Abstract
This study investigates the utility of satellite-based rainfall estimates in simulating flash floods in Karpuz River Basin, Turkey, characterized by limited rain gauge network. Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) product was evaluated with the rain gauge network at daily and monthly time-scales considering seasonality, elevation zones, extreme events and rainfall intensity thresholds. Statistical analysis indicated that GSMaP shows acceptable linear correlation coefficient with rain gauges, however, suffers from significant underestimation bias. Statistical measures exhibited a remarkable deterioration with increasing elevation-following a linear relationship; for example, percent bias was found to increase by a rate of 11.7% with every 400 m interval. A multiplicative bias correction scheme was devised, and Hydrological River Basin Environmental Assessment Model (Hydro-BEAM) was implemented to simulate flash floods driven by the uncorrected/corrected GSMaP data. Analysis of intensity thresholds revealed that appropriate threshold selection is critically important for the bias correction procedure. The hydrological model was calibrated for flash flood events during October–December 2007 and 2012 and validated during October–December, 2009 and 2010. Flash floods simulations were improved by the local bias correction procedure applied to the GSMaP data, but the degree of improvement varied from one period to another. The results of the study indicate that bias factors incorporating multiple variables such as extreme events and elevation variability have the potential to further improve flood simulations.
1. Introduction
Globally, flash floods are among the most devastating natural hazards regarding both mortality and economic loss [1,2]. In particular, the Mediterranean region is projected to become increasingly exposed to flash floods due to the projected increase in hydrologic extremes [3] and rapid population growth. Flood early warning systems are important tools to effectively mitigate flood-induced hazards. Operation of early warning systems requires good-quality observations (precipitation, streamflow, etc.), reliable model(s)—for hydrologic and weather prediction—and adequate lead time for the warning to be issued. However, each of the above factors are problematic when it comes to predicting flash floods; for example, see [4]. In the Mediterranean region, flash floods are triggered by heavy precipitation events with accumulated rainfall higher than 100 mm, often within a few hours. Such intense rainfall events are naturally induced by quasi-stationary mesoscale convective systems [5]. The concurrence of such heavy rainfall events superimposed on the Mediterranean catchments, characterized by small area, steep topography, and very poor land cover, often triggers devastating flash flood events. Thus, both small scale occurrence and rapid onset of flash flood events hinder observation, prediction and warning efforts. Although coordinated efforts have been made to improve the flash flood forecast skill in the Mediterranean region (e.g., The Hydrological Cycle in the Mediterranean Experiment (HyMeX) program and EU Project HYDRATE [6] in Europe), these efforts do not span the whole Mediterranean region, and the accuracy of the models is still insufficient. Estimates of extreme rainfall rates by weather radar at space and time scales appropriate for flash floods is seen as the cornerstone for flash flood modelling [7]. However, complex topography associated with the Mediterranean basins complicates the radar signal with ground clutter and mountain blockage [6]. Majority of the Mediterranean basins are poorly gauged or ungauged, hence making satellite-based precipitation (SBP) retrieval algorithms potentially attractive for basin scale hydrologic studies over these regions.
Although SBP products are freely available for most regions of the world, they have certain limitations, primarily due to the indirect nature of precipitation retrieval. Satellite-based precipitation algorithms estimate precipitation rate based on remote sensing features of clouds derived from the sensors that are sensitive to visible (reflectivity of clouds), infrared (IR; cloud-top temperature; [8], and microwave (scattering from rain/ice particles; [9] portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Visible and IR sensors are accessible on geostationary orbiting satellites and hence offer data at fine temporal scales. However, precipitation estimates by these sensors are rather crude because the cloud-top temperature is indirectly—and often poorly—related to precipitation. Passive Microwave (PMW) sensors on polar-orbiting satellites provide more precise estimates of precipitation but with low temporal resolutions. Recent SBP products merge information from several sources, such as rain gauges, PMW, and IR, to get the benefit of the strengths of such sources. A few free and open access SBP products to note are The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA; [10,11], Climate Prediction Center (CPC) MORPHing technique (CMORPH) [12,13]), PERSIANN: Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks [14] and PERSIANN-CDR [15], Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) [16,17], and IMERG [18]. Some of these quasi-global SBP products incorporate rain gauge information from globally available datasets (such as GPCC) which are generally insufficient for resolving spatio-temporal characteristics of rainfall required for basin scale hydrologic applications. Hence, many researchers developed bias adjustment algorithms to correct satellite-only SBP products with locally-available, relatively dense gauge networks reporting at or near real time. The nature of the bias adjustment algorithms highly depend on the density of the available gauge networks, and include deterministic bias correction models such as additive [19], multiplicative [20] or a combination of the additive/multiplicative models [21], inverse distance weighting [22], linear regression models [23], artificial neural networks [24] and geostatistical models such as various types of Kriging [25,26]. In the literature, many studies conclude that bias correction of satellite-based precipitation products using ground-based observations leads to improvement in hydrological model performance [27].
Satellite-based remote sensing products are increasingly becoming more applicable in hydrological studies. Therefore, techniques focusing on enhancement of the quality as well as spatial and temporal resolutions of the satellite-based rainfall measurements are crucial to understanding the hydrological processes in many regions that suffer from a lack of dense ground-based measurement network. The availability of such products at spatial and temporal scales that are relevant to hydrologic and hydraulic modeling studies can sensibly improve the reliability of the simulated variables of interest [28]. As such, the MOXXI (Measurements and Observations in the XXI century) Working Group highlighted and proposed multi-disciplinary and innovative approaches for merging all the available rainfall data sources such as rain gauges, radar data, and satellite-based products, that could provide a better rainfall estimation to improve the quality of hydrological analysis. For example, a distributed rainfall methodology was developed from satellite-based soil moisture observations by Brocca et al. [29].
The literature on the utility of SBP products for flood simulation has been rapidly growing over the last decade [30,31]. Mei et al. [32] investigated the errors in SBP products and its propagation in streamflow simulations regarding rainfall and runoff volumes and time series shape in the Eastern Italian Alps. The study concluded that the SBP products can capture the shape parameters of the events better and that the gauge adjustments have an effect on the volumetric parameters but not on the shape parameters. Kim, et al. [33] examined the uncertainty in the satellite-derived precipitation data and its propagation through the hydrological model. They stated that GSMaP and CMORPH products suffer from the consistent underestimation of precipitation and more significantly during the wet periods. The feasibility of using satellite rainfall estimates to simulate flash floods was investigated at complex terrain basins in Northern Italy [34]. They found that the simulated hydrographs only become meaningful after recalibration of the model, separately for each satellite precipitation products.
Only a few studies have investigated the utility of SBP products in the Mediterranean region. In particular, Stampoulis et al. [35] studied the error analysis of SBP products for flood producing heavy precipitation events over complex terrain basins in Italy and France and found that precipitation type has an important effect on the SBP product accuracy. Similarly, Mei et al. [32] investigated the error in SBP-driven hydrological model simulation over complex terrain in Eastern Italian Alps and found that error characteristics revealed the dependency on the flood type (rain floods vs. flash floods). They concluded that random error dampening effect is less evident for the flash flood events. Ciabatta et al. [36] stated that integration of observed and satellite rainfall data led to more accurate rainfall input with respect to ground observations for discharge simulation over Italy. Milewski et al. [37] evaluated the TMPA products against 125 rain gauges in northern Morocco and found that TMPA products overestimated precipitation in arid regions and underestimated in high elevations. Tramblay et al. [38] evaluated various SBP products for hydrological modelling in Makhazine catchment, Morocco and reported that hydrological model driven by the TMPA product (Version 7) resulted in poor performance in simulating daily discharge while being adequate at the monthly timescale. Although several studies have evaluated SBP products over Turkey [39,40], the performance of these products has not yet been evaluated over the Mediterranean region of Turkey in hydrologic modelling.
In general, most of the previous studies for floods simulation were conducted by using the hydrological models, but recently, hydraulic models have been increasingly used in such applications. Several studies have been performed for coupling of hydrological and hydraulic models (e.g., [41,42,43]), and application for hydrodynamics models (e.g., [44,45,46,47,48]). An investigation of the coupled models in improving the flow simulations and reducing the uncertainty in arid and semi-arid regions would provide interesting perspectives. For instance, coupling the hydrological models for the upstream catchments and hydraulic models for the downstream and floods plains could potentially improve the model performance, especially for flash floods in arid and semi-arid regions.
