Comparing Bias Correction Methods Used in Downscaling Precipitation and Temperature from Regional Climate Models: A Case Study from the Kaidu River Basin in Western China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
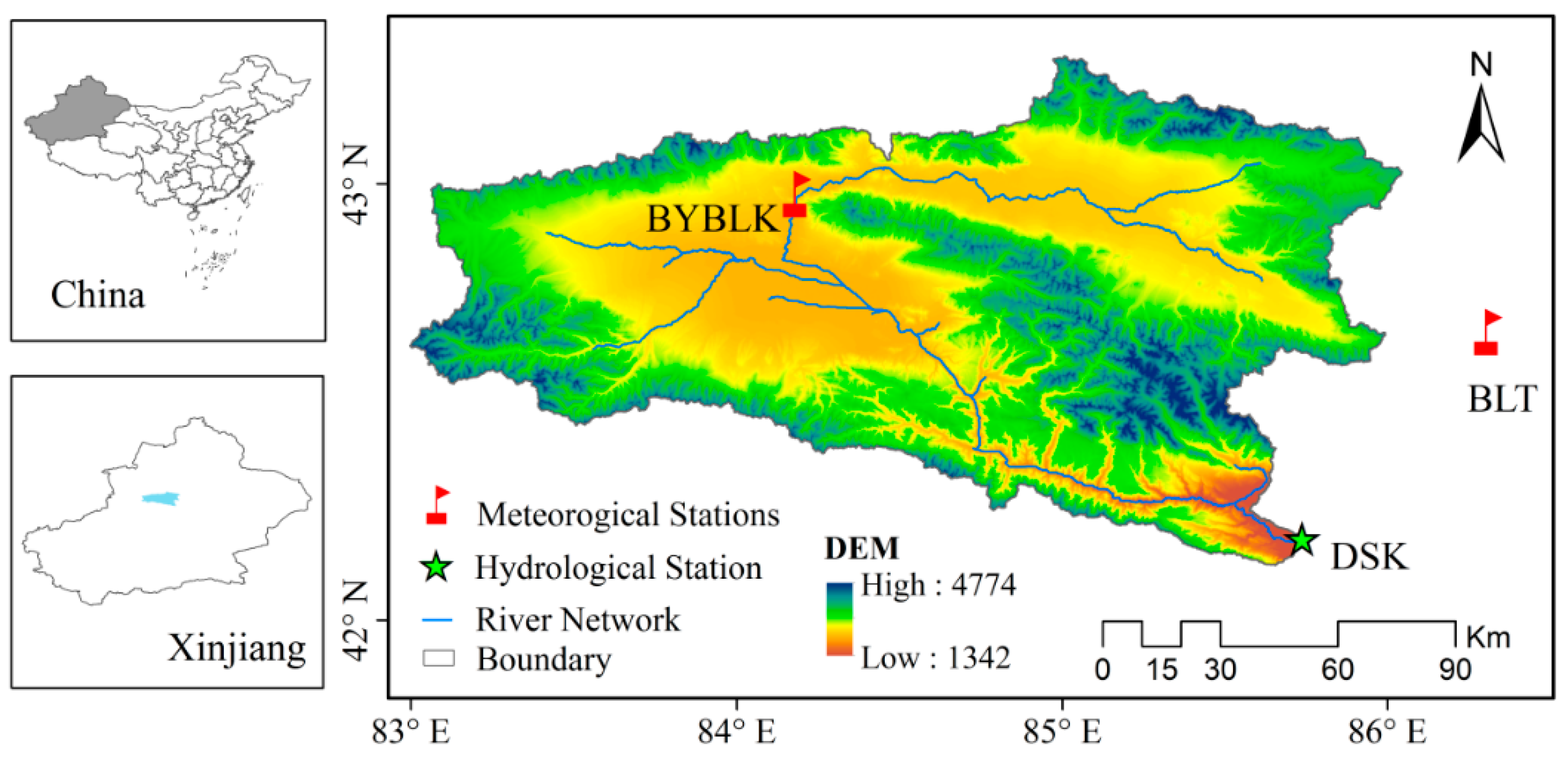
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Review of Bias Correction Methods
3.1.1. Linear Scaling (LS) Method for Precipitation and Temperature
3.1.2. Daily Translation (DT) Method for Precipitation and Temperature
3.1.3. Local Intensity Scaling (LOCI) Method for Precipitation
3.1.4. Daily Bias Correction (DBC) Method for Precipitation
3.1.5. Power Transformation (PT) of Precipitation
3.1.6. Variance Scaling (VARI) of Temperature
3.1.7. Distribution Mapping (DM) of Precipitation and Temperature
3.1.8. Empirical Quantile Mapping (EQM) of Precipitation and Temperature
3.2. Hydrological Modelling
3.3. Performance of Statistical Evaluation
4. Results
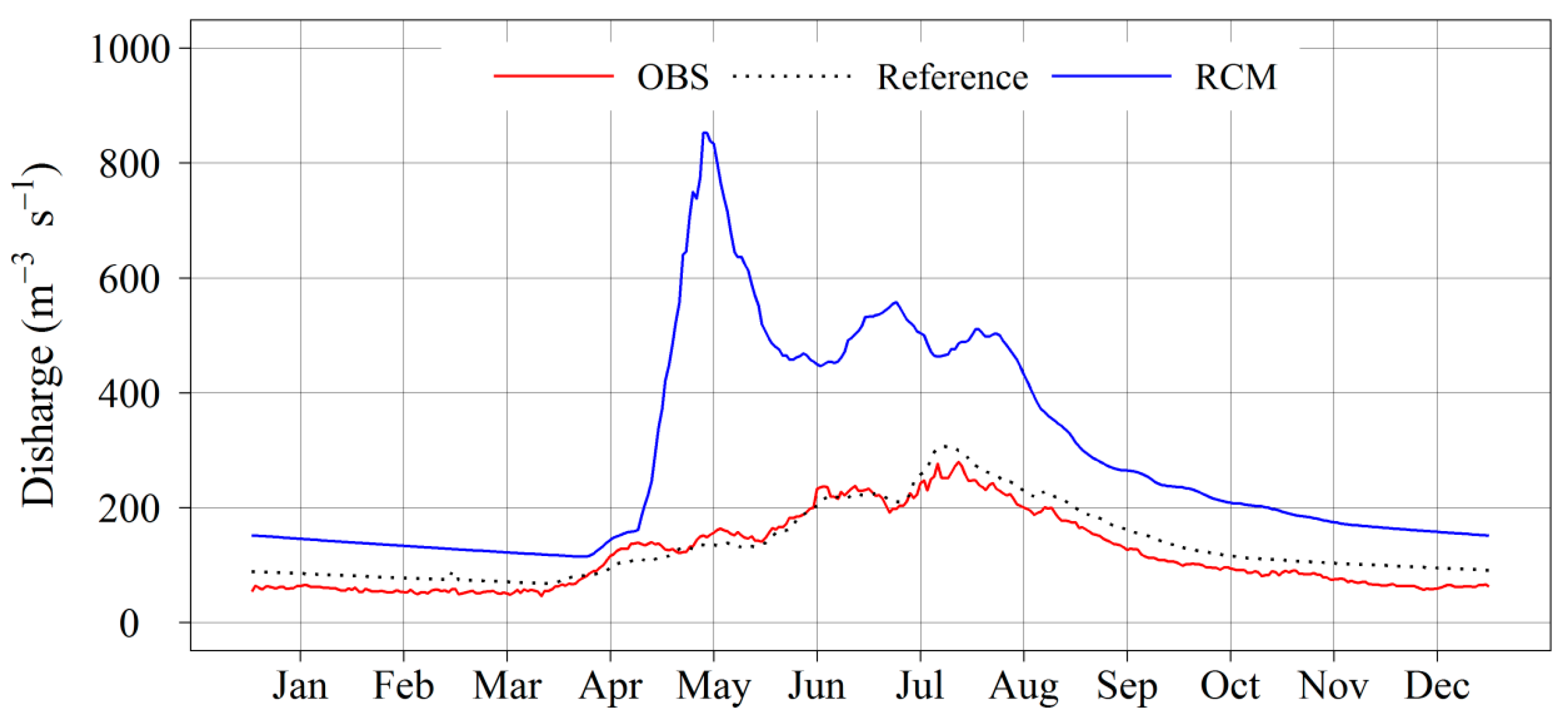
4.1. Performance of RCM Outputs in Reproducing Discharges
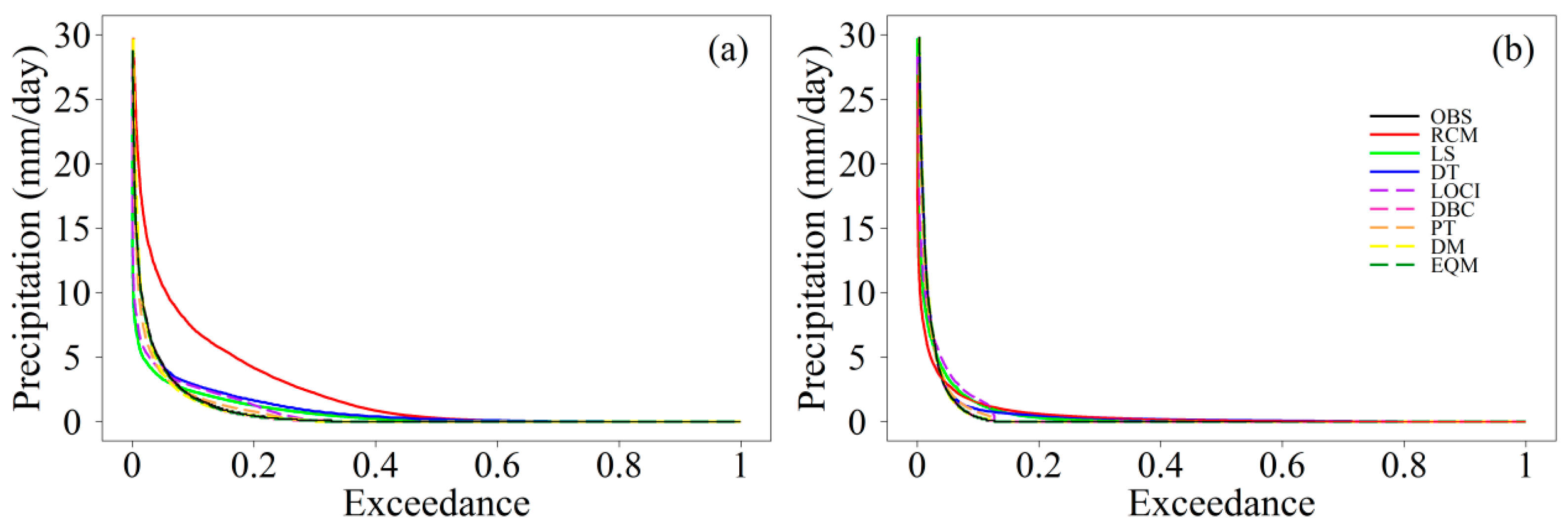
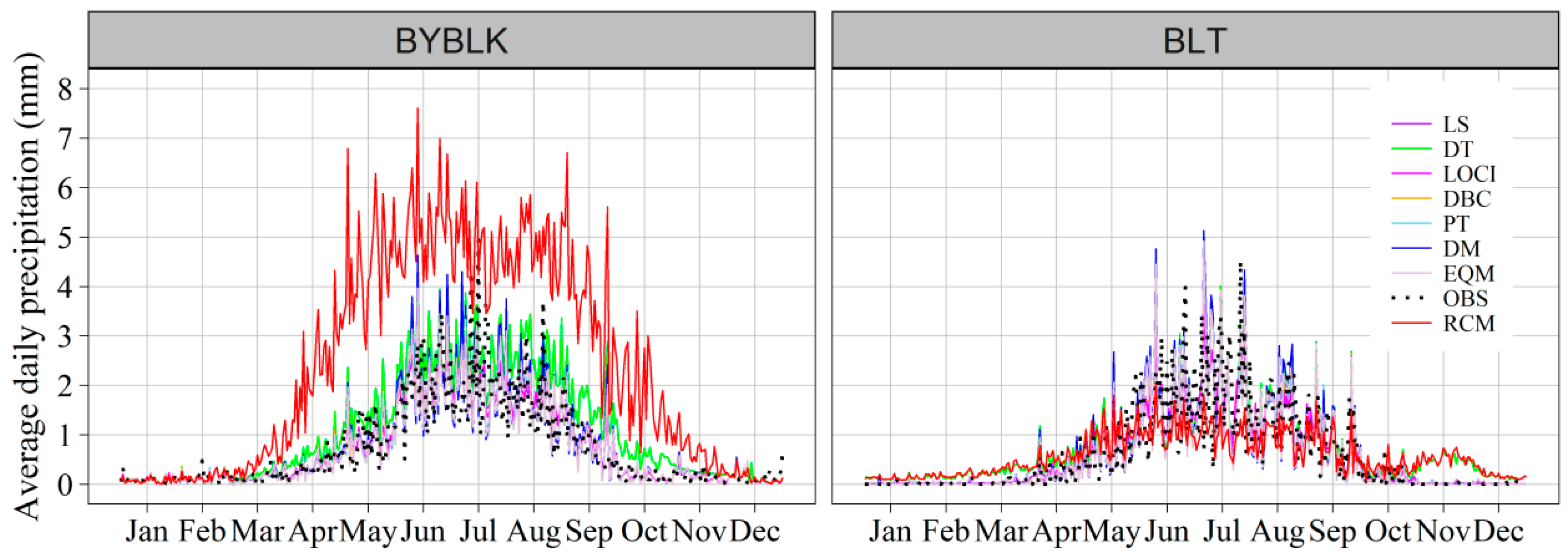
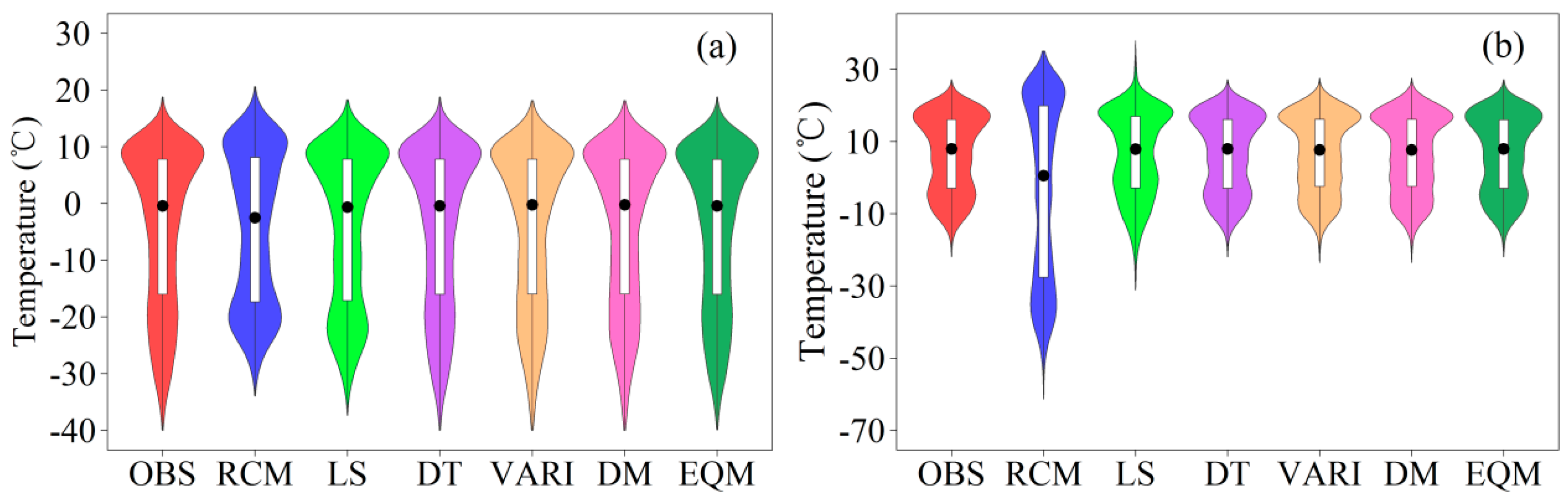
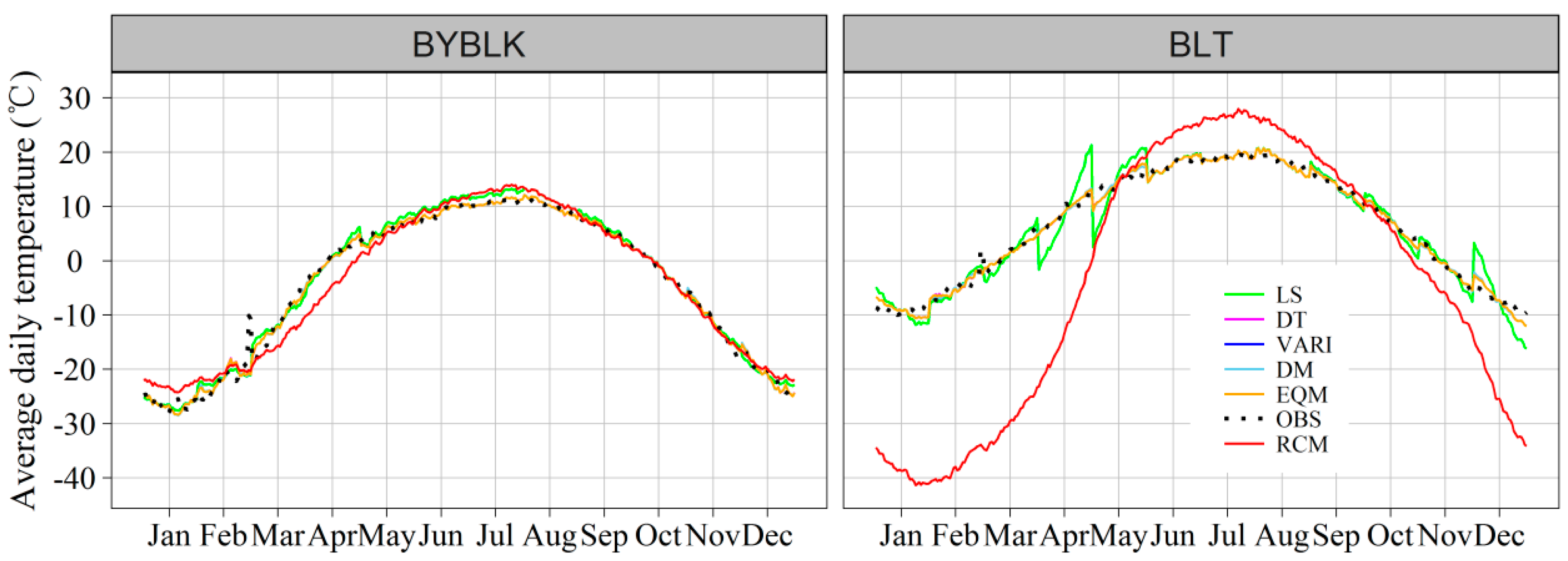
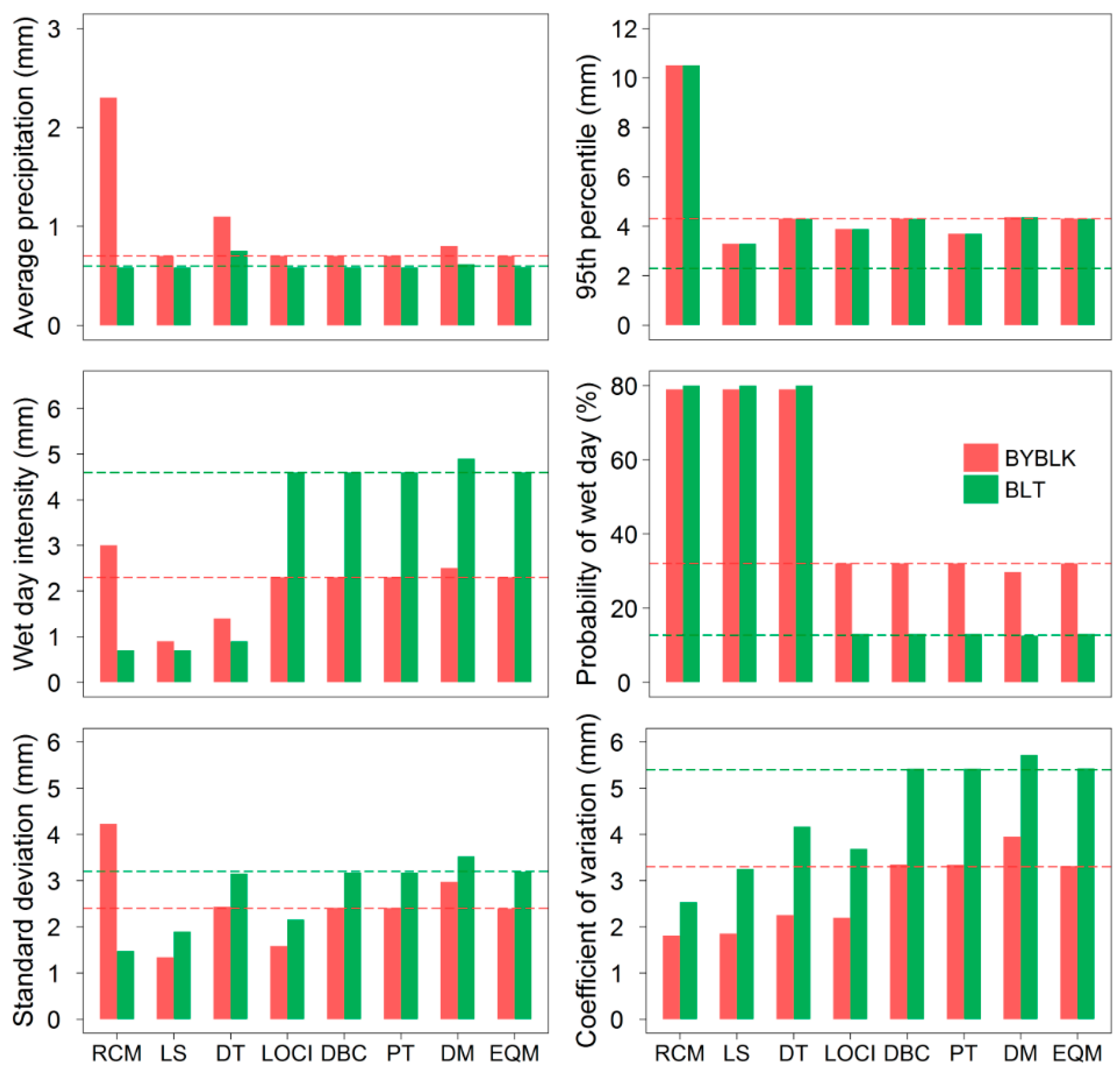
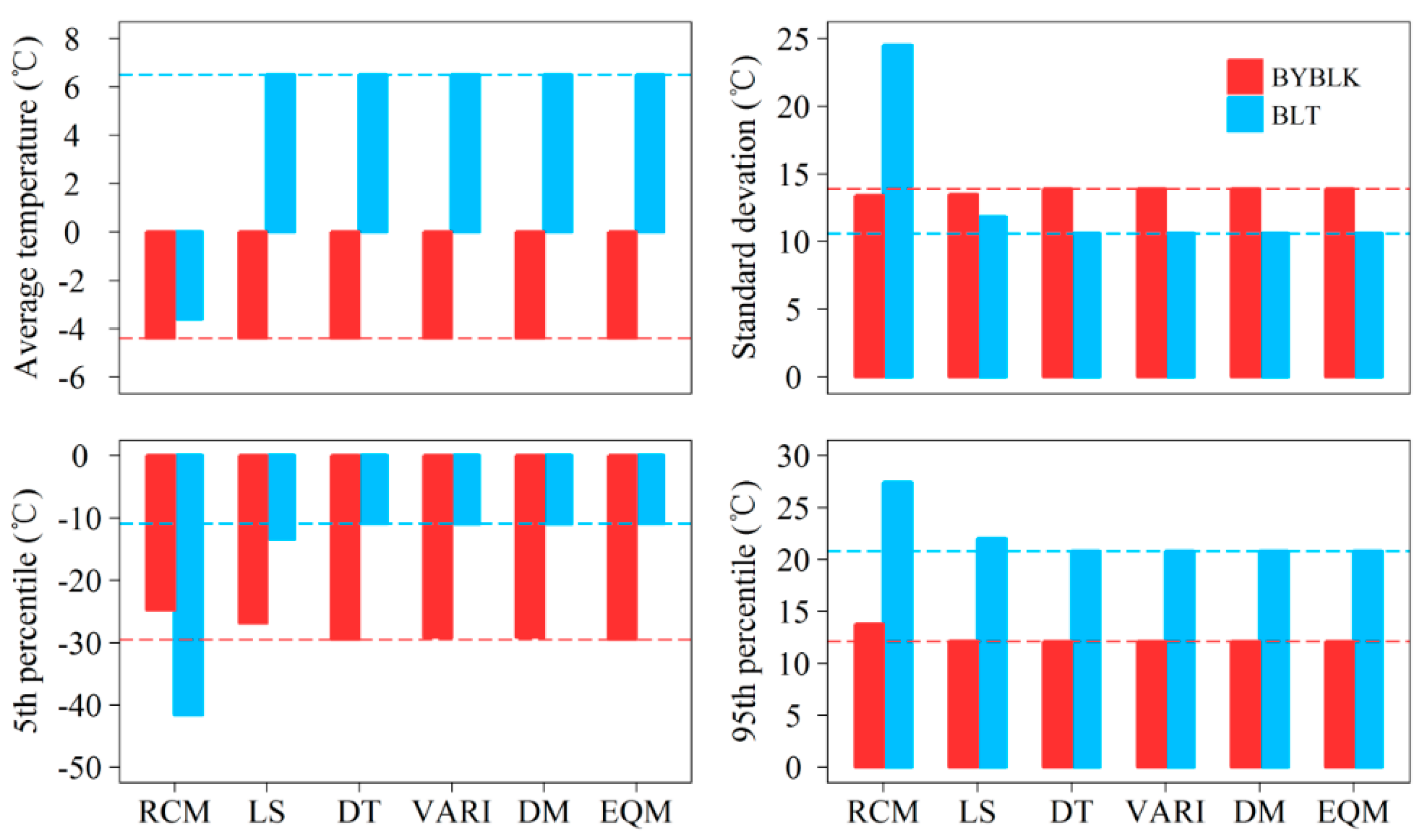
4.2. Validation of Original Precipitation and Temperature
4.3. Validation of Corrected Precipitation and Temperature
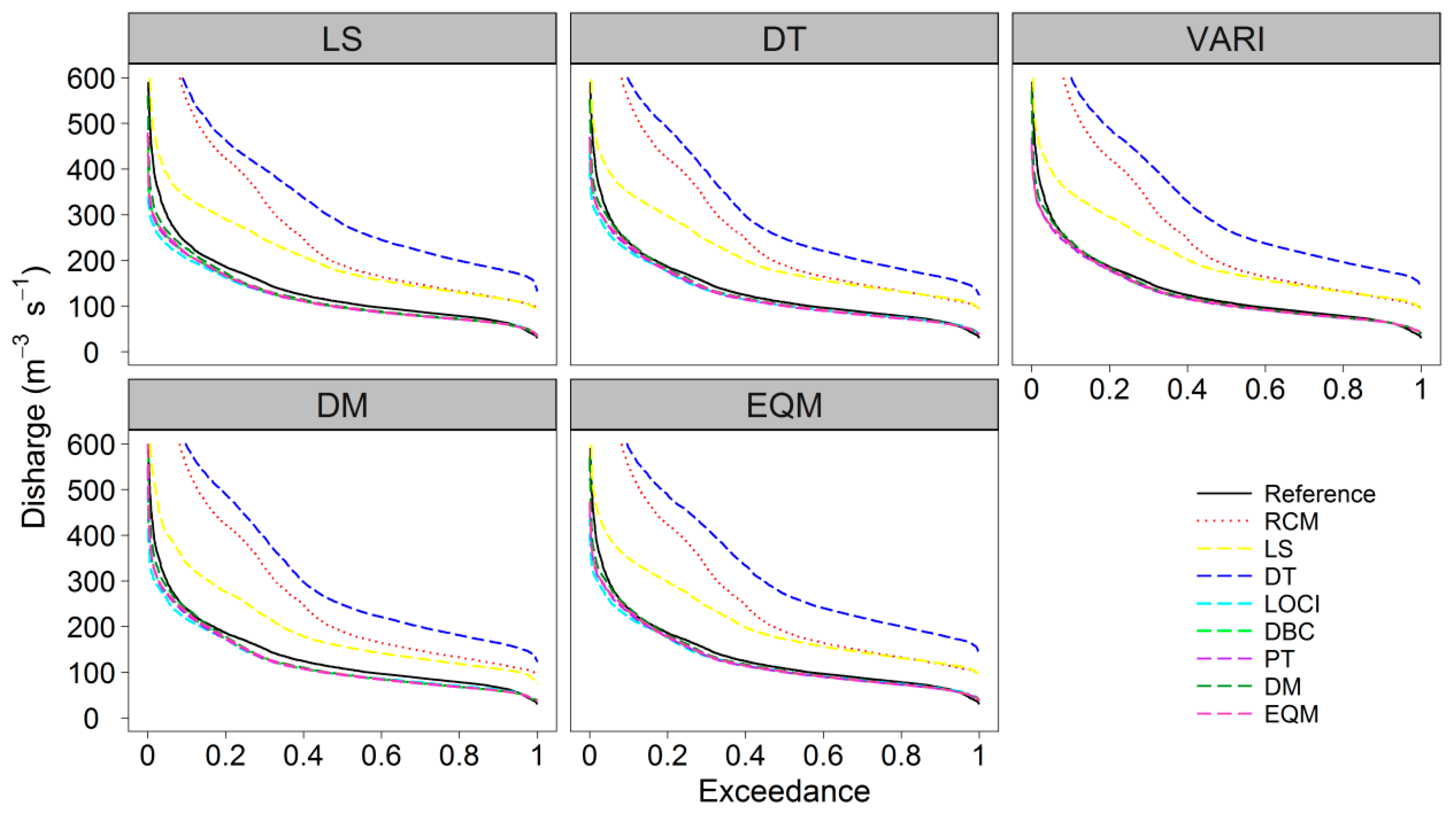
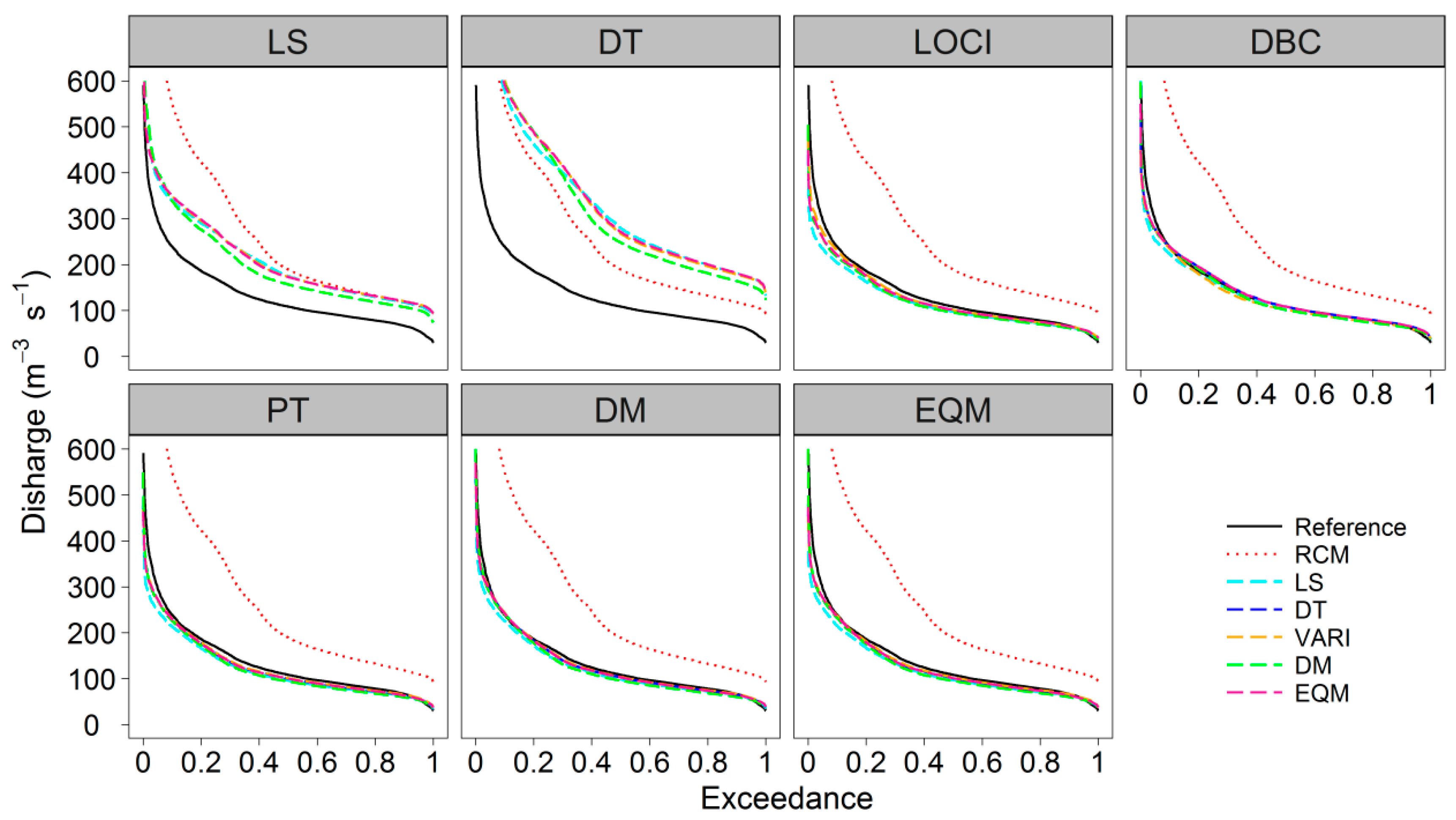
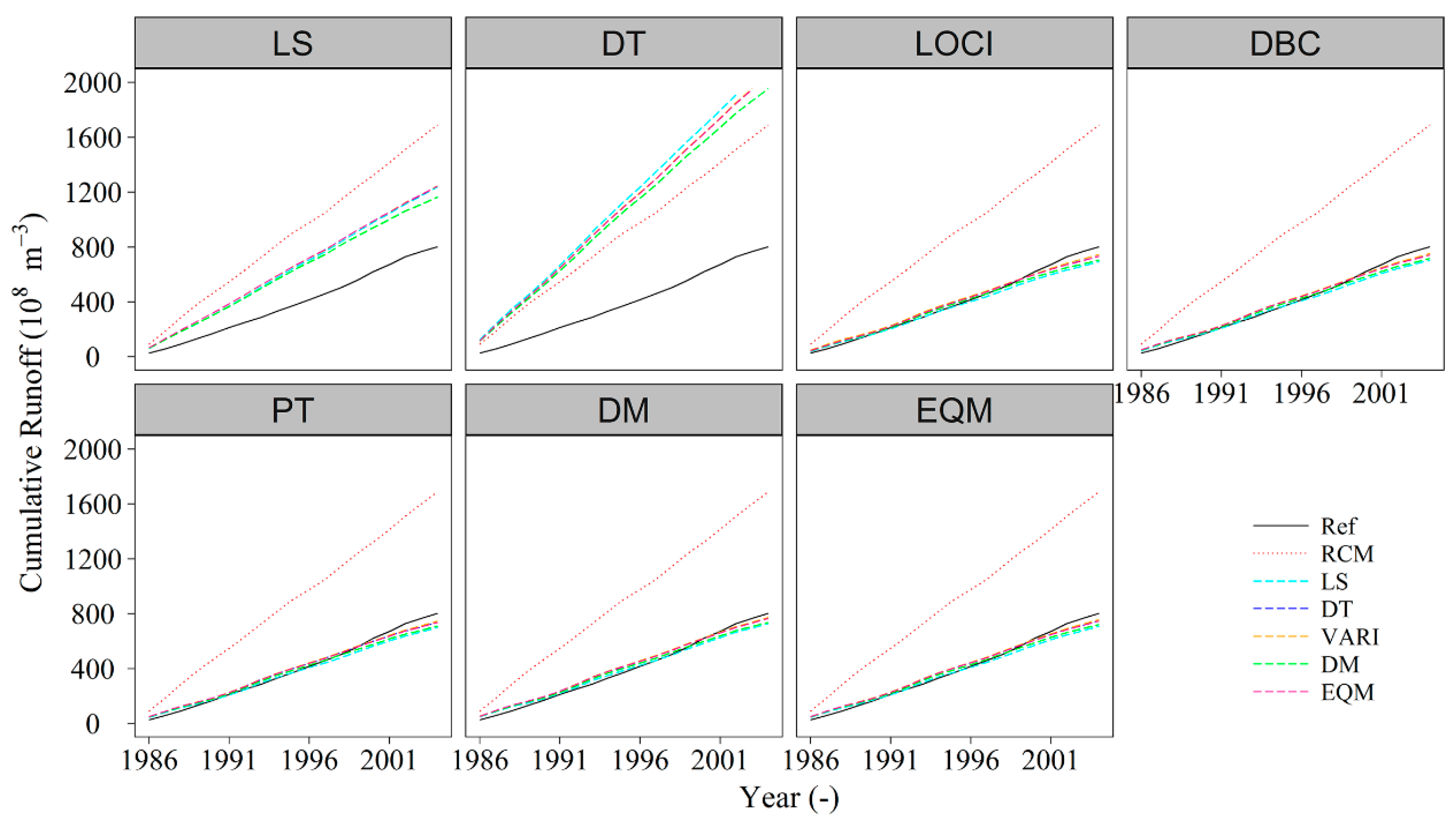
4.4. The Performance of Bias Correction Methods for Hydrological Modelling
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mpelasoka, F.S.; Chiew, F.H. Influence of rainfall scenario construction methods on runoff projections. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 1168–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Regional climate models for hydrological impact studies at the catchment scale: A review of recent modeling strategies. Geogr. Compass 2010, 4, 834–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomo, E.; Jones, R.; Huntingford, C.; Hannaford, J. On