Rainfall Infiltration Modeling: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
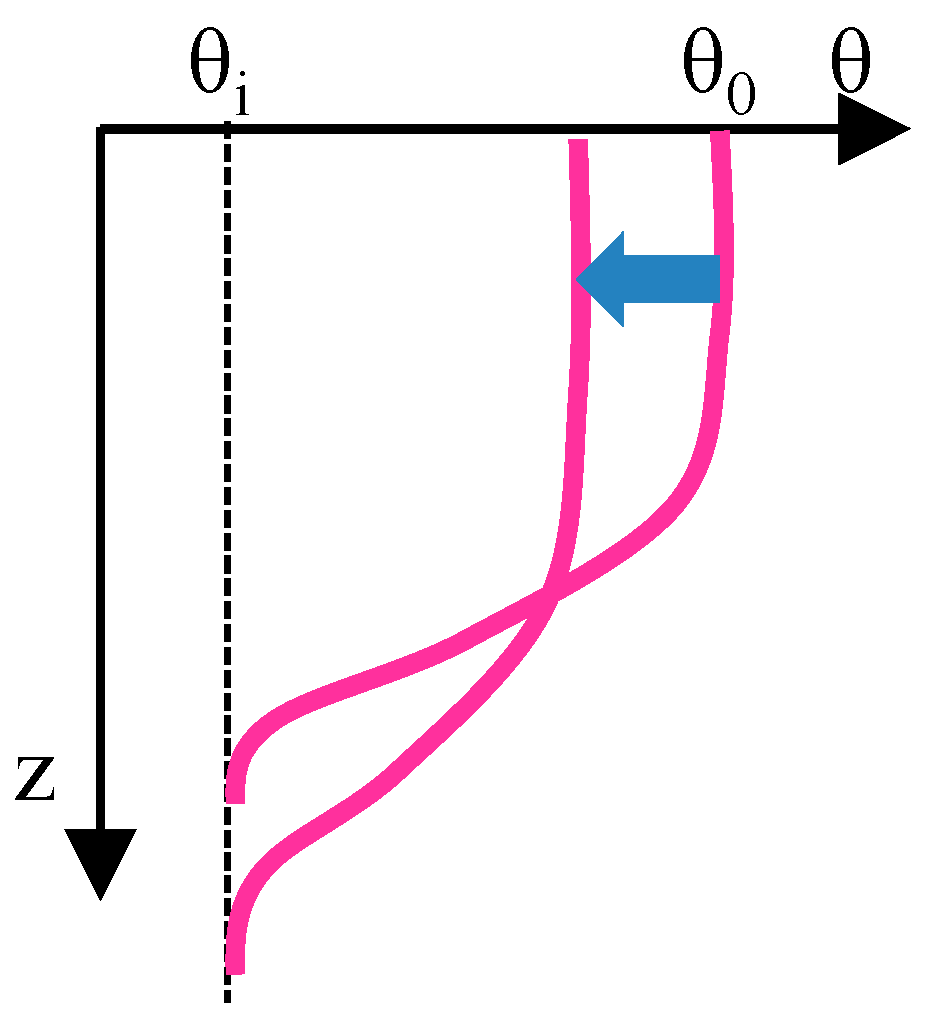
2. Basic Physical Models for Infiltration
3. Point Infiltration Modeling for Homogeneous Soils
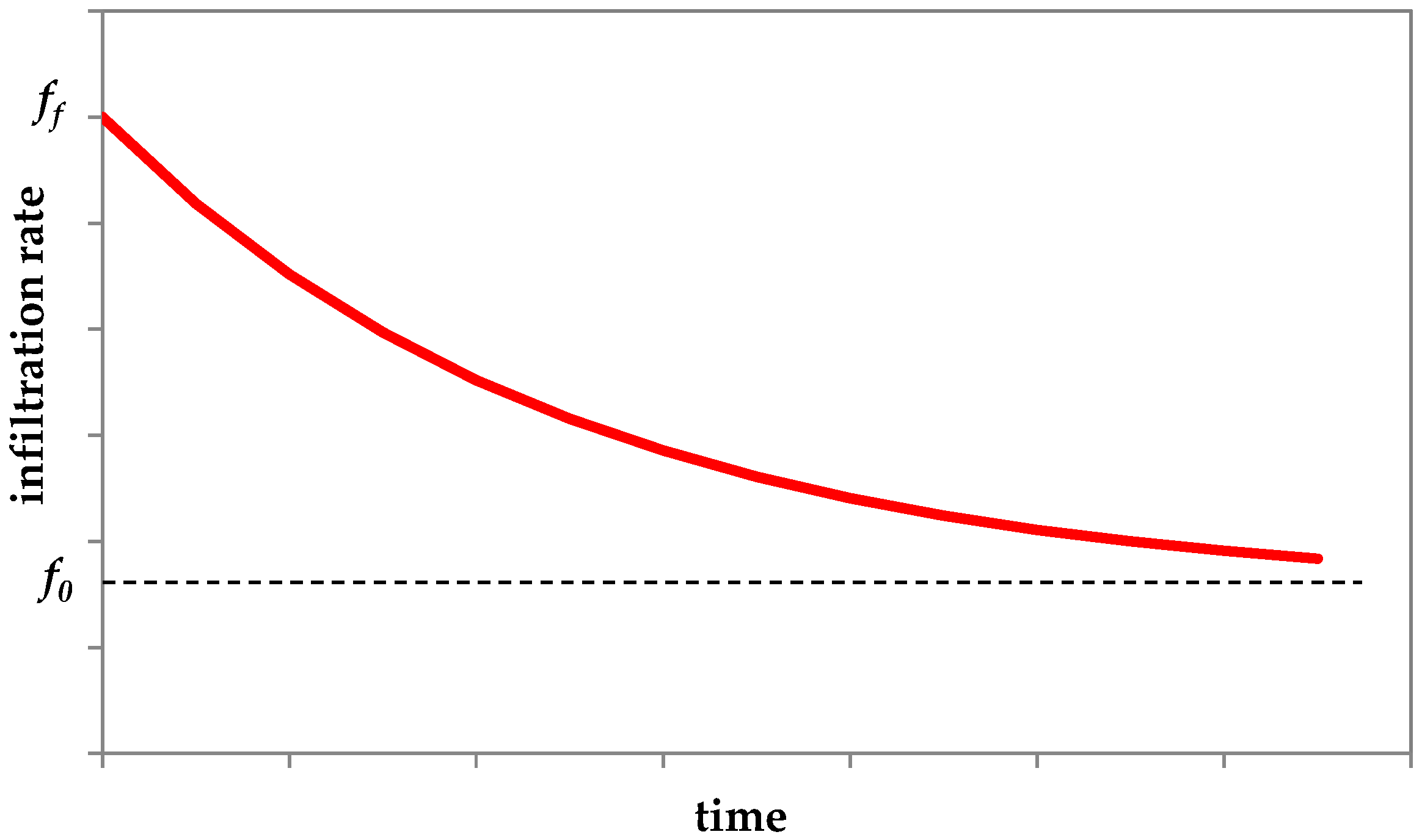
3.1. Horton Empirical Equation
3.2. Philip Equation
3.3. Green–Ampt Model
3.4. Parlange–Lisle–Braddock–Smith Model
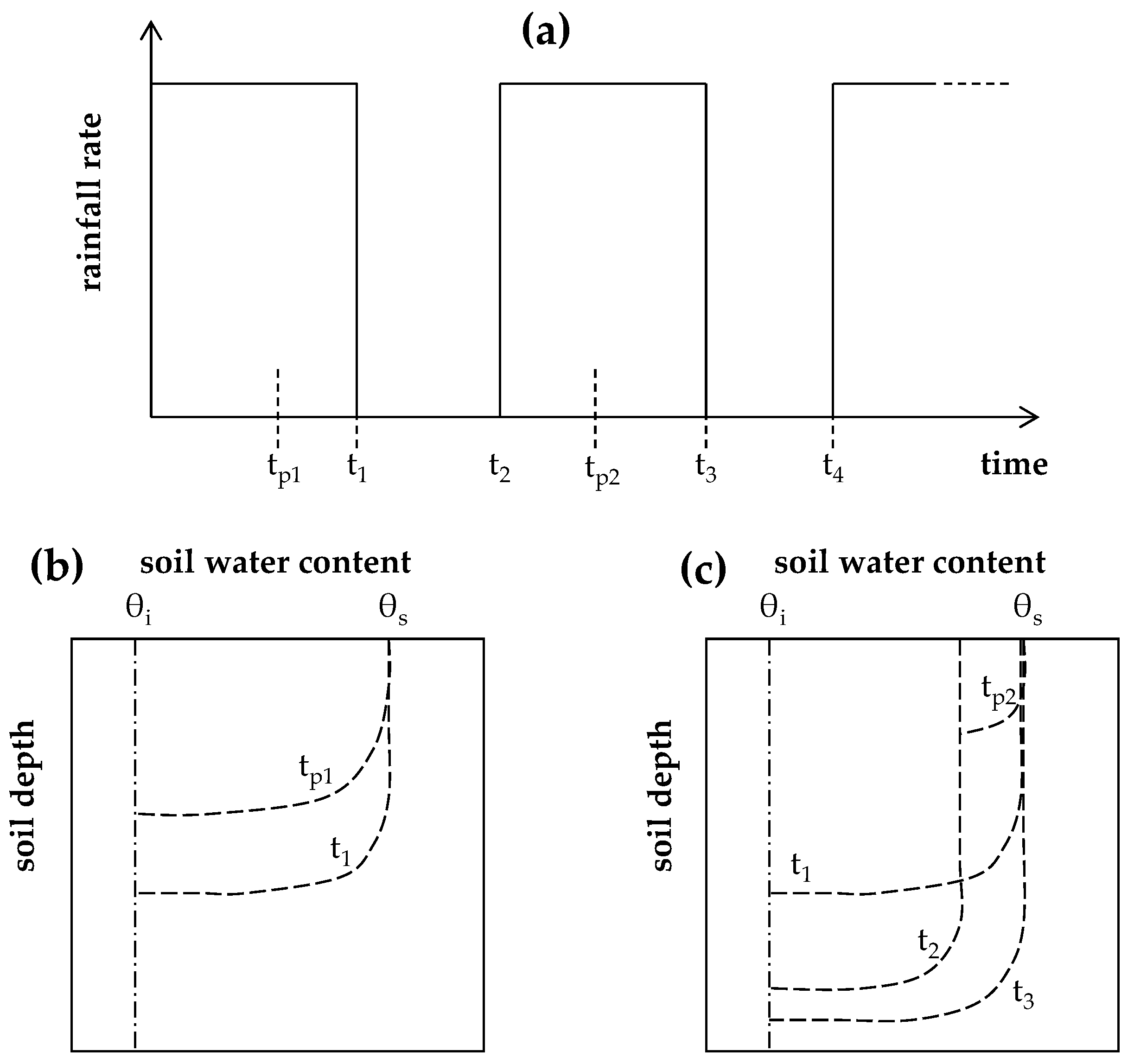
3.5. Corradini–Melone–Smith Semi-Analytical/Conceptual Model
4. Point Infiltration Modeling for Vertically Non-Uniform Soils
4.1. Green–Ampt-Based Model for a Layered Soil
4.2. Corradini–Melone–Smith Semi-Analytical/Conceptual Model for a Two-Layered Soil
5. Areal Infiltration Models over Soil with Variable Hydraulic Properties
5.1. Smith and Goodrich Approach
5.2. Govindaraju–Corradini–Morbidelli Semi-Analytical/Conceptual Model
6. Conclusions and Open Problems
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brutsaert, W. Hydrology—An Introduction; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0521824798. [Google Scholar]
- Assouline, S. Infiltration into soils: Conceptual approaches and solutions. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1755–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E. Infiltration Theory for Hydrologic Applications; Water Resources Monograph; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 15, ISBN 9780875903194. [Google Scholar]
- Green, W.A.; Ampt, G.A. Studies on soil physics: 1. The flow of air and water through soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1911, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostiakov, A.N. On the dynamics of the coefficient of water-percolation in soils and on the necessity for studying it from a dynamic point of view for purposes of amelioration. Trans. Sixth Comm. Int. Soc. Soil Sci. 1932, 1 Pt A, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.E. An approach toward a physical interpretation of infiltration-capacity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1940, 5, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtan, H.N. A Concept for Infiltration Estimates in Watershed Engineering; USDA Bulletin: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; pp. 41–51.
