Abstract
This paper examines two successive debris flows that deposited a total of 1.4 million m3 of sediment into the Parlung Tsangpo River in China in 2010. As a result of these deposits, a partial-debris dam was formed in the river. This dam rerouted the discharge in the river along one of the riverbanks, which supported a highway. The rerouted discharge eroded the riverbank and the highway eventually collapsed. To enhance our understanding of the threat posed by partial-debris dams, a field investigation was carried out to measure the discharge in the river and to collect soil samples of the collapsed riverbank. Findings from the field investigation were then used to back-analyze fluvial erosion along the riverbank using a combined erosion framework proposed in this study. This combined framework adopts a dam-breach erosion model which can capture the progressive nature of fluvial erosion by considering the particle size distribution of the soil being eroded. The results from the back-analysis were then evaluated against unique high-resolution images obtained from satellites. This case study not only highlights the consequences of the formation of partial-debris dams on nearby infrastructure, but it also proposes the use of a combined erosion framework to provide a first-order assessment of riverbank stability. Unique high-resolution satellite images are used to assess the proposed erosion framework and key challenges in assessing erosion are discussed.
1. Introduction
Debris flows entering rivers from tributaries can significantly alter the morphological settings [1,2,3]. The deposition of large volumes of sediments into rivers can form debris dams [4]. These dams impound water, leading to back-flooding, or if the dam fails, catastrophic flooding can occur downstream [5,6]. A lesser variant of a debris dam is when deposited sediments only partially block a river, thereby forming a partial-debris dam. This type of dam reroutes the discharge of water along an alternative path. If the riverbank forms part of the rerouted path, then the concentrated discharge expedites the rate of fluvial erosion of the soil along the riverbank [7]. Although fluvial erosion is a progressive phenomenon, it presents hazards that are difficult to predict. For instance, unstable riverbanks from prolonged erosion can collapse, posing significant threats to nearby infrastructure, such as railway embankments, highways, and bridge piers [8].
Fluvial erosion depends on the rate of discharge and the shear resistance of the soil forming the riverbank [9,10,11,12]. The particle size of the soil principally governs the shear resistance against fluvial erosion [13]. More specifically, finer particles are more susceptible to erosion because of lower friction angles and lower resistance to inertial viscous shearing by the river. By contrast, coarser particles have higher bulk friction angles and require higher inertial viscous stresses by the river to shear the soil [14] from the riverbank. Evidently, particle size effects are an important feature that warrants consideration when analyzing fluvial erosion of riverbank soil.
The evolution of riverbank erosion is most commonly assessed using an approach proposed by [15]. More specifically, the lateral erosion, , is calculated as follows:
where is the critical shear stress of the soil forming the riverbank (Pa); is the applied shear stress by the river (Pa); is the erosion duration (s); and is the bulk unit weight of the riverbank soil (kN/m3). The critical shear stress of the soil in this approach is based on the sodium absorption ratio of the interstitial fluid between soil grains. The sodium absorption ratio of the interstitial fluid governs the degree of osmotic suction [16] and, thereby, the critical shear stress induced on the soil. Equation (1) is relatively straightforward and assumes a homogeneous and fine-grained soil. More importantly, the effects of particle size are not explicitly considered, and progressive changes in the profile of the riverbank during erosion are not considered.
Jiang et al. [17] proposed another approach to improve the estimation of lateral riverbank erosion as proposed by [15]. Improvements were made by considering the erosion profile of the riverbank. More specifically, Jiang et al. [17] assumed that the slip surface always passes through the toe of the riverbank. With an assumed slip surface, limit equilibrium analysis [18,19,20] is carried out to assess the stability of the riverbank profile. During limit equilibrium analysis, if the riverbank profile is unstable, then the slip surface of the unstable riverbank profile is taken as the new riverbank profile. Iterations are carried out for a defined timeframe. Similarly, with the approach proposed by [15], this method does not explicitly consider the effects of particle size, which is fundamental in capturing the progressive nature of fluvial erosion. However, this modified approach considers the progressive changes in the profile—and, therefore, the stability—of the riverbank.