Mediterranean coast of Turkey is prone to frequent flash floods. In Turkey, flooding is the second most important natural hazards, after the earthquakes with 22 floods and 19 deaths per year on average [49]. Turkey is the fourth Mediterranean country with the highest loss from flash floods after Italy, France, and Romania [50]. Moreover, the Mediterranean region of Turkey is marked by rapid population growth and urbanization, which will likely exacerbate the impacts of flash floods. Therefore, the main goal of this paper is to investigate the utility of SBP products in modelling flash flood events over the Mediterranean catchments characterized by scarce ground-based observations and steep topography. This goal is achieved in three major steps. First, SBP estimates from the GSMaP product is compared with the rain gauge-based estimates around Karpuz River basin located in the city of Antalya, Turkey. Next, a simple bias correction scheme is devised to correct the GSMaP precipitation estimates using a relatively scarce rain gauge network. Lastly, a distributed hydrologic model suited to flash flood simulation is driven by GSMaP-based precipitation estimates before and after the bias correction scheme, and the simulation performance is assessed using observed hydrographs of flash flood events together with performance statistics. This last step is seen as an independent check on the accuracy of the GSMaP product before and after the bias correction.
2. Study Area, Datasets and Hydrologic Model
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located to the east of Antalya city in the Mediterranean region of Turkey (Figure 1). According to the Köppen climate classification, the climate of the Mediterranean region is characterized by hot, dry, sunny summers and rainy winters. The study area is located between 36.00 N–37.50 N latitude bands and 30.50 E–32.50 E longitude bands covering an area of about 1920 km2. Note that only the land area within this bounding grid was considered for the analysis (Figure 1a). This area was considered for the satellite data in comparison to the rain gauges due to the coarse resolution of satellite data. However, for flash floods simulation, Karpuz River basin (Figure 1b) was selected. Karpuz River basin (Figure 1b) is located in the study area between 36.6–37 N latitude bands, and 31.5–32.1 E longitude bands, and covers an area of 303 km2.
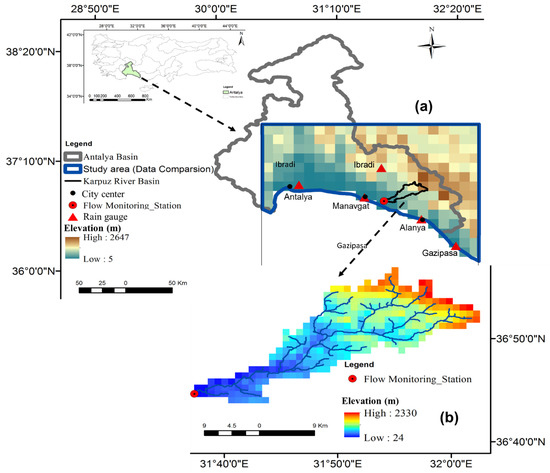
Figure 1.
The study area selected for the comparison between GSMaP and rain gauge data (a), Karpuz River basin and the digital elevation model (DEM) at 1 km × 1 km spatial resolution grids matching the hydrologic model resolution (b).
Settlements located around Karpuz Stream valley are Akseki, Gündoğmuş, Taşkent, Manavgat, Alanya and İbradı towns. Karpuz Stream flows through the mountains and discharges into Mediterranean sea near Manavgat [51]. The study region is topographically complex including mountainous regions with elevations reaching up to 2500 m (Figure 2a). Based on AVHRR satellite land cover classification [52], the dominant land cover in the study area varies between grassland and shrub lands with sparse woodlands (Figure 2b). The daily rainfall data (Figure 2c) show that the region is characterized by a dry season (April–September), and a wet season (October to March). The extreme rainfall events usually occurred in the rainy seasons, especially in November and December. Climatologically, the region has a Mediterranean climate conditions with hot to dry summer and rainy winter. Temperature is variable between 2 °C in the winter and 36 °C during the summer (Figure 2d).
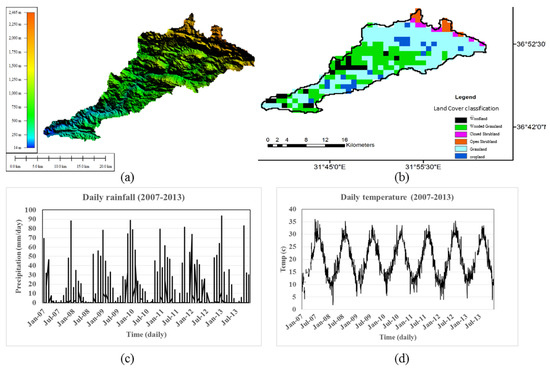
Figure 2.
Topography of the study area based on ASTER Global DEM (a), Land cover classification obtained from AVHRR satellite data (b), daily precipitation data (c), and daily air temperature (°C) data (d).
2.2. Satellite-Based and Rain Gauge-Based Precipitation Datasets
The GSMaP project was supported by Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and promoted by the JAXA Precipitation Measuring Mission (PMM) Science Team, and was disseminated by the Earth Observation Research Center, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The GSMaP algorithm combines the information from microwave and infrared radiometers aboard multiple satellites [53]. The algorithmic structure of the GSMaP products was discussed in detail in the literature [16,54,55,56]. GSMaP products are offered at two spatial resolutions: 0.1° × 0.1° and 0.25° × 0.25° grids, and two temporal scales: hourly and daily. The GSMaP product is provided at various processing levels (satellite-only vs. corrected) as listed in Table A1 (See Appendix A). In this study, we used hourly GSMaP data with 0.1° × 0.1° spatial resolution.
Daily precipitation data from five rain gauge stations distributed over the study area were obtained from the General Directorate of Meteorology in Turkey (Table A2 in Appendix A). The rain gauge data and GSMaP product span different time periods, thus an overlapping period (2007–2013) was selected for the study. The time stamps of both GSMaP and rain gauge data were adjusted for proper comparison.
2.3. Hydrologic Model Description and Implementation
The Hydrological River Basin Environmental Assessment Model (Hydro-BEAM) was chosen to simulate flash floods in the study basin. Hydro-BEAM is a distributed hydrological model originally developed by [57], which subsequently was adopted to simulate flash floods in arid regions [58,59,60], and later utilized to investigate the flash floods response with respect to geomorphic parameters in wadi basins [61]. HydroBEAM model was also used as a tool for integrated water management [62,63] and for climate change applications in Japan [64,65]. The Hydro-BEAM model includes a GIS interface for data input and visualization, surface runoff and stream routing components based on the kinematic wave approximation. The initial and transmission losses are estimated based on the Curve Number approach [66] and Walter’s equation [67], respectively, and groundwater component is represented by a linear storage model. Hydro-BEAM is a distributed model consisting of horizontal spatial discretization, the scale of which could be adjusted based on the basin scale. Each pixel is vertically represented by a combination of one surface layer and three subsurface layers. The surface and subsurface layers are noted as A, B, C and D. A-Layer and the river channel are governed by the kinematic wave model for the overland flow estimation and the subsurface layers are modeled based on the linear storage model. The Hydro-BEAM model has been widely used for flash floods modeling in arid regions such as in Oman, Egypt, and Saudi Arabia [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69], mainly due to its advantages including spatially distributed representation of the catchment processes and capability for daily and hourly simulations. Moreover, the model code is written in FORTRAN language, thus enabling easy and rapid reproduction and modification of the code for various hydrological applications.
The model setup was implemented using spatial characteristics of the study basin (i.e., elevation, flow direction, basin boundary, river channel, land use/landcover types and spatial grid resolution). ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model [70] having a 30 m spatial resolution was used to identify the stream network and to delineate the watershed boundary. Global Land Cover Characterization (GLCC) dataset [71] having a 1 km2 spatial resolution was used to classify the land use types. The Hydro-BEAM model was implemented at 1 km × 1 km spatial resolution. Hourly GSMaP rainfall data before and after bias correction (see Section 3.1.2) was used as the input to the model. Thornthwaite method was used to calculate daily mean potential evapotranspiration for each grid considering the data availability.
3. Methodology
3.1. Comparison of GSMaP Product with Rain Gauge Dataset
The objective of the comparison was to evaluate the GSMaP product with the rain gauge dataset in the surroundings of the Karpuz River Basin. The evaluation period spans the years 2007 through to 2013 based on the rain gauge data availability. The rain gauge rainfall data were interpolated to a 0.1° × 0.1° spatial resolution grid to be consistent with the spatial resolution of the GSMaP data using the automated Thiessen polygon generation algorithm [72], based on the distance formula:
where, D is the distance between the target pixel centroid (x, y), and the rain gauge i and j refer to the number of stations and the pixel numbers, respectively. In this technique, the pixels are allocated to the same rainfall rate with the adjacent station. We note that the selection of the interpolation technique depends highly on the density of the available gauge network and may introduce additional errors to the rainfall dataset. Interpolation by using more comprehensive geostatistical models, such as kriging, requires a denser gauge network to characterize the error structure [26].
