Hydrogeological Properties Estimation from Groundwater Level Natural Fluctuations Analysis as a Low-Cost Tool for the Mexicali Valley Aquifer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Barometric Pressure Analysis
2.2. Solid-Earth Tide Analysis
2.3. Aquifer Properties Estimation
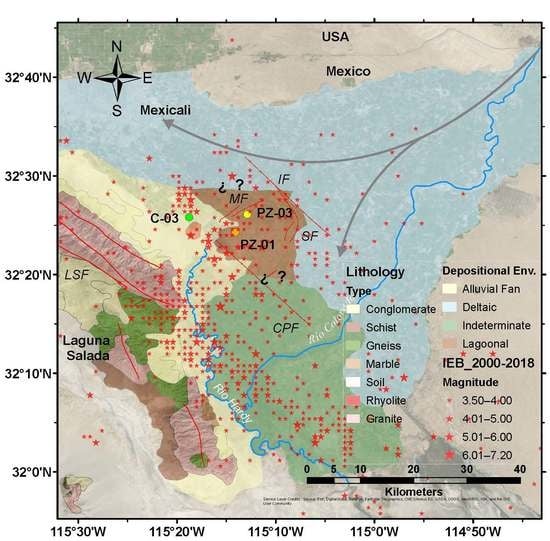
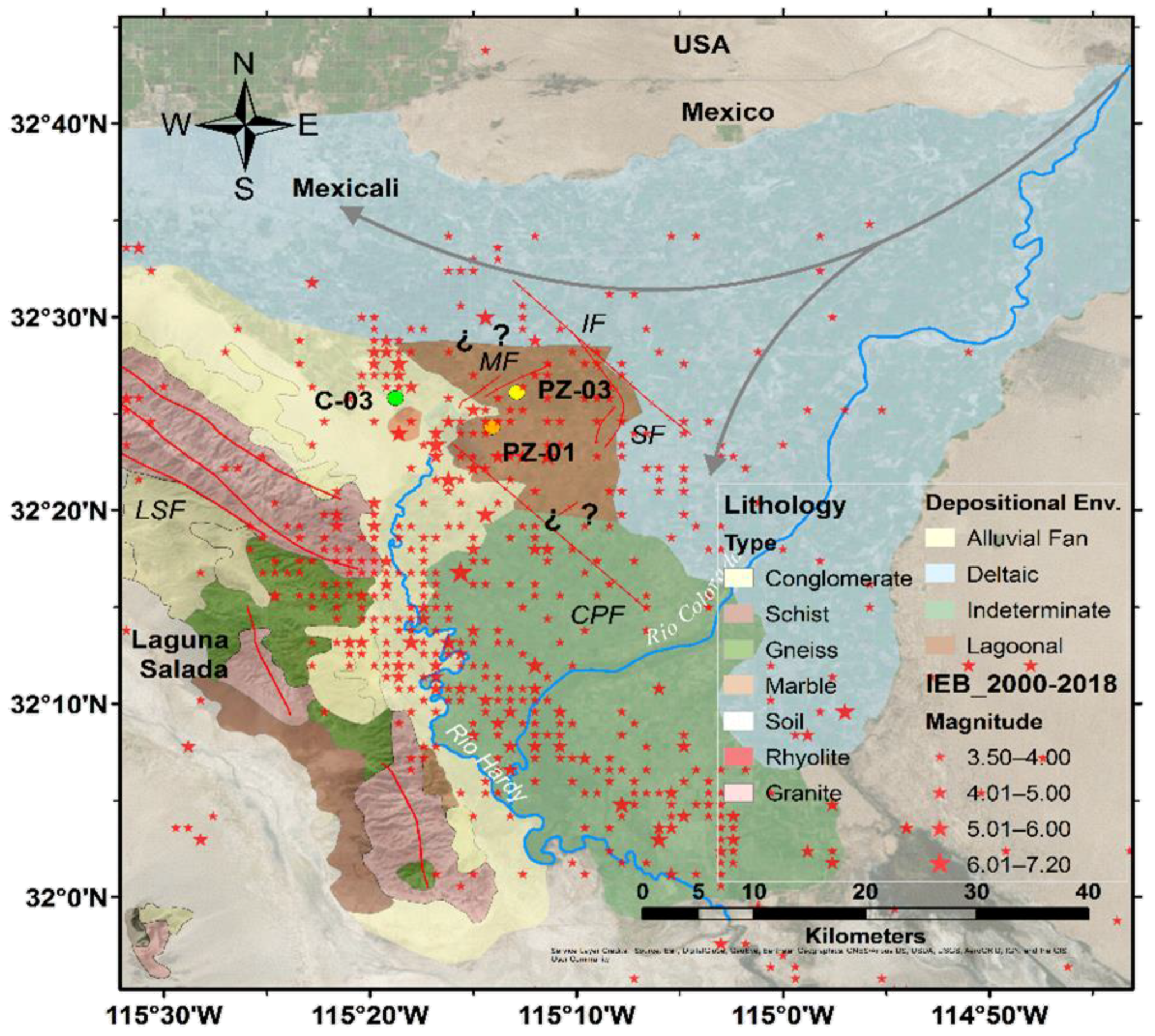
2.4. Study Area
2.5. Data
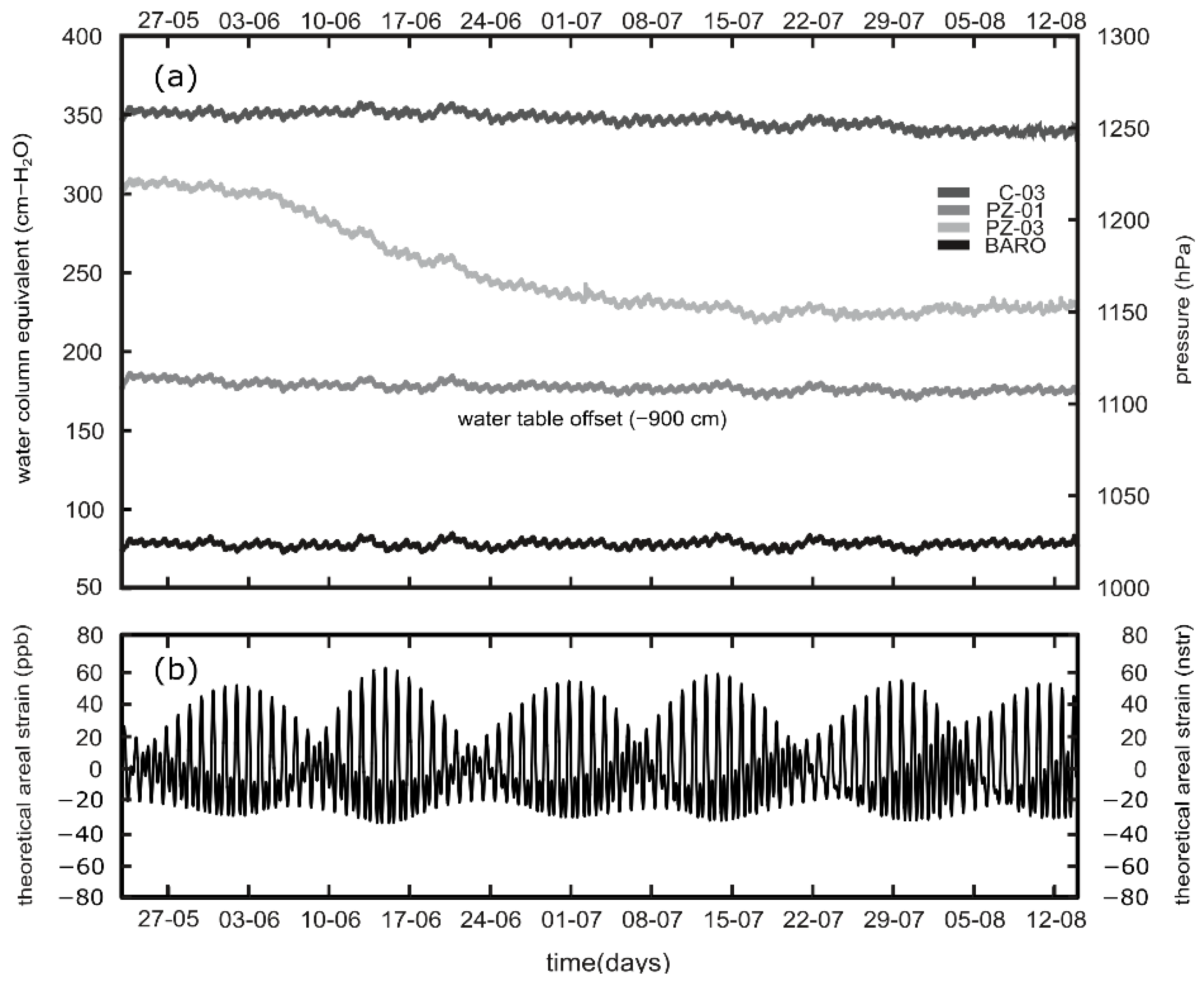
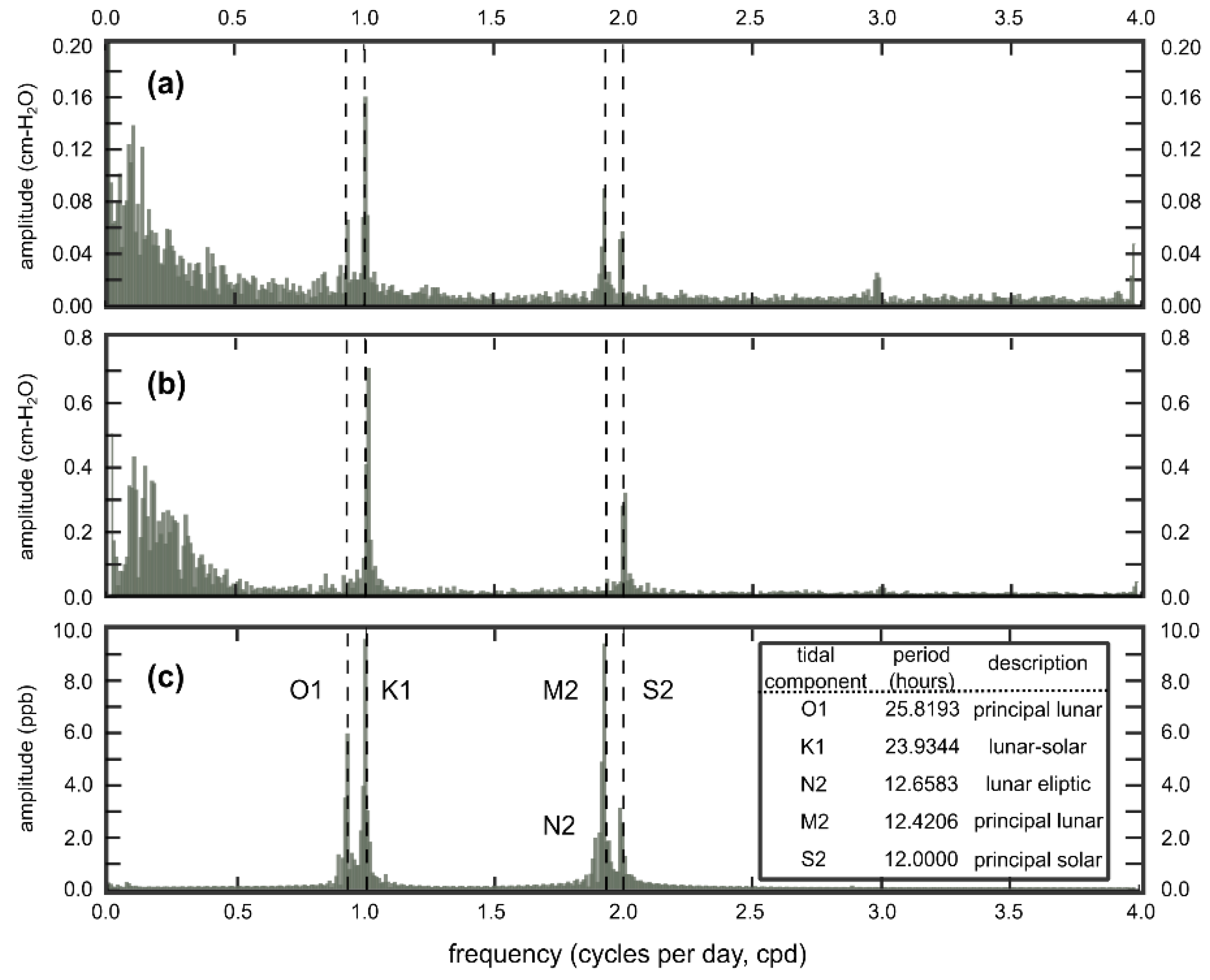
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, C.E. On the flow of water in an elastic artesian aquifer. Eos Trans. AGU 1940, 21, 321–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H.; Bredehoeft, J.D.; Papadopoulos, I.S.; Bennett, R.R. The response of well-aquifer system to seismic waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 3915–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredehoeft, J.D. Response of well-aquifer systems to earth tides. J. Geophys. Res. 1967, 72, 3075–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kamp, G.; Gale, J.E. Theory of earth tide and barometric effects in porous formations with compressible grains. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeloffs, E. Hydrologic precursors to earthquakes: A review. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1988, 126, 177–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojstaczer, S.; Agnew, D.C. The influence of formation material properties on the response of water levels in wells to Earth tides and atmospheric loading. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 12403–12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrit, M.L. Estimating Hydraulic Properties of the Floridan Aquifer System by Analysis of Earth-Tide, Ocean Tide, and Barometric Effects, Collier and Hendry Counties, Florida; USGS Water-Resources Investigations Report 03-4267; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004; 70p. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/wri034267/wri03_4267.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2018).
