Geochemical Evolution of Fluoride and Implication for F− Enrichment in Groundwater: Example from the Bilate River Basin of Southern Main Ethiopian Rift
Abstract
1. Introduction
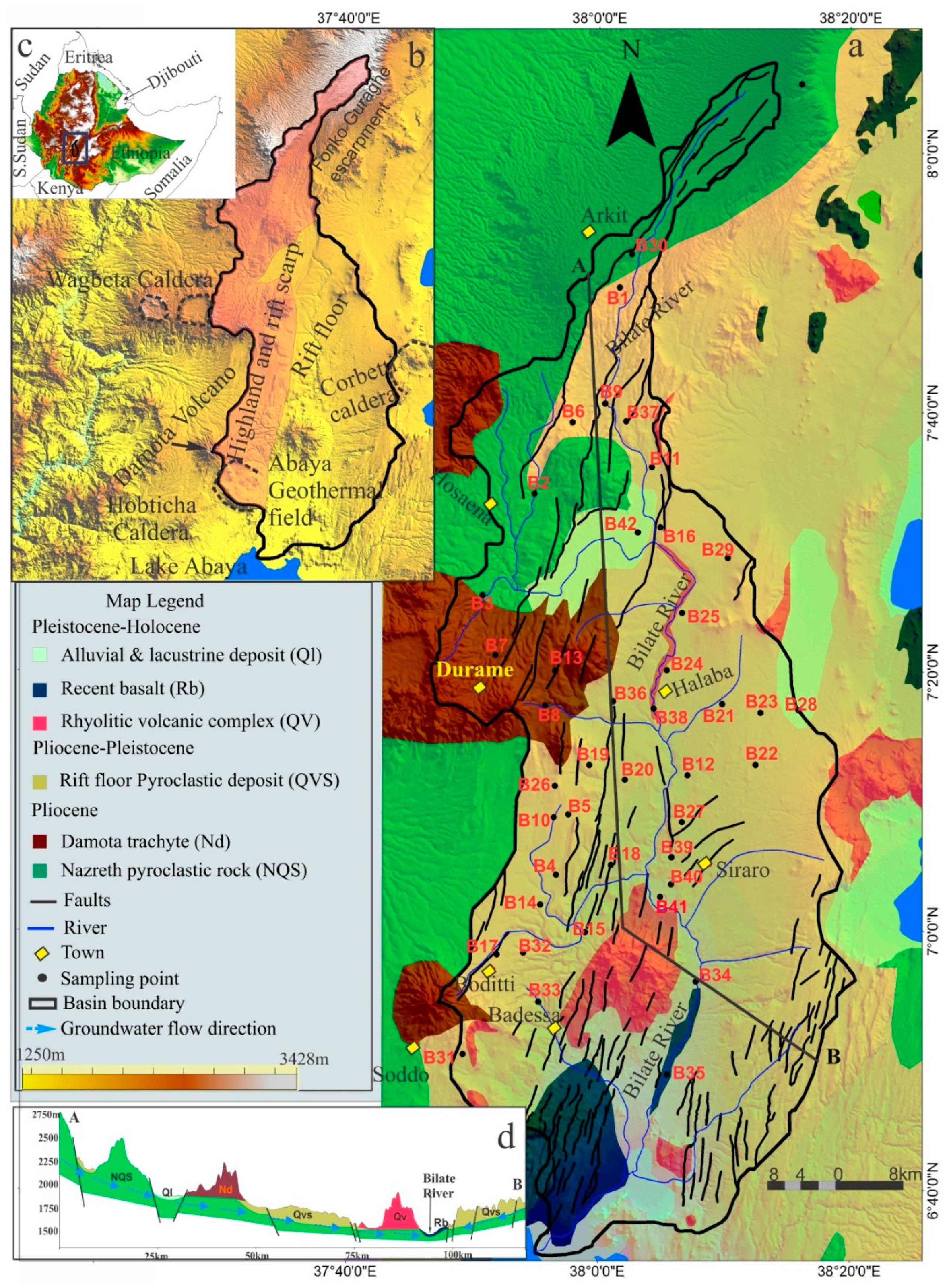
2. Description of the Study Area
