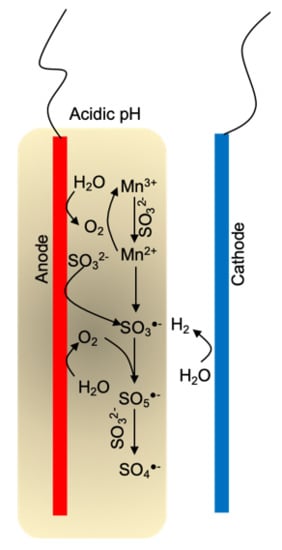
Electrolysis-Assisted Mn(II)/Sulfite Process for Organic Contaminant Degradation at Near-Neutral pH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Batch Reaction of BPA Removal
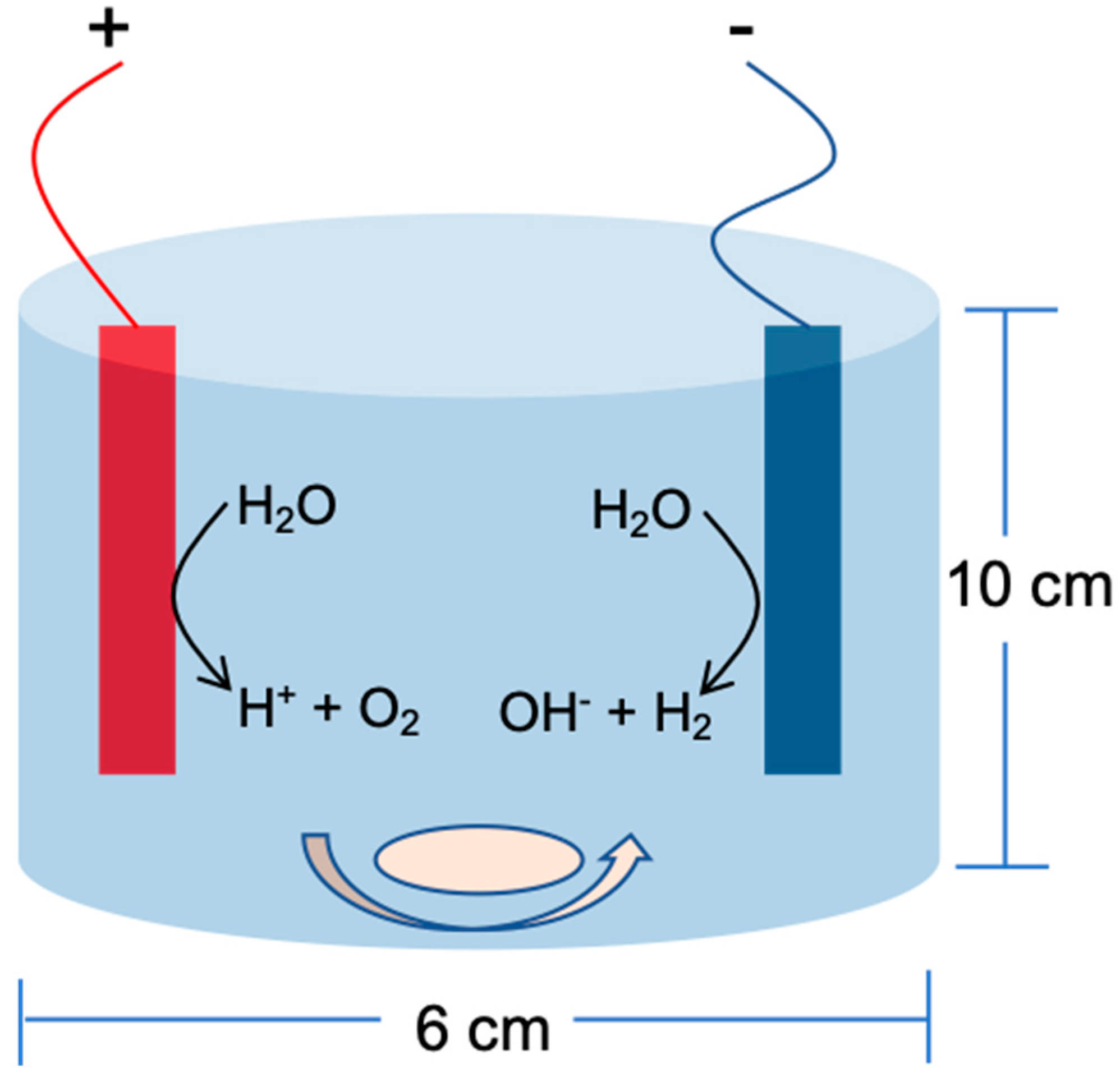
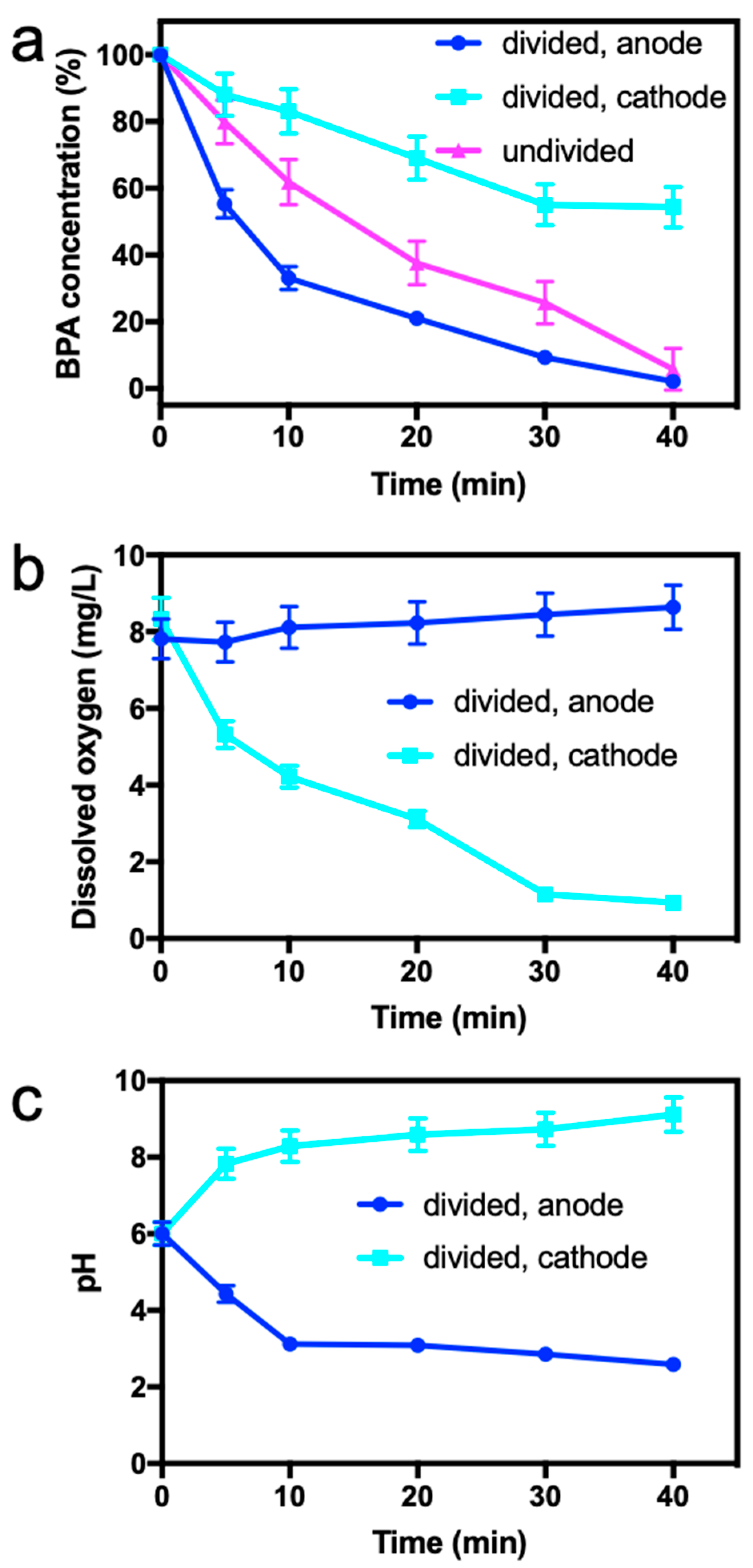
2.3. BPA Removal by Electro/Mn(II)/Sulfite Process in Divided Electrochemical Cell
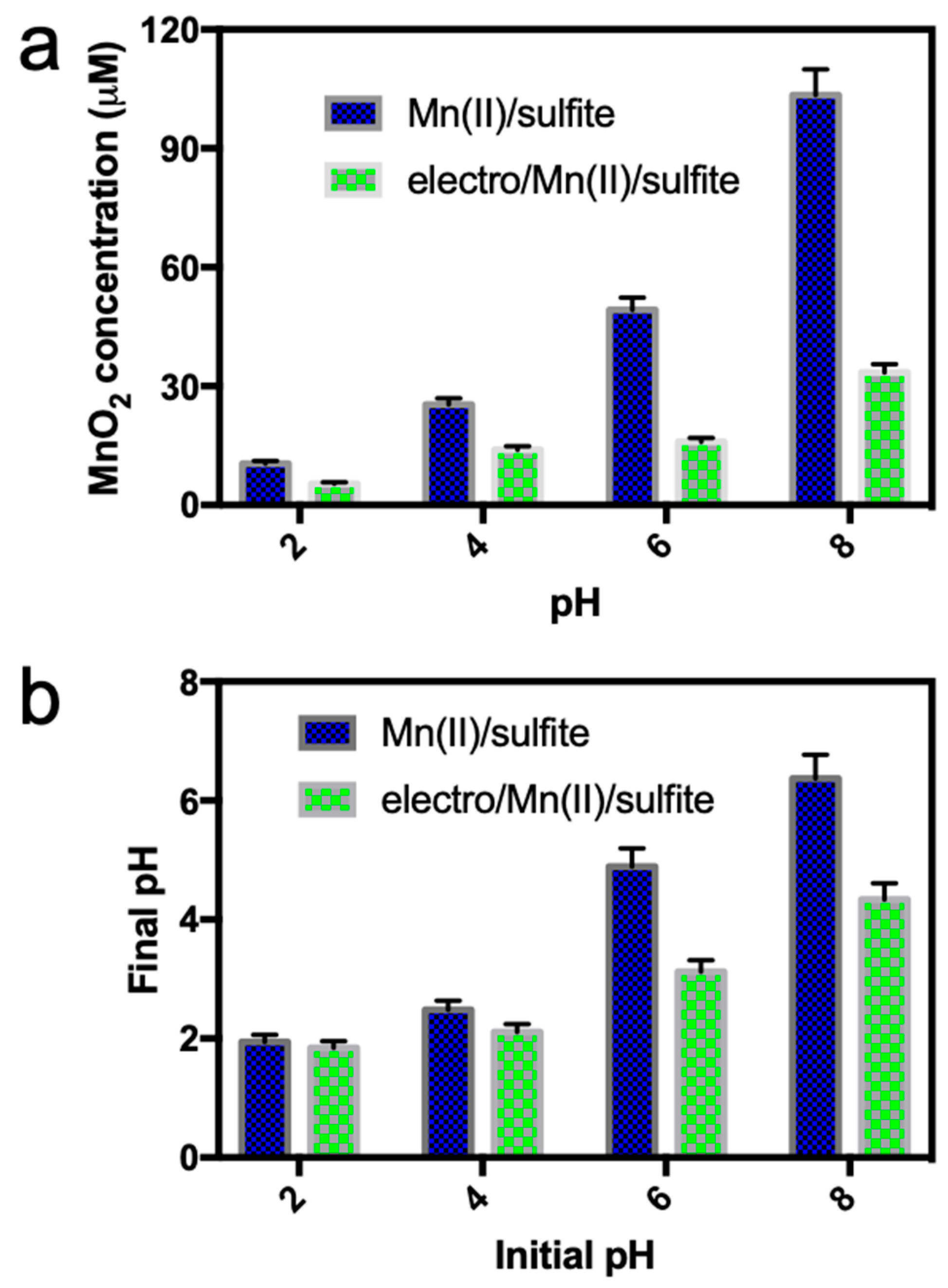
2.4. Measurement of MnO2 Concentration
2.5. Measurement of Formaldehyde Concentration
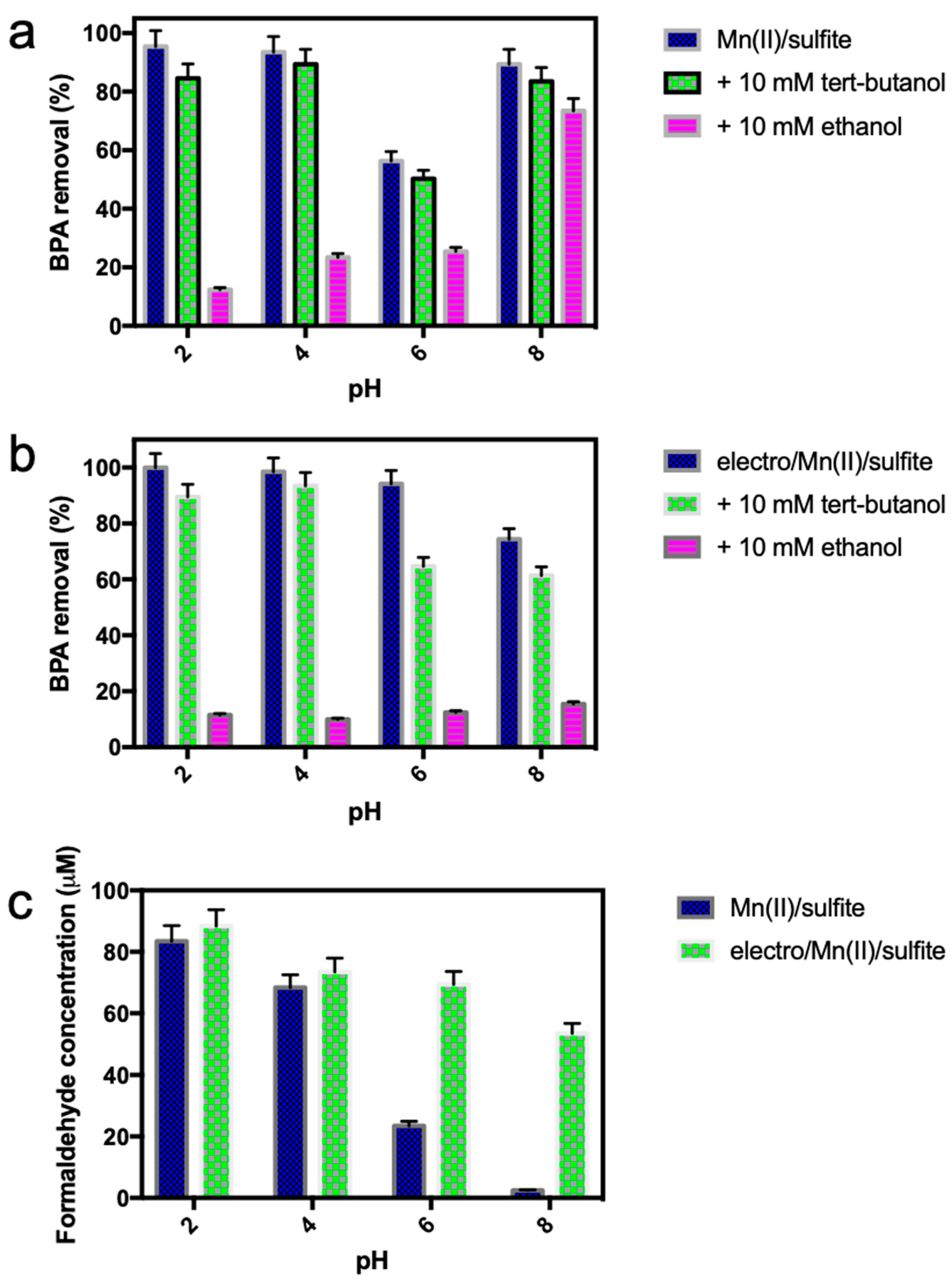
2.6. Radical-Scavenging Assay
3. Results and Discussion
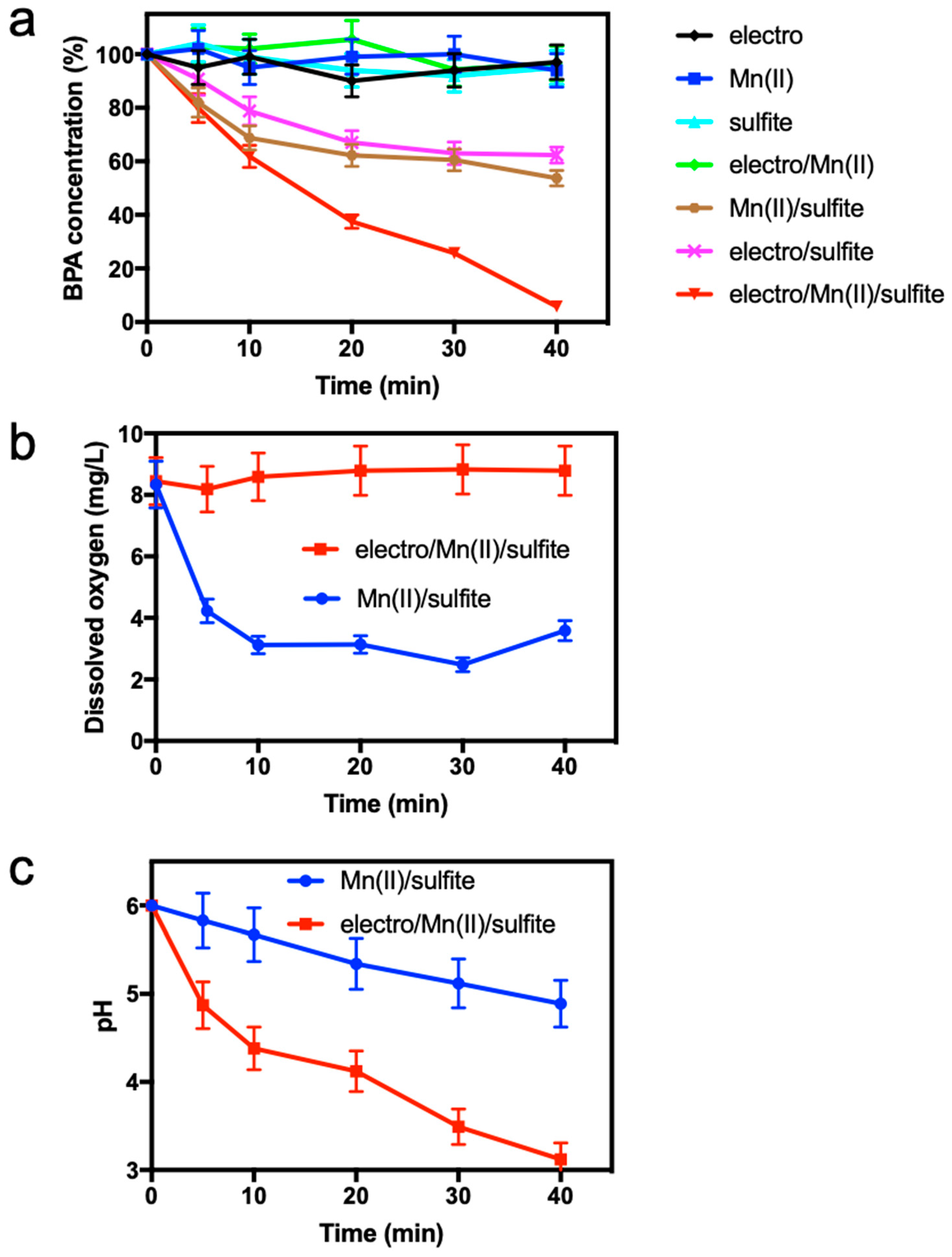
3.1. Removal of BPA by Electro/Mn(II)/Sulfite Process
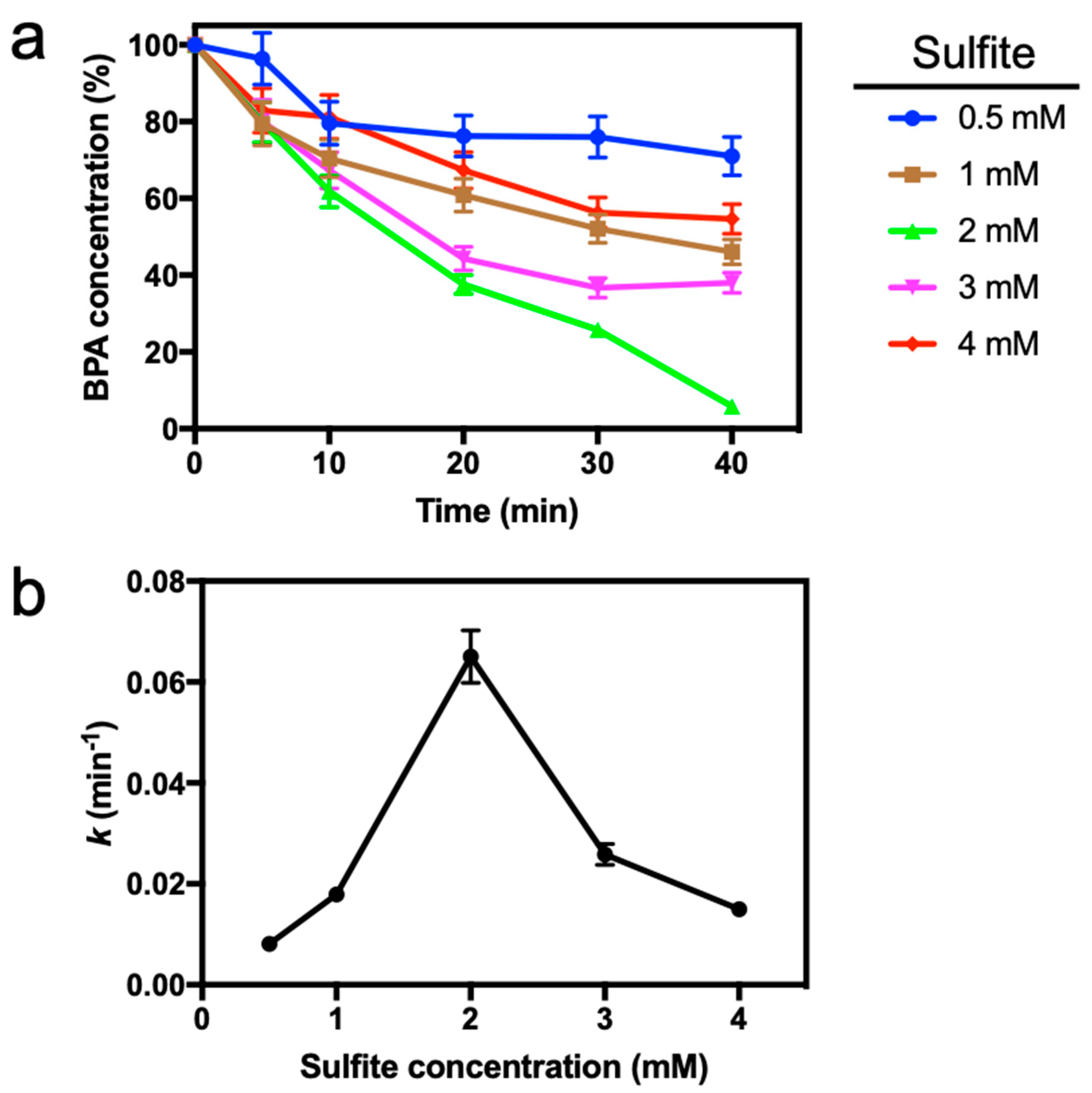
3.2. Effect of Sulfite Dose
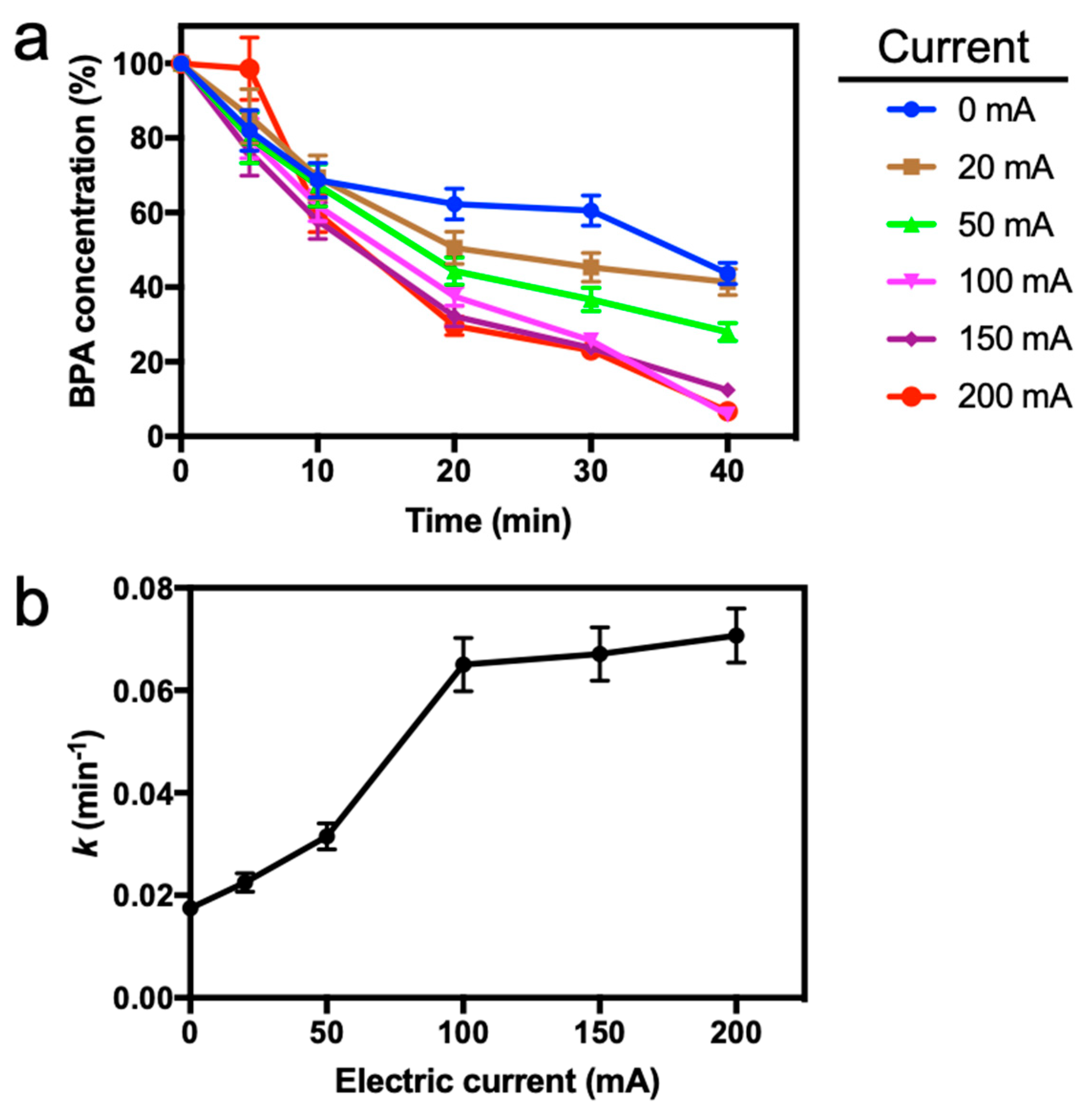
3.3. Effect of Current Intensity
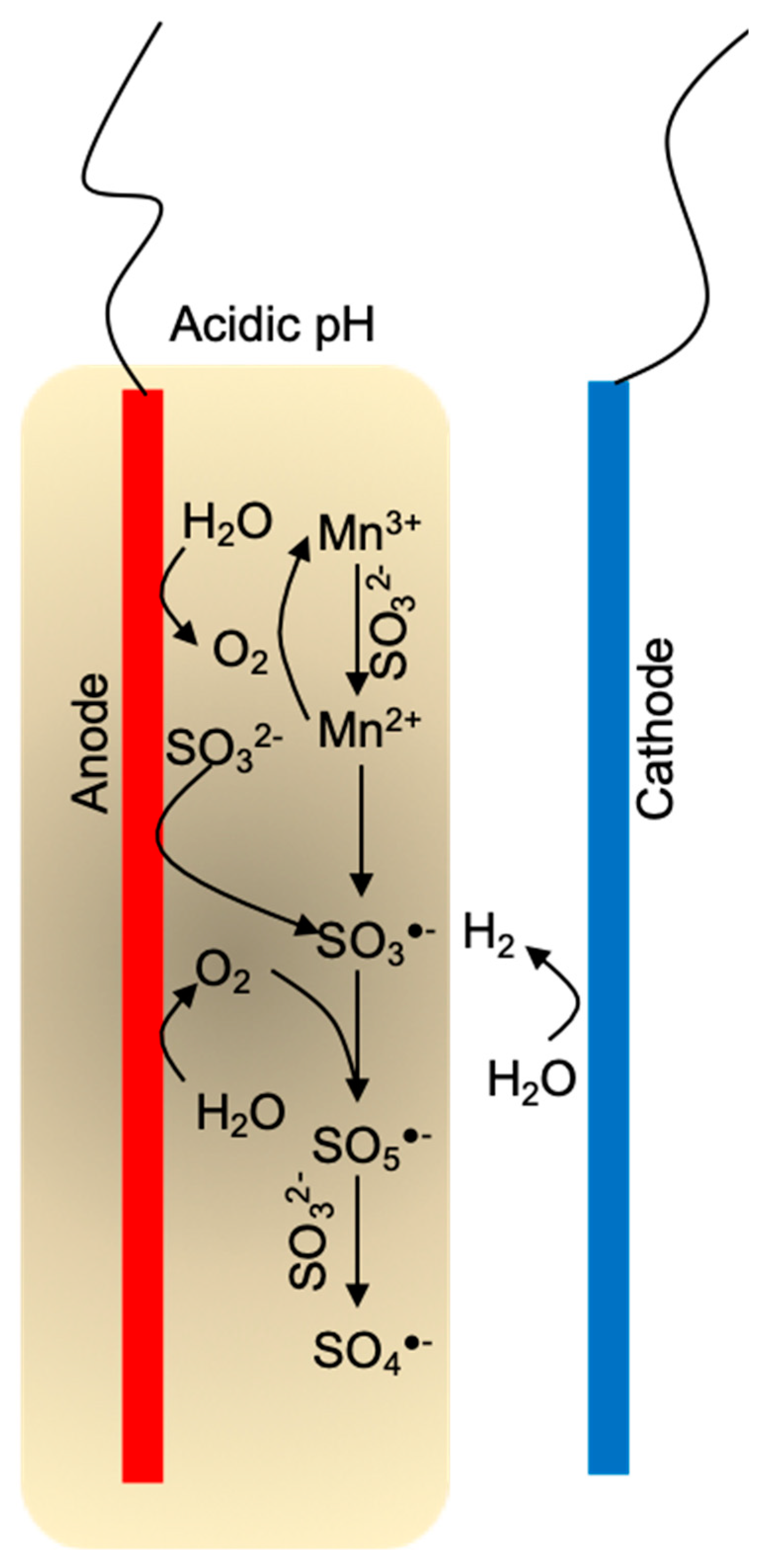
3.4. Mechanism Study
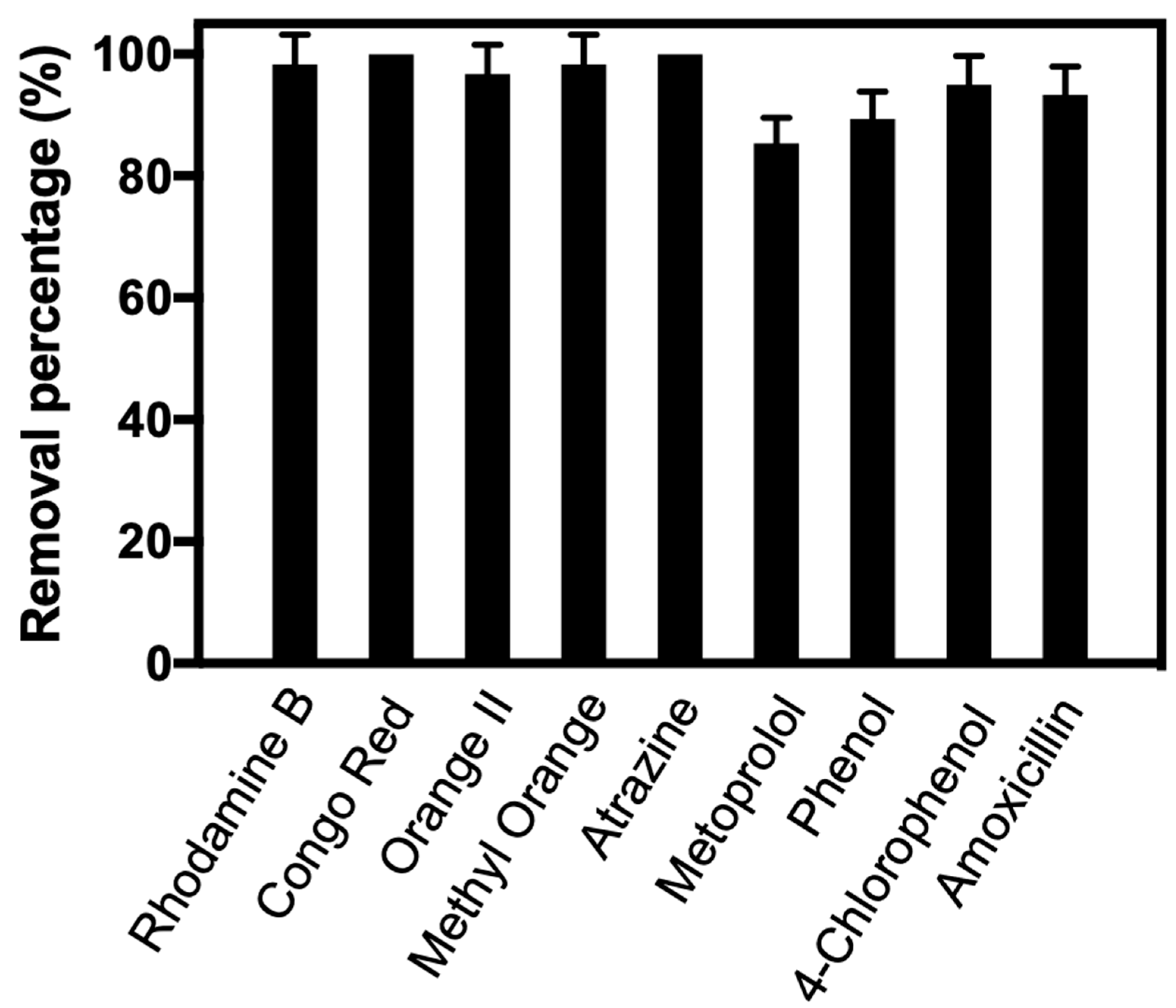
3.5. Degradation of Other Organic Pollutants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wardman, P. Reduction Potentials of One-Electron Couples Involving Free Radicals in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1989, 18, 1637–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in wastewater treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Mantzavinos, D.; Poulios, I.; Rodrigo, M.A. New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, A.; Raman, A.A.A.