- Swartzendruber, D. A quasi solution of Richard equation for downward infiltration of water into soil. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 5, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 1. The infiltration equation and its solution. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 2. The profile at infinity. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 4. Sorptivity algebraic infiltration equation. Soil Sci. 1957, 84, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlange, J.-Y. Theory of water-movement in soils: 2. One-dimensional infiltration. Soil Sci. 1971, 111, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlange, J.-Y. Theory of water-movement in soils: 8. One-dimensional infiltration with constant flux at surface. Soil Sci. 1972, 114, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Conservation Service (SCS). National Engineering Handbook; Section 4, Hydrology; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Brutsaert, W. The concise formulation of diffusive sorption of water in a dry soil. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Vertical infiltration in dry soils. Water Resour. Res. 1977, 13, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Parlange, J.-Y. A parameter-efficient hydrologic infiltration model. Water Resour. Res. 1978, 14, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbridge, P.; White, I. Constant rate rainfall infiltration: A versatile nonlinear model. 1. Analytic solution. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.; Broadbridge, P. Constant rate rainfall infiltration: A versatile nonlinear model. 2. Application of solutions. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, G.; Bresler, E. Unsaturated flow in spatially variable fields. 1. Derivation of models of infiltration and redistribution. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, R.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Starr, J.L.; Schmitz, G.; Fuentes, C. Infiltration under ponded conditions: 3. A predictive equation based on physical parameters. Soil Sci. 1990, 149, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Corradini, C.; Melone, F. Modeling infiltration for multistorm runoff events. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Melone, F.; Smith, R.E. Modeling infiltration during complex rainfall sequences. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.J.; Parlange, J.-Y. Comparing exact and numerical solutions of Richards equation for one-dimensional infiltration and drainage. Soil Sci. 1994, 157, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, D.A.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Haverkamp, R.; Ross, P.J. Infiltration under ponded conditions: 4. An explicit predictive infiltration formula. Soil Sci. 1995, 160, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Melone, F.; Smith, R.E. A unified model for infiltration and redistribution during complex rainfall patterns. J. Hydrol. 1997, 192, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, A.; Warrick, A.W.; Zerihun, D.; Sanchez, C.A. Modified Kostiakov infiltration function: Accounting for initial and boundary conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. A simple analytical infiltration model for short-duration rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. The role of infiltration in the hydrological cycle. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1933, 14, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. Analysis of runoff plat experiments with varying infiltration capacity. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1939, 20, 693–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y.; Assouline, S.; Eltahan, D. Effect of rainfall-induced soil seals on soil water regime: Wetting processes. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Gresillon, J.M.; Clothier, B.E. Modelling the link between hillslope water movement and stream flow: Application to a small Mediterranean forest watershed. J. Hydrol. 1997, 203, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D.; Gardner, W.R. Transient infiltration into crust-topped profile. Soil Sci. 1970, 109, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, L.R. Modeling infiltration into surface-sealed soils by the Green-Ampt approach. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Infiltration into a class of vertical non-uniform soils. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1984, 29, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandervaere, J.-P.; Vauclin, M.; Haverkamp, R.; Peugeot, C.; Thony, J.-L.; Gilfedder, M. Prediction of crust-induced surface runoff with disc infiltrometer data. Soil Sci. 1998, 163, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selker, J.S.; Duan, J.F.; Parlange, J.