Effect of Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio on Water Quality and Community Structure Evolution in Suspended Growth Bioreactors through Biofloc Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setup of Reactor and Operation
2.2. Analysis of Water Samples
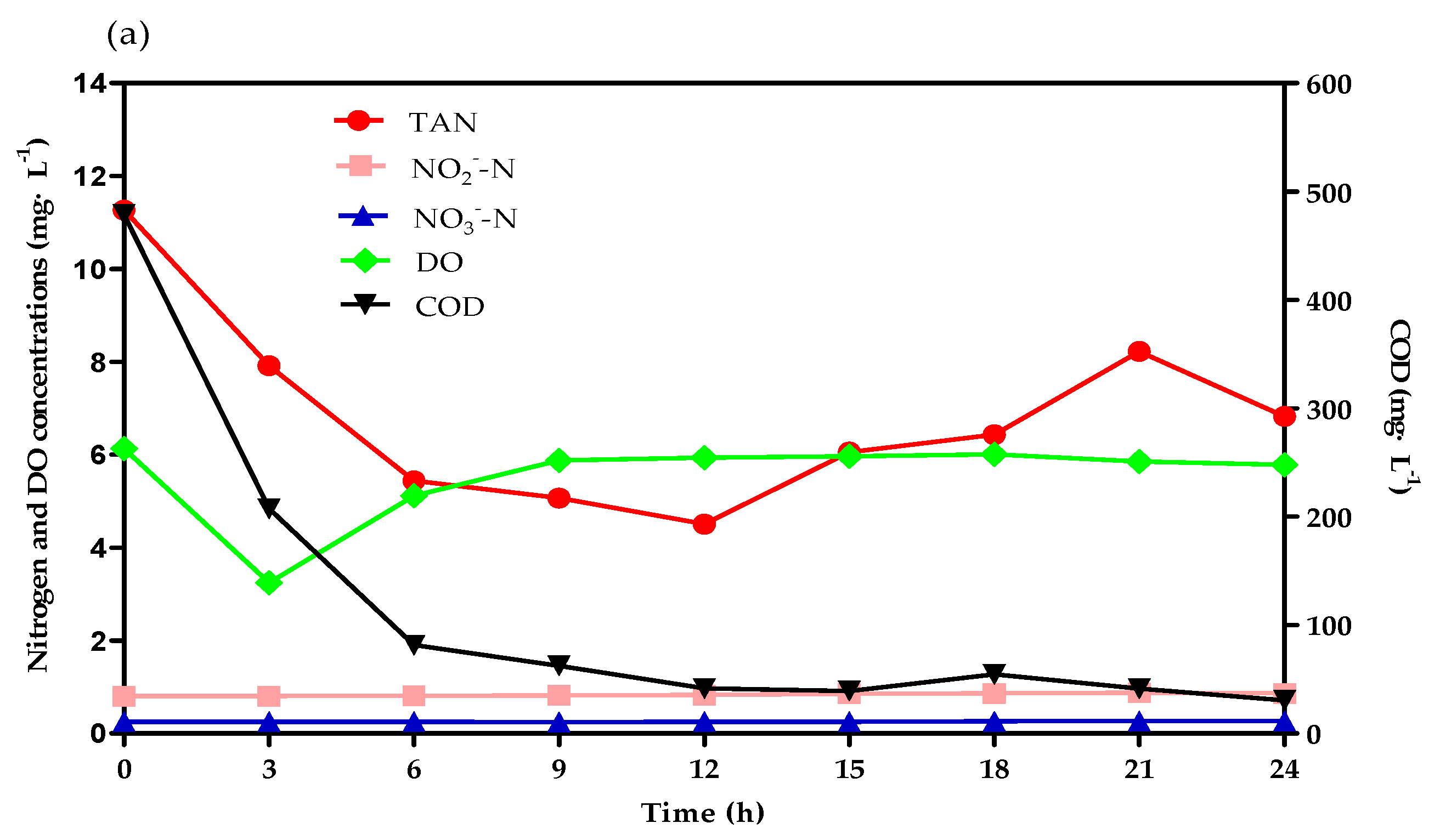
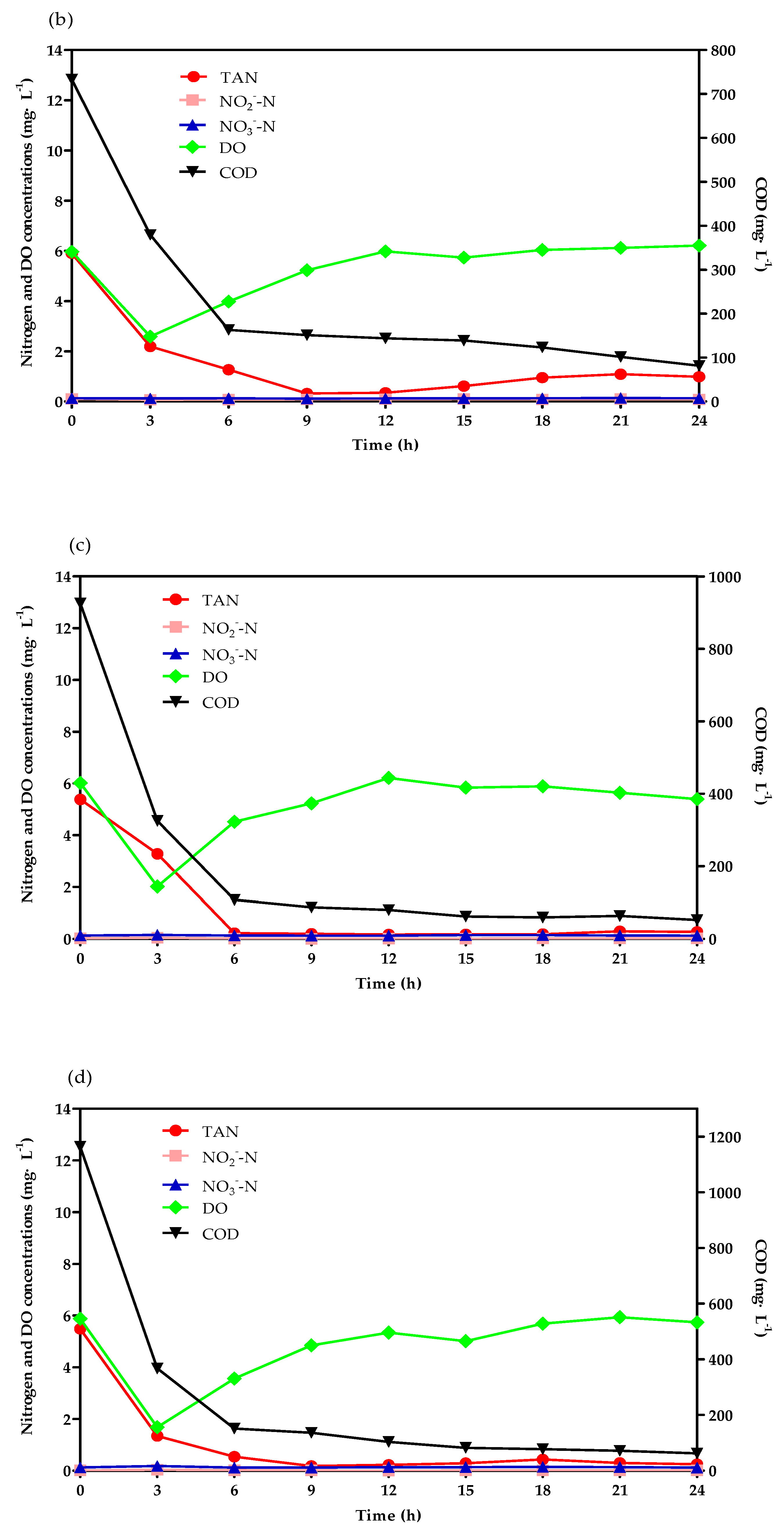
2.3. TAN Removal Tracking Test
2.4. Bioflocs Parameters and Measurement of Biomass
2.5. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing of 16S rRNA
2.6. Microbial Community Diversity Analysis
3. Results
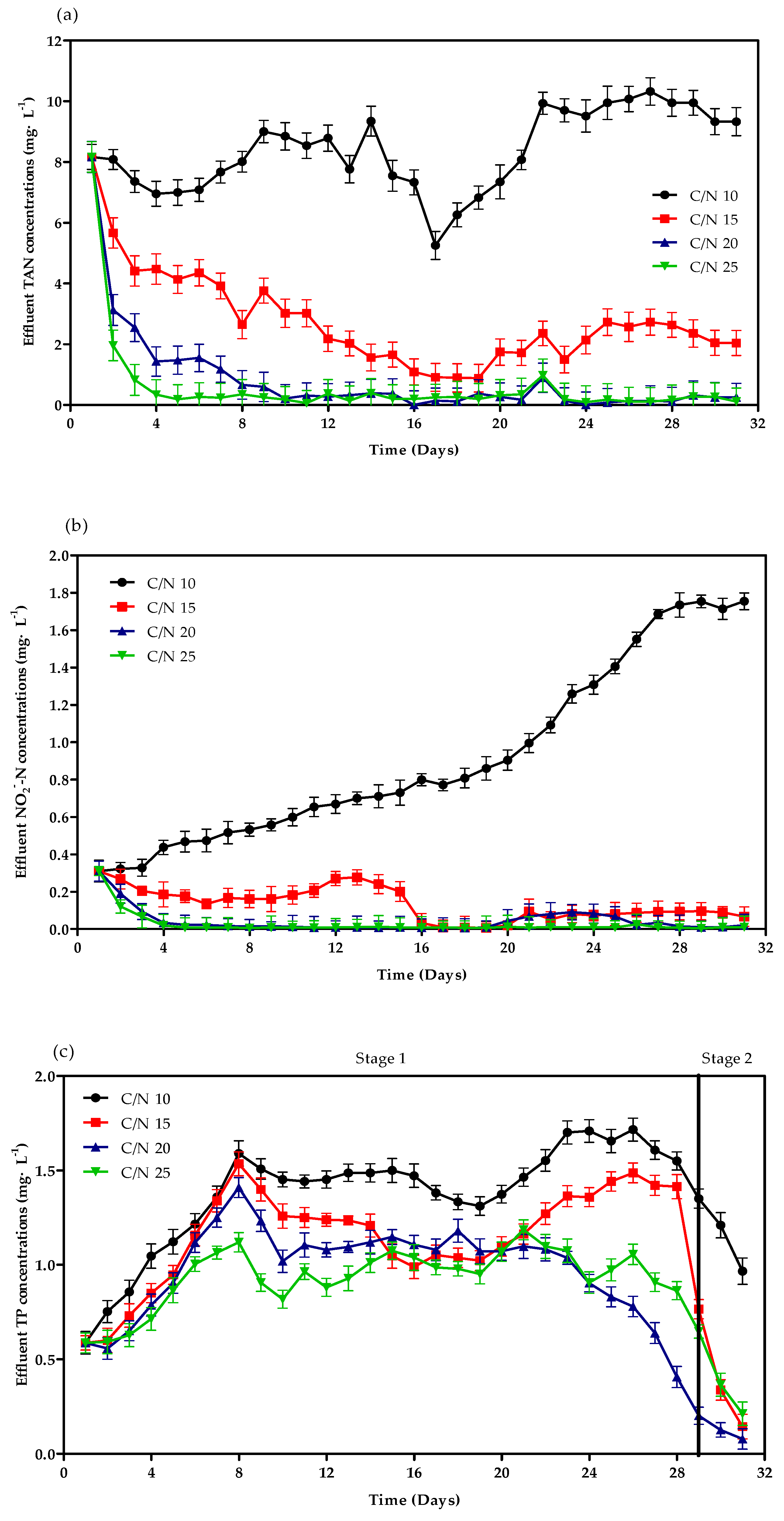
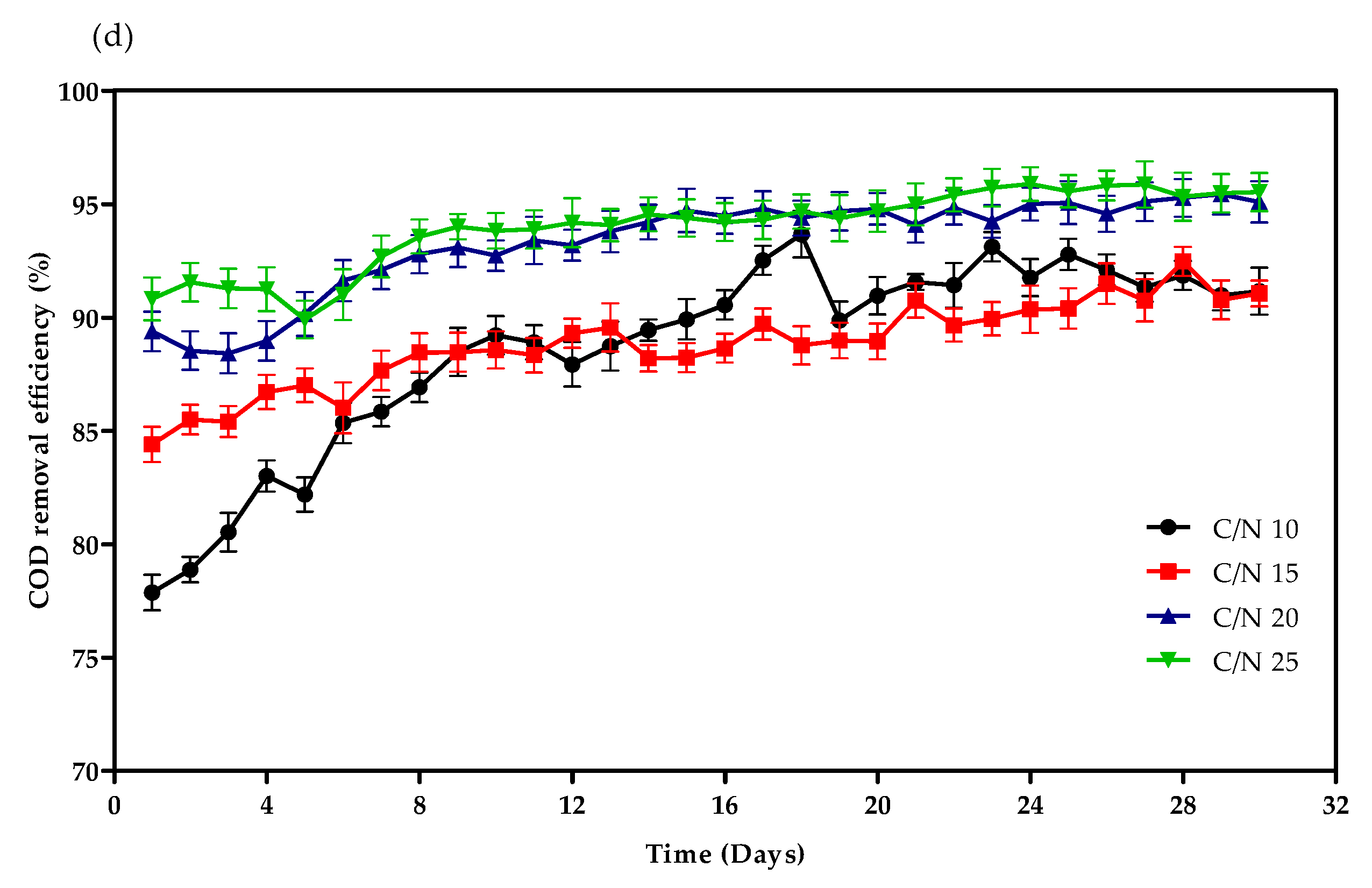
3.1. Reactor Performance for Treating Simulative Wastewater
3.2. TAN Removal Tracking Test Analysis
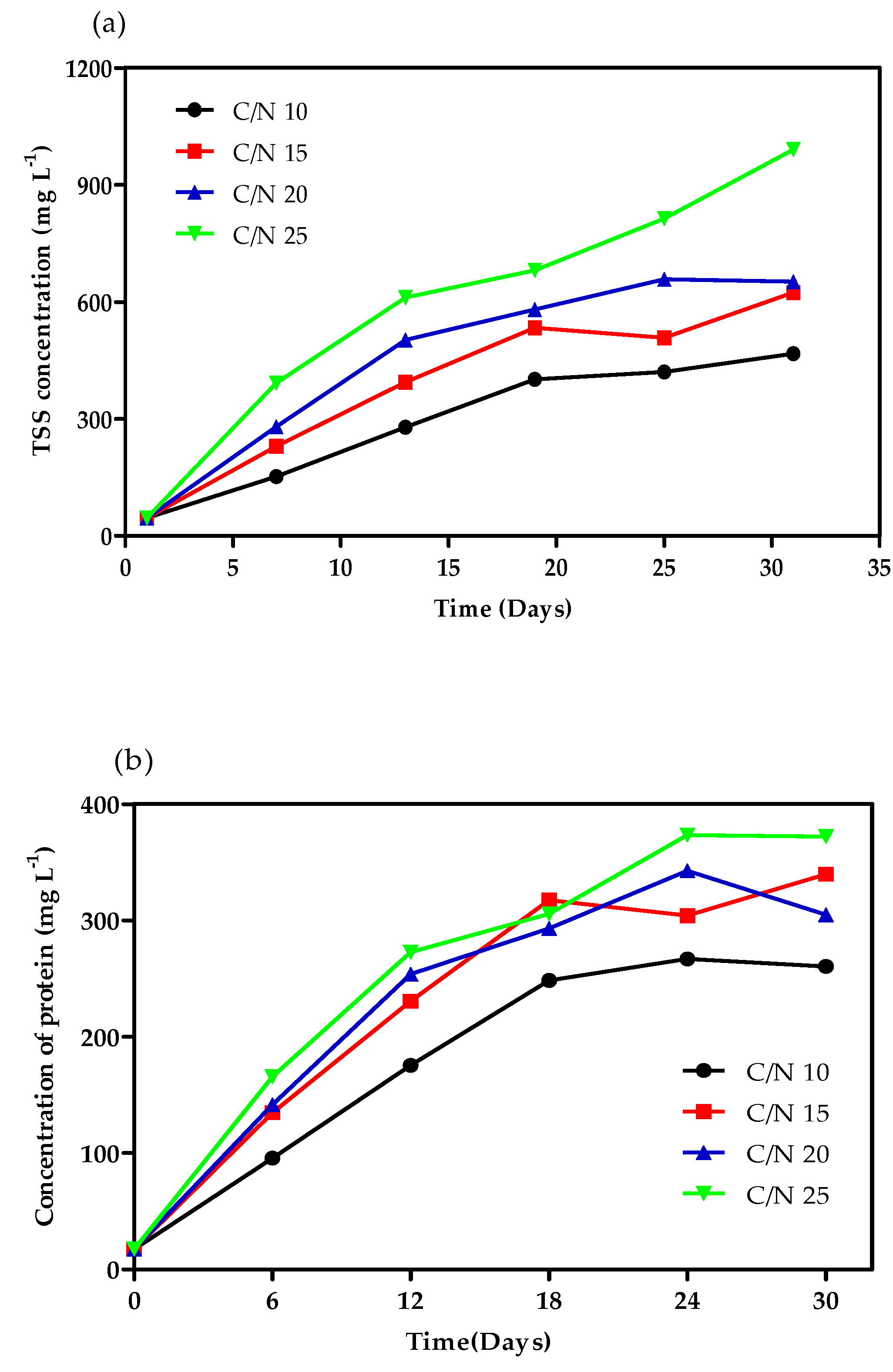
3.3. Bioflocs Parameters Analysis
3.4. Microbial Community Dynamics
3.4.1. Preliminary Analysis of 16S rRNA Sequencing
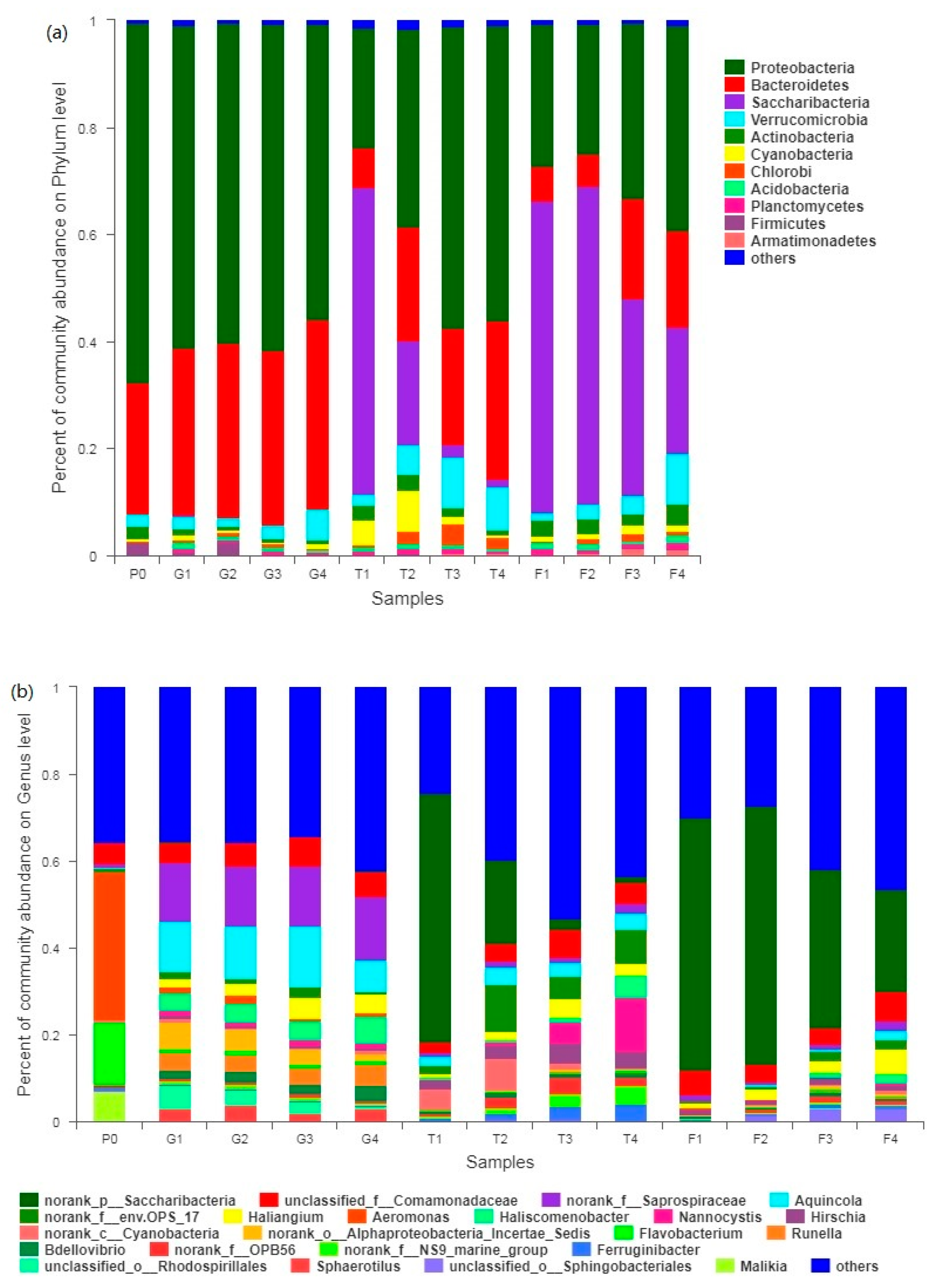
3.4.2. Evolution of Bacterial Community Structure
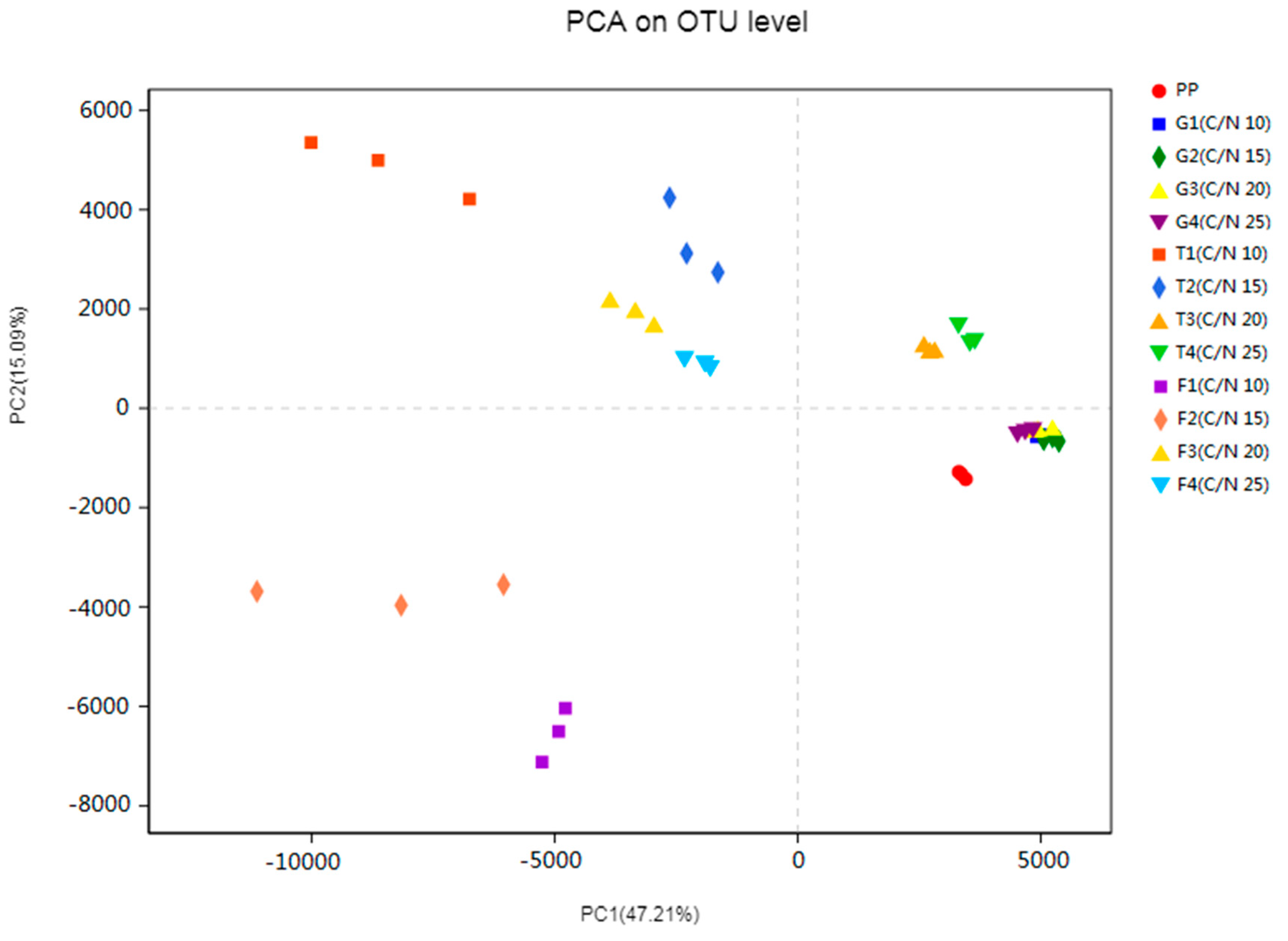
3.4.3. Microbial Community Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Indicators in SGBRs
4.2. Bioflocs Parameters Analysis
4.3. Evolution of Bacterial Community Structure
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Biofloc technology in aquaculture: Beneficial effects and future challenges. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.D.; Lawrence, A.L.; Crockett, J.; Taylor, D. Evaluation of bioflocs derived from confectionary food effluent water as a replacement feed ingredient for fishmeal or soy meal for shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.Z.; Zhang, N.; Tan, H.X.; Hou, Z.W.; Liu, W.C. Efficiency of producing bioflocs with aquaculture waste by using poly-hydroxybutyric acid as a carbon source in suspended growth bioreactors. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 76, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Morris, T.C.; Samocha, T.M. Effects of C/N ratio on biofloc development, water quality, and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles in a biofloc-based, high-density, zero-exchange, outdoor tank system. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. C/N ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 1999, 176, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.G.; Xu, Q.Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.A.; Li, J.N.; Wang, L.S. Effect of feed C/N ratio promoted bioflocs on water quality and production performance of bottom and filter feeder carp in minimum-water exchanged pond polyculture system. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, K.R.; Wasielesky, W.J.; Abreu, P.C. Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in the biofloc production of the Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2013, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Morris, T.C.; Samocha, T.M. Effects of two commercial feeds for semi-intensive and hyper-intensive culture and four C/N ratios on water quality and performance of Litopenaeus vannamei juveniles at high density in biofloc-based, zero-exchange outdoor tanks. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Chielens, B.; Wille, M.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. The effect of different carbon sources on the nutritional value of bioflocs, a feed for Macrobrachium rosenbergii postlarvae. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.F.; Liao, S.A.; Wang, A.L. The effect of different carbon sources on the nutritional composition, microbial community and structure of bioflocs. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C.; Bron, J.E. Microbial protein production in activated suspension tanks manipulating C: N ratio in feed and the implications for fish culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 99, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schryver, P.; Verstraete, W. Nitrogen removal from aquaculture pond water by heterotrophic nitrogen assimilation in lab-scale sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, O.; Sereti, V.; Eding, E.H.; Verreth, J.A.J. Heterotrophic bacterial production on solid fish waste: TAN and nitrate as nitrogen source under practical RAS conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1924–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Wahab, M.A.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Huque, S.; Salam, M.A.; Azim, M.E. C/N ratio control and substrate addition for periphyton development jointly enhance freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii production in ponds. Aquaculture 2008, 280, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, P.; Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. The basics of bioflocs technology: The added value for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.J.; Lewis, B.L.; Browdy, C.L.; Leffler, J.W. Suspended solids removal to improve shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) production and an evaluation of a plant-based feed in minimal-exchange, superintensive culture systems. Aquaculture 2010, 299, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Gollas-Galván, T. From microbes to fish the next revolution in food production. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Chen, J.Y.; Gou, J.W.; Hou, J.; Li, D.P.; He, X.G. The effect of different carbon sources on water quality, microbial community and structure of biofloc systems. Aquaculture 2018, 482, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostins, B.; Wasielesky, W.; Decamp, O.; Bossier, P.; De Schryver, P. Managing input C/N ratio to reduce the risk of Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) outbreaks in biofloc systems-A laboratory study. Aquaculture 2019, 508, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekasari, J.; Azhar, M.H.; Surawidjaja, E.H.; Nuryati, S.; De Schryver, P.; Bossier, P. Immune response and disease resistance of shrimp fed biofloc grown on different carbon sources. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Yu, G.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Lu, Y.Q.; Li, Q.H. Start-up of the completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite process with a submerged aerated biological filter and the effect of inorganic carbon on nitrogen removal and microbial activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC International (Association of Analytical Communities): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.M.; Liao, M.J.; Zhang, M.; Qi, P.Z.; Xie, C.X.; He, X.G. A rapid DNA extraction method for quantitative real-time PCR amplification from fresh water sediment. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Herlemann, D.P.; Labrenz, Z.; Jurgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, H.F.; He, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Zhou, H.W. Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in freshwater, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of illumina tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.J.; Gao, D.W. Effect of dissolved oxygen on nitrogen removal and process control in aerobic granular sludge reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 178, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, B.; Winsley, T.; Ji, M.; Nielan, B. Insights into the distribution and abundance of the ubiquitous Candidatus Saccharibacteria phylum following tag pyrosequencing. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasielesky, W.; Atwood, H.; Stokes, A.; Browdy, C.L. Effect of natural production in a zero exchange suspended microbial floc based super-intensive culture system for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Li, X.Y. Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the characteristics of activated sludge under non-steady-state conditions. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzakhani, N.; Ebrahimi, E.; Jalali, S.A.H.; Ekasari, J. Growth performance, intestinal morphology and nonspecific immunity response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fry cultured in biofloc systems with different carbon sources and input C: N ratios. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Peng, J.; Feng, C.; Fang, F.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluation of simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrification processes and bacterial community structure analysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2015, 99, 6527–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xu, X.C.; Gong, Z.; Gao, F.; Yang, F.L.; Zhang, H.M. Study of simultaneous partial nitrification, ANAMMOX and denitrification (SNAD) process in an intermittent aeration membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Gong, B.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Wen, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; He, Q. The potential multiple mechanisms and microbial communities in simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process treating high carbon and nitrogen concentration saline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Kunming, F.U.; Qian, D.; Zhu, Z.; Meng, X. Effect of C/N ratio on nitrite accumulation in dentrifying process with methanol as carbon source. Ciesc. J. 2010, 61, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, P.R. Changing paradigms in shrimp farming: IV. Low protein feeds and feeding strategies. Glob. Aquac. Advocate 2010, 3, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, P.S.S.; Kohli, M.P.S.; Kumar, S.; Sundaray, J.K.; Roy, S.D.; Venkateshwarlu, G.; Sinha, A.; Pailan, G.H. Effect of dietary supplementation of biofloc