A Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
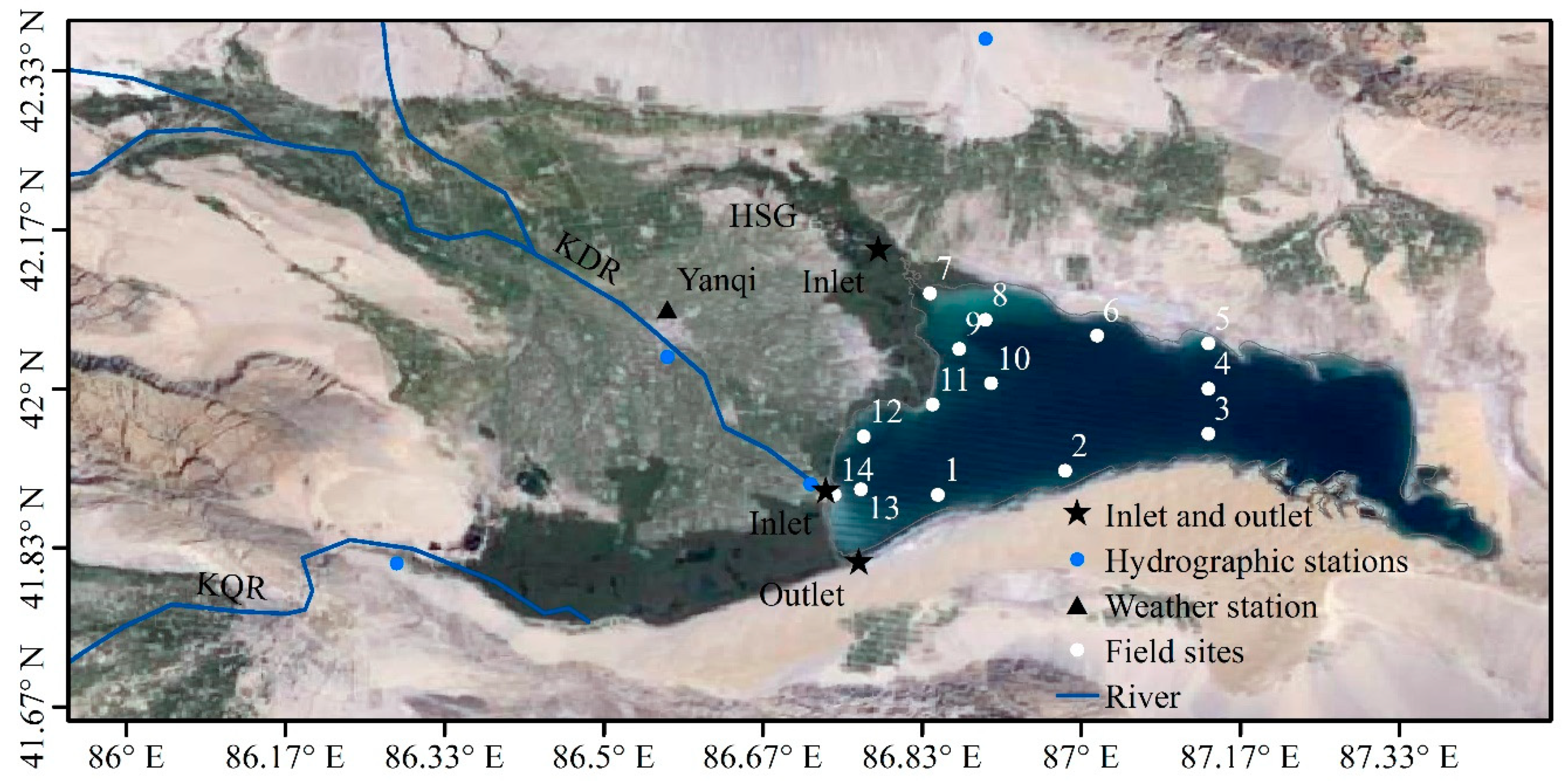
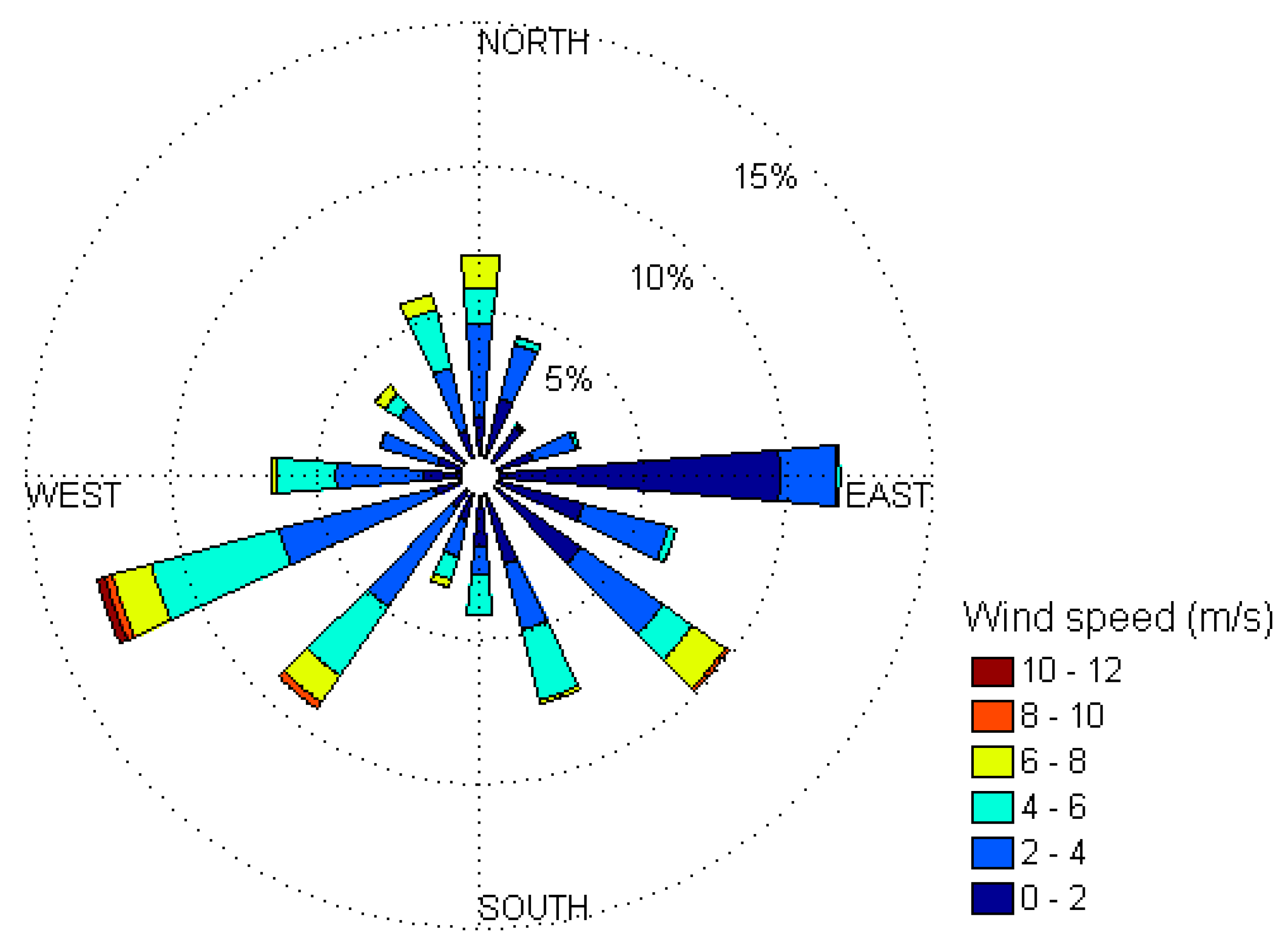
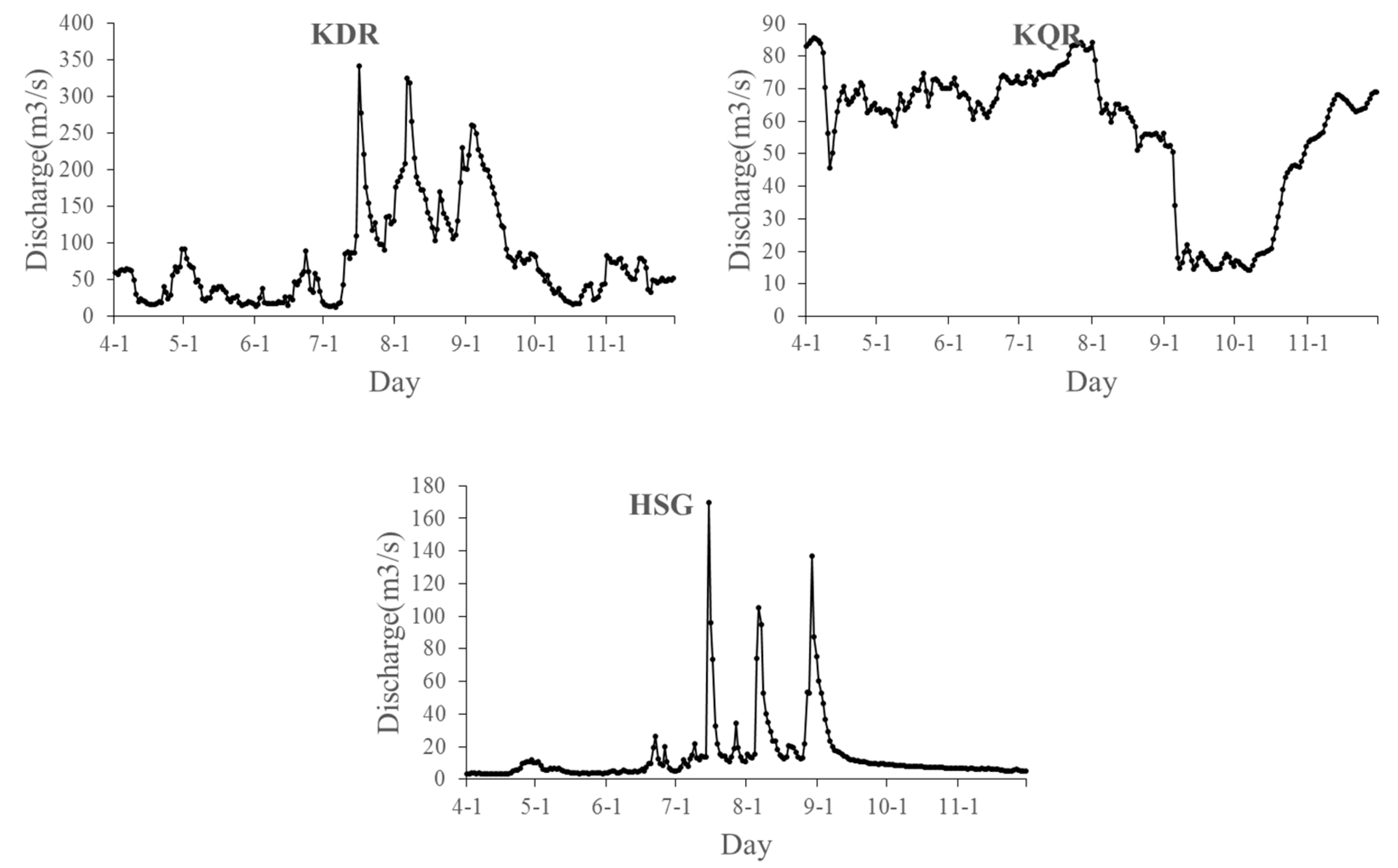
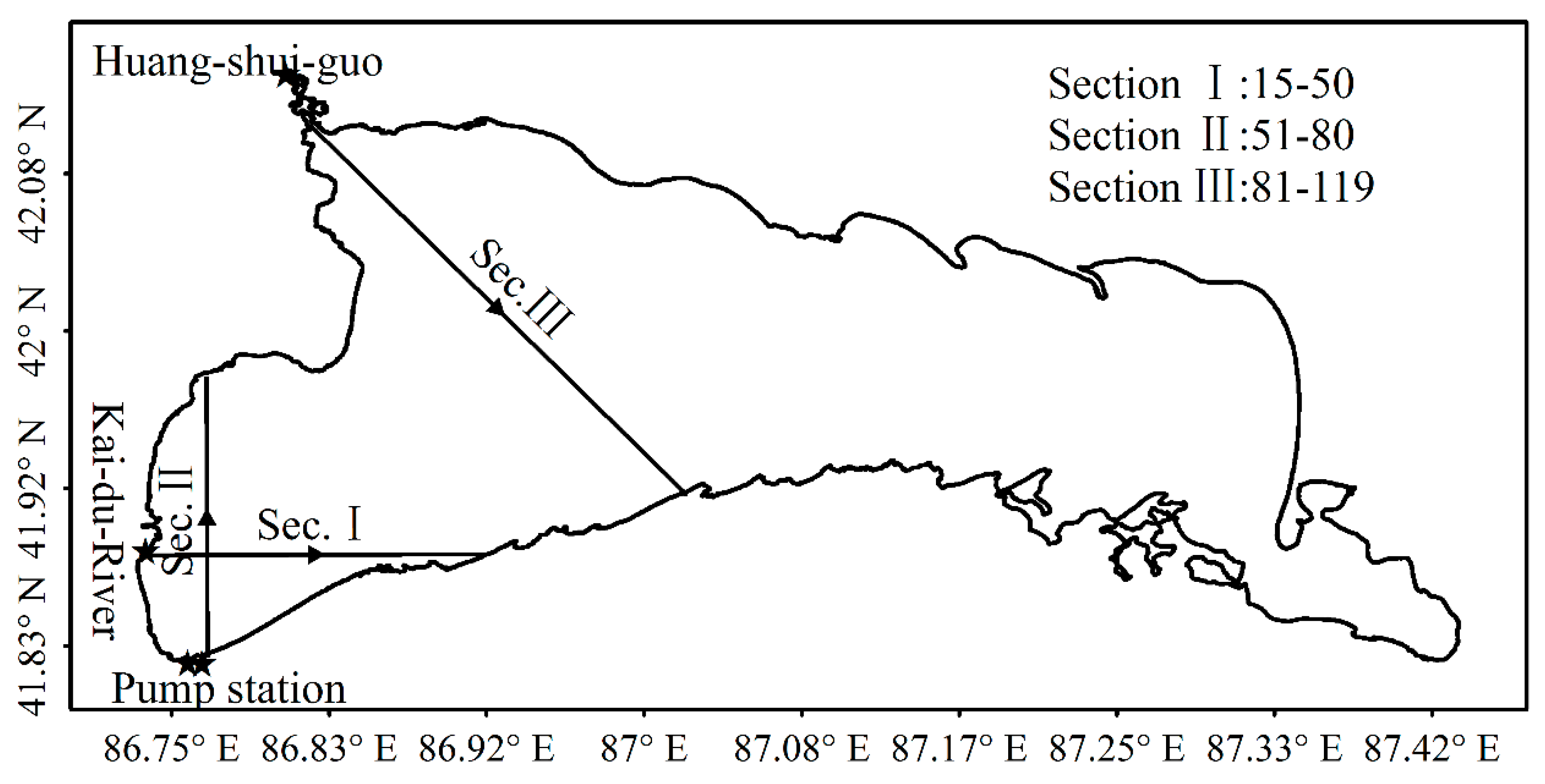
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Model Description
3. Results and Discussion
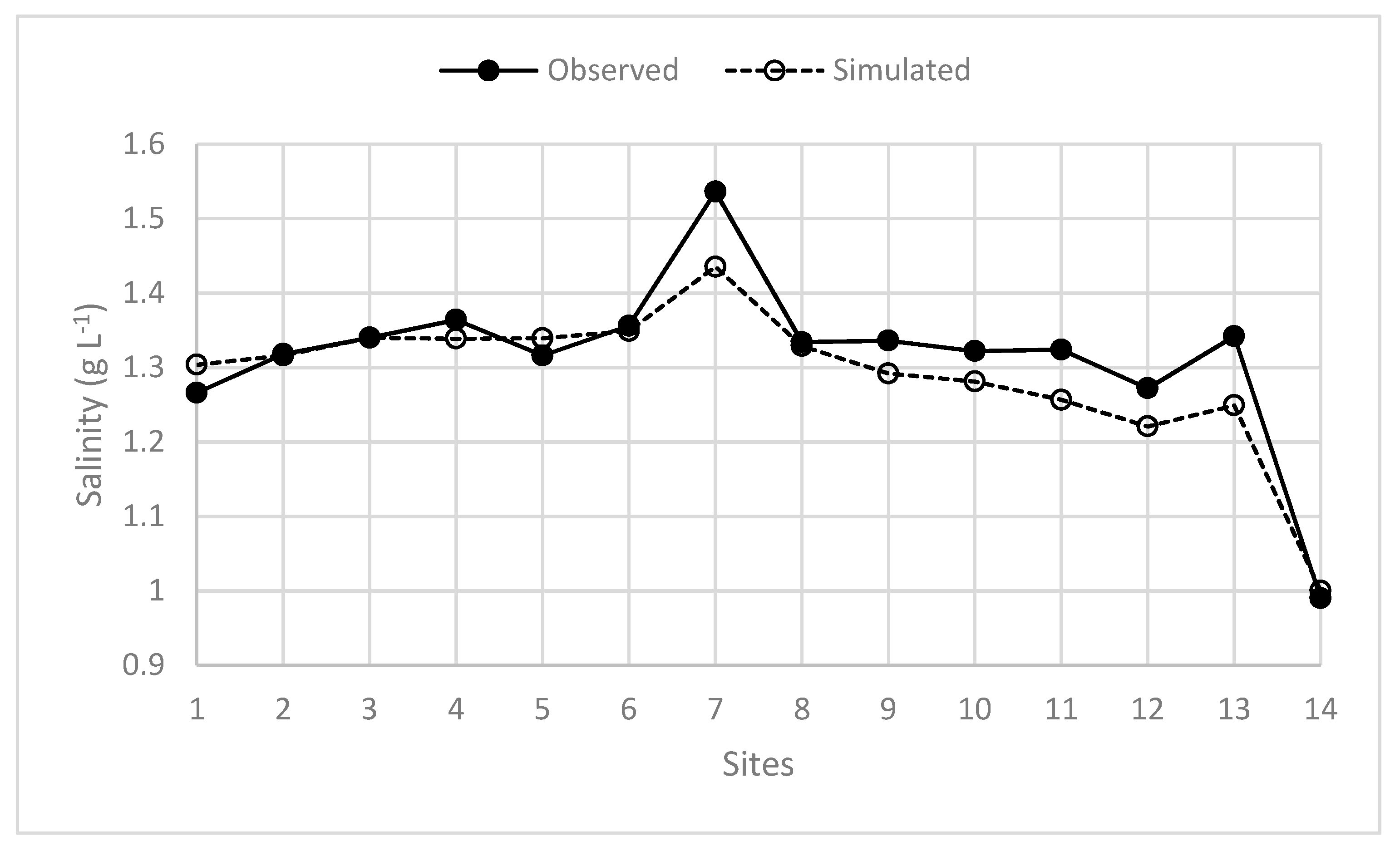
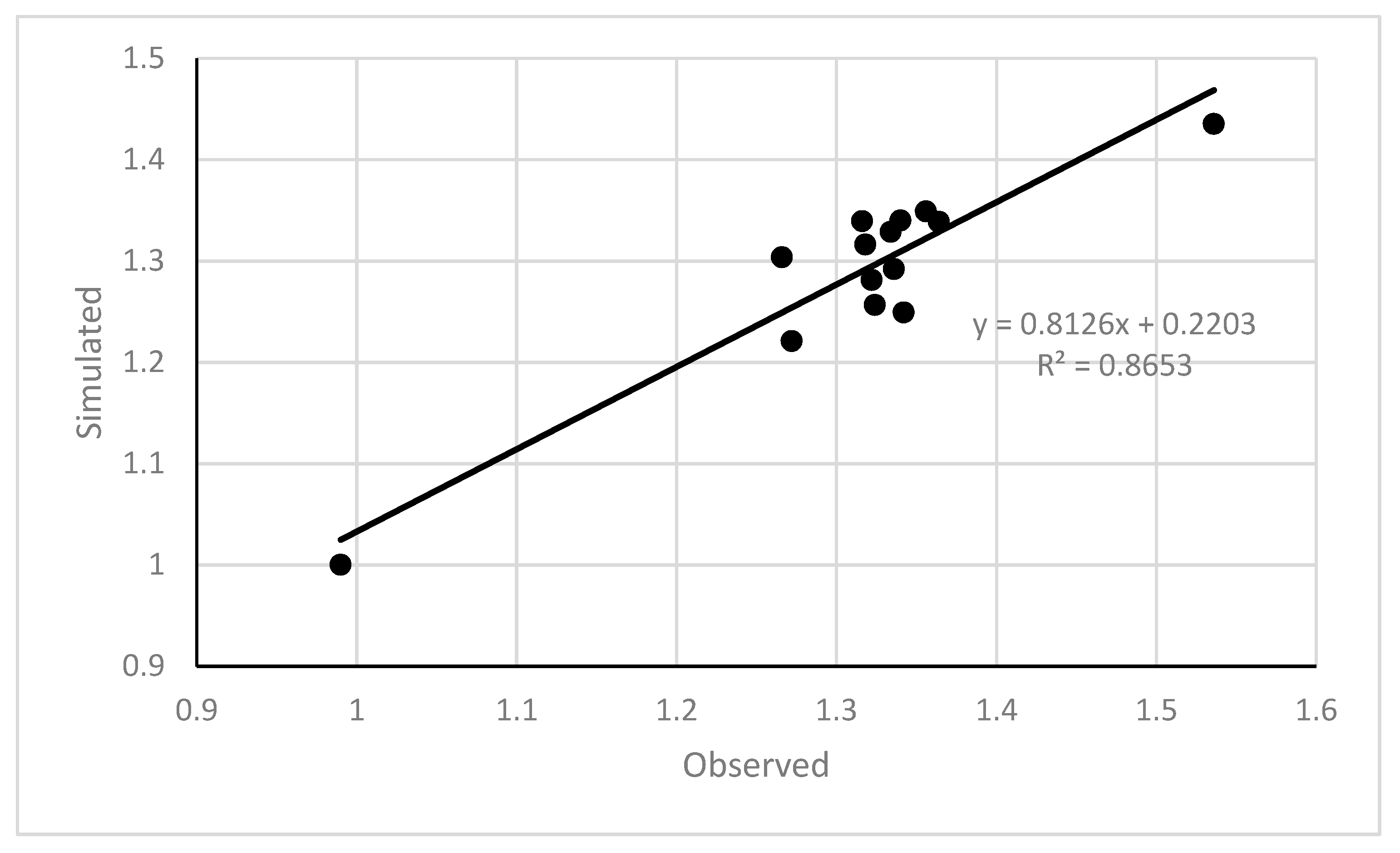
3.1. Model Validation
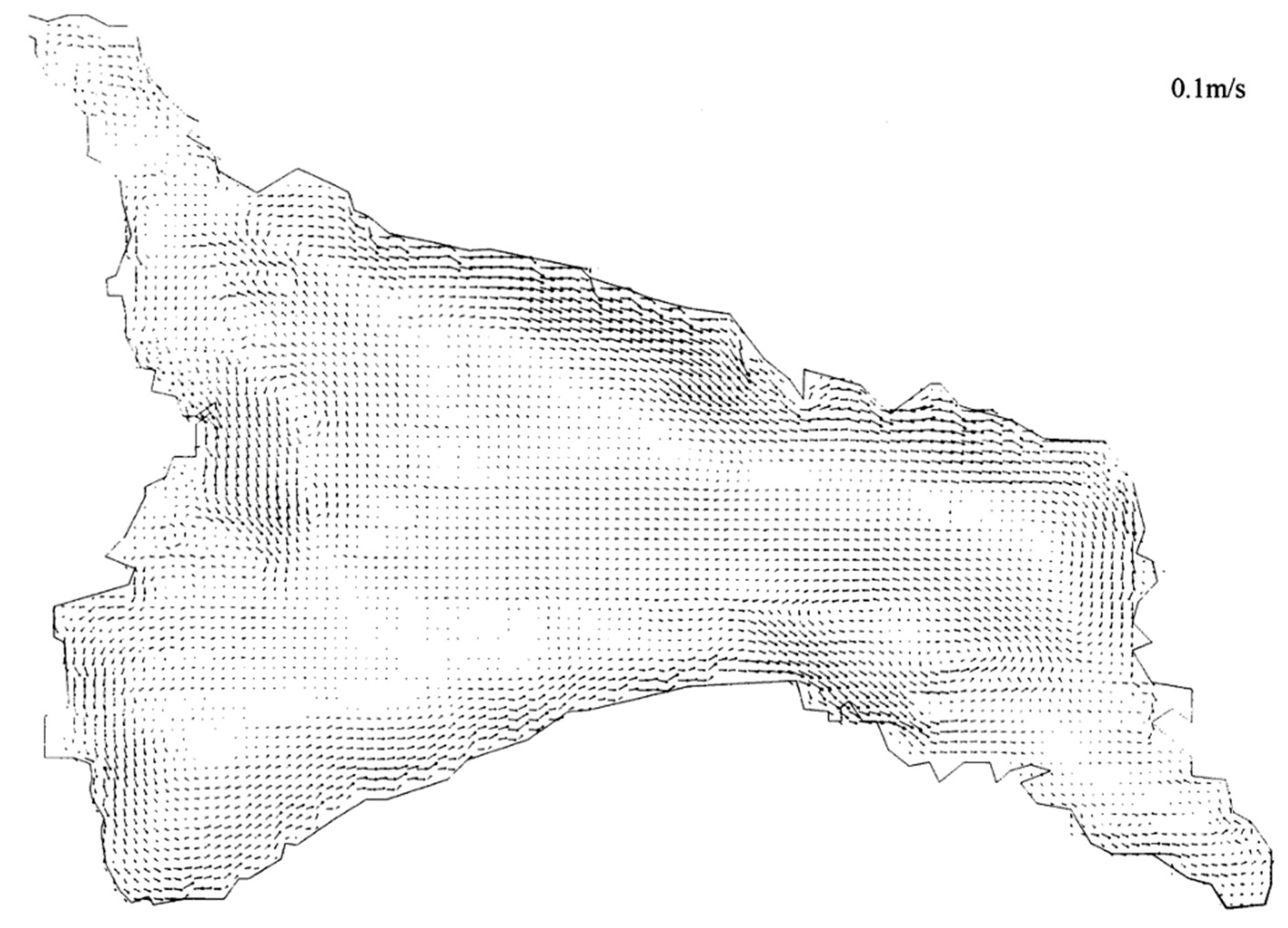
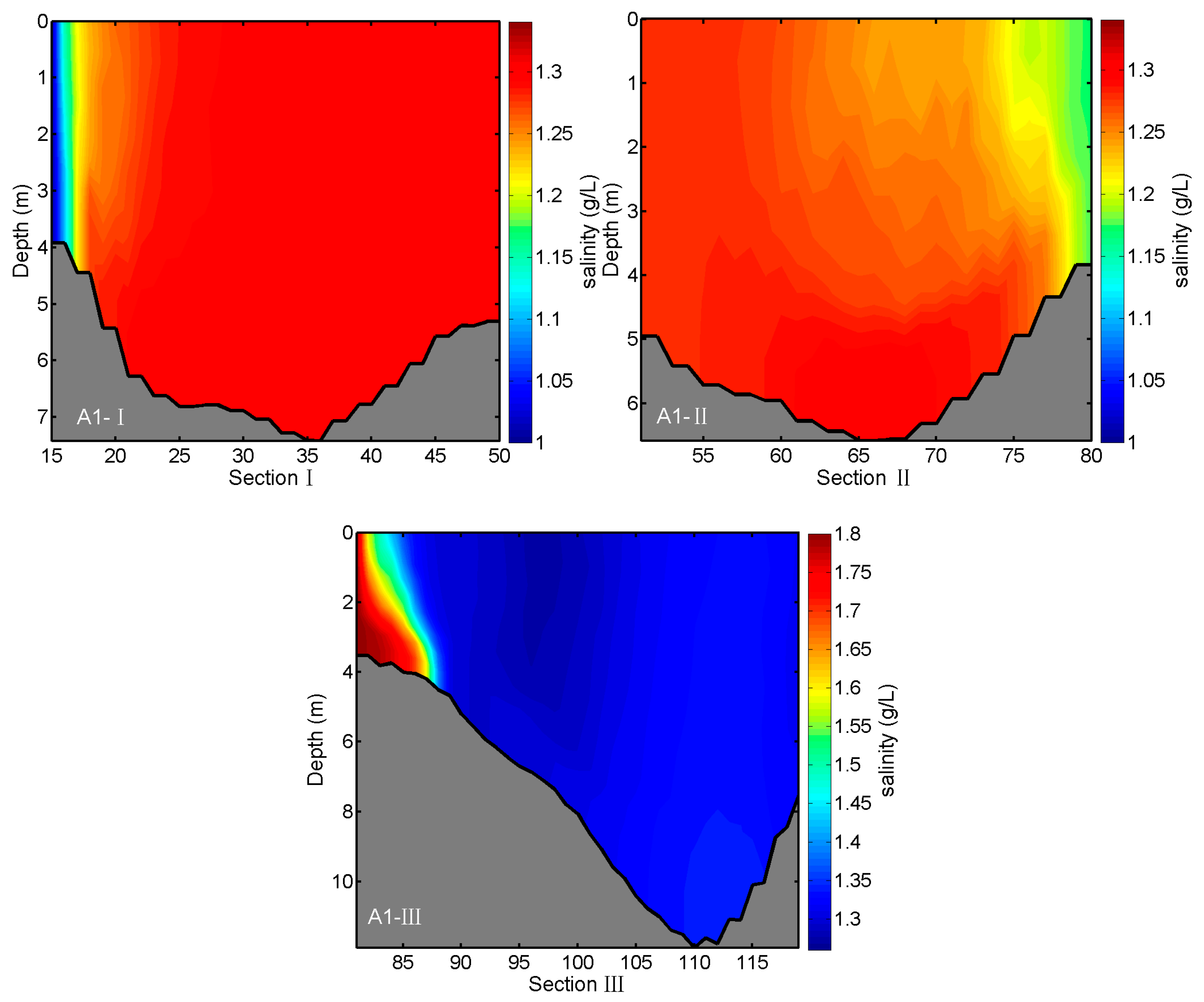
3.2. Analyses of Model Results
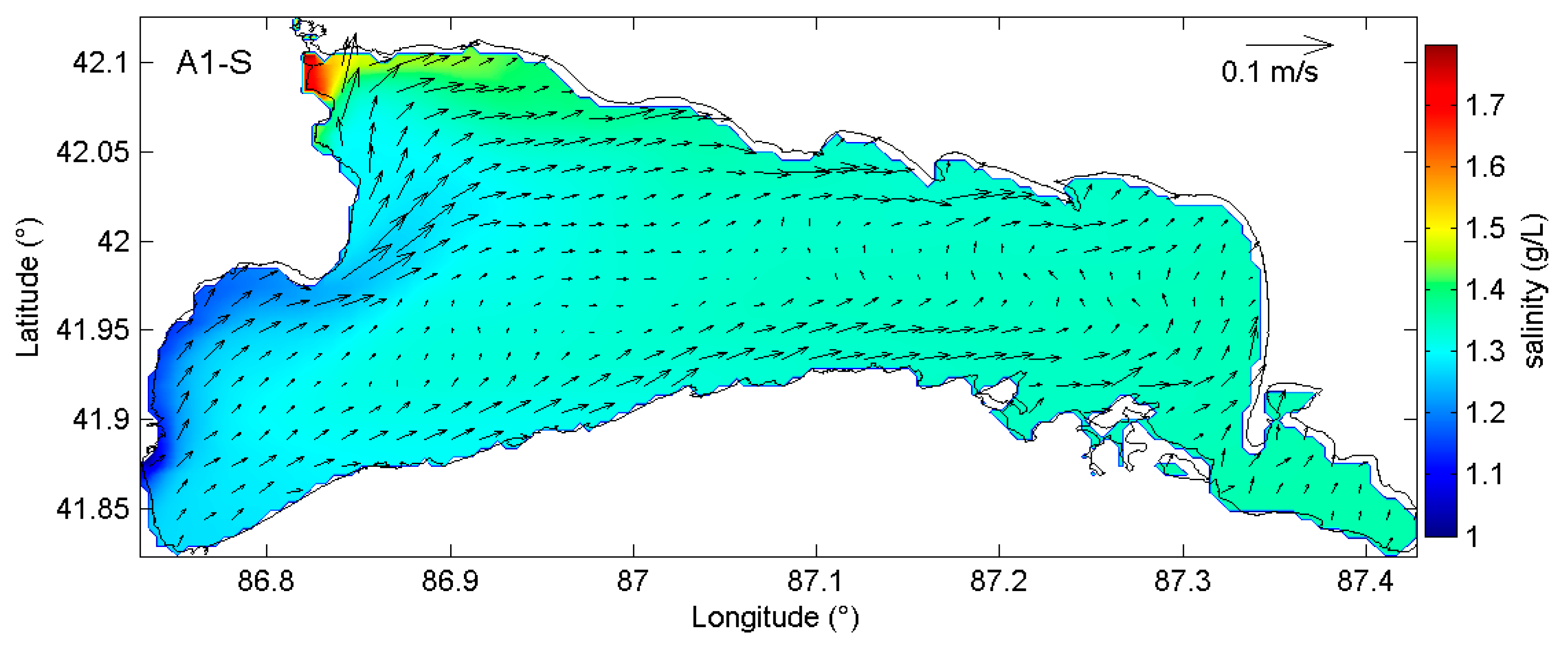
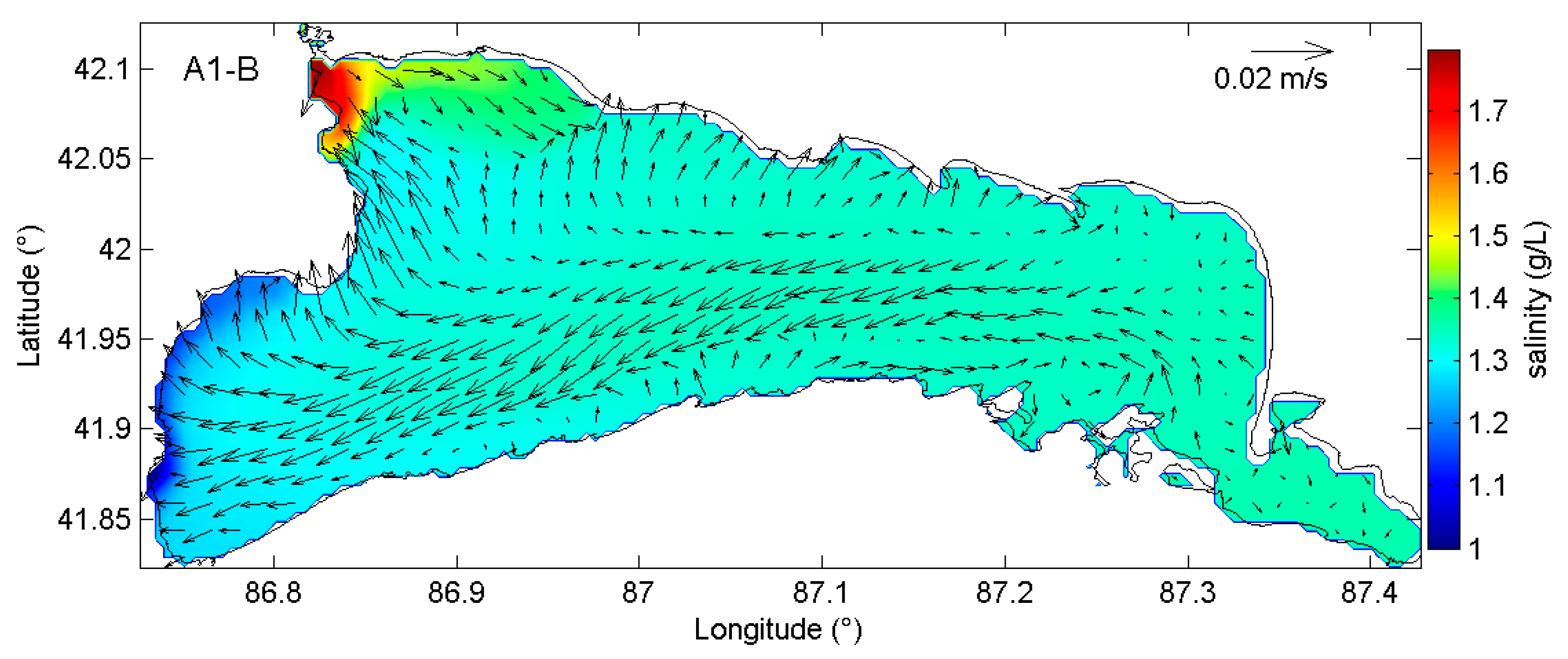
3.3. Effects of River Discharges on Salinity Distributions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schofield, N.J.; Ruprecht, J.K. Regional analysis of stream salinisation in southwest Western Australia. J. Hydrogeol. 1989, 112, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Dou, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, K.F. Physically-based model for studying the salinization of Bosten Lake in China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Anthropogenic salinisation of inland waters. Hydrobiologia 2001, 466, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, J.; Escobar, E.; Lugo, A. Water use (and abuse) and its effects on the crater-lakes of Valle de Santiago, Mexico. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2000, 5, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Cheng, G.D. Current situation, problems and rational utilization of water resources in arid northwestern China. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 40, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Migahid, M.M. Effect of salinity shock on some desert species native to the northern part of Egypt. J. Arid Environ. 2003, 53, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.M.; Xie, G.J.; Shao, K.Q.; Bayartu, S.; Chen, Y.G.; Gao, G. Influence of salinity on the bacterial community composition in Lake Bosten, a large oligosaline lake in arid northwestern China. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2012, 78, 4748–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, W.D. Salinisation: A major threat to water resources in the arid and semi-arid regions of the world. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1999, 4, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.L.; Yang, L.; Fang, H. Changes in the area of inland lakes in arid regions of central Asia during the past 30 years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 178, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.M.; Cai, Y.; Gao, G. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity of water quality and succession patterns in Lake Bosten during the past 50 years. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 988–998. [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont, P. Agricultural and environmental changes in the upper Euphrates catchment of Turkey and Syria and their political and economic implications. Appl. Geogr. 1996, 16, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, E.; Vengosh, A.; Gavrieli, I.; Marie, A.; Bullen, T.D.; Mayer, B.; Holtzman, R.; Segal, M.; Shavit, U. The origin and mechanisms of salinization of the Lower Jordan River. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, T.K.; Burkhalter, J.P.; Labadie, J.W.; Valliant, J.C.; Broner, I. Monitoring and modelling flow and salt transport in a salinity-threatened irrigated valley. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2002, 128, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, T.H.S.; Watanabe, T.; Ogino, Y.; Tanji, K.T. Soil salinization in the Nile Delta and related policy issues in Egypt. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillsbury, A.F. The salinity of rivers. Sci. Am. 1981, 245, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.F.; Stoner, R.F.; Perry, J.H. Disposal of drainage water from irrigated alluvial plains. Water Sci. Technol. 