Phosphorus Availability and Growth of Benthic Primary Producers in Littoral Lake Sediments: Are Differences Linked to Induced Bank Filtration?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
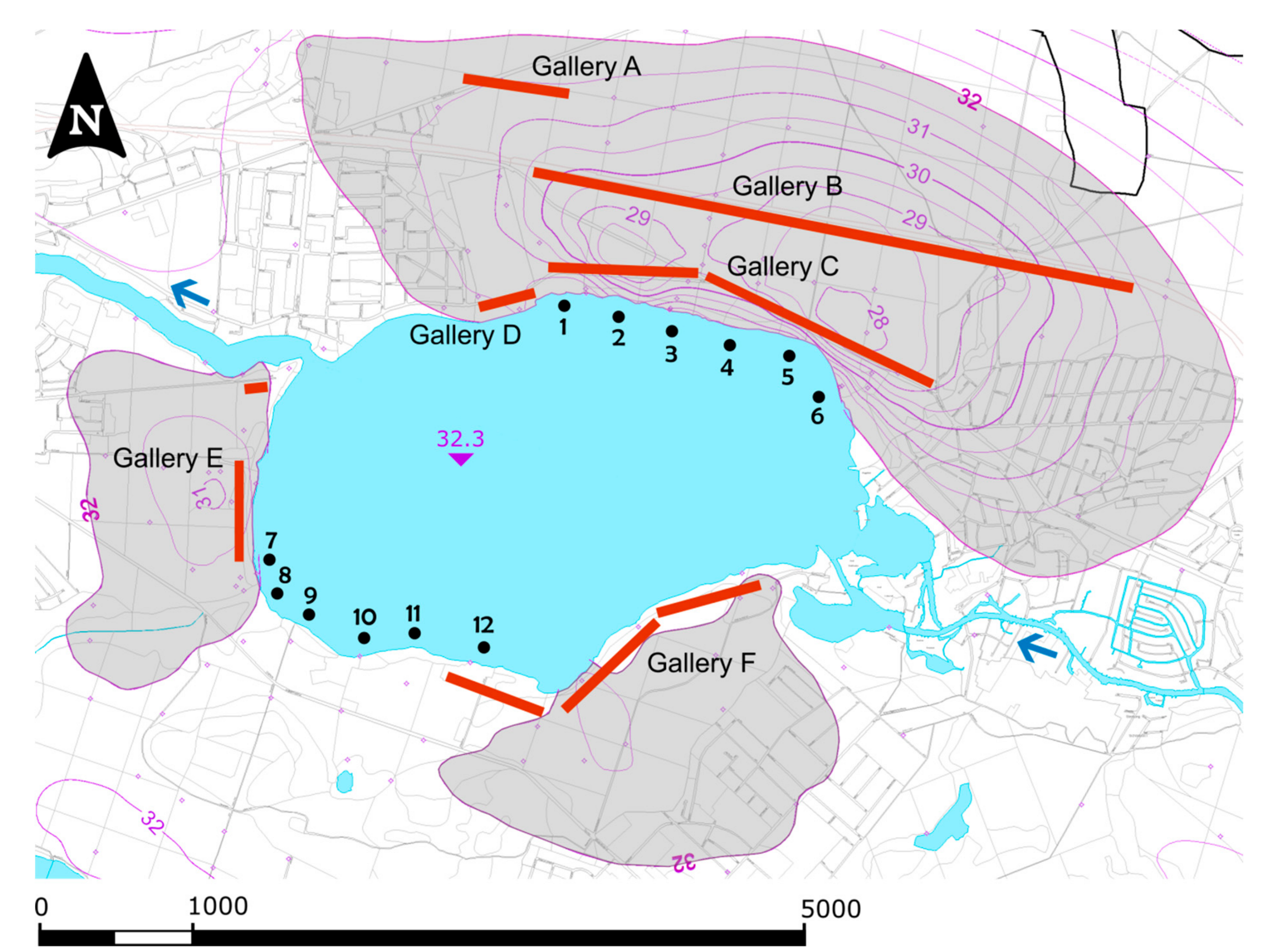
2.1. Studied Lake System and Impact of Bank Filtration
2.2. Sampling of Sediments and Plant Tubers
2.3. Sediment Analysis
2.3.1. Description
2.3.2. Phosphorus Availability
2.3.3. Further Sediment Analysis
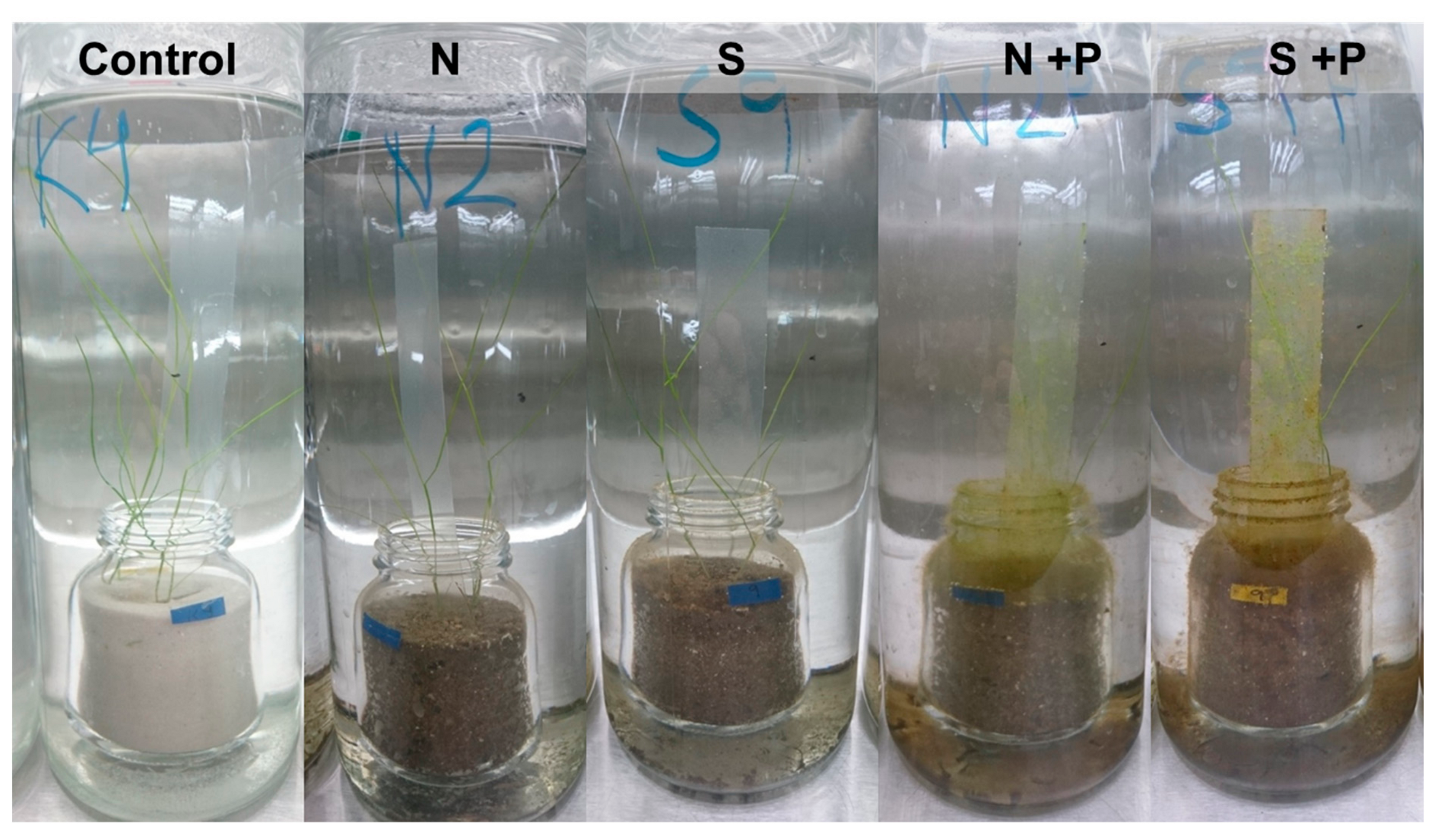
2.4. Growth Experiment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
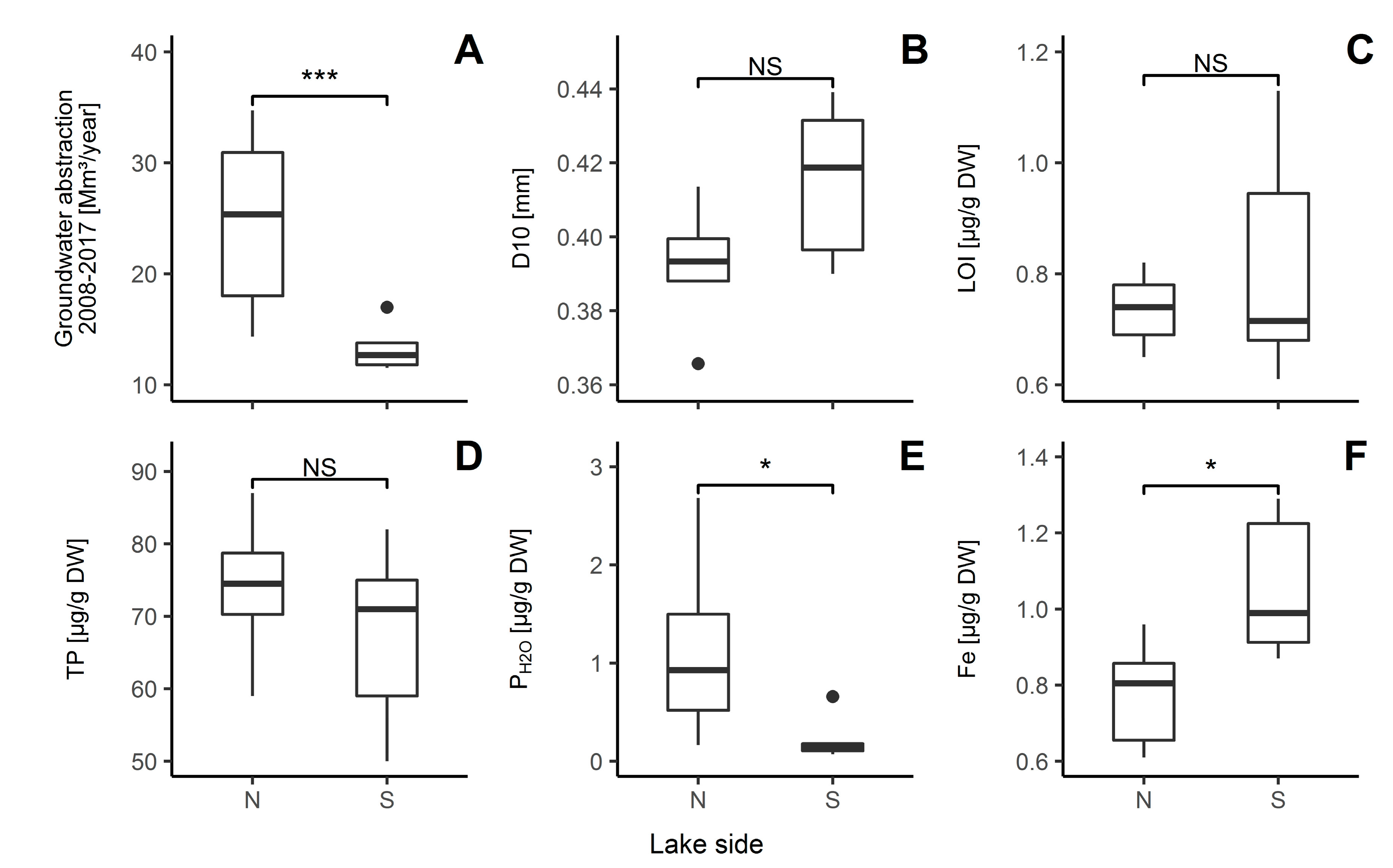
3.1. Sediment Characteristics
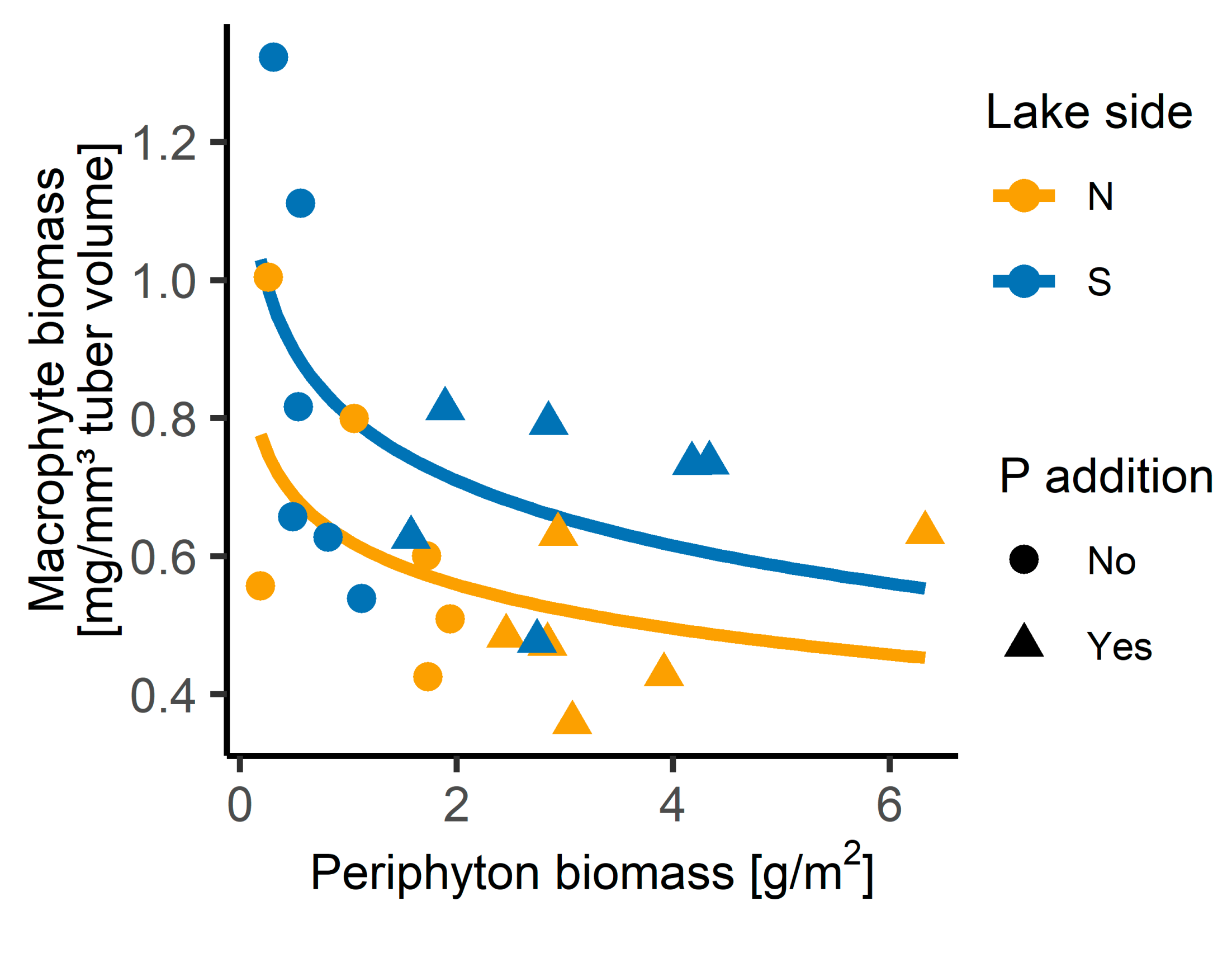
3.2. Growth Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Sediment Characteristics
4.2. Differences in Growth of Benthic Primary Producers
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Vander Zanden, M.J.; Lodge, D.M. Putting the Lake Back Together: Reintegrating Benthic Pathways into Lake Food Web Models. BioScience 2002, 52, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Brothers, S.; Jeppesen, E.; Veraart, A.J.; Kosten, S. Translating Regime Shifts in Shallow Lakes into Changes in Ecosystem Functions and Services. BioScience 2017, 67, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, S.M.; Hilt, S.; Meyer, S.; Köhler, J. Plant community structure determines primary productivity in shallow, eutrophic lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2264–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanjian, G.; Flury, S.; Attermeyer, K.; Kalettka, T.; Kleeberg, A.; Premke, K.; Köhler, J.; Hilt, S. Primary production in nutrient-rich kettle holes and consequences for nutrient and carbon cycling. Hydrobiologia 2018, 806, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; McIntyre, P.B.