Wang et al. [21] proposed an alternative method to estimate the erosion of quake dams in Tianjiashan. Contrary to both the approaches proposed by [15,17], this approach considers the particle size distribution of the soil forming a quake dam, which is used to estimate the critical shear stress of the soil. The particle size distribution is reflected by the mean particle diameter, . The characteristic particle diameter was selected based on interpretation of data from the Tianjiashan quake dam in China. From this particular case study, observations from the field were used to further validate that fines are scoured before coarse grains are eroded. The consequence of this erosion mechanism is that the critical shear stress of the soil forming the dam increases with time. As a result of considering the mean particle diameter, the critical shear stress is explicitly captured in the quake dam–breach erosion model.
This paper examines a case study of the accumulation of up to 1.4 M m3 of debris flow deposits, from the Tianmo Watershed, in the Parlung Tsangpo River in Tibet, China [22] in the year 2010. Deposited sediments formed a partial-debris dam in the river and rerouted discharge along one of the riverbanks of the Parlung Tsangpo River. The rerouted and concentrated discharge along the riverbank enhanced the rate of erosion and eventually undermined about 800 m of highway adjacent to the river. To back-analyze the erosion process of the riverbank, a combined framework based on the work of [15,17,21] is proposed. This new framework was then validated using unique high-resolution images obtained from satellites.
2. New Framework to Analyze Riverbank Erosion
Fluvial erosion in this study was estimated based on the quake dam model [21]. According to [15], lateral erosion was calculated and limit equilibrium analysis was carried out. Generally, this framework consists of four steps. First, the critical shear stress is calculated as follows [23]:
where is the unit weight of water (kN/m3), is the bulk density of soil in the river bank, and is the median particle diameter (m). Second, the flow-induced shear stress (kPa) is determined as follows [21]:
where is the Manning coefficient, is the flow velocity (m/s), and is the flow depth (m). Third, the shear stresses are used to determine the lateral erosion distance as follows [21]:
where is the erodibility coefficient of the riverbank soil () based on experiments from [24]. Fourth, the calculated lateral erosion is used to assess the profile of the riverbank. The stability of the riverbank profile is then analyzed using limit equilibrium analysis. In this study, a Slope/W [25] was used to interpret changes in the factor of safety of the slope during fluvial erosion of the riverbank. The Factor of Safety (FOS) is given as follows [18]:
where is the slice index, is effective cohesion, is the effective internal angle of friction, is the width of each slice, is the weight of each slice, is the angle between each slice and horizontal, and is the pore water pressure at the base of each slice. Iterations of these four steps are carried out until the FOS reaches a stable value.
3. Tianmo Watershed and 2010 Debris Flows
The Tianmo Watershed is situated in Bomi County, Tibet, China and serves as a tributary to the Parlung Tsangpo River (Figure 1a). The watershed has an area of 17.8 km2 and a maximum elevation difference of about 2460 m (Figure 1c). Frequently occurring monsoons, which develop in the Indian Ocean, provide precipitation that can last up to six months. The annual average rainfall intensity is about 880 mm [26]. In addition to rainfall, snow-melt and glacial recession provide additional sources of runoff in the watershed. Glacial recession also provides an abundance of deposits in this watershed. The combination of ample rainfall and runoff, and thick deposits provide ideal conditions for the development of large-scale debris flows.
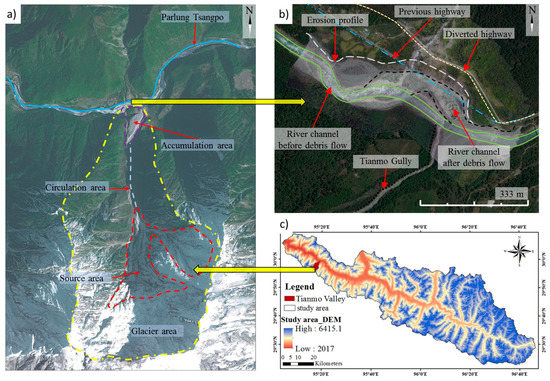
Figure 1.
(a) High-resolution image of Tianmo Watershed; (b) Plan view junction between Tianmo tributary and Parlung Tsangpo River in 2010 and 2017 in Google Earth Imagery (acquisition date: 10 January, Image © 2018 DigitalGlobe); (c) Geomorphologic information of Parlung Tsangpo River and the related tributary.