on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities in Penaeus monodon. Aquaculture 2014, 418, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, N.V.; Thuy, V.N.; Hideaki, M.; Doan, Y. Factors that Affect the Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorous from Piggery Wastewater Using Microalgae –Bacteria Consortium. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Q.; Li, W.G.; Zhang, S.M.; Wu, C.D.; Wang, K. Effects of sucrose amendment on ammonia assimilation during sewage sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lise, M.H.; Gabriele, L.; Wilson, W.J.; Paulo, C.A. Biofilm versus biofloc: Are artificial substrates for biofilm production necessary in the BFT system? Aquac. Inter. 2016, 24, 921–930. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, E.; Gueguen, Y.; Magre, K.; Lorgeoux, B.; Piquemal, D.; Pierrat, F.; Noguier, F.; Saulnier, D. Bacterial community characterization of water and intestine of the shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris in a biofloc system. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Yasumoto-Hirose, M.; Katsuta, A.; Sekiguchi, H.; Matsuda, S.; Kasai, H.; Yokota, A. Coraliomargarita akajimensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the phylum “Verrucomicrobia” isolated from seawater in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solyanikova, I.P.; Golovleva, L.A. Physiological and biochemical properties of actinobacteria as the basis of their high biodegradative activity (Review). Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 2015, 51, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hanada, A.; Kurogi, T.; Giang, N.M.; Yamada, T.; Kamimoto, Y.; Kiso, Y.; Hiraishi, A. Bacteria of the candidate phylum TM7 are prevalent in acidophilic nitrifying sequencing-batch reactors. Microbes. Environ. 2014, 29, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, H.-D.; Park, J.