Distributions, Relationship and Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements in Waters of Bosten Lake, the Former Largest Inland and Freshwater Lake of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
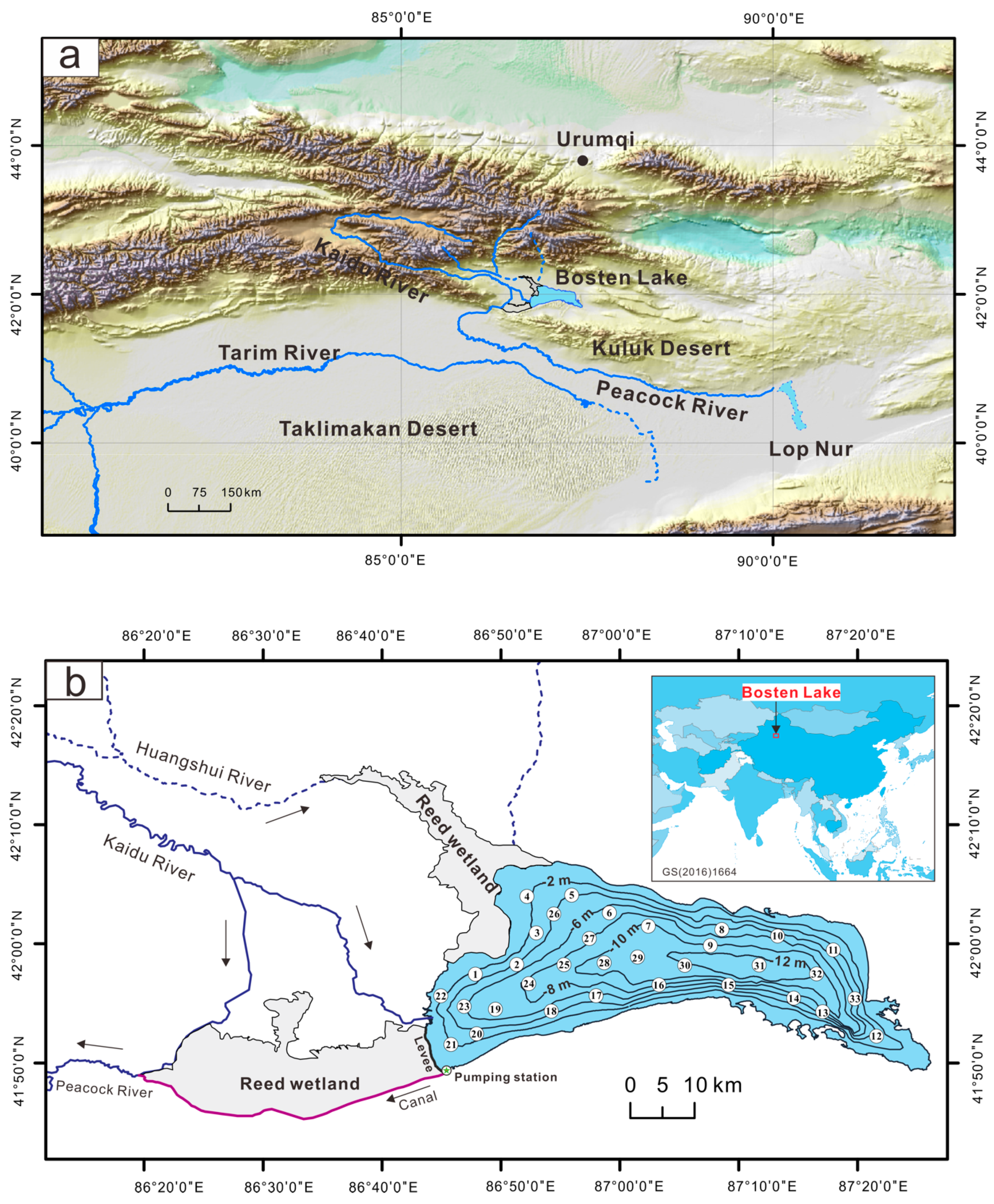
2. Geographic Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Analytical Techniques
3.2. Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements
3.3. Statistical Analyses
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The average TDS of Bosten Lake in 2018 was 1.56 g/L and 1.32 g/L for the measured and calculated values, respectively. The average pH value of the lake water body is 8.47, indicating this is an alkaline lake. The water type of Bosten Lake belongs to the sulfate, sodium group, type II (HCO3− < Ca2+ + Mg2+ < HCO3− + SO42−).