The 25 July 2010 and 4 September 2010 debris flows were triggered by the effects of both rainfall and temperature. Rising temperatures accelerated snow-melt and glacial recession. Runoff from snow and glaciers infiltrated the loose sediments and reduced its shear strength [27], thereby enhancing the scale of debris flows through entrainment. For the 25 July 2010 and 4 September 2010 debris flows, the average temperature for the 30 days preceding the flows was 18 °C, which was 2 °C higher than the average temperature in the region. Aside from the higher-than-usual temperatures, rainfall was another pertinent factor in triggering the debris flows. There was continuous rainfall from 15 to 25 July 2010; the rainfall on the initiation day of this debris flow was 33.3 mm, and the total amount of rainfall in those 10 days was recorded as 102.7 mm [22,28]. During this time, two intense rainfalls with intensities of 12 mm/day and 8 mm/day were recorded on 15 July 2010 and 25 July 2010, respectively. For the debris flow that occurred on 4 September 2010, continuous rainfall occurred onwards from 24 August 2010. During this time, two intense rainfall events with intensities of 21 mm/day and 25 mm/day were recorded on 23 August 2010 and 4 September 2010, respectively. The four intensities mentioned above were much higher than the annual average rainfall intensity of 1.55 mm/day [29].
The 25 July 2010 and 4 September 2010 debris flows deposited about 900,000 m3 and 450,000 m3 of sediments into the Parlung Tsangpo River [22], respectively. The deposits partially blocked the river and formed a partial-debris dam. The width of the river channel was reduced from 180 m to 100 m [22,28]. The location where the debris flow entered the river is shown in Figure 1b. Solid lines are used to illustrate the original configuration of the river channel before the debris flows. The diverted route of the river is also shown using dashed lines. The erosion damaged about 900 m of the highway (G318) adjacent to the river. This section of the damaged highway was eventually diverted 170 m north of the existing alignment.
4. Field Investigation
A field investigation was carried out to measure the flow rates of the Parlung Tsangpo River in July 2010. The flow rate was measured at two monitoring sections. The upstream monitoring section was located at the junction between the tributary from the Tianmo Watershed and the Parlung Tsangpo River. The downstream monitoring section was located at the Jiamaqimei station, just 15 km downstream from the upstream monitoring section. The average annual flow rate at the monitoring sections was 421 m3/s [30]. This flow rate was adopted to calculate the evolution of erosion of the riverbank.
Generally, flow-type landslides are characterized based on their solid volume fractions. A debris flow is considered to have a solid volume fraction greater than 0.6 [31,32]. Unfortunately, the debris flows in this study had already deposited by the time the field investigation was carried out. As a result, the deposits were significantly reworked by subsequent debris floods, which often follow the coarse granular fronts of a debris flow. Also, the transport capacity of the river likely reworked the sediment concentrations of the deposited debris flows. Further complicating matters, the main challenge in the back-analysis of the river bank is that there is a dearth of field data available. For instance, sediment loads were not monitored, which could have provided a much more in-depth understanding of the problem.
From the field investigation, particle sizes ranged from 0.04 m to 1.0 m; however, the likelihood that much larger boulders were entrained within the riverbank cannot be precluded. Given the wide range of particle sizes, characterizing the particle size distribution using a single parameter remains a significant scientific challenge. This challenge is certainly a limitation in the back-analysis of the erosion of the riverbank using continuum-based approaches. From the field investigation, boulders along the riverbank were observed to have a relatively high sphericity, but the particle shape effects were not comprehensively sampled at the time of the debris flows in 2010, which has hindered a detailed interpretation of the particle shape effects on river bank erosion.
It is acknowledged that the morphology has changed significantly since the debris flow events in 2010. However, a qualitative analysis on the effects of the particle debris dam on fluvial transport capacity was carried out in September 2017 to try to obtain a better understanding of the fluvial characteristics of the study area (Figure 2a). Figure 2a shows that a partial-debris dam impounded water (Figure 2b). This feature generally alters the ability of the river to transport sediment downstream [33]. If the transport capacity of the river exceeds that of the available supply of sediments, then sediment-starvation may occur, which enhances the erosion of the river banks and river bed downstream of the partial debris dam. In this study, a slight back water effect induced a reduction in the flow velocity immediately upstream of the partial-debris dam. Correspondingly, a decrease in drag forces on the suspended particles is expected, which would increase sediment deposition and sedimentation velocity. This effect greatly reduces the sediment concentration downstream of the dam [34]. The decrease in total suspended solid concentration downstream of the partial-debris dam in this study could be considered as a clear-water-erosion condition (low sediment concentration). Notwithstanding, detailed measurements of the sediment loads in the river were not monitored in 2010 immediately after the debris flow events.