the robustness of changes in extreme precipitation over Europe from two high resolution climate change simulations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 133, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Chaumont, D.; Braun, M. Performance and uncertainty evaluation of empirical downscaling methods in quantifying the climate change impacts on hydrology over two North American river basins. J. Hydrol. 2013, 479, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.; Llasat, M.C.; Herrera, S.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Bias correction and downscaling of future rcm precipitation projections using a mos-analog technique. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2631–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durman, C.; Gregory, J.M.; Hassell, D.C.; Jones, R.; Murphy, J. A comparison of extreme European daily precipitation simulated by a global and a regional climate model for present and future climates. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S.; Fita, L.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J. Evaluation of the mean and extreme precipitation regimes from the ensembles regional climate multimodel simulations over Spain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D21117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, A.L.; Rianna, G.; Mercogliano, P.; Tommasi, P.; Comegna, L. Validation of a simulation chain to assess climate change impact on precipitation induced landslides. In Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Crochemore, L.; Ramos, M.-H.; Pappenberger, F. Bias correcting precipitation forecasts to improve the skill of seasonal streamflow forecasts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3601–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Buishand, A.; Deursen, W.V. Estimates of future discharges of the river rhine using two scenario methodologies: Direct versus delta approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Toumi, R. The limitations of bias correcting regional climate model inputs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2907–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Chaumont, D.; Braun, M. Finding appropriate bias correction methods in downscaling precipitation for hydrologic impact studies over North America. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4187–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, T.; Frankl, A.; Duan, Y.; Meng, F.; Bao, A.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Defining spatiotemporal characteristics of climate change trends from downscaled gcms ensembles: How climate change reacts in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2538–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Willems, P.; Pan, X.; Bao, A.M.; Chen, X.; Veroustraete, F.; Dong, Q. Climate change impact on water resource extremes in a headwater region of the Tarim Basin in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 6593–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Quantifying the effects of climate variability and human activities on runoff for Kaidu River Basin in arid region of northwest China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 111, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Chen, X.; Bao, A.; Li, L. The simulation of snowmelt runoff in the ungauged kaidu river basin of Tianshan Mountains, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; De Maeyer, P. Impact of gcm structure uncertainty on hydrological processes in an arid area of China. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, nh2017227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, P.Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, C.; Hong, Y. Combining bpann and wavelet analysis to simulate hydro-climatic processes—A case study of the Kaidu River, northwest China. Front. Earth Sci. 2013, 7, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Lu, F. Climate change and its effects on runoff of Kaidu River, Xinjiang, China: A multiple time-scale analysis. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of climate fluctuations on runoff in the headwater region of the Kaidu River in northwestern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.-J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Hyun, Y.-K.; Cho, C.; Kwon, W.-T.; Marzin, C.; Gan, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Choi, D.-H. Climate change in the 21st century simulated by hadgem2-ao under representative concentration pathways. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 49, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearns, L.O.; Gutowski, W.; Jones, R.; Leung, R.; McGinnis, S.; Nunes, A.; Qian, Y. A regional climate change assessment program for North America. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidli, J.; Frei, C.; Vidale, P.L. Downscaling from gcm precipitation: A benchmark for dynamical and statistical downscaling methods. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, H.; Ekström, M.; Blenkinsop, S.; Smith, A. Estimating change in extreme European precipitation using a multimodel ensemble. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D18104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, E.G.; Gachon, P.; Vrac, M.; Monette, F. Which downscaled rainfall data for climate change impact studies in urban areas? Review of current approaches and trends. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 127, 685–699. [Google Scholar]
- Leander, R.; Buishand, T.A.; van den Hurk, B.J.; de Wit, M.J. Estimated changes in flood quantiles of the river meuse from resampling of regional climate model output. J. Hydrol. 2008, 351, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terink, W.; Hurkmans, R.; Torfs, P.; Uijlenhoet, R. Evaluation of a bias correction method applied to downscaled precipitation and temperature reanalysis data for the rhine basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zammit, C. Comparing bias correction methods in downscaling meteorological variables for a hydrologic impact study in an arid area in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brissette, F.P.; Poulin, A.; Leconte, R. Overall