Treatment and Re-Use of Raw Blackwater by Chlorella vulgaris-Based System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blackwater Collection and Characterization
2.2. Microalgae Inoculum Preparation
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Monitoring of the Microalgae-Based System
2.4.1. Microalgal Growth
2.4.2. Chemical Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
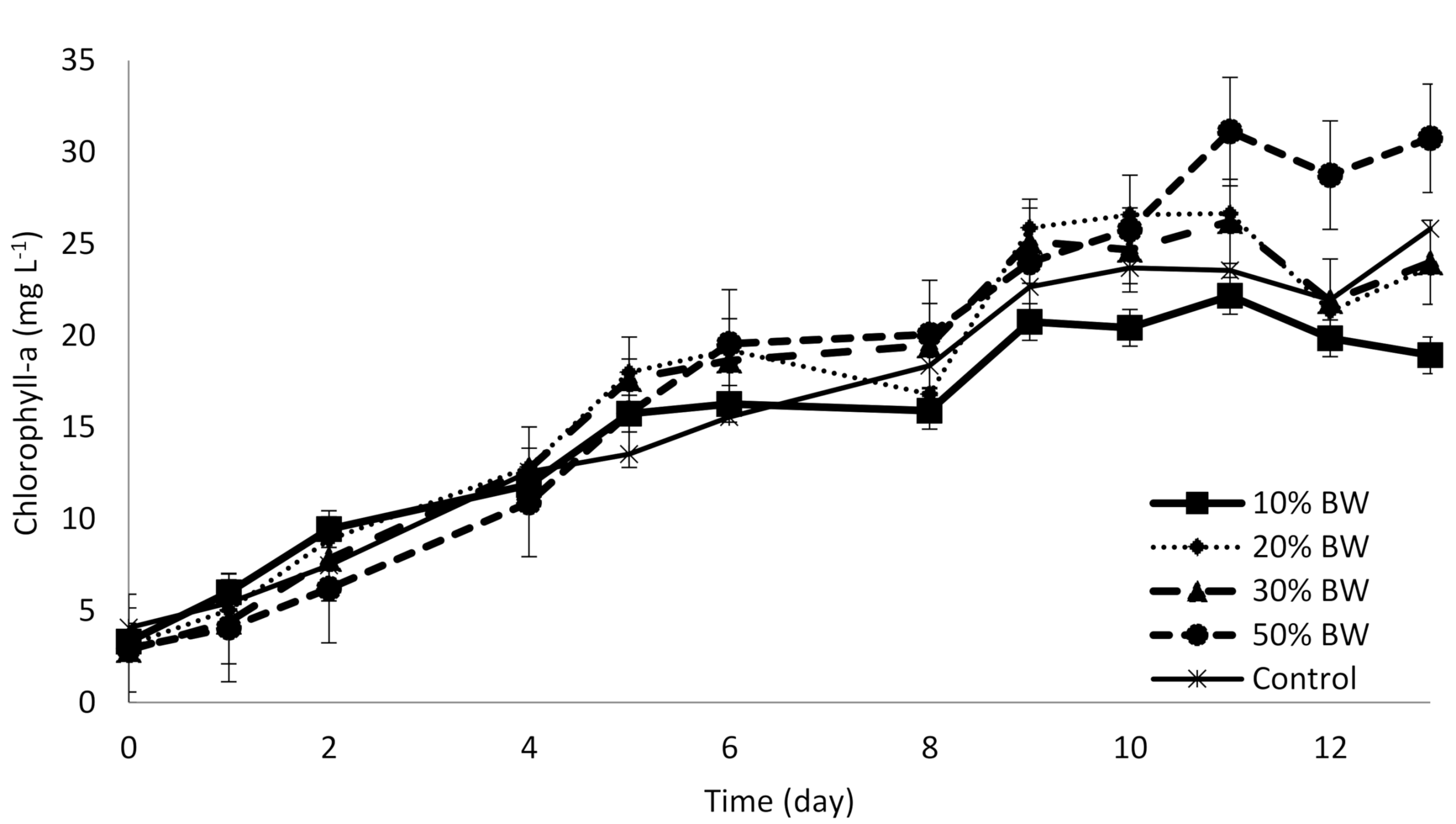
3.1. The Microalgae Growth and Biomass Productivity on Blackwater
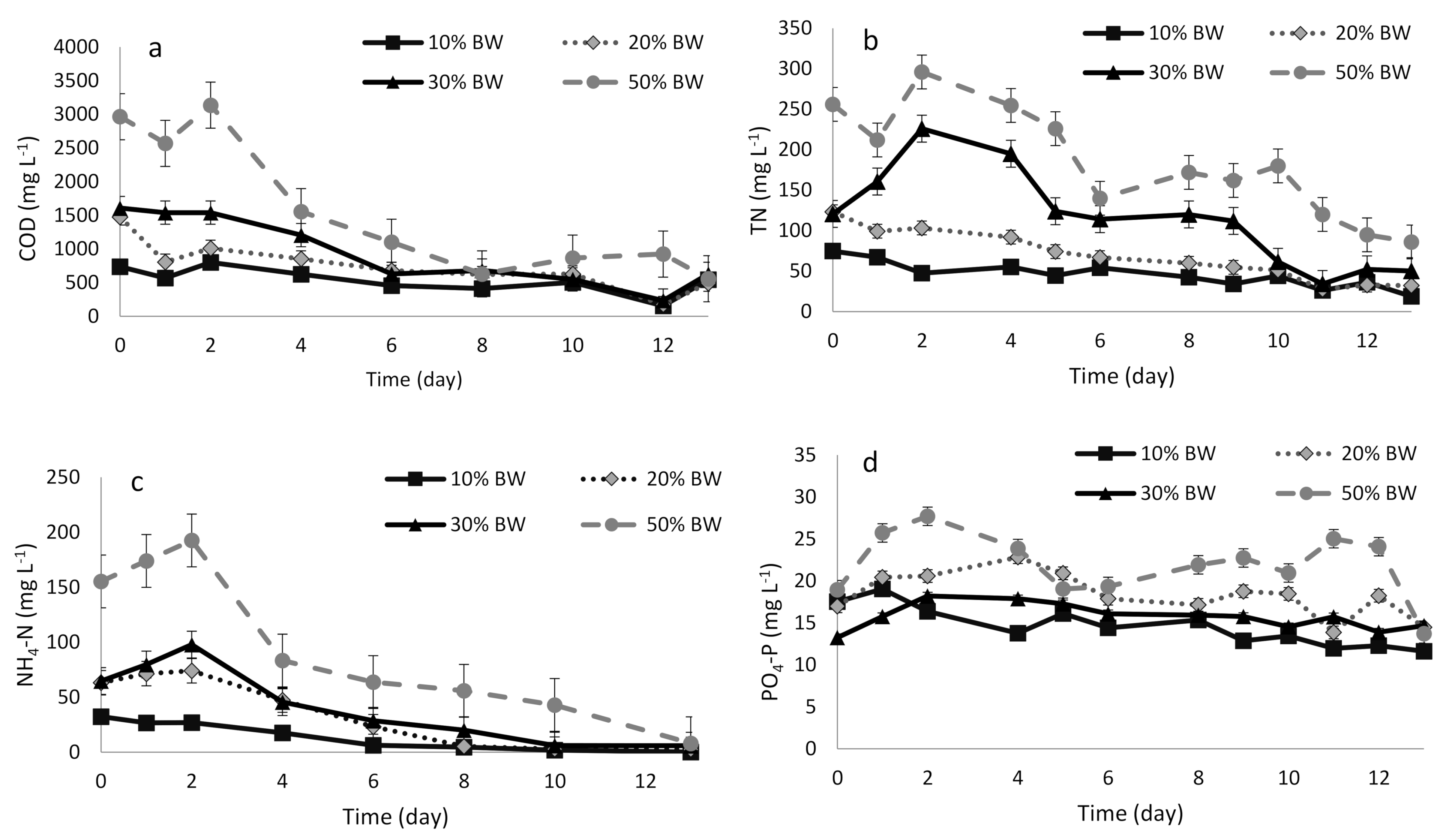
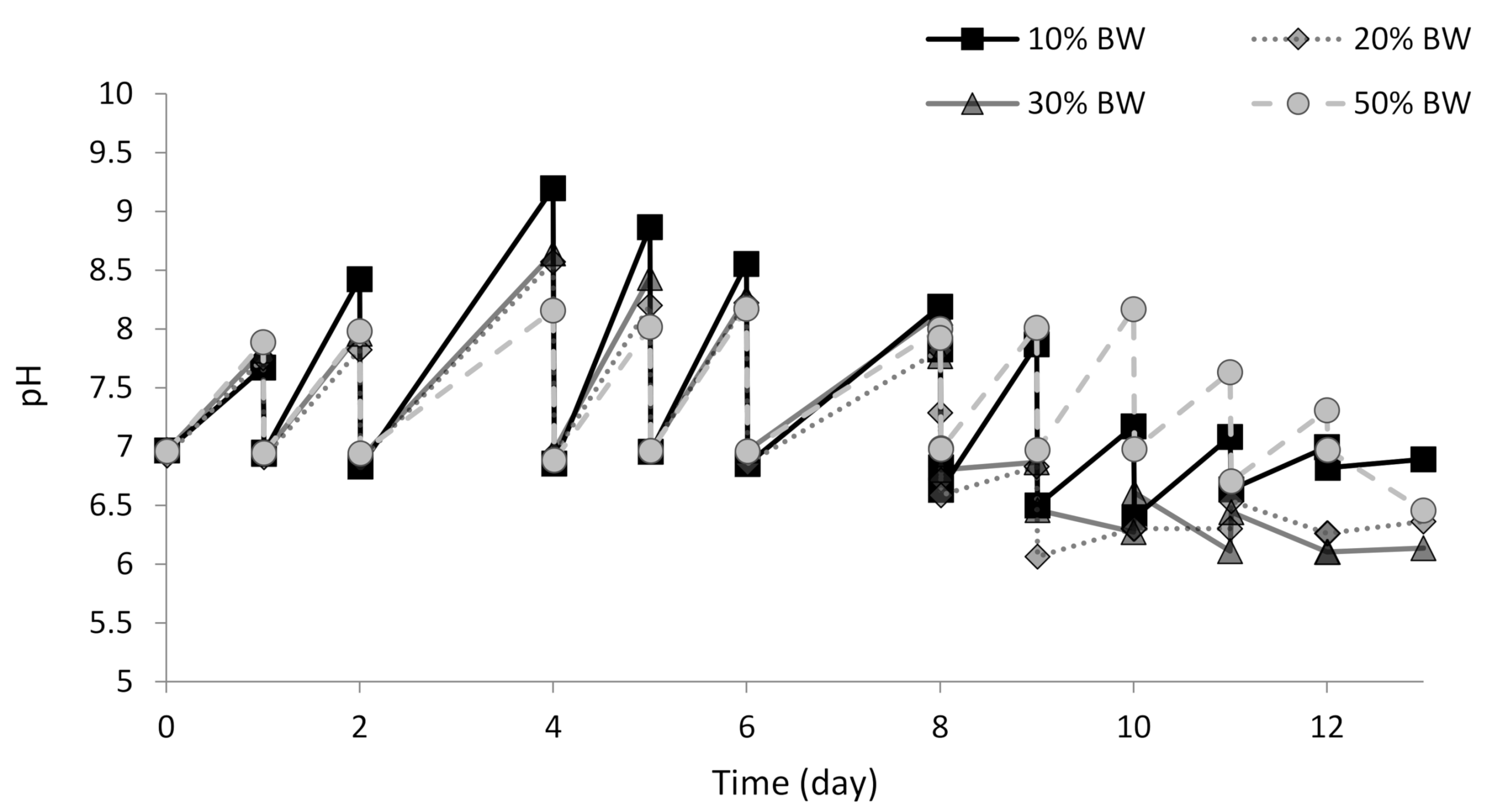
3.2. Performance of the Microalgae-Based System
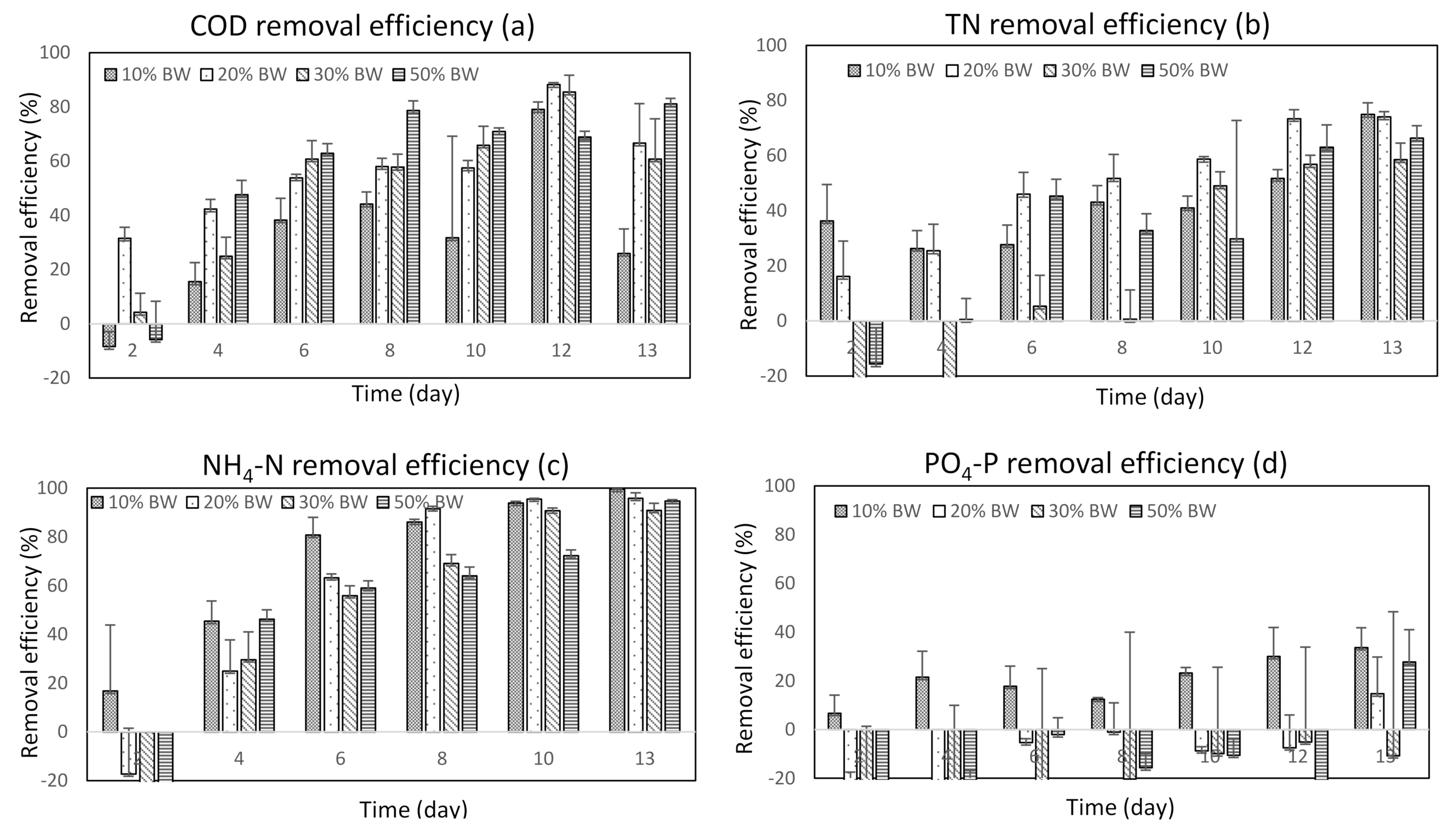
3.2.1. COD Removal
3.2.2. NH4-N and TN Removal
3.2.3. PO4-P Removal
3.3. The Role of N:P Ratio
3.4. Microalgae-Based Systems for Blackwater Treatment in a Real-Scale
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.; Wen, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, H.; Dai, X.; Bi, X.; Wagner, M.; Chen, H. Full-scale semi-centralized wastewater treatment facilities for resource recovery: Operation, problems and resolutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Guida, S.; Jefferson, B.; Soares, A. Economic evaluation of ion-exchange processes for nutrient removal and recovery from municipal wastewater. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrein, P.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Osseweijer, P.; Garfí, M.; Dewulf, J.; Posada, J. A critical review of resource recovery from municipal wastewater treatment plants—market supply potentials, technologies and bottlenecks. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 877–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, N.A.; Aziz, H.A. The design for wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) with GPS X modelling. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastrzębska, M.; Kostrzewska, M.K.; Saeid, A. Can Phosphorus from Recycled Fertilisers Replace Conventional Sources? An Agronomic Evaluation in Field-Scale Experiments on Temperate Luvisols. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.B.; Moore, G.A.; Weatherley, A.J.; Arora, M. Key sustainability challenges for the global phosphorus resource, their implications for global food security, and options for mitigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihelcic, J.R.; Fry, L.M.; Shaw, R. Global potential of phosphorus recovery from human urine and feces. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, M.E.; Heistad, A.; Heidorn, T. Nutrient recovery from anaerobically treated blackwater and improving its effluent quality through microalgae biomass production. Water 2020, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oarga-Mulec, A.; Jenssen, P.D.; Krivograd Klemenčič, A.; Uršič, M.; Griessler Bulc, T. Zero-discharge solution for blackwater treatment at remote tourist facilities. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaff, M.S.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Energy and phosphorus recovery from black water. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, D.; Rocha, A.C.; Pereira, L.; Verdelhos, T. Microalgae Water Bioremediation: Trends and Hot Topics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Yen, H.W.; Ho, S.H.; Lo, Y.C.; Cheng, C.L.; Ren, N.; Chang, J.S. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris JSC-6 with swine wastewater for simultaneous nutrient/COD removal and carbohydrate production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrinovičs, A.; Juhna, T. Review on challenges and limitations for algae-based wastewater treatment. Constr. Sci. 2018, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, F.; Gutiérrez, R.; Brockmann, D.; Steyer, J.P.; García, J.; Ferrer, I. Microalgae production in wastewater treatment systems, anaerobic digestion and modelling using ADM1. Algal Res. 2015, 10, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, L.; Graça, S.; Sousa, C.; Ambrosano, L.; Ribeiro, B.; Botrel, E.P.; Neto, P.C.; Ferreira, A.F.; Silva, C.M. Microalgae biomass production using wastewater: Treatment and costs: Scale-up considerations. Algal Res. 2016, 16, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Immobilized microalgae for removing pollutants: Review of practical aspects. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.V.; Suárez-Muñoz, M.; Trebuch, L.M.; Verbraak, P.J.; Van de Waal, D.B. Toward an ecologically optimized N:P Recovery from wastewater by microalgae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, M.E.; Todt, D.; Janka, E.; Heistad, A.; Bakke, R. Sludge blanket anaerobic baffled reactor for source-separated blackwater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huihui, H.; Xiaowen, J.; Xianchuan, X.; Xinchun, D.; Fang, W.; Jue, D.; Zibin, H.; Rong, T. Energy and economic evaluation of three generations of anaerobic reactors for starch wastewater treatment. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2019, 31, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Jinzhong, L.; Shenglin, Y.; Zhourong, Y.; Min, Z.; Hainan, K.; Xiangyong, Z. Treatment via the Living Machine system of blackwater collected from septic tanks: Effect of different plant groups in the systems. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, I.T.K.; Sung, Y.Y.; Jusoh, M.; Wahid, M.E.A.; Nagappan, T. Chlorella vulgaris: A perspective on its potential for combining high biomass with high value bioproducts. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žitnik, M.; Šunta, U.; Godič Torkar, K.; Krivograd Klemenčič, A.; Atanasova, N.; Griessler Bulc, T. The study of interactions and removal efficiency of Escherichia coli in raw blackwater treated by microalgae Chlorella Vulgaris. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 13 978-0875530475. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Maia, R.; Bernard, O.; Gonçalves, A.; Bensalem, S.; Lopes, F. Influence of temperature on Chlorella vulgaris growth and mortality rates in a photobioreactor. Algal Res. 2016, 18, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliry, S.; Hallajisani, A.; Roshandeh, J.M.; Nouri, H.; Golzary, A. Investigation of optimal condition for Chlorella vulgaris microalgae growth. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2017, 3, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo-Mirquez, L.; Lopes, F.; Taidi, B.; Pareau, D. Nitrogen and phosphate removal from wastewater with a mixed microalgae and bacteria culture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Leal, L.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C. Characterisation and biological treatment of greywater. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, N.; Khan, S. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus concentrations, pH and salinity ranges on growth, biomass and lipid accumulation of Chlorella vulgaris. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.K.; Craggs, R.J. Wastewater treatment and algal production in high rate algal ponds with carbon dioxide addition. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.T.; Shrestha, R.; Sui, Y.; Papini, G.; Zeeman, G.; Vet, L.E.M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Lamers, P. Closing domestic nutrient cycles using microalgae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12450–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, R.A. Primary Production in Aquatic Environments. Internal Biology Program. Handbook; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1969; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Moheimani, N.R.; Borowitzka, M.A.; Isdepsky, A.; Sing, S.F. Standard Methods for Measuring Growth of Algae and Their Composition. In Algae for Biofuels and Energy. Developments in Applied Phycology; Borowitzka, M.A., Moheimani, N.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 265–284. ISBN 978-94-007-5479-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converti, A.; Casazza, A.A.; Ortiz, E.Y.; Perego, P.; Del Borghi, M. Effect of temperature and nitrogen concentration on the growth and lipid content of Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella vulgaris for biodiesel production. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, O. Further Treatment of Digested Blackwater for Extraction of Valuable Components. Ph.D. Thesis, Hamburg Technical University, Hamburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Shukla, S.K.; Park, J.; Lee, T.K. Effect of algal inoculation on COD and nitrogen removal, and indigenous bacterial dynamics in municipal wastewater. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Min, M.; Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Growing wastewater-born microalga Auxenochlorella protothecoides UMN280 on concentrated municipal wastewater for simultaneous nutrient removal and energy feedstock production. Appl. Energ. 2012, 98, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Min, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, R. Cultivation of green algae Chlorella sp. in different wastewaters from municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Martinez, A.; Martin Garcia, N.; Romero, I.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Microalgae cultivation in wastewater: Nutrient removal from anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 126, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadas, E.; Del Mar Morales, M.; Gomez, C.; Acién, F.G.; Muñoz, R. Influence of pH and CO2 source on the performance of microalgae-based secondary domestic wastewater treatment in outdoors pilot raceways. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, O.; Velasquez Orta, S.B.; Monje-Ramirez, I.; Noguez, I.Y.; Harvey, A.P.; Orta Ledesma, M.T. Biodiesel production from indigenous microalgae grown in wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiong, H.; Hui, Z.; Zeng, X. Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa with diluted primary piggery wastewater to produce lipids. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zheng, B.; Deng, W.; Shao, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; et al. A study on the relationship between metabolism of Cyanobacteria and chemical oxygen demand in Dianchi Lake, China. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Petrini, S.; Nessenzia, M.; Andreottola, G. Enhanced nitrogen removal and energy saving in a microalgal-bacterial consortium treating real municipal wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, S.M. Effect of the N/P ratio on biomass productivity and nutrient removal from municipal wastewater. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Giannis, A.; Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.-C.; Wang, J.-Y. Air stripping process for ammonia recovery from source-separated urine: Modeling and optimization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Wang, X. Study on dynamics model of biodegration of organic matter in aerobic mesophilic composting reactor for sanitary disposal of human feces. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 281, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Godos, I.; Blanco, S.; García-Encina, P.A.; Becares, E.; Muñoz, R. Long-term operation of high rate algal ponds for the bioremediation of piggery wastewaters at high loading rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Mennerich, A.; Urban, B. Municipal wastewater treatment and biomass accumulation with a wastewater-born and settleable algal-bacterial culture. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistocchi, A.; Husemann, J.; Masi, F.; Nanu, C. Wastewater Treatment in the Danube Region: Opportunities and Challenges. Lessons Learnt from a “Synthesis Centres” Exercise; JRC: Luxemburg, 2020; ISBN 978-92-76-16429-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istenič, D.; Atanasova, N.; Krivograd Klemenčič, A.; Prosenc, F.; Griessler Bulc, T. Evaluation and Cost-Efficiency of On-Site Wastewater Reuse Systems. In Book of Abstracts. 3rd IWA Resource Recovery Conference, Venice, Italy, 8–12 September 2019; IWA: Venice, Italy, 2019; pp. 140–141. [Google Scholar]
| Unit | 50% BW | 30% BW | 20% BW | 10% BW | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilution factor | - | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | - |
| BW volume | mL | 640 | 384 | 256 | 128 | - |
| Distilled water | mL | 640 | 896 | 1024 | 1152 | - |
| C. vulgaris inoculum * | mL | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 |
| Nutrient medium | mL | - | - | - | - | 1280 |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.2 |
| Total suspended solids (TSS) | mg L−1 | 2600 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) | mg L−1 | 3000 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg L−1 | 6568 |
