface area of between 1 and 54 km2. The main characteristic of its watercourses is their ephemeral nature, remaining dry most of the time. The appearance of runoff in this semiarid environment is associated with river flooding—in some cases up to 80% of total annual precipitation can occur in a single event, involving tremendous erosive power. Thus, more than 100 check dams (solid-concrete dams, gabions and masonry dams) are distributed along this slope. Approximately 60% of these dams are located on permeable rock (limestone and/or dolomites), characterized by its high infiltration capacity. What is more, infiltration is not only induced by these human-made structures, but it is also the consequence of losses due to transmission in the riverbeds themselves.
A study was conducted to analyze those basins with dams which indicate that nearly 60% of the volume drained infiltrates riverbeds, in which cases this volume is conditioned by the permeability of their materials and dimensions (Figure 7). The lowest sections register the greatest losses due to transmission and, therefore, the greatest infiltration, as the most permeable materials are common at these points (substantial thickness of alluvial sediment); 20% of runoff infiltrates directly in the reservoir of the dam when it is located above permeable bedrock.
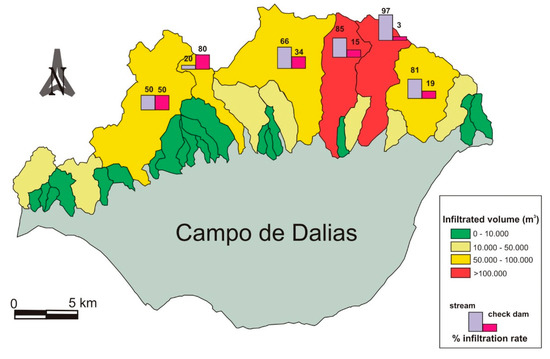
Figure 7.
Watershed classification according to the total volume infiltrated. Bars represent the infiltration rate (%) in check dams and streams at the main sub-basins.
4.2.2. Gravel Pits
The cultivation system in the Campo de Dalias area is based on greenhouses that require silty-clay and gravel which are obtained from a series of pits excavated in the distal parts of the alluvial fans in Sierra de Gador. The volume of material extracted (basically lutites), is in the order of 8 · 106 m3, giving an idea of their importance [45]. Moreover, extensive extractive activities have also been carried out in the apical parts of the alluvial fans for construction purposes. This practice has left large pits, which can fill with water during flooding. Given the high transmissivity of these materials, a high percentage of this water infiltrates, converting these gravel pits into very efficient vehicles for the infiltration of surface runoff.
4.3. Desalination and Wastewater Reuse
The prevailing need for water to satisfy all the demands of the Campo de Dalias agricultural system has made it necessary to seek out new water sources. Most notable among these is the desalination of seawater.
Given the geographic characteristics of the Campo de Dalias, a coastal plain with maximum levels of 150 m above sea level, desalination is a strategic and ideal source to compensate for water deficit. The most important drawback of this freshwater production system is the costs of the energy demands it requires. However, plastic-covered agriculture practiced in the Campo de Dalias is an intensive system with high economic profits, meaning it could afford the costly price per cubic meter of desalinated water (0.6 €/m3) against lower priced well water (0.25 €/m3) [46].
In 2014, construction of the desalination plant in Campo de Dalias finished, allowing the desalination of 97,200 m3/day with a capacity of 30 · 106 m3/year. This volume is used to supply 300,000 inhabitants and for the irrigation of 8000 hectares of greenhouses in the area. In this system, water intake occurs via a submarine pipe whose point of entry is located 1200 m from the coastline and at 14 m depth. This plant uses an inverse osmosis process and also features a second phase of inverse osmosis to reduce the boron concentration to below 0.5 mg/L, for possible use in irrigation. Once desalinated, the water is pumped to a storage tank located 310 m above sea level, from where it is then distributed by gravity throughout the entire Campo de Dalias plain [47]. The resulting brine from the osmosis process is evacuated through a 2 km-long outlet into the sea.