- Lai, G.; Ge, H.; Wang, W. Transfer functions of the well-aquifer systems response to atmospheric loading and Earth tide from low to high-frequency band. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 1904–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojstaczer, S. Intermediate period response of water wells to crustal strain: Sensitivity and noise level. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 13619–13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojstaczer, S. Determination of fluid flow properties from the response of water levels in wells to atmospheric loading. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojstaczer, S.; Riley, F.S. Response of the water level in a well to earth tides and atmospheric loading under unconfined conditions. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 1803–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, K.A.; Halihan, T. Identifying aquifer type in fractured rock aquifers using harmonic analysis. Ground Water 2013, 50, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darner, R.A.; Sheets, R.A. Using existing data to estimate aquifer properties, Great Lakes region, USA. Ground Water 2012, 50, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureau of Reclamation. Colorado River Basin Natural Flow and Salt Data. 2015. Available online: http://www.usbr.gov/lc/region/g4000/NaturalFlow/documentation.html (accessed on 27 November 2017).
- Meko, D.M.; Woodhouse, C.A.; Baisan, C.A.; Knight, T.; Lukas, J.J.; Hughes, M.K.; Salzer, W. Medieval drought in the upper Colorado River Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, N.; Wood, A.W.; Voisin, N.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Palmer, A.N. The effects of climate change on the hydrology and water resources of the Colorado River Basin. Clim. Chang. 2004, 62, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.L.; Thomas, B.F.; Reager, J.T.; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S.C.; Famiglietti, J.S. Groundwater depletion during drought threatens future water security of the Colorado River Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5904–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Cabrera, P. Numerical Simulation of the Upper Aquifer of the Mexicali Valley, Baja California, Mexico. Master’s Thesis, Centro de Investigación Científica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Feirstein, E.; Zamora-Arroyo, F.; Vionnet, L.; Maddock, T. Simulation of Groundwater Conditions in the Colorado River Delta, Mexico; Department of Hydrology and Water Resources, University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Burgueño, J.E. Modelación Geohidrológica Transitoria de la Relación Acuífero-río de la Zona FFCC-Vado Carranza del Río Colorado con Propósito de Manejo de la Zona Riparia. Master’s Thesis, Instituto de Ingenieria, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California, Mexicali, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Gonzalez, R. Geohydrological conditions of the shallow aquifer in the Cerro Prieto geothermal field zone. Geoterm. Rev. Mex. Geoenergia 1999, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sarychikhina, O.; Glowacka, E.; Mellors, R.; Vazquez-Gonzalez, R.; Munguia, L.; Guzman, M. Surface displacement and groundwater level changes associated whit the 24 May 2006 Mw 5.4 Morelia Fault earthquake, Mexicali Valley, Baja California, Mexico. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 2180–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Arreazola, M.A.; Vazquez-Gonzalez, R. Estimation of some geohydrological properties in a set of monitoring wells in Mexicali Valley, B.C., Mexico. Ing. Agua 2016, 20, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.C.; Crawford, L.A. Identifying and removing barometric pressure effects in confined and unconfined aquifers. Ground Water 1997, 35, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, E.P. Barometric fluctuations in wells tapping deep unconfined aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutillo, P.A.; Bredehoeft, J.D. Estimating aquifer properties from the water level response to earth tides. Ground Water 2011, 49, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, W.E. Computing the barometric efficiency of a well. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1967, 93, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Toll, N.J.; Rasmussen, T.C. Removal of barometric pressure effects and earth tides from observed water levels. Ground Water 2007, 45, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahi, K.A. Estimating the Hydraulic Parameters of the Arbuckle-Simpson Aquifer by Analysis of Naturally-Induced Stresses. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Geology, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.; Rojstaczer, S. Analysis of the frequency response of water levels in wells to earth tides and atmospheric loading. In Fourth Canadian/American Conference in Hydrogeology; Canada National Ground Water Association: Banff, AB, Canada, 1988; pp. 