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Borders of Biodiversity: Life at the Edge of the World’s Large Lakes. Bioscience 2011, 61, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Périllon, C.; Hilt, S. Groundwater influence differentially affects periphyton and macrophyte production in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 778, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périllon, C.; Hilt, S. Groundwater discharge gives periphyton a competitive advantage over macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 154, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.; Willby, N.; Moss, B. Submerged macrophyte decline in shallow lakes: What have we learnt in the last forty years? Aquat. Bot. 2016, 135, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, B.; Andersen, J.M.; Fleischer, S.; Jansson, M. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périllon, C.; Pöschke, F.; Lewandowski, J.; Hupfer, M.; Hilt, S. Stimulation of epiphyton growth by lacustrine groundwater discharge to an oligo-mesotrophic hard-water lake. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillefalk, M.; Massmann, G.; Nützmann, G.; Hilt, S. Potential Impacts of Induced Bank Filtration on Surface Water Quality: A Conceptual Framework for Future Research. Water 2018, 10, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.; Schubert, J.; Linsky, R.B.; Melin, G. Introduction. In Riverbank Filtration: Improving Source-Water Quality; Ray, C., Melin, G., Linsky, R.B., Eds.; Water science and technology library; Kluwer Acad. Publ.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-1-4020-1133-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, C. Worldwide potential of riverbank filtration. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2008, 10, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillefalk, M.; Mooij, W.M.; Teurlincx, S.