Daily and monthly rainfall averages were estimated from hourly GSMaP data, and daily rain gauges with the same spatial resolution. Statistical analysis was performed to compare GSMaP data with the gauged-based rainfall dataset. The comparison includes several scenarios involving different time scales (daily, monthly, seasonal), spatial scales (areal average, grid-based and grid vs. point-based), elevation zones and rainfall intensity thresholds (e.g., ≥0 mm (detection), ≥1 mm, ≥2 mm, ≥5 mm, and ≥10 mm (heavy rainfall)). In this comprehensive analysis, additional consideration was given to evaluate the GSMaP product for the extreme events in an effort to explore its potential use in flash floods simulations.
3.1.1. Evaluation Statistics
Statistical measures utilized to evaluate GSMaP product with rain gauge observations include:
- The correlation coefficient (R, Equation (2)) refers to the agreement between satellite-based rainfall and gauge-based rainfall. R ranges between −1 and +1. The value of +1 indicates a perfect positive fit, in other words, a perfect linear correlation.
- RMSE: Root Mean Square Error (Equation (3)) is one of the most commonly used methods [73,74] to measure the absolute average error and is sensitive to the larger errors.
- The Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE, Equation (4)) is a normalized indicator that determines the relative magnitude of the residual variance (“noise”) compared to the observed data variance (“information”) [75]. NSE point out how well the satellite estimates match the rain gauge estimates, and it ranges between negative infinity and unity; the latter being the best score.
- Percent bias (PBIAS; Equation (5)) indicates the average tendency of the satellite-based rainfall fields to be larger or smaller than the rain gauges; the best value is 0.0; negative (positive) values indicate an underestimation (overestimation) by GSMaP [76].
Additionally, two categorical verification statistics, namely, Probability of Detection (POD) and False-alarm Rate (FAR) were used to evaluate the consistency between GSMaP product and rain gauge dataset for various rainfall magnitude thresholds. These categorical measures are based on a 2 × 2 contingency table [a: GSMaP yes, Gauge yes; b: GSMaP yes, Gauge no; c: GSMaP no, Gauge yes; and d: GSMaP no, Gauge no]. The POD [=a/(a + c)], also known as hit rate, represents the fraction of correctly detected rain events and ranges from 0 to 1; 1 being the best score. The FAR [=b/(a + b)] gives the fraction of rain events that were false alarms and ranges from 0 to 1; 0 being the best score. Note that a rain event (yes) and a no rain event (no) indicated above means that the product (GSMaP/gauge) reported a rain event and not reported a rain event above the given threshold (e.g., ≥0.0 mm, ≥1 mm, ≥2 mm, ≥5 mm, and ≥10 mm), respectively.
3.1.2. Bias Correction of the GSMaP Rainfall
Using accurate satellite-based precipitation estimates has the potential to reduce the uncertainty in flash floods simulation [77]. Thus, we investigated whether an improvement in the flash flood simulation performance of the hydrological model is possible through bias correction of the GSMaP product with the local rain gauge network. Due to the availability of relatively scarce rain gauge network within the study area, we employed a simple multiplicative bias correction procedure. Tian et al. [78] evaluated additive and multiplicative bias correction schemes and suggested the use of multiplicative error model for bias removal of daily satellite-based precipitation products. In the procedure, monthly bias factors (Equation (6)) were used to correct the hourly GSMaP data product (Equation (7)):
where GSMaP(Tm) and Rain gauge(Tm) are the GSMaP-based and rain gauge-based rainfall estimates at the monthly timescale (one bias factor is calculated for each month in a year), are the GSMaP data for hour at grid before and after the bias correction procedure.
3.2. Calibration and Performance Assessment of the Hydrologic Model
The HydroBEAM distributed hydrological model was calibrated using the Shuffled Complex Evolution Algorithm [79]. Among the four hourly flow time series consisting of flash flood events and each spanning a period of 3 months (October, November, December), years 2007 and 2012 were selected as the model calibration period, and years 2009 and 2012 were selected as the model validation period. The time periods were selected based on the occurrence of flash flood events and the availability of the hourly stream flow data for the Karpuz River outlet (Figure 1). During calibration, the model was driven by the corrected GSMaP product that was mapped to 1 km x 1 km grid of the hydrologic model. The model performance during calibration and validation periods was assessed by statistical measures such as correlation coefficient (R), Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE), in addition to NSE and RMSE. The Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE), is an alternative model performance criterion developed by [80]:
where ED is the Euclidian distance from the ideal point; is the ratio between the average simulated and observed flows, i.e., represents the bias; r is the linear correlation coefficient between simulated and observed flows and is the ratio between standard deviations of simulated and observed flows (an indicator of the relative variability of flows).
4. Results
4.1. Comparison of the GSMaP Product with Rain Gauge Dataset
The results of the statistical analysis (Table A3 in Appendix A) show that daily rainfall estimates derived from GSMaP product are well correlated (correlation coefficient values between 0.78 and 0.83) with rain gauges but remarkable underestimation of bias is evident (PBIAS values around negative 55%and negative 65%). These statistics improve over longer averaging timescales—monthly and annual—as expected. It was also found that the magnitude of bias slightly varied as a function of the season (complete time series, April–September (dry season), or October to March (wet season)), as well as the rainfall threshold (0 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm, 5 mm, 10 mm). The total average PBIAS for the daily and monthly data comparison indicated underestimation for the different thresholds in the case for the wet and whole time series, but overestimation bias was observed in the case of dry season at the daily time scale; which is likely due to division by precipitation values that are less than unity. This implies that GSMaP algorithm frequently report false precipitation values that are less than 1 mm/day. Hence, a minimum precipitation threshold should be set for bias correction and evaluation of SBPs. Direct comparison and correction of the data would lead to an unintentional increase in the bias (instead of correction). Consequently, that will contribute to the low performance of the hydrological model.
4.1.1. Evaluation for Different Rainfall Intensity Thresholds
In this section we compare the number of daily rainfall occurrences reported by the GSMaP product and rain gauge dataset above various intensity thresholds (mm/day) for the whole study area and rain gauge stations; Antalya, Gazipasa, and Ibradi (Figure 3). It is interesting to note that GSMaP product reports almost 50% more daily rainfall occurrences (larger than 0 mm threshold) compared to the rain gauges. Daily rainfall occurrences reported by GSMaP and rain gauges become comparable (only about 2% difference) when 1 mm/day and 2 mm/day thresholds are considered. Hence, to remove false GSMaP daily rainfall intensities that are less than 1 mm/day, we utilized a 1 mm/day threshold for the bias correction procedure. Also note that, GSMaP product significantly underestimated the number of daily rainfall occurrences greater than 10 mm/day. The tendency for the GSMaP product to underestimate the number of days with high rain rates (greater than 5 mm/day and 10 mm/day thresholds) was found to be more severe for Ibradi station located at higher elevation (1036 m) compared to other stations. For instance, at Ibradi station, the difference in daily rainfall occurrence reported by GSMaP and rain gauge was 141 days, whereas the difference was only 8 days at Antalya rain gauge situated at a lower elevation (50 m). This result infers that GSMaP data has difficulty in detecting rainfall at high elevations compared to low elevations. One possible explanation for this behavior is the snow cover, which poses a major challenge to SBP estimation algorithms over complex topography [39].
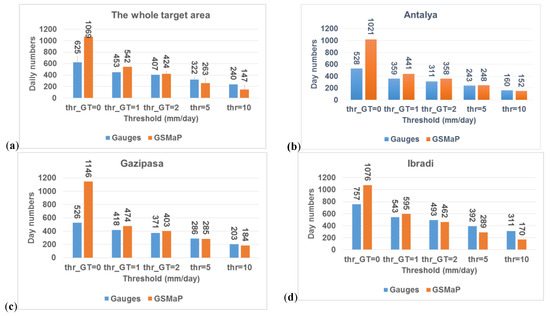
Figure 3.
Numbers of rainy days were estimated for the time period from 2007 to 2013 above selected threshold for (a) the whole study area (average), (b) Antalya rain gauge station (Elevation: 50 m), (c) Gazipasa rain gauge station (Elevation: 21 m), and (d) Ibradi rain gauge station (Elevation: 1036 m).