- (2)
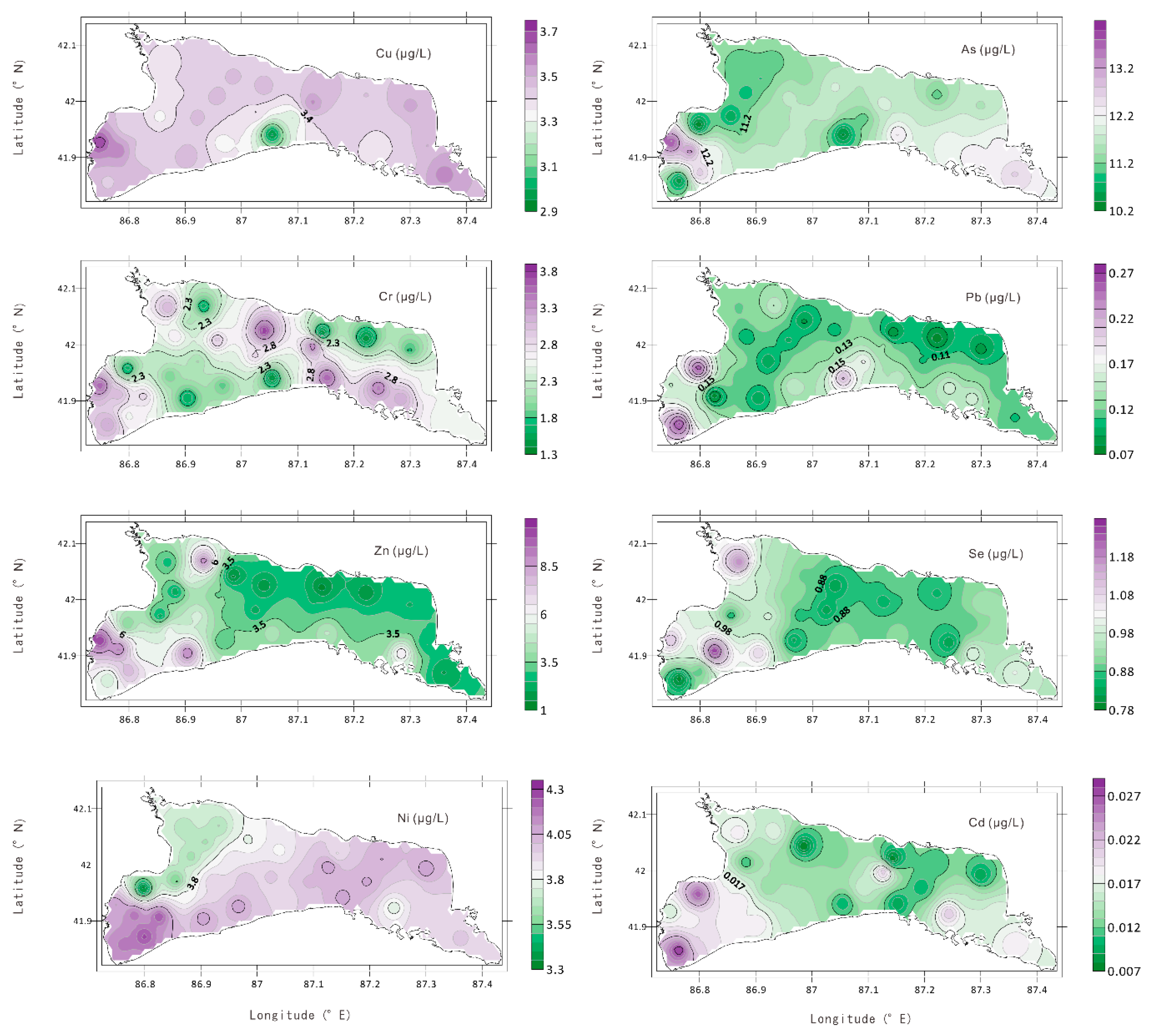
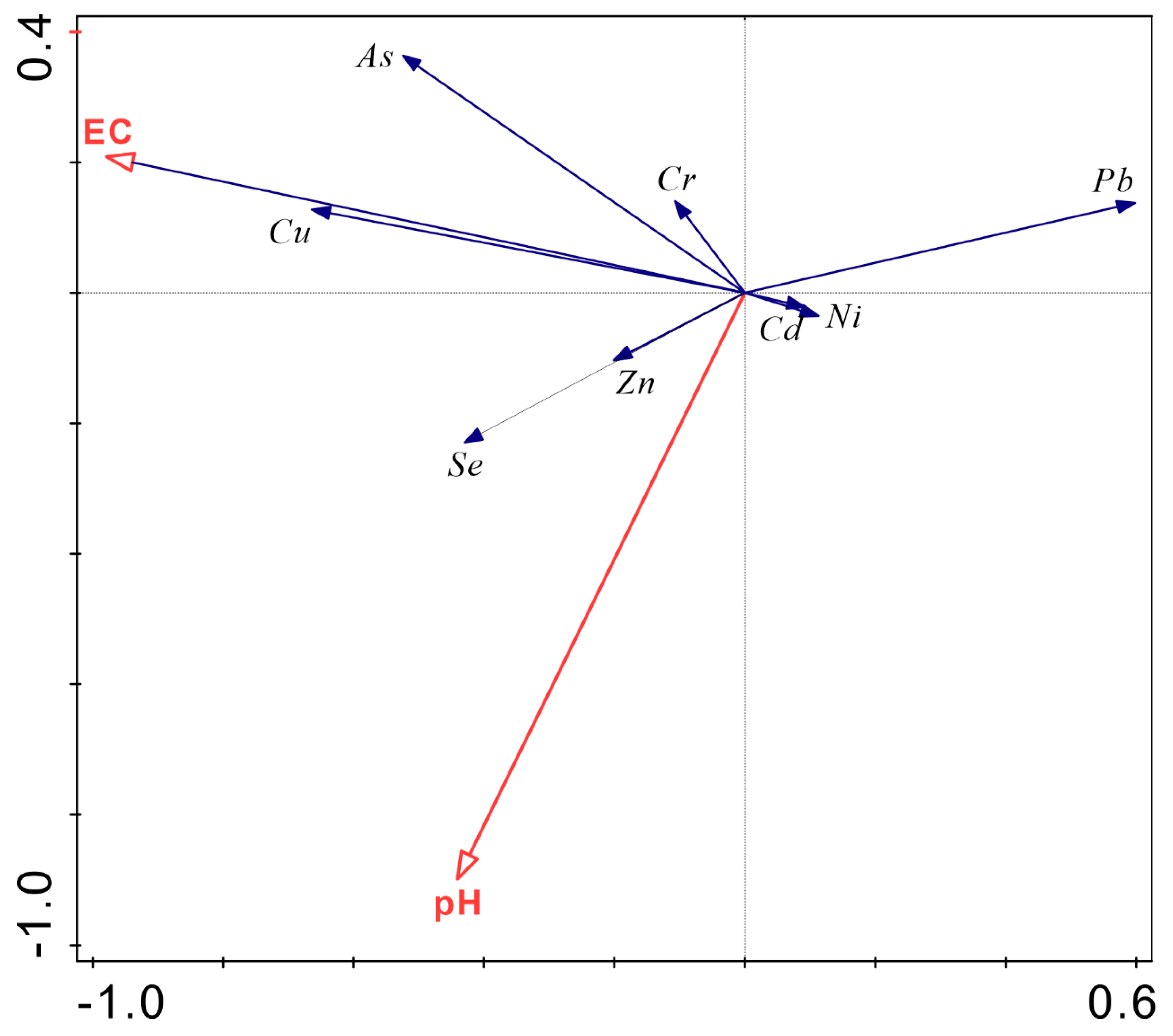
- From the perspective of spatial distribution, as the pH increases, the content of carbonate ions increases, while the content of bicarbonate ions decreases. The composition of other major ions is consistent with the change in the TDS. The spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements is more complicated. In general, the spatial distribution of Cu and As is more consistent with EC or TDS. The spatial distributions of Zn, Se and pH values are more consistent. The strength of the water exchange capacity may affect the spatial distribution of the TDS. The lake water chemistry is mainly affected by lake evaporation.