It is worth mentioning the existence of another desalination plant, in the city of Almeria, about 50 km away. This plant is not used to directly fulfill the water demands of the Campo de Dalias, yet it does so indirectly. Traditionally, water needed to supply the city of Almeria (Figure 1) was obtained from a series of wells that collect from the lower carbonate aquifer in Campo de Dalias. As a result of the opening of the Almeria Desalination Plant, some of these extractions are no longer necessary, meaning the aquifer system has increased 5 · 106 m3/year overall. Currently, there are plans by ACUAMED, state agency for water from the Mediterranean Basin, to reduce pumping from the wells in the Campo de Dalias by 20% thanks to the increase in production of desalinated water.
In addition to desalination, the treated urban wastewater would also be another water resource. In the Campo de Dalias, there are three main wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) located in the largest towns in the area that collectively reach a total population of 200,000 inhabitants. A portion of this water is used for irrigation [46].
5. Discussion
Semi-arid regions have serious problems in maintaining sustainable economic development. The scarcity of water is possibly the greatest limiting factor. Not only can the traditional use of water be an enemy to sustainability, but also disinformation and the administration’s failure to apply clear criteria when managing resources. Experience has shown that the best option is carrying out small infrastructure works which, without large economic investments, greatly benefit the management of water resources in the area. The design of these works, when done properly, can obtain significant results at a very low environmental cost (Figure 8). Similarly, if there is true interest in conducting serious initiatives in this regard, it seems crucial that in-depth hydroeconomic studies be conducted to adequately quantify the actual costs involved in the said actions. However, based on the fact that the greatest consumer of water is agriculture, the more this sector does to contribute to water savings, the improvement of irrigation efficiency and the reutilization of treated wastewater, the more progress will be made towards improving management of the scarce water resources available.
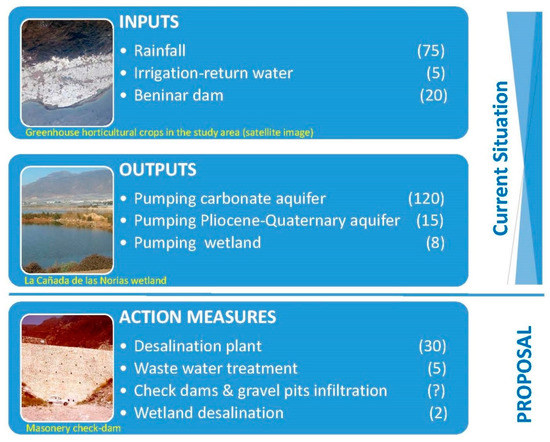
Figure 8.
Current and future water management plan in the study area. The figures in brackets are the approximate values · 106 m3/year of the main parameters in the water budget.
In addition to the proposals previously mentioned to address the problem of water supply, there are also other actions whose objective is to make use of runoff water, particularly that generated by heavy rainfall, which would also reduce the risk of damage caused by high flow volumes that occur during these events [48,49]. The elements that need to be considered in this case would be rainfall in terms of quantity and intensity, terrain characteristics, check dams built in riverbeds and numerous pits from gravel extraction quarries, as well as any reservoirs and ditches that may also be built.
Furthermore, the study of abandoned mining shafts could be of interest, considering Sierra de Gador in the 19th century was an important mining district for the extraction of lead and other metals and, subsequently, fluoride. There could be more than 1000 mining shafts throughout the entire mountain range. These shafts could serve as sinkholes for the infiltration of surface water by carrying out small interventions, which would help to channel water along the basin slope to these points. This solution would be a simple and ideal way to recharge the highly exploited lower aquifer in the Campo de Dalias. Despite the great number of mining shafts, the ore deposits are widely disseminated in the carbonate material, which act as a buffer neutralizing the acidification of the groundwater. In fact, the pH values and the metal concentrations of the groundwater in this carbonate aquifer do not show significant values that could make it impossible to use these waters for human consumption. Only in the most important mining area, some ions linked to mineralization exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) maximum recommended value for drinking water [50,51].