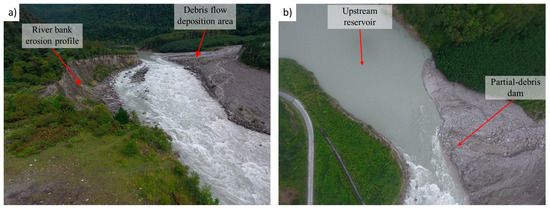
Figure 2.
Field investigation of (a) river bank erosion profile; (b) upstream reservoir (unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photo taken on 12 September 2017).
The flow rate of Parlung Tsangpo River was obtained from a hydrological station located 15 km downstream of the junction between the Tianmo Gully and the River. The flow rate was averaged over 20 years to ensure a representative discharge.
Aside from discharge measurements from the river, soil samples were taken from the riverbank (Figure 3). The unit weight, friction angle, and cohesion of the riverbank soil were measured as 20 kN/m3, 37°, and 33 kPa, respectively. The in situ particle size distribution was obtained using an image digitization (Figure 3), which is discussed in detail in [35]. This technique requires defining threshold values for filtering and calculations of the area and perimeter of each soil particle, which can then be used to determine the particle size distribution (Figure 4). The soil sample is granular and contains a great volume of cobbles and boulders. The median particle diameter, , of the soil sample is about 0.3 m. This characteristic diameter is dissimilar to the conventional obtained in geotechnical laboratory testing since the cobbles and boulders embedded inside the riverbank could not be sampled. Notwithstanding, obtaining a realistic from the field would undoubtedly provide a better estimation of the erosion process.
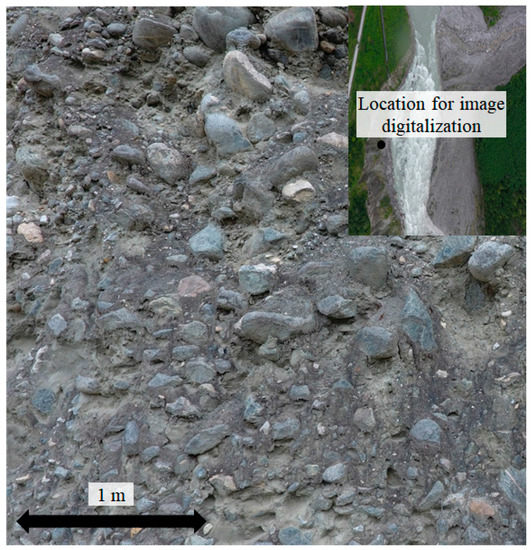

Figure 3.
Riverbank soil from the Parlung Tsangpo River: image of the particles.
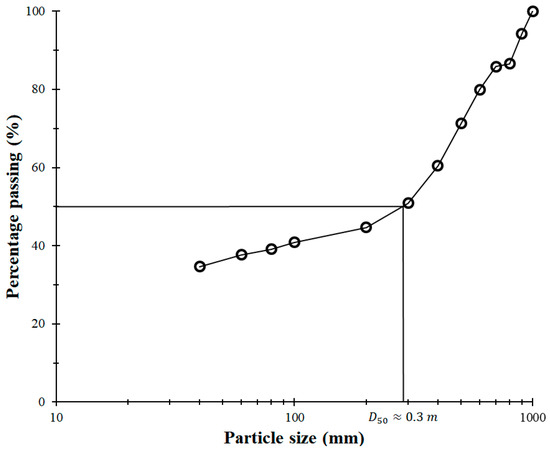
Figure 4.
Particle size distribution of the soil sample from image digitalization.