- (3)
- Based on a combination of the EC, SAR and Na %, the water of Bosten Lake is still at a permissible level for water irrigation; however, the evaluation of water pollution combined with pH, TDs, EC, major ions, and potentially toxic elements shows that Bosten Lake is moderately polluted and that the local site is close to a high pollution status. As one of the important water sources in the desert ecosystem of the Tarim Basin and the largest fishery base in Xinjiang, China, this pollution status is worthy of government and public attention.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A.; et al. Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladin, N.V.; Gontar, V.I.; Zhakova, L.V.; Plotnikov, I.S.; Smurov, A.O.; Rzymski, P.; Klimaszyk, P. The zoocenosis of the Aral Sea: Six decades of fast-paced change. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Recent Lake Area Changes in Central Asia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; You, C.-F.; Yu, J. Toward a geochemical mass balance of major elements in Lake Qinghai, NE Tibetan Plateau: A significant role of atmospheric deposition. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Fard, M.S.; Mehrabi, B.; Mehr, M.R. Occurrence, origin and health risk of arsenic and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in sediments and fish tissues from the geothermal area of the Khiav River, Ardebil Province (NW Iran). J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 208, 106347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygar, T.M.; Bábek, O.; Sedláček, J.; Lenďáková, Z.; Faměra, M.; Štojdl, J.; Pacina, J.; Tolaszová, J.; Kříženecká, S. Segregation and retention of As, potentially toxic metals, and organic pollutants in a reservoir from the Ohře River (the Czech Republic). J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2931–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X. Hydroclimatic changes of Lake Bosten in Northwest China during the last decades. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusuli, Y.; Li, L.; Ahmad, S.; Zhao, X. Dynamics model to simulate water and salt balance of Bosten Lake in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Major ion chemistry, weathering process and water quality of natural waters in the Bosten Lake catchment in an extreme arid region, NW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lu, J.; Tong, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, W. Environmentally sensitive grain-size component records and its response to climatic and anthropogenic influences in Bosten Lake region, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mischke, S.; Zheng, M.; Prokopenko, A.; Guo, F.; Feng, Z. Carbon and Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Surface-Sediment Carbonate in Bosten Lake (Xinjiang, China) and its Controlling Factors. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2009, 83, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L. Geochemistry of major and trace elements and their environmental significances in core sediments from Bosten Lake, arid northwestern China. J. Limnol. 2019, 78, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J. Anthropogenic Influences on Environmental Changes of Lake Bosten, the Largest Inland Freshwater Lake in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yao, S.; Xue, B.; Lu, X.; Gui, Z. Organic carbon burial in Chinese lakes over the past 150 years. Quat. Int. 2017, 438, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, P.E.; Demske, D.; Leipe, C.; Long, T.; Müller, S.; Hoelzmann, P.; Wagner, M. An 8500-year palynological record of vegetation, climate change and human activity in the Bosten Lake region of Northwest China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 516, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En, Z.K.; Xu, H.; Lan, J.H.; Yan, D.N.; Sheng, E.G.; Yu, K.K.; Fu, P.Q.; Xu, S. Variable Late Holocene 14C Reservoir Ages in Lake Bosten, Northwestern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Lan, H. Carbon burial in Bosten Lake over the past century: Impacts of climate change and human activity. Chem. Geol. 2015, 419, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Holmes, J.A.; Chen, J. Humid Little Ice Age in arid central Asia documented by Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischke, S.; Wünnemann, B. The Holocene salinity history of Bosten Lake (Xinjiang, China) inferred from ostracod species assemblages and shell chemistry: Possible palaeoclimatic implications. Quat. Int. 2006, 154–155, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.; Tong, Y.; Li, S. Concentration and distribution of antibiotics in water–sediment system of Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, E.; Brooks, S.J.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, F. Relationships between chironomids and water depth in Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, northwest China. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cai, J.; Bai, C.; Shao, K.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Tang, X. Hydraulic connectivity and evaporation control the water quality and sources of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Lake Bosten in arid northwest China. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, T.; Shen, T.; Gao, G. Seasonal and spatial variation in the sediment bacterial community and diversity of Lake Bosten, China. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z. Organochlorine pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and sediment of the Bosten Lake, Northwest China. J. Arid. Land 2017, 9, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Shao, K.; Dai, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Gao, G. Bacterial community composition in oligosaline lake Bosten: Low overlap of betaproteobacteria and bacteroidetes with freshwater ecosystems. Microbes Environ. 2015, 30, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, G.; Shao, K.; Bayartu, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, G. Influence of Salinity on the Bacterial Community Composition in Lake Bosten, a Large Oligosaline Lake in Arid Northwestern China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Tang, X.; Gao, G.; Chen, D.; Shao, K.; Cai, X.; Zhang, L. Effects of salinity and nutrients on sedimentary bacterial communities in oligosaline Lake Bosten, northwestern China. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Qi, R.; Zhao, L.; Xue, N.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y. Bacterial community rather than metals shaping metal resistance genes in water, sediment and biofilm in lakes from arid northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamat, Z.; Haximu, S.; yong Zhang, Z.; Aji, R. An ecological risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Bosten Lake, northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7255–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mu, S.; Bao, A.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Effects of salinity and (an) ions on arsenic behavior in sediment of Bosten Lake, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4707–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wufuer, R.; Liu, Y.; Mu, S.; Song, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Interaction of dissolved organic matter with Hg(II) along salinity gradient in Boston Lake. Geochem. Int. 2014, 52, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, R.; Singh, V.P.; Song, C. Low Flow Regimes of the Tarim River Basin, China: Probabilistic Behavior, Causes and Implications. Water 2018, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Saving the “Green Corridor”: Recharging groundwater to restore riparian forest along the lower Tarim River, China. Ecol. Restor. 2007, 25, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. New evidence on the age of the Taklimakan Desert. Geology 2009, 37, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, T. The age of the Taklimakan Desert. Science 2006, 312, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, A. Exploring the Effects of Hydraulic Connectivity Scenarios on the Spatial-Temporal Salinity Changes in Bosten Lake through a Model. Water 2020, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Zeng, H.; Ma, L.; Bai, R. Water Quantity and Quality of Six Lakes in the Arid Xinjiang Region, NW China. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, A.; Chen, X.; Zhong, R. A Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake. Water 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Hu, Q. Simulation of climate change impacts on streamflow in the Bosten Lake Basin using an artificial neural network model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Zeng, H. Water quality and quantity characteristics and its evolution in Lake Bosten, Xinjiang over the past 50 years. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Pisciotta, A.; De Maio, M. Evaluation of groundwater salinization and pollution level on Favignana Island, Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzien, S.; Mohamed, S.; Keiralla, K.; Attaj, O.; Hussein, H. Hydro-geochemical Signature in the Thermal Waters in Jebel Mara, Darfur Region Western Sudan. J. Geol. Geosci. 2013, 3, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; USDA Circular No. 969; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; p. 19.
- Sharma, P.; Sarma, H.P.; Mahanta, C. Evaluation of groundwater quality with emphasis on fluoride concentration in Nalbari district, Assam, Northeast India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Al-Ruwaih, F.; Shehata, M. Hydrogeochemical processes operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. J. Arid. Environ. 1999, 42, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ozdemir, O.; Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Do, D.D. The effect of zeolite treatment by acids on sodium adsorption ratio of coal seam gas water. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5247–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Tang, C.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Al-Arifi, N.S.N.; Ghrefat, H.; Zaidi, F.K.; El-Waheidi, M.M.; Batayneh, A.; Zumlot, T. A pragmatic approach to study the groundwater quality suitability for domestic and agricultural usage, Saq aquifer, northwest of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, T.; Elango, L.; Damodarasamy, S.R. Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Chithar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Geol. 2005, 47, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Patra, P.K. Water pollution index—A new integrated approach to rank water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed. 2011. Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241548151_eng.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2019).