-H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, F. Effect of different salinity adaptation on the performance and microbial community in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, J.; Park, K.C. Long-term effects of imbalanced fertilization on the composition and diversity of soil bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindaichi, T.; Yamaoka, S.; Uehara, R.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Nielsen, J.L. Phylogenetic diversity and ecophysiology of Candidate phylum Saccharibacteria in activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Zhang, G.R.; Shi, Z.C.; Yuan, Y.J.; Zheng, H.; Lin, L.; Wei, K.J.; Ji, W. Expression analysis of nine Toll-like receptors in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) responding to Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 63, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.I.; Vema, A.K.; Rani, A.M.B.; Rathore, G.; Saharan, N.; Gora, A.H. Growth, non-specific immunity and disease resistance of Labeo rohita against Aeromonas hydrophila in biofloc systems using different carbon sources. Aquaculture 2016, 457, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| C/N 10 | C/N 15 | C/N 20 | C/N 25 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent TAN (mg N·L−1) | 30 ± 0.6 | 29 ± 1.1 | 29 ± 0.9 | 30 ± 0.7 |
| Effluent TAN (mg N·L−1) | 8.37 ± 1.30 a | 2.76 ± 1.55 b | 0.84 ± 1.55 c | 0.58 ± 1.45 c |
| Effluent NO2−-N (mg N·L−1) | 0.90 ± 0.48 a | 0.12 ± 0.08 b | 0.04 ± 0.06 b | 0.02 ± 0.05 b |
| Effluent NO3−-N (mgN·L−1) | 0.24 ± 0.03 a | 0.13 ± 0.04 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 b |
| Effluent COD (mg·L−1) | 59.38 ± 26.59 a | 83.58 ± 16.26 b | 65.15 ± 23.30 bc | 72.26 ± 22.23 c |
| Effluent TN (mg N·L−1) | 9.57 ± 1.86 a | 3.42 ± 1.50 b | 0.97 ± 1.60 c | 0.69 ± 1.54 c |
| TAN removal efficiency (%) | 37.4 ± 6.3 a | 68.2 ± 9.9 b | 91.3 ± 8.3 c | 94.6 ± 3.8 c |