5. Back-Analysis of Riverbank Erosion
The erosion of the Parlung Tsangpo riverbank was analyzed using the new combined framework proposed in this study. The lateral erosion distance from 2010 to 2011 was around 135 m. Figure 5 shows the calculated time history, using limit equilibrium analysis, of the riverbank stability at the junction between the Parlung Tsangpo River and Tianmo Gully. The riverbank stability is expressed as the FOS of the riverbank. The time history starts just after the second debris flow on 4 September 2010 where the initial width, height, slope of the riverbank, and slope above the riverbank were 82 m, 19 m, 90°, and 13°, respectively. The riverbank profile was initially assumed to be vertical, and the depth of the river was measured as about 4 m, while the water table in the riverbank was assumed to be constant and hydrostatic. Furthermore, the soil properties such as the unit weight, angle of friction, and cohesion of the riverbank were obtained from the field investigation discussed previously. In addition, the method of ordinary slices [18] was selected for limit equilibrium analysis. This entails 30 slices and a minimum failure thickness of 0.1 m.

Figure 5.
Time history of the riverbank stability of the junction between the Parlung Tsangpo River and Tianmo Gully; Factor of Safety (FOS) less than 1 denotes riverbank failure.
Based on the results from the above settings and assumptions, the FOS at 10 days after the debris second flow event on 4 September 2010 exhibited an approximately twofold increase. This is because of the initial assumption that the riverbank profile is vertical, which is highly unstable. After the first iteration, the vertical profile becomes a shallower sloping profile. As erosion progresses, the riverbank exhibits cycles of collapse and subsequent stabilization. More specifically, the FOS rapidly decreases to less than unity at around 20 days. As the riverbank profile stabilizes to a shallower gradient, the FOS increases thereafter. The riverbank fails again at around 160 days. Subsequent increases in FOS are always less than that of the previous collapse (by up to 65%). The riverbank exhibits failure at about 340 days. Results also indicate that the duration between failure increases. This is plausible since erosion is a process that scours away fines, which increases the strength of the riverbank with time. Furthermore, a subsequent increase in FOS after the third failure of the riverbank was less than the FOS after second collapse by about 57%. Riverbank stability and instability continues to occur until almost no change in FOS was observed at 420 days. At this point, the riverbank is deemed to have stabilized. The final distance of riverbank erosion over 340 days is about 135 m. Figure 6 shows an evolution of the riverbank profile from 0 days to 340 days. The profile of the riverbank was vertical on 4 September 2010. Lateral erosion occurred until the riverbank became unstable after about 20 days. The riverbank profile then failed and the profile was approximated as an inclined surface. This profile was eroded horizontally until 160 days when the riverbank failed again, thereby forming an arc shape. Furthermore, erosion occurred until the riverbank failed at around 340 days and formed an arc shape again. The failure profile is observed to be consistent with the FOS calculation in Figure 5.
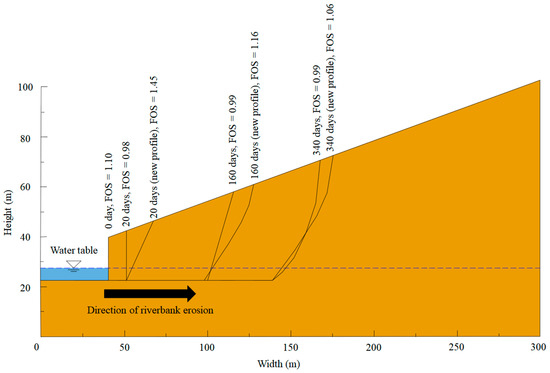
Figure 6.
Evolution of the riverbank from 0 days to 340 days after the debris flow event on 4 September 2010.
6. High-Resolution Satellite Images
The back-analyzed lateral riverbank erosion was compared with two unique high-resolution satellite images taken on 1 December 2010 (Figure 7a) and 27 August 2011 (Figure 7b). The satellite images show that the riverbank profile at the junction between the tributary from the Tianmo Watershed and the Parlung Tsangpo River had shifted about 100 m from the original profile.

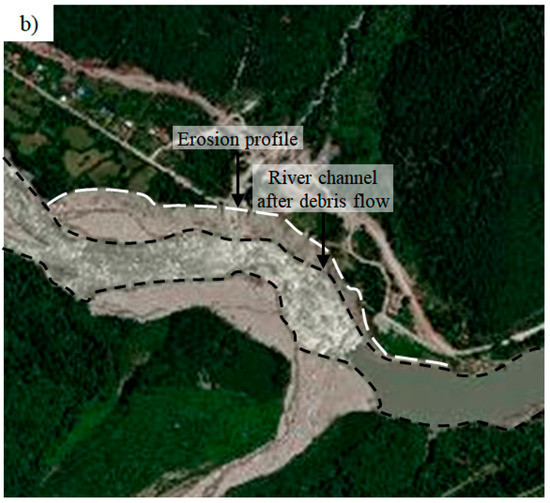
Figure 7.
