Decomposition and Attribution Analysis of Runoff Alteration of the Dongting Lake in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
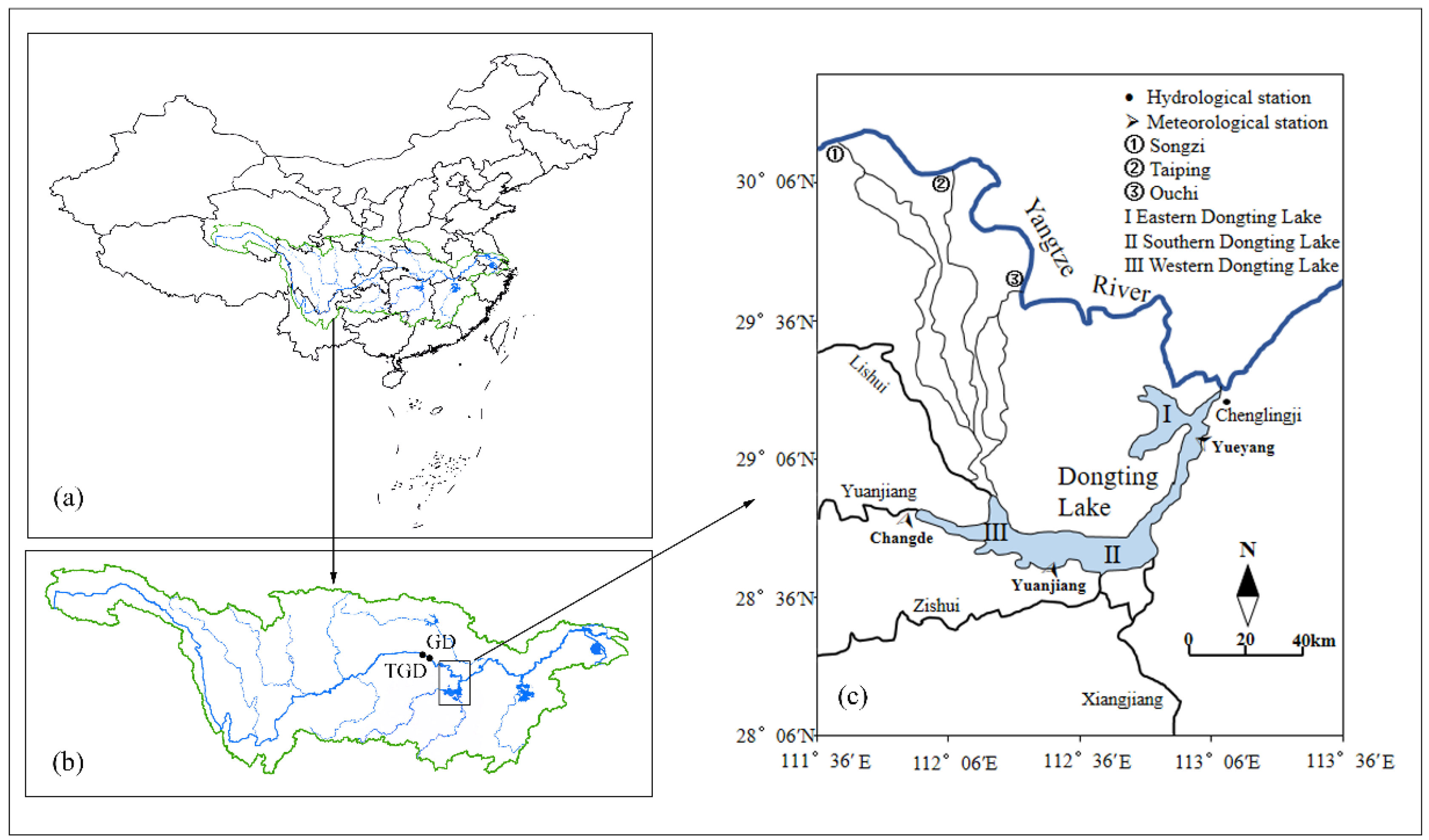
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Simple Linear Regression Method
2.3.2. Double-Mass Curve Method
2.3.3. Budyko-Based Methods
3. Results
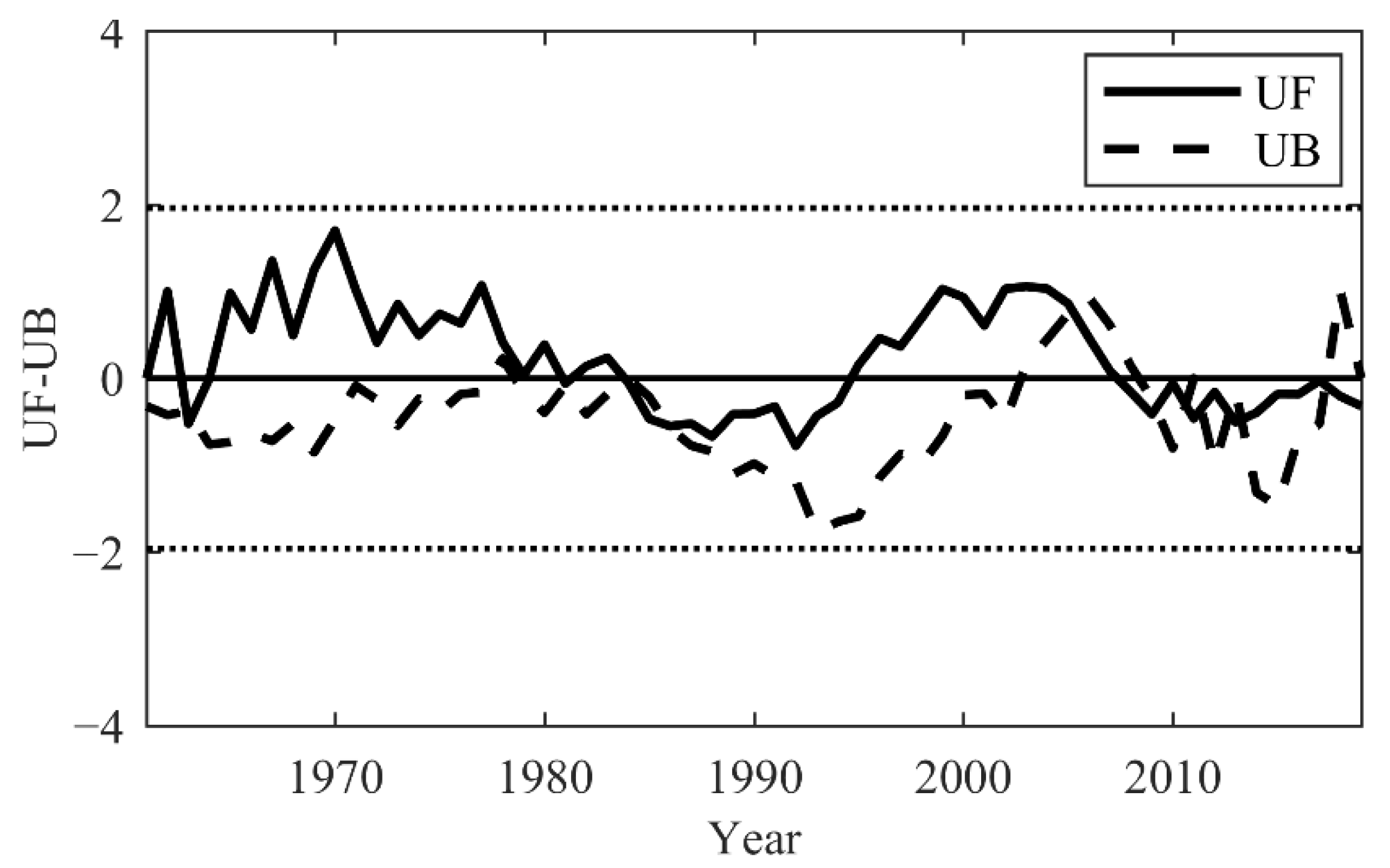
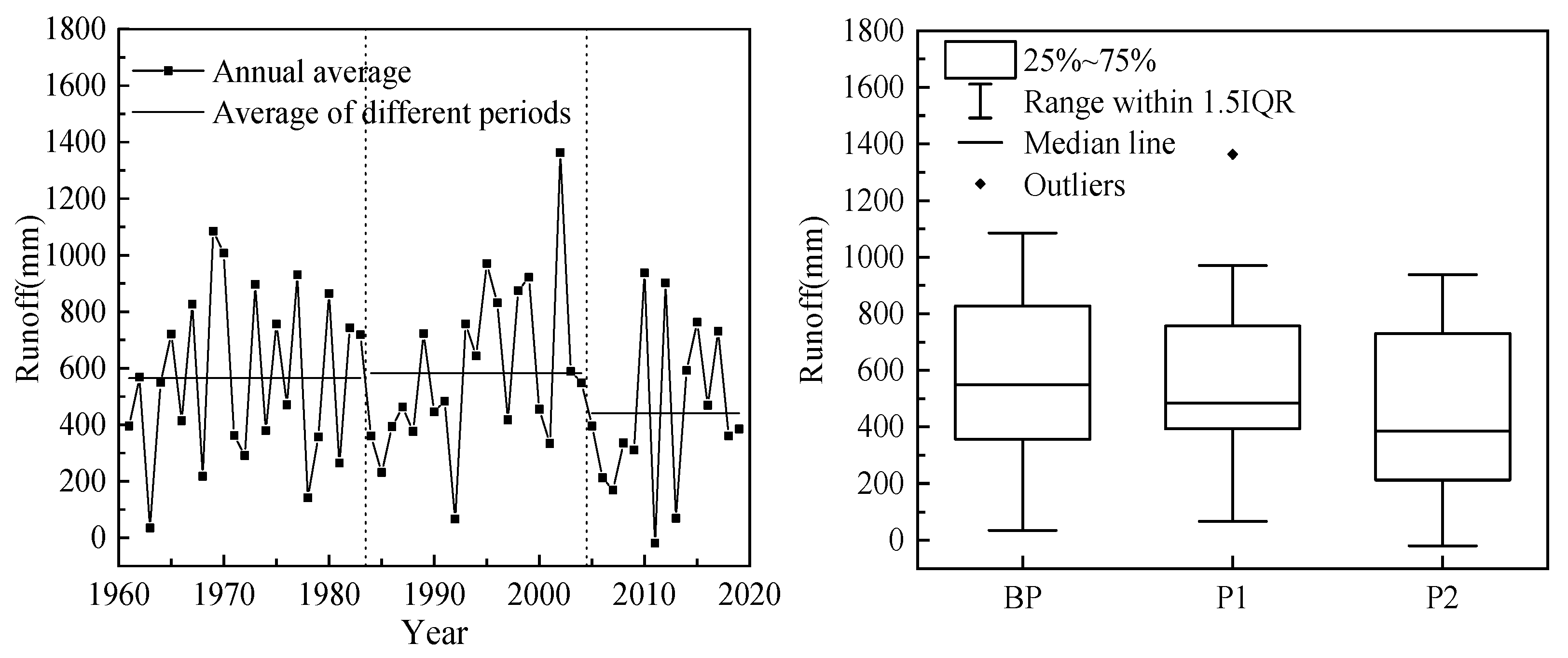
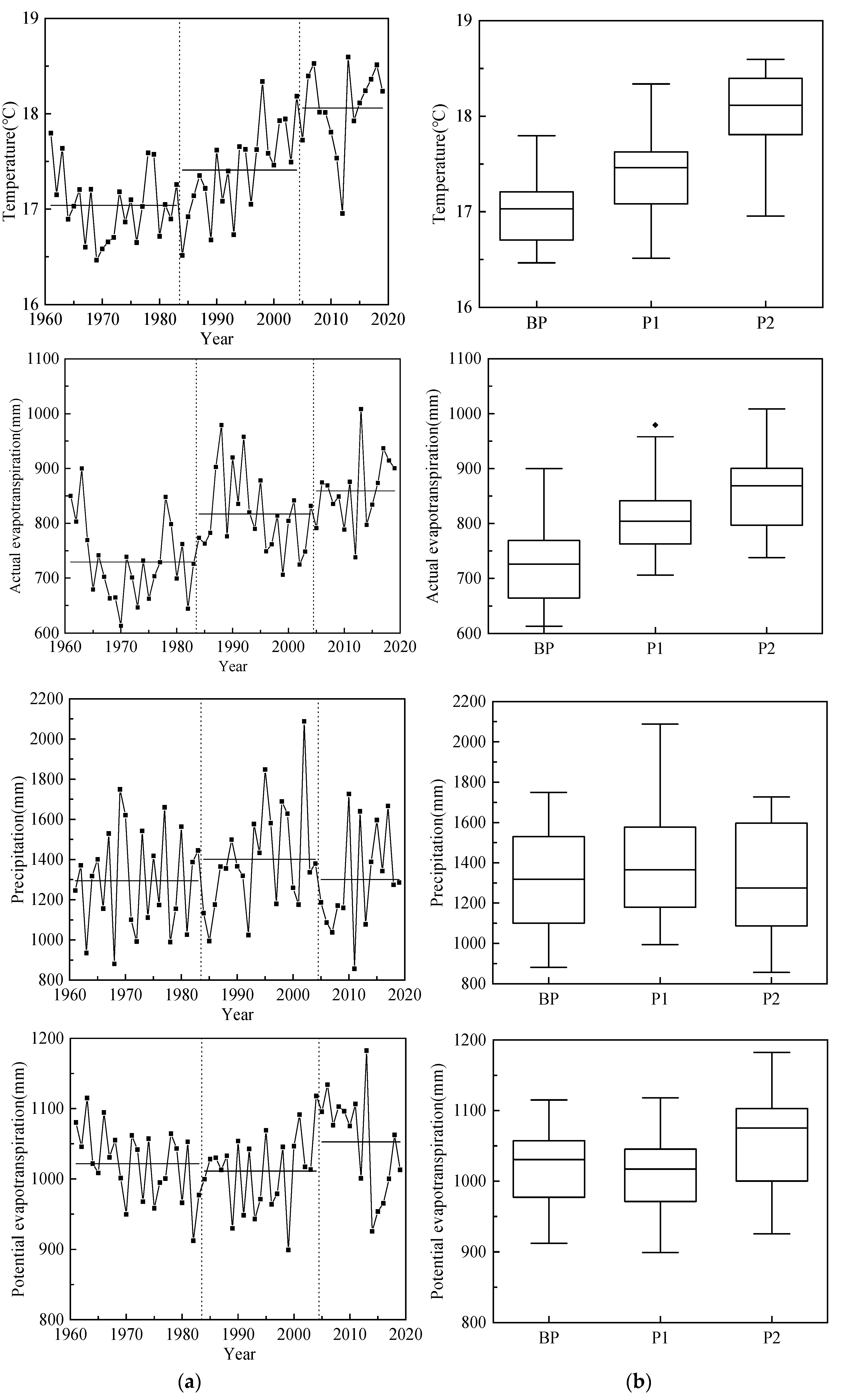
3.1. Meteorological Data and Hydrological Data Analysis
3.2. Assessing Contribution of Climate Change and Human Activity to Runoff Alteration
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence Factors for Runoff
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huntington, T.G. Evidence for intensification of the global water cycle: Review and synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomer, M.D.; Schilling, K. A simple approach to distinguish land-use and climate-change effects on watershed hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cuo, L.; Li, Q.J.; Liu, X.S.; Ma, X.L.; Liang, L.Q.; Ding, J. Impacts of Climate Change and Land Use/Cover Change on Streamflow in Beichuan River Basin in Qinghai Province, China. Water 2020, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.P.; Andréasson, J.; Carlsson, B. Assessing climate change impacts on hydrology from an ensemble of regional climate models, model scales and linking methods—A case study on the Lule River basin. Clim. Chang. 2007, 81, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Weng, B.S.; Man, Z.