-Y. Green and Ampt infiltration into soils of variable pore size with depth. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1685–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Marino, M.A. Determination of ponding condition and infiltration in layered soils under unsteady rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D. Infiltration equations modified for surface effects. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1981, 107, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.E. Analysis of infiltration through a two-layer soil profile. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. Infiltration into crusted soils. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Corradini, C.; Melone, F. A conceptual model for infiltration and redistribution in crusted soils. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Melone, F.; Smith, R.E. Modeling local infiltration for a two layered soil under complex rainfall patterns. J. Hydrol. 2000, 237, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R.; Flammini, A.; Govindaraju, R.S. A parameterized model for local infiltration in two-layered soils with a more permeable upper layer. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0071001748. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, D.R.; Biggar, J.W.; Erh, K.T. Spatial variability of field measured soil-water properties. Hilgardia 1973, 42, 215–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A.W.; Nielsen, D.R. Spatial Variability of Soil Physical Properties in the Field. Applications of Soil Physics; Hillel, D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 319–344. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, A.J. Field variability of soil physical properties. In Advances in Irrigation; Hillel, D., Ed.; Academic: San Diego, CA, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 189–221. ISBN 0-12-024302-4. [Google Scholar]
- Greminger, P.J.; Sud, Y.K.; Nielsen, D.R. Spatial variability of field measured soil-water characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.L.; Barron, R.J.W.; Fernie, M.S. Areal distribution of infiltration parameters and some soil physical properties in lateritic catchments. J. Hydrol. 1987, 94, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loague, K.; Gander, G.A. R-5 revisited, 1. Spatial variability of infiltration on a small rangeland catchment. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 957–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, S.D.; Jaynes, D.B. Spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity in a cultivated field at different times. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Bresler, E. Soil hydraulic properties as stochastic processes: 1. Analysis of field spatial variability. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Bresler, E. A univariate versus a multivariate parameter distribution in a stochastic-conceptual analysis of unsaturated flow. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.L.; Seely, E. Spatial variability and its effect on infiltration. In Proceedings of the Hydrology Water Resources Symposium; Institute of Engineering: Perth, Australia, 1979; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Maller, R.A.; Sharma, M.L. An analysis of areal infiltration considering spatial variability. J. Hydrol. 1981, 52, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafian, B.; Julien, P.Y.; Ogden, F.L. Similarity in catchment response: 1. Stationary rainstorms. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M.; Wood, E.F. Spatial heterogeneity and scale in the infiltration response of catchments. In Scale Problems in Hydrology; Water Science and Technology Library; Gupta, V.K., Rodríguez-Iturbe, I., Wood, E.F., Eds.; D. Reidel Publishing: Dordrecht, Holland, 1986; pp. 81–106. ISBN 978-94-010-8579-3. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, M.D.; Beckman, R.J.; Connover, W.J. A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 1979, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Goodrich, D.C. Model for rainfall excess patterns on randomly heterogeneous area. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, R.S.; Morbidelli, R.; Corradini, C. Areal infiltration modeling over soils with spatially-correlated hydraulic conductivities. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2001, 6, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S.; Morbidelli, R. Simplified modelling of areal average infiltration at the hillslope scale. Hydrol. Proc. 2002, 16, 1757–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Hebbert, R.H.B. A Monte Carlo analysis of the hydrologic effects of spatial variability of infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhiser, D.A.; Smith, R.E.; Giraldez, J.-V. Effects of spatial variability of saturated hydraulic conductivity on Hortonian overland flow. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R.; Melone, F. On the interaction between infiltration and Hortonian runoff. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, N.; Govindaraju, R.S.; Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R. Role of run-on for describing field-scale infiltration and overland flow over spatially variable soils. J. Hydrol. 2004, 286, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, C.; Govers, G.; Diels, J. Development and parameterization of an infiltration model accounting for water depth and rainfall intensity. Hydrol. Proc. 2013, 27, 3777–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, D.C.; Faurès, J.-M.; Woolhiser, D.A.; Lane, L.J.; Sorooshian, S. Measurement and analysis of small-scale convective storm rainfall variability. J. Hydrol. 1995, 173, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.F.; Ciach, G.J.; Habib, E. An analysis of small-scale rainfall variability in different climatic regimes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.F.; Sivapalan, M.; Beven, K. Scale effects in infiltration and runoff production. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Conjunctive Water Use; IAHS: Budapest, Hungary, 1986; ISBN 0-947571-85-X. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, F. A simplified stochastic model for infiltration into a heterogeneous soil forced by random precipitation. Adv. Water Resour. 1996, 19, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, R.S.; Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R. A semi-analytical model of expected areal-average infiltration under spatial heterogeneity of rainfall and soil saturated hydraulic conductivity. J. Hydrol. 2006, 316, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S. A field-scale infiltration model accounting for spatial heterogeneity of rainfall and soil saturated hydraulic conductivity. Hydrol. Proc. 2006, 20, 1465–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, C.; Flammini, A.; Morbidelli, R.; Govindaraju, R.S. A conceptual model for infiltration in two-layered soils with a more permeable upper layer: From local to field scale. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, R.S.; Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R. Local and field-scale infiltration into vertically non-uniform soils with spatially-variable surface hydraulic conductivities. Hydrol. Proc. 2012, 26, 3293–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.J. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-470-71459-1. [Google Scholar]
- Fiori, A.; Romanelli, M.; Cavalli, D.J.; Russo, D. Numerical experiments of streamflow generation in steep catchments. J. Hydrol. 2007, 339, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, S.H.; Wilson, E.M. The influence of slope and rain intensity on runoff and infiltration. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1975, 20, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Singh, H.; Pareek, O. Rainwater infiltration into a bar loamy sand. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1983, 28, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. The influence of slope angle on infiltration rate and hortonian overland flow volume. Z. Geomorphol. 1984, 49, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. Hillslope infiltration: Planar slopes. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; García-Fayos, P. The influence of slope angle on sediment, water and seed losses on badland landscapes. Geomorphology 1997, 18, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Bryan, R.B.; Price, A.G. The influence of slope angle on final infiltration rate for interrill conditions. Geoderma 1997, 80, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Le Bissonais, Y. Field measurements of interrill erosion under different slopes and plot sizes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2000, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeau, J.L.; Bricquet, J.P.; Planchon, O.; Valentin, C. Soil crusting and infiltration on steep slopes in northern Thailand. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dymanics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Young, M.H. Green-Ampt infiltration model for sloping surfaces. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W07420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essig, E.T.; Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R.; Govindaraju, R.S. Infiltration and deep flow over sloping surfaces: Comparison of numerical and experimental results. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolzi, O.; Patin, J.; Bresson, L.; Latsachack, K.; Mouche, E.