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Janse, J.H.; Chang, M.; Köhler, J.; Hilt, S. Modelling induced bank filtration effects on freshwater ecosystems to ensure sustainable drinking water production. Water Res. 2019, 157, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périllon, C.; van de Weyer, K.; Päzolt, J.; Kasprzak, P.; Hilt, S. Changes in submerged macrophyte colonization in shallow areas of an oligo-mesotrophic lake and the potential role of groundwater. Limnologica 2018, 68, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerthey, S.E.; Kerfoot, W.C. Spatial variation in groundwater-related resource supply influences freshwater benthic algal assemblage composition. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunkel, G.; Hoffmann, A. Bank filtration of rivers and lakes to improve the raw water quality for drinking water supply. In Water Purification; Gertsen, N., Sønderby, L., Eds.; Air, water and soil pollution science and technology series; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 137–169. ISBN 978-1-60741-599-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, A.; Gunkel, G. Carbon input, production and turnover in the interstices of a Lake Tegel bank filtration site, Berlin, Germany. Limnologica 2011, 41, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driescher, E.; Behrendt, H.; Schellenberger, G.; Stellmacher, R. Lake Müggelsee and its environment—Natural conditions and anthropogenic impacts. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. 1993, 78, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatwell, T.; Köhler, J. Decreased nitrogen loading controls summer cyanobacterial blooms without promoting nitrogen-fixing taxa: Long-term response of a shallow lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, S166–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Alirangues Nuñez, M.M.; Bakker, E.S.; Blindow, I.; Davidson, T.A.; Gillefalk, M.; Hansson, L.-A.; Janse, J.H.