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. China National Standards for Drinking Water Quality; GB5749-2006; Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Ye, C.; Butler, O.M.; Du, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q. Spatio-temporal dynamics, drivers and potential sources of heavy metal pollution in riparian soils along a 600 kilometre stream gradient in Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–496. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, T.; Pusuluri, N.; Mathias, K.; Cornelius, P.; Barnhisel, R.; Shearer, S. Map quality for ordinary kriging and inverse distance weighted interpolation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, H. Hydrogeochemical controls on arsenic contamination potential and health threat in an intensive agricultural area, northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S. Water quality. In Aquaculture: Farming Aquatic Animals and Plants; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2019; pp. 63–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Dame, J.; Nüsser, M. Hydrochemical and environmental isotope analysis of groundwater and surface water in a dry mountain region in Northern Chile. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kawamura, A.; Tong, T.N.; Nakagawa, N.; Amaguchi, H.; Gilbuena, R. Clustering spatio-seasonal hydrogeochemical data using self-organizing maps for groundwater quality assessment in the Red River Delta, Vietnam. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3: A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 2328–7055.
- Li, Y. Characteristics of Kaidu River Water Quality Changes along the Course (in Chinese). Henan Water Conserv. South-to-North Water Divers. 2010, 7, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Li, Y.; Abdyzhaparuulu, S.; Mu, S. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment for the Upper Reaches of Syr Darya River in Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia. Water 2019, 11, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Xue, B.; Zawisza, E.; Yao, S.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Effects of environmental change on subfossil Cladocera in the subtropical shallow freshwater East Taihu Lake, China. Catena 2020, 188, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, N.; Martín-López, B.; Sanabria-Fernandez, J.A.; Becerro, M.A. Alpha and beta diversity across coastal marine social-ecological systems: Implications for conservation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollice, A.; Jona-Lasinio, G.; Gaglio, M.; Blanchet, F.G.; Fano, E.A. Modelling the effect of directional spatial ecological processes for a river network in Northern Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cai, Y.; Gu, Z.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.-L.; Song, H.-L. Accumulation of sulfonamide resistance genes and bacterial community function prediction in microbial fuel cell-constructed wetland treating pharmaceutical wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, T. Effects of land use on the characteristics and composition of fluvial chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Yiluo River watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Xue, J.; Weaver, L.; Wakelin, S.A.