uncertainty study of the hydrological impacts of climate change for a Canadian watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Haerter, J.; Coppola, E. Statistical bias correction for daily precipitation in regional climate models over Europe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, H.C. A note on the gamma distribution. Mon. Weather Rev. 1958, 86, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Weedon, G.; Best, M.; Gomes, S.; Viterbo, P.; Hagemann, S.; Haerter, J. Statistical bias correction of global simulated daily precipitation and temperature for the application of hydrological models. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, A.V.; Hansen, J.W. Bias correction of daily gcm rainfall for crop simulation studies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 138, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenau, G.J.; Kehrig, R.A. Method for calculating degree-days to any base temperature. Energy Build. 1990, 14, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob Themeßl, M.; Gobiet, A.; Leuprecht, A. Empirical-statistical downscaling and error correction of daily precipitation from regional climate models. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Meng, F.; Liu, T.; Duan, Y.; Frankl, A.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Multi–model ensemble approaches to assessment of effects of local climate change on water resources of the Hotan River Basin in Xinjiang, China. Water 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibin, R.; Sudheer, K.; Chaubey, I. Sensitivity and identifiability of stream flow generation parameters of the swat model. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.; Haugen, J.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Downscaling rcm precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations—A comparison of methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D.; Wetterhall, F.; Ireson, A.; Chandler, R.; Kendon, E.; Widmann, M.; Brienen, S.; Rust, H.; Sauter, T.; Themeßl, M. Precipitation downscaling under climate change: Recent developments to bridge the gap between dynamical models and the end user. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, T.; Dadson, S.; Buys, G.; Prudhomme, C. Bias correction of daily precipitation simulated by a regional climate model: A comparison of methods. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellström, E.; Nikulin, G.; Hansson, U.; Strandberg, G.; Ullerstig, A. 21st century changes in the European climate: Uncertainties derived from an ensemble of regional climate model simulations. Tellus A 2011, 63, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerter, J.; Hagemann, S.; Moseley, C.; Piani, C. Climate model bias correction and the role of timescales. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Roderick, M.L.; Lim, W.H.; Farquhar, G.D. Hydroclimatic projections for the murray-darling basin based on an ensemble derived from intergovernmental panel on climate change ar4 climate models. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W00G02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bias Correction for Precipitation | Bias Correction for Temperature |
|---|---|
| Linear scaling (LS) | Linear scaling (LS) |
| Daily translation (DT) | Daily translation (DT) |
| Local intensity scaling (LOCI) | Variance scaling (VARI) |
| Daily bias correction (DBC) | Distribution mapping (DM) |
| Power transformation (PT) | Empirical Quantile Mapping (EQM) |
| Distribution mapping (DM) | |
| Empirical Quantile Mapping (EQM) |
| Component | Parameter Name | Description | Sensitivity Rate | Final Estimate Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snow | SFTMP | Snowfall temperature | 2 | 1.5 |
| SMTMP | Snow melt base temperature | 1 | 0.7 | |
| SMFMX | Melt factor for snow on 21 June | 6 | 7.5 | |
| SMFMN | Melt factor for snow on 21 December | 8 | 2.1 | |
| Subbasin condition | PLAPS | Precipitation lapse rate | 3 | 183 |
| TLAPS | Temperature lapse rate | 4 | −7.8 | |
| Land use/cover | OV_N | Manning’s “n” value for overland flow | 10 | 0.2 |
| CN | Moisture constitution II curve number | 5 | 68 | |