4.1.2. Temporal Analysis over the Whole Study Area
GSMaP product and rain gauge dataset were spatially averaged over the whole study area and compared using scatterplots (Figure 4) and statistical measures (Figure 5). The analysis was performed using two rainfall intensity thresholds—a 1 mm/day threshold due to discussion provided in the previous section and a 10 mm/day threshold to investigate GSMaP performance for high rainfall events. The results indicate that most of the scenarios investigated exhibit an underestimation by GSMaP. For instance, at the daily time scale, the correlation between GSMaP and rain gauge data are over 0.65 and 0.60, respectively. However negative PBIAS value is evident for the whole time series and wet seasons, but positive values are observed for the dry seasons, or low rainfall periods. This indicates that GSMaP has a general tendency to underestimate precipitation with an exception of dry-season overestimation tendency, which is possibly due to reporting of non-realistic low-rainfall occurrences as discussed during our earlier analysis (see Figure 3 and Figure 4). The average PBIAS is about negative 56% at the daily time scale and about negative 48% at both monthly and annual time scales. Most of the statistics for monthly and annual scales show similar trends as daily timescale, except with increasing RMSE values due to the time scale differences. Note that the results for area-averaged analysis for the thresholds (0 mm, 1 mm, 2 mm) are similar; the reason being due to the GSMaP having the tendency to underestimate. GSMaP, however, frequently reports unrealisticly low rainfall which in the overall average could give the same statistics in comparison with rain gauges for the low threshold values (from 0 mm to 2 mm). As noted earlier, consideration of less than 1 mm/day rainfall intensities for the bias correction will mislead to unrealistic events and hence it is not recommended. Consequently, our results indicate that 1 mm/day threshold (or in some cases 2 mm/day) is a reasonable choice for the following reasons: (1) The number of days with rainfall occurrence is similar between the rain gauges and GSMaP data above these thresholds (Figure 3), and (2) low rainfall values that might lead to high uncertainty in case of bias correction are eliminated. Analysis of categorical measures (Figure 5) indicate that rainfall detection capacity of the GSMaP deteriorates as the rainfall intensity increases, accompanied by slight reduction (better) in false alarm rate.
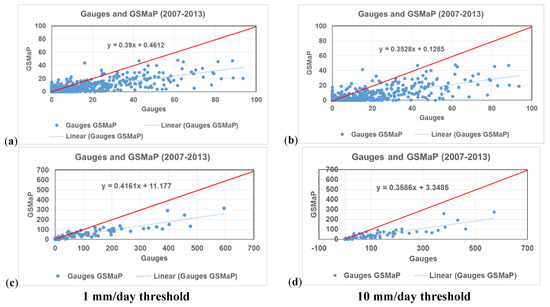
Figure 4.
Scatterplots of (a,b) daily, and (c,d) monthly precipitation between GSMaP and rain gauges for the period 2007–2013. Precipitation threshold set to 1 mm/day (left column), and 10 mm/day (right column).
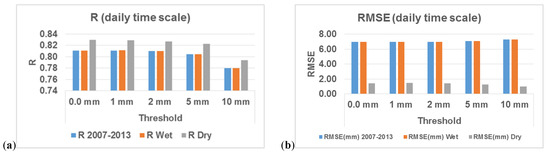
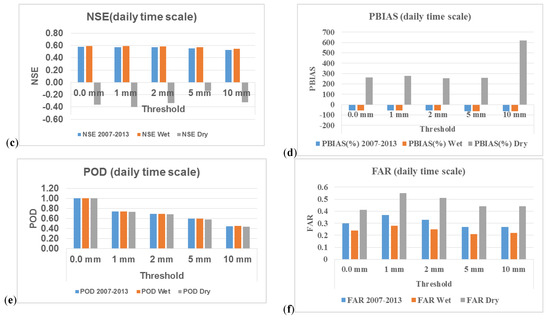
Figure 5.
Statistical measures between GSMaP and rain gauge precipitation for daily time scale considering different thresholds; R, RMSE, NSE, PBIAS, POD, and FAR (a–f) respectively.
4.1.3. Wet Season and Extreme Events
In this section, the performance of the GSMaP product was evaluated for the complete time series, rainy season, and for the selected extreme events. The threshold of 1 mm/day rainfall was applied for two rainy periods including the months of October to December in 2007 and 2009. We tested the performance of GSMaP product with rain gauges over the whole target basin considering three cases: (1) daily time scale average from 2007–2013, (2) only two rainy seasons (October to December) in years 2007 and 2009, (3) Selected extreme events occurred during 4–16 December 2007 (two rainfall peaks, 88 mm/day and 30 mm/day), 3–6 November 2009 (two peaks, 88 mm/day and 63 mm/day), and 10–14 December 2009 (one peak, 74 mm/day)). The results (Figure 6) indicate that GSMaP suffers from more significant underestimation (more negative PBIAS) during the wet season and extreme event situations; PBIAS is around 5% and 13% more negative, respectively, compared to the whole time series from 2007–2013. Also, POD and FAR values deteriorated for the rainy season and for extreme events compared to the complete time series. POD values are 0.74, 0.23, and 0.10 for the whole time period, rainy season, and for extreme events, respectively, revealing that GSMaP suffers from rainfall detection performance during the rainy season and more significantly, for the extreme events. Categorical measures POD and FAR are 0.10 and 0.41 for the extreme events, and around 0.74 and 0.37 for the whole time series, generally indicating a better performance for the latter case. PBIAS values are strongly negative in all cases but more significant in the case of extreme events (around negative 70%). GSMaP product shows good correlations with rain gauge dataset for all time periods/events considered. This analysis implies that GSMaP is able to catch the extreme event occurrence, but with a significant systematic underestimation bias, which could be corrected through a methodology based on the estimated bias factors.
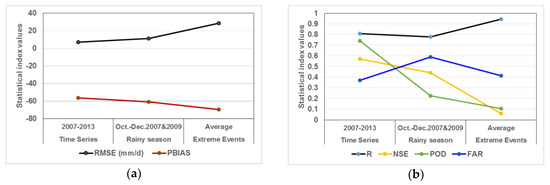
Figure 6.
Analysis of statistical measures for GSMaP and rain gauge daily precipitation considering the whole time series, rainy season from October to December in 2007 and 2009, and average for three extreme flash floods events, (a) RMSE, and PBIAS, (b) R, NSE, POD, FAR (1 mm/day threshold is considered in this comparison).
4.1.4. Elevation Zones
Earlier studies that evaluated the performance of satellite-based precipitation products indicated that the algorithms are still challenged by estimation at high elevations (e.g., [81,82,83]). We, therefore, examine the performance of GSMaP product over different elevation zones at daily and monthly temporal scales. The study region is topographically complex including mountainous regions with elevations reaching up to 2600 m. For the sake of the analysis, we considered the elevation values less than or equal to 500 m as low lands and greater than 500 m as high lands. The performance comparison between the two elevation zones (Figure 7 and Table 1) indicate that GSMaP shows elevation dependent underestimation; values of high land PBIAS (−62.99%) is about −27% higher than the low land PBIAS (−36.45%). This finding is in line with the results of [33] who evaluated multi-satellite precipitation products over the mountainous area in South Korea. Statistical measures such as RMSE and NSE also show better performance in low land compared to the high elevations for all the time scales considered. Additionally, the ability of detection is also better in the case of the low lands (0.83) than high lands (0.79), however, with similar values for FAR measure. These results strongly support the previous findings, in which the satellite-based rainfall products were challenged in topographically complex regions, especially in the high lands.
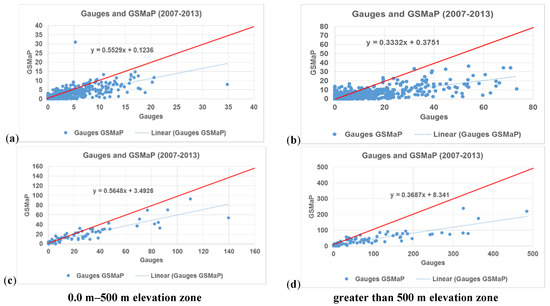
Figure 7.
Scatterplots of (a,b) daily and (c,d) monthly precipitation between GSMaP and rain gauges for the period 2007–2013 for 0 m–500 m elevation zone (left column) and for >500 m elevation zone (right column).

Table 1.
Statistical analysis of GSMaP performance for different elevations zones; <500 m, and ≥500 m (rainfall intensity threshold is set to 1 mm/day).
Next, we investigated the elevation dependency of the GSMaP product in a more detailed manner through investigating linear regression relationships between performance statistics and elevation zones. We classified the study area into four elevation zones (0–400 m, 400–800 m, 800–1200 m, and ≥1200 m) and calculated the values of statistical and categorical measures for the whole period (considering 1 mm/day threshold). Based on the linear slope rate for the discussed elevation ranges (Figure 8), we could estimate the average range of decreasing GSMaP performance with increasing elevation. As shown in Figure 8, the values of R, RMSE, NSE, PBIAS, and POD are deteriorating with a rate of 1.5%, 1 mm (100%), 20%, 11.7%, 1.2%, respectively. These rates of change reveal that GSMaP data has a reasonable linear correlation with the rain gauges at both low and high elevations where R is about 0.75, and POD value is greater than 0.8; indicating that GSMaP is capable of detecting the events regardless of the elevation, but with a significantly high negative bias as confirmed by RMSE and PBIAS values. The results of this analysis indicate that in the study area, GSMaP product shows good correlation with a possibility of detecting rainfall events similarly in high and low lands, but the bias and mean error become more negative with increasing elevation.