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 87, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacławek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grübel, K.; Padil, V.V.; Černík, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation of organic contaminants in water with sulfate radicals generated by the conjunction of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, R.; Tlili, S.; Chiron, S.; Barbati, S. Removal of carbamazepine from urban wastewater by sulfate radical oxidation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Long, M. Cobalt-catalyzed sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation: A review on heterogeneous catalysts and applications. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 181, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitonaki, A.; Petri, B.; Crimi, M.; Mosbæk, H.; Siegrist, R.L.; Bjerg, P.L. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, R.R.; Rivas, F.J.; Tierno, M. Monopersulfate photocatalysis under 365 nm radiation. Direct oxidation and monopersulfate promoted photocatalysis of the herbicide tembotrione. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, R.R.; Rivas, F.J.; Chávez, A.M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Simulated solar photo-assisted decomposition of peroxymonosulfate. Radiation filtering and operational variables influence on the oxidation of aqueous bezafibrate. Water Res. 2019, 162, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, R.R.; Rivas, F.J.; Gimeno, O. Removal of aqueous metazachlor, tembotrione, tritosulfuron and ethofumesate by heterogeneous monopersulfate decomposition on lanthanum-cobalt perovskites. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 200, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracking the Acute Toxicity of Sodium Sulfite. Available online: http://www.chemcas.com/material/cas/archive/7727-21-1.asp (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Tracking the Acute Toxicity of Potassium Peroxymonosulfate. Available online: http://datasheets.scbt.com/sc-253223.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Sra, K.S.; Thomson, N.R.; Barker, J.F. Stability of activated persulfate in the presence of aquifer solids. Soil Sediment Contam. 2014, 23, 820–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, P.A.; Brown, R.A.; Robinson, D. Novel activation technologies for sodium persulfate in situ chemical oxidation. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on the remediation of chlorinated and recalcitrant compounds, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.H.; Chen, K.F.; Kao, C.M.; Liang, S.H.; Chen, T.Y. Application of persulfate to remediate petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil: Feasibility and comparison with common oxidants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.J.; Teel, A.L. Treatment of contaminated soils and groundwater using ISCO. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2006, 10, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bruton, T.A.; Doyle, F.M.; Sedlak, D.L. In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated groundwater by persulfate: Decomposition by Fe (III)-and Mn (IV)-containing oxides and aquifer materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10330–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, F. Decolorization of Orange II in aqueous solution by an Fe (II)/sulfite system: Replacement of persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13632–13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, M.; Luo, K.; Xu, J.; Zhou, D.; Wu, F. Efficient bacterial inactivation by transition metal catalyzed auto-oxidation of sulfite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12663–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Luo, T.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, F. Efficient metoprolol degradation by heterogeneous copper ferrite/sulfite reaction. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wu, F. Transition metal catalyzed sulfite auto-oxidation systems for oxidative decontamination in waters: A state-of-the-art minireview. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracking the Acute Toxicity of Potassium Persulfate. Available online: http://www.chemcas.com/material/cas/archive/7757-83-7_v1.asp (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Reddy, K.B.; Van Eldik, R. Kinetics and mechanism of the sulfite-induced autoxidation of Fe(II) in acidic aqueous solution. Atmos. Environ. Part A 1992, 26, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, P.; Huie, R.E. Free-radical chemistry of sulfite. Environ. Health Perspect. 1985, 64, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Gong, S. Transition metal-catalyzed oxidation of atmospheric sulfur: Global implications for the sulfur budget. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D02309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, J.; Elding, L.I. Manganese-catalysed autoxidation of dissolved sulfur dioxide in the atmospheric aqueous phase. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, P.K.; Palmer, H.J. Uncatalyzed oxidation of aqueous sodium sulfite and its ability to simulate bacterial respiration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1991, 37, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, E.C.; Crist, R.H. The rate of oxidation of sulfite ions by oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1941, 63, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Guan, X.; Fang, J.; Tratnyek, P.G. Activation of manganese oxidants with bisulfite for enhanced oxidation of organic contaminants: The involvement of Mn(III). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12414–12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Dong, H.; He, D.; Rao, D.; Guan, X. Modeling the kinetics of contaminants oxidation and the generation of manganese (III) in the permanganate/bisulfite process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Xiao, Z.; Dong, H.; Ma, S.; Wei, G.; Cao, T.; Guan, X. Bisulfite triggers fast oxidation of organic pollutants by colloidal MnO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 363, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, S.T.; Tiehm, A. Application of electrolysis to stimulate microbial reductive PCE dechlorination and oxidative VC biodegradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7098–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Chen, M.; Mao, X.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. A three-electrode column for Pd-catalytic oxidation of TCE in groundwater with automatic pH-regulation and resistance to reduced sulfur compound foiling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Xu, G.; Rui, Z.