| River course | CH_N2 | Manning’s “n” value for the main channel | 9 | 0.18 |
| CH_K2 | Effective hydraulic conductivity in main channel alluvium | 7 | 240 |
| Parameter | Method | MAE (mm/°C) | PBIAS (%) | NSE (−) | R2 (−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr | RCM | 1.65 | 224.20 | −5.71 | 0.59 |
| LS | 0.27 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.72 | |
| DT | 0.47 | 49.50 | 0.29 | 0.65 | |
| LOCI | 0.29 | −0.20 | 0.69 | 0.69 | |
| DBC | 0.34 | −0.20 | 0.56 | 0.60 | |
| PT | 0.33 | −0.20 | 0.57 | 0.61 | |
| DM | 0.37 | 4.20 | 0.46 | 0.56 | |
| EQM | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.56 | 0.60 | |
| Tas | RCM | 1.99 | 0.7 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| LS | 0.89 | −0.2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| DT | 0.76 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| VARI | 0.78 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| DM | 0.78 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| EQM | 0.76 | 0 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Method (Pr) | Method (Tas) | MAE (m3s−1) | PBIAS (%) | NSE (−) | R2 (−) | Method (Pr) | Method (Tas) | MAE (m3s−1) | PBIAS (%) | NSE (−) | R2 (−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS | LS | 35.26 | 54.60 | −0.88 | 0.70 | PT | LS | 9.76 | −12.80 | 0.81 | 0.91 |
| DT | 35.56 | 55.20 | −0.73 | 0.86 | DT | 6.63 | −8.00 | 0.90 | 0.93 | ||
| VARI | 35.71 | 55.30 | −0.73 | 0.87 | VARI | 5.92 | −6.90 | 0.91 | 0.93 | ||
| DM | 29.37 | 45.20 | −0.33 | 0.87 | DM | 8.75 | −11.50 | 0.85 | 0.92 | ||
| EQM | 35.56 | 55.20 | −0.74 | 0.86 | EQM | 6.58 | −8.10 | 0.90 | 0.93 | ||
| DT | LS | 106.34 | 165.00 | −17.35 | 0.21 | DM | LS | 7.92 | −9.10 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| DT | 92.54 | 143.60 | −12.09 | 0.63 | DT | 5.58 | −4.60 | 0.92 | 0.93 | ||
| VARI | 101.05 | 156.80 | −14.19 | 0.47 | VARI | 5.04 | −3.50 | 0.93 | 0.93 | ||
| DM | 92.54 | 143.60 | −12.09 | 0.63 | DM | 7.85 | −8.10 | 0.88 | 0.91 | ||
| EQM | 100.62 | 156.10 | −13.91 | 0.50 | EQM | 5.53 | −4.50 | 0.92 | 0.93 | ||