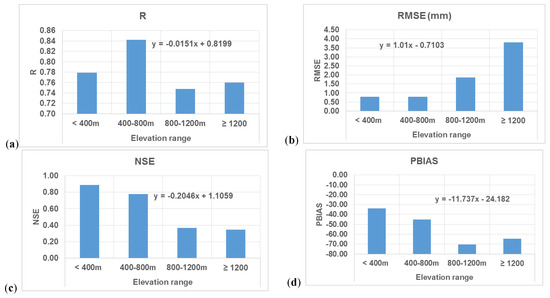
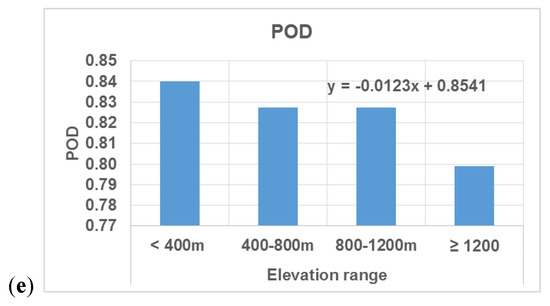
Figure 8.
Statistical and categorical measures showing the GSMaP performance (daily time scale) as a function of elevation. Elevation zones are (<400 m), (400 m–800 m), (800 m–1200 m), and (≥1200 m). Measures include R, RMSE, NSE, PBIAS, and POD (a–e), respectively.
The tendency of underestimation of GSMaP data in relation with the extreme events (Section 4.1.3) could be due to the coarse scale of the product which may not resolve small scale convective precipitation and that in relation with the elevation (Section 4.1.4) might be due to the snow cover effect [39]. The limitation of the gauge networks over the highlands may be one of the reasons stated by [84]. They found that the rain gauge network in the high Himalayas is not sufficient to characterize the orographic precipitation correctly. Moreover, the extreme rainfall events are usually localized [84] and not well recorded by the scattered ground-based gauges. Hence, the evaluation of satellite data is challenging during the extreme events as well as at the orographic regions.
4.1.5. Point vs. Grid Scale Rainfall Comparison
Point-scale rainfall measurements at Antalya meteorological station (50 m elevation) were compared with the corresponding single grid of the GSMaP product at daily and monthly time scales using several rainfall intensity thresholds (Table 2, and Figure 9). The results of the comparison show that the correlation values are around 0.64, and 0.85 between GSMaP product and the rain gauge data for daily and monthly time scales, respectively. PBIAS values for the three time series show that GSMaP underestimates rainfall compared to rain gauges with PBIAS values around negative 18% for 1 mm/day threshold and negative 25% for 10 mm/day threshold; indicating more significant underestimation for high rainfall intensities. This situation is more clearly shown for each daily rainfall occurrence (points) in the scatterplots given in Figure 9. It is clear from Figure 9a,b that points scattered below the diagonal line (shown in red), thus, indicating underestimation tendency of the GSMaP product, is more significant for the high daily rainfall rates. Categorical performance measures POD and FAR values are 0.82 and 0.33, respectively, at daily timescale for 1 mm/day threshold indicating the relatively high performance of rainfall detection over Antalya Station. These measures also deteriorate for rainfall intensities above 5 mm/day threshold.

Table 2.
Statistical and categorical measures for various thresholds (0.0–10 mm), in case of point to grid comparisons (Antalya station vs. overlying GSMaP grid).
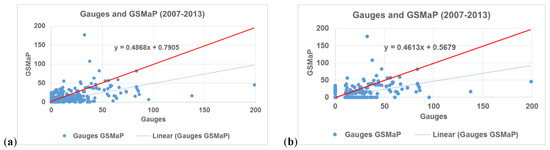
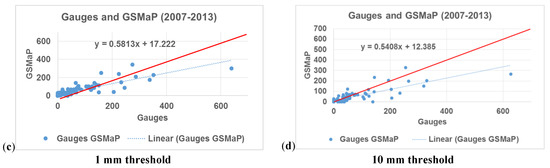
Figure 9.
Scatterplots of (a,b) daily and (c,d) monthly precipitation between Antalya station and overlying GSMaP grid for the period 2007–2013 for (left) 1 mm/day and (right) 10 mm/day rainfall intensity thresholds. Red line represents equal precipitation for both axes.
4.1.6. Bias Correction of GSMaP Product and Spatial Distribution of Rainfall over the Study Area
The analysis presented in the previous sections indicated that GSMaP product suffers from seasonal, elevation and rainfall magnitude (i.e., extreme events) dependent bias. Hence, a bias correction procedure is deemed necessary prior to using the GSMaP product as input to the hydrological model. In an effort to reduce the GSMaP bias, we employed a multiplicative correction procedure detailed in Section 3.1.2. Moreover, GSMaP product was found to report frequent false light rainfall (less than 1 mm/day). To remove these false GSMaP rainfall occurrences, we set a rainfall intensity threshold of 1 mm/day. The results are shown in Table 3 and Figure 10, which indicate that significant improvements were obtained for the bias corrected daily GSMaP product compared to the original GSMaP product. Note that R, RMSE, NSE, PBIAS, POD, FAR were improved from (0.81 to 0.98), (6.97 to 1.21), (0.57 to 0.99), (−56.44 to −0.20), (0.74 to 0.88), (0.37 to 0.25), respectively, for 1 mm/day threshold. Also, note that the statistics of 1 mm/day threshold show better performance compared to the 10 mm/day threshold.

Table 3.
Statistical analysis comparing original and corrected daily GSMaP data for different rainfall thresholds.
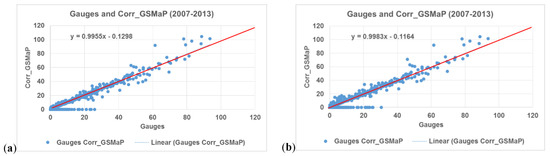
Figure 10.
Improvement of GSMaP data compared to the rain gauge data after bias correction using different thresholds, (a) 1 mm/day, and (b) 2 mm/day.
Figure 11 exhibits the spatial distribution of GSMaP product before and after the bias correction procedure for the day of 4 November 2009. Note that the magnitude of the rainfall for the corrected GSMaP is similar to the rain gauges, while the spatial distribution is similar to the original GSMaP product. For the maps shown in Figure 11, the average rainfall values for GSMaP data was improved from 12.27 mm/day to 30.73 mm/day after correction which closely matches the average rainfall obtained from the rain gauges (33.27 mm/day).
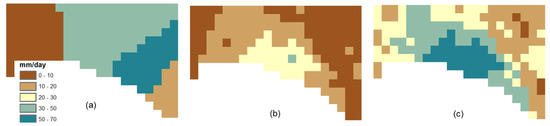
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of daily rainfall data for the date 2009-11-04, obtained from (a) rain gauges, (b) GSMaP, and (c) corrected GSMaP.
4.2. Flash Floods Modeling at Karpuz River Basin
This section investigates the potential of SBP estimates (GSMaP) for flash floods simulation in the Karpuz River Basin before and after the bias correction procedure. The motivation is that the satellite-based rainfall products have a more complete spatial coverage compared to rain gauges and are available at hourly temporal resolution without gaps—these factors are important for hydrologic modelling studies focusing on flash floods simulation. Note that, due to the availability of raingauge data at the daily time scale, precipitation comparison and bias correction analysis were performed using daily datasets, but the flash floods simulation study was performed using the hourly GSMaP data before and after the bias correction procedure assuming that the bias is preserved across the time scales.
