Spatiotemporal Evolution of Droughts and Their Teleconnections with Large-Scale Climate Indices over Guizhou Province in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
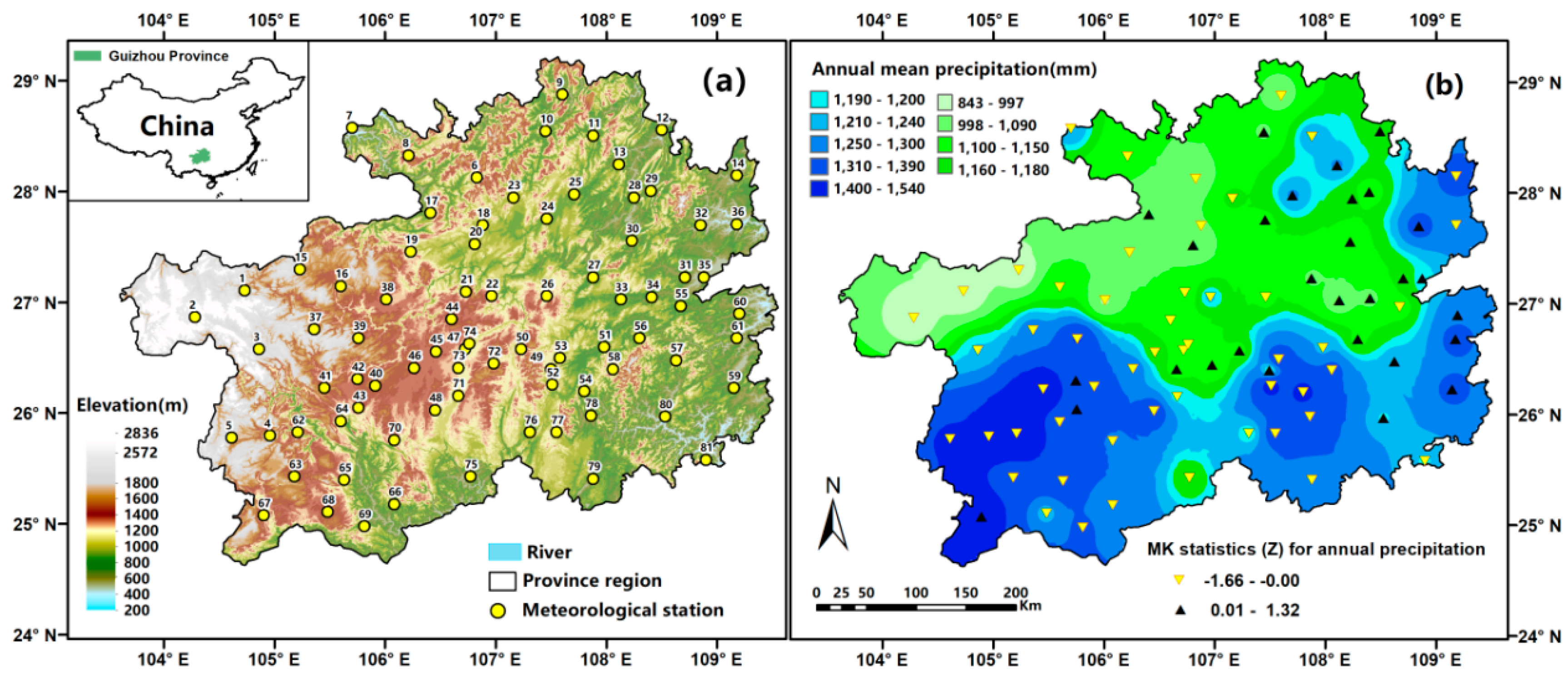
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methods
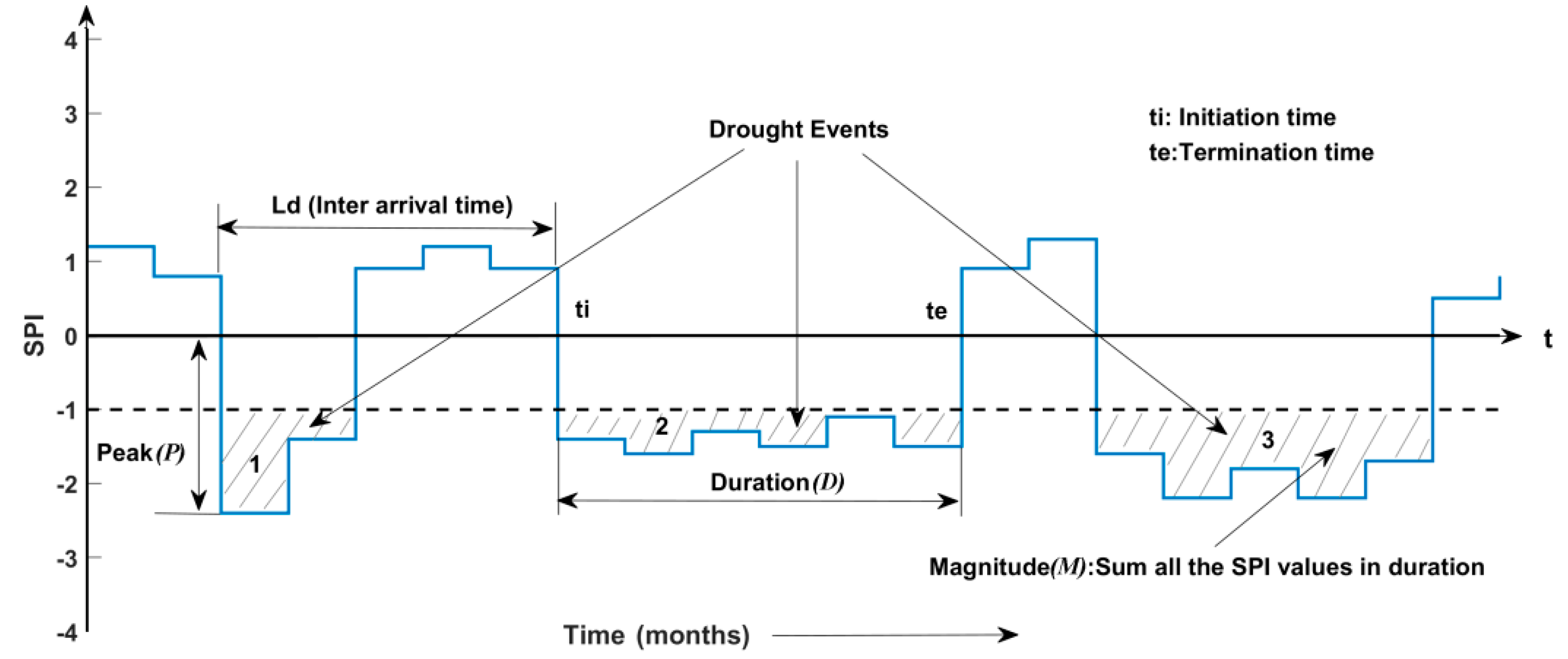
3.1. SPI and Drought Characteristics
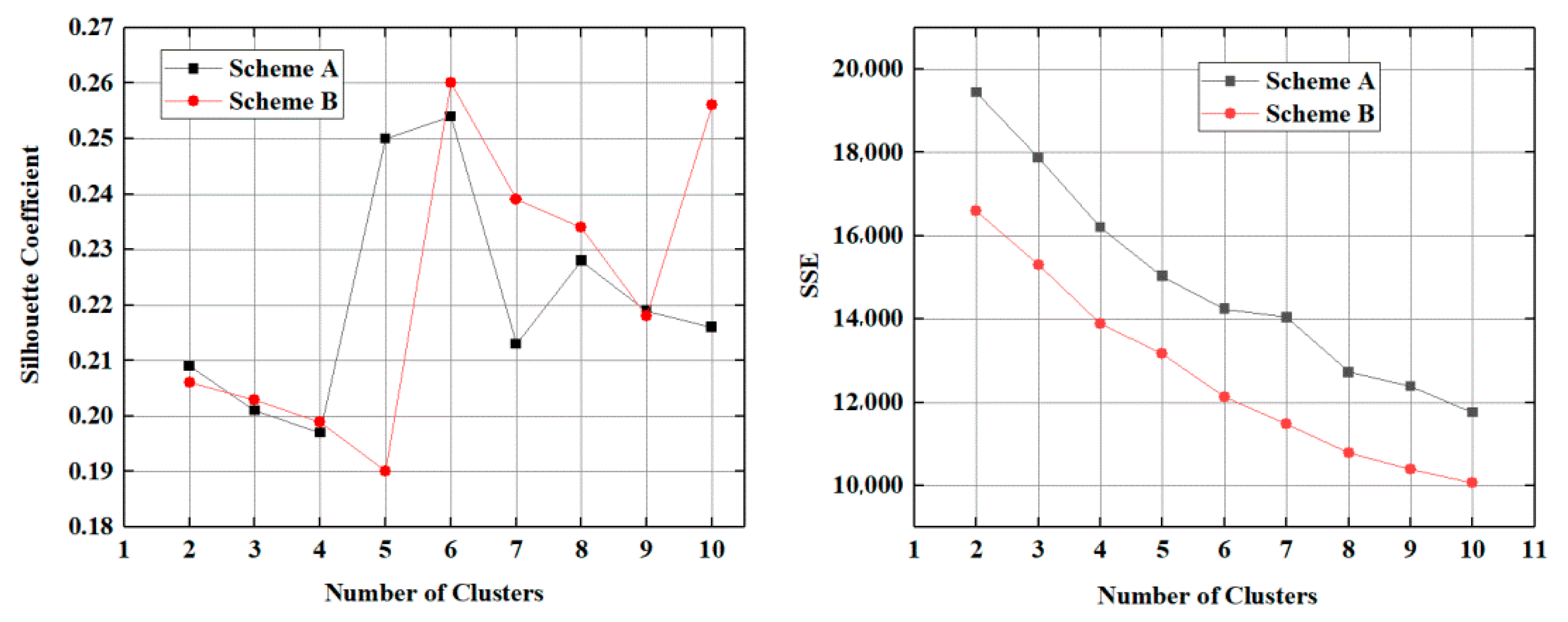
3.2. Cluster Analysis for Identifying Similarity of SPI Series Between Sites
3.3. Detection of Spatial and Temporal Evolutions of the Sub-Regional Droughts
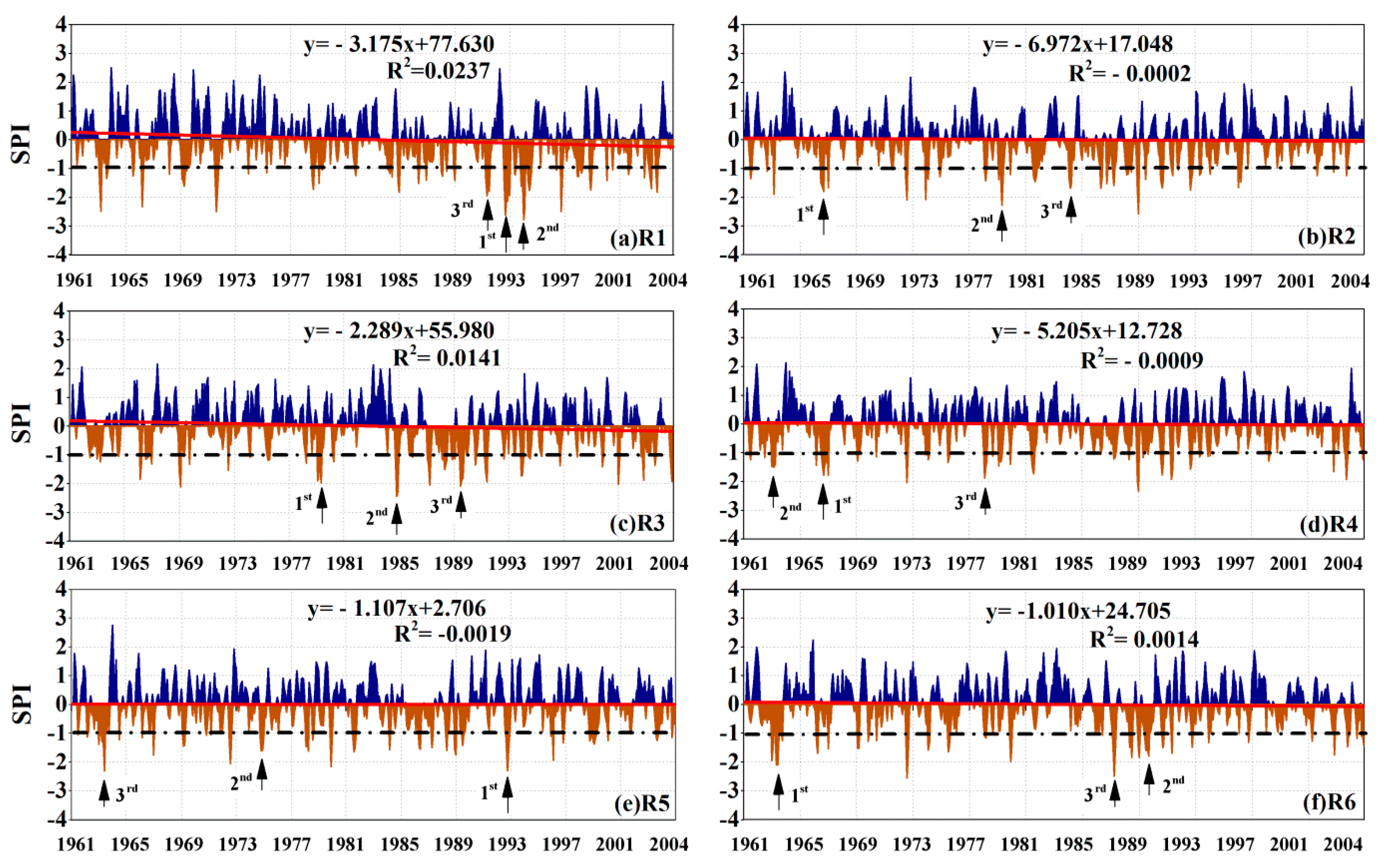
3.3.1. Trend Test for the Sub-Regional SPI Series
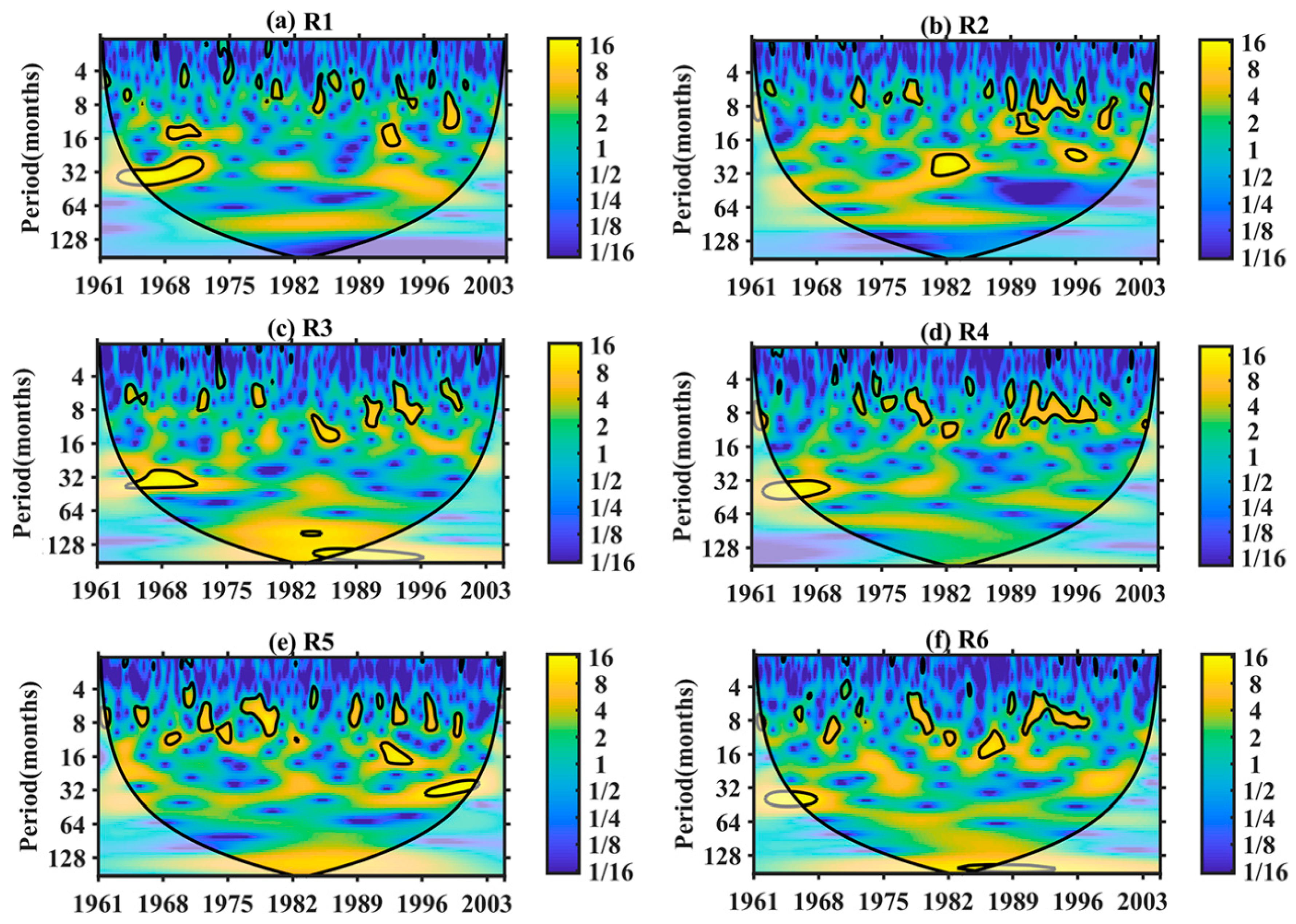
3.3.2. Periodicity Detection for the Sub-Regional SPI Series
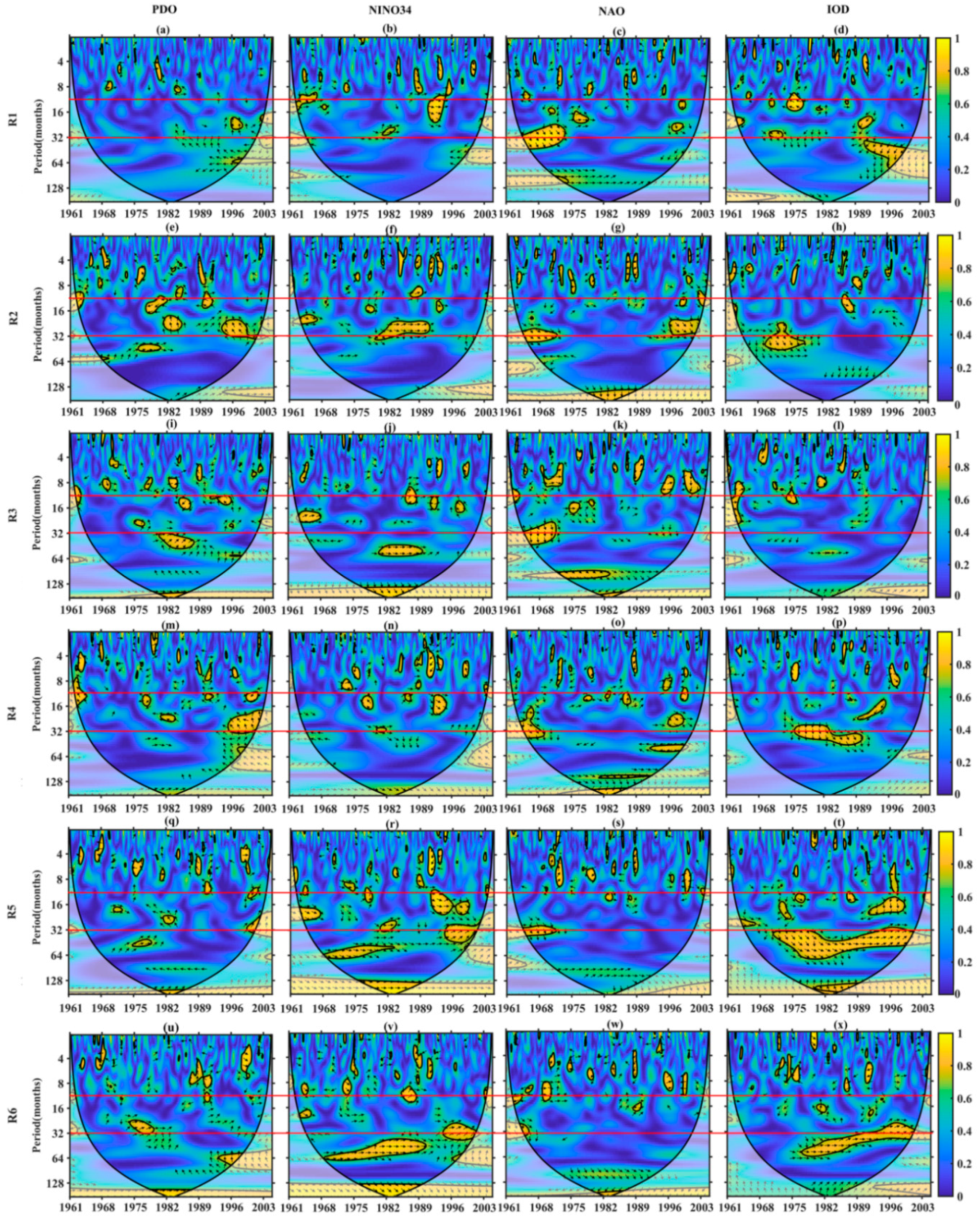
3.4. Teleconnection of Drought Evolutions with Large-Scale Climate Anomalies
4. Results
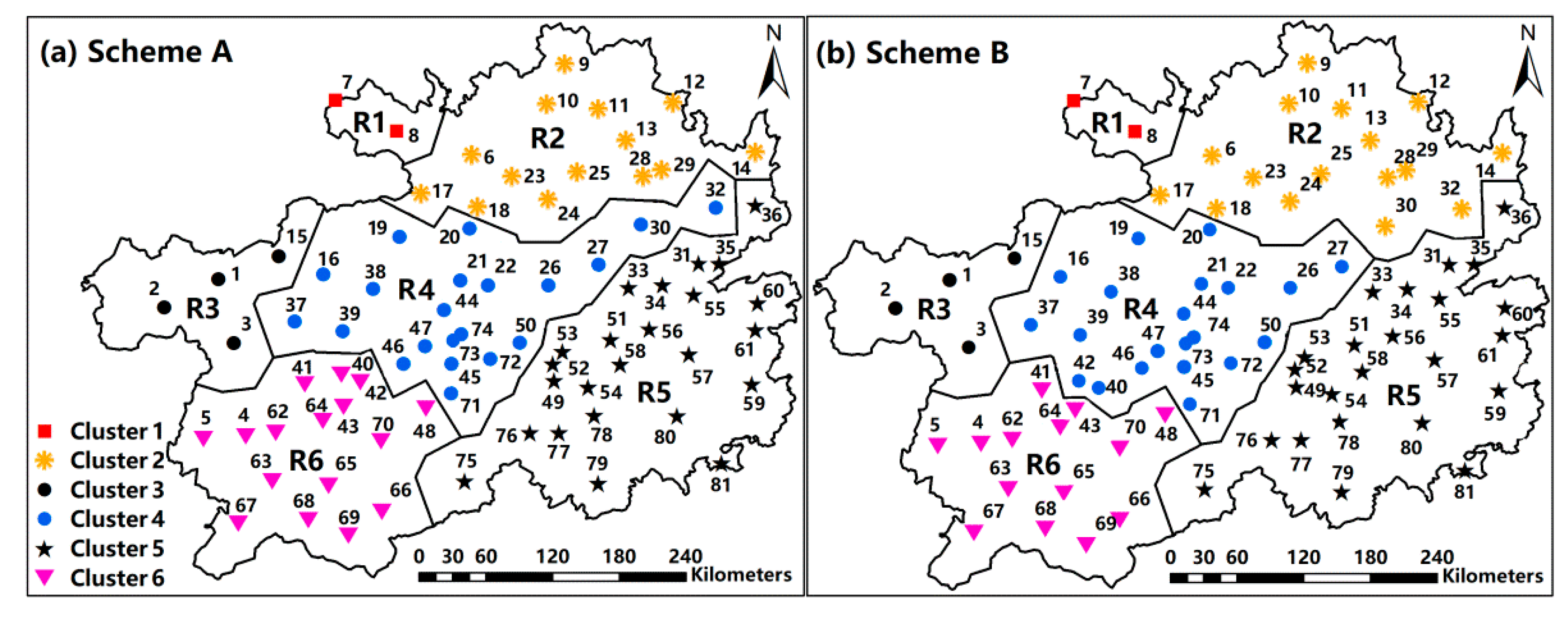
4.1. Identified Homogeneous Sub-Regions of Drought
4.2. Spatial Characteristics of Sub-Regional Droughts
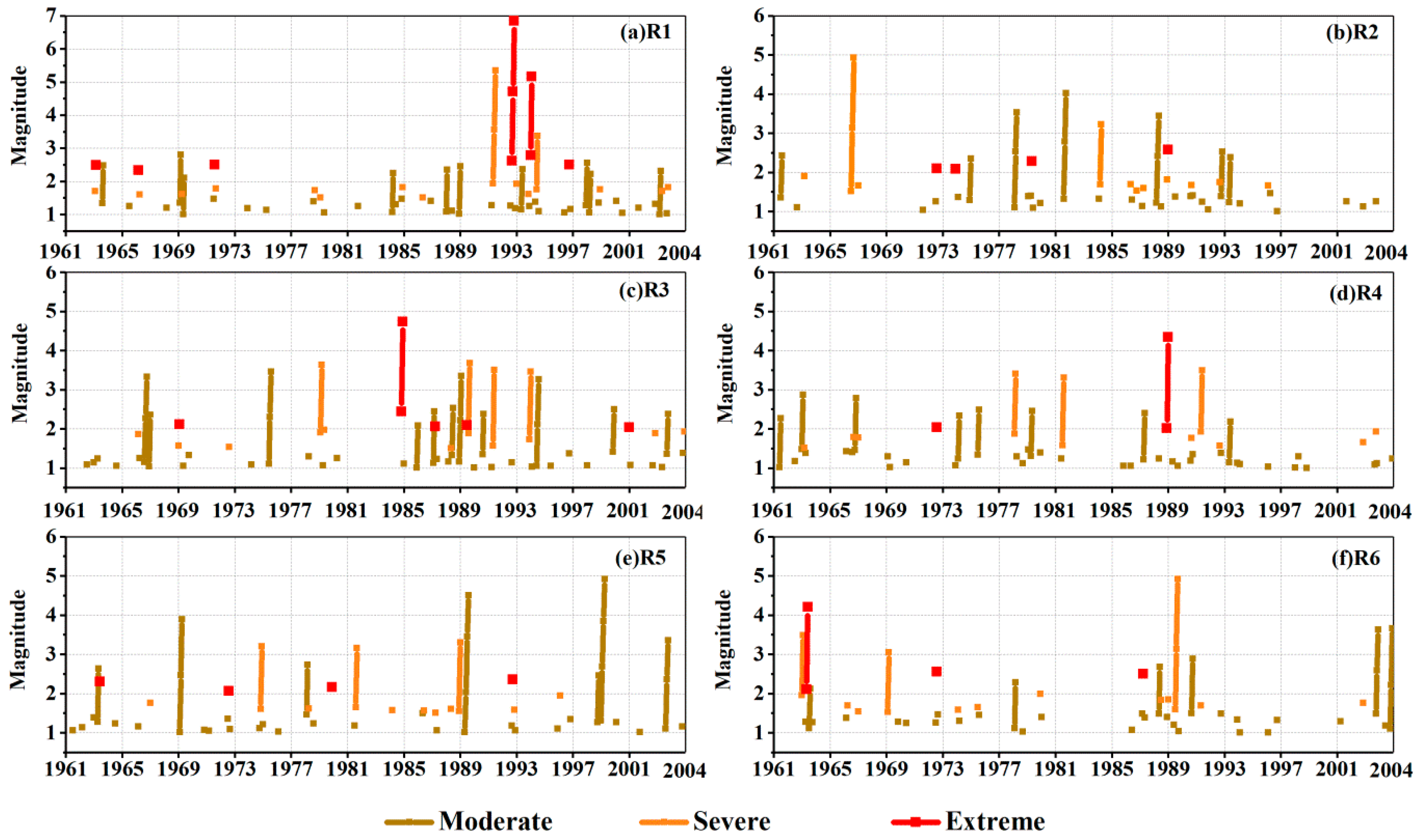
4.3. Temporal Evolution of the Sub-Regional Drought Characteristics
4.4. Coherence between Sub-Regional Droughts and Large-Scale Anomaly Climate Indices
5. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPI | Standardized precipitation index |
| SPEI | Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index |
| PDSI | Palmer drought severity index |
| SWSI | Surface water supply index |
| RDI | Reconnaissance drought index |
| CI | Comprehensive meteorological drought index |
| SAD | Severity–area–duration |
| EOF | Empirical orthogonal function |
| REOF | rotated empirical orthogonal function |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| CA | Cluster Analysis |
| SST | Sea surface temperature |
| PDO | Pacific Decadal Oscillation |
| ENSO | El Niño Southern Oscillation |
| NAO | North Atlantic Oscillation |
| IOD | Indian Ocean Dipole |
| NINO34 | Niño 3.4 (5° N–5° S, 120°–170° W) sea surface temperature index |
| D | Drought duration |
| M | Drought magnitude |
| P | Drought peak |
| F | Drought frequency |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| SSE | Sum of Squared Error |
