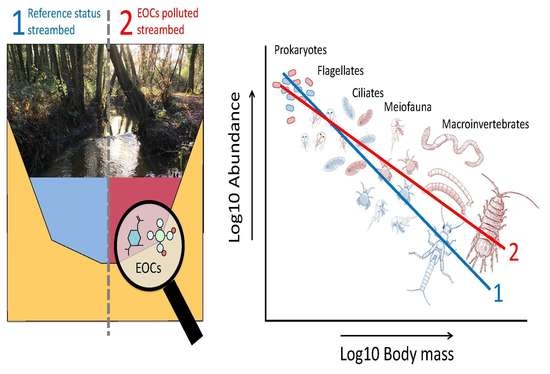
Mapping Micro-Pollutants and Their Impacts on the Size Structure of Streambed Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
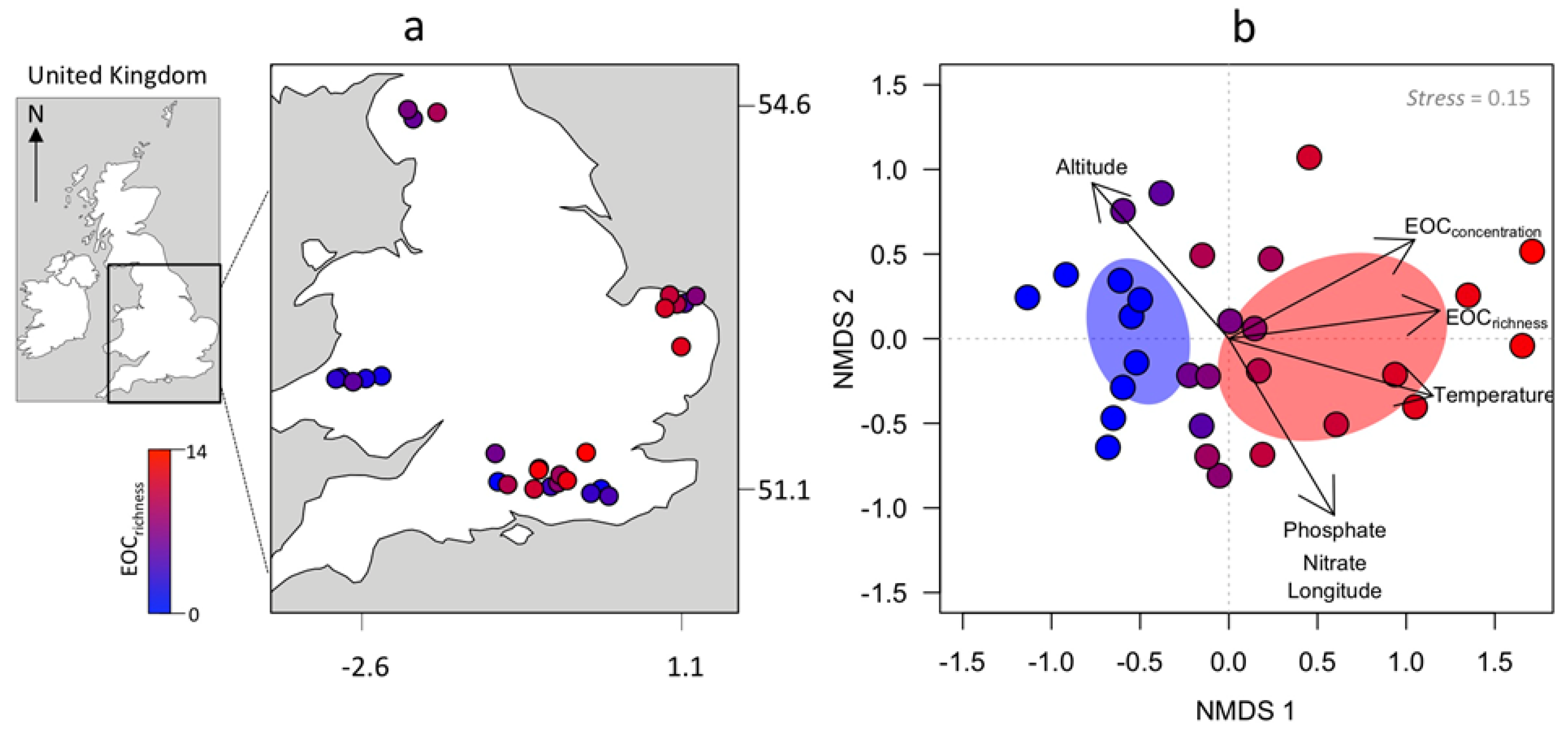
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Sampling and Processing of EOCs
2.3. Statistical Analysis
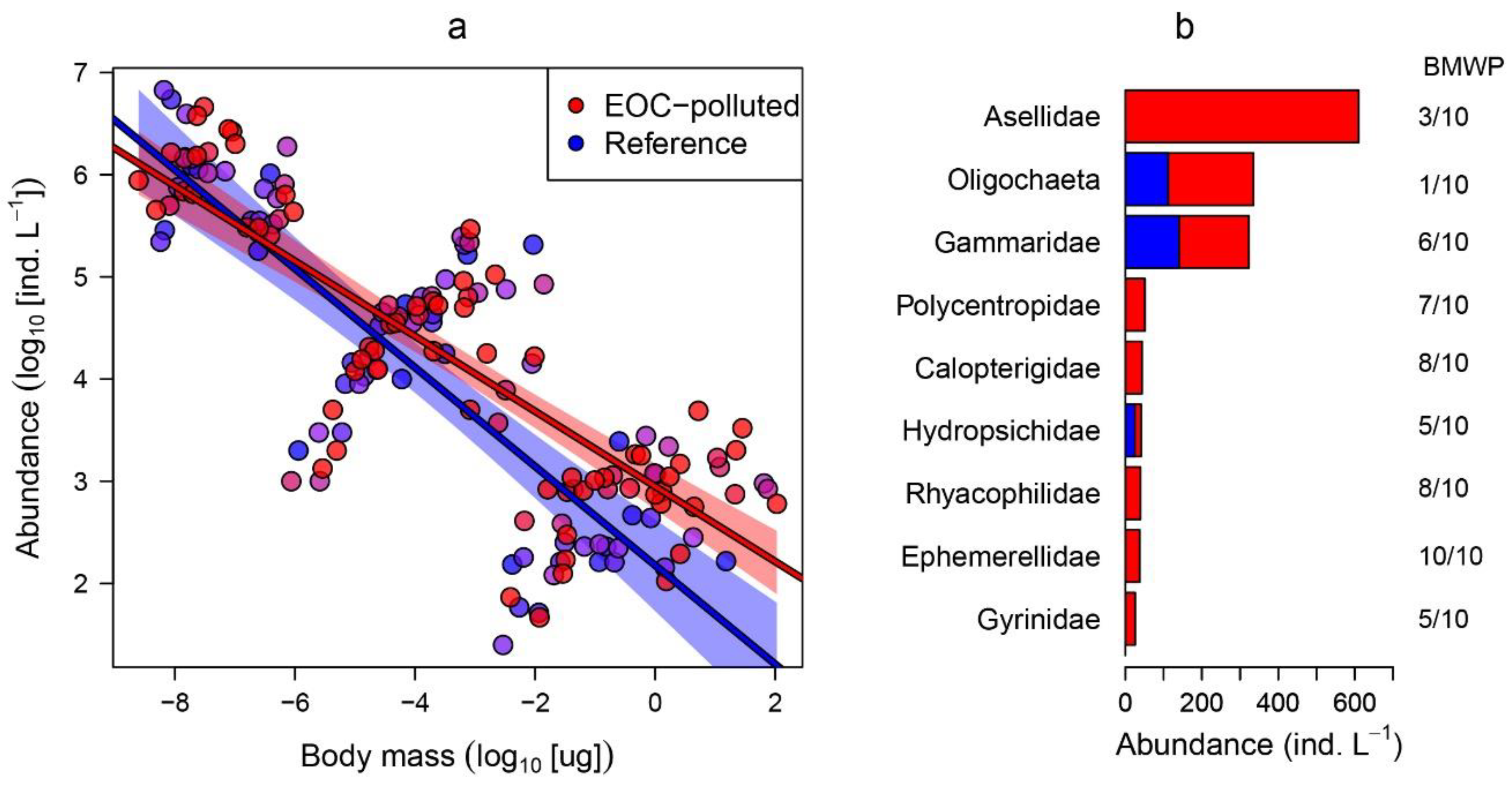
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Schoups, G.; Van De Giesen, N. Organic pollution of rivers: Combined threats of urbanization, livestock farming and global climate change. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaj, E.; Peter, C.; Grote, M.; Kühne, R.; Mondy, C.P.; Usseglio-Polatera, P. Organic chemicals jeopardize the health of freshwater ecosystems on the continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9549–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reemtsma, T.; Weiss, S.; Mueller, J.; Petrovic, M.; González, S.; Barcelo, D.; Ventura, F.; Knepper, T.P. Polar pollutants entry into the water cycle by municipal wastewater: A European perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5451–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.H.; Lin, A.Y.C.; Reinhard, M. Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: Review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, K.A.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Mills, K.H.; Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Flick, R.W. Collapse of a fish population after exposure to a synthetic estrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8897–8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, M.; Rangarajan, S.; Lai, A.; Shaya, L.; Balshine, S.; Wilson, J.Y. Effects of chronic, parental pharmaceutical exposure on zebrafish (Danio rerio) offspring. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 151, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, C.; Räsänen, K.; Burdon, F.J.; Altermatt, F.; Jokela, J.; Joss, A.; Ackermann, M.; Eggen, R.I. Unravelling the impacts of micropollutants in aquatic ecosystems: Interdisciplinary studies at the interface of large-scale ecology. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2016, 55, 183–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kubec, J.; Hossain, S.; Grabicová, K.; Randák, T.; Kouba, A.; Grabic, R.; Roje, S.; Buřič, M. Oxazepam alters the behavior of crayfish at diluted concentrations, venlafaxine does not. Water 2019, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.; Arnon, S.; Banks, E.; Batelaan, O.; Betterle, A.; Broecker, T.; Coll, C.; Drummond, J.D.; Garcia, J.G.; Galloway, J.; et al. Is the Hyporheic Zone Relevant beyond the Scientific Community? Water 2019, 11, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posselt, M.; Jaeger, A.; Schaper, J.L.; Radke, M.; Benskin, J.P. Determination of polar organic micropollutants in surface and pore water by high-resolution sampling-direct injection-ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, E.K.; Grace, M.R.; Kelly, J.J.; Reisinger, A.J.; Rosi, E.J.; Walters, D.M. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) are ecological disrupting compounds (EcoDC). Elem. Sci. Anth. 2017, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, S. Importance of surface-subsurface exchange in stream ecosystems: The hyporheic zone. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, E.T.; Young, K.I.; Widdowson, M.A. Mixing of surface and groundwater induced by riverbed dunes: Implications for hyporheic zone definitions and pollutant reactions. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5221–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirats, J.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Mandaric, L.; Acuña, V.; Balcázar, J.L.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C.M. Wastewater pollution differently affects the antibiotic resistance gene pool and biofilm bacterial communities across streambed compartments. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5567–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirats, J.; Timoner, X.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Balcázar, J.L.; Acuña, V.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C.M. Emerging contaminants and nutrients synergistically affect the spread of class 1 integron-integrase (intI1) and sul1 genes within stable streambed bacterial communities. Water Res. 2018, 138, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Láng, J.; Kőhidai, L. Effects of the aquatic contaminant human pharmaceuticals and their mixtures on the proliferation and migratory responses of the bioindicator freshwater ciliate Tetrahymena. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althakafy, J.T.; Kulsing, C.; Grace, M.R.; Marriott, P.J. Determination of selected emerging contaminants in freshwater invertebrates using a universal extraction technique and liquid chromatography accurate mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.H.; Ng, K.T.; Bury, S.T.; Bury, S.E.; Bury, N.R.; Barron, L.P. Biomonitoring of pesticides, pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in a freshwater invertebrate to estimate toxic or effect pressure. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Maraver, I.; Perkins, D.M.; Thompson, M.S.; Fussmann, K.; Reiss, J.; Robertson, A.L. Comparing biotic drivers of litter breakdown across stream compartments. J. An. Ecol. 2019, 88, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F.; Allen, A.P.; Savage, V.M.; West, G.B. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 2004, 85, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.P.; Ernest, S.M.; Kerkhoff, A.J.; Enquist, B.J. Relationships between body size and abundance in ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebilco, R.; Baum, J.K.; Salomon, A.K.; Dulvy, N.K. Ecosystem ecology: Size-based constraints on the pyramids of life. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, S.R.; Dickie, L.M. The Biomass Spectrum: A PredatorPrey Theory of Aquatic Production; Columbia University Press: Chichester, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, D.M.; Durance, I.; Edwards, F.K.; Grey, J.; Hildrew, A.G.; Jackson, M.; Jones, J.I.; Lauridsen, R.B.; Layer-Dobra, K.; Thompson, M.S.; et al. Bending the rules: Exploitation of allochthonous resources by a top-predator modifies size-abundance scaling in stream food webs. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Maraver, I.; Robertson, A.L.; Perkins, D.M. Depth and vertical hydrodynamics constrain the size structure of a lowland streambed community. Biol. Lett. 2019, 15, 20190317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchey, O.L.; Morin, P.J.; Hulot, F.D. Contributions of aquatic model systems to our understanding of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. In Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning—Synthesis and Perspectives; Loreau, M., Naeem, S., Inchausti, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Petchey, O.L.; Belgrano, A. Body-size distributions and size-spectra: Universal indicators of ecological status? Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sobek, A.; Radke, M. Fate of pharmaceuticals and their transformation products in four small European rivers receiving treated wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5614–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, J.L.; Posselt, M.; Bouchez, C.; Jaeger, A.; Nuetzmann, G.; Putschew, A.; Singer, G.; Lewandowski, J. Fate of Trace Organic Compounds in the Hyporheic Zone: Influence of Retardation, the Benthic Biolayer, and Organic Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4224–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechelke, J.; Vermeirssen, E.L.; Hollender, J. Passive sampling of organic contaminants across the water-sediment interface of an urban stream. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Communities in R: Vegan Tutorial. 2015. Available online: http://cc.oulu.fi/~jarioksa/opetus/metodi/veg-antutor.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Peralta-Maraver, I.; Robertson, A.L.; Rezende, E.L.; Lemes da Silva, A.L.; Tonetta, D.; Lopes, M.; Schmitt, R.; Leite, N.K.; Nuñer, A.; Petrucio, M.M. Winter is coming: Food web structure and seasonality in a subtropical freshwater coastal lake. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4534–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.M.; Robinson, J.P.; Plank, M.J.; Baum, J.K.; Blanchard, J.L. Testing and recommending methods for fitting size spectra to data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, C.; Elser, J.J. Soil acidity, ecological stoichiometry and allometric scaling in grassland food webs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layer, K.; Riede, J.O.; Hildrew, A.G.; Woodward, G. Food web structure and stability in 20 streams across a wide ph gradient. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2010, 42, 265–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.J.; Savaliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.0–10. 2013. Available online: http://CRAN.R–project.org/ package=vegan (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Dossena, M.; Yvon-Durocher, G.; Grey, J.; Montoya, J.M.; Perkins, D.M.; Trimmer, M.; Woodward, G. Warming alters community size structure and ecosystem functioning. Proc. Biol. Sci. Replaces Proc. R. Soc. 2012, 279, 3011–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, E.J.; Pichler, D.E.; Adams, G.; Benstead, J.P.; Cohen, H.; Craig, N.; Cross, W.F.; Demars, B.O.; Friberg, N.; Gislason, G.M.; et al. Impacts of warming on the structure and functioning of aquatic communities: Individual-to ecosystem-level responses. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2012, 47, 81–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, H.A. Origin and development of the biological monitoring working party score system. Water Res. 1998, 32, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Prestinaci, F.; Bottoni, P.; Carere, M. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of pharmaceuticals with a focus to the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhí, A.; Acuña, V.; Barceló, D.; Huerta, B.; Mor, J.R.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Sabater, S. Bioaccumulation and trophic magnification of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in a Mediterranean river food web. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, E.K.; Rosi, E.J.; Walters, D.M.; Fick, J.; Hamilton, S.K.; Brodin, T.; Sundelin, A.; Grace, M.R. A diverse suite of pharmaceuticals contaminates stream and riparian food webs. Nat. Commun. 2019, 9, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.N.; Paxéus, N.; Förlin, L.; Larsson, D.J. Variations in bioconcentration of human pharmaceuticals from sewage effluents into fish blood plasma. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 24, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fick, J.; Lindberg, R.H.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.J. Predicted critical environmental concentrations for 500 pharmaceuticals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 58, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerge, I.J.; Buser, H.-R.; Kahle, M.; Müller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Ubiquitous occurrence of the artificial sweetener acesulfame in the aquatic environment: An ideal chemical marker of domestic wastewater in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4381–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, A.; Posselt, M.; Betterle, A.; Schaper, J.; Mechelke, J.; Coll, C.; Lewandowski, J. Spatial and Temporal Variability in Attenuation of Polar Organic Micropollutants in an Urban Lowland Stream. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.; Coll, C.; Posselt, M.; Mechelke, J.; Rutere, C.; Betterle, A.; Raza, M.; Mehrtens, A.; Meinikmann, K.; Portmann, A.; et al. Using recirculating flumes and a response surface model to investigate the role of hyporheic exchange and bacterial diversity on micropollutant. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| River | Lat | Lon | Acesu | Aceta | Sita | O.Des | 11.D.C. | Napro | Guan | Metf | Venl | M.Acid | Carba | Oxa | Prop | Sota | 4.H.D. | Trama | Diclo | 1.H.B. | Ibu | 11.D.C. | C.Acid2 | Furo | Meto | Gem | Tot EOCs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beverly Brooks | 51.44 | 0.25 | 13.8 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 44.8 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 14 | ||||||||||
| Loddon | 51.42 | 1.72 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 9.7 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 13 | |||||||||||
| Wey | 51.19 | 0.68 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 5.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 12 | ||||||||||||
| Waveney | 52.42 | 1.36 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 9 | |||||||||||||||
| Wensum | 52.42 | 1.36 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Deadwater | 51.17 | 0.85 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stiffkey | 52.92 | 0.89 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tat | 52.82 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| River Leith | 54.61 | −2.62 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Nadder | 51.12 | 0.90 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Test | 51.14 | 1.47 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Glaven | 52.93 | 1.63 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Lamports | 51.15 | 1.72 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Lyde | 51.29 | 1.72 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| GI1 | 52.14 | −3.84 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Howe Beck | 54.68 | −2.59 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bure | 52.82 | 1.21 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| River Crowdundle | 51.15 | 1.72 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kennet | 51.42 | 1.72 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| River Lyvennet | 54.68 | −2.61 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| LI7 | 52.13 | −3.75 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LI8 | 52.16 | −3.75 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LI3 | 52.14 | −3.73 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Old Lodge | 54.65 | −2.64 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lone Oak | 51.77 | 0.13 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LI6 | 51.44 | 0.25 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Broadstone Stream | 51.89 | 0.57 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oakhanger | 51.45 | 0.79 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anton | 51.15 | 1.46 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morland Beck | 51.23 | 1.72 | 0 |
| Response | Predictors | N | AIC | ΔAIC | LogLik | wi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log 10 (N) | log10(M) × EOCs + pH + Temp + Lon + Lat + Alt + Nit + Phos | 12 | 403.82 | 9.23 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| log10(M) × EOCs + pH + Temp + Lon + Lat + Alt + Nit | 11 | 402.30 | 7.70 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| log10(M) × EOCs + pH + Temp + Lon + Lat + Alt | 10 | 402.35 | 7.75 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| log10(M) × EOCs + pH + Temp + Lon + Lat | 9 | 401.17 | 6.57 | 0.04 | 0.02 | |
| log10(M) × EOCs + pH + Temp + Lon | 8 | 399.18 | 4.59 | 0.10 | 0.05 | |
| log10(M) × EOCs + pH + Temp | 7 | 397.32 | 2.72 | 0.26 | 0.12 | |
| log10(M) × EOCs + pH | 6 | 396.15 | 1.55 | 0.46 | 0.22 | |
| log10(M) × EOCs | 5 | 394.60 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.47 | |
| log10(M) + EOCs | 4 | 397.88 | 3.28 | 0.19 | 0.09 | |
| log10(M) | 3 | 401.22 | 6.62 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Fixed Equation Terms | Coef | SE | t Value | p Value | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 2.95 | 0.12 | 25.20 | > 0.001 | *** |
| Log10 body mass | −0.37 | 0.03 | −13.87 | > 0.001 | *** |
| Presence/absence of EOCs | −0.77 | 0.24 | −3.22 | 0.001 | *** |
| Log10 body mass * EOC pollution | −0.12 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.02 | * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peralta-Maraver, I.; Posselt, M.; Perkins, D.M.; Robertson, A.L. Mapping Micro-Pollutants and Their Impacts on the Size Structure of Streambed Communities. Water 2019, 11, 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122610
Peralta-Maraver I, Posselt M, Perkins DM, Robertson AL. Mapping Micro-Pollutants and Their Impacts on the Size Structure of Streambed Communities. Water. 2019; 11(12):2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122610
Chicago/Turabian StylePeralta-Maraver, Ignacio, Malte Posselt, Daniel M. Perkins, and Anne L. Robertson. 2019. "Mapping Micro-Pollutants and Their Impacts on the Size Structure of Streambed Communities" Water 11, no. 12: 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122610
APA StylePeralta-Maraver, I., Posselt, M., Perkins, D. M., & Robertson, A. L. (2019). Mapping Micro-Pollutants and Their Impacts on the Size Structure of Streambed Communities. Water, 11(12), 2610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122610