Capture and Release of Phosphorus by Periphyton in Closed Water Systems Influenced by Illumination and Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
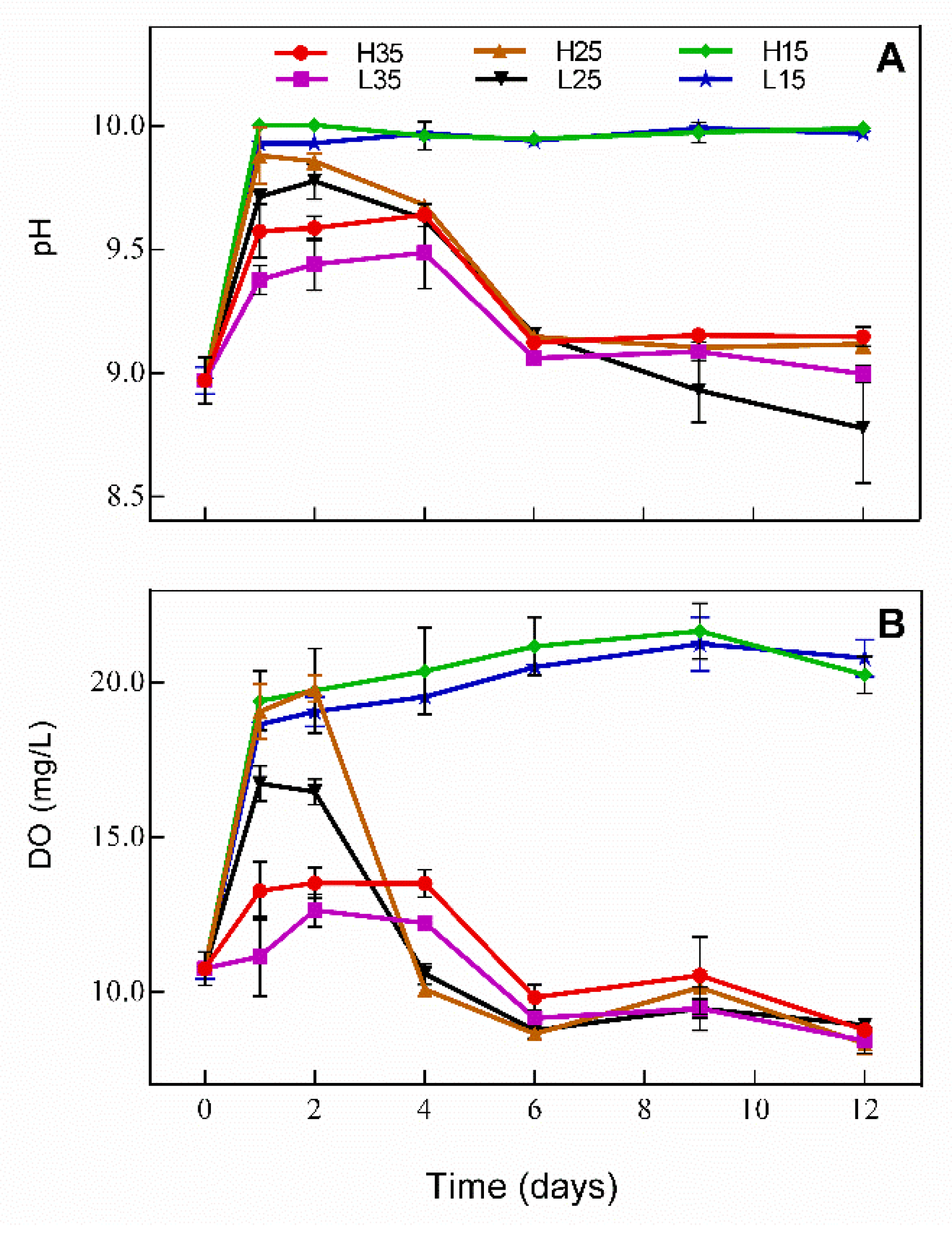
3.1. Changes in DO and pH in Water
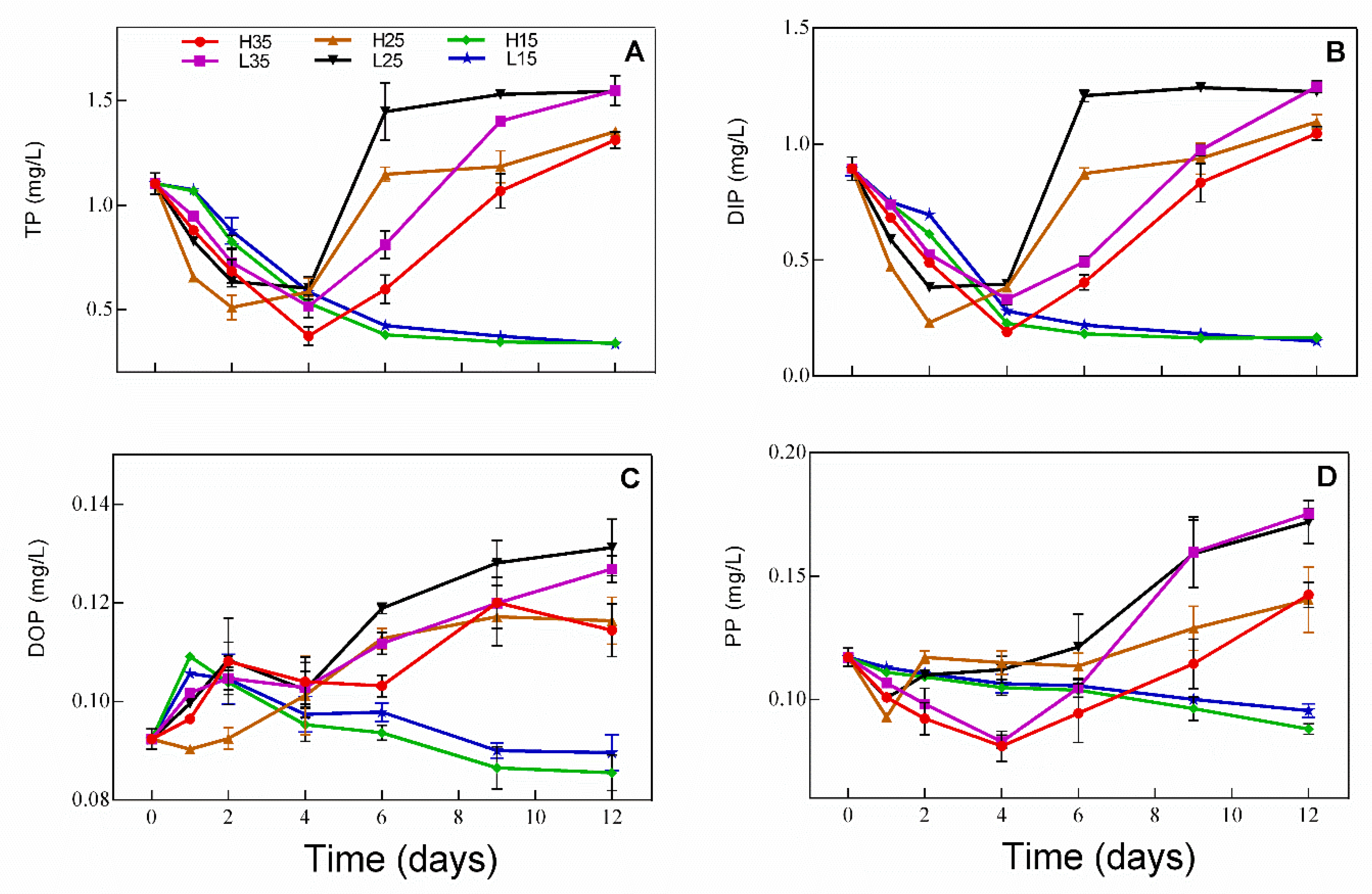
3.2. Changes in Phosphorus in Water
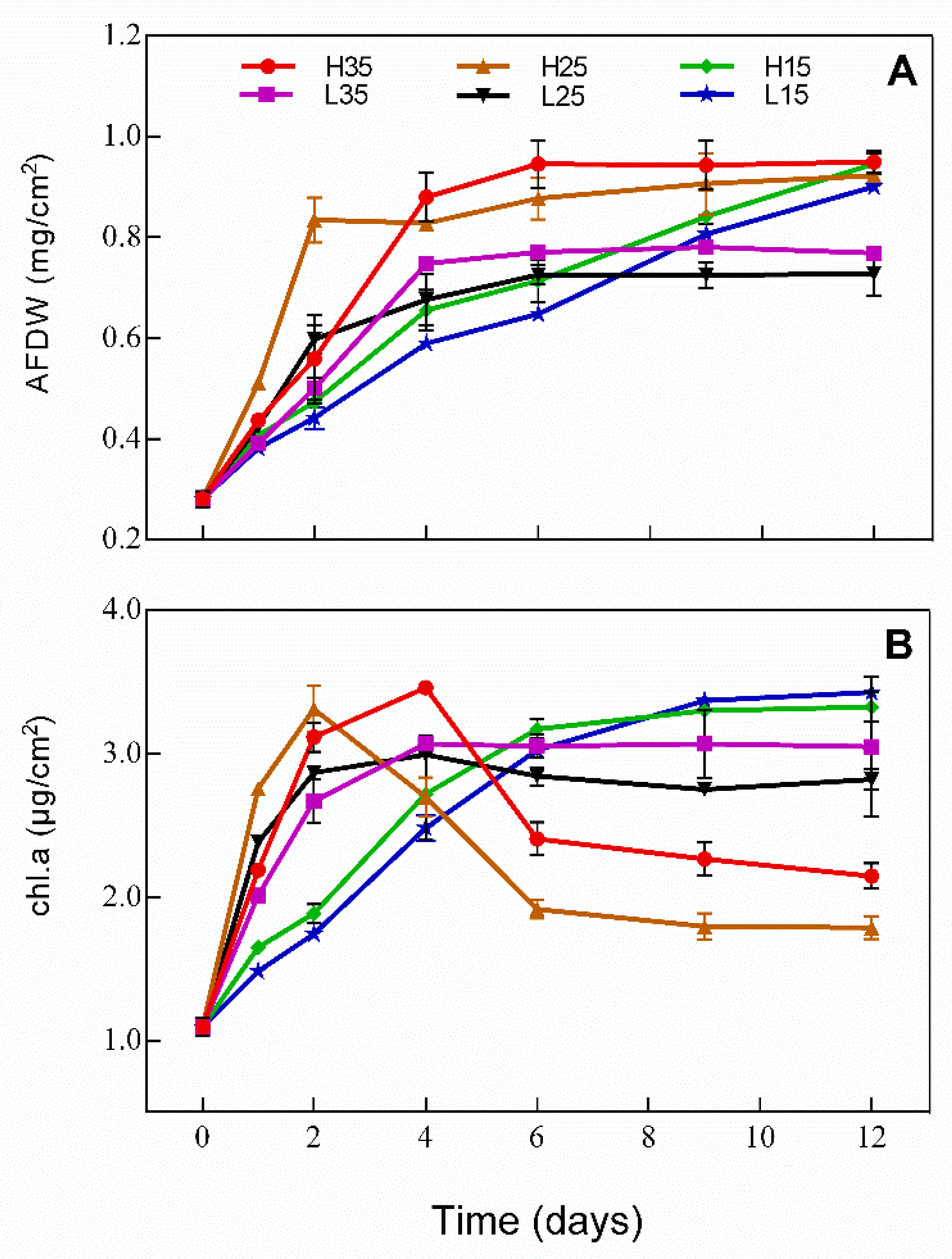
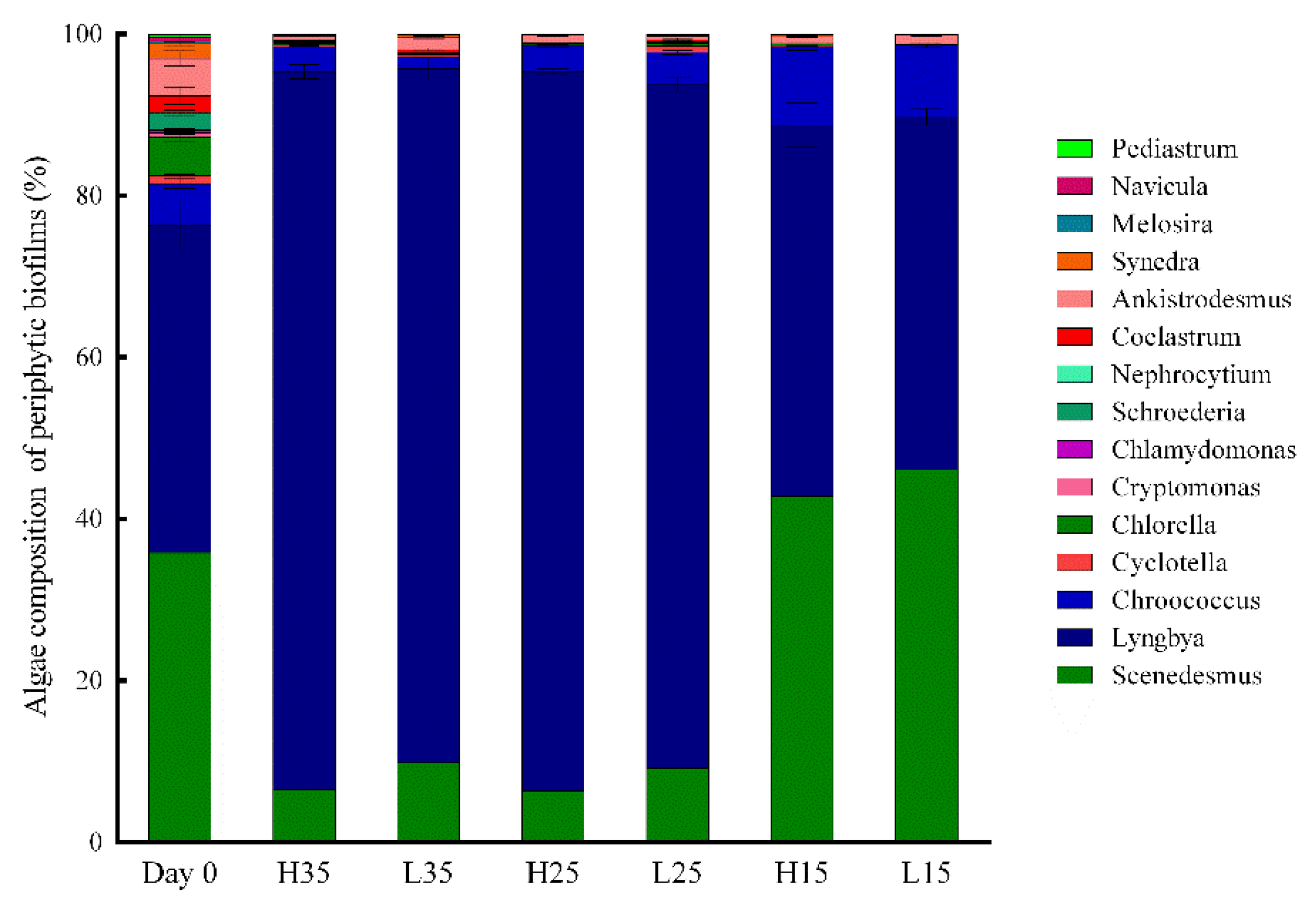
3.3. Development of Periphyton
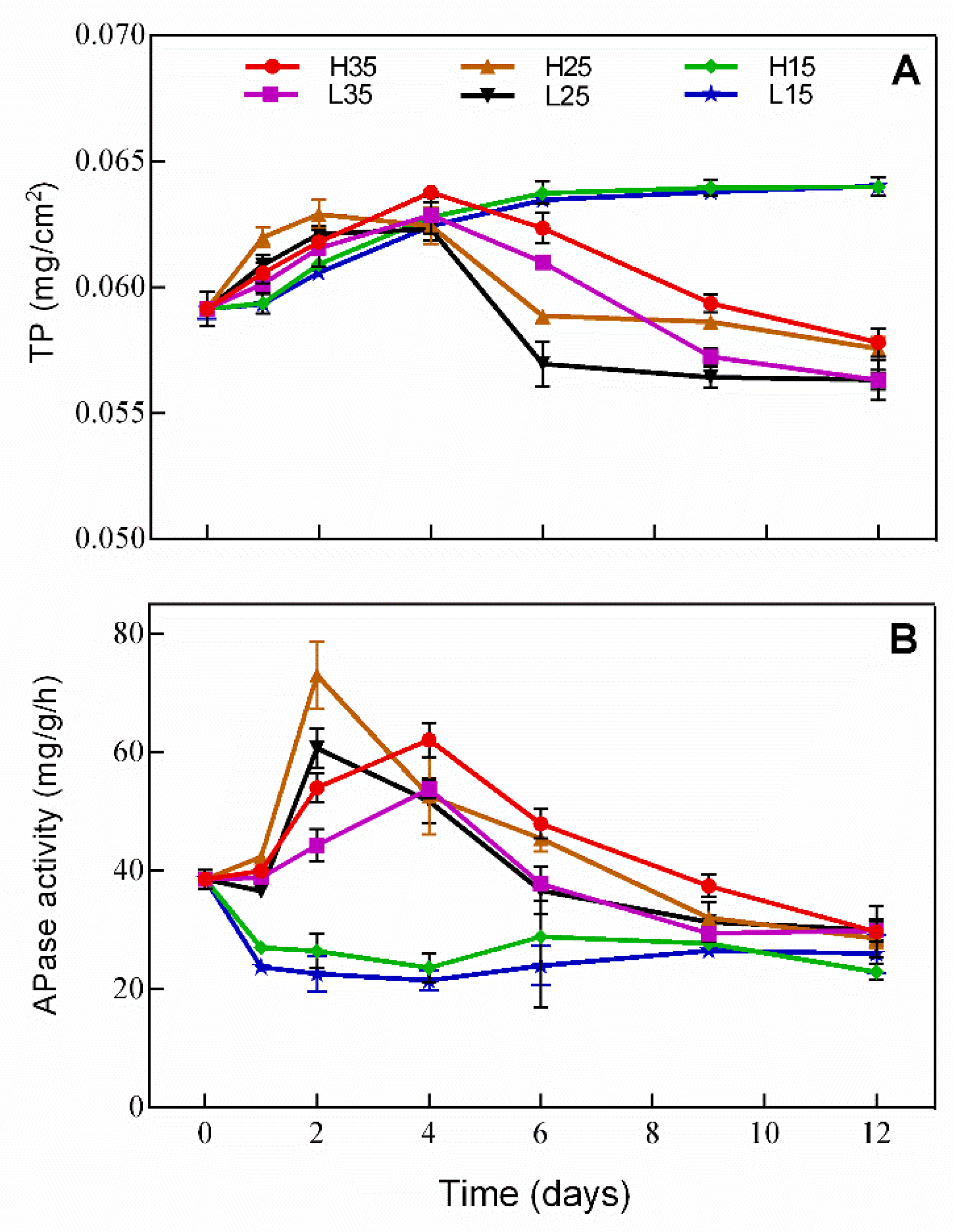
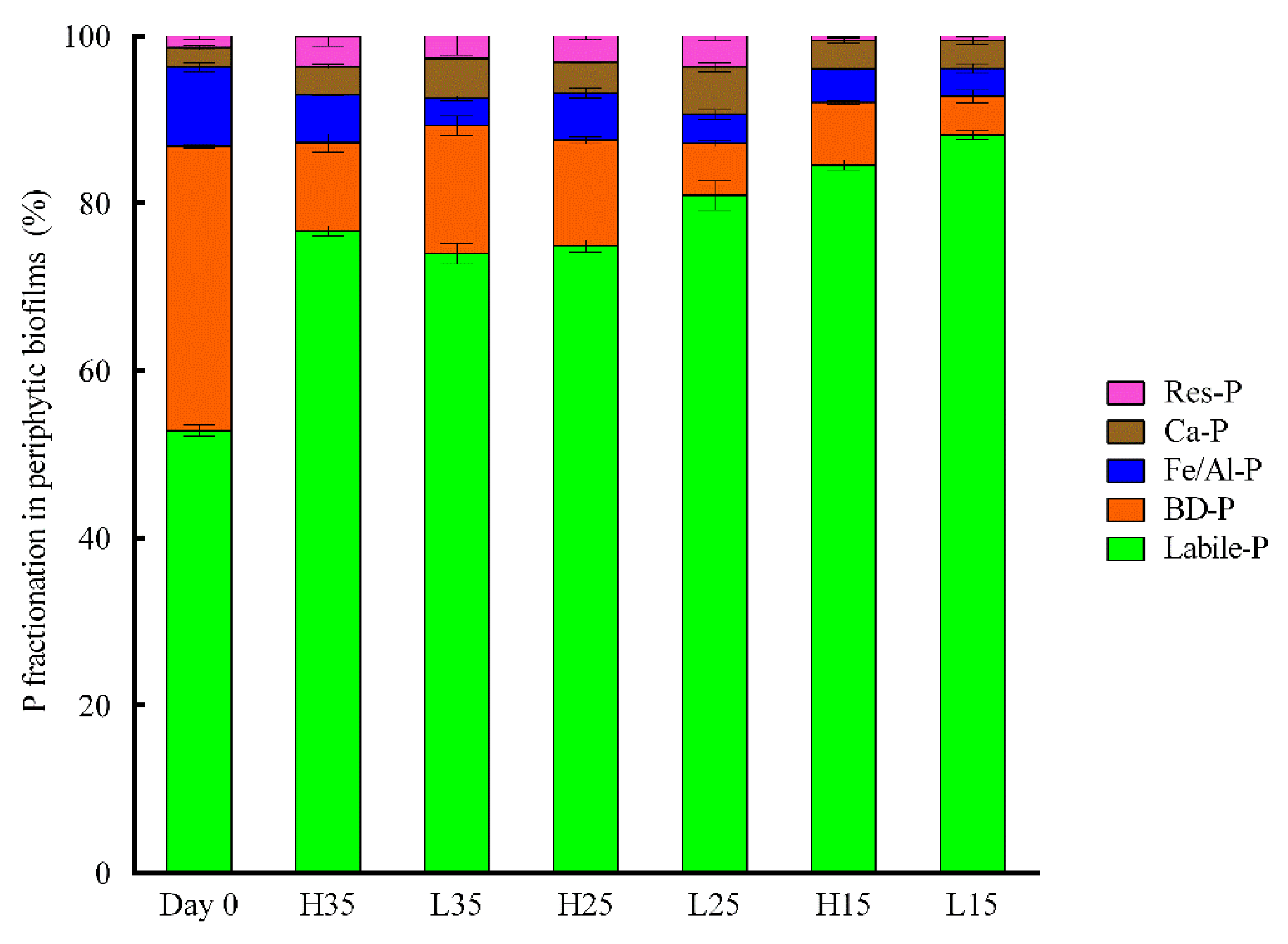
3.4. Changes of Phosphorus and APase Activity in Periphyton
3.5. Effects of Time and Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verdegem, M.; Van Dam, A.; Azim, M.; Beveridge, M. Periphyton ecology, exploitation and management: Knowledge gaps and directions for future research. In Periphyton: Ecology, Exploitation and Management; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2005; pp. 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Steinman, A.D. Periphyton function in lake ecosystems. Sci. World J. 2002, 2, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, W.K. The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 39, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilker, U.; Ashvini, C.; Ogram, A.V. Cellulolytic, fermentative, and methanogenic guilds in benthic periphyton mats from the Florida Everglades. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 61, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, J.E.; Lind, O. Phosphorus uptake and turnover by periphyton in the presence of suspended clays. Limnology 2010, 11, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelee, N.; Temmink, H.; Janssen, M.; Buisman, C.; Wijffels, R. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater effluent using microalgal biofilms. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5925–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzon, A.; Bohn, A.; Diociaiuti, M.; Albertano, P. Cultured phototrophic biofilms for phosphorus removal in wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4357–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukačová, K.; Trtílek, M.; Rataj, T. Phosphorus removal using a microalgal biofilm in a new biofilm photobioreactor for tertiary wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2015, 71, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shao, H.; Yang, L. Responses of periphyton morphology, structure, and function to extreme nutrient loading. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochine, C.; Guerrieri, M.E.; Liboriussen, L.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of nutrient loading, temperature regime and grazing pressure on nutrient limitation of periphyton in experimental ponds. Freshwater Biol. 2014, 59, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Besemer, K.; Burns, N.R.; Battin, T.J.; Bengtsson, M.M. Light availability affects stream biofilm bacterial community composition and function, but not diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 17, 5036–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, L.F.; Guariento, R.D.; Caliman, A.; Bozelli, R.L.; Esteves, F.A. Effects of nutrients and light on periphytic biomass and nutrient stoichiometry in a tropical black-water aquatic ecosystem. Hydrobiologia 2011, 669, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, V.D.; Font, J.; Schwartz, T.; Romaní, A.M. Biofilm formation at warming temperature: Acceleration of microbial colonization and microbial interactive effects. Biofouling 2011, 27, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkworth, C.L.; Salis, R.K.; Matthaei, C.D. Interactive multiple-stressor effects of the antibiotic monensin, cattle effluent and light on stream periphyton. Freshwater Biol. 2015, 60, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pippo, F.; Ellwood, N.T.W.; Guzzon, A.; Siliato, L.; Micheletti, E.; de Philippis, R.; Albertano, P.B. Effect of light and temperature on biomass, photosynthesis and capsular polysaccharides in cultured phototrophic biofilms. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEPC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of China). Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods; China Environ. Sci. Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Scott, J.T.; Lang, D.A.; King, R.S.; Doyle, R.D. Nitrogen fixation and phosphatase activity in periphyton growing on nutrient diffusing substrata: Evidence for differential nutrient limitation in stream periphyton. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2009, 28, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow lakes with different trophic status, China. Aquat. Bot. 2015, 125, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.J.; Wei, Y.X. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Sci. Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Grossart, H.P.; Czub, G.; Simon, M. Algae–bacteria interactions and their effects on aggregation and organic matter flux in the sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wu, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Influence of light and temperature on the development and denitrification potential of periphytic biofilms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duport, J.P. Responses of lotic periphyton to pulses of phosphorus: P-flux controlled growth rate. Freshwater Biol. 2012, 57, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar]
- Verchot, L.V.; Borelli, T. Application of para -nitrophenol (pNP) enzyme assays in degraded tropical soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.; Mayes, M.A.; Wang, G. Kinetic parameters of phosphatase: A quantitative synthesis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lou, L.; Cui, X.; Jie, T.; Li, P.; Cao, R. Significance of biological effects on phosphorus transformation processes at the water–sediment interface under different environmental conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kvíderová, J.; Kaštánek, P.; Lukavský, J. The green alga Dictyosphaerium chlorelloides biomass and polysaccharides production determined using cultivation in crossed gradients of temperature and light. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, G.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Physiological acclimation of the green tidal alga Ulva prolifera to a fast-changing environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 137, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorson, H.M.; Scott, E.E.; Entrekin, S.A.; Evans-White, M.A.; Scott, J.T. Light and dissolved phosphorus interactively affect microbial metabolism, stoichiometry and decomposition of leaf litter. Freshwater Biol. 2016, 61, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccormick, P.V.; Iii, R.B.E.S.; Chimney, M.J. Periphyton as a potential phosphorus sink in the Everglades Nutrient Removal Project. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 27, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, W.M.; Scott, J.T.; Haggard, B.; Sharpley, A.; Rogers, C.W.; Grantz, E.M. The effect of periphyton stoichiometry and light on biological phosphorus immobilization and release in streams. Limnology 2012, 13, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Wu, C.; Kerr, P. Periphyton: An important regulator in optimizing soil phosphorus bioavailability in paddy fields. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21377–21384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Shao, H.; Wu, Y. Periphytic biofilm: A buffer for phosphorus precipitation and release between sediments and water. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Mei, X.Y. Effects of benthic algae on release of soluble reactive phosphorus from sediments: A radioisotope tracing study. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Depree, C.; Brown, L.; Mcallister, T.; Hawes, I. Entrapped Sediments as a Source of Phosphorus in Epilithic Cyanobacterial Proliferations in Low Nutrient Rivers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Source | df | pH | DO | AFDW | Chl.a | TP | DIP | DOP | PP | APase Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | 6 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| I | 1 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.024 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| T | 2 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| Day × I | 6 | 0.000 * | 0.001 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| Day × T | 12 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| T× I | 2 | 0.001 * | 0.231 | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.053 |
| Day × I × T | 12 | 0.052 | 0.024 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.000 * | 0.034 * | 0.001 * | 0.45 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiong, X.; Wu, C. Capture and Release of Phosphorus by Periphyton in Closed Water Systems Influenced by Illumination and Temperature. Water 2019, 11, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051021
Zhao Y, Chen X, Xiong X, Wu C. Capture and Release of Phosphorus by Periphyton in Closed Water Systems Influenced by Illumination and Temperature. Water. 2019; 11(5):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051021
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yanhui, Xiaofei Chen, Xiong Xiong, and Chenxi Wu. 2019. "Capture and Release of Phosphorus by Periphyton in Closed Water Systems Influenced by Illumination and Temperature" Water 11, no. 5: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051021
APA StyleZhao, Y., Chen, X., Xiong, X., & Wu, C. (2019). Capture and Release of Phosphorus by Periphyton in Closed Water Systems Influenced by Illumination and Temperature. Water, 11(5), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051021




