Effects of the Notch Angle, Notch Length and Injection Rate on Hydraulic Fracturing under True Triaxial Stress: An Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Notch Angle
3.2. Effect of Notch Length
3.3. Effect of Injection Rate
3.4. Fracture Geometry
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A larger notch length and injection rate but a smaller notch angle is responsible for the decrease in fracture initiation pressure.
- (2)
- The fracture propagation geometry may not be directly related to the notch length and injection rate but rather, governed by the notch angle.
- (3)
- The propagation direction of a hydraulic fracture is at an angle to the horizontal direction and the surface of hydraulic fracture is a curved surface when the notch plane is not perpendicular to the direction of the minimum principal stress.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fallahzadeh, S.; Hossain, M.; Cornwell, A.J.; Rasouli, V. Near wellbore hydraulic fracture propagation from perforations in tight rocks: The roles of fracturing fluid viscosity and injection rate. Energies 2017, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, B.; Tsang, C.F.; Rutqvist, J.; Niemi, A. The effects of nearby fractures on hydraulically induced fracture propagation and permeability changes. Eng. Geol. 2017, 228, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Cheng, L.; Ge, Z.L.; Xia, B.W.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.F. Analysis on the initial cracking parameters of cross-measure hydraulic fracture in underground coal mines. Energies 2015, 8, 6977–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Cheng, Y.G.; Ge, Z.L.; Cheng, L.; Zuo, S.J.; Zhong, J. Determination