| S | Silhouette index |
| MK | Mann–Kendall trend test |
| TFPW | Trend-free pre-whitening |
| CWT | Continuous wavelet transform |
| WCO | wavelet coherence |
| COI | Cone of influence |
| AR1 | first order autoregressive |
References
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multi-scalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The Standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index-SPEI. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; Volume 30.
- Shafer, B.A.; Dezman, L.E. Development of a Surface Water Supply Index (SWSI) to Assess the Severity of Drought Conditions in Snowpack Runoff Areas. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Western Snow Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 19–23 April 1982; pp. 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F. Characteristics of global and regional drought, 1950–2000: Analysis of soil moisture data from off-line simulation of the terrestrial hydrologic cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F. Global Trends and Variability in Soil Moisture and Drought Characteristics, 1950–2000, from Observation-Driven Simulations of the Terrestrial Hydrologic Cycle. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 432–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Chopa, P.; Dadhwal, V.K. Analyzing spatial patterns of meteorological drought using Standardized Precipitation Index. Meteorol. Appl. 2007, 14, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M. Differences in spatial patterns of drought on different time scales: An analysis of the Iberian Peninsula. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B. A spatio-temporal structure-based approach to drought characterization. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Yang, D.W.; Yang, H.B.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in China during 1961–2012: A climatic perspective. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, K.; Bloschl, G. Space-time patterns of meteorological drought events in the European Greater Alpine Region over the past 210 years. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 9807–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.M.; Ndayisaba, F.; Liu, T.; Jiapaer, G.; El-Tantawi, A.; Maeyer, P.D. Space-time characterization of drought events and their impacts on vegetation in Central Asia. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadis, K.M.; Clark, E.A.; Wood, A.W.; Hamlet, A.F.; Lettermaier, D.P. Twentieth-century drought in the conterminous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroulis, A.G.; Vrohidou, A.E.K.; Tsanis, I.K. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Meteorological Drought for the Island of Crete. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 206–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.B. SPI based meteorological drought assessment over a humid basin: Effects of processing schemes. Water 2016, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, A.M.; Liu, T.; Jiapaer, G.; Ndayisaba, F.; Jiang, L.L.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Spatial and temporal characteristics of droughts in Central Asia during 1966–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M. Spatial and temporal analysis of droughts in the Iberian Peninsula (1910–2000). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabozorgi, S.; Shirkhorshidi, A.S.; Wah, T.Y. Time-series clustering—A decade review. Inf. Syst. 2015, 53, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.F.; Pulido-Calvo, I.; Portela, M.M. Spatial and temporal variability of droughts in Portugal. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhong, S.B.; Yao, G.N.; Huang, Q.Y. BME spatiotemporal estimation of annual precipitation and detection of drought hazard clusters using space-time scan statistics in Yun-Gui-Guang region, mainland china. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2017, 56, 2301–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, T.; Yu, W. Cause of severe droughts in Southwest China during 1951–2010. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhou, W.; Huang, G. Teleconnected influence of tropical northwest Pacific sea surface temperature on interannual variability of autumn precipitation in southwest China. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2527–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhou, W.; Huang, G. Drought in Southwest China: A review. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett. 2015, 8, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, F.F.; Zhao, J.X.; Qi, L.; Ren, H.L. The possible influence of a nonconventional El Niño on the severe autumn drought of 2009 in southwest China. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8392–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Analyses of the causes of severe drought occurring in southwest China from the fall of 2009 to the spring of 2010. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 443–457. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.P.; Gao, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.B.; Deng, H.J.; Chen, X.W. Temporal-Spatial Characteristics of Drought in Guizhou Province, China, Based on Multiple Drought Indices and Historical Disaster Records. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 4721269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Xiao, Z.N.; Yang, J.; Liu, H. Characteristics of clustering extreme drought events in China during 1961–2010. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2013, 27, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, B.B.; Quan, X.W.; Liao, Z.M.; Bai, X.J. Use of the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) to characterize the drying trend in southwest China from 1982–2012. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10917–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, N.B.; Xu, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wang, J.Q. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of meteorological drought in Guizhou Province. J. Arid. Land. Resour. Environ. 2015, 29, 82–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.K.; Xu, J.X.; Lei, H.J.; Hu, J.P. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of drought and its regional response to climate change in Guizhou province. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 72–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Q.B.; Peng, T.; Zhang, Y.F.; J, Z.H. Hydrogeology of Epikarst in Karst Mountains—A case study of the Chenqi Catchment. Earth Environ. 2011, 39, 19–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Cai, Y.L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, X.L. An analysis of the spatial pattern of summer persistent moderate-to-heavy rainfall regime in Guizhou Province of Southwest China and the control factors. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 97, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.L.; Chen, T.; Yang, N.; Qu, L.; Li, M.C.; Chen, D. Spatial and temporal distribution of rainfall and drought characteristics across the pearl river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Standardized Precipitation Index User Guide; WMO-No. 1090; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, N.B. Comparing the Palmer drought index and the standardized precipitation index. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevjevich, V. An Objective Approach to Definitions and Investigations of Continental Hydrologic Droughts; Hydrologic Paper No. 23; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Phinney, B.; Cavadias, G. The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1807–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Proc. Geoph. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timo, Z.E.; Wheater, H.S.; Bonsal, B.; Razavi, S.; Kurkute, S. Historical drought patterns over Canada and their teleconnections with large-scale climate signals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3105–3124. [Google Scholar]
- Räsänen, T.A.; Lindgren, V.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Buckley, B.M.; Kummu, M. On the spatial and temporal variability of ENSO precipitation and drought teleconnection in mainland Southeast Asia. Clim. Past 2016, 12, 1889–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Wang, N.N.; Ni, Z.Y. Influence of the Tibetan Plateau uplift on climate evolution in southwestern China: From the monsoon perspective. J. Earth Environ. 2018, 9, 444–454. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.G.; Fu, X.H. Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, J.; Wu, R.G. Roles of ENSO and PDO in the link of the East Asian Winter Monsoon to the following Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Tam, C.Y.; Zhou, W. Different impacts of El Niño and El Niño Modoki on China rainfall in the decaying phases. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Fong, S.K.; Leong, K.C. Different impacts of two types of pacific ocean warming on southeast Asian rainfall during boreal winter. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D24122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H. Relations of water vapor transport from Indian monsoon with that over East Asia and the summer rainfall in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.F.; Chen, X.H. Long-term change in precipitation structure over the karst area of Southwest China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Categories | SPI | Cumulative Probability |
|---|---|---|
| Wet | 1.0 | (0.841,1.0) |
| Near normal | (−1.0,1.0) | (0.159,0.841) |
| Moderate drought | (−1.5,−1.0) | (0.067,0.159) |
| Severe drought | (−2.0,−1.5) | (0.023,0.067) |
| Extreme drought | −2.0 | (0,0.023) |
| Sub-Region | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drought frequency () | 37 | 35 | 39 | 39 | 33 | 31 | |
| Drought duration () (months) | Mean | 1.97 | 1.66 | 1.85 | 1.59 | 1.85 | 1.87 |
| Max | 6.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 5.00 | |
| Drought magnitude (M) | Mean | 2.94 | 2.33 | 2.52 | 2.16 | 2.52 | 2.71 |
| Max | 11.22 | 4.93 | 6.67 | 5.98 | 6.19 | 7.60 | |
| Drought peak | Mean | 1.57 | 1.49 | 1.43 | 1.38 | 1.47 | 1.55 |
| Max | 2.79 | 2.57 | 2.44 | 2.33 | 2.35 | 2.55 | |
| Sub-Region | Rank | Persistent Period (yyyy.mm) | Duration (Months) | Magnitude | Peak Intensity | Peak Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1 | August 1992–January 1993 | 6 | 11.22 | 2.62 | September 1992 |
| 2 | November 1993–February 1994 | 4 | 8.03 | 2.79 | January 1994 | |
| 3 | April 1991–July 1991 | 4 | 6.62 | 1.94 | May 1991 | |
| R2 | 1 | July 1966–September 1966 | 3 | 4.93 | 1.80 | September 1966 |
| 2 | April 1979–June 1979 | 3 | 4.78 | 2.28 | May 1979 | |