The construction of large desalination plants, which represent an almost definitive solution from a technical point of view, carries the problem of the real production cost of this type of system [52]. Many growers are not willing to pay its price. However, coordination between city use of desalinated water and the subsequent use of treated wastewater in agriculture would make it possible to increase water availability and to decrease current pumping activity, thereby mitigating the negative effects already caused. In short, progress would be made towards sustainability.
Water transfers from other nearby basins must not be discounted, given that the conditions are appropriate. For example, this would logically not make sense if costs surpassed those of desalinated seawater. Ultimately, however, any decision made should be supported by detailed feasibility studies, with the participation of all sectors involved and all parties affected, in which sustainability and environmental conservation are adequately evaluated parameters.
However, the greatest challenge is successfully applying the dynamic principles of sustainable management in a deteriorating environment, while respecting and recovering ecosystems without infringing upon the legitimate right of citizens to enjoy a healthy environment. Such efforts must include the active participation of all parties affected, maintaining absolute transparency and complying with regulations and the agreements with the European Union.
A great deal of uncertainty associated with planning in these regions must be replaced by the acquisition of in-depth knowledge on ecosystem services. Some of the actions that could be undertaken include researching and producing procedures and methods that more accurately quantify such important elements as aquifer recharge and its spatial and time variations. Other actions include densifying and improving the efficiency of observation and registration networks of basic parameters related to water quantity and quality [53]. Finally, it would be useful to further investigate the practice of combining surface water and groundwater, attempting to apply the adequate specific weight to an aquifer as natural infrastructure that is not always properly understood or optimally used [54].
Finally, awareness must be increased regarding the availability of a wide range of technologies and methods [55,56] that help to successfully address most of the problems related to water quantity and quality. However, it should also be taken into account that these solutions are costly and require payment. Raising awareness about all these factors and actively educating on these principles would contribute to a general solution to the problems in this area. Given the severe state of overexploitation of the main aquifers in the region, and the growing need for water, all the measures must be carried out in the immediate time frame. For this, a collaboration among the state, regional and local water management agencies is necessary.
6. Conclusions
The water supply scheme in Campo de Dalias is not sustainable with the current approaches in force, which could collapse the production system unless the proper changes are made. Water savings and treated wastewater reuse are two of the essential solutions required, yet they are not enough.
Nonetheless, other steps should also be considered to establish sustainable management of water resources in semi-arid areas. It is necessary to conduct in-depth analyses in this study area, as each location can present different alternatives. Desalination may provide tangible benefits over inter-basin transfers as a means of solving water deficits. In the case of the Sierra de Gador-Campo de Dalias system, there is also the possibility of conducting artificial recharge by means of small water infrastructure, such as check dams, gravel pits and mining shafts, without discounting the desalination of water from the La Cañada de las Norias wetland. An evaluation of groundwater management strategies needs to involve consideration of surface water resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P.-B.; methodology, A.V., F.S. and L.M.; formal analysis, F.S. and L.M.; writing−original draft preparation, A.P.-B., A.V., F.S. and L.M.; writing−review and editing, A.V. and F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work is part of the general research lines promoted by the CEI-MAR Campus of International Excellence, and it was supported by MICINN through Project PID2019-108832GB-I00.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dregne, H.E. Global status of desertification. Ann. Arid Zone 1991, 30, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Keese, K.E.; Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E.; Gaye, C.