Satellite images: (a) 1 December 2010 and (b) 27 August 2011.
The image taken in 2010 shows that the lateral erosion distance is about 85 m, which differs from the analysis in this study by up to 55%. The erosion in 2011 enlarged to 110 m, which differs by 18% compared to the analysis in this study. Obvious factors that may have caused the discrepancy between the measured and computed results are the empirical factors adopted in this study. For example, the parameter in this study was obtained from the morphological and geological settings based on an amalgamation of rivers from Mainland China. Since the value of is site-specific, this parameter needs clear physical meaning and to be fine-tuned for the Parlung Tsangpo River [24].
The effects of particle size also strongly influence the critical shear stress of the riverbank [36,37]. The characteristic grain diameter, , in Equation (2) was obtained from image digitalization [38]. However, based on the field investigation, a multitude of large particles, cobbles, and boulders are likely embedded in the riverbank, resulting in an underestimated . This underestimation may lead to lower FOSs than that calculated. More importantly, these large particles may also affect the validity of the unit weight of the soil adopted in the limit equilibrium analysis.
The back-analyzed riverbank erosion assumes a hydrostatic water table. In reality, the discharge in a river varies based on the morphology [39,40]. However, since observation wells and measurements were not available, a hydrostatic water table was assumed. Furthermore, the soil strength parameters obtained from the riverbank soil were quite large and had to be filtered in order to carry out soil specimen testing in the laboratory. The removal of these larger particles reduces the soil strength parameters used in this study. Also, the soil samples were reconstituted and not intact; this may have destroyed any cohesion, which may have further contributed to the total shear strength of the riverbank soil. Finally, the change of the water table was ignored, meaning that variation of pore water pressures along the morphology of the river was grossly simplified as constant and hydrostatic. Furthermore, rainfall infiltration, vegetation cover, and hydraulic effects of plant–soil interaction may also affect slope stability [41,42]. However, these effects were not taken into consideration in this study. Therefore, the effective stress of soil forming the riverbank may be overestimated, resulting in a higher FOS for the riverbank compared with actual conditions in the field. This discrepancy implies that the actual regressive rate of the riverbank is likely much faster than the rate calculated in the analysis.
7. Summary
A case study of two debris flows entering the Parlung Tsangpo River from the Tianmo Watershed in the latter half of 2010 was presented. The results from this study were evaluated against high-resolution images obtained using remote sensing. The lateral erosion distance, using limit equilibrium analysis, was estimated as 135 m from 2010 to 2011, which exhibited up to a 5% difference when compared with unique high-resolution satellite images. The unique case study not only highlights the consequences of the formation of a partial-debris dam on nearby infrastructure, but it demonstrates the use of a combined framework, consisting of a quake dam–breach erosion framework, to provide a quick first-order assessment of riverbank stability. More importantly, this study corroborates that assessing erosion of riverbanks accurately remains a pertinent scientific challenge. More specifically, comprehensive groundwater monitoring, pre and post river profile measurements, and proper techniques to sample soil properties, such as the particle size distribution and soil shear strength, are necessary for any fruitful analysis. Also, existing approaches to back-analyze riverbank erosion often entail empirical parameters that are site-specific and comprehensive sensitivity analysis is crucial to grasping the effects of these parameters. With these challenges in mind, the use of temporary physical countermeasures such as living or dead plants may be more suitable solutions to protect the riverbank after partial-debris dams form [43]. Although the service life of vegetation is limited, it promotes a means to protect nearby infrastructure until the discharge in the river returns to normal levels. On a final note, assessing erosion requires not just detailed accounts of the site postdeposition, but also records of the discharge rates in the river and the degree of erosion before the river morphology changes. Without addressing these challenges, any framework aimed at providing quick assessments of the threat posed by partial-debris dams remains a scientific challenge. Therefore, a continuous monitoring method surveyed by multitemporal terrestrial laser scanning [44,45,46] is required in the future to obtain a detailed erosion profile over time immediately after the debris event. Furthermore, optical fiber sensors for the simultaneous measurement of hydrostatic pressure in soil embankments is another useful technology that can help obtain changes in the water table and also any seepage effect [47]. Besides this, interferometry [48] can be installed along the riverbank to monitor the degree of deformations. The shear strength of the riverbank also needs to be determined based on both saturated and unsaturated conditions [49]. These data are valuable to back-analyzing the evolution of the riverbank profile.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the support from the theme-based research grant T22-603/15N and general research fund 16209717 of the Hong Kong Research Grants Council. Also, the authors are grateful for the financial sponsorship from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (5170091039) and the Hong Kong Jockey Club Charities Trust. The authors are grateful for financial sponsorship from the Opening Fund of State Key Laboratory of Hydraulics and Mountain River Engineering (SKHL1609). Finally, the authors are grateful for the support of the HKUST Jockey Club Institute for Advanced Study and the financial support by the Hong Kong Jockey Club Disaster Preparedness and Response Institute (HKJCDPRI18EG01).