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Jeppesen, E.; et al. Response of Submerged Macrophyte Communities to External and Internal Restoration Measures in North Temperate Shallow Lakes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.; Kroker, J.; Körner, S.; Nicklisch, A. The role of periphyton during the re-colonization of a shallow lake with submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, B. Quagga Mussel Invasion and Its Consequences in the Shallow Eutrophic LAKE Müggelsee, Berlin. Master’s Thesis, Technical University, Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hupfer, M.; Gächter, R.; Giovanoli, R. Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 57, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünscher, R. A Comparison of Different Phosphorus Extraction Methods with the Phosphorus Uptake of Wheat. Master’s Thesis, Universität für Bodenkultur Wien, Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Körner, S.; Nicklisch, A. Allelopathic growth inhibition of selected phytoplankton species by submerged macrophytes. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.E.; Hootsmans, M.J.M. Intraspecific variation in Potamogeton pectinatus L.: A controlled laboratory experiment. In Lake Veluwe, a Macrophyte-Dominated System under Eutrophication Stress; van Vierssen, W., Hootsmans, M.J.M., Vermaat, J.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, A.; Gunkel, G. Bank filtration in the sandy littoral zone of Lake Tegel (Berlin): Structure and dynamics of the biological active filter zone and clogging processes. Limnologica 2011, 41, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunkel, G.; Beulker, C.; Hoffmann, A.; Kosmol, J. Fine particulate organic matter (FPOM) transport and processing in littoral interstices—Use of fluorescent markers. Limnologica 2009, 39, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, E.; Goda, Z. Coupling Riverbank Filtration with Reverse Osmosis May