Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics of Bottled Water in China: A Consideration of Water Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
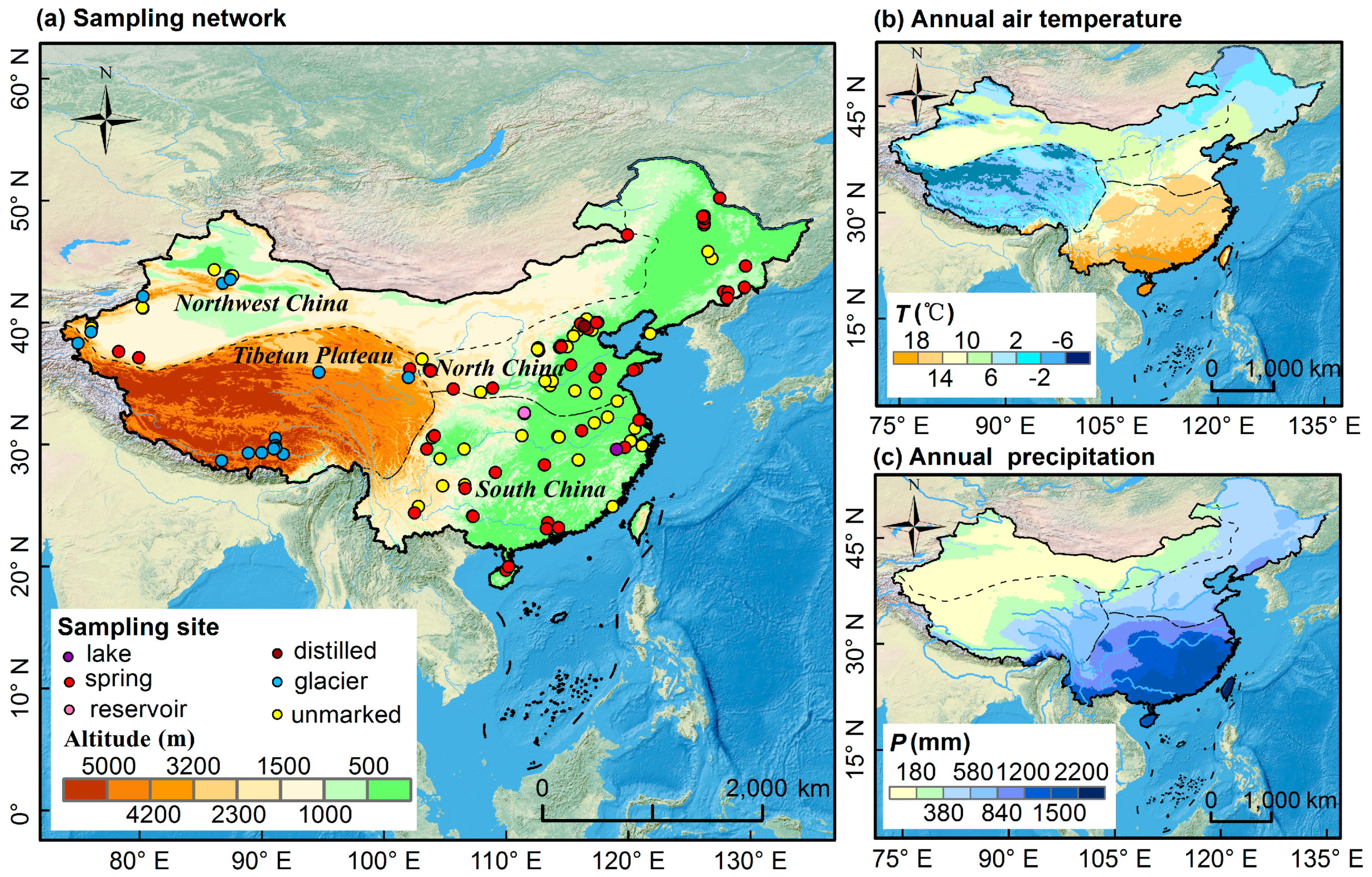
2.1. Bottled Water Isotope Database
2.2. Precipitation Isotope Database
2.3. Tap Water Database
2.4. Other Databases
2.5. Bottled Water Isoscape Prediction AND Other Methods
3. Results and Discussion
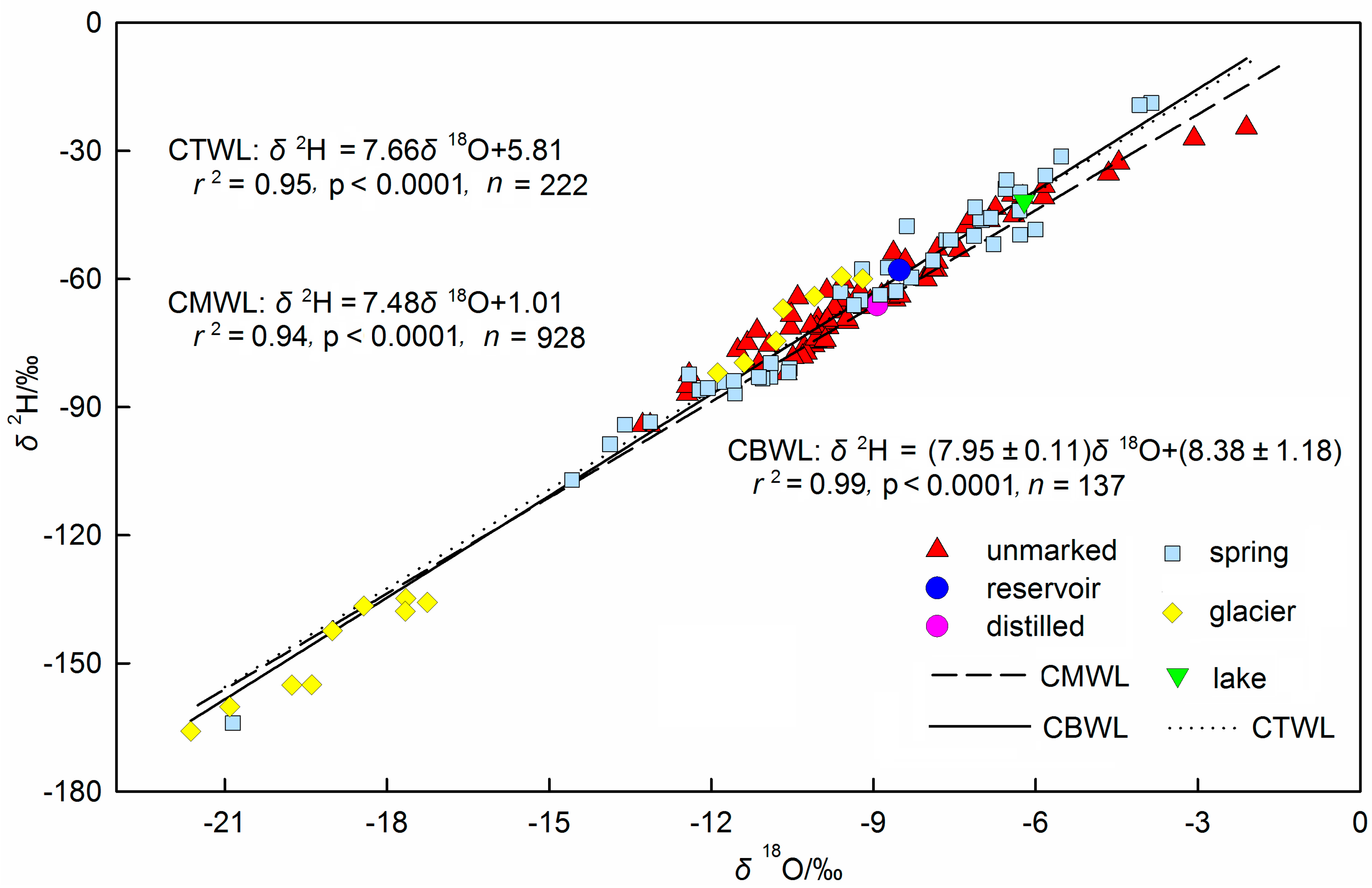
3.1. Basic Isotopic Characteristics of Bottled Water
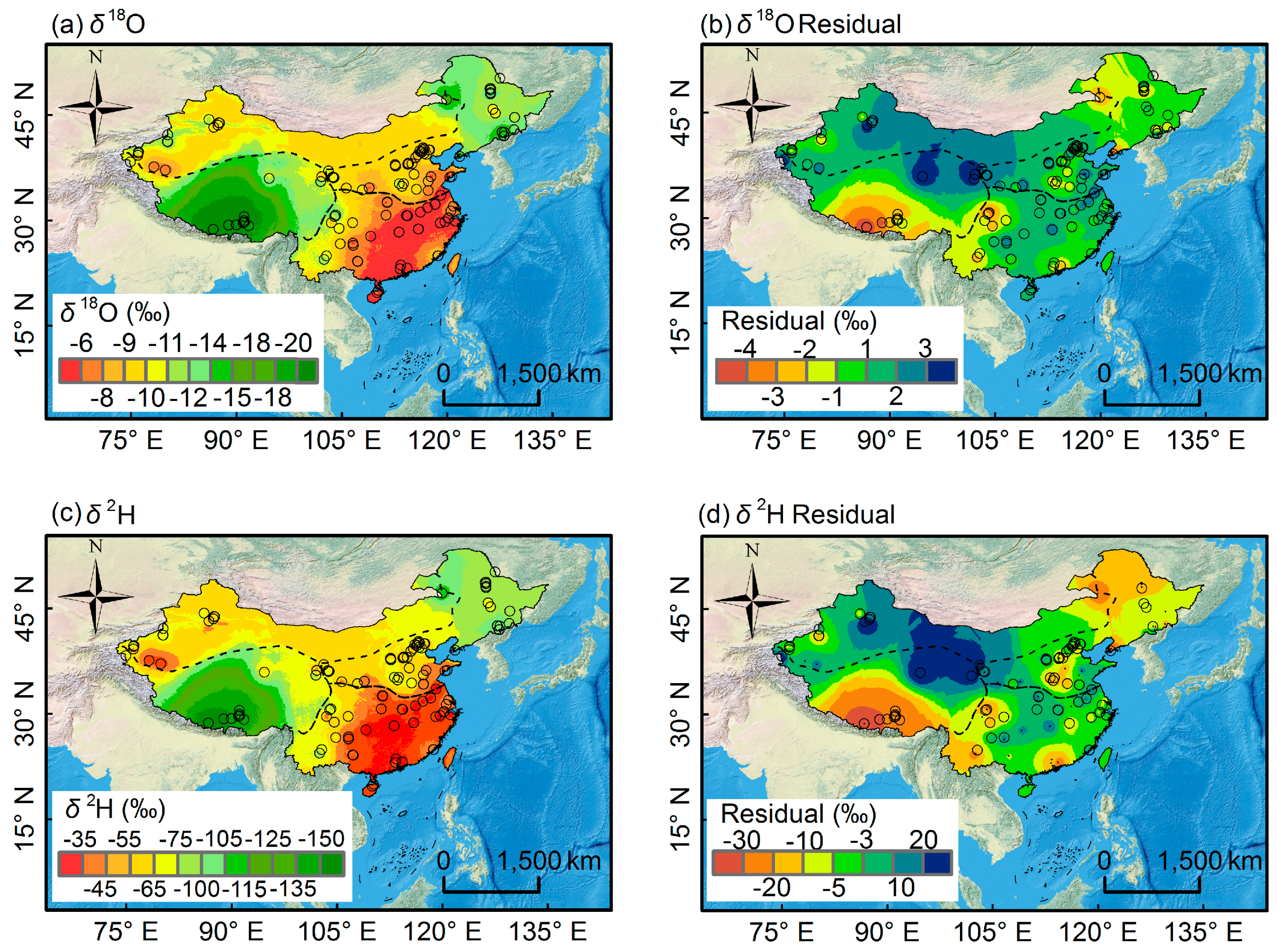
3.2. Isoscape of Chinese Bottled Water
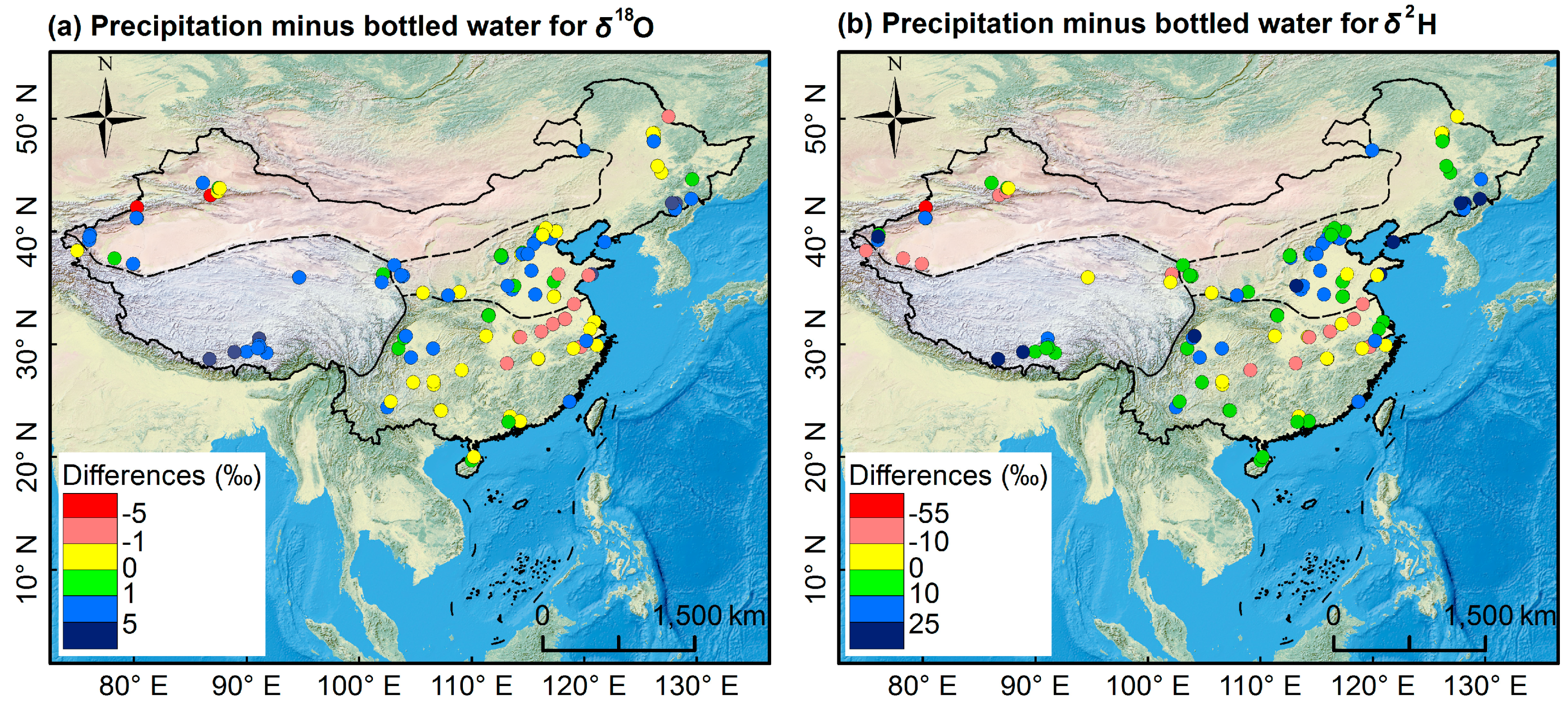
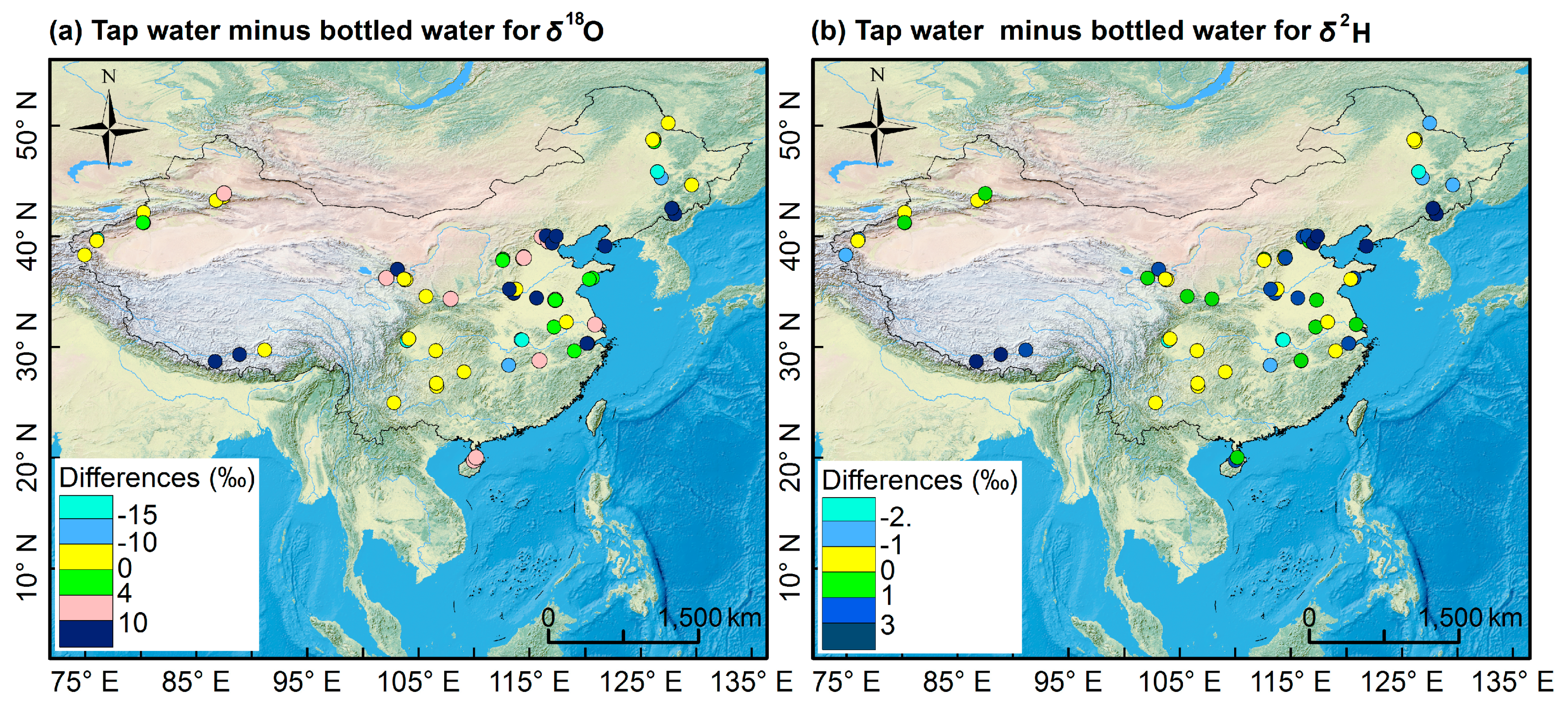
3.2.1. Spatial Pattern of Bottled Water Isotopes
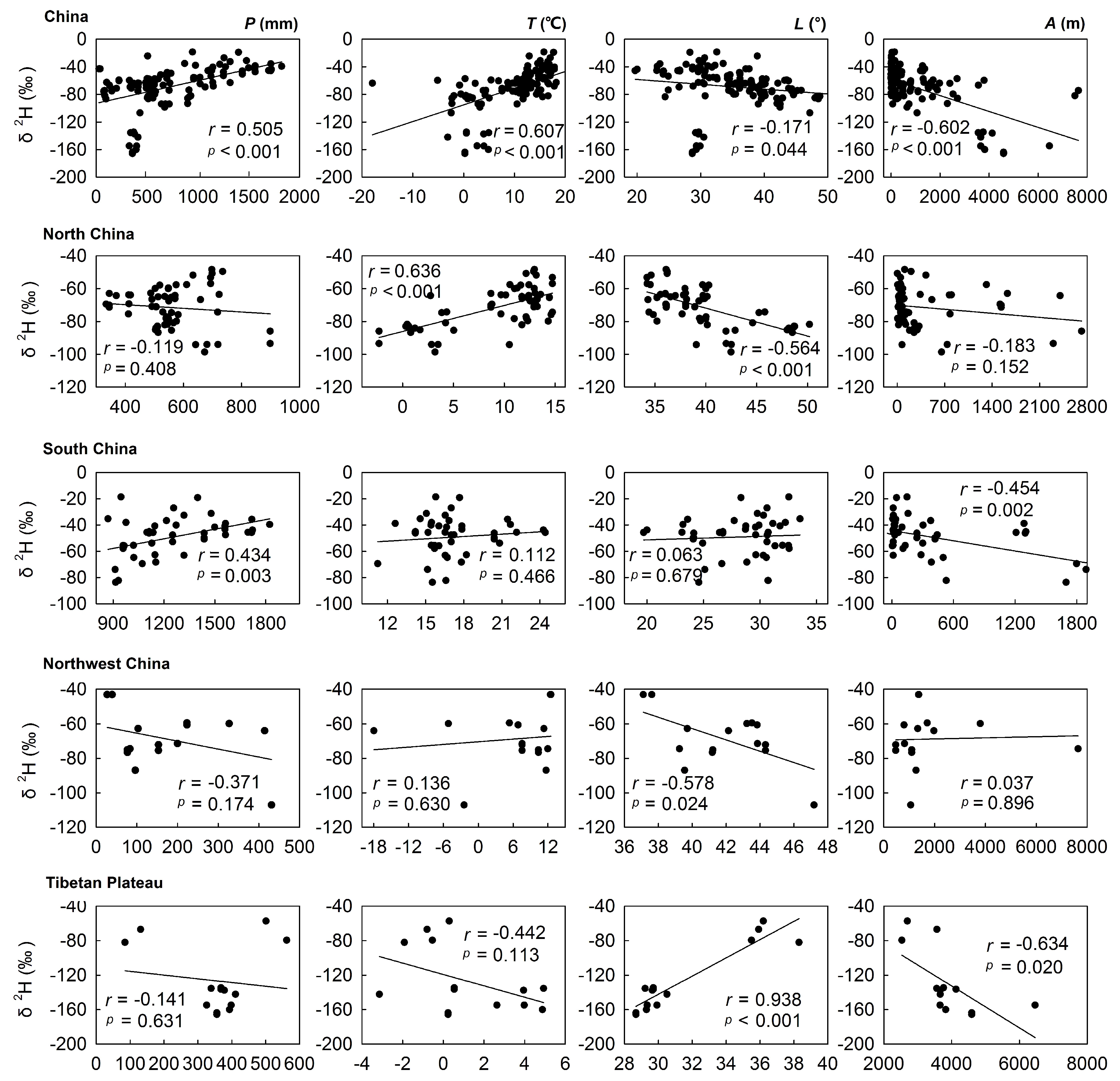
3.2.2. Correlations between Isotope Values in Bottled Water and Environmental Parameters
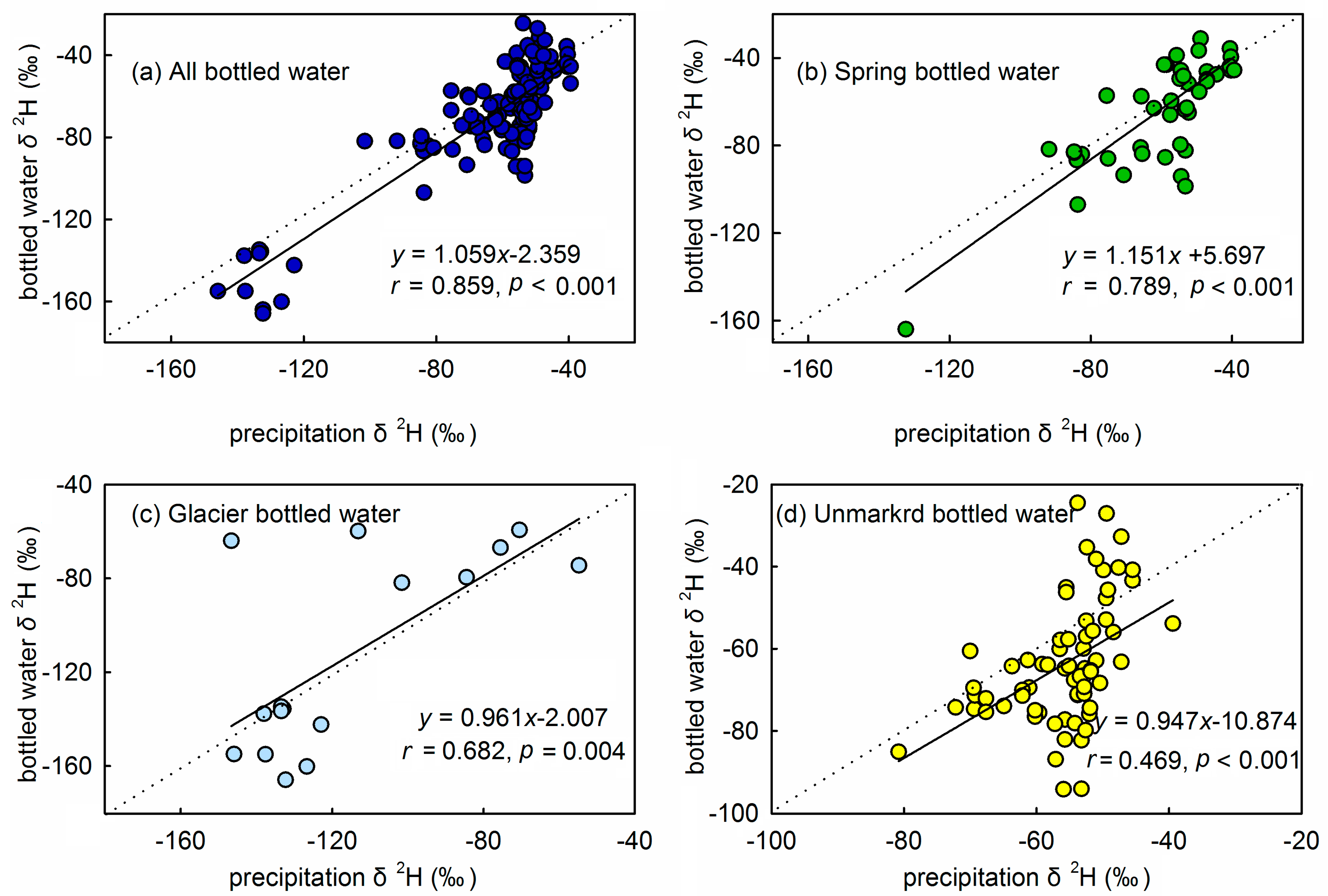
3.3. Relationship between Isotopes in Bottled Water and Precipitation Isotopes
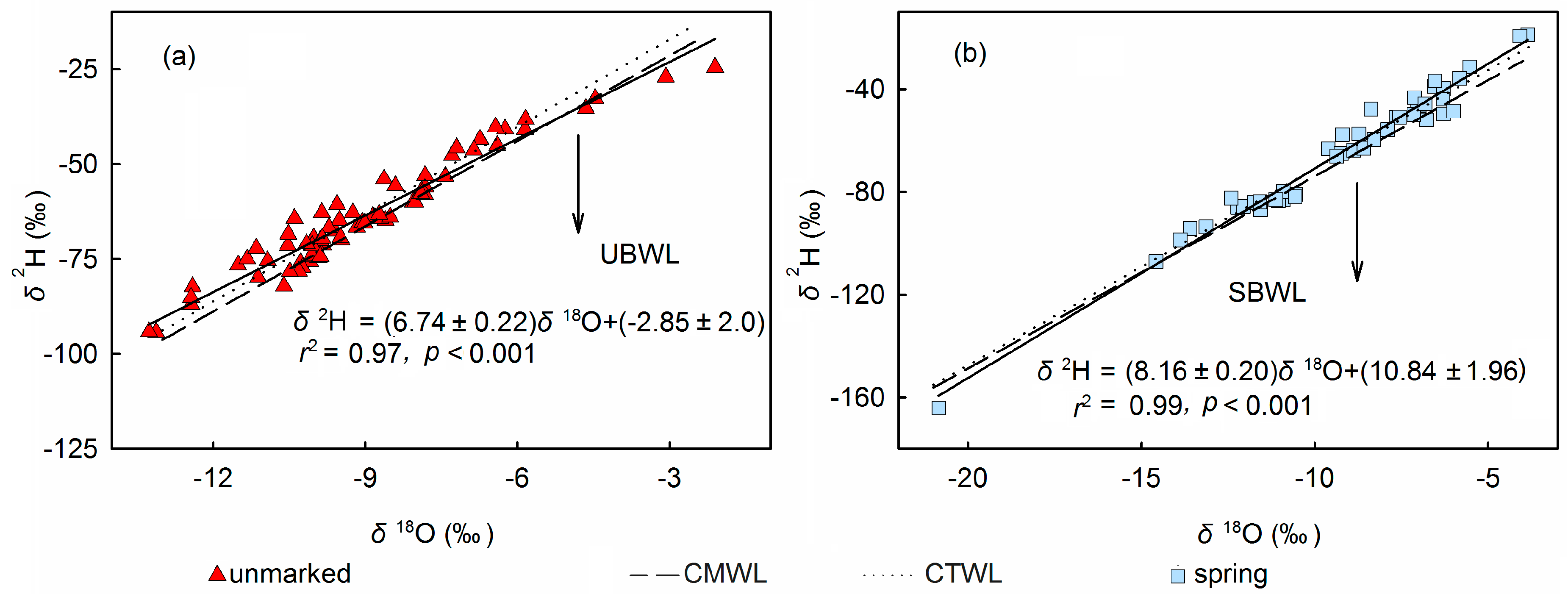
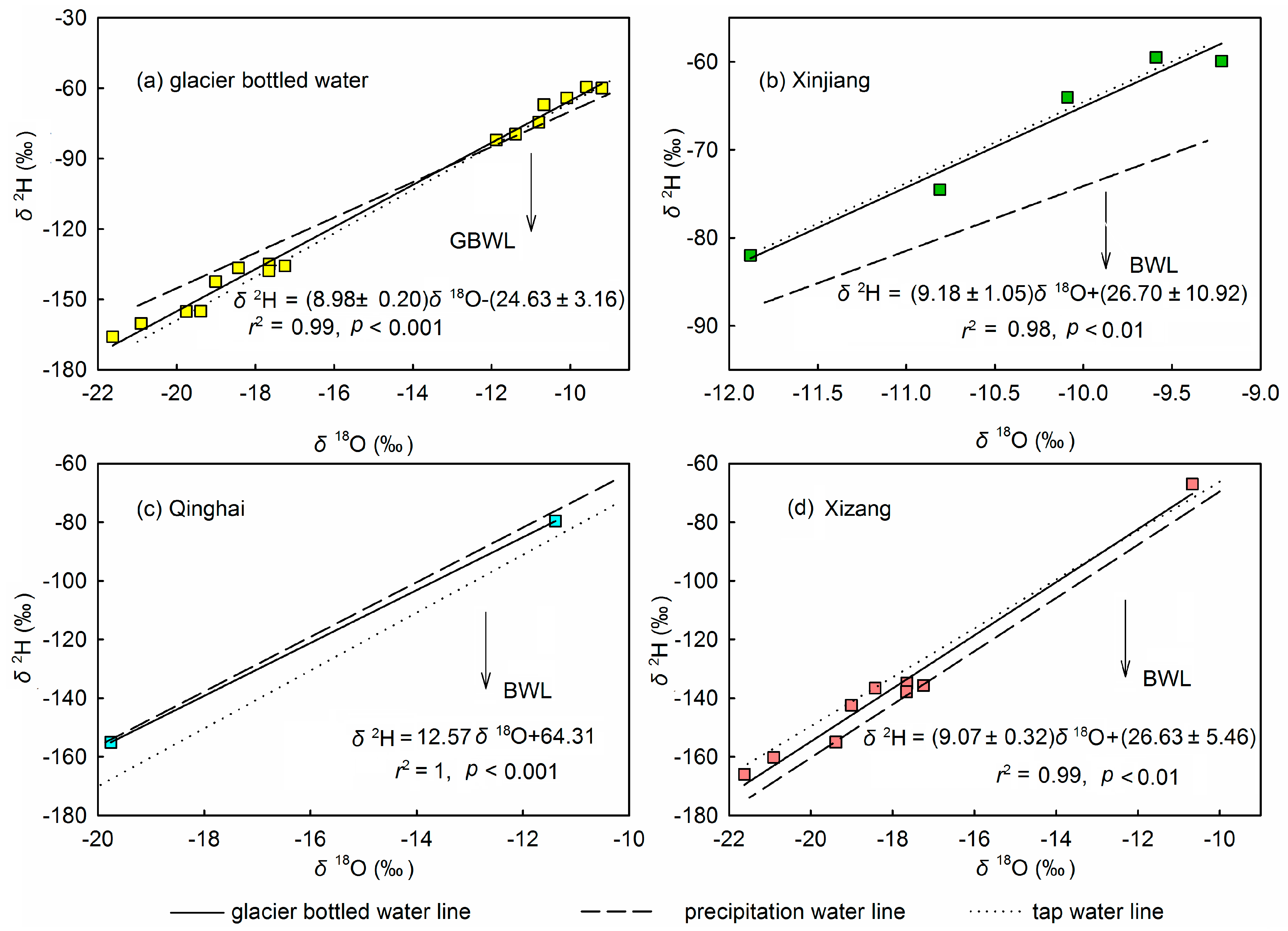
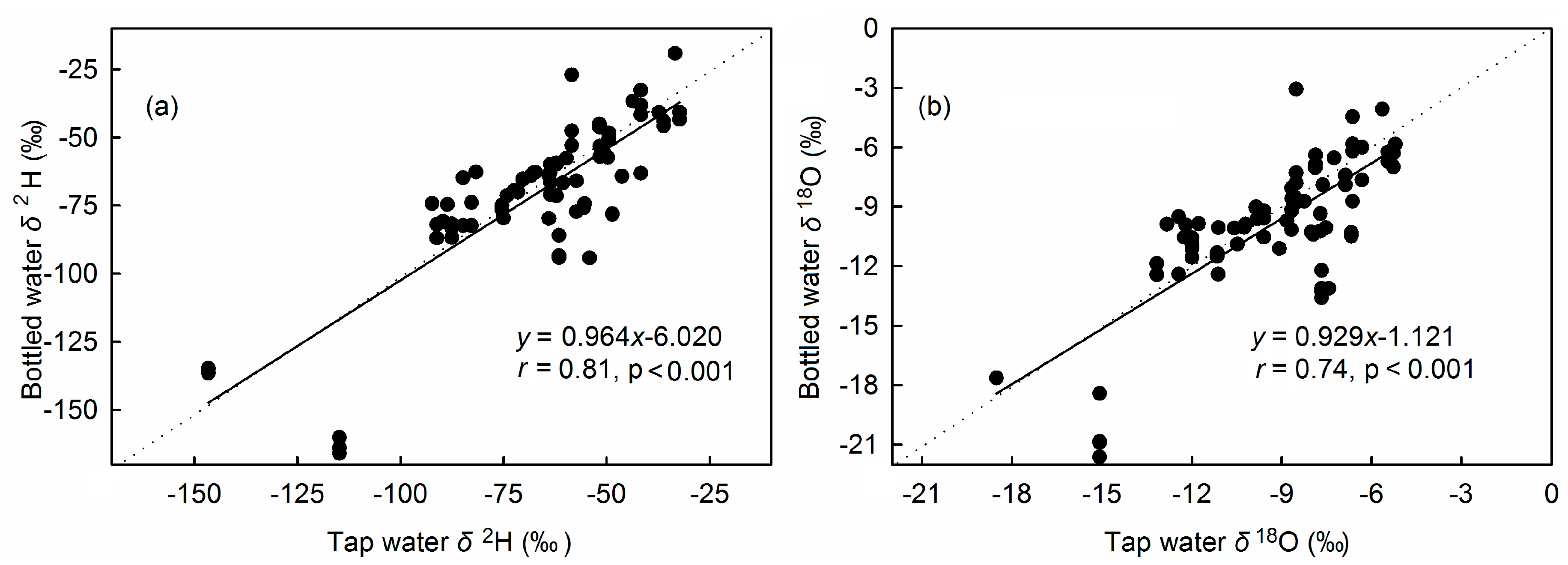
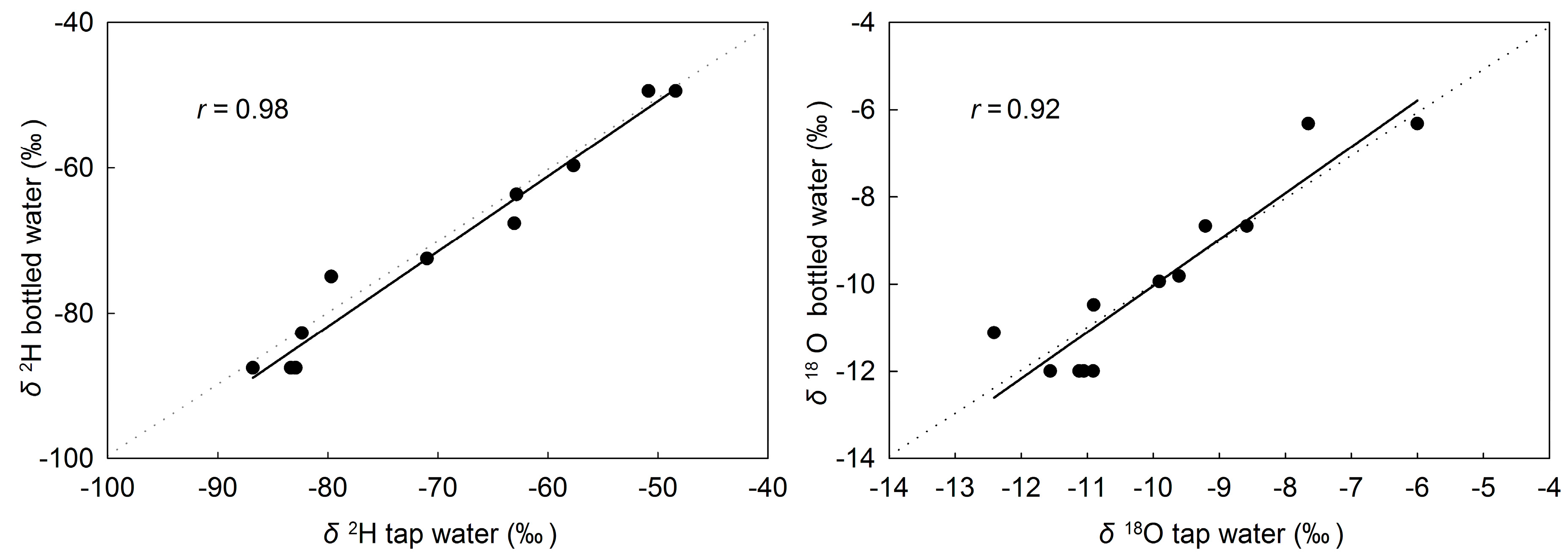
3.4. Source Water Relationship
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mustafe, P.; Arbenita, Q. The Bottled Water Market and Consumer Behavior. Int. J. Sustain. Econ. Manag. (IJSEM) 2018, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.F.; Yates, H.S.A.; Tinggi, U. Isotopic and Elemental Composition of Roasted Coffee as a Guide to Authenticity and Origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5771–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.F.; Yates, H.S.A.; Tinggi, U. Stable Isotope and Chemical Compositions of European and Australasian Ciders as a Guide to Authenticity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singerling, S.A.; Burkemper, L.K.; Sharp, Z.D. Measurement