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.C. New Computer Programs for the Calculation of Earth Tides; Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/University of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, J.; Beaumont, C. An analysis of tidal strain observations from the United States of America II: The inhomogeneous tide. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1821–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.C. Cavity and topographic effects in tilt and strain measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.E. Flow of groundwater. In Engineering Hydraulic; Rouse, H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1950; pp. 321–386. ISBN 978-0471742838. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, P.A.; Bredehoeft, J.D.; Rojstaczer, S.A. Response of well-aquifer systems to Earth tides: Problem revisited. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.R.; Cleary, M.P. Some basic stress diffusion solutions for fluid-saturated elastic porous media with compressible constituents. Rev. Geophys. 1976, 14, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, G.; Wakita, H. Tidal responses and earthquake-related changes in the water level of deep wells. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 4269–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.C. Earth tides. In Treatise on Geophysics and Geodesy; Herring, T.A., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 163–195. ISBN 9780444534606. [Google Scholar]
- Doodson, A.T.; Warburg, H.D. Admiralty Manual of Tides; Her Majesty’s Stationary Office: London, UK, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Melchior, P. Die gezeiten in unteriridschen flussigkerten. Erdoel Kohle 1960, 13, 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Melchior, P. Earth tides. In Research in Geophysics; Odishaw, H., Ed.; Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964; Volume 2, pp. 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, P.A.; Bredehoeft, J.D.; Farr, J.M. Determination of the aquifer transmissivity from earth tide analysis. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, J.M.; Martín-Barajas, A.; Suárez-Vidal, F.; Miller, M.M. Miocene to Holocene extensional tectonics and volcanic stratigraphy of NE Baja California, Mexico. In Geological Excursions in Southern California and Mexico; Walawender, M.J., Hanan, B., Eds.; Department of Geological Sciences, California State University: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Kamp, P.C. Holocene continental sedimentation in the Salton basin, California: A reconnaissance. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1973, 84, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Vidal, F.; Mendoza-Borunda, R.; Nafarrete-Zamarripa, L.M.; Ramírez, J.; Glowacka, E. Shape and dimensions of the Cerro Prieto pull-apart basin, Mexicali, Baja California, Mexico, based on the regional seismic record and surface structures. Int. Geol. Rev. 2008, 50, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommitz, C.; Mooser, F.; Allen, C.R.; Brune, J.N.; Thatcher, W. Seismicity and tectonics of the northern Gulf of California region, Mexico, preliminary results. Geofís. Int. 1970, 10, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Frez, J.; González, J.J. Crustal structure and seismotectonics of Northern Baja California. In The Gulf and Peninsular Province of the Californias; Dauphin, J.P., Simoneit, B.R.T., Eds.; Memoir #47; American Association of Petroleum Geologist: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elders, W.A.; Hoagland, J.R.; McDowell, S.D.; Cobo, J.M. Hydrothermal mineral zones in the geothermal reservoir of Cerro Prieto. Proceedings/Actas of the First Symposium on the Cerro Geothermal Field, Baja California, Mexico, 20–22 September 1978; Berkeley Department of Energy: San Diego, CA, USA, 1979; pp. 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lira-Herrera, H. Update of the conceptual geological model for the geothermal reservoir in Cerro Prieto. Geotermia. Rev. Mex. Geoenergia 2005, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Rosales, J. Overview of the geohydrology of Cerro Prieto, B.C., Mexico. Geoterm. Rev. Mex. Geoenergia 1999, 15, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Rodríguez-Burgueño, J.; Ramírez-Hernández, J. Groundwater response to the 2014 pulse flow in the Colorado River Delta. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRIS-Earthquake Browser. Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology, IRI. Available online: https://ds.iris.edu/ieb/index.html?format=text&nodata=404&starttime=2000-01-01&endtime=2018-01-01&orderby=mag- (accessed on 25 November 2017).