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Demonstration of a feasible energy-water-environment nexus: Waste sulfur dioxide for water treatment. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Aasi, D.; Katayama, Y. Bisphenol A in the aquatic environment and its endocrine-disruptive effects on aquatic organisms. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.; Sun, Y.; Shao, B.; Qiao, J.; Guan, X. Activation of oxygen with sulfite for enhanced Removal of Mn(II): The involvement of SO4•−. Water Res. 2019, 157, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, A.; Qiu, Y.; Chan Li, Q. HPLC-UV method development and validation for the determination of low level formaldehyde in a drug substance. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dreisinger, D.B.; Cooper, W.C. Anodic oxidation of sulphite ions on graphite anodes in alkaline solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://mmsphyschem.com/tblSRP.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Huie, R.E.; Neta, P. The chemical behavior of SO3•− and SO5•− radicals in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5665–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deister, U.; Warneck, P. Photooxidation of sulfite (SO32−) in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibenberger, H.; Steenken, S.; O’Neill, P.; Schulte-Frohlinde, D. Pulse radiolysis and electron spin resonance studies concerning the reaction of SO4•− with alcohols and ethers in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1978, 82, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; Doong, R.A.; Huang, C.P.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Activation of persulfate by CoO nanoparticles loaded on 3D mesoporous carbon nitride (CoO@ meso-CN) for the degradation of methylene blue (MB). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kong, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Liu, G.; Li, F.; Lv, W. A sulfate radical based ferrous–peroxydisulfate oxidative system for indomethacin degradation in aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22802–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, K.A.; Mezyk, S.P. Kinetics and mechanisms of sulfate radical oxidation of β-lactam antibiotics in water. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M.; Gohari, F. Degradation of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol in aqueous solutions using peroxymonosulfate/activated carbon/UV process via sulfate and hydroxyl radicals. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2016, 9, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayon, E.; Treinin, A.; Wilf, J. Electronic spectra, photochemistry, and autoxidation mechanism of the sulfite-bisulfite-pyrosulfite systems. SO2−, SO3−, SO4−, and SO5−radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (⋅OH/⋅O−) in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Structure | Chemical Formula | Quantification Method | Mobile Phase | Detection Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhodamine B | 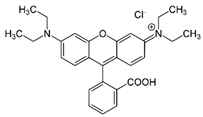 | C28H31ClN2O3 | UV–Vis spectrometer | n.a. | 545 |
| Congo Red | 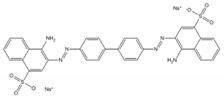 | C32H22N6Na2O6S2 | UV–Vis spectrometer | n.a. | 498 |
