A Novel Method for Determination of the Natural Toxin Ptaquiloside in Ground and Drinking Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
2.2. Stock Solutions and Calibration Standards
2.3. Water Samples
2.4. Preservation Method for PTA
2.4.1. Data Analysis—Plackett–Burman Design
2.4.2. Robustness of the Preservation Method
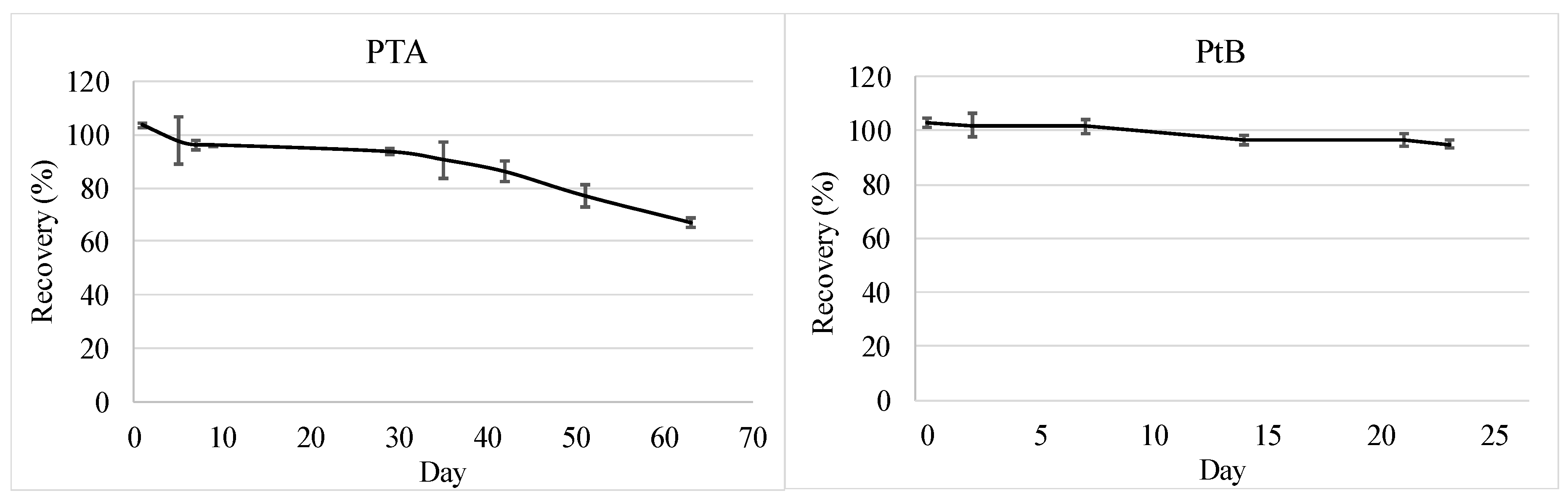
2.4.3. Stability of PTA and PtB in Groundwater
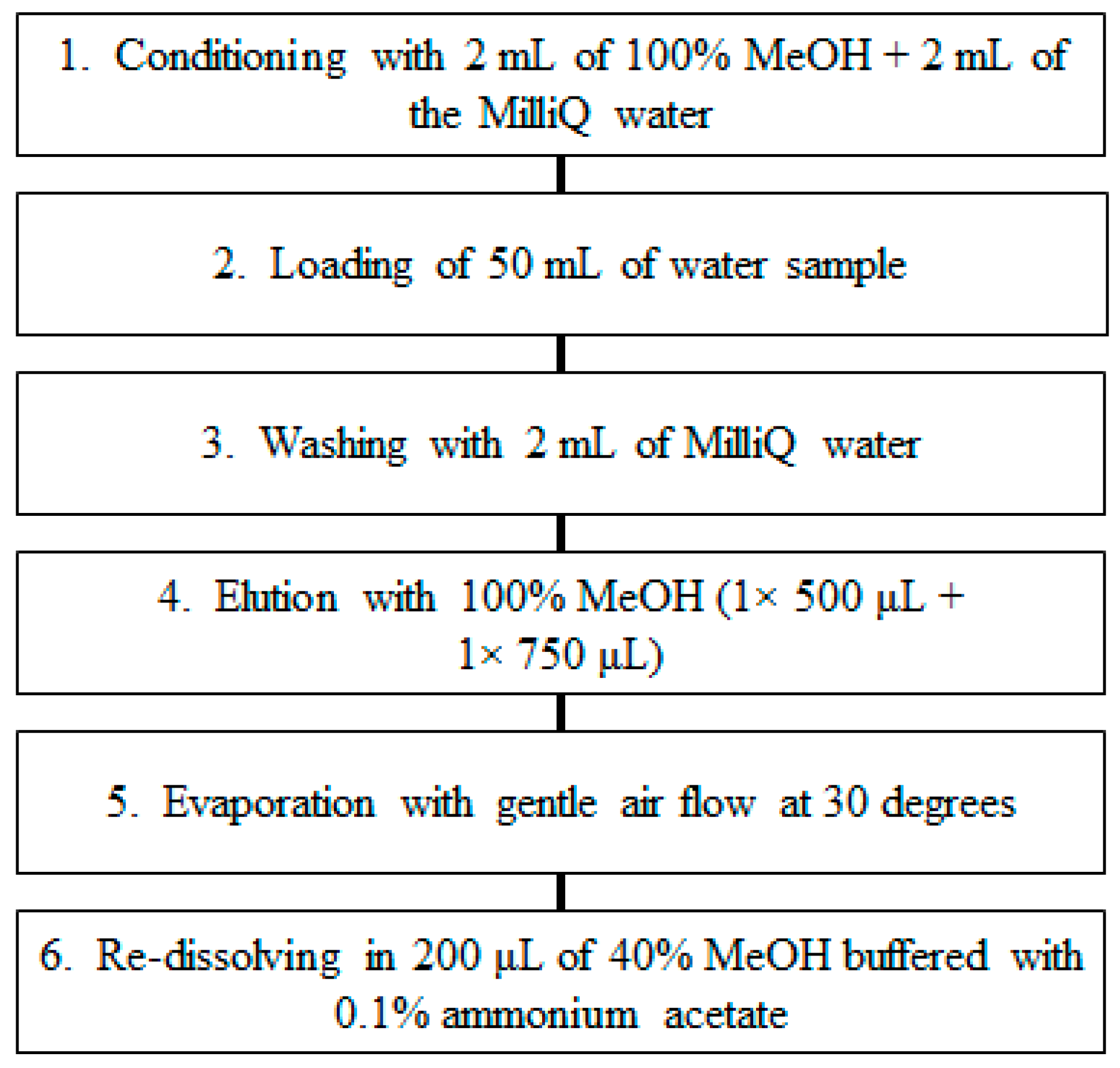
2.5. SPE Method Optimisation
2.5.1. Robustness of the SPE Method
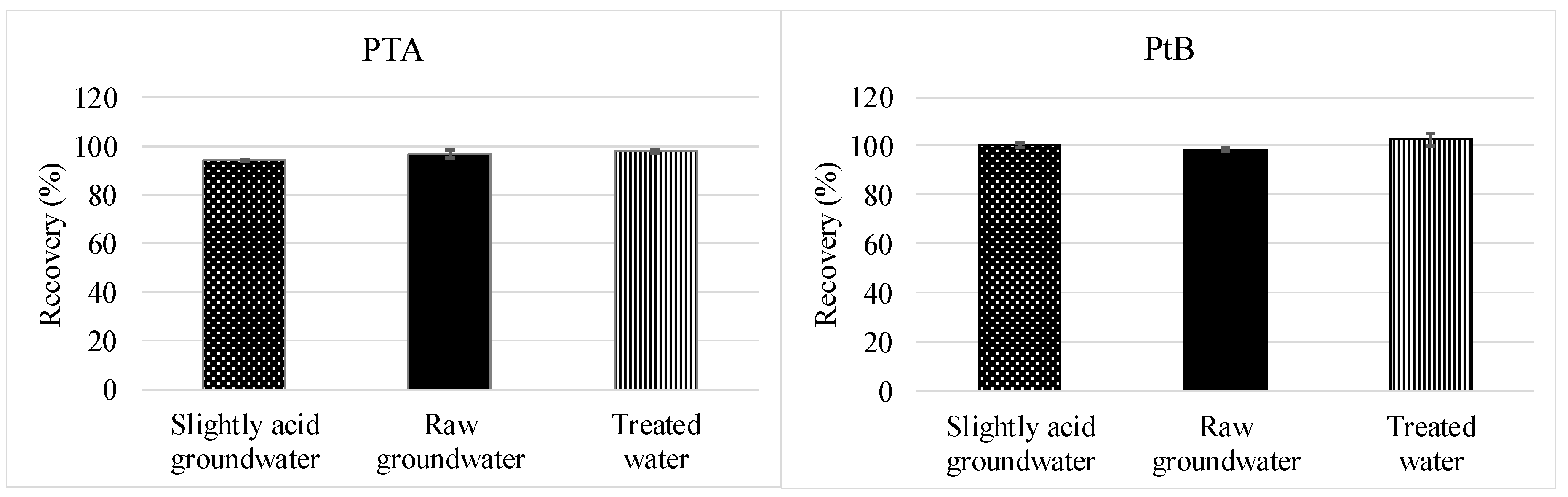
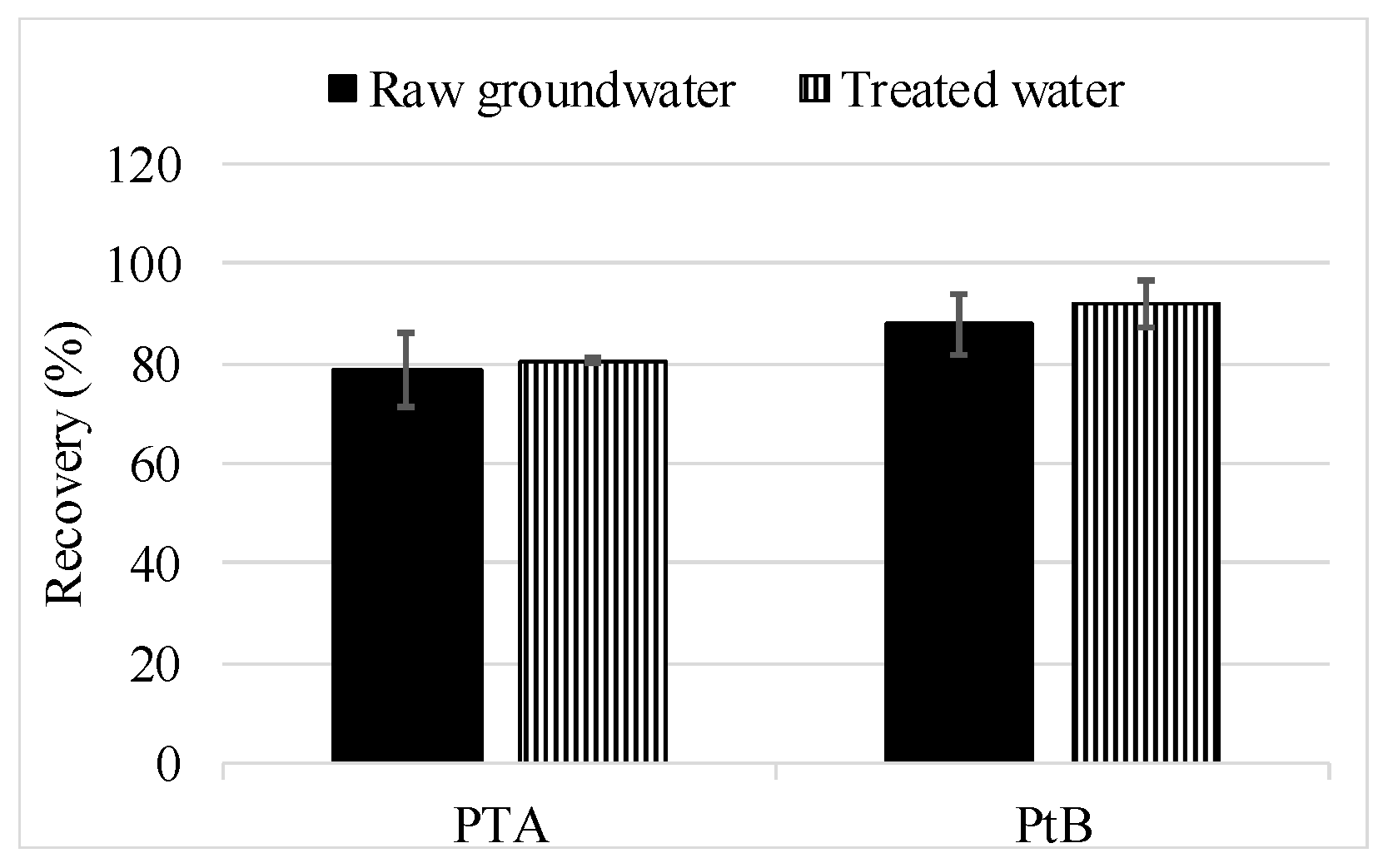
2.5.2. Full Method Validation Including Preservation and SPE
2.6. LC-MS Analysis of Water Samples
2.6.1. Validation of the Analytical Method (LC-MS)
2.6.2. Application of the Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preservation Method for PTA
3.1.1. Robustness of the Preservation Method
3.1.2. Stability of PTA and PtB in Groundwater
3.2. SPE Method Optimisation
3.2.1. Robustness of the SPE Method
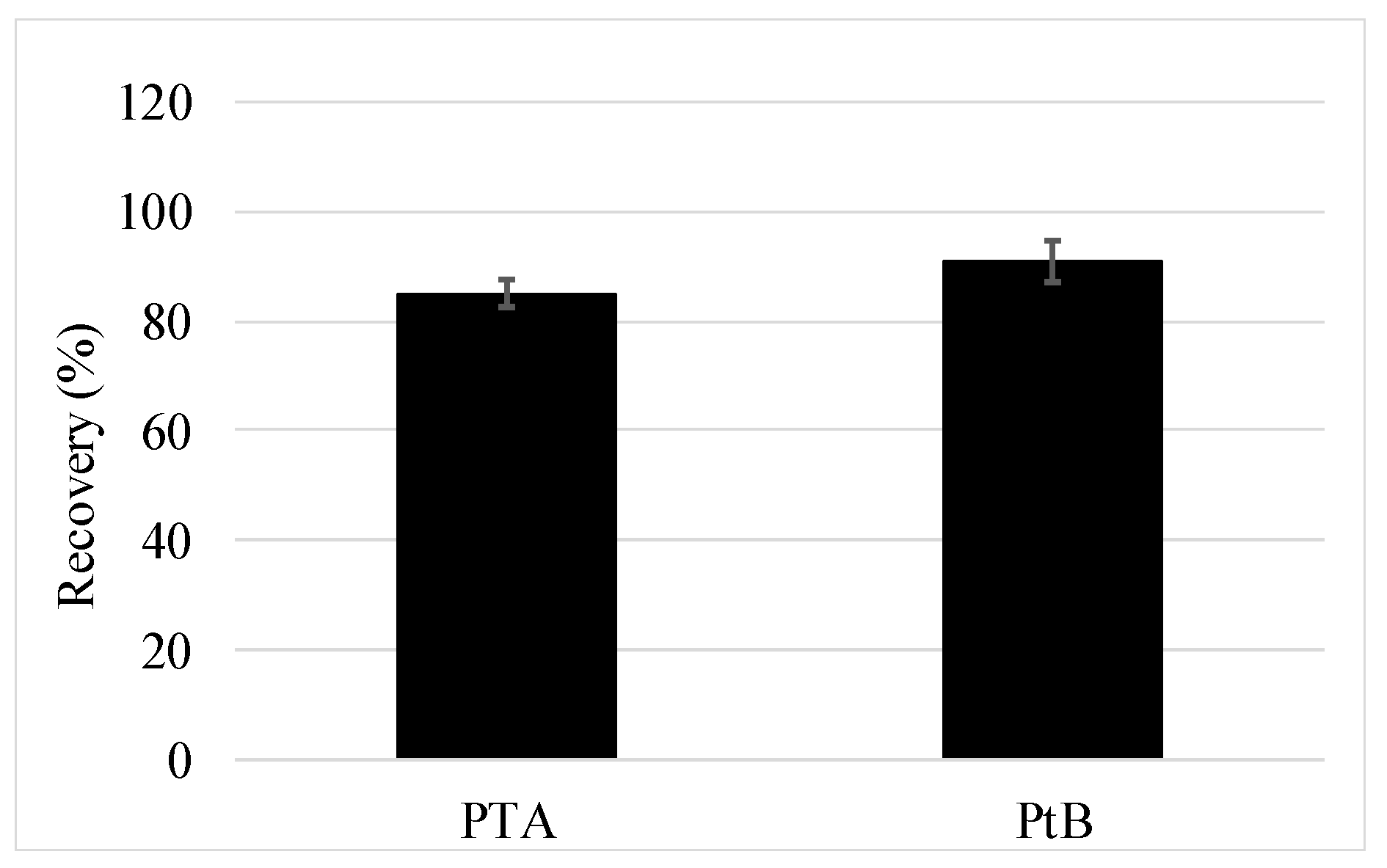
3.2.2. Full Method Validation Including Preservation and SPE
3.2.3. Application of the Method and PTA Findings in Groundwater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, J.A. The bracken problem: A global perspective. AIAS Occas. Publ. 1990, 40, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.L. The toxicity of bracken fern (genus Pteridium) to animals and its relevance to man. Handb. Plant Fungal Toxic. 1997, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, K.; Rödel, H.G.; Beck, E. Short-and long-term effects of weed control on pastures infested with Pteridium arachnoideum and an attempt to regenerate abandoned pastures in South Ecuador. Weed Res. 2011, 51, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matongera, T.N.; Mutanga, O.; Dube, T.; Sibanda, M. Detection and mapping the spatial distribution of bracken fern weeds using the Landsat 8 OLI new generation sensor. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakeman, R.J.; Marrs, R.H.; Howard, D.C.; Barr, C.J.; Fuller, R.M. The bracken problem in Great Britain: Its present extent and future changes. Appl. Geogr. 