Estimating Typhoon-Induced Sea Surface Cooling Based upon Satellite Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A1
- A2
- The minimum SST during the typhoon’s passage (MT) minus the average SST over three days before the typhoon’s arrival (RT) [32];
- A3
- The SST averaged over 24 h to four days after the typhoon passage (MT) minus the SST averaged during 10 to 3 days before the typhoon’s arrival (RT) [33];
- A4
- The so-called grid-based maximum response (GMR) method, which treats the average SST 2 days before the initial forcing time as RT and the minimum SST from the arrival to 5 days after the terminal forcing time as MT [34]. Hereafter, this will also be referred to as the LI method;
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Typhoon Track Data and Basic Information
2.1.2. Satellite Observations
2.2. Methods
3. Results
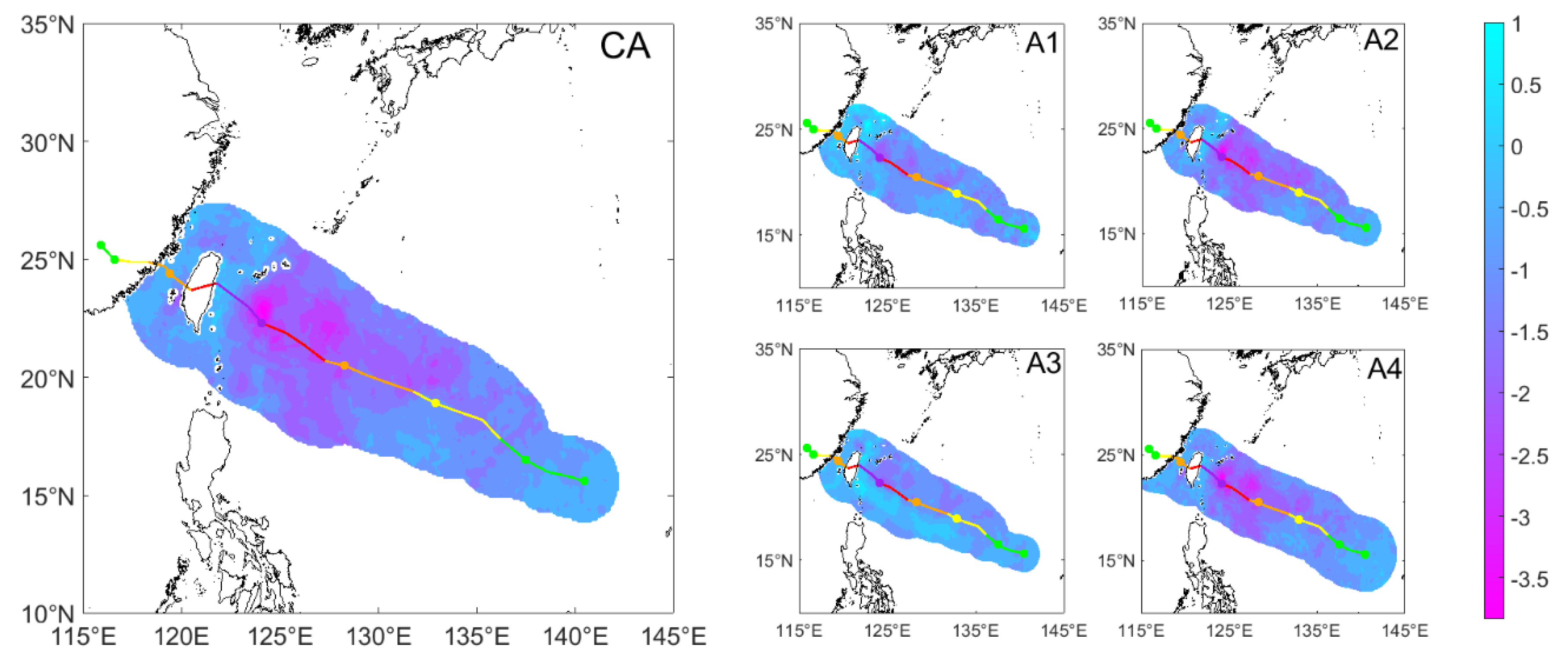
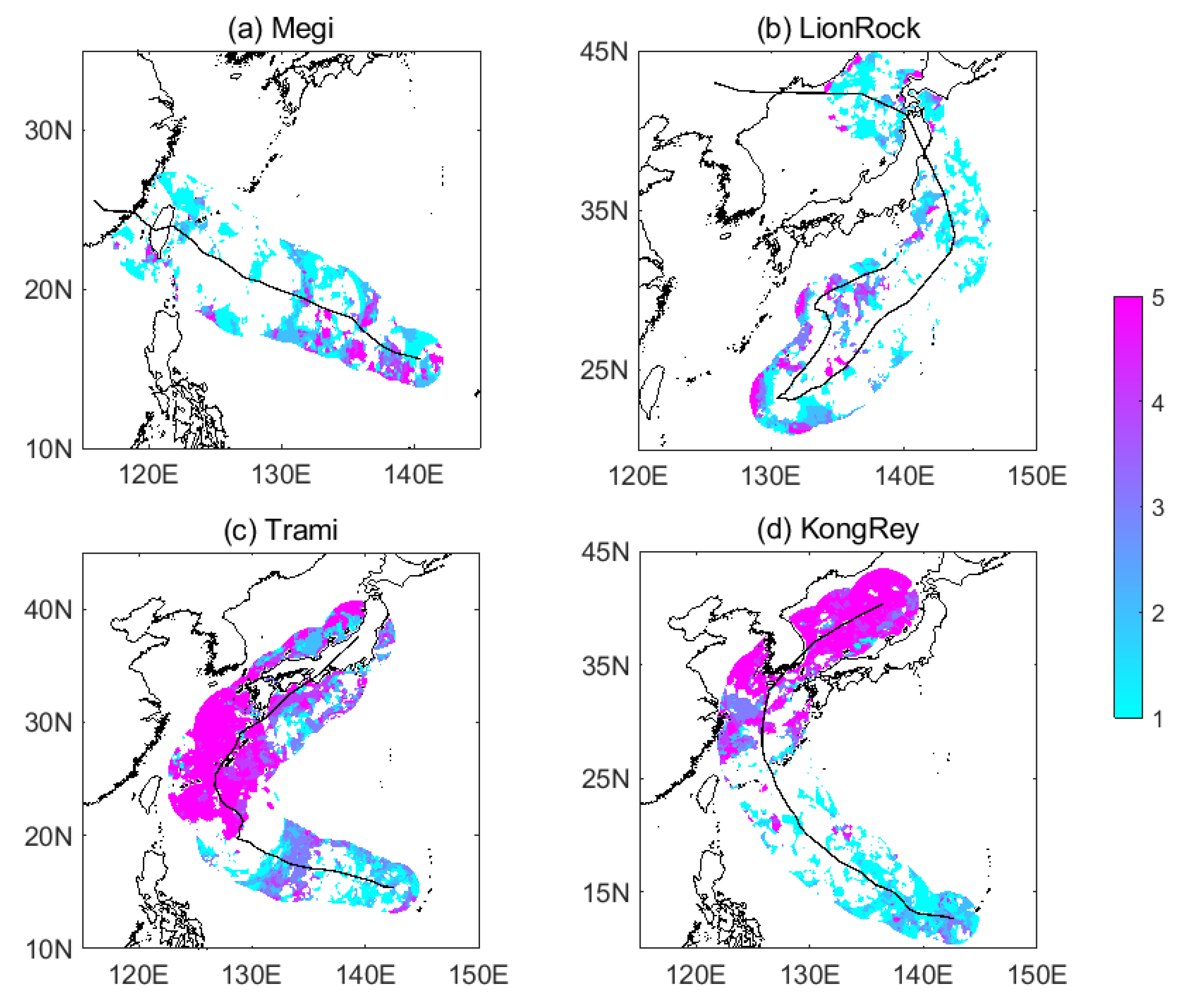
3.1. Megi
3.2. LionRock
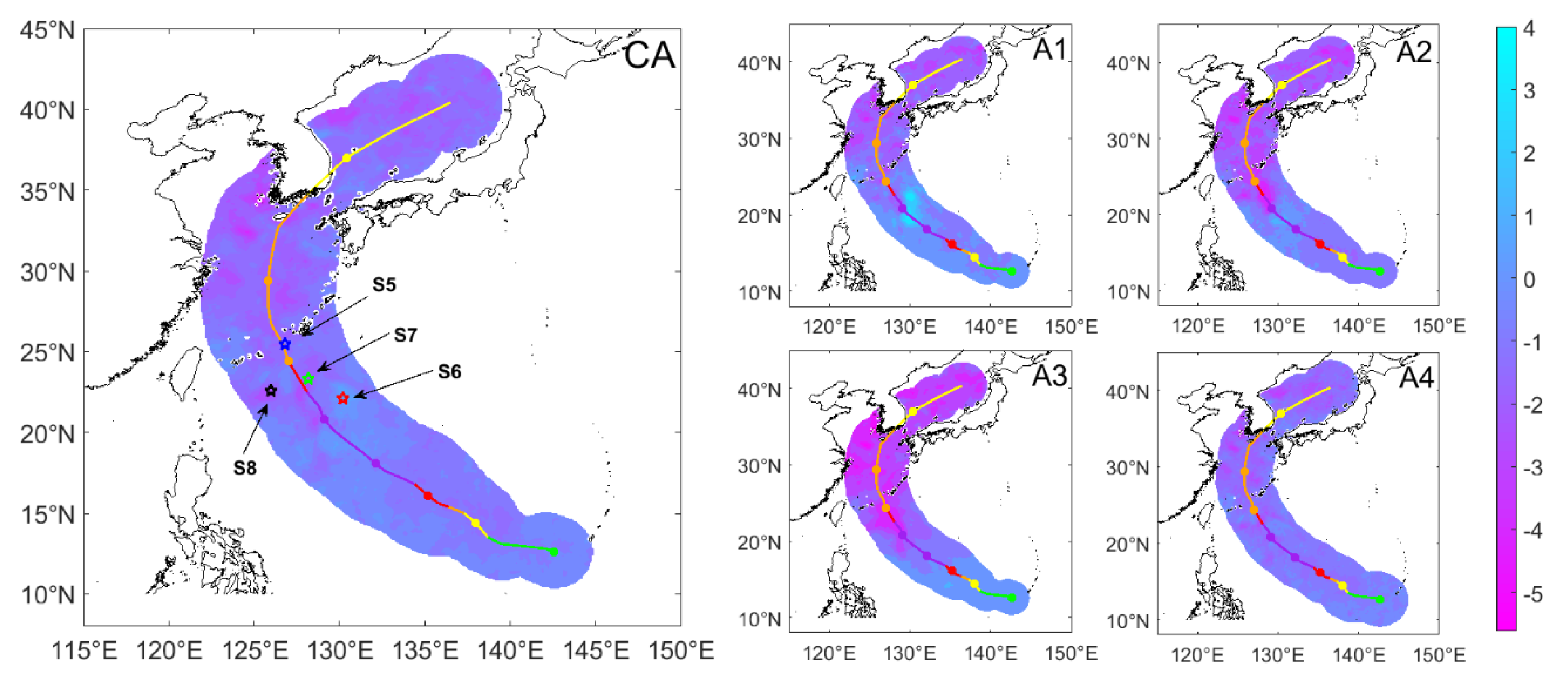
3.3. Successive Typhoons: Trami and KongRey
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.W.; Kang, J.C.; Gu, C.L.; Xu, Y.; Tang, M.; Lu, K. Variation characteristics of the extreme sea surface temperature events in the Northwest Pacific and its relationship with ENSO over the past 33 Years. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 221–232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.C.; Chen, M.N.; Chen, D.W. Changes of tropical cyclones in China and Fujian over the past 60 years. Mar. Forecast 2010, 27, 34–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Song, L.L.; Liu, A.J.; Pan, W.J. Analysis of the climatic features of landfall tropical cyclones in China during the past 58 years. Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao/Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2008, 47, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, D.K.; Lei, X.T.