| 3 | February 1984–April 1984 | 3 | 4.54 | 1.70 | March 1984 | |
| R3 | 1 | February 1979–May 1979 | 4 | 6.67 | 1.97 | May 1979 |
| 2 | November 1984–January 1985 | 3 | 5.85 | 2.44 | November 1984 | |
| 3 | July 1989–September 1989 | 3 | 5.77 | 2.08 | July 1989 | |
| R4 | 1 | August 1966–November 1966 | 4 | 5.98 | 1.79 | September 1966 |
| 2 | January 1963–April 1963 | 4 | 5.76 | 1.52 | March 1963 | |
| 3 | February 1978–April 1978 | 3 | 4.70 | 1.88 | February 1978 | |
| R5 | 1 | September 1992–December 1992 | 4 | 6.19 | 2.35 | October 1992 |
| 2 | October 1974–January 1975 | 4 | 5.53 | 1.61 | November 1974 | |
| 3 | April 1963–June 1963 | 3 | 4.94 | 2.31 | June 1963 | |
| R6 | 1 | April 1963–August 1963 | 5 | 7.60 | 2.10 | May 1963 |
| 2 | June 1989–October 1989 | 5 | 7.16 | 1.79 | September 1989 | |
| 3 | March 1987–May 1987 | 3 | 5.37 | 2.50 | April 1987 |
| SPI and Drought Characteristics | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-regional SPI | −4.23 * | −1.27 | −3.53 * | −0.90 | −0.41 | −2.13 * |
| Drought duration () | 0.32 | −0.86 | 0.29 | −0.53 | 0.69 | −0.82 |
| Drought magnitude | 0.04 | −1.48 | 0.19 | −1.33 | 0.67 | −1.19 |
| Drought peak | −0.11 | −1.62 | 0.48 | −1.04 | −0.33 | −1.87 |
| Sub-Region | Significant Periods (Month) | Dominant Periods (Month) | Intervals of Variance | Significant Link with Climate Indices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 4–48 | 24–48 | 1964–1972 | NAO |
| R2 | 4–36 | 16–32; 4–12 | 1979–1984; 1991–1997 | NINO34; IOD |
| R3 | 4–36 | 24–36 | 1965–1971 | NAO |
| R4 | 4–48 | 4–12; 32–48 | 1990–1997; 1964–1969 | PDO, NAO, and IOD; NAO |
| R5 | 4–36 | 12–20; 24–36 | 1991–1994; 1996–2002 | NINO34 and IOD; NINO34 and IOD |
| R6 | 4–48 | 32–48; 4–12 | 1964–1968; 1989–1996 | NAO; PDO, NINO34, IOD, and NAO |
| Sub-Region | Rank | Persistent Time (yyyy.mm) | PDO Period (Month) | NINO34 Period (Month) | NAO Period (Month) | IOD Period (Month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1 | August 1992–January 1993 | / | 4–10 (←) | / | 24–48 |
| 2 | November 1993–February 1994 | / | 8–24 (→) | / | / | |
| 3 | April 1991–July 1991 | / | 12–30 (→) | / | 4–8, 16–64 | |