1996, 16, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrs, R.H.; Watt, A.S. Biological flora of the british isles: Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn. J. Ecol. 2006, 94, 1272–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, R.M.G.; Bastos, M.; Oliveira, P.A.; Lopes, C. Bracken-associated human and animal health hazards: Chemical, biological and pathological evidence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 203, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)—Summaries & Evaluations, Bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum) and Some of Its Constituents. 1998. Available online: http://www.inchem.org/documents/iarc/vol40/brackenfern.html (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs. 2018. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/list-of-classifications-volumes/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Van der Hoeven, J.C.M.; Lagerweij, W.J.; Posthumus, M.A.; Van Veldhuizen, A.; Holterman, H.A.J. Aquilide A, a new mutagenic compound isolated from bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn). Carcinogenesis 1983, 4, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Sugie, S.; Hirono, I.; Yamada, K.; Niwa, H.; Ojika, M. Genotoxicity of ptaquiloside, a bracken carcinogen, in the hepatocyte primary culture/DNA-repair test. Mutat. Res. Lett. 1985, 143, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Magalhães, A.; Michel, V.; Amado, I.F.; Aranha, P.; Ovesen, R.G.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Gärtner, F.; Reis, C.A.; Touati, E. Pteridium aquilinum and its ptaquiloside toxin induce DNA damage response in gastric epithelial cells, a link with gastric carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.; Smith, B.L.; Worral, S.; Moore, M.R.; Seawright, A.A.; Prakash, A.S. Bracken Fern carcinogenesis: Multiple intravenous doses of activated Ptaquiloside induce DNA adducts, Monocytosis, increased TNFα levels, and mammary gland carcinoma in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 244, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, I.; Aiso, S.; Yamaji, T.; Mori, H.; Yamada, K.; Niwa, H.; Ojika, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Kigoshi, H.; Niiyama, K. Carcinogenicity in rats of ptaquiloside isolated from bracken. GANN Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1984, 75, 833–836. [Google Scholar]