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.H.; Han, G.J. Progress and perspective on interactions between ocean and typhoon. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 64, 60–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper ocean response to a hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.B.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.G.; Xu, Y. Ocean response to Typhoon Ketsana traveling over the northwest Pacific and a numerical model approach. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 21606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q. Responses to 2012 Typhoon Tembin in terms of near-surface flow and thermohaline. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2015, 3, 13–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.M.; Jiang, Y.W. Mechanism of the Ocean Water Cooling Caused by Typhoon Sinlaku in 2008. J. Xiamen Univ. 2012, 51, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, Y.-J.; Xian, T.; Lu, Z.; Fu, Y.-F. Strong enhancement of chlorophyll a concentration by a weak typhoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 404, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.J.; Dickey, T.D. Observations and analyses of upper ocean responses to tropical storms and hurricanes in the vicinity of Bermuda. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, S.L.; Li, L.; Sun, F.Q.; Wu, J.Y.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, D.W.; Ning, X.R.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Shang, S.P. Changes of temperature and bio-optical properties in the South China Sea in response to Typhoon Lingling, 2001. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, I.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, C.C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Liang, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.K. New evidence for enhanced primary production triggered by tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, P.Y.; Lin, X.P. Changes in Upper Ocean Temperature, Salt and Sea level During Typhoon SOULIK (2013). Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 3, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dare, R.A.; Mcbride, J.L. Sea surface temperature response to tropical cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 3798–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L. The Impact of Typhoon on sea Surface Temperature; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Guan, S.D.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J. Influence of tropical cyclones parameters on the sea surface temperature cooling. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 44, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wang, D.X.; Hu, J.Y.; Gao, R.Z. Responses of upper layer of the Northern South China Sea to two locally-generated tropical cyclones. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2008, 27, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Guo, L.; Duan, Z.; Xiang, L. Impact of Major Typhoons in 2016 on Sea Surface Features in the Northwestern Pacific. Water 2018, 10, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, J.F.; Sanford, T.B.; Forristall, G.Z. Forced stage response to a moving hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, L.K.; Black, P.G.; Mariano, A.J.; Hawkins, J.D.; Elsberry, R.L. Upper ocean response to Hurricane Gilbert. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 20227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Asaro, E.A.; Black, P.G.; Centurioni, L.R.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, S.S.; Foster, R.C.; Graber, H.C.; Harr, P.; Hormann, V.; Lien, R.C.; et al. Impact of typhoons on the ocean in the Pacific. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, P.J.; Das, S.; Mani, M.R. Contrasting Chl-a responses to the tropical cyclones Thane and Phailin in the Bay of Bengal. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 165, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Han, G.L.; Qi, Y.Q.; Li, W. Impact of barrier layer on typhoon-induced sea surface cooling. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2011, 52, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; Su, J. The impact of typhoons on sea surface temperature in the Western North Pacific Ocean. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2007, 37, 17–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Xu, J.P.; Zhu, B.K.; Sun, C.H.; Zhang, L.F. Upper ocean response to tropical cyclones in northwestern Pacific during 2001-2004 by Argo data. J. Trop. Oceanoraphy 2006, 25, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Young, O.K.; Price, J.F. Argo array observation of ocean heat content changes induced by tropical cyclones in the north Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Wu, L.W.; Johnson, N.C.; Ling, Z. Observed three-dimensional structure of ocean cooling induced by Pacific tropical cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7632–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Lin, Y.L.; Chavas, D.R.; Mei, W. Tropical cyclone cold wake size and its applications to power dissipation and ocean heat uptake estimates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.P.; Liu, C.X.; Qi, Y.Q. The Simulation of Typhoon Krovanh Using a Coupled Air-Sea Mode. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 33, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, L.K.; Goni, G.L.; Black, P.G. Effects of a warm oceanic feature on Hurricane Opal. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Chang, M.