| R2 | 1 | July 1966–September 1966 | / | 16–24 (→) | 24–40 | 4–8 |
| 2 | April 1979–June 1979 | 8–16, 32–64 | 12–16 | 6–8 | / | |
| 3 | February 1984–April 1984 | / | 16–32 (→) | / | / | |
| R3 | 1 | February 1979–May 1979 | / | / | 10–16 | / |
| 2 | November 1984–January 1985 | 32–64 | 48–64 (→) | / | / | |
| 3 | July 1989–September 1989 | 4–8 | 48–64 (→) | 4–8 | 6–8 | |
| R4 | 1 | 1966.08–November 1966 | / | / | 16–48 | / |
| 2 | January 1963–April 1963 | 6–16 | / | 6–8, 30–60 | 2–4 | |
| 3 | February 1978–April 1978 | 12–16 | 12–20 (←) | 12–16 | 24–48 | |
| R5 | 1 | September 1992–December 1992 | / | 8–24 (→) | / | 32–64 (→) |
| 2 | October 1974–January 1975 | / | 48–64 (→) | / | 32–64 (→) | |
| 3 | April 1963–June 1963 | / | 16–32 (→) | 32–60 | 20–32 | |
| R6 | 1 | April 1963–August 1963 | 4–6 | 16–24 (→) | 12–16 | / |
| 2 | June 1989–October 1989 | 4–8 | 32–64 (→) | 12–20 | 32–64 (→) | |
| 3 | March 1987–May 1987 | 6–8 | 32–64 (→) | / | 32–64 (→) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Droughts and Their Teleconnections with Large-Scale Climate Indices over Guizhou Province in Southwest China. Water 2019, 11, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102104
Xiao L, Chen X, Zhang R, Zhang Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Droughts and Their Teleconnections with Large-Scale Climate Indices over Guizhou Province in Southwest China. Water. 2019; 11(10):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102104
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Liying, Xi Chen, Runrun Zhang, and Zhicai Zhang. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Evolution of Droughts and Their Teleconnections with Large-Scale Climate Indices over Guizhou Province in Southwest China" Water 11, no. 10: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102104
APA StyleXiao, L., Chen, X., Zhang, R., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Spatiotemporal Evolution of Droughts and Their Teleconnections with Large-Scale Climate Indices over Guizhou Province in Southwest China. Water, 11(10), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102104