- da Costa, R.M.G.; Neto, T.; Estêvão, D.; Moutinho, M.; Félix, A.; Medeiros, R.; Lopes, C.; Bastos, M.M.S.M.; Oliveira, P.A. Ptaquiloside from bracken (Pteridium spp.) promotes oral carcinogenesis initiated by HPV16 in transgenic mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3298–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Jensen, L.S.; Hansen, H.C.B. Distribution of the carcinogenic terpene ptaquiloside in bracken fronds, rhizomes (Pteridium aquilinum), and litter in Denmark. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Lauren, D. Sorption, degradation and mobility of ptaquiloside, a carcinogenic Bracken (Pteridium sp.) constituent, in the soil environment. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Pedersen, H.Æ. Screening for ptaquiloside in ferns: Using herbarium specimens for qualitative mapping purposes. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 28, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.; Lauren, D.; Smith, B.; Hansen, H. Variation in ptaquiloside content in bracken (Pteridium esculentum (Forst. f) Cockayne) in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2008, 56, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.d.S.F.; Keller, K.M.; Soto-Blanco, B. Ptaquiloside and Pterosin B Levels in Mature Green Fronds and Sprouts of Pteridium arachnoideum. Toxins 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, T.; Saito, K.; Hirayama, E.; Uchikoshi, K.; Koyama, K.; Natori, S.; Morisaki, N.; Iwasaki, S.; Matsushima, T. Mutagenicity of ptaquiloside, the carcinogen in bracken, and its related illudane-type sesquiterpenes I. Mutagenicity in Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1989, 215, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Hansen, H.C.B. Growth of Bracken in Denmark and the Content of Ptaquiloside in Fronds. In Poisonous Plants and Related Toxins; Acamovic, T., Stewart, C.S., Pennycott, T., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Donnelly, E.; Strobel, B.W.; Holm, P.E.; Hansen, H.C.B. Land management of bracken needs to account for bracken carcinogens–a case study from Britain. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.H.; Kroghsbo, S.; Frisvad, J.C.; Hansen, H.C.B. Occurrence of the carcinogenic Bracken constituent ptaquiloside in fronds, topsoils and organic soil layers in Denmark. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Luis, K.B.; Hansen, P.B.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Hansen, H.C.B. Kinetics of ptaquiloside hydrolysis in aqueous solution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2006, 25, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauson-Kaas, F.; Jensen, P.H.; Jacobsen, O.S.; Juhler, R.K.; Hansen, H.C.B. The naturally occurring carcinogen ptaquiloside is present in groundwater below bracken vegetation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauson-Kaas, F.; Ramwell, C.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Strobel, B.W. Ptaquiloside from bracken in stream water at base flow and during storm events. Water Res. 2016, 106, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, C.; Ramwell, C.; Harhen, B.; Morrison, L.; Clauson-Kaas, F.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Campbell, G.; Sheahan, J.; Misstear, B.; Xiao, L. Ptaquiloside in Irish bracken ferns and receiving waters, with implications for land managers. Molecules 2016, 21, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, A.; Hirosawa, A.; Natori, S.; Iwasaki, S.; Toshio, S.; Ishidate, M., Jr. Mutagenicity of ptaquiloside, the carcinogen in bracken, and its related illudane-type sesquiterpenes: II. Chromosomal aberration tests with cultured mammalian cells. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1989, 215, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojika, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Niwa, H.; Yamada, K. Ptaquiloside, a potent carcinogen isolated from bracken fern pteridiumaquilinum var. latiusculum: Structure elucidation based on chemical and spectral evidence, and reactions with amino acids, nucleosides, and nucleotides. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 5261–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ojika, M.; Kigoshi, H. Ptaquiloside, the major toxin of bracken, and related terpene glycosides: Chemistry, biology and ecology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihira, K.; Fukuoka, M.; Kuroyanagi, M.; Natori, S. Further Characterization of 1-Indanone Derivatives from Bracken, Pteridium aquilinum var. latiu8culum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1972, 20, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovesen, R.G.