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Simmers, I. Global synthesis of groundwater recharge in semiarid and arid regions. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3335–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Water for a Sustainable World. Facts and figures; The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, S.; Boer, M.M.; Alcalá, F.J.; Domingo, F.; García, M.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Puigdefábregas, J. An ecohydrological modelling approach for assessing long-term recharge rates in semiarid karstic landscapes. J. Hydrol. 2008, 351, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, J.M.; Alcalá, F.J.; Vallejos, A.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Recharge to mountainous carbonated aquifers in SE Spain: Different approaches and new challenges. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuma, H.; Bruggeman, A.; Camera, C.; Eliades, M.; Kostarelos, K. The Impact of a Check Dam on Groundwater Recharge and Sedimentation in an Ephemeral Stream. Water 2017, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Rosillo, S.; Ruiz-Constán, A.; González-Ramón, A.; Mediavilla, R.; Martín-Civantos, J.M.; Martínez-Moreno, F.J.; Jódar, J.; Martín-Lechado, C.; Medialdea, A.; Galindo-Zaldivar, J. The oldest managed aquifer recharge system in Europe: New insights from the Espino recharge channel (Sierra Nevada, southern Spain). J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rosales, W.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, A.; Gisbert, J.; Andreu, J.M.; Sánchez-Martos, F. Hydrological implications of desertification in Southeastern Spain. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 1146–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, A.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Daniele, L.; Martín Rosales, W. The intensive exploitation of aquifers and its implications for sustainable water management in a semi-arid zone (Almeria, SE Spain). In Proceedings of the IAHR International Groundwater Symposium. Estambul, Istanbul, Turkey, 18–20 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, E. Aspectos Hidrológicos, Ambientales, Económicos, Sociales y Éticos del Consumo de Reservas de Agua Subterránea en España: Minería del Agua Subterránea en España. UPC-Aqualogy; Iniciativa Digital Politècnica, Oficina de Publicacions Acadèmiques Digitals de la UPC: Barcelona, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, E. Salinización de las Aguas Subterráneas en los Acuíferos Costeros Mediterráneos e Insulares Españoles. Proyecto SASMIE; UPC-CETAQUA: Barcelona, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Valenciano, J.; de Uribe-Toril, P.; Milán-García, J.; Ruiz-Real, J.L.; Torres Arriaza, J.A. Auxiliary Companies of the horticultural sector as a competitiveness element: The case of Almeria (Spain). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Healy, R.W.; Cook, P.G. Choosing appropriate techniques for quantifying groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E.; Kwicklis, E.M.; Fabryka-Martin, J.T.; Bodvarsson, G.S. Estimating recharge at Yucca Mountain, Nevada, USA: Comparison of methods. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo, B.; Vías, J.; Durán, J.J.; Jiménez, P.; López-Geta, J.A.; Carrasco, F. Methodology for groundwater recharge assessment in carbonate aquifers: Application to pilot sites in southern Spain. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, F.J.; Custodio, E. Natural uncertainty of spatial average aquifer recharge through atmospheric chloride mass balance in continental Spain. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 642–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, J. Evaluación de la recarga por la lluvia mediante balances de agua: Utilización, calibración e incertidumbres. Boletín Geológico Minero 1998, 109, 31–54. [Google Scholar]
- Custodio, E.; Andreu-Rodes, J.M.; Aragón, R.; Estrela, T.; Ferrer, J.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Manzano, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, L.; Sahuquillo, A.; del Villar, A. Groundwater intensive use and mining in south-eastern peninsular Spain: Hydrogeological, economic and social aspects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Contreras, S.; Solé-Benet, A.; Cantón, Y.; Domingo, F.; Lázaro, R.; Lin, H.; Van Wesemael, B.; Puigdefábregas, J. Controls of infiltration–runoff processes in Mediterranean karst rangelands in SE Spain. Catena 2011, 86, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, A.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Martin-Rosales, W.; Calvache, M.L. Contribution of environmental isotopes to the understanding of complex hydrologic systems. A case study: Sierra de Gador, SE Spain. Earth Surf. Process. Landform. 