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chang, H.I.; Jan, S.; Wei, C.L. The role of enhanced velocity shears in rapid ocean cooling during Super Typhoon Nepartak 2016. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.Y.; Yu, C.C.; Wu, K.J. Response of Sea Surface Temperature to Typhoon in South China Sea. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2017, 6, 67–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, H. Accurate Evaluation of Sea Surface Temperature Cooling Induced by Typhoons Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Observations. Water 2020, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.M.; Lengaigne, M.; Madec, G.; Vialard, J.; Samson, G.; Jourdain, N.C.; Menkes, C.E.; Jullien, S. Processes setting the characteristics of sea surface cooling induced by tropical cyclones. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, C02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, Y.H.; Zhang, R.H.; Chen, D.K. Upper ocean response to tropical cyclone wind forcing: A case study of typhoon Rammasun (2008). Sci. China 2015, 58, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashem, M.; Ahmed, M.K. The response of the upper ocean to tropical cyclone Viyaru over the Bay of Bengal. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Xu, Q.; Feng, T.; Zhang, H. Upper Ocean Response to Two Sequential Tropical Cyclones over the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, A.; Chung, Y.; Liu, X.; Ye, Q. The Interannual Variations of the Summer Monsoon Onset over the South China Sea. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1998, 59, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ho, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.M. Definition of South China Sea Monsoon Onset and Commencement of the East Asia Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