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Hansen, H.C.B. Degradation kinetics of ptaquiloside in soil and soil solution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2008, 27, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Ovesen, R.G.; Sørensen, J. Microbial degradation and impact of Bracken toxin ptaquiloside on microbial communities in soil. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauson-Kaas, F.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Strobel, B.W. UPLC-MS/MS determination of ptaquiloside and pterosin B in preserved natural water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7981–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E.; Castillo, U.; De Jongh, F. Passage of the bracken fern carcinogen ptaquiloside into bovine milk. Lait 1993, 73, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Amelot, M.E.; Castillo, U.; Smith, B.L.; Lauren, D.R. Excretion, through milk, of ptaquiloside in bracken-fed cows. A quantitative assessment. Lait 1998, 78, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, M.T.; Reichmann, K.G.; Brock, I.J.; McKenzie, R.A.; Blaney, B.J. Residue potential of norsesquiterpene glycosides in tissues of cattle fed Austral bracken (Pteridium esculentum). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8518–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranha, P.C.R.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Strobel, B.W.; Friis, C. Determination of ptaquiloside and pterosin B derived from bracken (Pteridium aquilinum) in cattle plasma, urine and milk. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 951, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Jorgensen, D.B.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Abrahamsen, P.; Diamantopoulos, E.; Garc, D.B. A novel model concept for modelling the leaching of natural toxins: Results for the case of ptaquiloside. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H.; Jacobsen, O.S.