Author Contributions
Clarence Edward Choi and Yifei Cui designed the research and drafted the manuscript. Kelvin Yuk Kit Au and Haiming Liu performed the numerical analysis related to river bank erosion. Dingzhu Liu, Jiao Wang and Hao Wang contributed to the literature review, field investigation and data collection. All authors revised the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gregory, K.J.; Gurnell, A.M.; Hill, C.T. The permanence of debris dams related to river channel processes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1985, 30, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanites, B.J.; Webb, R.H.; Griffiths, P.G.; Magirl, C.S. Debris flow deposition and reworking by the Colorado River in Grand Canyon, Arizona. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, L. Study on features of river-blocked by debris flow and criterion of disaster at the opposite river bank. J. Sichuan Univ. (Eng. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 44, 93–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Petley, D. Understanding the Seti River Landslide in Nepal. Available online: https://blogs.agu.org/landslideblog/2012/05/23/understanding-the-seti-river-landslide-in-nepal/ (accessed on 18 December 2017).
- Costa, J.E.; Schuster, R.L. The formation and failure of natural dam. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1988, 100, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Tang, C.X.; van Western, C.J.; Alkema, D. Simulating dam-breach flood scenarios of the Tangjiashan landslide dam induced by the Wenchuan Earthquake. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 3031–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, R.Z.; Sulaiman, M.S.; Yusoff, N. Erosion risk assessment: A case study of the Langat River bank in Malaysia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, R.; Kawahara, Y.; Sayama, T. Analysis of hydraulic and geomorphic condition causing railway embankment breach due to inundation flow. J. Hydrosci. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 30, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.T. Reclamation: Managing Water in the West Denver, Colorado; Sedimentation and River Hydraulics Group, Technical Service Center, Bureau of Reclamation, U.S. Department of Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Julien, P.Y. Erosion and Sedimentation, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sulaiman, M.S.; Sinnakaudan, S.K.; Shukor, M.R. Near bed turbulence measurement with acoustic doppler velocimeter (ADV). KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 17, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A. River Processes: An Introduction to Fluvial Dynamics; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Couper, P.R.; Maddock, I.P. Subaerial river bank erosion processes and their interaction with other bank erosion mechanism on the River Arrow, Warwickshire, UK. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koos, E.; Linares-Guerrero, E.; Hunt, M.L.; Brennen, C.E. Rheological measurements of large particles in high shear rate flows. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 013302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.M.; Thorne, C.R. Riverbank stability analysis: Theory. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1988, 114, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagaraj, T.; Rao, S.M. Influence of osmotic suction on the soil-water characteristic curves of compacted expansive clay. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, X. Numerical simulation method of bank collapse based on theory of critical slip field. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 21–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fellenius, W. Calculation of stability of earth dams. In Proceedings of the 2nd Congress on Large Dams, Washington, DC, USA, 7–12 September 1936; Volume 4, pp. 445–462. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern, N.R.; Price, V.E. The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces. Géotechnique 1965, 15, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.W. The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of earth slopes. Géotechnique 1971, 5, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, F.; Fu, X.; Li, T. Simulation of dam breach development for emergency treatment of the Tangjiashan Quake Lake in China. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 2009, 51, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Cui, P.; Su, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Case history of the disastrous debris flows of Tianmo Watershed in Bomi County, Tibet, China: Some mitigation suggestions. J. Mt. Sci. 2014, 11, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Peter, E.; Muller, R. Formulas for bed-load transport. In Proceedings of the IAHSR 2nd Meeting, Stockholm, Sweden, 7–9 June 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Su, D. River channel scour and scour rate of clear water flow. J. Sediment Res. 1998, 42, 3–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GEO-SLOPE International. Stability Modeling with SLOPE/W; GEO-SLOPE International Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2012; pp. 1–238. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Fletcher, J.O. The relationship between Tibet-tropical ocean thermal contrast and internannual variability of Indian monsoon rainfall. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1985, 24, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhou, X. Experimental study on the moving characteristics of fine grains in wide grading unconsolidated soil under heavy rainfall. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.F.; Chen, N.S.; Liu, M. Meteorological factors driving glacial till variation and the associated periglacial debris flow in Tianmo Valley, south-eastern Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Huang, K.; Sonechkin, D.M. Annual regional precipitation variations from a 700-year tree-ring record in South Tibet, Western China. Clim. Res. 2012, 53, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Tang, B.; Zhu, P. Debris Flow and Environment in Tibet; Chengdu Science and Technology University Press: Chengdu, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grant, G.E.; Schmidt, J.C.; Lewis, S.L. A geological framework for interpreting downstream effects of dams on rivers. In A Peculiar River; O’Connor, J.E., Grant, G.E., Eds.; Water Science and Application, American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; Volume 7, pp. 203–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; Varis, O. Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomophology 2007, 85, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M. The physics of debris flows. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, T.C. Dating young geomorphic surfaces using age of colonizing Douglas fir in southwestern Washington and northwestern Oregon, USA. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 811–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, J.; Ping, G. Detection of distribution dimension of the earth-rock aggregate based on digital image process. J. Sichuan Univ. Sci. Eng. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 25, 37–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Chen, X.P. Research progress on stability analysis of embankment under effects of river scouring. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2009, 29, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, A.; Li, F.; Liu, H.; Duan, G.; Zhou, X. Characteristics of particle size distributions for the collapsed riverbank along the desert reach of the upper Yellow River. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Simon, A.; Throne, C.R. The effects of variability in bank material properties on riverbank stability: Goodwin Creek, Mississippi. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, G.; Zaslavsky, D.; Golany, P. The effect of soil surface curvature on moisture and yield, Beer-Sheva observation. Soil Sci. 1981, 132, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.C.; Moore, R.D. Relations between topography and water table depth in a shallow forest soil. Hydrol. Process. 1996, 10, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.; Preti, F.; Giadrossich, F.; Lehmann, P.; Or, D. Quantifying the role of vegetation in slope stability: A case study in Tuscany (Italy). Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B. Soil erodibility and processes of water erosion on hillslope. Geomorphology 2000, 32, 385–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scottish Environment Protection Agency. Engineering in the Water Environment Good Practice Guide Bank Protection: Rivers and Lochs. Available online: https://www.sepa.org.uk (accessed on 5 December 2017).
- Longoni, L.; Papini, M.; Brambilla, D.; Barazzetti, L.; Roncoroni, F.; Scaioni, M.; Ivanov, V.I. Monitoring riverbank erosion in mountain catchments using terrestrial laser scanning. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, D.P.; Gupta, S.C.; Bauer, M.E.; Kirchoff, C. Airborne laser scanning for riverbank erosion assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, M.A.; Pizzuto, J.E. The rates and spatial patterns of annual riverbank erosion revealed through terrestrial laser-scanner surveys of the South River, Virginia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenato, L.; Aneesh, R.; Palmieri, L.; Galtarossa, A.; Pasuto, A. Fiber optic sensor for hydrostatic pressure and temperature measurement in riverbanks monitoring. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 82, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantianuparp, P.; Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; Balz, T.; Liao, M. Characterization of landslide deformations in three gorges area using multiple InSAR data stacks. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2704–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.C.W.; Mu, Q.Y.; Zhou, C. Effects of soil structure on the shear behaviour of an unsaturated loess at different suctions and temperatures. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 54, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).