Analysis of the Hydrologic Model Performance
A comprehensive analysis of the HydroBEAM model performance for simulating flash flood events was conducted to understand the degree of improvement in model performance before and after the bias correction of the GSMaP product. Among the four hourly time series each spanning 3-months (October, November, December), years 2007 and 2012 were selected as the model calibration period and years 2009 and 2012 were selected as the model validation period. Figure 12a,b show the observed hydrographs together with the simulated hydrographs driven by the GSMaP and corrected GSMaP during the calibration period; October–December 2007 and October–December 2012, respectively. Note that simulated flows driven by the GSMaP product are capable of detecting the flow events, however, significantly underestimate the peak flows for both periods (more significant for the year 2012). This result is expected due to our earlier finding that GSMaP product significantly underestimates the precipitation in the study area. Simulated hydrographs driven by the corrected GSMaP represent the observed hydrographs better, more specifically, the high flow events. Flow underestimation bias was significantly reduced and a few events were overestimated by the model driven by the corrected GSMaP. Figure 12c,d summarize the change in performance statistics for the model driven by GSMaP and corrected GSMaP during the model calibration period; October–December 2007 and October–December 2012, respectively. A significant improvement in all the performance statistics (higher R, KGE and NSE values and lower RMSE values) is evident when the model is driven by the corrected GSMaP instead of the GSMaP product. In summary, R, KGE, NSE and RMSE statistics changed from 0.67, 0.12, 0.29, 13.68 to 0.71, 0.66, 0.48 and 11.70 for the October–December 2007 period and from 0.69, 0.08, 0.26, 12.00 to 0.77, 0.72, 0.60 and 8.88 for the October–December 2012 period.
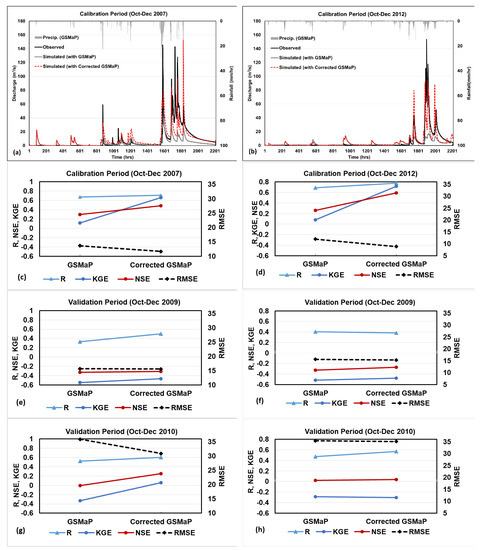
Figure 12.
Discharge hydrographs for calibration period (a) October–December, 2007 and (b) October–December, 2012. Performance statistics R, KGE, NSE and RMSE, showing the change in the performance of the model driven by the GSMaP and bias corrected GSMaP (x-axis), (c) for the calibration period October–December 2007 and for the validation periods (e) October–December, 2009, and (g) October–December, 2010; (d) for the calibration period Oct–December, 2012 and for the validation periods (f) October–December, 2009, and (h) October–December, 2010. Note that the first column shows the results for the model calibrated for October–December, 2007 period and the second column shows the results for the model calibrated for October–December, 2012 period, respectively.
Although the model performance improvement during the calibration period is important to assess the influence of the GSMaP bias correction on the model simulation, the model performance assessment during evaluation period is another crucial step. For example, Figure 12 shows the performance statistics during validation period, namely October–December 2009 and October–December 2010, respectively, for the model calibrated to the October–December 2007 period. Figure 12f,h shows the same information but for the model calibrated to the October–December 2012 period. It can be seen from these figures that the model performance significantly deteriorates during the validation period compared to the calibration period. Among the four validation cases tested, only one case (Figure 12g) revealed noticeable improvement in model performance upon using corrected GSMaP instead of GSMaP to drive the hydrological model. In this case, R, KGE, NSE and RMSE statistics changed from 0.52, −0.33, 0.01, 35.89 to 0.60, 0.06, 0.26 and 30.92 upon using the corrected GSMaP. In other validation cases tested, statistical measures either slightly improved or did not change when using the corrected GSMaP instead of GSMaP. The generally poor performance behavior of the model during the validation period is likely due to a combination of factors including short calibration period, inherent errors in precipitation measurements (especially for flash floods with a scarce gauge network) and satellite-based precipitation products, and limitations in the bias correction procedure utilized.
Hence a more comprehensive approach for bias correction is needed to account for the high (negative) bias inherent in the GSMaP, especially for the extreme events. Also note that the bias increases with the elevation as described earlier. Use of a dense gauge network in bias correction procedure will be likely to increase the model performance [31]. However, this option is not available for the study area. The hydrograph of the calibration period (Figure 12a,b) shows that high and low flow magnitudes are well simulated by the model. However, there is a shift in the timing of the events, as detected by the correlation statistic (Figure 12c,d). Westerberg et al. [85] stated that recalibration based on satellite precipitation data is not always a reliable approach because satellite errors can lead to biased inferences in the subsequent hydrological model calibration.
In summary, although the bias correction procedure resulted in improved simulated hydrographs, the uncertainty of the hydrological model output is still controlled by many factors including the limitation of the bias correction approach. We also found that seasonal, elevation and magnitude (extreme events) dependent bias deteriorates the model performance and increase uncertainty in model performance slightly during the calibration and more significantly during the evaluation periods. Moreover, although the model performance generally improved upon driven by corrected GSMaP, the performance varied from one event to another. Therefore, improved bias correction schemes incorporating multiple attributes (such as elevation, seasonality, and precipitation magnitude) should also be investigated in regions where denser gauge network and longer time series datasets are available.
Another possibility of the model uncertainty is due to the underestimation or overestimation of the precipitation by the rain gauges. There are several causes of the rain gauge errors such as the wind effects [86,87,88], wetting losses [86,89], evaporation, and splashing effects [86,90]. Recently, Grimaldi et al. [91] investigated the errors stemming from the scale (orifice dimension) of standard rain gauges through introducing a giant rain gauge with collecting a surface area of 100 square meters. They found major discrepancies in standard gauges, especially for the low time resolutions (less than 15 min) and also in the case of high rainfall intensities. In summary, the uncertainty in hydrological models could stem from several issues, thus addressing and highlighting the reasons of such uncertainty in the future studies are important to increase the reliability and to enhance the performance of the hydrological models.
5. Conclusions
The Mediterranean region is projected to become increasingly vulnerable to flash floods due to a combination of factors including the projected increase in hydrologic extremes and rapid population growth. On the contrary, the Mediterranean basins are characterized by poor observation networks and complex topography which in turn hinders the efficacy of ground-based observational networks. This situation makes satellite-based precipitation (SBP) retrieval algorithms potentially attractive for modeling flash floods. Thus, the main goal of this paper was to explore the utility of a satellite-based precipitation product, GSMaP, in modelling flash flood events over the Mediterranean catchments. This goal was achieved in three major steps. First, SBP estimates from the GSMaP product was compared and evaluated with the gauge-based precipitation estimates around Karpuz River basin located in the city of Antalya, Turkey. Next, a simple bias correction scheme was devised to correct the GSMaP precipitation estimates using the relatively scarce rain gauge network. Lastly, a distributed hydrologic model, Hydro-BEAM, suited to the simulation of flash floods was driven by GSMaP-based precipitation estimates before and after the bias correction scheme, and the simulation performance was assessed using the observed hydrographs of flash flood events together with several performance statistics.
The comparison of GSMaP data with the rain gauge dataset consisted of several scenarios including different time scales (daily, monthly, seasonal), spatial scales (areal average, grid-based and grid vs. point-based/gauge-based), elevation zones and rainfall intensity thresholds. This analysis indicated that GSMaP product generally suffers from a tendency to underestimate precipitation compared to the rain gauge network as a function of the season, elevation and rainfall intensity; however, showed reasonable linear correlations. Specifically, the underestimation by GSMaP was more significant for high elevations and for high rainfall intensities, which is alarming for flash flood monitoring efforts. Moreover, GSMaP product significantly underestimated the number of daily rainfall occurrences for high rainfall intensity events (greater than 10 mm/day). On the contrary, significant overestimation by GSMaP product for low rainfall intensity events (less than 1 mm/day) was evident. Hence we suggest to include threshold-based analysis in studies focusing on evaluation and bias correction of satellite-based rainfall products. For instance, in this study, false daily light rainfall intensities (less than 1 mm/day) reported by GSMaP product were not included in the comparison and bias correction procedure.
Next, a multiplicative bias correction scheme was employed to correct the hourly GSMaP rainfall estimates using the monthly bias factors computed as the ratio of monthly total rainfall reported by GSMaP and rain gauges for each month of the year. The effectiveness of this rather simple correction scheme was tested through the investigation of the performance of the hydrological model, Hydro-BEAM, in simulating the hourly hydrographs of flash flood events in Karpuz River Basin. The results of the model simulations indicated that the performance of the model improves upon using the bias-corrected GSMaP product as input compared to using the uncorrected GSMaP product in most cases studied but others show some limitation, especially during the evaluation periods. Investigation of alternative schemes that incorporate local hydroclimatic and physiographic variables such as elevation, season and extreme events in the bias correction procedure will shed further light on the impact of these factors on the flash flood simulation and early warning system performance.