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Juhler, R.K. Quantification of ptaquiloside and pterosin B in soil and groundwater using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9848–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.d.S.F.; Keller, K.M.; Melo, M.M.; Soto-Blanco, B. Determination of ptaquiloside in cow’s milk by HPLC-UV. Semin. Ciências Agrárias 2019, 40, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.K.; Sharma, R.; Kumari, A.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Patil, R.D.; Bhar, R. Survey of ferns and clinico-pathological studies on the field cases of enzootic bovine haematuria in Himachal Pradesh, a north-western Himalayan state of India. Toxicon 2017, 138, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisielius, V.; Lindqvist, D.N.; Thygesen, M.B.; Rodamer, M.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Rasmussen, L.H. Fast LC-MS quantification of ptesculentoside, caudatoside, ptaquiloside and corresponding pterosins in bracken ferns. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1138, 121966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Fei, W.; Zhu, C.; Qian, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, Q. Determination of ptaquiloside in Pteridium aquilinum by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2018, 9, 4601–4606. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, M.T.; Brock, I.J.; Reichmann, K.G.; McKenzie, R.A.; Blaney, B.J. Norsesquiterpene Glycosides in Bracken Ferns (Pteridium esculentum and Pteridium aquilinum subsp. wightianum) from Eastern Australia: Reassessed Poisoning Risk to Animals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5133–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Groundwater Database JUPITER, GEUS Database (Denmark). Available online: https://www.geus.dk/produkter-ydelser-og-faciliteter/data-og-kort/national-boringsdatabase-jupiter/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Plackett, R.L.; Burman, J.P. The design of optimum multifactorial experiments. Biometrika 1946, 33, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, K.; Shobha Rani, R.H. Design of experiments: Concept and applications of Plackett Burman design. Clin. Res. Regul. Aff. 2007, 24, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, E.; Barwick, V. Quality Assurance in Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- National Centers for Environmental Information, NOAA. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/cdo-web/ (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Danish Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://mst.dk/natur-vand/vand-i-hverdagen/drikkevand/hvem-leverer-drikkevandet/ (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Kördel, W.; Egli, H.; Klein, M. Transport of pesticides via macropores (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 105–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ptaquiloside | Pterosin B | |
|---|---|---|
| CAS number | 87625-62-5 | 34175-96-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C20H30O9 | C14H18O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 398.45 g mol−1 | 218.29 g mol−1 |
| Log Kow a | −0.63 [35] | 3.33 [25] |
| Rate constant for hydrolysis at neutral conditions (4.4 < pH < 6.4) (22 °C) | 9.49 ± (6.02) × 10−4 h−1 [35] | - |
| Hydrolysis of PTA | ||
 | ||
| Water Type | Location (Denmark) | pH | T (°C) | EC (mS/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw groundwater a | Vigersted | 7.36 | 7.3 | 72 |
| Raw groundwater | Esbjerg | 6.43 | 8.5 c | 29 c |
| Treated water b | Vigersted | 7.84 | 7.8 | 100 |
| Variable | First Level (+) | Second Level (−) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: Water type | Raw groundwater | Treated water | ||||||
| B: Bottle type | Plastic | Glass | ||||||
| C: Filtering (0.2 μm) | Yes | No | ||||||
| D: pH | 5.5 | 6 | ||||||
| E: Transportation time | 2 h | 6 h | ||||||
| F: Transportation conditions | No ice | With ice | ||||||
| G: Sample storage conditions | 4 °C | −18 °C | ||||||
| Experiment no. | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | Results |
| 1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | l |
| 2 | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | m |
| 3 | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | p |
| 4 | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | w |
| 5 | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | v |
| 6 | − | + | − | − | + | − | + | x |
| 7 | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | y |
| 8 | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | z |
| Compound | Observed Linearity Range (µg L−1) | R2 | LOD (µg L−1) | LOQ (µg L−1) | Precision of the Instrument CV% (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTA | 1–100 | 0.999 | 1.5 | 4.6 | 1.0 |