of Adjuncts in Hard Ciders Obtainable in the United States Using Carbon Isotopes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11422–11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behkami, S.; Zain, S.M.; Gholami, M.; Bakirdere, S. Isotopic ratio analysis of cattle tail hair: A potential tool in building the database for cow milk geographical traceability. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Tang, C.; Yu, X.; Zhan, T.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J. Application of isotopic and elemental fingerprints in identifying the geographical origin of goat milk in China. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchini, F.; Portarena, S.; Ciolfi, M.; Brugnoli, E.; Lauteri, M. Isoscapes of carbon and oxygen stable isotope compositions in tracing authenticity and geographical origin of Italian extra-virgin olive oils. Food Chem. 2016, 202, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Winter, D.A.; Spero, H.J.; Zierenberg, R.A.; Reeder, M.D.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios of bottled waters of the world. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesson, L.A.; Valenzuela, L.O.; O’Grady, S.P.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Links between Purchase Location and Stable Isotope Ratios of Bottled Water, Soda, and Beer in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7311–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenčič, M.; Vreca, P. Identification of sources and production processes of bottled waters by stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenčič, M.; Vreča, P. The use of a finite mixture distribution model in bottled water characterisation and authentication with stable hydrogen, oxygen and carbon isotopes—Case study from Slovenia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotsika, E.; Poutoukis, D.; Raco, B.; Psomiadis, D. Stable isotope composition of Hellenic bottled waters. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, Y.-S.; Ryu, J.-S.; Lee, K.-S. Characterizing the origins of bottled water on the South Korean market using chemical and isotopic compositions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 631, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-E.; Shin, W.-J.; Ryu, J.-S.; Choi, M.-S.; Lee, K.-S. Identification of the origin and water type of various Korean bottled waters using strontium isotopes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, R.; Ghosh, P. Tracing the source of bottled water using stable isotope techniques. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3323–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Gu, H.; Yu, Y.; Chi, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characteristics of Bottled Drinking Water and Its Instruction Significance. Earth Envrion. 2015, 43, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.-R.; Liang, W.-J.; Liu, T.-S.; Lin, Y.-W.; Zhan, W.-J. Assessing the authenticity of commercial deep-sea drinking water by chemical and isotopic approaches. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 51, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuribayashi, T.; Sugawara, M.; Sato, K.; Nabekura, Y.; Aoki, T.; Kano, N.; Joh, T.; Kaneoke, M. Stable Isotope Analysis of Hydrogen and Oxygen in a Traditional Japanese Alcoholic Beverage, Sake, from Niigata Prefecture in Japan and Other Countries. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mook, W.G. Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle. Principles Appl. 2002, 37, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S. A New Scheme for Comprehensive Physical Regionalization in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 1983, 38, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzer, S.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Araguás-Araguás, L.J.; Aggarwal, P.K. Global isoscapes for δ18O and δ2H in precipitation: Improved prediction using regionalized climatic regression models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4713–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency). Regionalized Cluster-Based Water Isotope Prediction (RCWIP); IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Christner, E.; Kohler, M.; Schneider, M. The influence of snow sublimation and meltwater evaporation on δD of water vapor in the atmospheric boundary layer of central Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1207–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, A.M.; Buizert, C.; Baggenstos, D.; Brook, E.J.; Ahn, J.; Yang, J.W.; Severinghaus, J.P. Does δ18O of O2 record meridional shifts in tropical rainfall? Clim. Past 2017, 13, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Bowen, G.J.; Liu, X.; Du, M.; Chen, F.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L.; Che, Y.; Zhao, G. Water source signatures in the spatial and seasonal isotope variation of Chinese tap waters. Water Resour. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA/WMO (International Atomic Energy Agency/World Meteorological Organization). Water Isotope System for Data Analysis, Visualization and Electronic Retrieval (WISER); IAEA/WMO: Vienna, Austria; Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Yuan, G.; Sun, X.; Yang, L. Stable isotopic compositions of precipitation in China. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2014, 66, 22567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tian, L.; Chai, X.; Yao, T. A model-based determination of spatial variation of precipitation δ18O over China. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Revenaugh, J. Interpolating the isotopic composition of modern meteoric precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykoudis, S.P.; Argiriou, A.A. Gridded data set of the stable isotopic composition of precipitation over the eastern and central Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; Hultine, K.R.; Burtch, K.G.; Ehleringer, J.R. Seasonal variations in moisture use in a piñon–juniper woodland. Oecologia 2007, 153, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Qin, X.; Wu, J. The application of modified BW method in studying spatial distribution of δ18O in precipitation over China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2014, 36, 1430–1439. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hollins, S.E.; Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J.; Cendón, D.I.; Meredith, K.T. Rainfall isotope variations over the Australian continent—Implications for hydrology and isoscape applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Chesson, L.A.; Stange, E.; Cerling, T.E. Stable isotope ratios of tap water in the contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Tie, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C. Divergence of stable isotopes in tap water across China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, T.; Cifuentes, J.; Iacumin, P.; Selmo, E. Local Meteoric Water Line of Northern Chile (18° S–30° S): An Application of Error-in-Variables Regression to the Oxygen and Hydrogen Stable Isotope Ratio of Precipitation. Water 2019, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourcy, L.L.; Groening, M.; Aggarwal, P.K. Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in precipitation. In Isotopes in the Water Cycle; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jouzel, J.; Lorius, C.; Petit, J.R.; Genthon, C.; Barkov, N.I.; Kotlyakov, V.M.; Petrov, V.M. Vostok ice core: A continuous isotope temperature record over the last climatic cycle (160,000 years). Nature 1987, 329, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poage, M.A.; Chamberlain, C.P.J.A.J.o.S. Empirical Relationships between Elevation and the Stable Isotope Composition of Precipitation and Surface Waters: Considerations for Studies of Paleoelevation Change. Am. J. Sci. 2001, 301, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R.; Roche, M.-A.; Olivry, J.-C.; Fontes, J.-C.; Zuppi, G.M. The altitude effect on the isotopic composition of tropical rains. Chem. Geol. 2001, 181, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hughes, C.E.; Zhu, X.; Dong, L.; Ren, Z.; Chen, F. Factors controlling stable isotope composition of precipitation in arid conditions: An observation network in the Tianshan Mountains, central Asia. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2016, 68, 26206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yun, H.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of the hydrological contributions of permafrost to the thermokarst lakes on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau using stable isotopes. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yao, T.; Numaguti, A.; Sun, W. Stable Isotope Variations in Monsoon Precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. Ii 2001, 79, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Stievenard, M.; Yao, T.; Jouzel, J. Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 28081–28088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yao, T.; MacClune, K.; White, J.W.C.; Schilla, A.; Vaughn, B.; Vachon, R.; Ichiyanagi, K. Stable isotopic variations in west China: A consideration of moisture sources. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Origin Types | δ2H (‰) | δ18O (‰) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Average | Max | Min | Average | |
| spring | −19 | −164 | −64 | −3.9 | −20.9 | −9.1 |
| glacier | −59.5 | −166 | −113 | −9.2 | −21.6 | −15.3 |
| unmarked | −24 | −94 | −63 | −2.1 | −13.3 | −8.9 |
| all | −19 | −166 | −69 | −2.1 | −21.6 | −9.8 |
| Equation | r2 | radj2 | n | AIC | MBE | MAE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ18O | δ = −0.0479L2 + 2.474L − 0.012A − 83.432 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 137 | 954.44 | 0.00 | 1.83 | 2.57 |
| δ = −0.0186O − 0.107L − 0.00164A − 2.42497 | 0.443 | 0.431 | 137 | 956.02 | 0.00 | 1.83 | 2.57 | |
| δ = 0.249T + 0.001461P − 13.455 | 0.412 | 0.403 | 137 | 963.73 | 0.00 | 1.89 | 2.68 | |
| δ = 0.212594T − 0.002013P − 0.000052137R + 3.252138V + 0.81497S − 6.856 | 0.466 | 0.446 | 137 | 954.10 | 0.00 | 1.83 | 2.53 | |
| δ = −0.002871A + 0.000000246A2 − 0.001690L2 − 5.6691 | 0.501 | 0.490 | 137 | 940.70 | 0.00 | 1.86 | 2.45 | |
| δ = 12.009V − 4.293V2 + 0.011T2 − 18.510 | 0.520 | 0.509 | 137 | 935.50 | 0.00 | 1.82 | 2.40 | |
| δ = −18.4118 + 25.47523V − 0.000474A − 6.544752V2 − 0.00000715436P2 − 0.014221P − 0.374248T | 0.669 | 0.654 | 137 | 909.36 | 0.00 | 1.62 | 2.14 | |
| δ2H | δ = −0.0479L2 + 2.474L − 0.012A − 83.432 | 0.420 | 0.407 | 137 | 1541.50 | 0.00 | 15.00 | 21.25 |
| δ = −0.31286O − 0.837651L − 0.0137A + 7.3092 | 0.424 | 0.412 | 137 | 1540.51 | 0.00 | 14.93 | 21.17 | |
| δ = 1.921313T + 0.0126991P − 98.7966 | 0.391 | 0.382 | 137 | 1546.34 | 0.00 | 14.84 | 21.77 | |