| pH | 8.31 ± 0.19 a | 8.24 ± 0.19 a | 8.24 ± 0.19 a | 8.21 ± 0.16 a |
| DO (mg·L−1) | 6.2 ± 0.5 | 5.9 ± 0.8 | 6.1 ± 0.6 | 6.0 ± 0.7 |
| TDS (mg·L−1) | 503.7 ± 17.2 a | 485.4 ± 13.3 c | 475.5 ± 9.8 b | 486.6 ± 14.4 c |
| Parameters | C/N 10 | C/N 15 | C/N 20 | C/N 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFV (mL·L−1) | 18.7 ± 4.7 a | 30.6 ± 8.5 b | 36.4 ± 12.0 b | 60.0 ± 15.4 c |
| TSS (mg·L−1) | 322.58 ± 127.51 a | 439.11 ± 167.06 ab | 514.61 ± 177.48 b | 670.18 ± 247.35 c |
| SVI (mL·g−1) | 67.69 ± 40.95 a | 80.37 ± 44.98 a | 82.13 ± 65.23 a | 91.38 ± 71.66 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, J.; Hong, C.U.; Deng, M.; Chen, J.; Hou, J.; Li, D.; He, X. Effect of Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio on Water Quality and Community Structure Evolution in Suspended Growth Bioreactors through Biofloc Technology. Water 2019, 11, 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081640
Gou J, Hong CU, Deng M, Chen J, Hou J, Li D, He X. Effect of Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio on Water Quality and Community Structure Evolution in Suspended Growth Bioreactors through Biofloc Technology. Water. 2019; 11(8):1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081640
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Jingwei, Chol Ung Hong, Min Deng, Jieyu Chen, Jie Hou, Dapeng Li, and Xugang He. 2019. "Effect of Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio on Water Quality and Community Structure Evolution in Suspended Growth Bioreactors through Biofloc Technology" Water 11, no. 8: 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081640
APA StyleGou, J., Hong, C. U., Deng, M., Chen, J., Hou, J., Li, D., & He, X. (2019). Effect of Carbon to Nitrogen Ratio on Water Quality and Community Structure Evolution in Suspended Growth Bioreactors through Biofloc Technology. Water, 11(8), 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081640