Author Contributions
Both Authors (M.S. and K.K.Y.) contributed equally to develop the idea, conducting the data analysis and model simulation, as well as writing the manuscript. Thanks for the editors and the reviewers for their significant comments to improve the manuscript contents.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK, Program 2221). Authors are thankful to the General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works and General Directorate of Meteorology in Ankara for providing the streamflow data and rain gauge data, respectively, used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
GSMaP data products used in the analysis (Last access, 1 March 2016).
Table A1.
GSMaP data products used in the analysis (Last access, 1 March 2016).
| Data Product | ftp | Spatio-Temporal Resolution | Available Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard gauges (v5) | ftp://hokusai.eorc.jaxa.jp/standard_gauge/v5/hourly/ | 0.1° × 0.1°, Hourly | 2000/03–2010/11 |
| reanalysis gauge (v6) | ftp://hokusai.eorc.jaxa.jp/reanalysis_gauge/v6/gauge_hr/ | 0.1° × 0.1°, Hourly | 2011/01–2014/02 |
| Real time | ftp://hokusai.eorc.jaxa.jp/realtime/archive/ | 0.1° × 0.1°, Hourly | 2008/10–2016/02 |

Table A2.
Meteorological stations used in the study.
Table A2.
Meteorological stations used in the study.
| Station Name | Station ID | Start Year | End Year | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antalya | 17300 | 1965 | 2015 | 36.91 | 30.80 | 50 |
| Gazipasa | 17974 | 1970 | 2015 | 36.26 | 32.31 | 21 |
| Manavgat | 17954 | 1965 | 2015 | 36.78 | 31.43 | 38 |
| Alanya | 17310 | 1965 | 2015 | 36.55 | 31.98 | 5.88 |
| Ibradi | 27 | 2007 | 2015 | 37.09 | 31.59 | 1036 |

Table A3.
Statistical and categorical measures between GSMaP product and rain gauge dataset at daily and monthly time scales over the whole area considering different rainfall thresholds and climatic seasons.
Table A3.
Statistical and categorical measures between GSMaP product and rain gauge dataset at daily and monthly time scales over the whole area considering different rainfall thresholds and climatic seasons.
| Time Scale | Parameters | Time Period | Threshold | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 mm | 1 mm | 2 mm | 5 mm | 10 mm | |||
| Daily | R | 2007–2013 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.78 |
| Wet | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.78 | ||
| Dry | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.79 | ||
| RMSE (mm) | 2007–2013 | 6.97 | 6.97 | 7.00 | 7.10 | 7.32 | |
| Wet | 6.97 | 6.97 | 7.00 | 7.10 | 7.32 | ||
| Dry | 1.43 | 1.46 | 1.41 | 1.24 | 0.98 | ||
| NSE | 2007–2013 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.53 | |
| Wet | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.55 | ||
| Dry | −0.37 | −0.40 | −0.34 | −0.14 | −0.32 | ||
| PBIAS (%) | 2007–2013 | −55.83 | −56.44 | −58.12 | −62.73 | −65.84 | |
| Wet | −55.83 | −56.44 | −58.12 | −62.73 | −65.84 | ||
| Dry | 260.73 | 278.89 | 254.03 | 259.44 | 619.41 | ||
| POD | 2007–2013 | 0.91 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 0.44 | |
| Wet | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.60 | 0.45 | ||
| Dry | 0.87 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.43 | ||
| FAR | 2007–2013 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.27 | |
| Wet | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.22 | ||
| Dry | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.44 | ||
| Monthly | R | 2007–2013 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.87 |
| Wet | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.84 | ||
| Dry | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.83 | ||
| RMSE (mm) | 2007–2013 | 94.89 | 95.26 | 96.14 | 98.48 | 101.70 | |
| Wet | 860.13 | 863.24 | 871.01 | 891.60 | 920.14 | ||
| Dry | 128.27 | 130.73 | 133.36 | 140.64 | 148.85 | ||
| NSE | 2007–2013 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.31 | |
| Wet | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.13 | ||
| Dry | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.92 | ||
| PBIAS (%) | 2007–2013 | −47.14 | −48.23 | −49.72 | −53.99 | −60.75 | |
| Wet | −53.63 | −54.22 | −55.17 | −58.29 | −60.75 | ||
| Dry | −8.96 | −12.65 | −16.90 | −27.04 | −60.75 | ||
References
- Fattorelli, S.; Dalla Fontana, G.; Da Ros, D. Flood hazard assessment and mitigation. In Floods and landslides: Integrated Risk Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Creutin, J.D.; Borga, M.; Gruntfest, E.; Lutoff, C.; Zoccatelli, D.; Ruin, I. A space and time framework for analyzing human anticipation of flash floods. J. Hydrol. 2013, 482, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, J.A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Holloway, T.; Foley, J.A. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature 2005, 438, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools, J.; Vanderkimpen, P.; El Afandi, G.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Fockedey, S.; El Sammany, M.; Abdallah, G.; El Bihery, M.; Bauwens, W.; Huygens, M. An early warning system for flash floods in hyper-arid egypt. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrocq, V.; Braud, I.; Davolio, S.; Ferretti, R.; Flamant, C.; Jansa, A.; Kalthoff, N.; Richard, E.; Taupier-Letage, I.; Ayral, P.A.; et al. Hymex-sop1: The field campaign dedicated to heavy precipitation and flash flooding in the northwestern mediterranean. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1083–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, M.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Blöschl, G.; Creutin, J.D. Flash flood forecasting, warning and risk management: The hydrate project. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, M.; Tonelli, F.; Moore, R.J.; Andrieu, H. Long-term assessment of bias adjustment in radar rainfall estimation. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Mallick, K.; Patel, N.; Parihar, J. Regional clear sky evapotranspiration over agricultural land using remote sensing data from indian geostationary meteorological satellite. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The trmm multisatellite precipitation analysis (tmpa): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T. Trmm and Other Data Precipitation Data Set Documentation; NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2013; Volume 28.
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. Cmorph: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Joyce, R.; Wu, S.; Yoo, S.-H.; Yarosh, Y.; Sun, F.; Lin, R. Reprocessed, bias-corrected cmorph global high-resolution precipitation estimates from 1998. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1617–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of persiann system satellite–based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. Persiann-cdr: Daily precipitation climate data record from multisatellite observations for hydrological and climate studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Iwanami, K. Global precipitation map using satellite-borne microwave radiometers by the gsmap project: Production and validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.I.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M.; et al. A kalman filter approach to the global satellite mapping of precipitation (gsmap) from combined passive microwave and infrared radiometric data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J. V04 Imerg Final Run Release Notes; NASA Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2017.