Favor Short Distances between Wells and Riverbanks at RBF Sites on the River Danube in Hungary. Water 2019, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greskowiak, J.; Prommer, H.; Massmann, G.; Johnston, C.D.; Nützmann, G.; Pekdeger, A. The impact of variably saturated conditions on hydrogeochemical changes during artificial recharge of groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psenner, R.; Pucsko, R.; Sager, M. Fractionation of organic and inorganic phosphorous compounds in lake sediments, An attempt to characterize ecologically important fractions. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1984, 70, 111–155. [Google Scholar]
- Hecky, R.E.; Smith, R.E.; Barton, D.R.; Guildford, S.J.; Taylor, W.D.; Charlton, M.N.; Howell, T. The nearshore phosphorus shunt: A consequence of ecosystem engineering by dreissenids in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordhuis, R.; van Zuidam, B.G.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; van Geest, G.J. Further improvements in water quality of the Dutch Borderlakes: Two types of clear states at different nutrient levels. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.; Hachoł, J.; Hilt, S. Regulation of submersed macrophyte biomass in a temperate lowland river: Interactions between shading by bank vegetation, epiphyton and water turbidity. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, C.G.; Diehl, S. Resource competition across habitat boundaries: Asymmetric interactions between benthic and pelagic producers. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 84, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.I.; Sayer, C.D. Does the Fish–Invertebrate–Periphyton Cascade Precipitate Plant Loss in Shallow Lakes? Ecology 2003, 84, 2155–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Hilt, S.; Pei, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, X.; Chang, X. Growth