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O.; Silvera, N.; Thiébaux, J.P.; Valentin, C. Impact of slope gradient on soil surface features and infiltration on steep slopes in northern Laos. Geomorphology 2011, 127, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patin, J.; Mouche, E.; Ribolzi, O.; Chaplot, V.; Sengtaheuanghoung, O.; Latsachak, K.O.; Soulileuth, B.; Valentin, C. Analysis of runoff production at the plot scale during a long-term survey of a small agricultural catchment in Lao PDR. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Hao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. Conditions for lateral downslope unsaturated flow and effects of slope angle on soil moisture movement. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Cifrodelli, M.; Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S. Infiltration on sloping surfaces: Laboratory experimental evidence and implications for infiltration modelling. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Yu, F.; Li, C.; Xie, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, N. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on runoff and soil moisture content on different growing stages of spring maize. Water 2015, 7, 2990–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Gong, Y.; Hu, T.; Lal, R.; Zheng, J.; Justine, M.F.; Azhar, M.; Che, M.; Zhang, H. Effect of slope, rainfall intensity and mulch on erosion and infiltration under simulated rain on purple soil of south-western Sichuan province, China. Water 2016, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Cifrodelli, M.; Picciafuoco, T.; Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S. Laboratory investigation on the role of slope on infiltration over grassy soils. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Yu, Z. Modeling rainfall infiltration on hillslopes using flux-concentration relation and time compression approximation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Govindaraju, R.S. Role of slope on infiltration: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, H.H. Preferential flow description for structured soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 382–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; Jarvis, N.J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Gardenas, A. Review and comparison of models describing non-equilibrium and preferential flow and transport in the vadose zone. J. Hydrol. 2003, 272, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, E. Studies on the Movement of Soil Moisture; US Department of Agriculture, Bureau of Soils No. 38; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1907.
- Brooks, R.H.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Hydrology Paper; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964; Volume 3, p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacimov, A.; Obnosov, Y. Pseudo-hysteretic double-front hiatus-stage soil water parcels supplying a plant-root continuum: The Green-Ampt-Youngs model revisited. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mein, R.G.; Larson, C.L. Modeling infiltration during a steady rain. Water Resour. Res. 1973, 9, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.T.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Aylor, D.E. Edge effects in linear diffusion. Acta Mech. 1978, 21, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlange, J.-Y.; Lisle, I.; Braddock, R.D.; Smith, R.E. The three-parameter infiltration equation. Soil Sci. 1982, 133, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagleson, P.S. Dynamic Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Raudkivi, A.J. Hydrology; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1979; ISBN 978-0080242613. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. Theory of infiltration. In Advances in Hydroscience; Chow, W.T., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; Volume 5, pp. 215–296. [Google Scholar]
- Youngs, E.G. An infiltration method measuring the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous materials. Soil Sci. 1964, 97, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mls, J. Effective rainfall estimation. J. Hydrol. 1980, 45, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péschke, G.; Kutilek, M. Infiltration model in simulated hydrographs. J. Hydrol. 1982, 56, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.C. Modified Horton’s infiltration equation. J. Hydrol. 1982, 58, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.; Miller, E.E. Estimating infiltration for erratic rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 1975, 11, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, H.A. Infiltration models for semi-infinite soil profiles. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W08516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, H.A. Infiltration models for soil profiles bounded by a water table. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melone, F.; Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C. Laboratory experimental check of a conceptual model for infiltration under complex rainfall patterns. Hydrol. Proc. 2006, 20, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melone, F.; Corradini, C.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A. Comparison of theoretical and experimental soil moisture profiles under complex rainfall patterns. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y.; Assouline, S. Modeling soil seal as a nonuniform layer. Water Resour. Res. 1989, 25, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, M.S.; Temper, W.D.; Nelson, S.D. Soil cohesion as affected by freezing, water content, time and tillage. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1988, 52, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, W.E. Season and erosion pavement influence on saturated soil hydraulic conductivity. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Corradini, C.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Rossi, E. Infiltration-soil moisture redistribution under natural conditions: Experimental evidence as a guideline for realizing simulation models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sela, S.; Svoray, T.; Assouline, S. The role of soil-surface sealing, microtopography, and vegetation patches in rainfall-runoff processes in semiarid areas. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5585–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Rossi, E.; Corradini, C. Soil water content vertical profiles under natural conditions: Matching of experiments and simulations by a conceptual model. Hydrol. Proc. 2014, 28, 4732–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Kinematic Wave Modeling in Water Resources: Surface Water Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-471-10945-2. [Google Scholar]
- Morbidelli, R.; Corradini, C.; Saltalippi, C.; Brocca, L. Initial soil water content as input to field-scale infiltration and surface runoff models. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1793–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, D.R. Handbook of Hydrology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 9780070397323. [Google Scholar]
- Bronstert, A.; Bardossy, A. The role of spatial variability of soil moisture for modelling surface runoff generation at the small catchment scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1999, 3, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Germann, P. Macropores and water flow in soils revisited. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3071–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T. Modeling nonequilibrium flow and transport processes using HYDRUS. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireson, A.M.; Butler, A.P. Controls on preferential recharge to Chalk aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, J.C.; Groenendijk, P.; Hendriks, R.F.A.; Kroes, J.G. Advances of modeling water flow in variability saturated soils with SWAP. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Cifrodelli, M.; Picciafuoco, T.; Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S. In-situ measurements of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity: Assessment of reliability through rainfall-runoff experiments. Hydrol. Proc. 2017, 31, 3084–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammini, A.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.M.; Picciafuoco, T.; Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S. Reassessment of a semi-analytical field-scale infiltration model through experiments under natural rainfall events. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
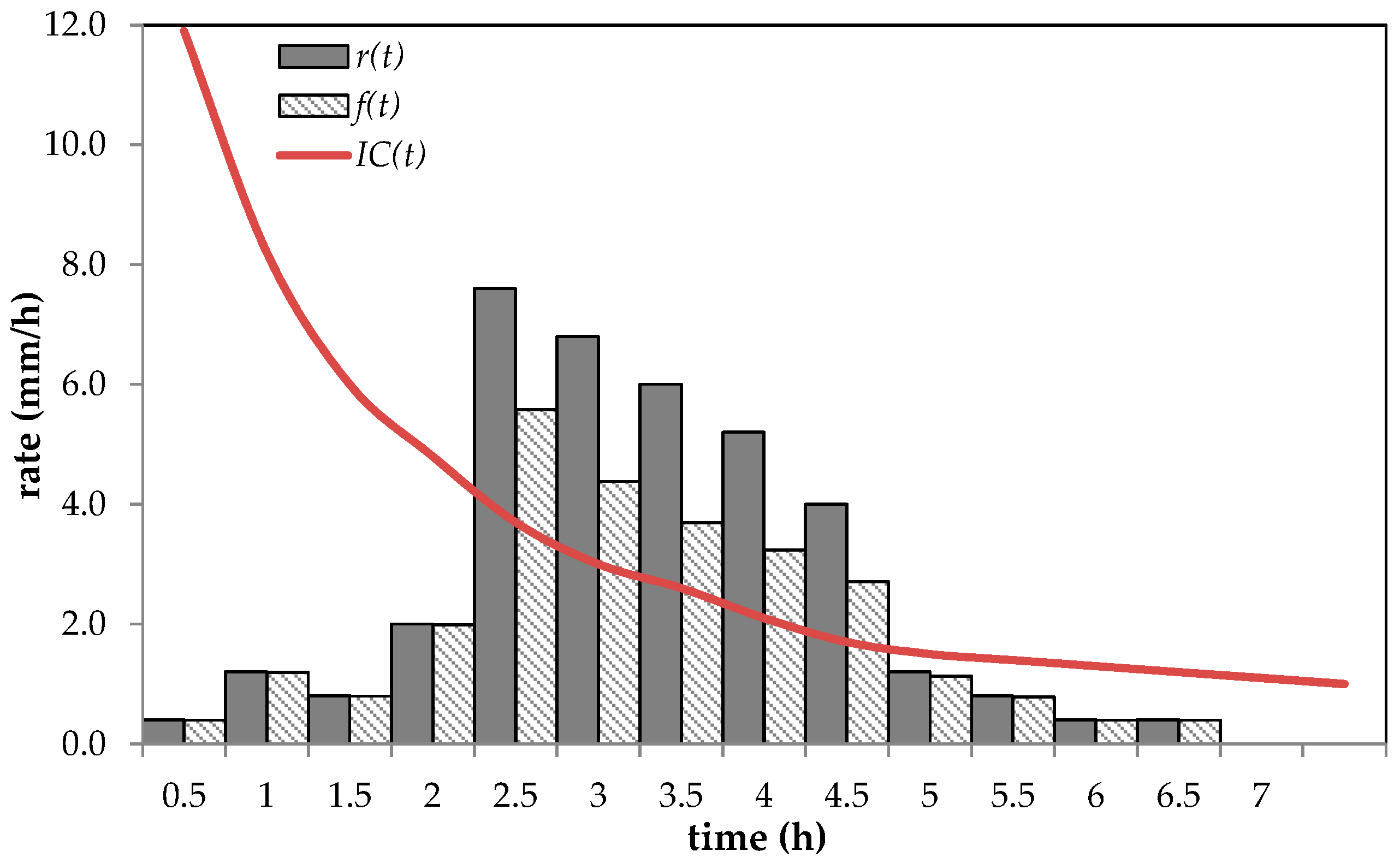
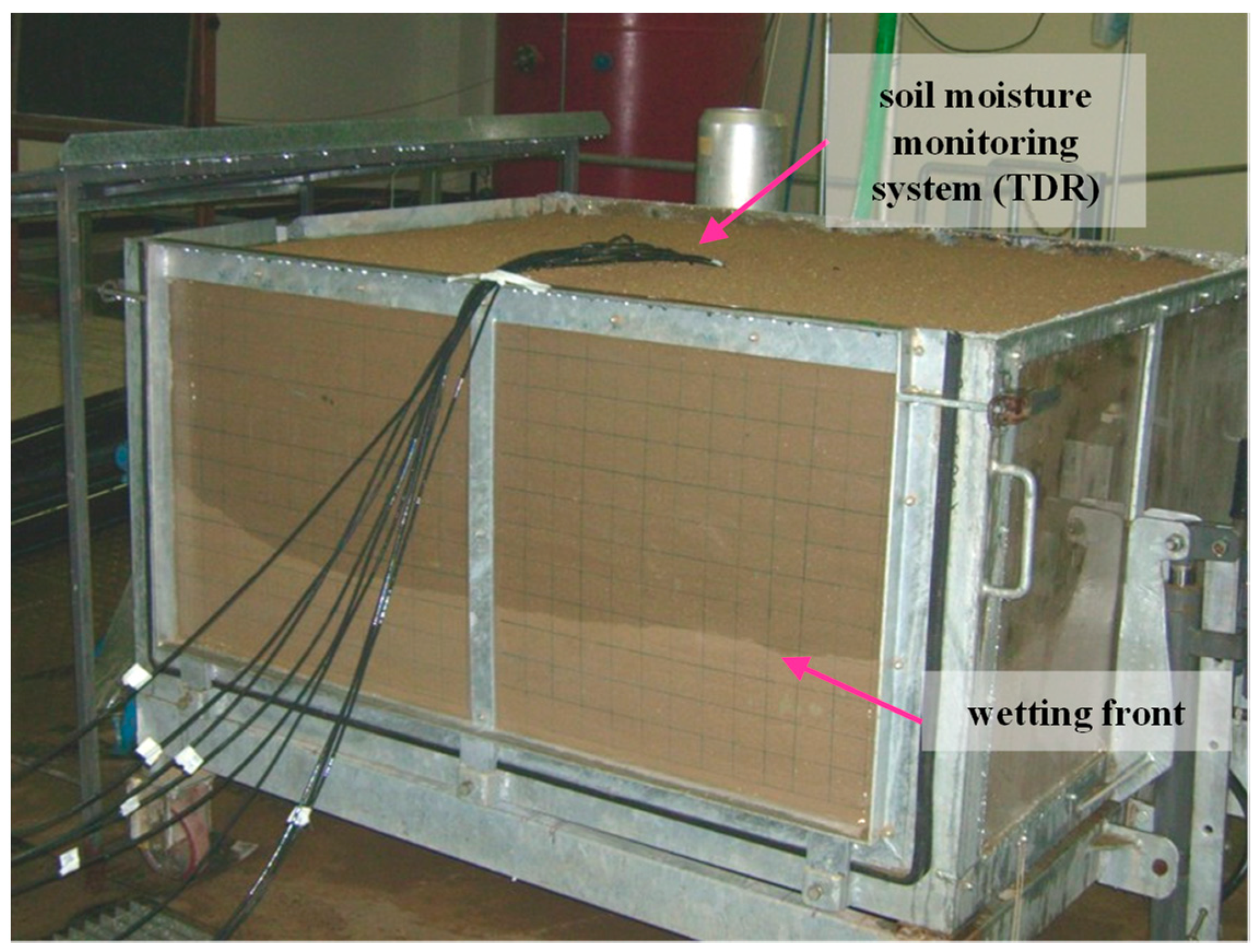
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morbidelli, R.; Corradini, C.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Dari, J.; Govindaraju, R.S. Rainfall Infiltration Modeling: A Review. Water 2018, 10, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121873
Morbidelli R, Corradini C, Saltalippi C, Flammini A, Dari J, Govindaraju RS. Rainfall Infiltration Modeling: A Review. Water. 2018; 10(12):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121873
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorbidelli, Renato, Corrado Corradini, Carla Saltalippi, Alessia Flammini, Jacopo Dari, and Rao S. Govindaraju. 2018. "Rainfall Infiltration Modeling: A Review" Water 10, no. 12: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121873
APA StyleMorbidelli, R., Corradini, C., Saltalippi, C., Flammini, A., Dari, J., & Govindaraju, R. S. (2018). Rainfall Infiltration Modeling: A Review. Water, 10(12), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121873