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z. Changes in microbial community structure during pig manure composting and its relationship to the fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Ghaly, A.; Mahmoud, N.; Cote, R. Phytoaccumulation of heavy metals by aquatic plants. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-X.; Rainbow, P.S. Comparative approaches to understand metal bioaccumulation in aquatic animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 148, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Klimaszyk, P.; Niedzielski, P.; Marszelewski, W.; Borowiak, D.; Nowiński, K.; Baikenzheyeva, A.; Kurmanbayev, R.; Aladin, N. Pollution with trace elements and rare-earth metals in the lower course of Syr Darya River and Small Aral Sea, Kazakhstan. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 2020, 368, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
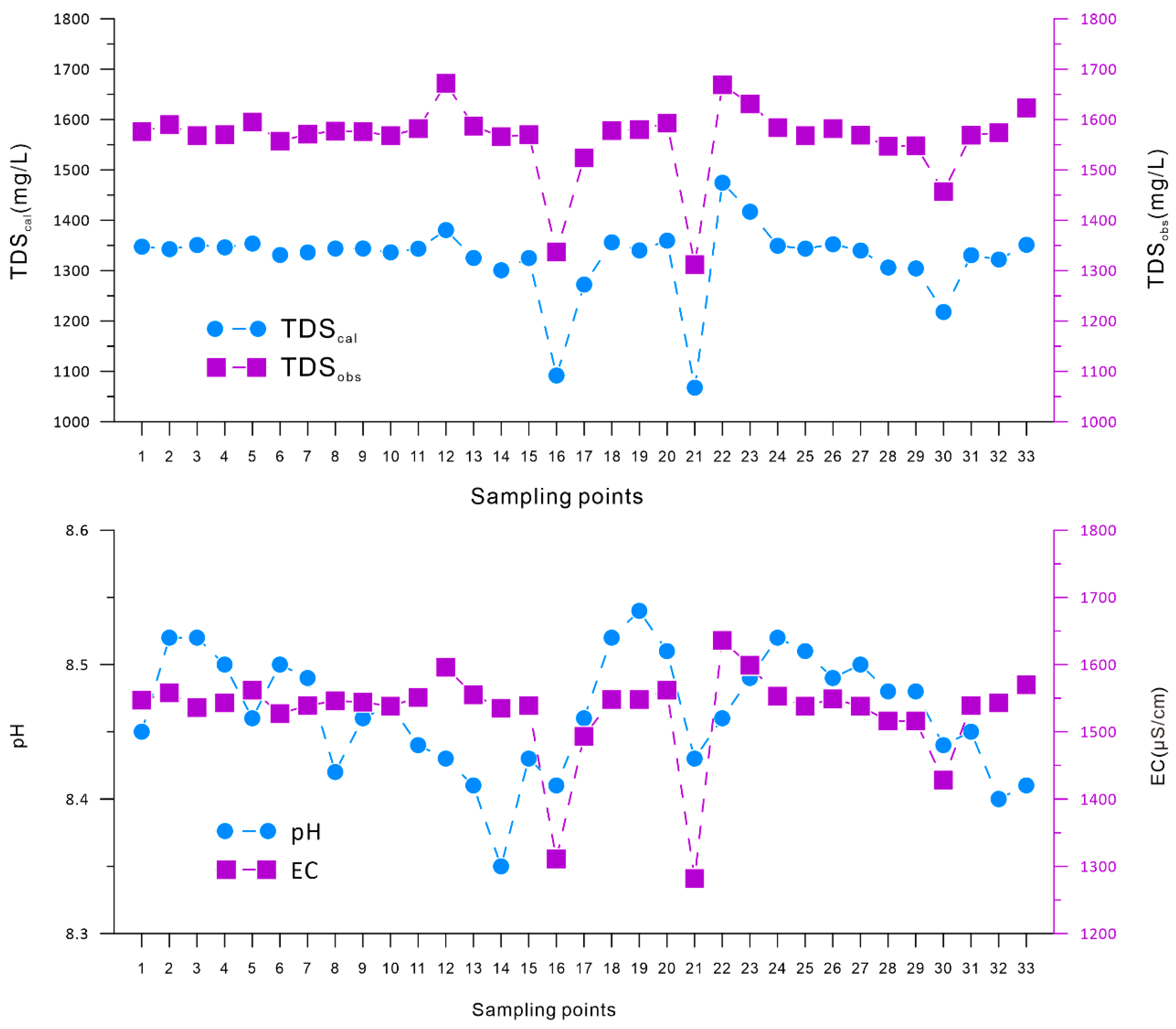
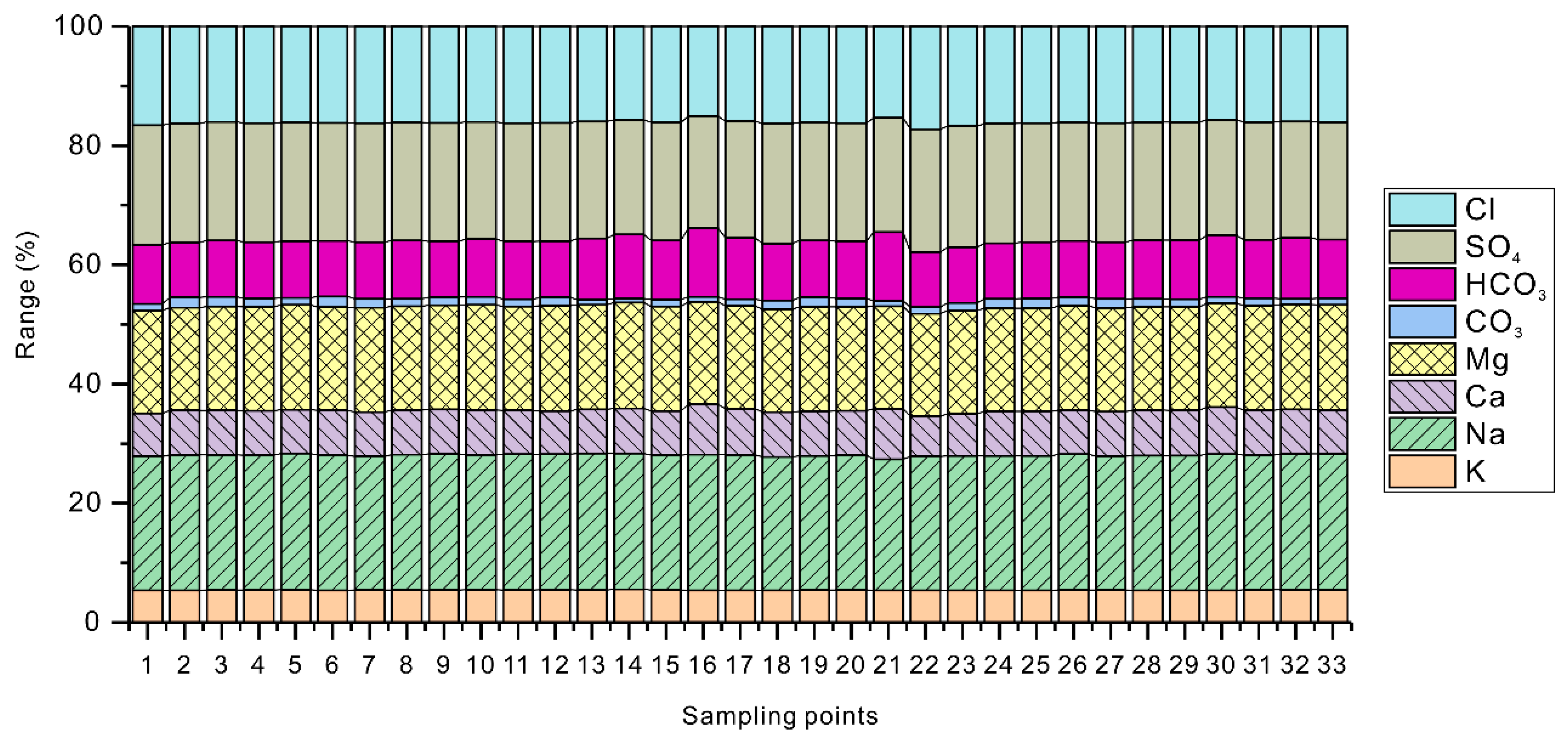
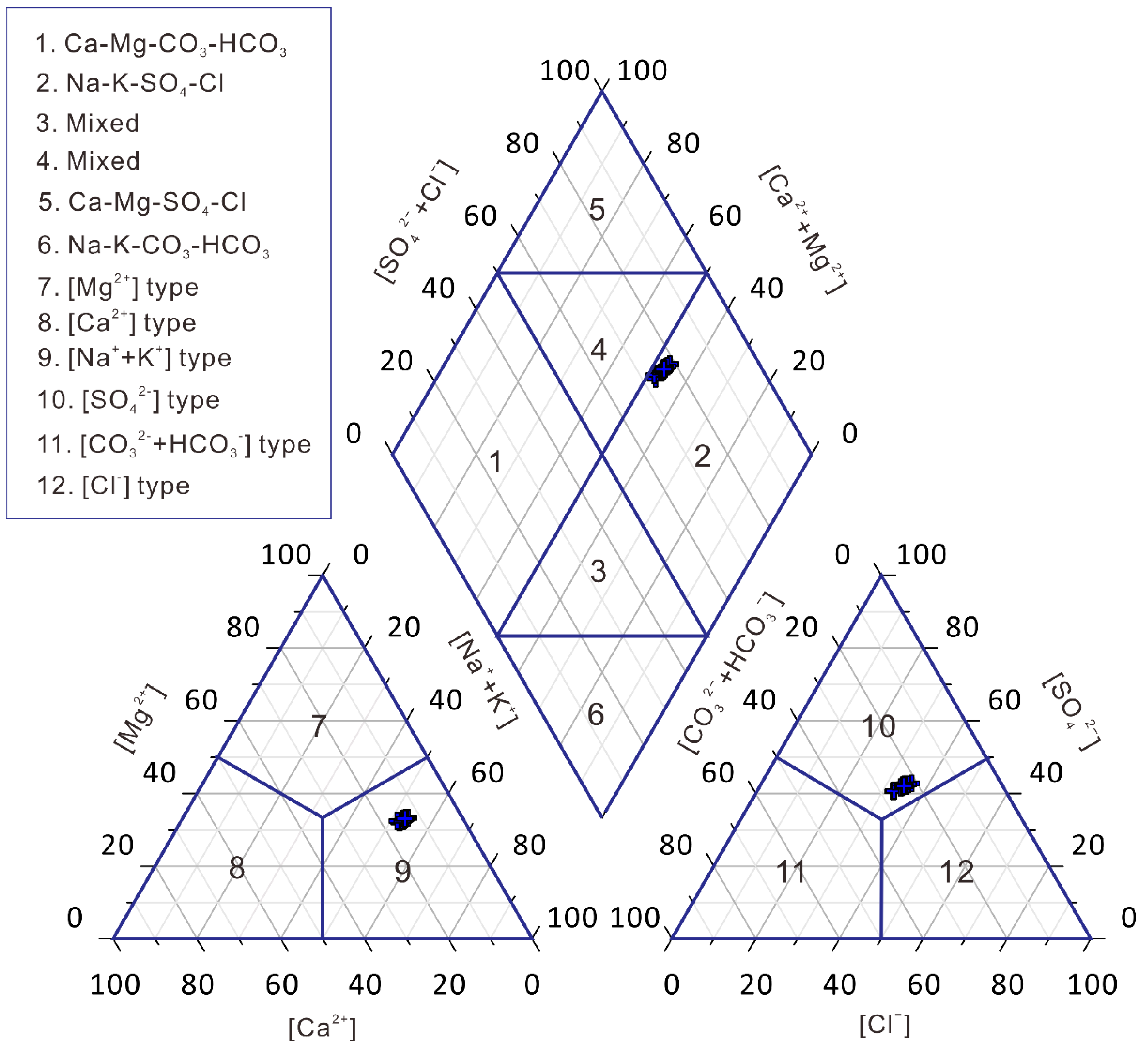
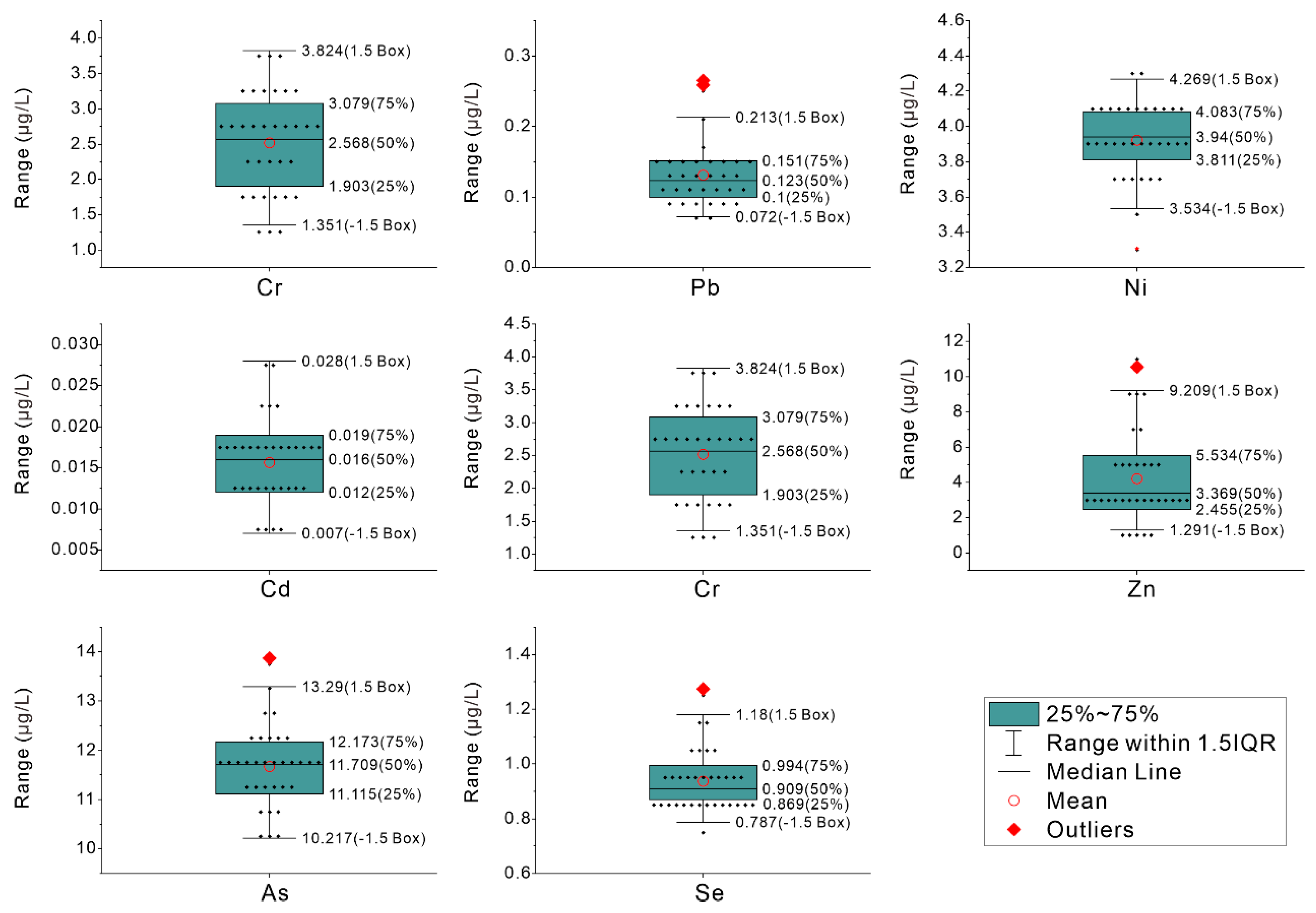
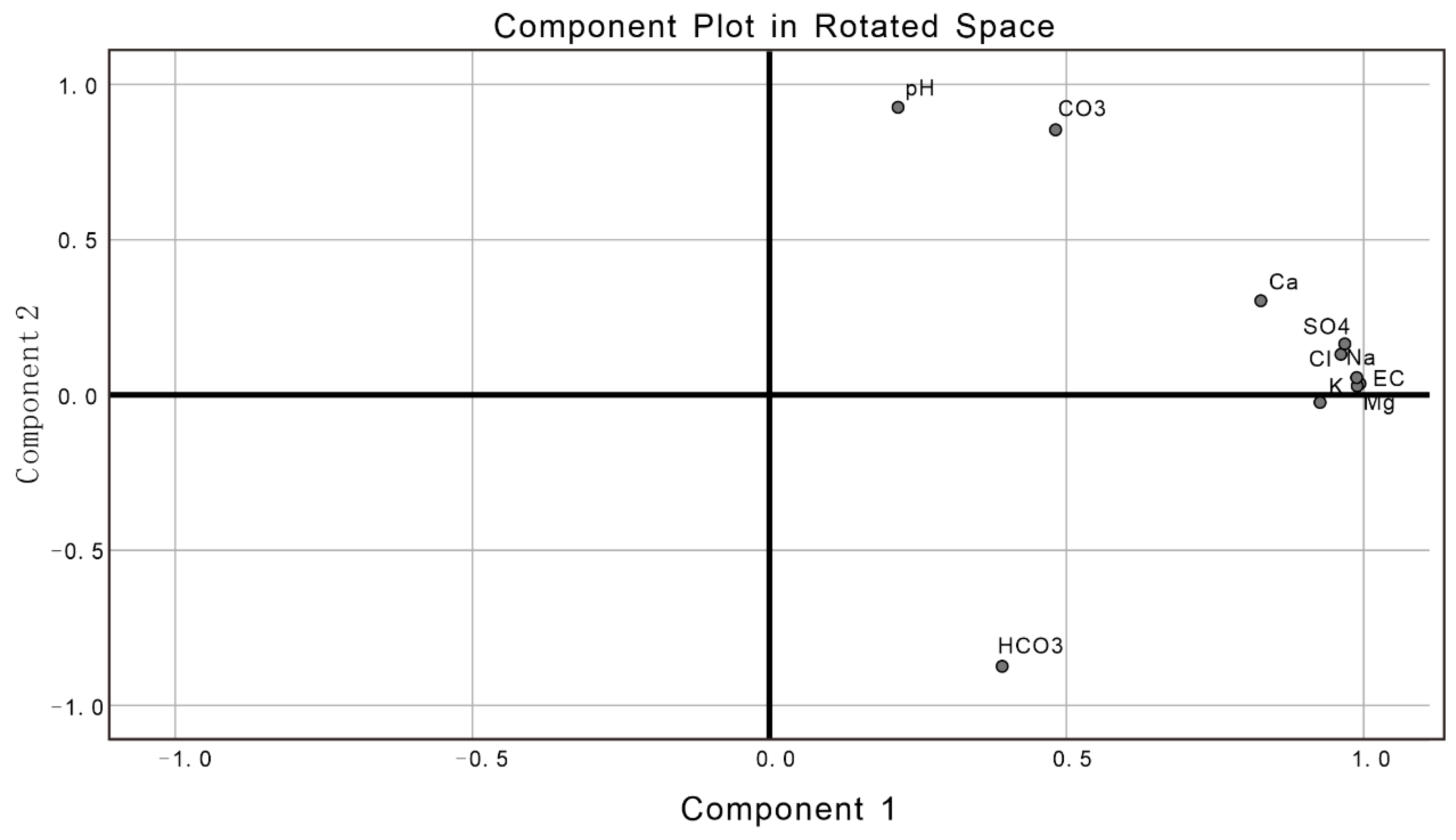
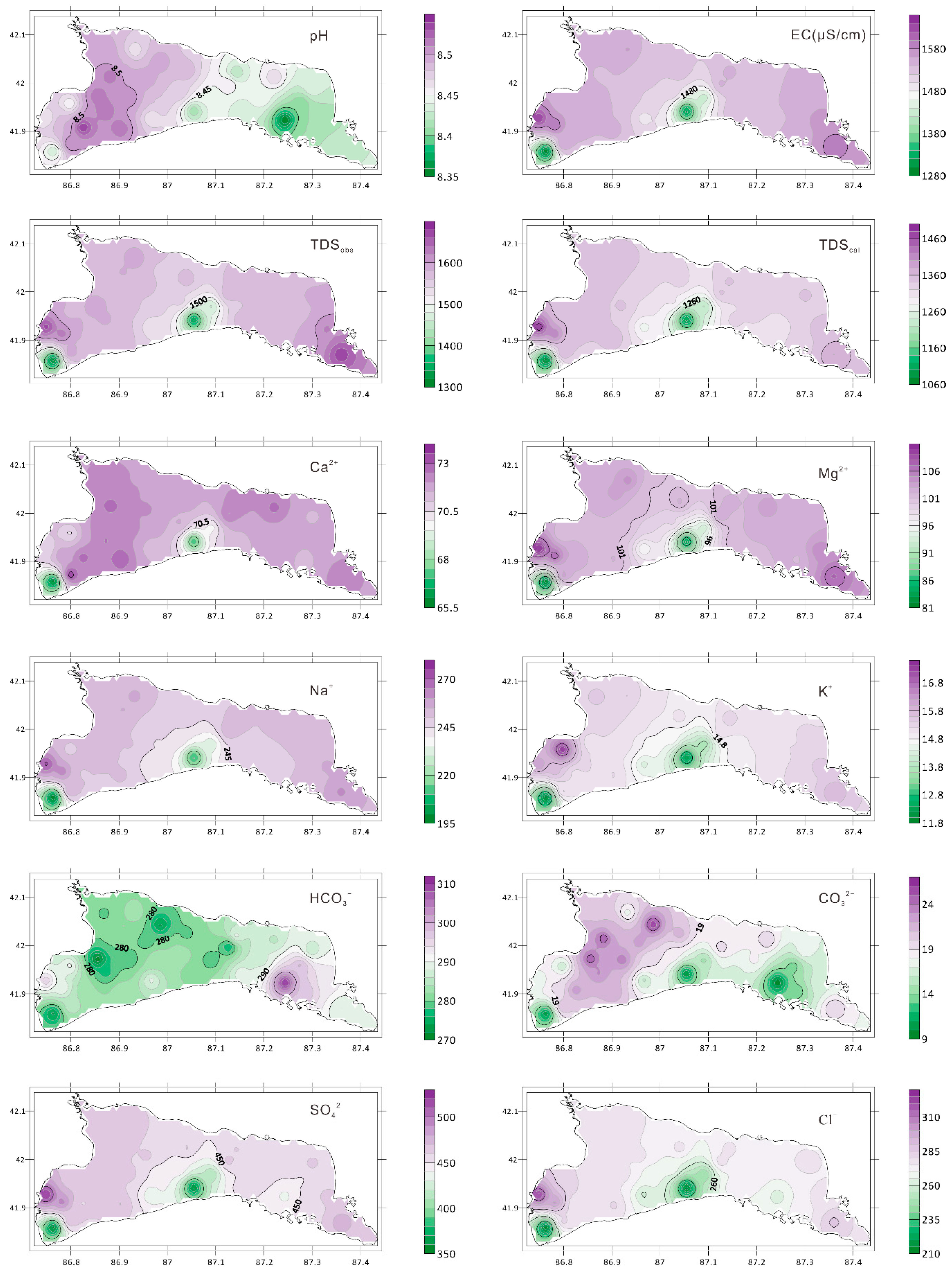
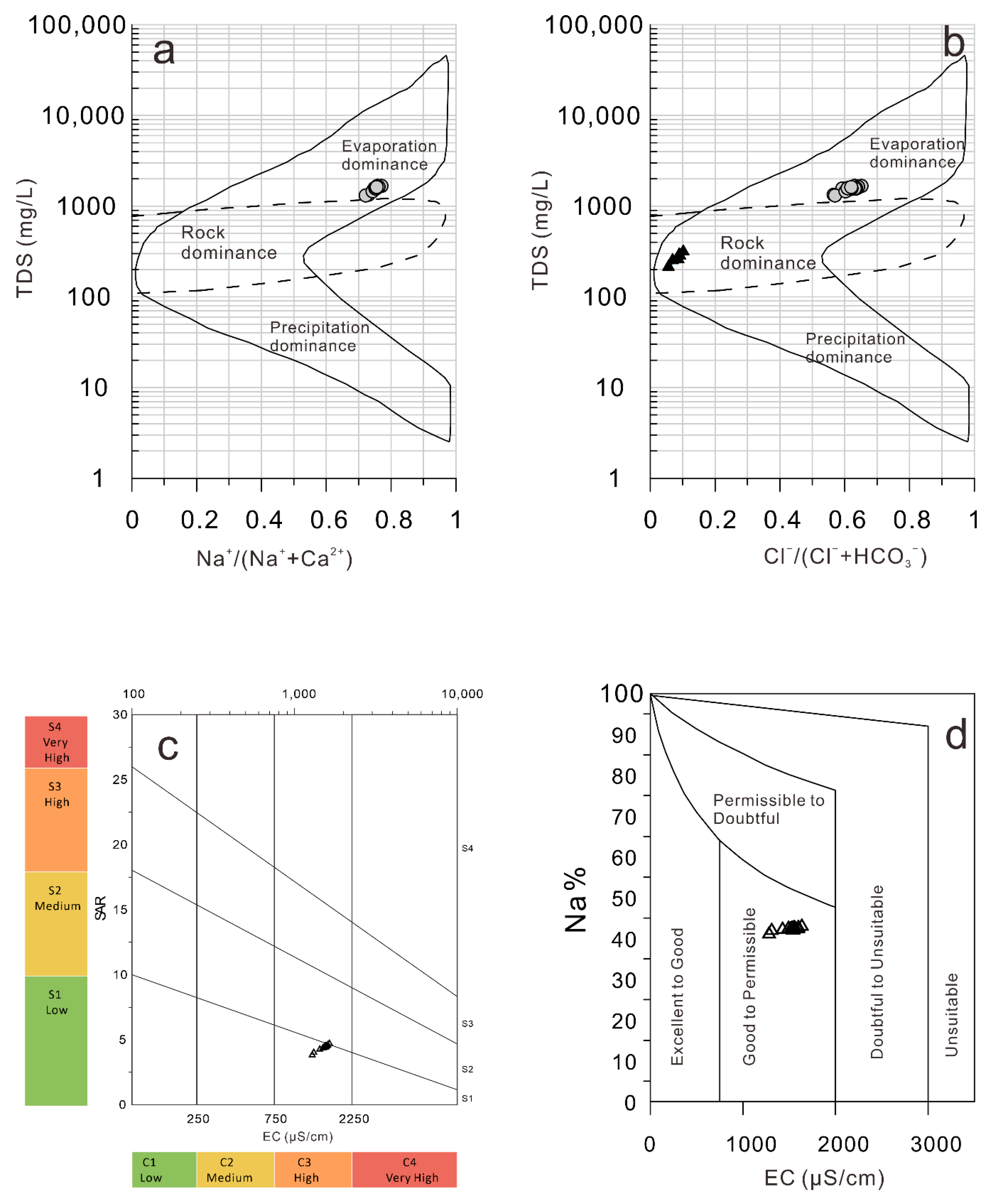

| Parameter | Unit | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Error | Standard Deviation | Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.35 | 8.54 | 8.4652 | 0.008 | 0.044 | 0.11 | 0.86 b | |
| EC | μS/cm | 1282 | 1636 | 1529.85 | 11.942 | 68.603 | 0.32 | 0 a |