phase-dependent allelopathic effects of cyanobacterial exudates on Potamogeton crispus L. seedlings. Hydrobiologia 2016, 767, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.T.; Whitwell, T.; Riley, M.B.; Bernard, C.R. Evaluating semiaquatic herbaceous perennials for use in herbicide phytoremediation. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1999, 124, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuteson, S.L.; Whitwell, T.; Klaine, S.J. Influence of plant age and size on simazine toxicity and uptake. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragon, K.; Górski, J.; Kruć, R.; Drożdżyński, D.; Grischek, T. Removal of Natural Organic Matter and Organic Micropollutants during Riverbank Filtration in Krajkowo, Poland. Water 2018, 10, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gillefalk, M.; Herzog, C.; Hilt, S. Phosphorus Availability and Growth of Benthic Primary Producers in Littoral Lake Sediments: Are Differences Linked to Induced Bank Filtration? Water 2019, 11, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051111
Gillefalk M, Herzog C, Hilt S. Phosphorus Availability and Growth of Benthic Primary Producers in Littoral Lake Sediments: Are Differences Linked to Induced Bank Filtration? Water. 2019; 11(5):1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051111
Chicago/Turabian StyleGillefalk, Mikael, Christiane Herzog, and Sabine Hilt. 2019. "Phosphorus Availability and Growth of Benthic Primary Producers in Littoral Lake Sediments: Are Differences Linked to Induced Bank Filtration?" Water 11, no. 5: 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051111
APA StyleGillefalk, M., Herzog, C., & Hilt, S. (2019). Phosphorus Availability and Growth of Benthic Primary Producers in Littoral Lake Sediments: Are Differences Linked to Induced Bank Filtration? Water, 11(5), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051111