| δ = 1.40594T − 0.01761P − 0.00047895R + 29.336S + 4.727976V − 30.054 | 0.470 | 0.450 | 137 | 1533.11 | 0.00 | 14.81 | 20.32 | |
| δ = −0.445895O − 0.025A − 0.01212L2 + 0.0000194A2 + 12.575 | 0.482 | 0.456 | 137 | 1528.64 | 0.19 | 15.14 | 20.14 | |
| δ = −279.0 −0.0171A + 0896T − 0.0000000097A − 0.003088630R − 0.002789O2 + 0.000012A2 + 0.1107P | 0.679 | 0.666 | 137 | 1464.07 | 0.94 | 12.48 | 15.85 | |
| δ = −138.2152 + 216.728V − 0.00346A − 55.045V2 − 0.000067P2 − 0.1321P − 3.3981472T | 0.615 | 0.597 | 137 | 1305.60 | −0.02 | 13.61 | 17.32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Argiriou, A.A.; Liu, X.; Su, B.; Qiu, X.; Jiao, R.; Shi, M.; Zhou, S.; et al. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics of Bottled Water in China: A Consideration of Water Source. Water 2019, 11, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051065
Guo R, Wang S, Zhang M, Argiriou AA, Liu X, Su B, Qiu X, Jiao R, Shi M, Zhou S, et al. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics of Bottled Water in China: A Consideration of Water Source. Water. 2019; 11(5):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051065
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Rong, Shengjie Wang, Mingjun Zhang, Athanassios A. Argiriou, Xuemei Liu, Bo Su, Xue Qiu, Rong Jiao, Mengyu Shi, Su’e Zhou, and et al. 2019. "Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics of Bottled Water in China: A Consideration of Water Source" Water 11, no. 5: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051065
APA StyleGuo, R., Wang, S., Zhang, M., Argiriou, A. A., Liu, X., Su, B., Qiu, X., Jiao, R., Shi, M., Zhou, S., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Characteristics of Bottled Water in China: A Consideration of Water Source. Water, 11(5), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051065