| PtB | 2–100 | 0.998 | 2.7 | 8.1 | 3.0 |
| PTA intraday | 1–100 | 0.999 | 1.7 | 5.1 | 1.1 |
| PtB intraday | 2–100 | 1.000 | 1.4 | 4.1 | 3.2 |
| Groundwater Well | Well Type | Sampling Date | Location | pH | EC (mS/m) | Owner | Depth (m) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Deep | 03.07.2019 | 55.47599, 11.90715 | 7.3 | 692 | HOFOR | 42 | Drinking water |
| 2. | Deep | 03.07.2019 | 55.47479, 11.90556 | 7.1 | 782 | HOFOR | 42 | Drinking water |
| 3. | Deep | 03.07.2019 | 55.47407, 11.90258 | 7.8 | 741 | HOFOR | 42 | Drinking water |
| 4. | Shallow | 03.07.2019; 08.09.2019 | 55.475063, 11.907543 | 7.0 6.9 | 320 340 | Private | 8 | Technical water a |
| 5. | Shallow | 03.07.2019 | 55.47616, 11.90973 | 6.9 | 592 | Private | - | Technical water a |
| 6. | Shallow | 03.07.2019 | 55.47134, 11.91239 | 7.2 | 476 | Private | 10 | Drinking water |
| Tested Loading Volumes | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|
| 10 mL | 99 ± 1 |
| 25 mL | 99 ± 3 |
| 50 mL | 85 ± 2 |
| 100 mL | 79 ± 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skrbic, N.; Pedersen, A.-K.; Christensen, S.C.B.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Rasmussen, L.H. A Novel Method for Determination of the Natural Toxin Ptaquiloside in Ground and Drinking Water. Water 2020, 12, 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102852
Skrbic N, Pedersen A-K, Christensen SCB, Hansen HCB, Rasmussen LH. A Novel Method for Determination of the Natural Toxin Ptaquiloside in Ground and Drinking Water. Water. 2020; 12(10):2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102852
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkrbic, Natasa, Ann-Katrin Pedersen, Sarah C. B. Christensen, Hans Christian Bruun Hansen, and Lars Holm Rasmussen. 2020. "A Novel Method for Determination of the Natural Toxin Ptaquiloside in Ground and Drinking Water" Water 12, no. 10: 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102852
APA StyleSkrbic, N., Pedersen, A.-K., Christensen, S. C. B., Hansen, H. C. B., & Rasmussen, L. H. (2020). A Novel Method for Determination of the Natural Toxin Ptaquiloside in Ground and Drinking Water. Water, 12(10), 2852. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102852