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhao, J.L. Analyzing the contributions of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Northeast Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Z.; Liu, W.X.; Wang, W.G.; Shao, Q.X.; Jiao, X.Y.; Yu, Z.B.; Xing, W.Q.; Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.X.; Luo, Y.F. Estimating the Effects of Climatic Variability and Human Activities on Streamflow in the Hutuo River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.H.; Chen, X.H. Evaluation of impacts of climate change and human activities on streamflow in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2562–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X. Advances in separating effects of climate variability and human activity on stream discharge: An overview. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 71, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Miao, C.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Yang, T.T.; Duan, Q.Y. Detecting the quantitative hydrological response to changes in climate and human activities. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 586, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Mu, X.M.; Wang, F.; Li, R. Changes in streamflow and sediment discharge and the response to human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Zou, X.Q.; Liu, Q.; Yao, Y.L.; Li, Y.L.; Wu, X.W.; Wang, C.L.; Yu, W.W.; Wang, T. Assessing natural and anthropogenic influences on water discharge and sediment load in the Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaake, J.C. From climate to flow. In Climate Change and U.S. Water Resources; Waggoner, P.E., Ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Sankarasubramanian, A.; Vogel, R.M.; Limbrunner, J.F. Climate elasticity of streamflow in the United States. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.K. The use of the aridity index to assess climate change effect on annual runoff. J. Hydrol. 2002, 265, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and Life; Miller, D.H., Translator; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.Y.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Liang, W.; Jiang, X.H. Determining the hydrological responses to climate variability and land use/cover change in the Loess Plateau with the Budyko framework. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 557, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Shang, S.Y.; Yang, W.H.; Clary, C.R.; Yang, D.W. Simulation of land use–soil interactive effects on water and sediment yields at watershed scale. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, D.W.; Tan, S.K.; Gao, B.; Hu, Q.F. Impact of climate variability and human activity on streamflow decrease in the Miyun Reservoir catchment. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, X.C. Impacts of Three Gorges Reservoir on the sedimentation regimes in the downstream-linked two largest Chinese freshwater lakes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.A.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, X.S.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.Y.; Xie, Y.H. Crucial sites and environmental variables for wintering migratory waterbird population distributions in the natural wetlands in East Dongting Lake, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 655, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. Biodiversity crisis in the Yangtze River: The culprit was dams, followed by overfishing. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 1279–1299. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Mei, X.F.; Dai, Z.J.; Gao, J.J.; Li, J.B.; Wang, J.; Lou, Y.Y. Hydromorphological processes of Dongting Lake in China between 1951 and 2014. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Ma, J.R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, J.B.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Shi, K.; Brookes, J.D.; Jeppesen, E. Influence of the three Gorges Reservoir on the shrinkage of China’s two largest freshwater lakes. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 177, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.M.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, X.C.; Yu, G.; Liao, X.H. Effects of the dispatch modes of the Three Gorges Reservoir on the water regimes in the Dongting Lake area in typical years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.; Shaw, T.A. Circulation response to warming shaped by radiative changes of clouds and water vapour. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.J.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Liang, J.; Guo, S.L.; Huang, L.; Wu, H.P.; Hua, S.S. Quantitative assessment of the contribution of climate variability and human activity to streamflow alteration in Dongting Lake, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.H.; Feng, C.; Zhou, H.; Hu, G.W.; Li, Z.Z.; Guo, R.Z. Hunan Normal University; Province, C.H.A.W.R.S.B.O.H.; Hunan Industry University The runoff variation characteristics of Dongting Lake, China. Tecnol. Ciencias Agua 2017, 8, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration (guidelines for computing crop water requirements). FAO Irrig. Drain. Pap. 1998, 56, 205–226. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, N.S.N. Spatial Interpolation Methods: A Review. Am. Cartogr. 1983, 10, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.M.; Jiao, J.Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Quantifying the impact of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M.; Jiao, J.Y.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.Y.; Li, E.H.; Wei, Y.H.; Huang, J.C. Assessing response of sediment load variation to climate change and human activities with six different approaches. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 639, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, J.K.; Hardison, C.H. Double-mass curves, Manual of hydrology: Part 1. General Surface-Water Techniques. Geolog. Surv. Water-Supp. Paper 1950, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, R.J.; Roderick, M.L.; McVicar, T.R. Roots, storms and soil pores: Incorporating key ecohydrological processes into Budyko’s hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xiong, L.H.; Wang, D.B.; Liu, P.; Guo, S.L.; Xu, C.Y. Separating the impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff using the Budyko-type equations with time-varying parameters. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.B.; Wang, L.M.; W, W.R.; Qi, J.G.; Y, L.S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, P. An analytical approach to separate climate and human contributions to basin streamflow variability. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingman, S.L. Physical Hydrology; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, P. Uber die Beziehungen zwischen dem Niederschlag und der Wasserfu ¨hrung der Flu ¨ße in Mitteleuropa. Meteorol. Z. 1904, 21, 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Ol’dekop, E.M. On Evaporation from the Surface of River Basins: Transactions on Meteorological Observations. Lur-evskogo; Report. Univ. of Tartu: Tartu, Estonia, 1911. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pike, J. The estimation of annual run-off from meteorological data in a tropical climate. J. Hydrol. 1964, 2, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turc, L. Le bilan d’eau des sols. Relation entre la precipitation, l’evaporation et l’e’coulement. Ann. Agron. 1954, 5, 491–569. [Google Scholar]
- Budyko, M.I. Evaporation Under Natural Conditions; Isr. Program for Sci: Jerusalem, Israel, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.P. The calculation of the evaporation from land surface. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.Y.S.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: Irvine, CA, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate In 2019; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Wang, R.N.; Peng, W.Q.; Liu, X.B.; Jiang, C.L.; Wu, W.Q.; Chen, X.K. Characteristics of Runo Variations and Attribution Analysis in the Poyang Lake Basin over the Past 55 Years. Sustainability 2020, 12, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunan Water Resources Bulletin. 2001–2018. Available online: http://slt.hunan.gov.cn/xxgk/tjgb (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Long, Q.B.; Wang, S.B. Study on statistical caliber classification and sampling survey method of total water use in Hunan Province. Hunan Hydro Power. 2019, 220, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Wang, X.L.; Cai, X.B.; Li, E.H.; Jiang, L.Z.; Li, H.; Yan, R.R. Analysis of the relationship between inundation frequency and wetland vegetation in Dongting Lake using remote sensing data. Ecohydrology 2013, 7, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
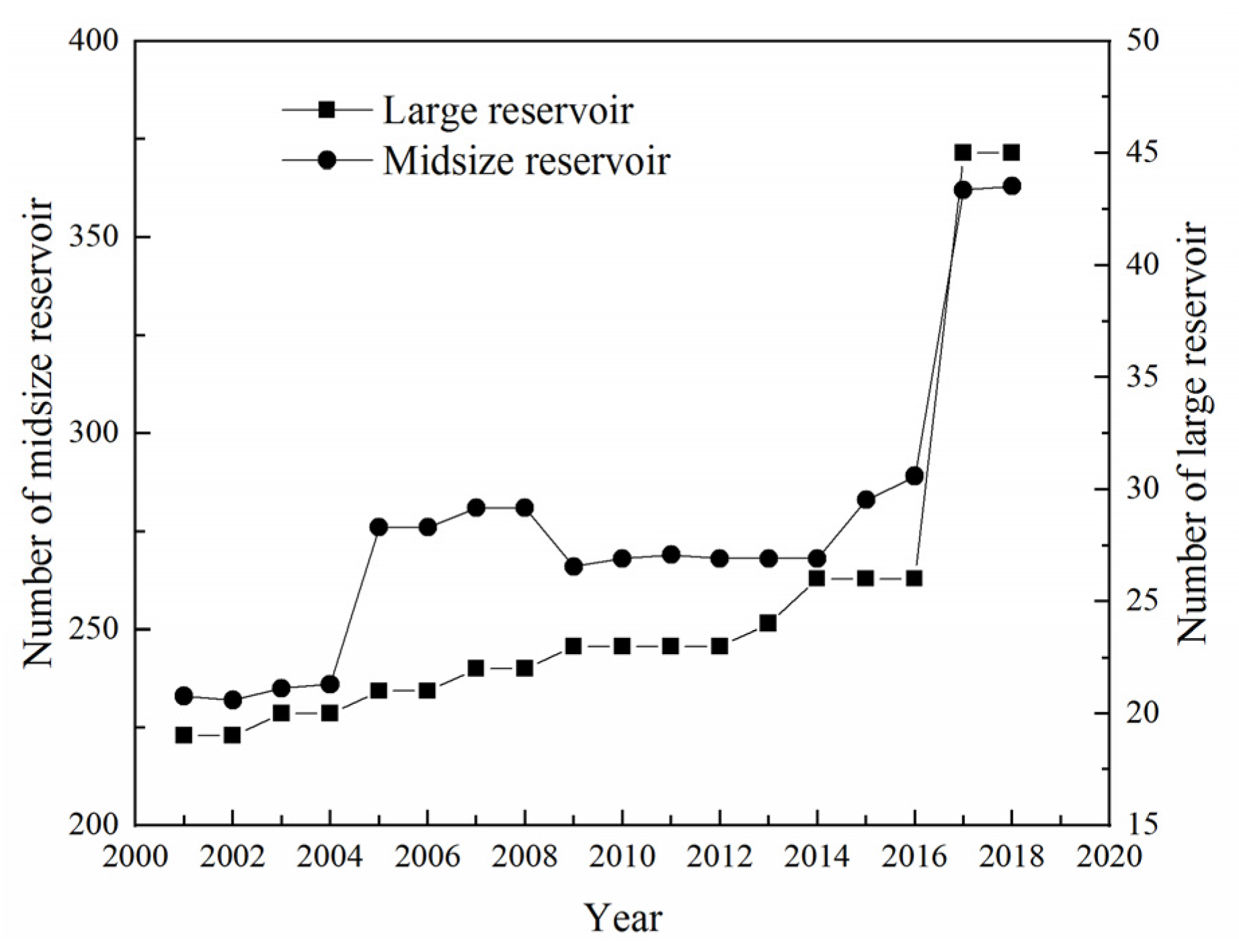
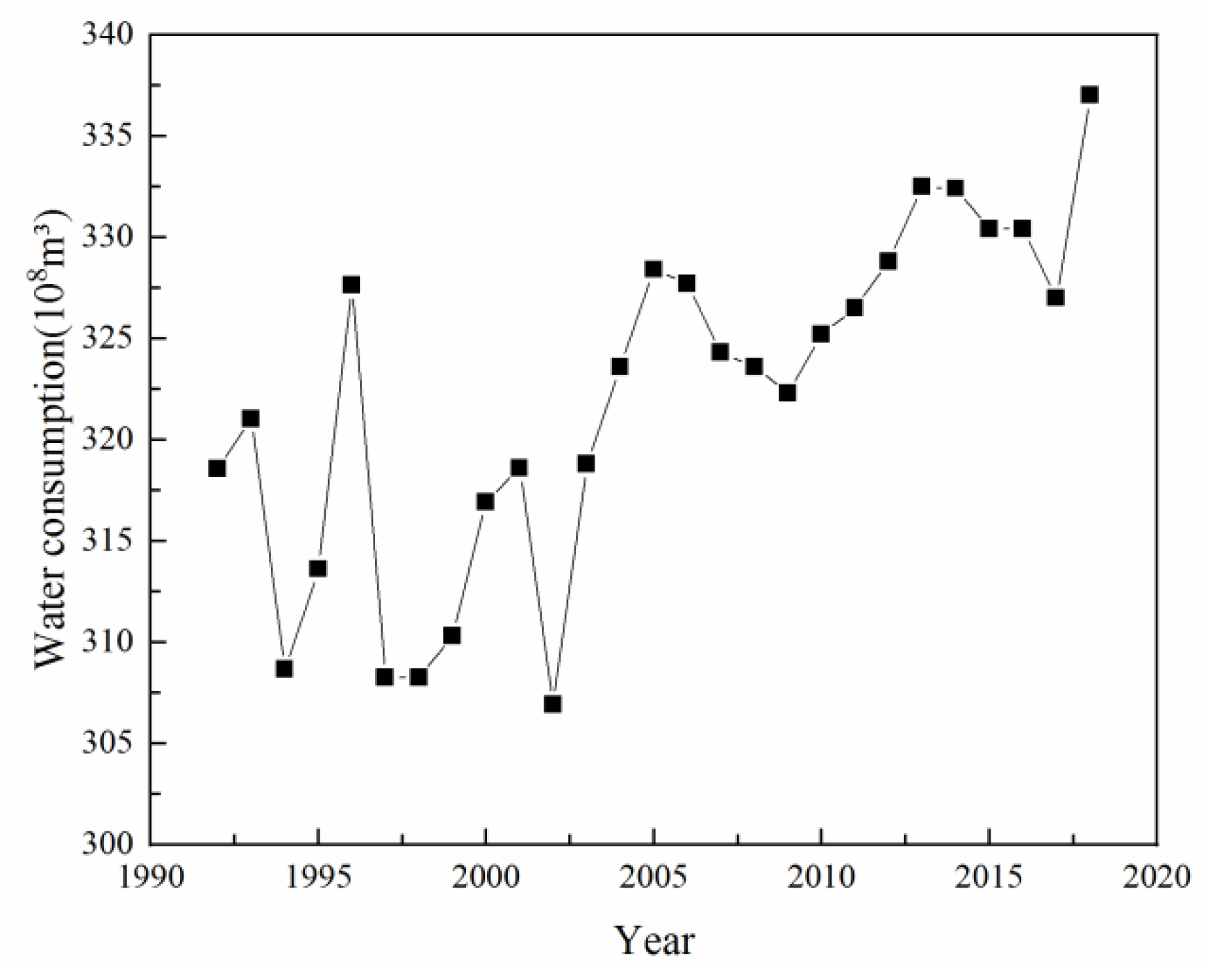
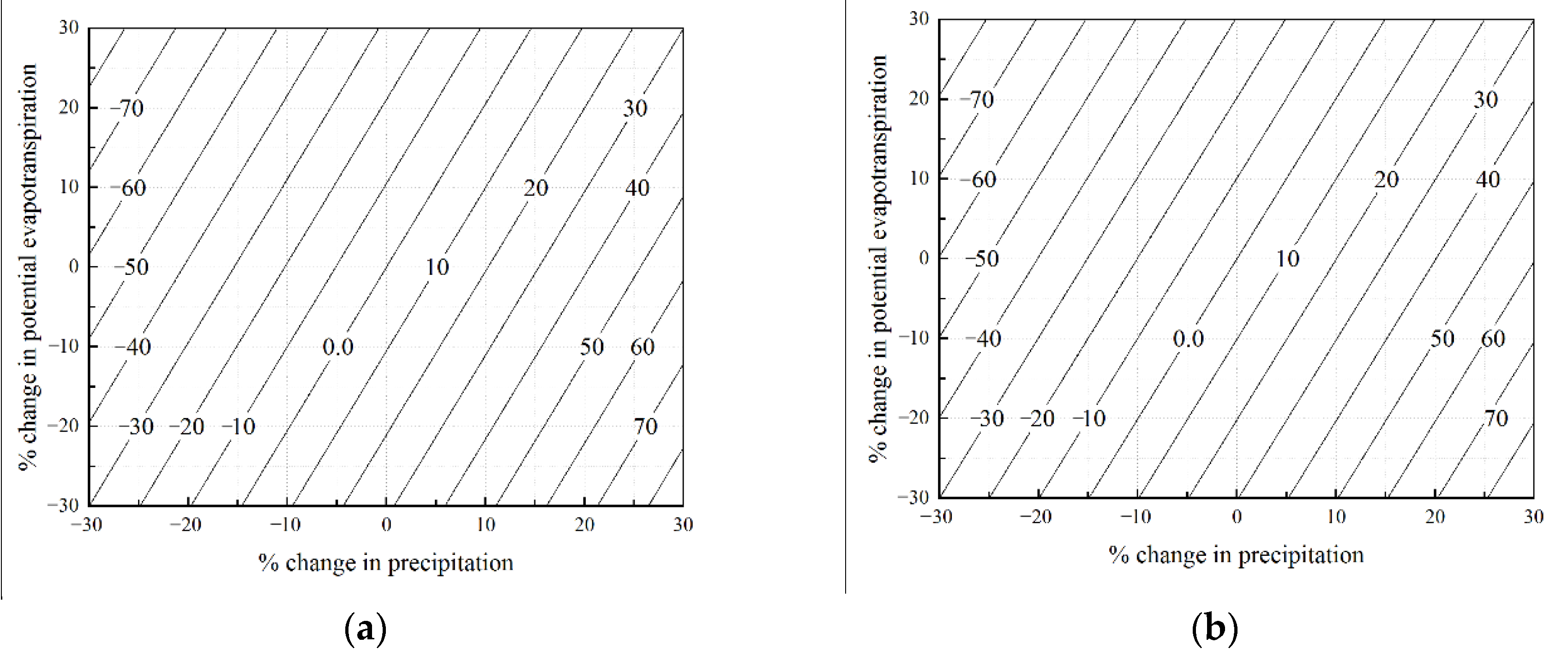
| Reference | Function | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Schreiber [38] | Non | |
| Ol’dekop [39] | Non | |
| Pike [40], Turc [41] | Non | |
| Budyko [42] | Non | |
| Fu [43] | m | |
| Zhang [44] | ω |
| Cv(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | E | P | E0 | Q | |
| BP | 2.16 | 10.01 | 19.37 | 4.97 | 52.16 |
| P1 | 2.77 | 9.11 | 19.20 | 5.44 | 50.62 |
| P2 | 2.42 | 7.83 | 19.95 | 6.93 | 66.05 |
| P1 | P2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(mm) | (mm) | (%) | (%) | (mm) | (mm) | (%) | (%) | ||
| The first group of methods | SLR | 121.51 | −103.35 | 668.88 | −568.88 | 6.12 | −130.42 | −4.92 | 104.92 |
| DMC | 70.14 | −51.98 | 386.11 | −286.11 | 22.91 | −147.21 | −18.43 | 118.43 | |
| The second group of methods | Schereiber | 83.81 | −65.65 | 461.36 | −361.36 | −8.49 | −115.81 | 6.83 | 93.17 |