| LOCI | LS | 10.10 | −13.80 | 0.79 | 0.91 | EQM | LS | 9.15 | −11.70 | 0.83 | 0.91 |
| DT | 6.62 | −8.70 | 0.89 | 0.94 | DT | 6.14 | −6.80 | 0.91 | 0.93 | ||
| VARI | 5.92 | −6.90 | 0.91 | 0.93 | VARI | 5.49 | −5.60 | 0.92 | 0.93 | ||
| DM | 8.37 | −120 | 0.86 | 0.93 | DM | 8.22 | −10.10 | 0.87 | 0.92 | ||
| EQM | 6.59 | −8.70 | 0.89 | 0.94 | EQM | 6.12 | −6.80 | 0.91 | 0.93 | ||
| DBC | LS | 9.45 | −12.20 | 0.82 | 0.91 | RCM | RCM | 71.31 | 110.60 | −10.13 | 0.42 |
| DT | 6.37 | −7.40 | 0.90 | 0.93 | |||||||
| VARI | 5.75 | −6.20 | 0.91 | 0.93 | |||||||
| DM | 8.52 | −10.80 | 0.86 | 0.92 | |||||||
| EQM | 6.33 | −7.40 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.; Liu, T.; Meng, F.; Duan, Y.; Frankl, A.; Bao, A.; De Maeyer, P. Comparing Bias Correction Methods Used in Downscaling Precipitation and Temperature from Regional Climate Models: A Case Study from the Kaidu River Basin in Western China. Water 2018, 10, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081046
Luo M, Liu T, Meng F, Duan Y, Frankl A, Bao A, De Maeyer P. Comparing Bias Correction Methods Used in Downscaling Precipitation and Temperature from Regional Climate Models: A Case Study from the Kaidu River Basin in Western China. Water. 2018; 10(8):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081046
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Min, Tie Liu, Fanhao Meng, Yongchao Duan, Amaury Frankl, Anming Bao, and Philippe De Maeyer. 2018. "Comparing Bias Correction Methods Used in Downscaling Precipitation and Temperature from Regional Climate Models: A Case Study from the Kaidu River Basin in Western China" Water 10, no. 8: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081046
APA StyleLuo, M., Liu, T., Meng, F., Duan, Y., Frankl, A., Bao, A., & De Maeyer, P. (2018). Comparing Bias Correction Methods Used in Downscaling Precipitation and Temperature from Regional Climate Models: A Case Study from the Kaidu River Basin in Western China. Water, 10(8), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081046