| TDSobs | mg/L | 1312 | 1672 | 1562.73 | 12.484 | 71.713 | 0.31 | 0 a |
| TDScal | mg/L | 1067.7 | 1474.46 | 1324.34 | 13.03 | 74.83 | 0.28 | 0.01 a |
| Cl− | mg/L | 210.61 | 321.03 | 272.87 | 3.46 | 19.87 | 0.25 | 0.02 a |
| SO42− | mg/L | 355.69 | 520.51 | 454.19 | 5.32 | 30.54 | 0.24 | 0.03 a |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 65.76 | 73.32 | 71.58 | 0.27 | 1.54 | 0.25 | 0.03 a |
| K+ | mg/L | 11.85 | 17.43 | 15.04 | 0.17 | 0.97 | 0.28 | 0.01 a |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 80.93 | 110.08 | 101.1 | 0.99 | 5.7 | 0.31 | 0.00 a |
| Na+ | mg/L | 195.85 | 271.31 | 248.5 | 2.39 | 13.73 | 0.3 | 0.00 a |
| CO32− | mg/L | 9.33 | 25.75 | 18.65 | 0.73 | 4.19 | 0.07 | 1.00 b |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 270.59 | 310.21 | 284.81 | 1.42 | 8.17 | 0.09 | 1.00 b |
| Cu | μg/L | 2.932 | 3.685 | 3.428 | 0.021 | 0.123 | 0.19 | 0.16 b |
| Ni | μg/L | 3.308 | 4.269 | 3.923 | 0.037 | 0.215 | 0.13 | 0.63 b |
| Cr | μg/L | 1.351 | 3.824 | 2.515 | 0.124 | 0.71 | 0.08 | 1.00 b |
| Pb | μg/L | 0.072 | 0.265 | 0.131 | 0.008 | 0.046 | 0.17 | 0.25 b |
| Cd | μg/L | 0.007 | 0.028 | 0.016 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.99 b |
| Zn | μg/L | 1.291 | 10.546 | 4.213 | 0.44 | 2.529 | 0.21 | 0.09 b |
| As | μg/L | 10.217 | 13.87 | 11.669 | 0.141 | 0.808 | 0.11 | 0.78 b |
| Se | μg/L | 0.787 | 1.273 | 0.938 | 0.018 | 0.106 | 0.15 | 0.41 b |
| Cl− | meq/L | 5.94 | 9.06 | 7.7 | 0.1 | 0.56 | / | / |
| SO42− | meq/L | 7.41 | 10.84 | 9.46 | 0.11 | 0.64 | / | / |
| Ca2+ | meq/L | 3.28 | 3.66 | 3.57 | 0.01 | 0.08 | / | / |