| Ammonium-nitrogen (NH4-N) | mg L−1 | 420 |
| Total nitrogen (TN) | mg L−1 | 715 |
| Total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) | mg L−1 | 713 |
| Total phosphorous (TP) | mg L−1 | 100 |
| Nitrate-nitrogen (NO3-N) | mg L−1 | 0.51 |
| Nitrite-nitrogen (NO2-N) | mg L−1 | <0.3 |
| Parameter | Unit | 50% BW | 30% BW | 20% BW | 10% BW | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth rate (µ) | d−1 | 0.188 ± 0.01 | 0.215 ± 0.02 | 0.227 ± 0.03 | 0.265 ± 0.01 | 0.178 ± 0.01 |
| Biomass productivity | mg Chla L−1 d−1 | 5.581 ± 0.30 | 5.417 ± 0.48 | 4.349 ± 1.16 | 4.177 ± 0.14 | 3.758 ± 0.56 |
| Cell concentration | No. of cells mL−1 | 5.96 × 107 ± 1.43 × 106 | 4.80 × 107 ± 2.20 × 106 | 4.75 × 107 ± 3.78 × 106 | 3.79 × 107 ± 9.34 × 105 | 5.16 × 107 ± 3.39 × 106 |
| Chlorophyll-a | mg L−1 | 29.79 ± 0.72 | 23.99 ± 1.10 | 23.74 ± 1.89 | 18.93 ± 0.47 | 25.82 ± 0.87 |
| Dry weight | mg L−1 | 332.82 ± 9.67 | 248.26 ± 12.40 | 229.83 ± 15.72 | 223.33 ± 5.89 | 279.67 ± 4.92 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segovia Bifarini, M.A.; Žitnik, M.; Griessler Bulc, T.; Krivograd Klemenčič, A. Treatment and Re-Use of Raw Blackwater by Chlorella vulgaris-Based System. Water 2020, 12, 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102660
Segovia Bifarini MA, Žitnik M, Griessler Bulc T, Krivograd Klemenčič A. Treatment and Re-Use of Raw Blackwater by Chlorella vulgaris-Based System. Water. 2020; 12(10):2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102660
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegovia Bifarini, Marco Antonio, Miha Žitnik, Tjaša Griessler Bulc, and Aleksandra Krivograd Klemenčič. 2020. "Treatment and Re-Use of Raw Blackwater by Chlorella vulgaris-Based System" Water 12, no. 10: 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102660
APA StyleSegovia Bifarini, M. A., Žitnik, M., Griessler Bulc, T., & Krivograd Klemenčič, A. (2020). Treatment and Re-Use of Raw Blackwater by Chlorella vulgaris-Based System. Water, 12(10), 2660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102660