1997, 22, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M. Palaeowaters in European coastal aquifers. The goals and main conclusions of the PALAEAUX project. Geol. Soc. Lond. Special Publ. 2001, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Puga, M.A.; Vallejos, A.; Sola, F.; Daniele, L.; Molina, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Groundwater flow and residence time in a karst aquifer using ion and isotope characterization. Int. J. Envir. Sci. Technol. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2579–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, J.; Bonet, A.; Peña, J.; Sánchez, J.R. Human impacts on land cover and water balances in a coastal Mediterranean county. Environ. Manag. 2007, 39, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frot, E.; Van Wesemael, B. Predicting runoff from semi-arid hillslopes as source areas for water harvesting in the Sierra de Gador, southeast Spain. Catena 2009, 79, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, Y.; Villagarcía, L.; Moro, M.J.; Serrano-Ortíz, P.; Were, A.; Alcalá, F.J.; Kowalski, A.S.; Solé-Benet, A.; Lázaro, R.; Domingo, F. Temporal dynamics of soil water balance components in a karst range in southeastern Spain: Estimation of potential recharge. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alcalá, F.J.; Cantón, Y.; Contreras, S.; Were, A.; Serrano-Ortiz, P.; Puigdefábregas, J.; Solé-Benet, A.; Custodio, E.; Domingo, F. Diffuse concentrated recharge evaluation using physical and tracer techniques: Results from a semiarid carbonate massif aquifer in southeastern Spain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rosales, W.; Gisbert, J.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, A.; Fernández-Cortés, A. Estimating groundwater recharge induced by engineering systems in a semiarid area (southeastern Spain). Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, J.M.; Roncero, F.J. Natural recharge and simulation of the management using the model “ERAS”. Application to the Penarrubia aquifer (Alicante). Boletín Geológico Minero 2005, 116, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Estrella, T. The problems of overexploitation of aquifers in semi-arid areas: The Murcia Region and the Segura Basin (South-east Spain) case. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 5729–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos, A.; Andreu, J.M.; Sola, F.; Pulido-Bosch, A. The anthropogenic impact on Mediterranean karst 607 aquifers: Cases of some Spanish aquifers. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JUNTA DE ANDALUCÍA. Proyecto de Plan Hidrológico de la Demarcación Hidrográfica de las Cuencas Mediterráneas Andaluzas. CMA; Agencia Andaluza del Agua: Andalucia, Spain, 2011; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Mulas, J.; Aragón, R.; Martínez, M.; Lambán, J.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Fernández-Grillo, A.I.; Hornero, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Rodríguez, J.M. Geotechnical and hydrogeological analysis of land subsidence in Murcia (Spain). RMZ Mater. Geoenviron. 2002, 50, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Robledano, F.; Esteve, M.A.; Farinós, P.; Carreño, M.F.; Martínez-Fernández, J. Terrestrial birds as indicators of agricultural induced changes and associated loss in conservation value of Mediterranean wetlands. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martos, F.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Molina, L.; Vallejos, A. Identification of the origin of salinization in groundwater using minor ions (Lower Andarax, Southeast Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 297, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Bosch, A.; Delgado, J.; Sola, F.; Vallejos, A.; Vicente, F.; López-Sánchez, J.M.; Mallorquí, J.J. Identification of potential subsidence related to pumping in the Almería basin (SE Spain). Hydrol. Process. 2011, 26, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rojas, I. Las Unidades Internas del Sector de la Sierra de Gádor: Estructura y Evolución Geodinámica. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Alicante, Alicante, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Puga, M.A.; Vallejos, A.; Daniele, L.; Sola, F.; Rodríguez-Delgado, D.; Molina, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. An oceanographic survey for the detection of a possible submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone of Campo de Dalias, SE Spain. In Advances in the Research of Aquatic Environment, Proceedings of the 9th International Hydrogeological Congress, Kalavrita, Grecia, 5–8 October 2011; Lambrakis, N., Stournaras, G., Katsanou, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Daniele, L.; Vallejos, A.; Corbella, M.; Molina, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Geochemical simulations to assess water–rock interactions in complex carbonate aquifers: The case of Aguadulce (SE Spain). Appl. Geochem. 