- AghaKouchak, A.; Mehran, A.; Norouzi, H.; Behrangi, A. Systematic and random error components in satellite precipitation data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Anagnostou, E.N. A two-dimensional satellite rainfall error model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, D.A.; De Goncalves, L.G.G.; Toll, D.L.; Rozante, J.R. Statistical evaluation of combined daily gauge observations and rainfall satellite estimates over continental south america. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Hailemariam, K.; Maidment, R.; Tarnavsky, E.; Connor, S. Combined use of satellite estimates and rain gauge observations to generate high-quality historical rainfall time series over ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2489–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M. Calibration of trmm rainfall climatology over saudi arabia during 1998–2009. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo-Duc, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Kamimera, H.; Bui, H.-H. Monthly adjustment of global satellite mapping of precipitation (gsmap) data over the vugia–thubon river basin in central vietnam using an artificial neural network. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2013, 7, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Villa, O.D.; Vélez, J.I.; Poveda, G. Improved long-term mean annual rainfall fields for colombia. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2194–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, B.; Buytaert, W.; Zulkafli, Z.; Lavado, W.; Willems, B.; Robles, L.A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.P. High-resolution satellite-gauge merged precipitation climatologies of the tropical andes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 1190–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Flamig, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Vergara, H.; Anagnostou, E.N. Hydrologic evaluation of rainfall estimates from radar, satellite, gauge, and combinations on ft. Cobb basin, oklahoma. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, F.; Selker, J.; van de Giesen, N.; Abrate, T.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Porfiri, M.; Manfreda, S.; Caylor, K.; Moramarco, T.; Benveniste, J. Measurements and observations in the xxi century (moxxi): Innovation and multi-disciplinarity to sense the hydrological cycle. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Hahn, S.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5128–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Hsu, K.L.; Chang, F.J.; Hong, Y.; Sorooshian, S. Merging multiple precipitation sources for flash flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2007, 340, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.W.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of gpm and trmm multi-satellite precipitation products in streamflow simulations in a data-sparse mountainous watershed in myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Zoccatelli, D.; Borga, M. Error analysis of satellite precipitation-driven modeling of flood events in complex alpine terrain. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.P.; Jung, I.W.; Park, K.W.; Yoon, S.K.; Lee, D. Hydrological utility and uncertainty of multi-satellite precipitation products in the mountainous region of south korea. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M. Using high-resolution satellite rainfall products to simulate a major flash flood event in northern italy. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampoulis, D.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Nikolopoulos, E.I. Assessment of high-resolution satellite-based rainfall estimates over the mediterranean during heavy precipitation events. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciabatta, L.; Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Gabellani, S.; Puca, S.; Wagner, W. Rainfall-runoff modelling by using sm2rain-derived and state-of-the-art satellite rainfall products over italy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 48, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewski, A.; Elkadiri, R.; Durham, M. Assessment and comparison of tmpa satellite precipitation products in varying climatic and topographic regimes in morocco. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5697–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Thiemig, V.; Dezetter, A.; Hanich, L. Evaluation of satellite-based rainfall products for hydrological modelling in morocco. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Yilmaz, K.K. Evaluation of multiple satellite-based precipitation products over complex topography. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1498–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, I. Assessment of a flash flood event using different precipitation datasets. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1889–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteaker, T.L.; Robayo, O.; Maidment, D.R.; Obenour, D. From a nexrad rainfall map to a flood inundation map. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancamaria, S.; Bates, P.D.; Boone, A.; Mognard, N.M. Large-scale coupled hydrologic and hydraulic modelling of the ob river in siberia. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Warnock, A.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Katopodes, N.D. Coupled modeling of hydrologic and hydrodynamic processes including overland and channel flow. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 37, 104–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviedes-Voullième, D.; García-Navarro, P.; Murillo, J. Influence of mesh structure on 2d full shallow water equations and scs curve number simulation of rainfall/runoff events. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.; Busse, T.; Hou, J.; Özgen, I.; Hinkelmann, R. A model for overland flow and associated processes within the hydroinformatics modelling system. J. Hydroinform. 2014, 16, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Özgen, I.; Hinkelmann, R.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.M. Shallow water simulation of overland flows in idealised catchments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 7307–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganier, O.; Ayral, P.; Salze, D.; Sauvagnargues, S. A coupling of hydrologic and hydraulic models appropriate for the fast floods of the gardon river basin (france). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, J.; Ricci, S.; Piacentini, A.; Jonville, G.; Le Pape, E.; Thual, O.; Goutal, N.; Zaoui, F.; Ata, R. Estimation of lateral inflows using data assimilation in the context of real-time flood forecasting for the marne catchment in france. In Advances in Hydroinformatics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Özgüler, H. Global Climate Change and Its Potential Impacts on Turkish Water Resources; DSİ Bulletin 2002, No: 491–492 (May–June 2002); DSİ: Ankara, Turkey, 2002. (In Turkish)
- Llasat, M.C.; Llasat-Botija, M.; Prat, M.A.; Porcú, F.; Price, C.; Mugnai, A.; Yair, Y. High-impact floods and flash floods in mediterranean countries: The flash preliminary database. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanci, S. Human impact on natural vegetation: A case study of karpuz stream basin (east of manavgat). In Environment and Ecology at the Beginning of 21st Century; St. Kliment Ohridski University Press: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2015; pp. 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.; Sohlberg, R. Global land cover classification at 1 km spatial resolution using a classification tree approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachi, M.; Kubota, T.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Aonashi, K.; Okamoto, K.I.; Oki, R. Development and utilization of “jaxa global rainfall watch” system based on combined microwave and infrared radiometers aboard satellites. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 2011, 131, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, S.; Kubota, T.; Kachi, M.; Oki, R.; Iguchi, T.; Takayabu, Y.N. Reduction of Discontinuity Due to the Orbit Boost in Trmm Precipitation Radar Product for Climate Studies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 644–647. [Google Scholar]
- Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K. Improvement of tmi rain retrievals in mountainous areas. J. Appl. Meteorol.Climatol. 2013, 52, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Yamamoto, M.K.; Taniguchi, A. Improvement of tmi rain retrieval over the indian subcontinent. Remote Sens. Terr. Water Cycle 2014, 206, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kojiri, T.; Tokai, A.; Kinai, Y. Assessment of river basin environment through simulation with water quality and quantity. Annu. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. Kyoto Univ. 1998, 41, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Kojiri, T.; Tanaka, K. Flash flooding simulation using hydrological modeling of wadi basins at nile river based on satellite remote sensing data. Annu. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. 2010, 53, 683–698. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, M. Hydrological Approaches of Wadi System Considering Flash Floods in Arid Regions. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Kojiri, T.; Tanaka, K.; Sumi, T. A physically based distributed hydrological model of wadi system to simulate flash floods in arid regions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.; Saber, M.; Kantoush, S.A.; Khalil, M.F.; Sumi, T.; Sefelnasr, A.M. A hydrological and geomorphometric approach to understanding the generation of wadi flash floods. Water 2017, 9, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Saber, M.; Kantoush, S.A. Japan-egypt hydro network: Modern methodologies for integrated water resources management in egypt. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.; Kantoush, S.; Sumi, T. Integrated management of flash flood in wadi system of egypt: Disaster prevention and water harvesting. Annu. Disasters Prev. Res. Inst. Kyoto Univ. 2015, 58, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- Kojiri, T.; Hamaguchi, T.; Ode, M. Assessment of global warming impacts on water resources and ecology of a river basin in japan. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2008, 1, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kojiri, T.; Michihiro, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakakita, E. Assessment of climate change impacts on river discharge in japan using the super-high-resolution mri-agcm. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3264–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA, SCS. Hydrology Section 4, Chapters 4–10. In National Engineering Handbook; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, M.O. Transmission losses in arid region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1990, 116, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.; Hamagutchi, T.; Kojiri, T.; Tanaka, K. Hydrological modeling of distributed runoff throughout comparative study between some arabian wadi basins. Annu. J. Hydraul. Eng. JSCE 2010, 54, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sumi, T.; Saber, M.; Kantoush, S.A. Japan-egypt hydro network: Science and technology collaborative research for flash flood management. J. Disaster Res. 2013, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, T.; Kaku, M.; Iwasaki, A.; Gesch, D.B.; Oimoen, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Danielson, J.J.; Krieger, T.; Curtis, B.; Haase, J. Aster Global Digital Elevation Model Version 2—Summary of Validation Results; Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center, NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. 27.
- USGS. Global Land Cover Characterization (GLCC). Available online: https://lta.cr.usgs.gov/GLCC (accessed on 1 November 2015).
- Han, D.; Bray, M. Automated thiessen polygon generation. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Shirmohammadi, A. Evaluation of the swat model's hydrology component in the piedmont physiographic region of maryland. Trans. ASAE 2004, 47, 1057–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Knapp, H.V.; Arnold, J.; Demissie, M. Hydrological modeling of the iroquois river watershed using hspf and swat. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardah, T.; Bakar, S.A.; Bardossy, A.; Maznorizan, M. Use of geostationary meteorological satellite images in convective rain estimation for flash-flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Tang, L.; Sapiano, M.; Maggioni, V.; Wu, H. Modeling errors in daily precipitation measurements: Additive or multiplicative? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and nse performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampoulis, D.; Anagnostou, E.N. Evaluation of global satellite rainfall products over continental Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.; Ropelewski, C. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romilly, T.G.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over ethiopian river basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, S.W.; Anders, A.M. Very high resolution precipitation climatologies from the tropical rainfall measuring mission precipitation radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerberg, I.; Guerrero, J.-L.; Younger, P.; Beven, K.; Seibert, J.; Halldin, S.; Freer, J.; Xu, C.-Y. Calibration of hydrological models using flow-duration curves. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevruk, B. Correction of Precipitation Measurements, Summary Report; Workshop on the Correction of Precipitation Measurements: Zurich, Switzerland, 1985; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.; Strangeways, I.; Roberts, A. Field evaluation of two aerodynamic raingauges. Weather 1993, 48, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E. How effective are tipping-bucket raingauges? A review. Weather 1995, 50, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevruk, B.; Klemm, S. Types of standard precipitation gauges. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Precipitation Measurement, WMO/IAHS/ETH, St. Moritz, Switzerland, 3–7 December 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Rodda, J.C. The rainfall measurement problem. Proc. IAHS Gen. Assem. Bern IAHS Publ. 1967, 78, 215–231. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, S.; Petroselli, A.; Baldini, L.; Gorgucci, E. Description and preliminary results of a 100 square meter rain gauge. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).