| Orange II | 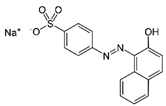 | C16H11N2NaO4S | UV–Vis spectrometer | n.a. | 485 |
| Methyl Orange |  | C14H14N3NaO3S | UV–Vis spectrometer | n.a. | 464 |
| Atrazine |  | C8H14ClN5 | HPLC | Methanol/water 60:40 | 230 |
| Metoprolol | 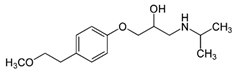 | C15H25NO3 | HPLC | Methanol/KH2PO4 (pH 3) 60:40 | 230 |
| Phenol | 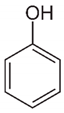 | C6H6O | HPLC | Methanol/water 65:35 | 270 |
| 4-Chlorophenol |  | C6H5ClO | HPLC | 5 mmol H2SO4/methanol 80:20 | 270 |
| Amoxicillin | 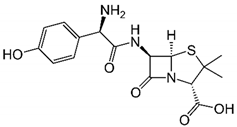 | C16H19N3O5S | HPLC | Acetonitrile/KH2PO4 (pH 3) 22:78 | 254 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, L.; Pei, X.; Yang, F. Electrolysis-Assisted Mn(II)/Sulfite Process for Organic Contaminant Degradation at Near-Neutral pH. Water 2019, 11, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081608
Jia L, Pei X, Yang F. Electrolysis-Assisted Mn(II)/Sulfite Process for Organic Contaminant Degradation at Near-Neutral pH. Water. 2019; 11(8):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081608
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Lixin, Xingwang Pei, and Fei Yang. 2019. "Electrolysis-Assisted Mn(II)/Sulfite Process for Organic Contaminant Degradation at Near-Neutral pH" Water 11, no. 8: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081608
APA StyleJia, L., Pei, X., & Yang, F. (2019). Electrolysis-Assisted Mn(II)/Sulfite Process for Organic Contaminant Degradation at Near-Neutral pH. Water, 11(8), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081608