- Berger, J.; Farrell, W.; Harrison, J.C.; Levine, J.; Agnew, D.C. ERTID 1: A Program for Calculation of Solid Earth Tides; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: La Jolla, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Agnew, D.C. SPOTL: Some Programs for Ocean-Tides Loading; Technical Report; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowicz, R.; Beardsley, B.; Lenz, S. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in Matlab using T_TIDE. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Main equations of flow, boundary conditions, and flow nets. In Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 58–74. ISBN 0-471-59762-7. [Google Scholar]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Physical properties and principles. In Groundwater; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 14–79. ISBN 0-13-365312-9. [Google Scholar]
| Well ID | Latitude 1 | Longitude 1 | LSE | BD | WLE | Lws = b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (dd) 2 | (dd) 2 | (MASL) | (m) | (MASL) | (m) | (m) | |
| C-03 | 32.4261 | −115.3102 | 13.38 | 201.00 | 2.67 | 0.05/0.05 | 51.00 |
| PZ-01 | 32.4045 | −115.2343 | 9.28 | 507.00 | −4.43 | 0.05/0.05 | 51.00 |
| PZ-03 2 | 32.4342 | −115.2140 | 11.40 | 159.00 | 8.30 | 0.05/0.05 | 42.70 |
| Well ID | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | |||||||
| C-03 | 45.82 | 9.94/13.14 | −86/86 | 12.21/19.14 | −44/37 | −42/49 | 8.14/6.86 |
| PZ-01 | 51.43 | 11.86/17.64 | −56/−32 | 12.22/19.15 | −44/37 | −12/−69 | 9.70/9.21 |
| PZ-03 | 50.72 | 6.95/12.89 | −12/−41 | 12.20/19.14 | −44/37 | 32/−78 | 5.69/6.78 |
| Well ID | () | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (-) | |||
| C-03 | 1.60/2.04 | 17.07/21.76 | 3.21/4.02 | 3.05/10.39 |
| PZ-01 | 1.19/1.52 | 14.22/18.14 | 6.03/7.70 | 29.15/1.38 |
| PZ-03 | 2.03/2.06 | 23.93/24.30 | 3.22/3.27 | 6.94/0.52 |
| Well ID | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-) | (-) | (-) | |||||
| C-03 | 7.62/7.97 | 7.31/7.75 | 15.48/16.51 | 14.67/15.57 | 3.05/4.50 | 0.60/0.59 | 0.74/0.75 |
| PZ-01 | 3.90/4.31 | 2.93/3.54 | 6.31/7.76 | 14.85/17.94 | 38.49/0.05 | 0.56/0.55 | 0.49/0.55 |
| PZ-03 | 8.21/6.69 | 8.99/6.86 | 21.15/15.79 | 14.29/10.90 | 5.55/0.37 | 0.55/0.55 | 0.76/0.70 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuentes-Arreazola, M.A.; Ramírez-Hernández, J.; Vázquez-González, R. Hydrogeological Properties Estimation from Groundwater Level Natural Fluctuations Analysis as a Low-Cost Tool for the Mexicali Valley Aquifer. Water 2018, 10, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050586
Fuentes-Arreazola MA, Ramírez-Hernández J, Vázquez-González R. Hydrogeological Properties Estimation from Groundwater Level Natural Fluctuations Analysis as a Low-Cost Tool for the Mexicali Valley Aquifer. Water. 2018; 10(5):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050586
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuentes-Arreazola, Mario A., Jorge Ramírez-Hernández, and Rogelio Vázquez-González. 2018. "Hydrogeological Properties Estimation from Groundwater Level Natural Fluctuations Analysis as a Low-Cost Tool for the Mexicali Valley Aquifer" Water 10, no. 5: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050586
APA StyleFuentes-Arreazola, M. A., Ramírez-Hernández, J., & Vázquez-González, R. (2018). Hydrogeological Properties Estimation from Groundwater Level Natural Fluctuations Analysis as a Low-Cost Tool for the Mexicali Valley Aquifer. Water, 10(5), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050586