2013, 29, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, S.; Benavente, J.; Cruz-Sanjulián, J.J.; Olías, M. Conjunctive use of water resources as an alternative to a leaky reservoir in a mountainous, semiarid area (Adra River basin, SE Spain). Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Puga, M.A. Caracterización Hidrogeológica e Hidrogeoquímica del Extremo Occidental de la Sierra de Gádor y Acuíferos Cercanos. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Almería, Almería, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejos, A.; Daniele, L.; Sola, F.; Molina, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Anthropic-induced salinization in a dolomite coastal aquifer. Hydrogeochemical processes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 209, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, L.; Sánchez-Martos, F.; Daniele, D.; Vallejos, A.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Interaction of aquifer-wetland in a zone of intensive agriculture: The case of Campo de Dalías (Almería, SE Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, A.; Molina, L.; Llop, A.; MacDonald, A.M. Impact of irrigated agriculture on groundwater-recharge salinity: A major sustainability concern in semi-arid regions. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACUAMED. Pliego de Cláusulas Reguladoras de la Contratación del Servicio de Ingeniería para la Redacción del Proyecto CONSTRUCTIVO “Tunel de Desagüe de la Balsa del Sapo (Almería)”; Technical report. 103; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Bosch, A.; Pulido-Leboeuf, P.; Molina, L.; Vallejos, A.; Martín-Rosales, W. Intensive agriculture, wetlands, quarries and water management. A case study (Campo de Dalías, SE Spain). Environ. Geol. 2000, 40, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrós-Martínez, J.L.; Rueda-Lópe, N.; Milán-García, J.; Valenciano, J.P. Public policies for sustainability and water security: The case of Almeria (Spain). Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, A.; López-Gunn, E.; Montero González, E.; Ramón Llamas, M. Desalination for securing water productivity in an intensively used coastal aquifer (Campo de Dalías, Spain). Proc. IAHS 2015, 366, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.K. Stormwater Infiltration; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; p. 269. [Google Scholar]
- Prinz, D. The Role of Water Harvesting in Alleviating Water Scarcity in Arid Areas. In Proceedings of the Keynote Lecture, Proceedings, International Conference on Water Resources Management in Arid Regions, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait, Asia, 23–27 March 2002; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Daniele, L.; Corbella, M.; Vallejos, A.; Díaz-Puga, M.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Geochemical simulations to assess the fluorine origin in Sierra de Gádor groundwater (SE Spain). Geofluids 2013, 13, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Puga, M.A.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Vallejos, A.; Sola, F.; Daniele, L.; Simón, M.; García, I. Impact of Mine Leachates on a Carbonate Aquifer (SE Spain). Mine Water Environ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Belmonte-Ureña, L.J.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Valera, D.L. Aquifer Sustainability and the Use of Desalinated Seawater for Greenhouse Irrigation in the Campo de Níjar, Southeast Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, W.; Guo, L.; Liao, F.; Zhou, P. Application of multiple approaches to investigate the hydrochemistry evolution of groundwater in an arid region: Nomhon, Northwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshall, A.S.; Arik, A.D.; El-Kadi, A.; Pierce, S.; Ye, M.; Burnett, K.M.; Wada, C.A.; Bremer, L.L.; Chun, G. Groundwater sustainability: A review of the interactions between science and policy. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 093004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PNUE/PAM. Stratégie Méditerranéenne pour le déVeloppement Durable 2016–2025; Valbonne. Plan Bleu, Centre d’Activités Régionales: La Marsa Tunis, Tunisia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schulterbrandt, R.; Anandhi, A.; Jiru, M.; Usher, K.M. A conceptualization of the urban food-energy-Water nexus sustainability paradigm: Modeling from theory to practice. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).