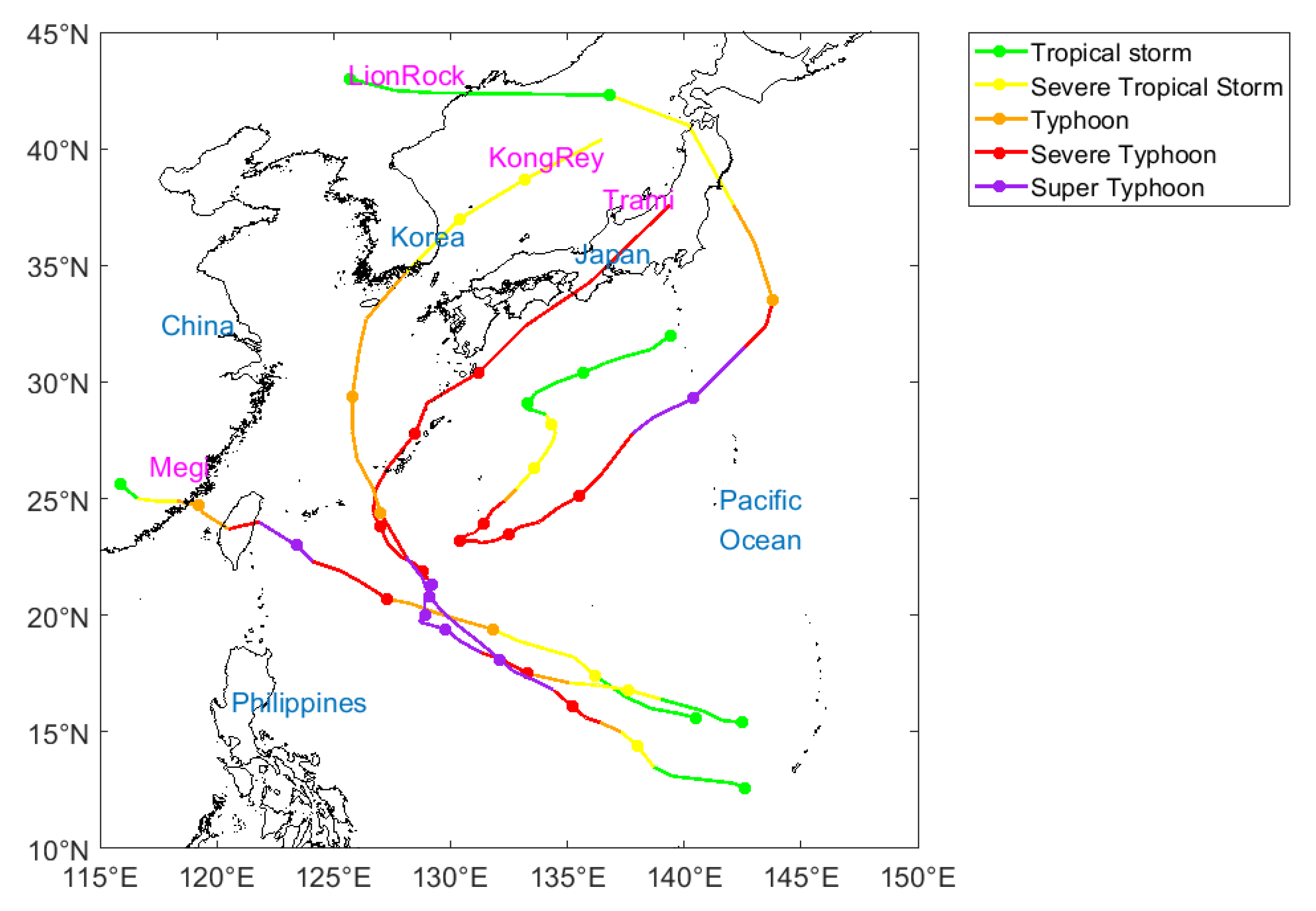




| Name | Code No. | Duration (h) | Max Wind Speed (m/s) | Min Pressure (hPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LionRock | 1610 | 276 | 50 | 935 |
| Megi | 1617 | 135 | 52 | 935 |
| Trami | 1824 | 222 | 60 | 920 |
| KongRey | 1825 | 180 | 60 | 920 |
| Dots | A1 (°C) | A2 (°C) | A3 (°C) | A4 (°C) | CA (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | −3.11 | −4.58 | −2.02 | −4.69 | −4.59 |
| S2 | −2.40 | −4.22 | −2.27 | −4.43 | −4.25 |
| S3 | −2.76 | −5.02 | −2.50 | −4.81 | −4.80 |
| S4 | −1.25 | −3.07 | −1.21 | −2.70 | −2.78 |
| Name | A1 (°C) | A2 (°C) | A3 (°C) | A4 (°C) | CA (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Megi | −2.16–1 | −3.82–0.5 | −1.90–1 | −3.84~0 | −3.82–0 |
| LionRock | −6.16–3 | −5.95–0 | −4.30–4 | −5.66–0 | −5.57–0 |
| Trami | −5.2–0.5 | −6.84–0 | −5.21–0.63 | −6.94–0 | −6.93–0 |
| KongRey | −4.38–4 | −4.53–2 | −5.62–1 | −4.25–−0.5 | −4.47–1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, D.; Xiang, L.; Guo, L.; Li, B. Estimating Typhoon-Induced Sea Surface Cooling Based upon Satellite Observations. Water 2020, 12, 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113060
Song D, Xiang L, Guo L, Li B. Estimating Typhoon-Induced Sea Surface Cooling Based upon Satellite Observations. Water. 2020; 12(11):3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113060
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Dan, Lulu Xiang, Linghui Guo, and Bo Li. 2020. "Estimating Typhoon-Induced Sea Surface Cooling Based upon Satellite Observations" Water 12, no. 11: 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113060
APA StyleSong, D., Xiang, L., Guo, L., & Li, B. (2020). Estimating Typhoon-Induced Sea Surface Cooling Based upon Satellite Observations. Water, 12(11), 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113060






