Quantitative Analysis of the Sub-Cloud Evaporation of Atmospheric Precipitation and Its Controlling Factors Calculated By D-Excess in an Inland River Basin of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Date and Method
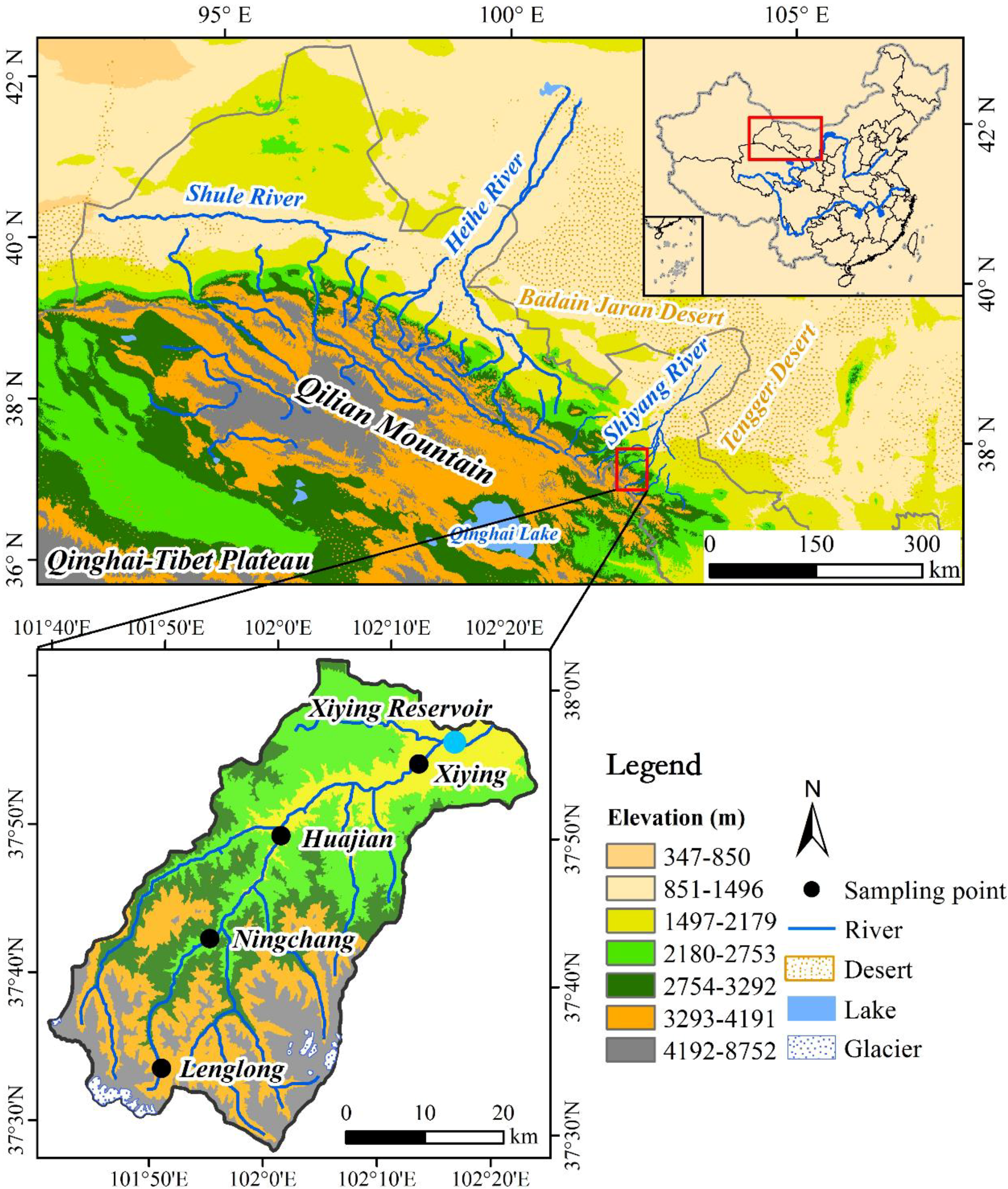
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Method
3. Result and Discussion
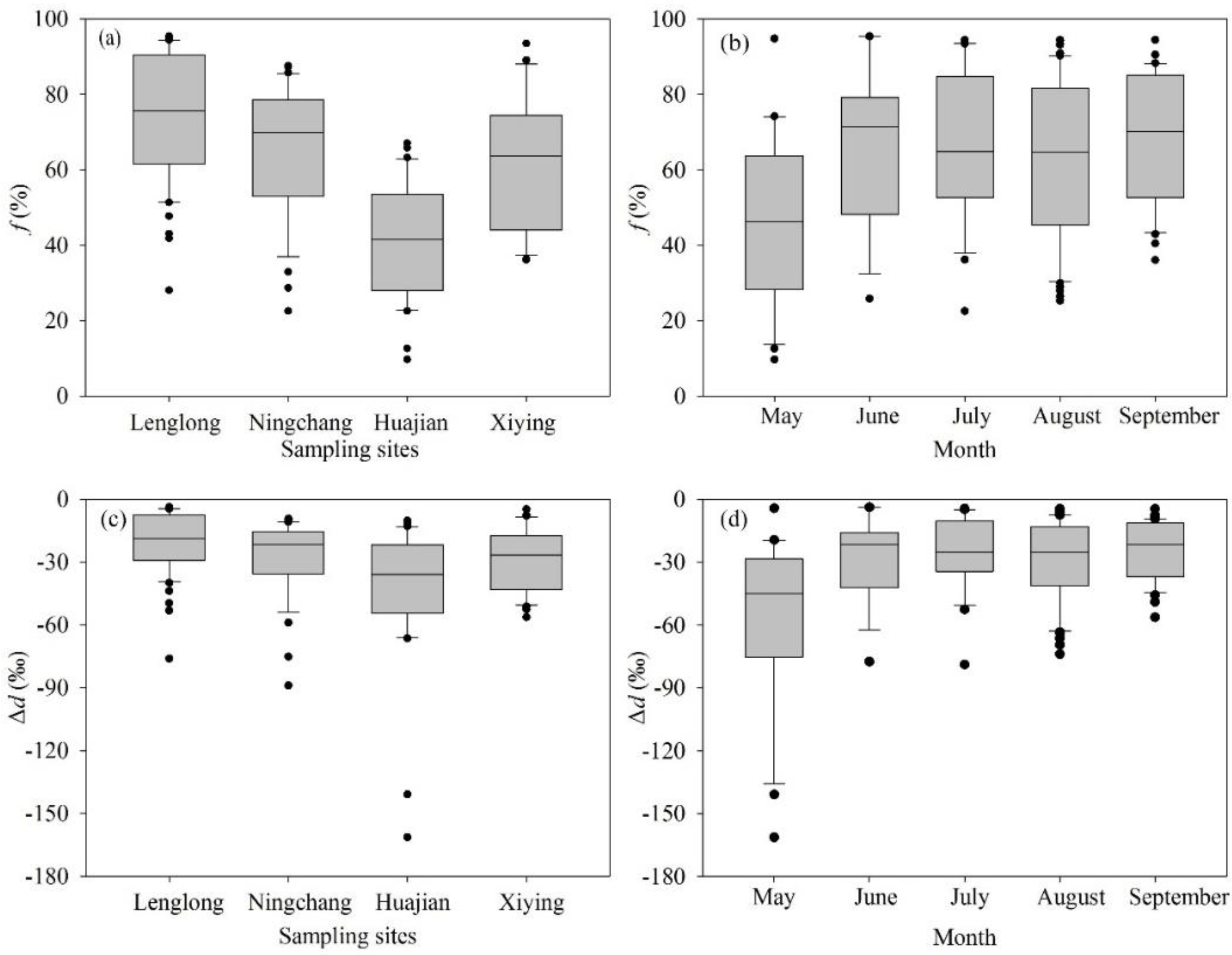
3.1. Variations of d-excess
3.2. Variations of Δd
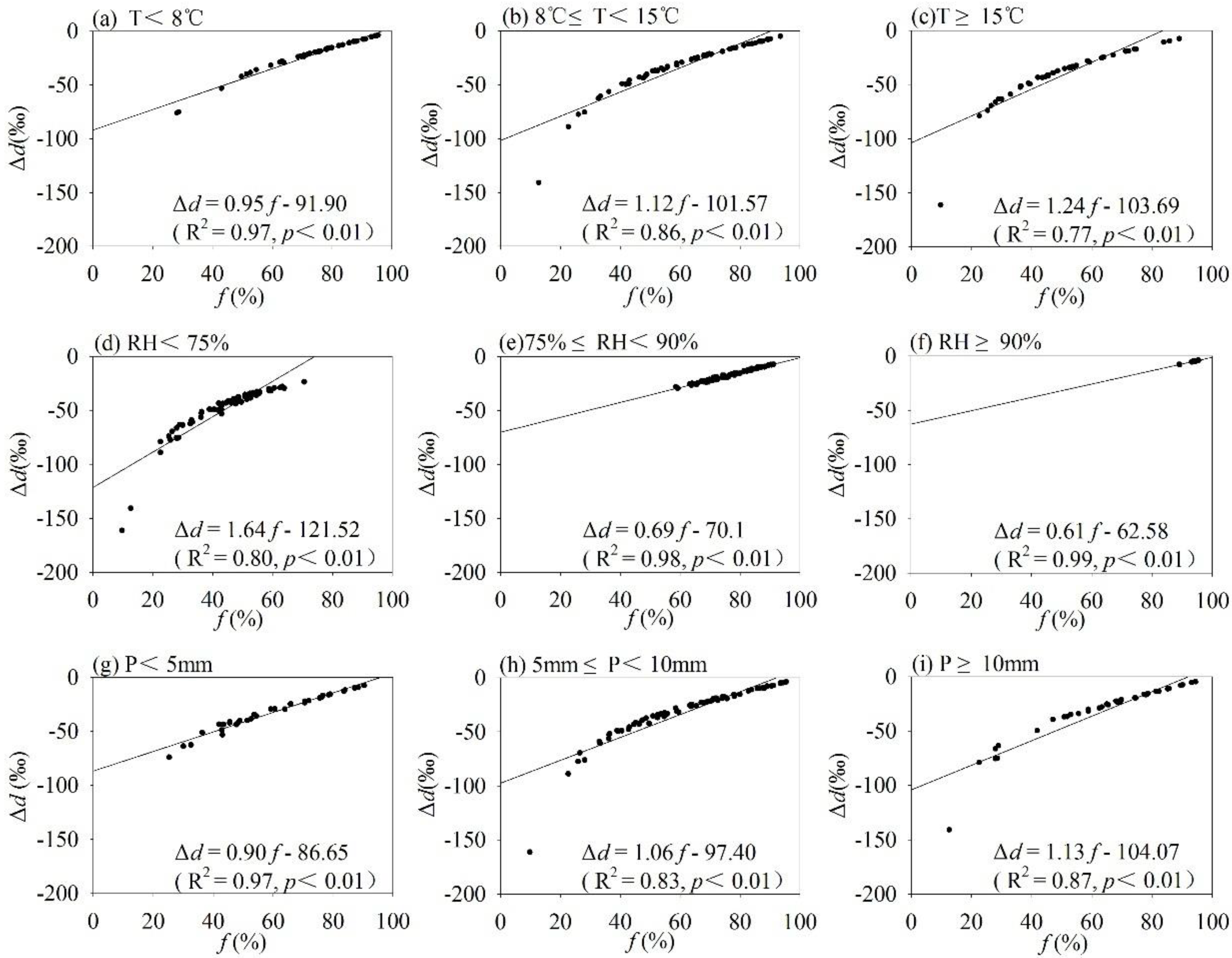
3.3. The Correlation between f and Δd
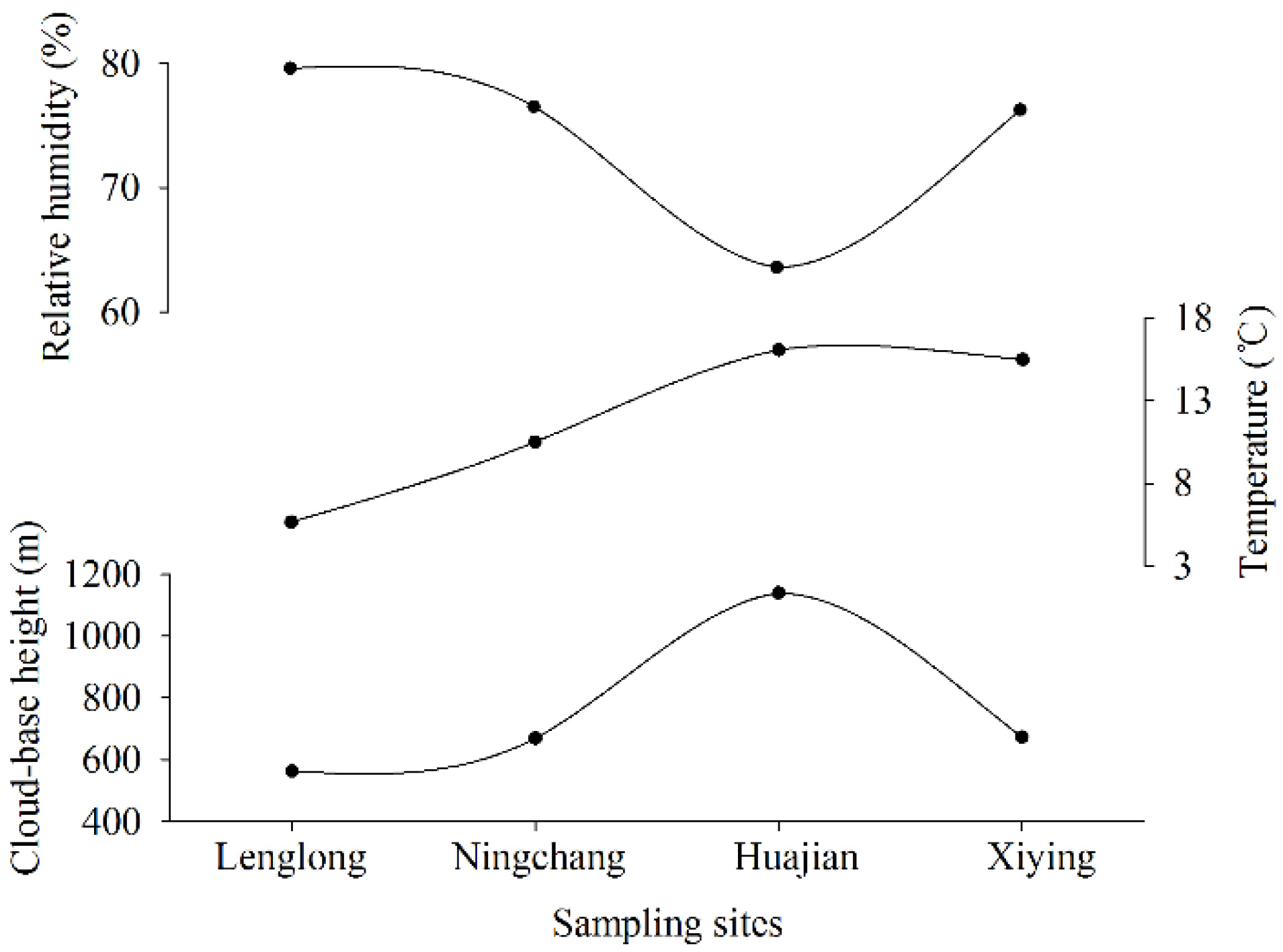
3.4. Influencing Factors of Sub-cloud Evaporation and Δd
3.4.1. Influence of Artificial Reservoir
3.4.2. Influence of Meteorological Factors
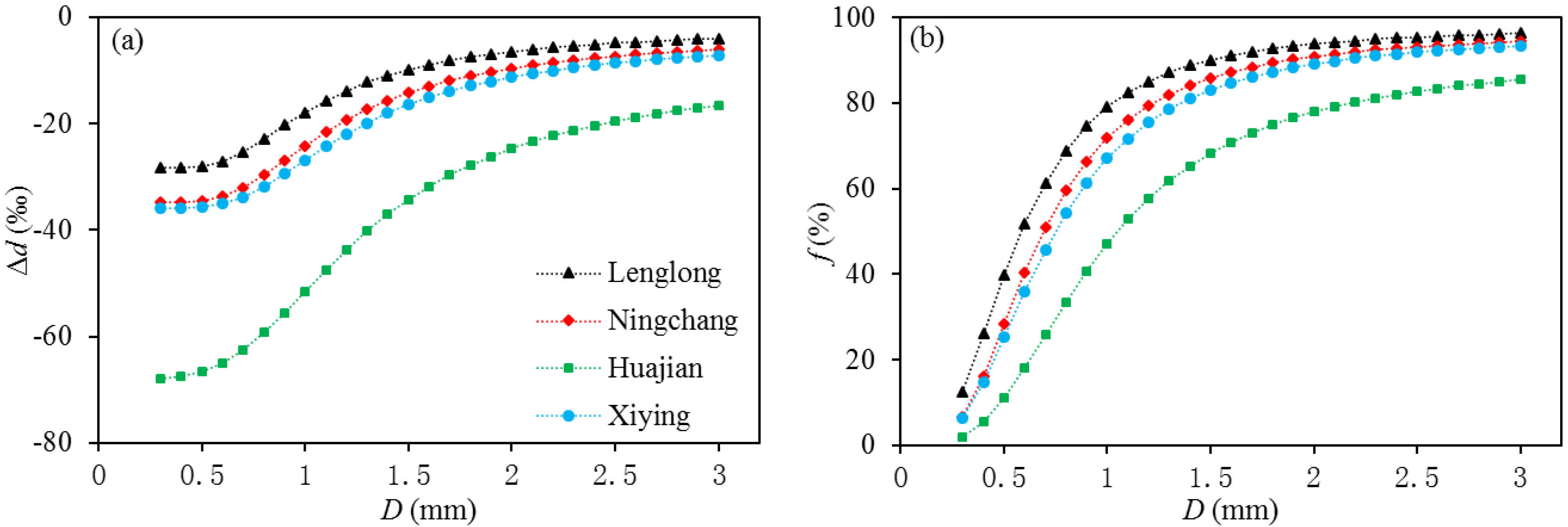
3.4.3. Influence of Raindrop Diameter
4. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Yuan, R.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, W.; Ning, T.; Gui, J.; et al. Climate background, relative rate, and runoff effect of multiphase water transformation in Qilian Mountains, the third pole region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers, in climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Thomas, S., Stocker, F., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.H.; Wang, H.J. New understanding of the scientific issues of climate change in China during the past 100 years. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1029–1041. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Chen, W.M.; Li, B.L.; Tong, C.M.; Zhao, M.; Wang, N. Simulation of the permafrost distribution on Qilian Mountains over past 40 years under the influence of climate change. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1275–1284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.B.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, H. Temporal-spatial variation characteristics of snow cover in Qilian Mountains from 2001 to 2017. Arid Zone Res. 2019, 42, 56–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.P.; Yao, X.J.; An, L.N.; Li, X.; Gong, P.; Qi, M. College of Geography and Environment Sciences, Northwest Normal University. Change of ice volume in the Qilian Mountains during the period from 2000 to 2010. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 325–333. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.X.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.J.; Yuan, R.F.; Gui, J.; Lv, Y.M. Climate background, fact and hydrological effect of multiphase water transformation in cold regions of the Western China: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 33–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. The abundance of 18O in atmospheric water and water vapor. Tellus B 1953, 5, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Romatschke, U.; Araguas-Araguas, L.; Belachew, D.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Berg, P.; Schumacher, C.; Funk, A. Proportions of convective and stratiform precipitation revealed in water isotope ratios. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, Z.; Harmon, R.S.; Fórizs, I. Stable isotope signatures of seasonal precipitation on the Pacific coast of central Panama. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershaw, J. Controls on deuterium excess across Asia. Geoscience 2018, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, E.; Dall’Olio, A.; Matsui, E.; Gat, J.R. Recycling of water in the Amazon Basin: An isotopic study. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R.; Bowser, C.J.; Kendall, C. The contribution of evaporation from the Great Lakes to the continental atmosphere: Estimate based on stable isotope data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, K.; Kralik, M.; Papesch, W.; Rank, D.; Scheifinger, H.; Stichler, W. Deuterium excess in precipitation of Alpine regions—Moisture recycling. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.-R.; Liu, K.-K.; Wang, C.-H.; Chuang, K.-H. A water isotope approach to assessing moisture recycling in the island-based precipitation of Taiwan: A case study in the western Pacific. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 08507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-F.; Li, J.; Shi, P.-J.; He, Y.-Q.; Cai, A.; Tong, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Yang, L. Relationship between sub-cloud secondary evaporation and stable isotope in precipitation in different regions of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Froehlich, K.; Huang, T.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Processes affecting isotopes in precipitation of an arid region. Tellus B 2011, 63, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamalikis, V.; Argiriou, A.; Dotsika, E. Isotopic modeling of the sub-cloud evaporation effect in precipitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbach, S.F.M.; Adkins, J.F.; Mayer, H.; Marwan, N.; Kumar, K.K.; Haug, G.H. Strong influence of water vapor source dynamics on stable isotopes in precipitation observed in Southern Meghalaya, NE India. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 292, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Alduchov, O.A.; Froehlich, K.O.; Araguas-Araguas, L.J.; Sturchio, N.C.; Kurita, N. Stable isotopes in global precipitation: A unified interpretation based on atmospheric moisture residence time. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 11705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.K. Stable isotope fractionation due to evaporation and isotopic exchange of falling water drops: Applications to atmospheric processes and evaporation of lakes. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Z.; Yao, T. Mathematical modeling of variations on stable isotopic ratios in falling raindrops. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1998, 12, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Mayer, B.; Harris, S.; Krouse, H.R. The influence of below-cloud secondary effects on the stable isotope composition of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation at Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Tellus B 2007, 59, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiaoyan, L.; Li, G.; Huang, Y. Seasonal variations of deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopes and their response to moisture source for precipitation events in the subtropical monsoon region. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 29, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Che, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X. Influence of below-cloud evaporation on deuterium excess in precipitation of arid central asia and its meteorological controls. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, X.; Dong, L. Relationship between sub-cloud secondary evaporation and stable isotopes in precipitation of Lanzhou and surrounding area. Quat. Int. 2015, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, T.R.; Körner, C. On the use of elevation, altitude, and height in the ecological and climatological literature. Oecologia 2012, 171, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.G.; Jia, W.X.; Zhu, G.F.; Ding, D.; Pan, H.; Xu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, R. Stable isotope composition of precipitation at different elevations in the monsoon marginal zone. Quat. Int. 2018, 493, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Guo, H.; Qin, D.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Ma, X. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in the monsoon marginal zone: Estimate based on stable isotope data. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criss, R.E. Principles of Stable Isotope Distribution; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, S.L. An empirical shortcut to the calculation of temperature and pressure at the lifted condensation level. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1968, 7, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzer, G.D.; Gunn, R. The evaporation, temperature and thermal relaxation-time of freely falling waterdrops. J. Meteorol. 1951, 8, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, A.C. Empirical formulae for the terminal velocity of water drops falling through the atmosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1950, 76, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Pang, Z.; Froehlich, K. Quantifying recycled moisture fraction in precipitation of an arid region using deuterium excess. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2013, 65, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberan-Santos, M.N.; Bodunov, E.N.; Pogliani, L. On the barometric formula. Am. J. Phys. 1997, 65, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Chen, F. An investigation of moisture sources and secondary evaporation in Lanzhou, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Demonstration of limited water level of Xiying reservoir before flood. Gansu Agric. 2006, 11, 388–389. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G. Analysis of Raindrop Size-Distribution in Orographic Clouds in Qilian Mountains, China; Peking University: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Sampling Sites | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation (m) | d-excess in Near Surface (‰) | d-excess in Cloud-base (‰) | Δd (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lenglong | 37.55° N | 101.85° E | 3600 | 19.72 | 40.01 | −20.29 |
| Ningchang | 37.70° N | 101.89° E | 2721 | 13.17 | 40.14 | −26.97 |
| Huajian | 37.82° N | 102.01° E | 2390 | 10.23 | 45.74 | −35.15 |
| Xiying | 37.89° N | 102.18° E | 2097 | 13.90 | 43.35 | −29.45 |
| Surface Air Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Evaporation Intensity (g·s−1) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lenglong | Ningchang | Huanjian | Xiying | Lenglong | Ningchang | Huanjian | Xiying | Lenglong | Ningchang | Huanjian | Xiying | |
| May | 3.1 | 8.4 | 13.7 | 8.2 | 69.7 | 63.3 | 47.5 | 63.8 | 0.49 | 0.87 | 1.60 | 0.67 |
| June | 5.3 | 8.3 | 12.8 | — | 78.2 | 77.6 | 59.3 | — | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.95 | — |
| July | 8.2 | 12.6 | 17.8 | 17.1 | 81.9 | 72.1 | 71.9 | 81.7 | 0.45 | 0.75 | 1.01 | 0.60 |