1983, 16, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zuo, Q.T.; Shao, M.C. Sustainable Management of Water Resources in Lake Bosten; Chinese Science Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.H.; Luo, G.P.; Li, C.; Tang, Q.C.; Li, H.G.; Wang, Q.M.; Fuikui, H. Environmental change in Bosten Lake and its relation with the oasis reclamation in Yanqi Basin. Geogr. Res. 2001, 20, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Chen, X. Water Planning and Management Meeting Sustainable Development; China Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.C.; Li, Y.A. Water-salt equilibrium and mineralization of Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Arid Land Geogr. 1997, 20, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.G.; Zhong, R.S.; Liu, F. Differentiation of Water-salt-interaction in Bostan Lake and Peacock River in Recent Fifty Year. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2006, 24, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Li, Y.A.; Wang, Y.G.; Tan, Y. Study on the change of inflow and salt content of the Bosten Lake, Xinjiang since the 1950s. Arid Zone Res. 2005, 22, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.F.; Qin, D.H.; Nagashima, H.; Lei, J.Q.; Wei, W.S. Analysis of mechanism of the salinization process and the salinity variation in Bosten Lake. Adv. Water Sci. 2007, 18, 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.X.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.T. Flow field and salinity distribution of large inland lake. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 111, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.Q.; Hou, J.; Qiu, X.Y.; Zhou, Z. Numerical simulation of salinity in Bosten Lake. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2002, 1, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.A.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, F.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Hu, R.J. Study on hydrological features of the Kaidu River and the Bosten Lake in the second half of 20th century. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2003, 25, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.C. Studies on Bosten Lake; Hehai Unversity Press: Nan Jing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mischke, S. Holocene environmental fluctuations of Lake Bosten (Xinjiang, China) inferred from ostracods and stable isotopes. In Proceedings of the EGS-AGU-EUG Joint Assembly, Nice, France, 6–11 