| K+ | meq/L | 2.07 | 2.82 | 2.59 | 0.03 | 0.15 | / | / |
| Mg2+ | meq/L | 6.66 | 9.06 | 8.32 | 0.08 | 0.47 | / | / |
| Na+ | meq/L | 8.52 | 11.8 | 10.81 | 0.1 | 0.6 | / | / |
| CO32− | meq/L | 0.31 | 0.86 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 0.14 | / | / |
| HCO3− | meq/L | 4.44 | 5.08 | 4.67 | 0.02 | 0.13 | / | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Lin, L. Distributions, Relationship and Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements in Waters of Bosten Lake, the Former Largest Inland and Freshwater Lake of China. Water 2020, 12, 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102859
Liu W, Ma L, Abuduwaili J, Lin L. Distributions, Relationship and Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements in Waters of Bosten Lake, the Former Largest Inland and Freshwater Lake of China. Water. 2020; 12(10):2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102859
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen, Long Ma, Jilili Abuduwaili, and Lin Lin. 2020. "Distributions, Relationship and Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements in Waters of Bosten Lake, the Former Largest Inland and Freshwater Lake of China" Water 12, no. 10: 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102859
APA StyleLiu, W., Ma, L., Abuduwaili, J., & Lin, L. (2020). Distributions, Relationship and Assessment of Major Ions and Potentially Toxic Elements in Waters of Bosten Lake, the Former Largest Inland and Freshwater Lake of China. Water, 12(10), 2859. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102859