| August | 7.6 | 13.0 | 17.1 | 16.5 | 84.8 | 79.7 | 66.4 | 77.4 | 0.37 | 0.56 | 1.01 | 0.65 |
| September | 4.2 | 9.5 | 14.5 | 10.7 | 80.9 | 79.9 | 65.4 | 71.4 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.67 |
| Sampling Site | Linear Regression | Coefficient of Determination (R2) |
|---|---|---|
| Lenglong | Δd = 0.83 f − 83.32 | 0.96 |
| Ningchang | Δd = 0.98 f − 95.84 | 0.95 |
| Huajian | Δd = 1.38 f − 117.54 | 0.76 |
| Xiying | Δd = 0.82 f − 82.07 | 0.98 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Jia, W.; Zhu, G.; Wang, S. Quantitative Analysis of the Sub-Cloud Evaporation of Atmospheric Precipitation and Its Controlling Factors Calculated By D-Excess in an Inland River Basin of China. Water 2020, 12, 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102798
Ma X, Jia W, Zhu G, Wang S. Quantitative Analysis of the Sub-Cloud Evaporation of Atmospheric Precipitation and Its Controlling Factors Calculated By D-Excess in an Inland River Basin of China. Water. 2020; 12(10):2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102798
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xinggang, Wenxiong Jia, Guofeng Zhu, and Shijin Wang. 2020. "Quantitative Analysis of the Sub-Cloud Evaporation of Atmospheric Precipitation and Its Controlling Factors Calculated By D-Excess in an Inland River Basin of China" Water 12, no. 10: 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102798
APA StyleMa, X., Jia, W., Zhu, G., & Wang, S. (2020). Quantitative Analysis of the Sub-Cloud Evaporation of Atmospheric Precipitation and Its Controlling Factors Calculated By D-Excess in an Inland River Basin of China. Water, 12(10), 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102798