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, Y.; Lee, T.Q.; Yao, P. Stable isotopic variations in oxygen and hydrogen of waters in Lake Bosten region, Southern Xinjiang, Western China. West. Pac. Earth Sci. 2002, 2, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jiu, X.; Liu, H.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, X. (Eds.) Eutrophication of Lakes in China (The 4th International Conference on the Conservation and Management of Lakes “Hangzhou 90”); The Conference: Hangzhou, China, 1990; 652p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, N.; Mecuthon, S.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W. Lake Bosten in Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang. In Lakes in China: Research of Their Environment; Jin, X., Ed.; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.L.; Guo, Y.P.; Li, W.H. Analysis on the water pollution in Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2003, 20, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Mellor, G.L. A Description of a Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Circulation Model. In Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Models; Heaps, N., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, A.F. An Estuarine and Coastal Ocean Version of POM. In Proceedings of the Princeton Ocean Model Users Meeting (POM96), Princeton, NJ, USA, 10–12 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A.F. A Primer for ECOMSED, Version 1.3; User’s Manual; HydroQual Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Mellor, G.L. A coastal ocean numerical model. In Mathematical Modelling of Estuarine Physics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Smagorinsky, J. General Circulation Experiments with the Primitive Equations, I. The Basic Experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.K.M.Q.; Blumberg, A.F. A three-dimensional hydrothermal model of Onondaga Lake, New York. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, A.; Miyakoda, K. A general circulation model for upper ocean simulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1601–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SLB. Hydrological Yearbook of the People’s Republic of China of Inland Rivers and Lakes in the Southern Tian-Shan Mountains; SLB: Xinjiang, China; Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]

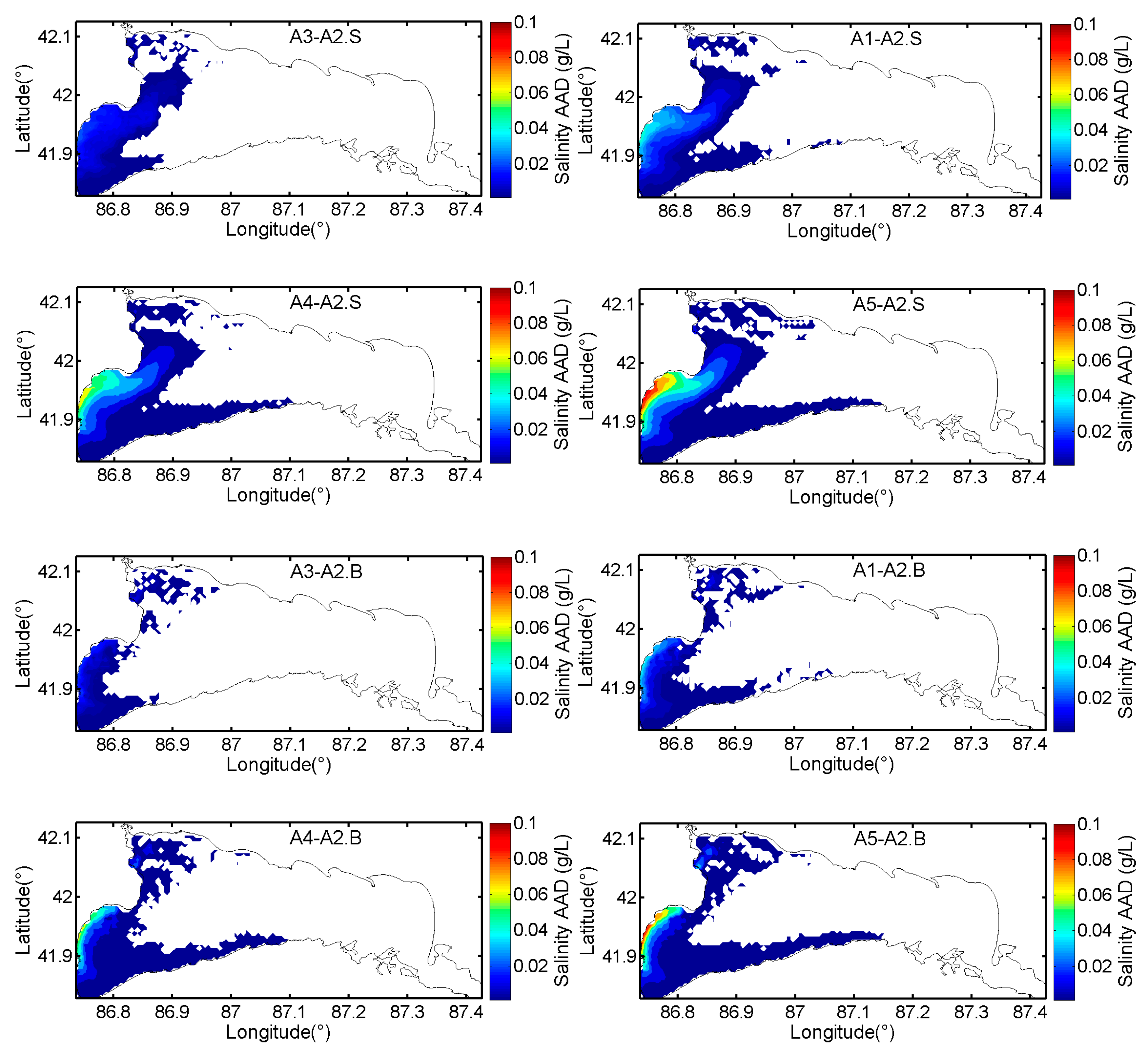
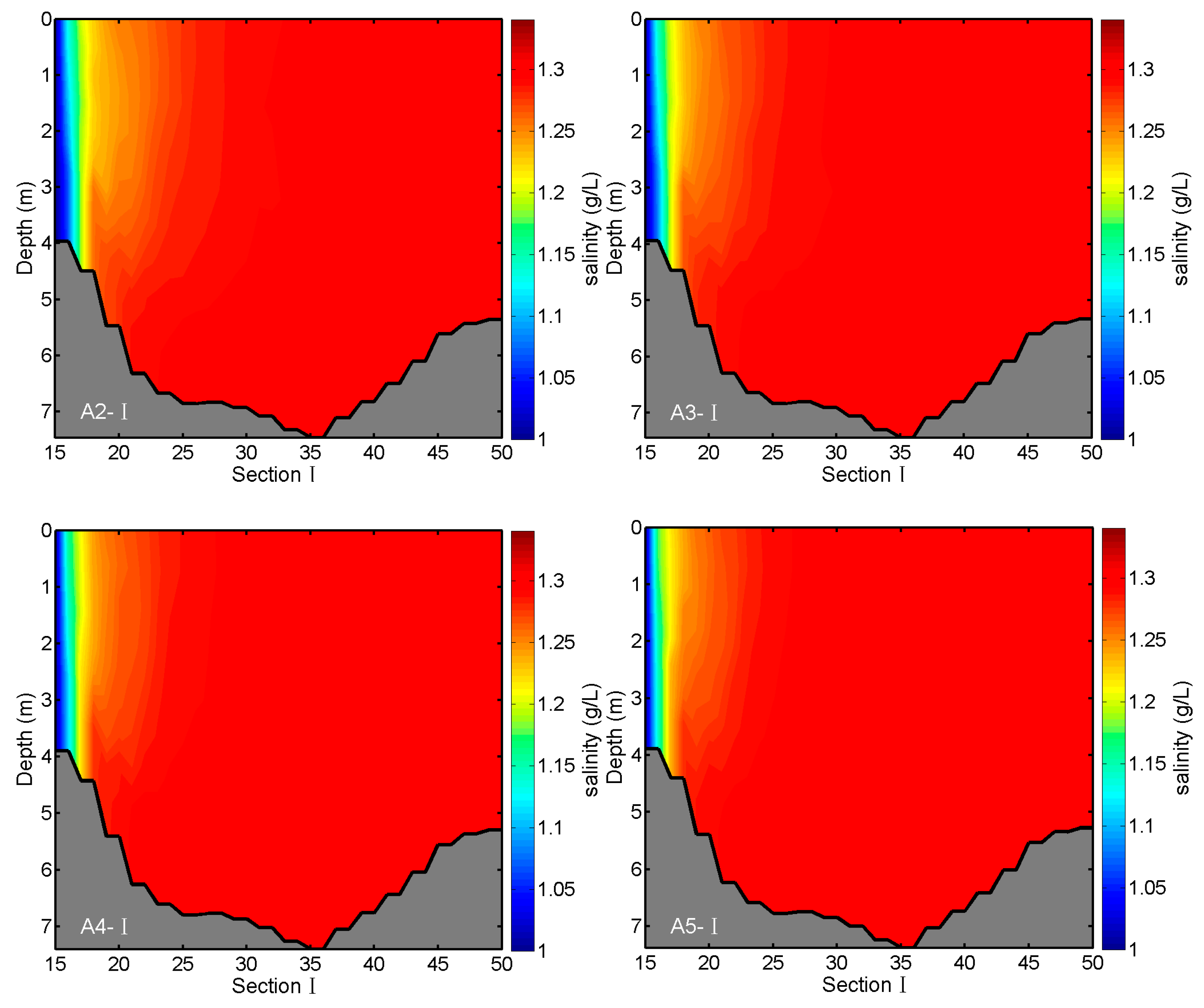
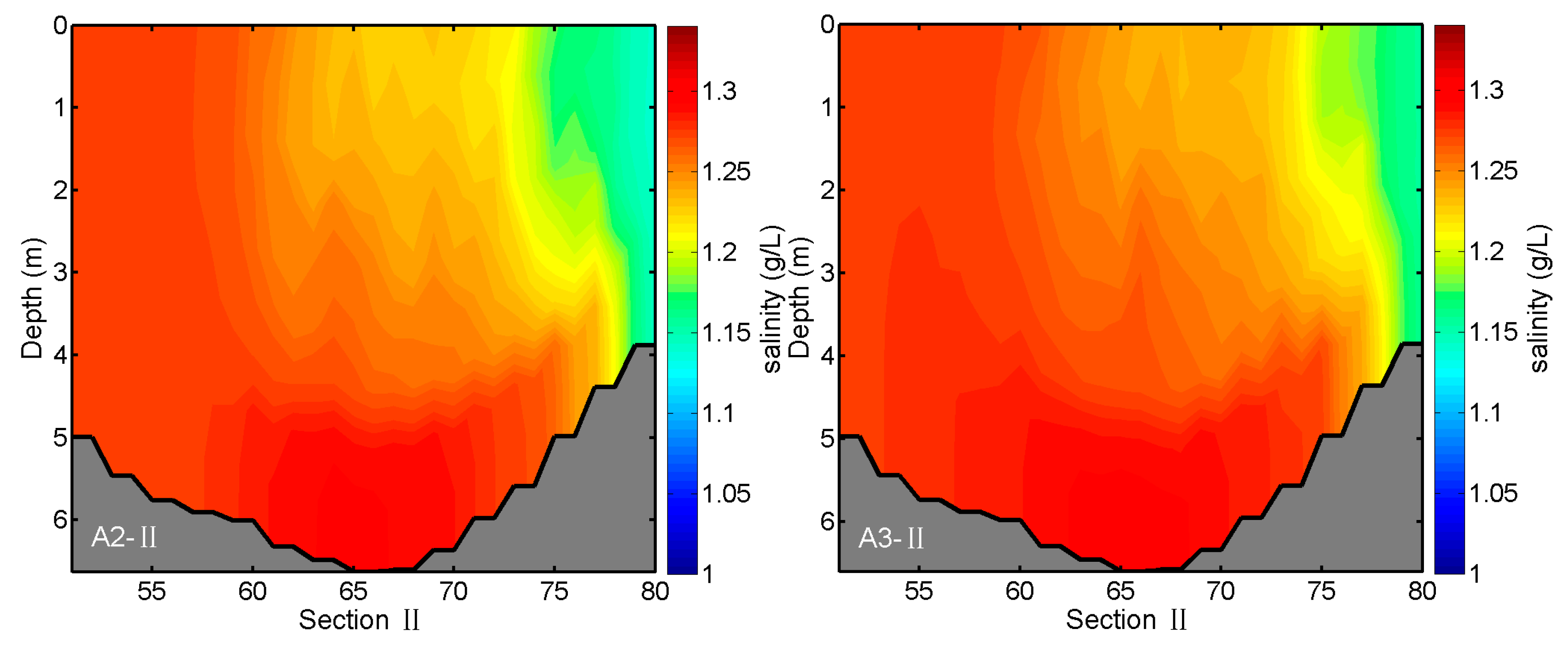
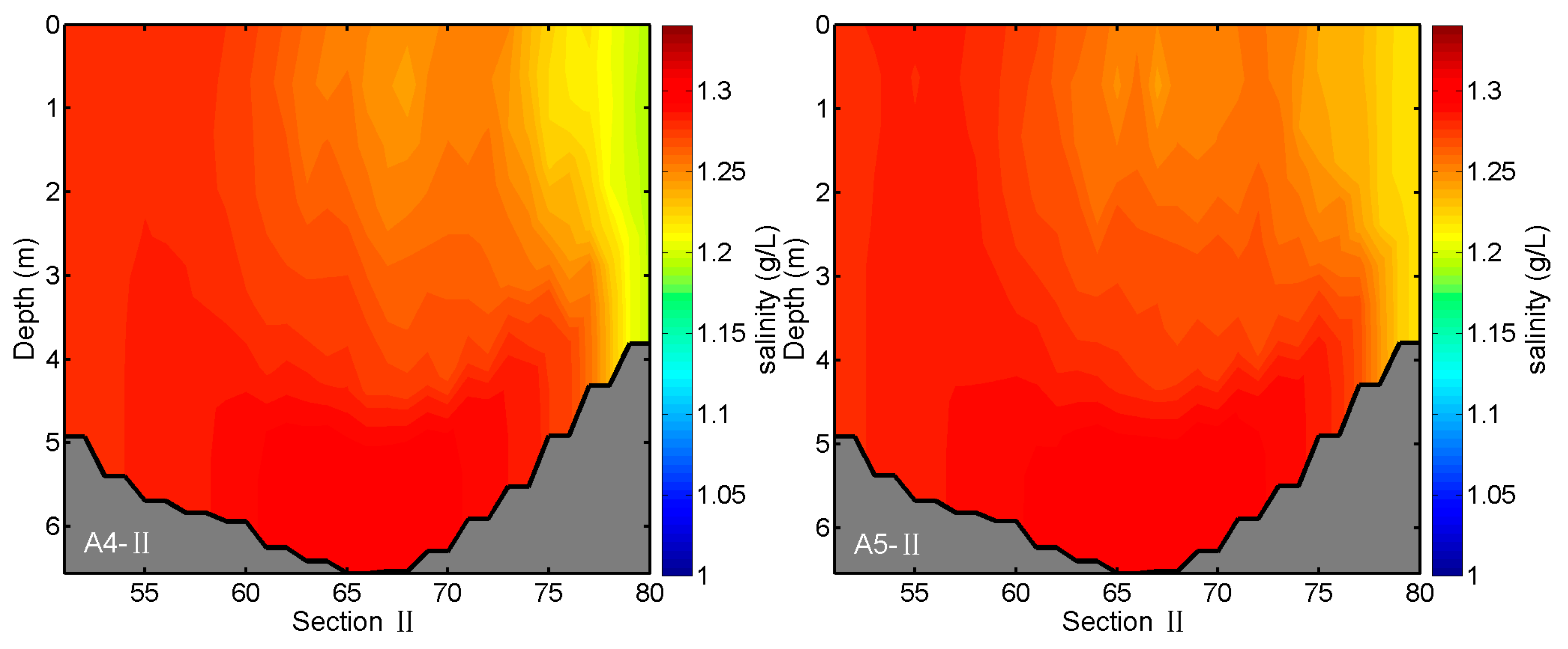
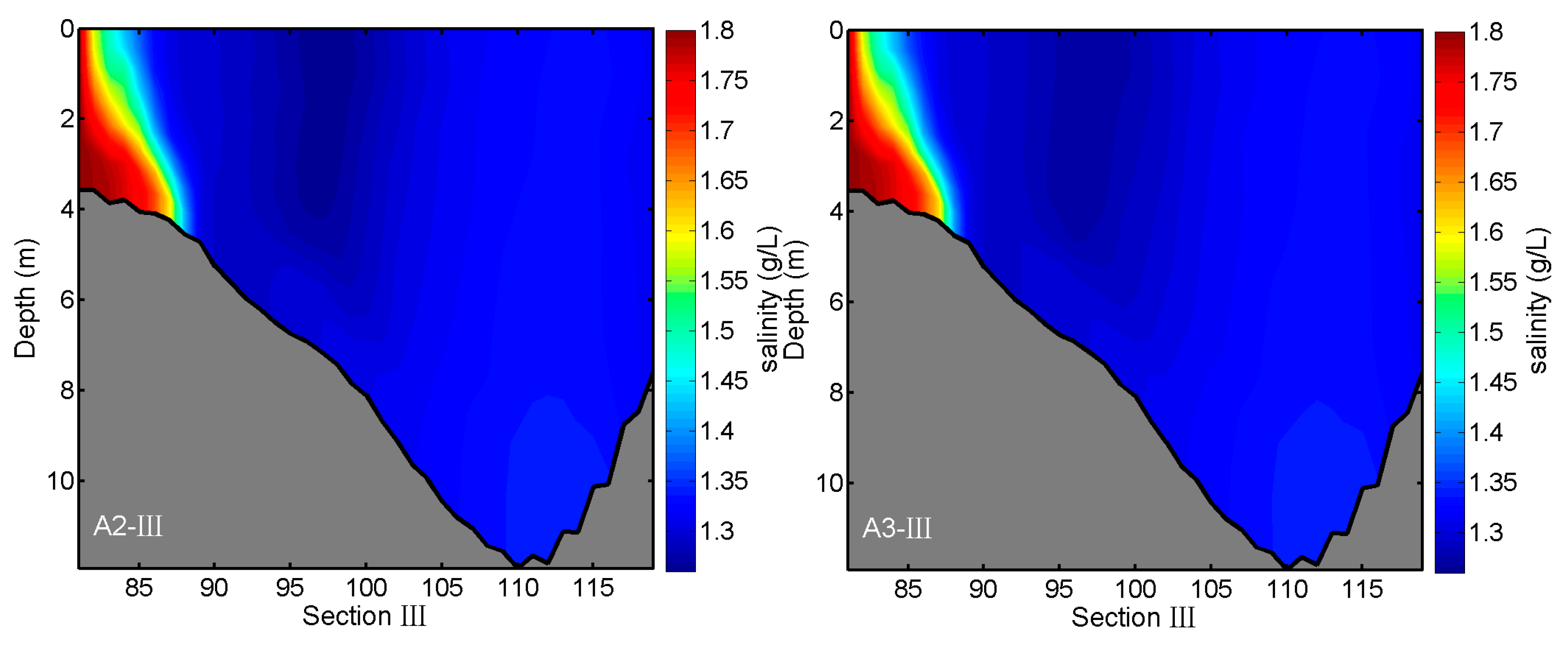
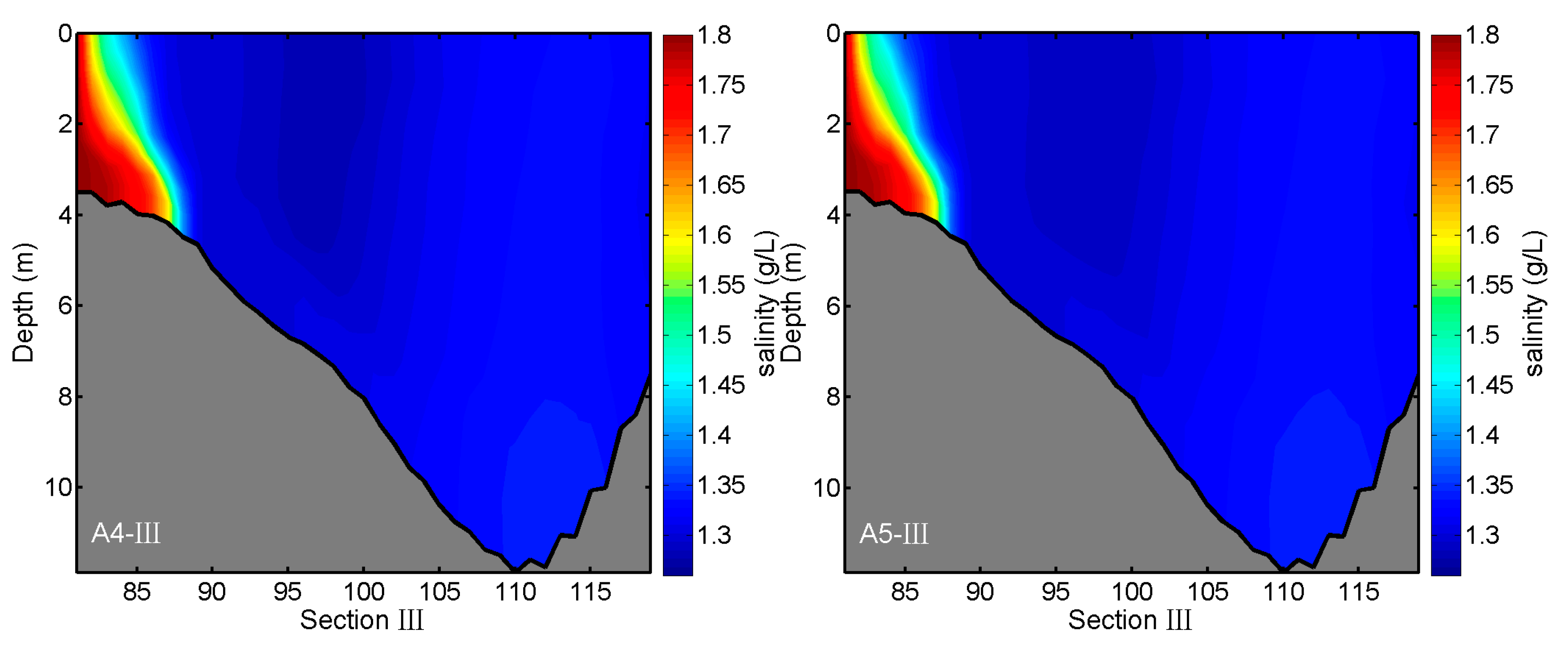