of fracture initiation locations during cross-measure drilling for hydraulic fracturing of coal seams. Energies 2016, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Zuo, S.J.; Ge, Z.L.; Xiao, S.Q.; Cheng, Y.G. Experimental study of crack initiation and extension induced by hydraulic fracturing in a tree-type borehole array. Energies 2016, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Ito, T.; Tamagawa, T.; Tezuka, K. A study of the effect of brittleness on hydraulic fracture complexity using a flow-coupled discrete element method. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 160, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Numerical investigation of fracture spacing and sequencing effects on multiple hydraulic fracture interference and coalescence in brittle and ductile reservoir rocks. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 157, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahzadeh, S.; Rasouli, V.; Sarmadivaleh, M. An investigation of hydraulic fracturing initiation and near-wellbore propagation from perforated boreholes in tight formations. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanniarachchi, W.A.M.; Gamage, R.P.; Perera, M.S.A.; Rathnaweera, T.D.; Gao, M.Z.; Padmanabhan, E. Investigation of depth and injection pressure effects on breakdown pressure and fracture permeability of shale reservoirs: An experimental study. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Narayan, S.P.; Yang, Z.; Rahman, S.S. An experimental investigation of hydraulic behaviour of fractures and joints in granitic rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2000, 37, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, G.Q. Analysis of fracture propagation behavior and fracture geometry using a tri-axial fracturing system in naturally fractured reservoirs. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2008, 45, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jin, Y.; Chen, M. Experimental investigation of hydraulic fracturing in random naturally fractured blocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2010, 47, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y. Critical hydraulic gradient for nonlinear flow through rock fracture networks: The roles of aperture, surface roughness, and number of intersections. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 88, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y. A fractal model based on a new governing equation of fluid flow in fractures for characterizing hydraulic properties of rock fracture networks. Comput. Geotech. 2016, 75, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X. A fractal model for characterizing fluid flow in fractured rock masses based on randomly distributed rock fracture networks. Comput. Geotech. 2015, 65, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, L. Estimating permeability of porous media based on modified Hagen–Poiseuille flow in tortuous capillaries with variable lengths. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, R.; Jiang, Y. Influences of hydraulic gradient, surface roughness, intersecting angle, and scale effect on nonlinear flow behavior at single fracture intersections. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
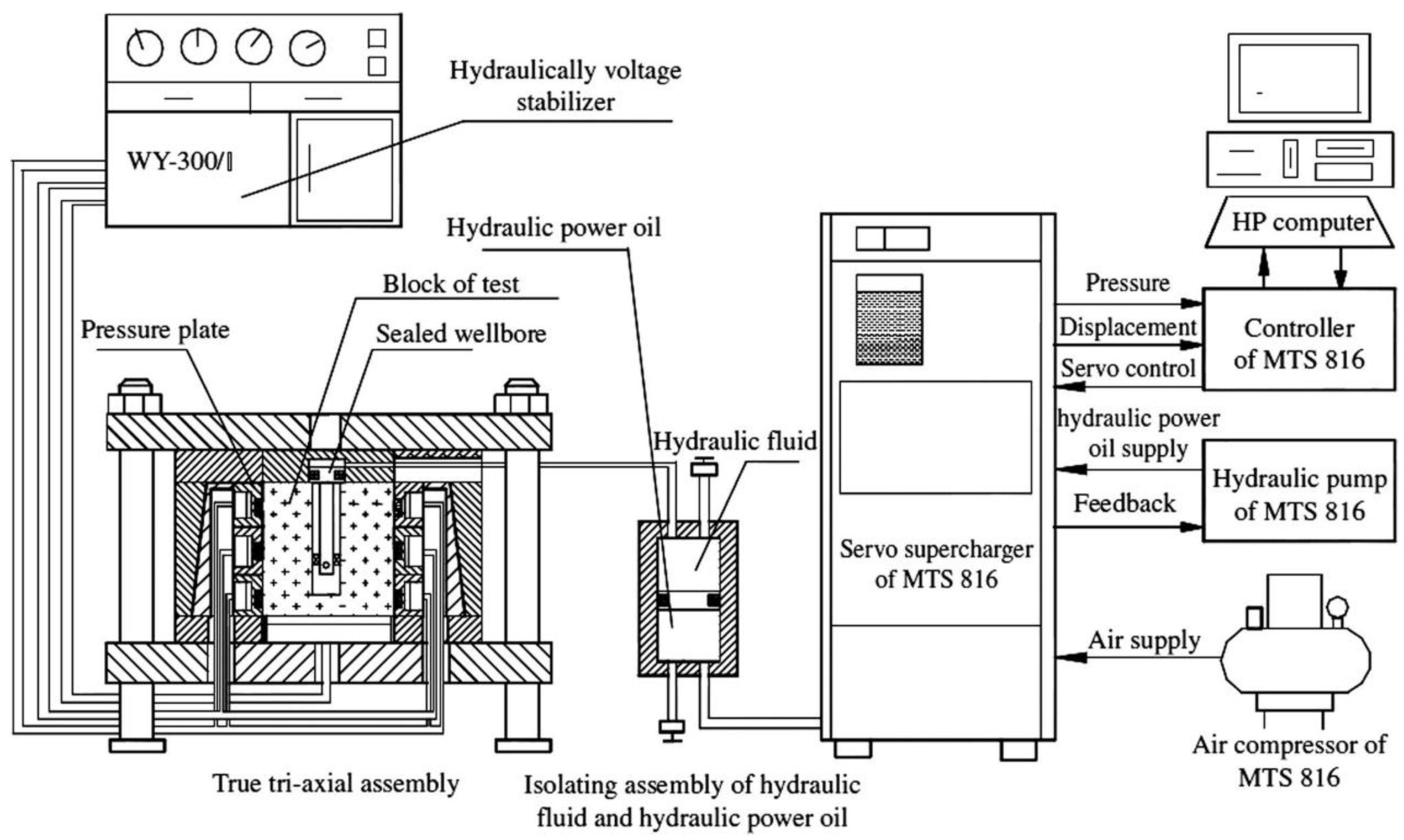
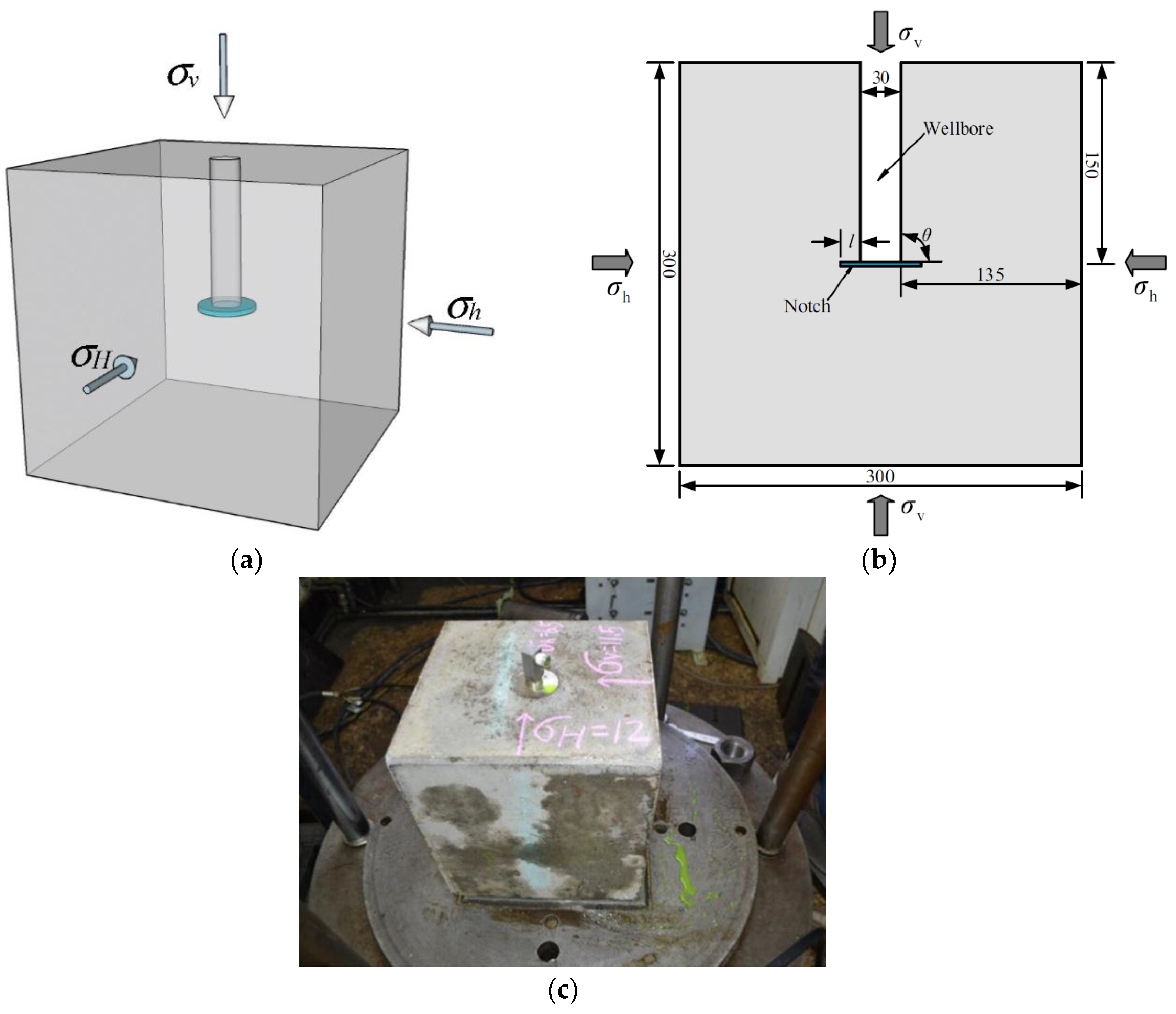
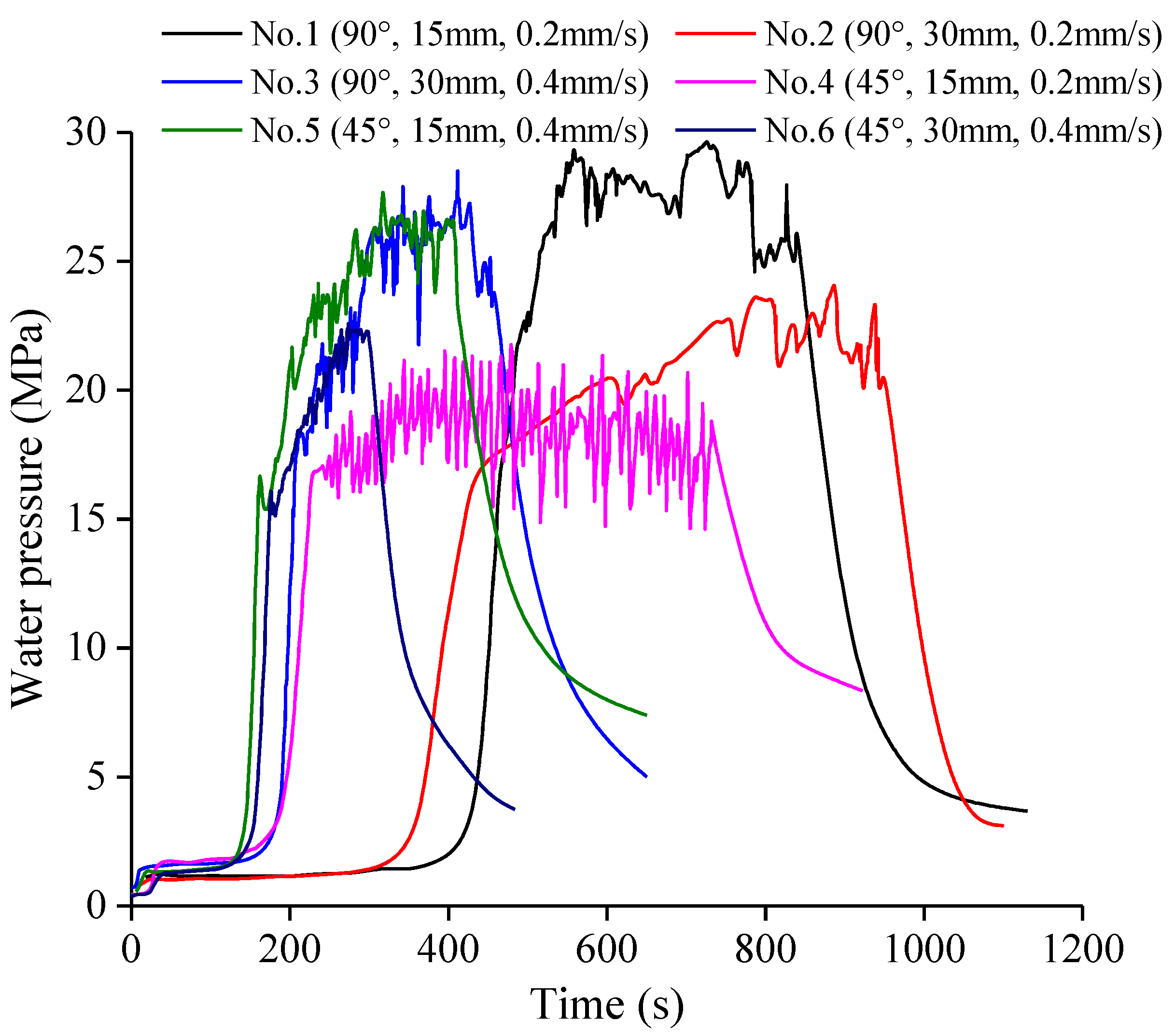
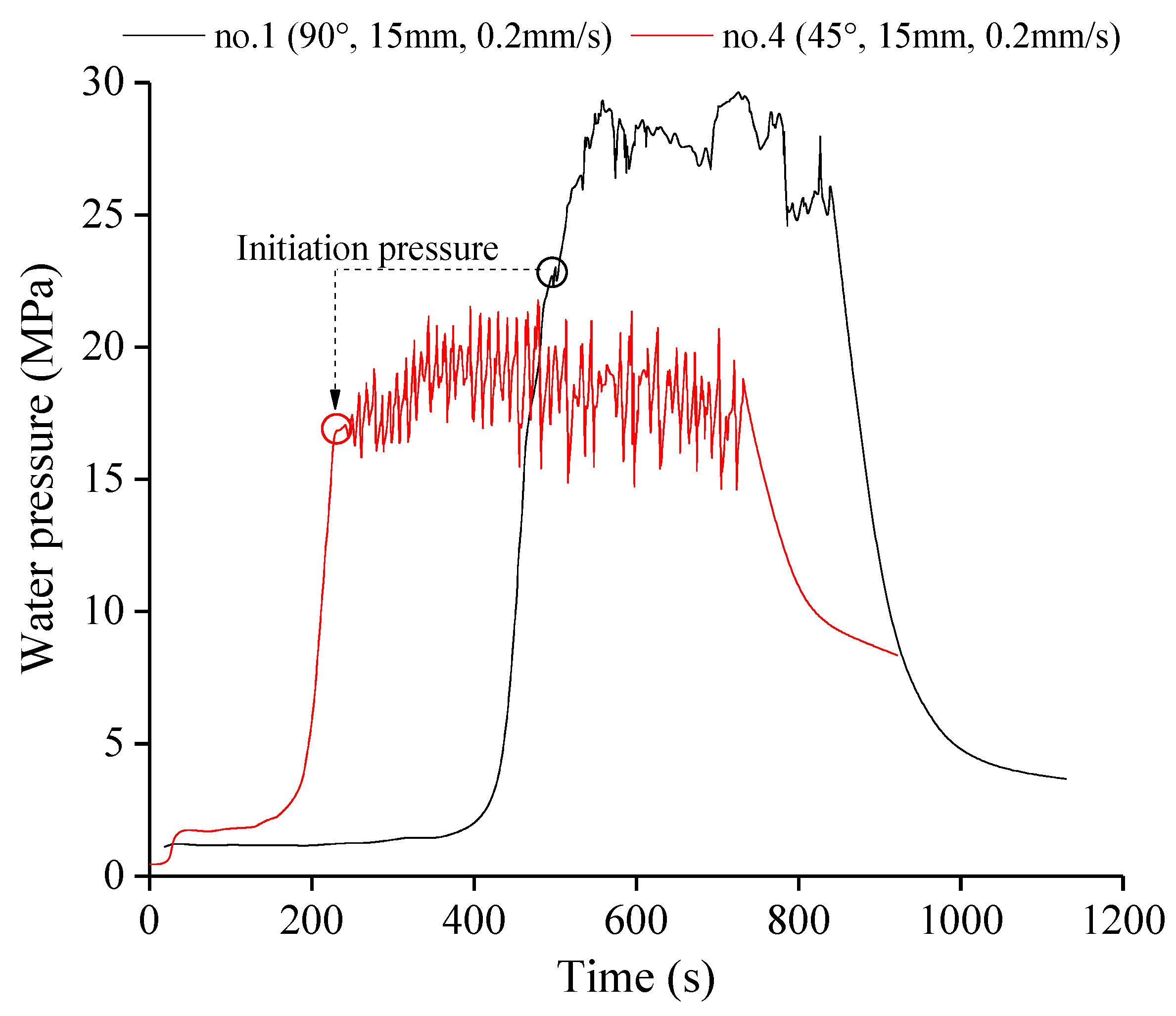