| OL’dekop | 105.81 | −87.64 | 582.45 | −482.45 | −14.34 | −109.96 | 11.53 | 88.47 | |
| Budyko | 92.59 | −74.48 | 509.97 | −409.97 | −10.82 | −113.48 | 8.71 | 91.29 | |
| Pike | 94.59 | −76.42 | 520.67 | −420.67 | −11.36 | −112.95 | 9.14 | 90.86 | |
| Fu | 96.01 | −77.84 | 528.48 | −428.48 | −11.55 | −112.75 | 9.29 | 90.71 | |
| Zhang | 88.33 | −70.16 | 486.21 | −386.21 | −9.59 | −114.71 | 7.72 | 92.28 | |
| P1 | P2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schereiber | 1.76 | −0.76 | 1.80 | −0.80 |
| OL’dekop | 2.19 | −1.19 | 2.24 | −1.24 |
| Budyko | 1.93 | −0.93 | 1.97 | −0.97 |
| Pike | 1.97 | −0.97 | 2.01 | −1.01 |
| Fu | 1.99 | −0.99 | 2.03 | −1.03 |
| Zhang | 1.84 | −0.84 | 1.88 | −0.88 |
| Average | 1.95 | −0.95 | 1.99 | −0.99 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Yu, M.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y. Decomposition and Attribution Analysis of Runoff Alteration of the Dongting Lake in China. Water 2020, 12, 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102729
Huang Y, Yu M, Tian H, Liu Y. Decomposition and Attribution Analysis of Runoff Alteration of the Dongting Lake in China. Water. 2020; 12(10):2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yuyun, Minghui Yu, Haoyong Tian, and Yujiao Liu. 2020. "Decomposition and Attribution Analysis of Runoff Alteration of the Dongting Lake in China" Water 12, no. 10: 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102729
APA StyleHuang, Y., Yu, M., Tian, H., & Liu, Y. (2020). Decomposition and Attribution Analysis of Runoff Alteration of the Dongting Lake in China. Water, 12(10), 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102729