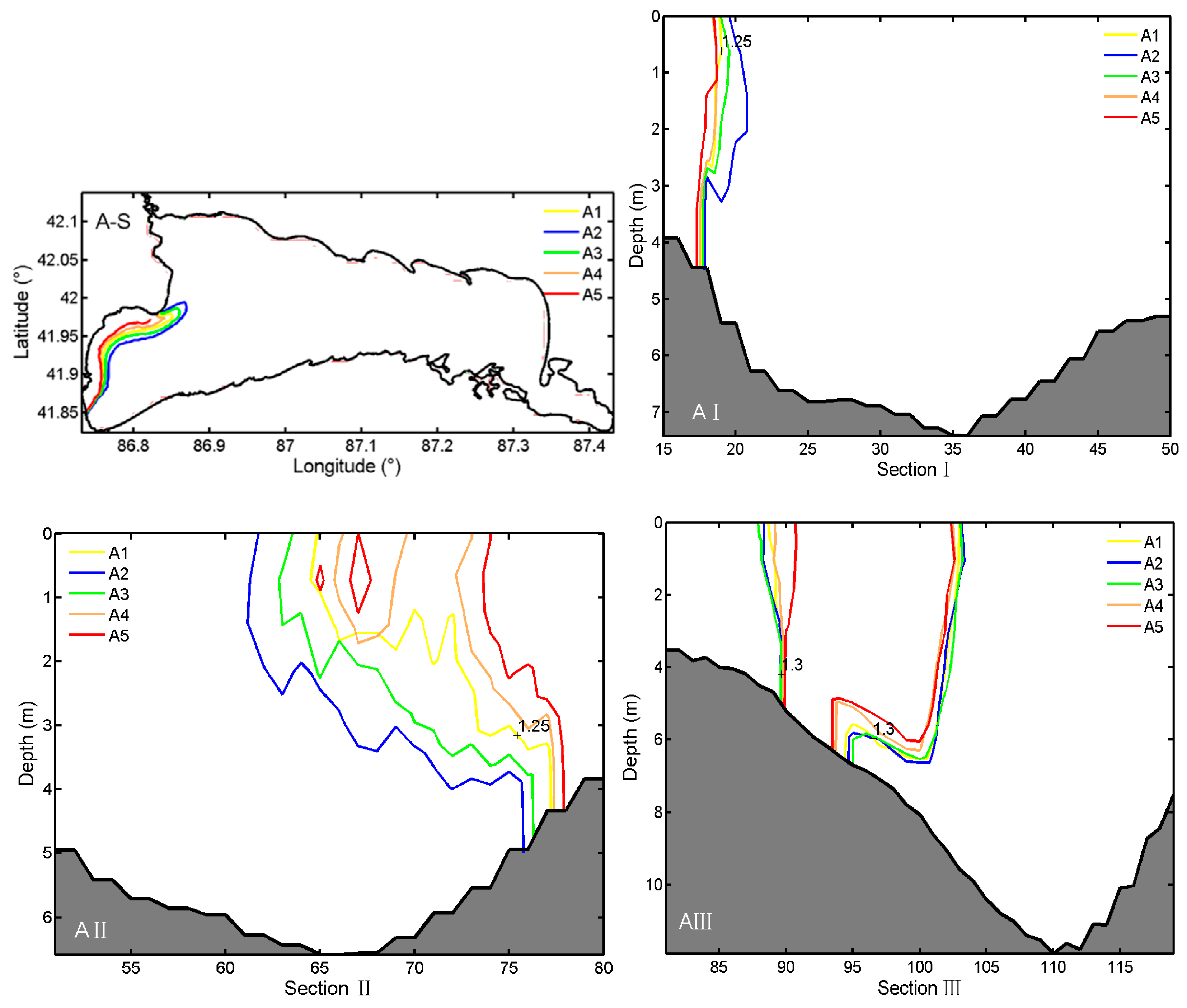
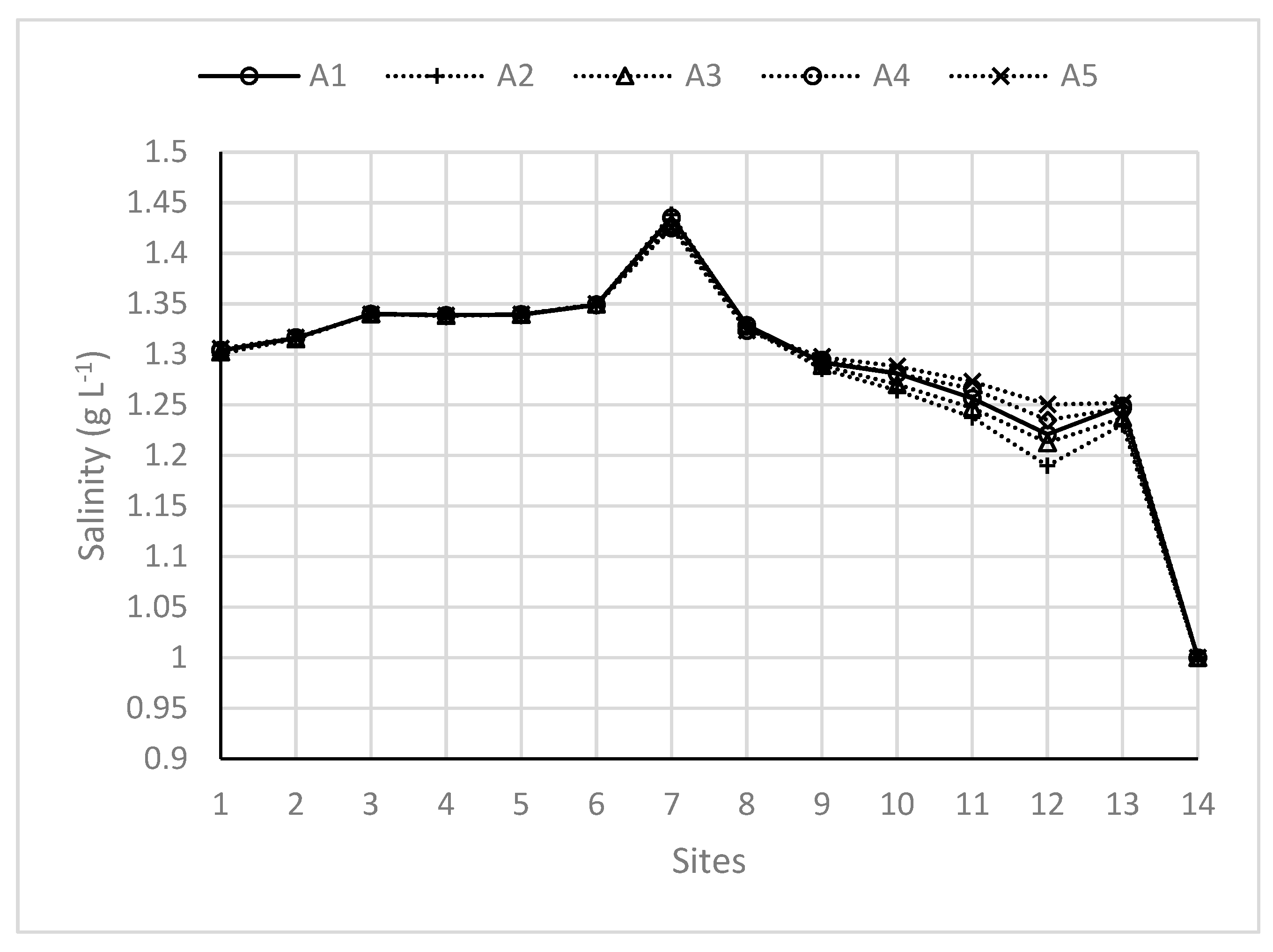
| Experiments | Conditions |
|---|---|
| A1 | Driven by winds from 1 April to 30 November 2005 and daily discharges |
| A2 | Same as A1, but the discharge of Kaidu River is increased by a factor of 0.5 |
| A3 | Same as A1, but the discharge of Kaidu River is increased by a factor of 0.25 |
| A4 | Same as A1, but the discharge of Kaidu River is decreased by a factor of 0.25 |
| A5 | Same as A1, but the discharge of Kaidu River is decreased by a factor of 0.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Bao, A.; Chen, X.; Zhong, R. A Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake. Water 2019, 11, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010008
Liu Y, Bao A, Chen X, Zhong R. A Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake. Water. 2019; 11(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ying, Anming Bao, Xi Chen, and Ruisen Zhong. 2019. "A Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake" Water 11, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010008
APA StyleLiu, Y., Bao, A., Chen, X., & Zhong, R. (2019). A Model Study of the Discharges Effects of Kaidu River on the Salinity Structure of Bosten Lake. Water, 11(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010008