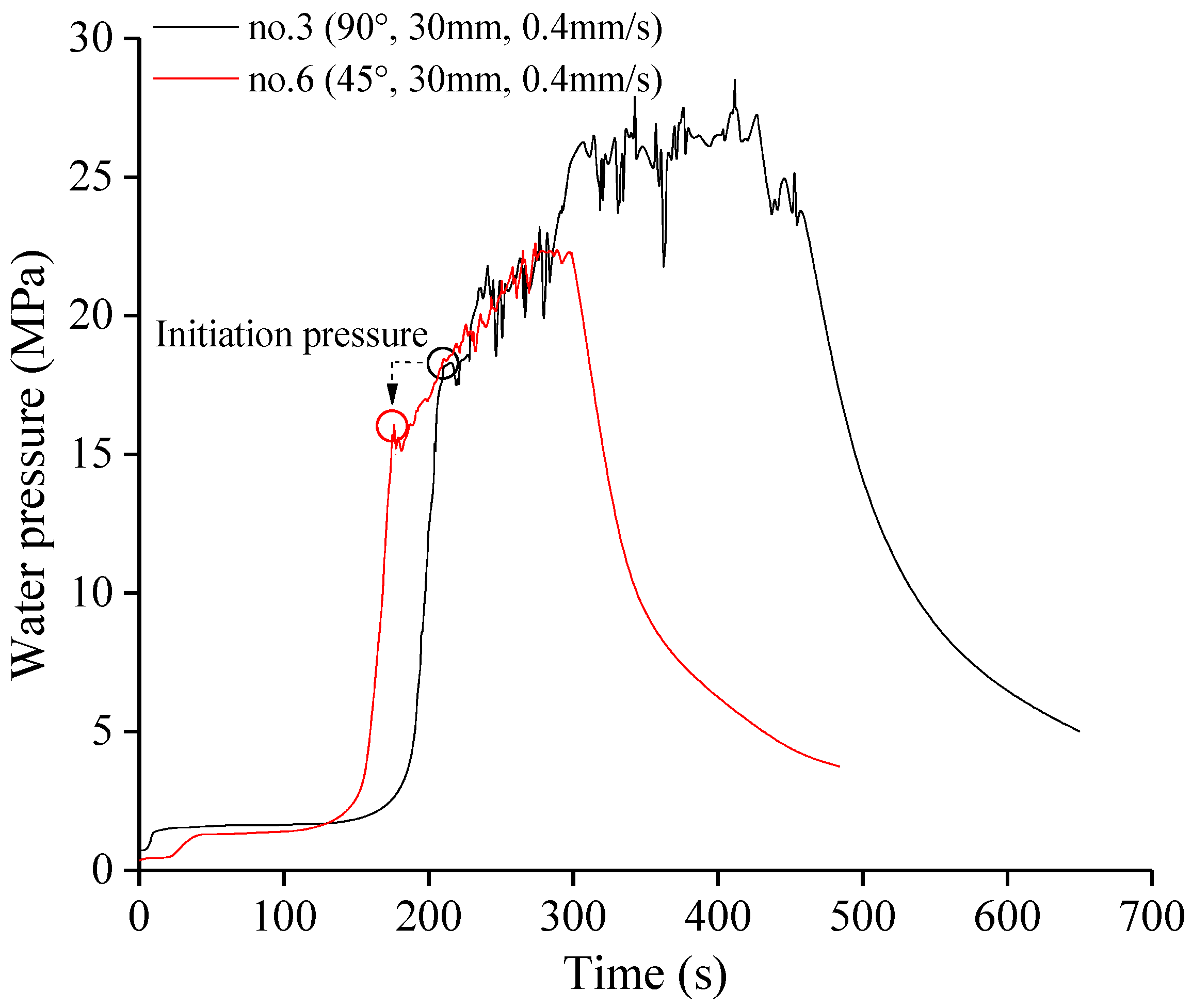
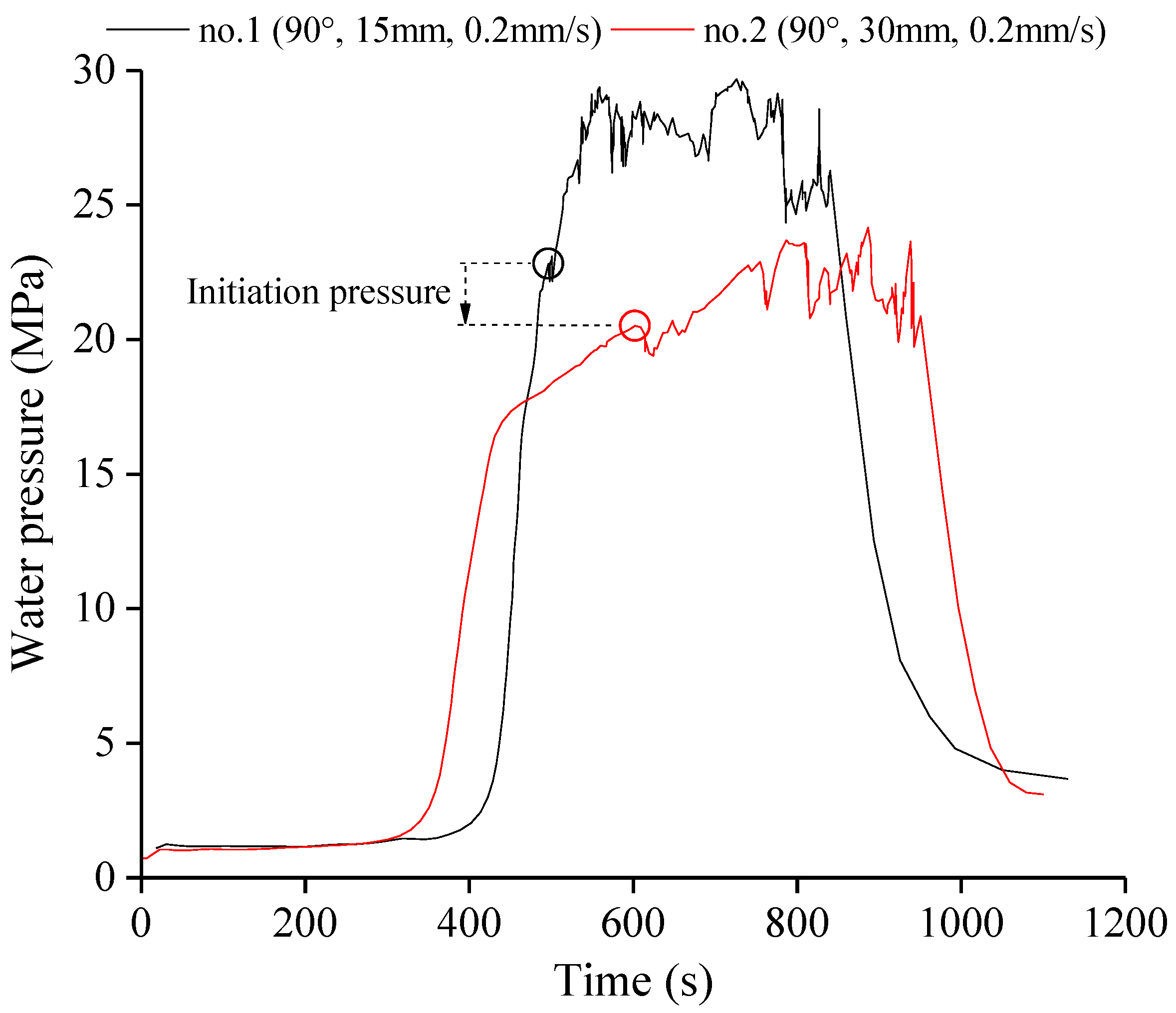

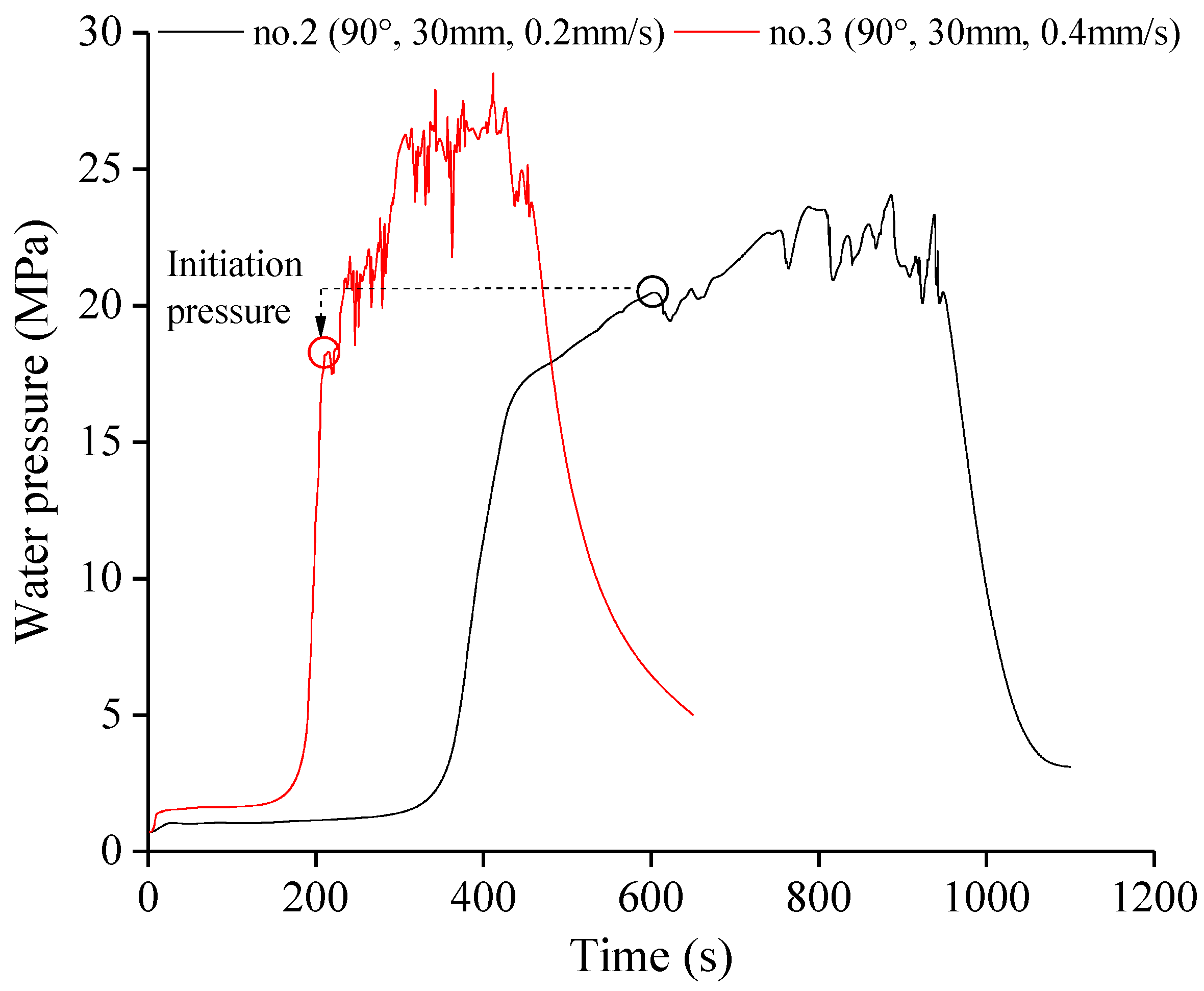
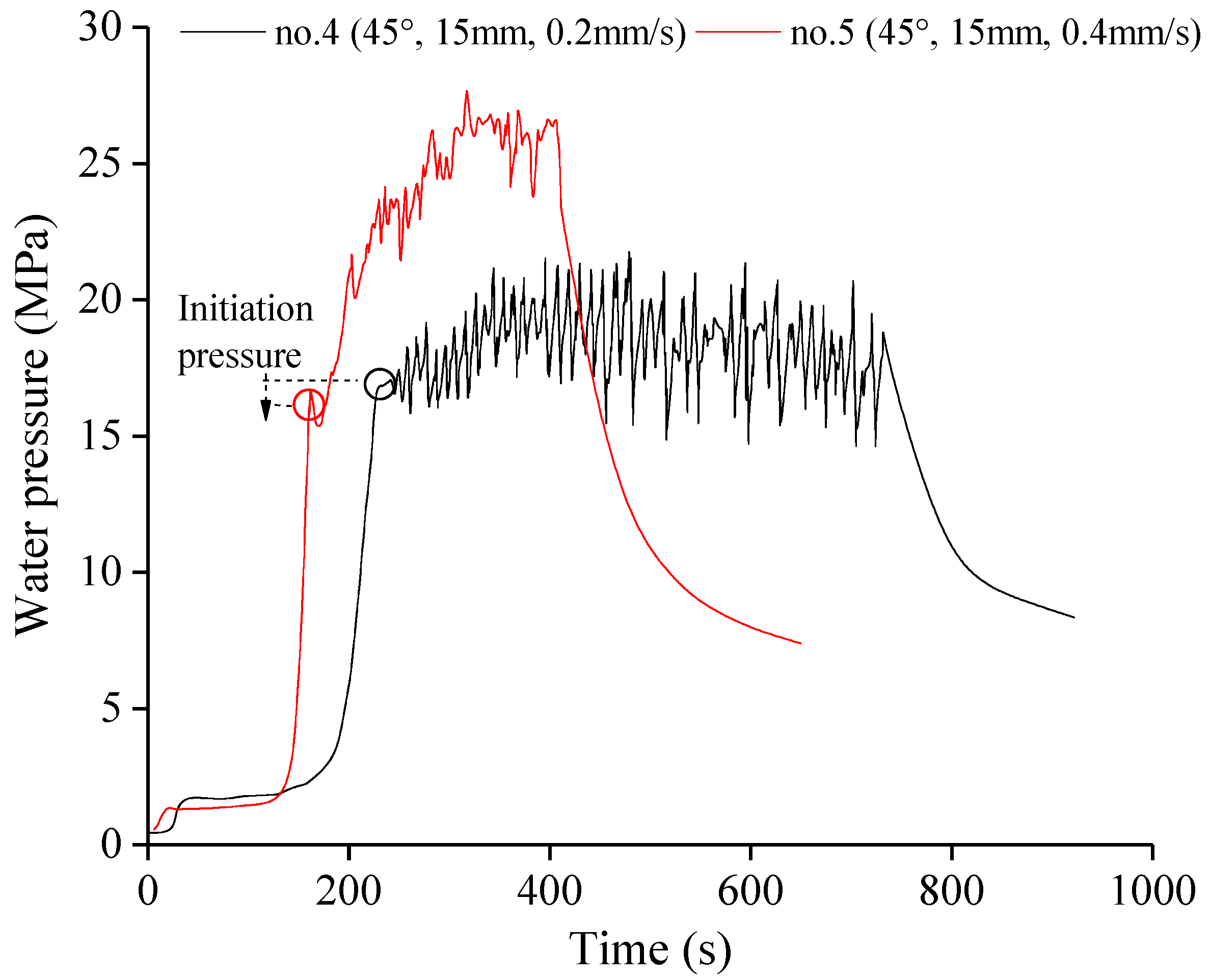
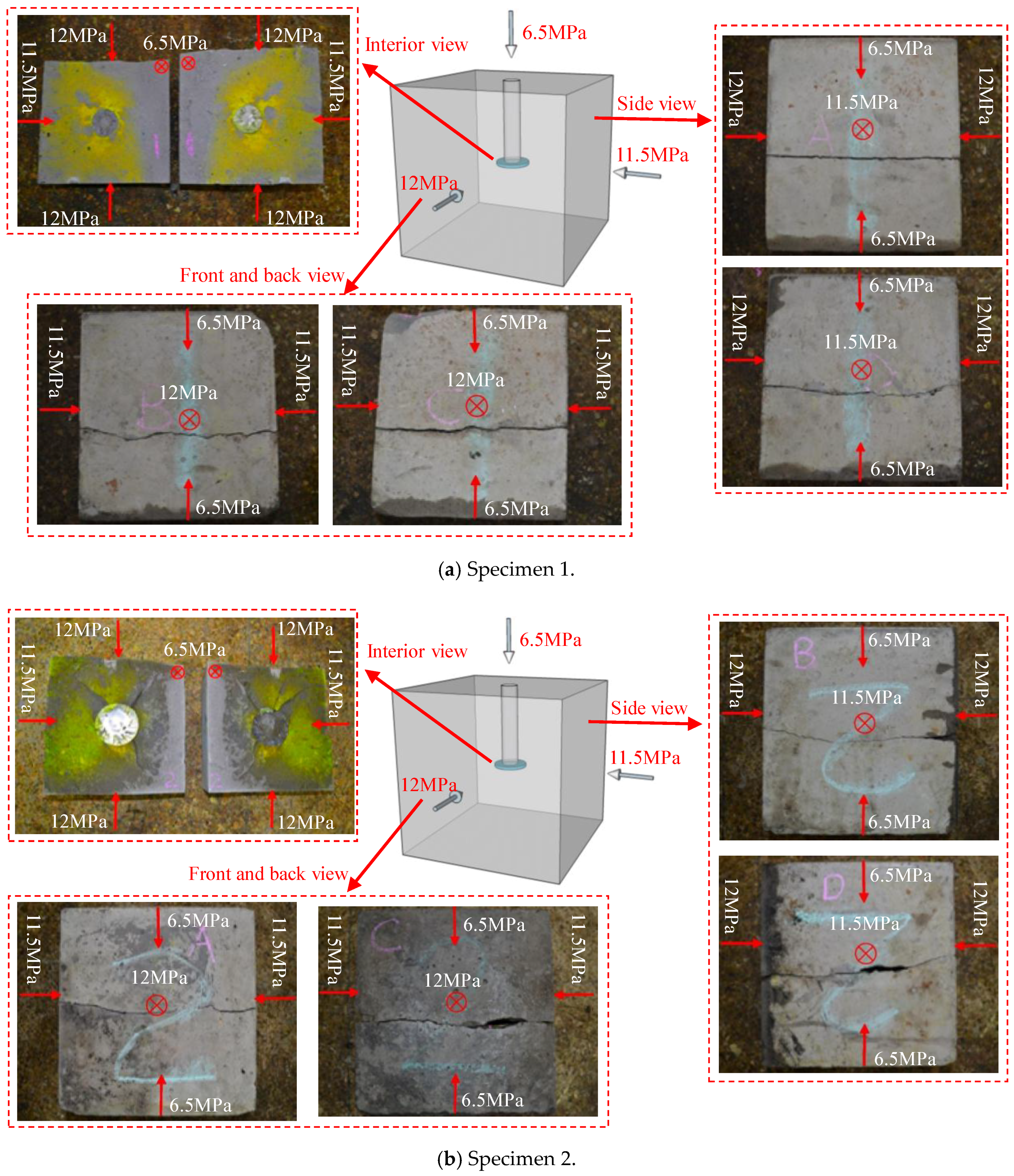
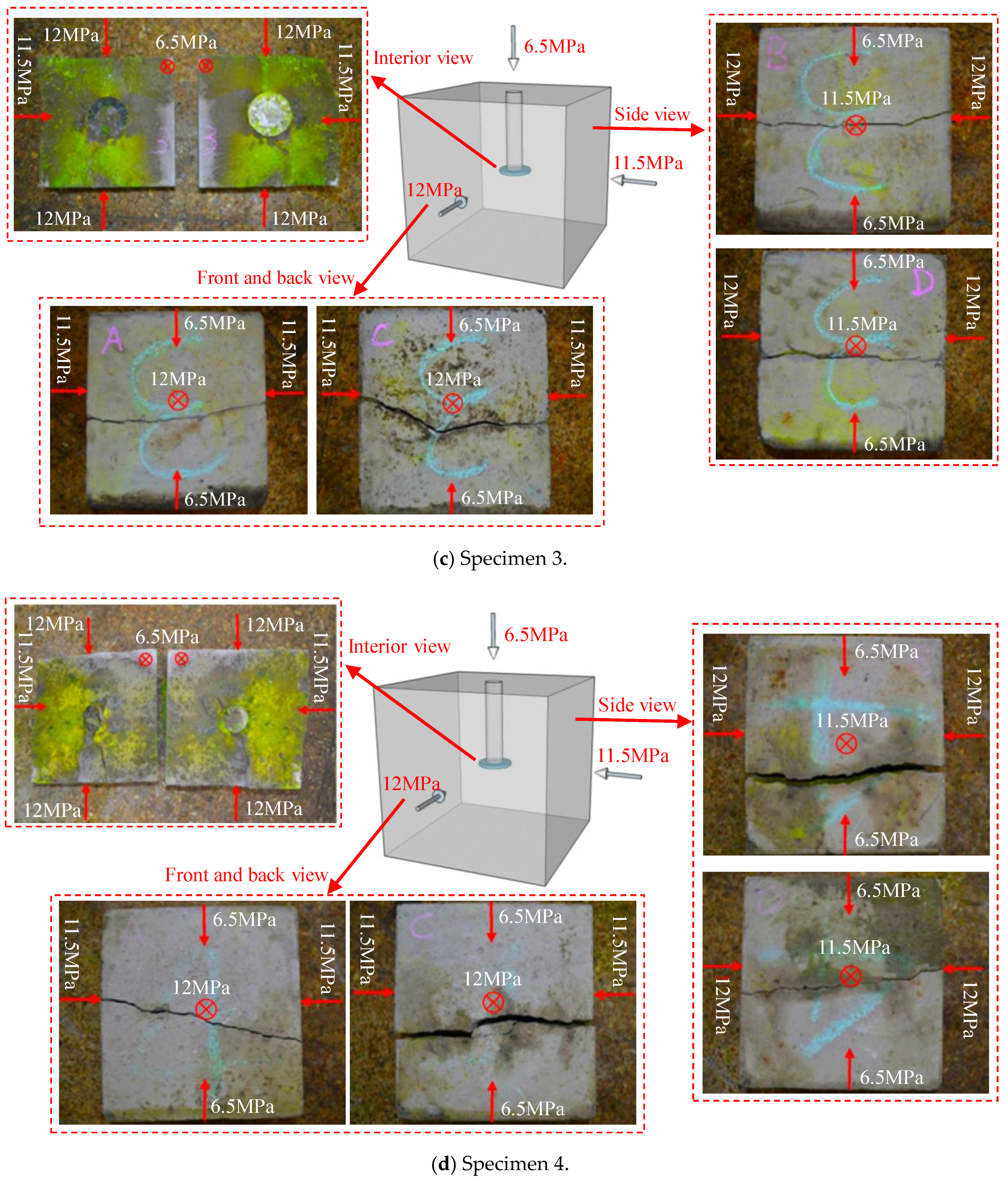
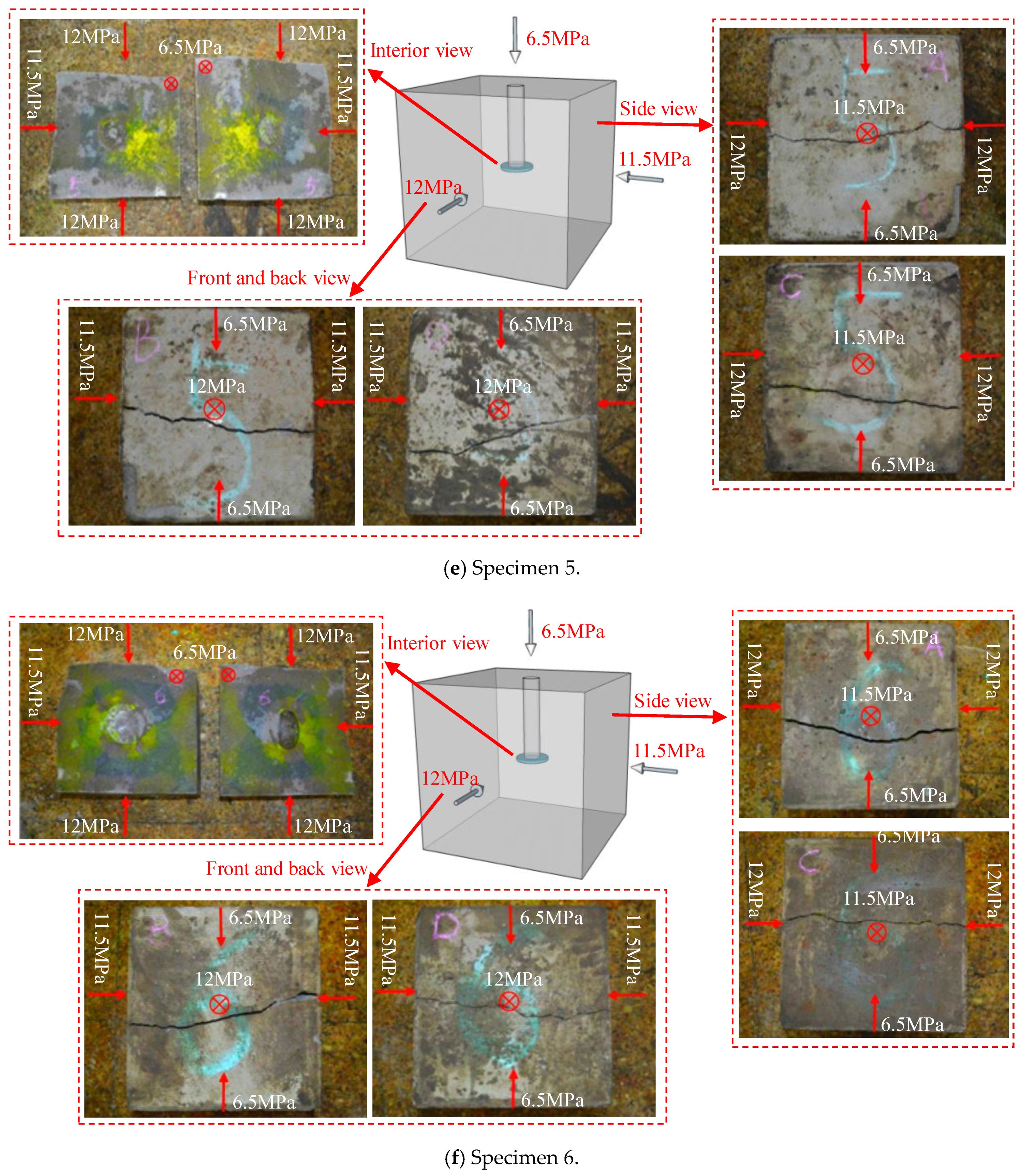
| Specimen | Stress State | θ (°) | l (mm) | v (mm/s) | pi (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | σv = 6.5 MPa, σH = 12.0 MPa, σh = 11.5 MPa | 90 | 15 | 0.2 | 22.81 |
| 2 | 90 | 30 | 0.2 | 20.50 | |
| 3 | 90 | 30 | 0.4 | 18.29 | |
| 4 | 45 | 15 | 0.2 | 16.90 | |
| 5 | 45 | 15 | 0.4 | 16.15 | |
| 6 | 45 | 30 | 0.4 | 16.02 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, J. Effects of the Notch Angle, Notch Length and Injection Rate on Hydraulic Fracturing under True Triaxial Stress: An Experimental Study. Water 2018, 10, 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10060801
Chen Y, Meng Q, Zhang J. Effects of the Notch Angle, Notch Length and Injection Rate on Hydraulic Fracturing under True Triaxial Stress: An Experimental Study. Water. 2018; 10(6):801. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10060801
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yulong, Qingxiang Meng, and Jianwei Zhang. 2018. "Effects of the Notch Angle, Notch Length and Injection Rate on Hydraulic Fracturing under True Triaxial Stress: An Experimental Study" Water 10, no. 6: 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10060801
APA StyleChen, Y., Meng, Q., & Zhang, J. (2018). Effects of the Notch Angle, Notch Length and Injection Rate on Hydraulic Fracturing under True Triaxial Stress: An Experimental Study. Water, 10(6), 801. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10060801