3. Geological and Hydrogeological Settings
4. Methodology
4.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
4.2. Mineral Speciation Modeling and Inverse Geochemical Modeling
5. Results
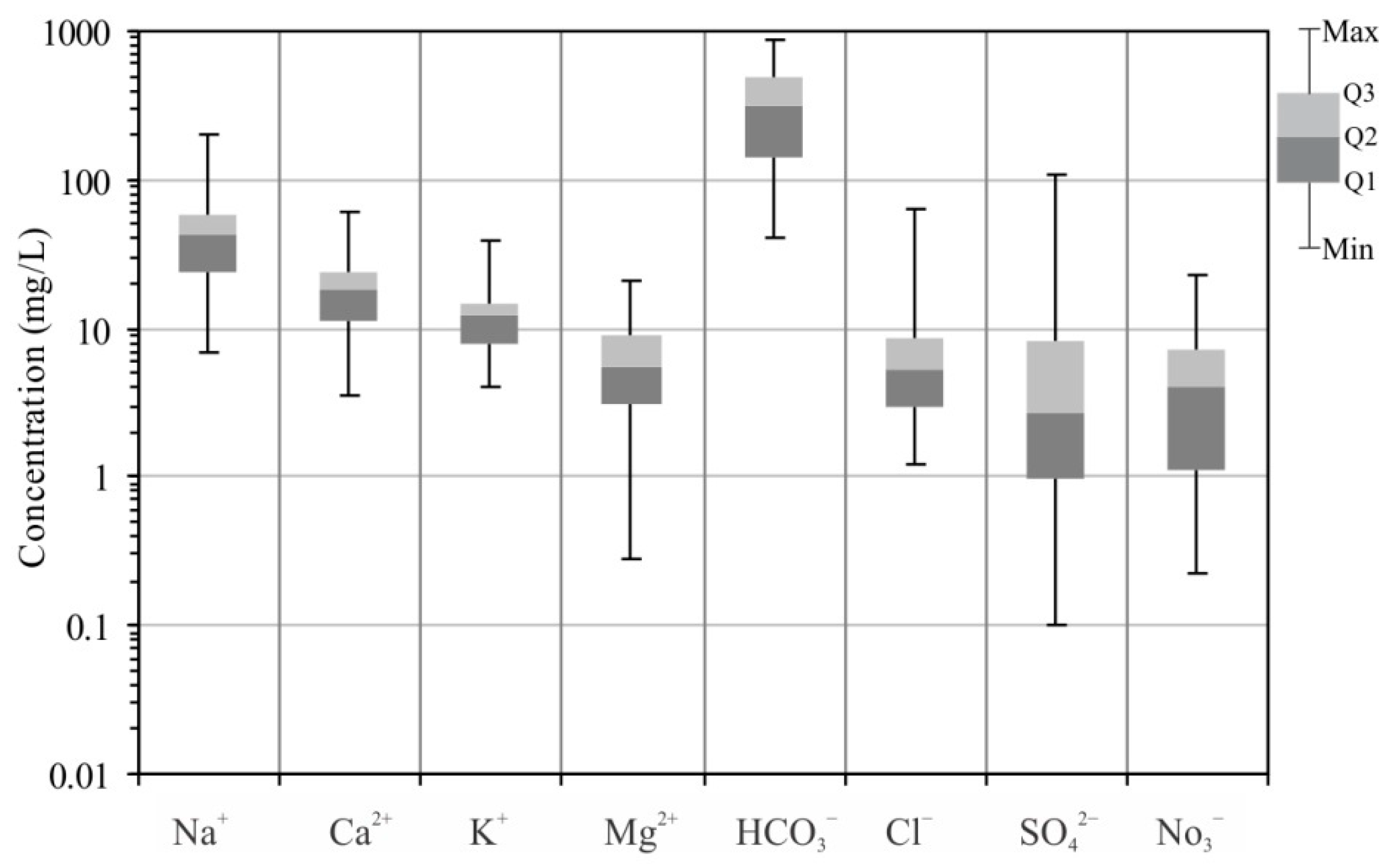
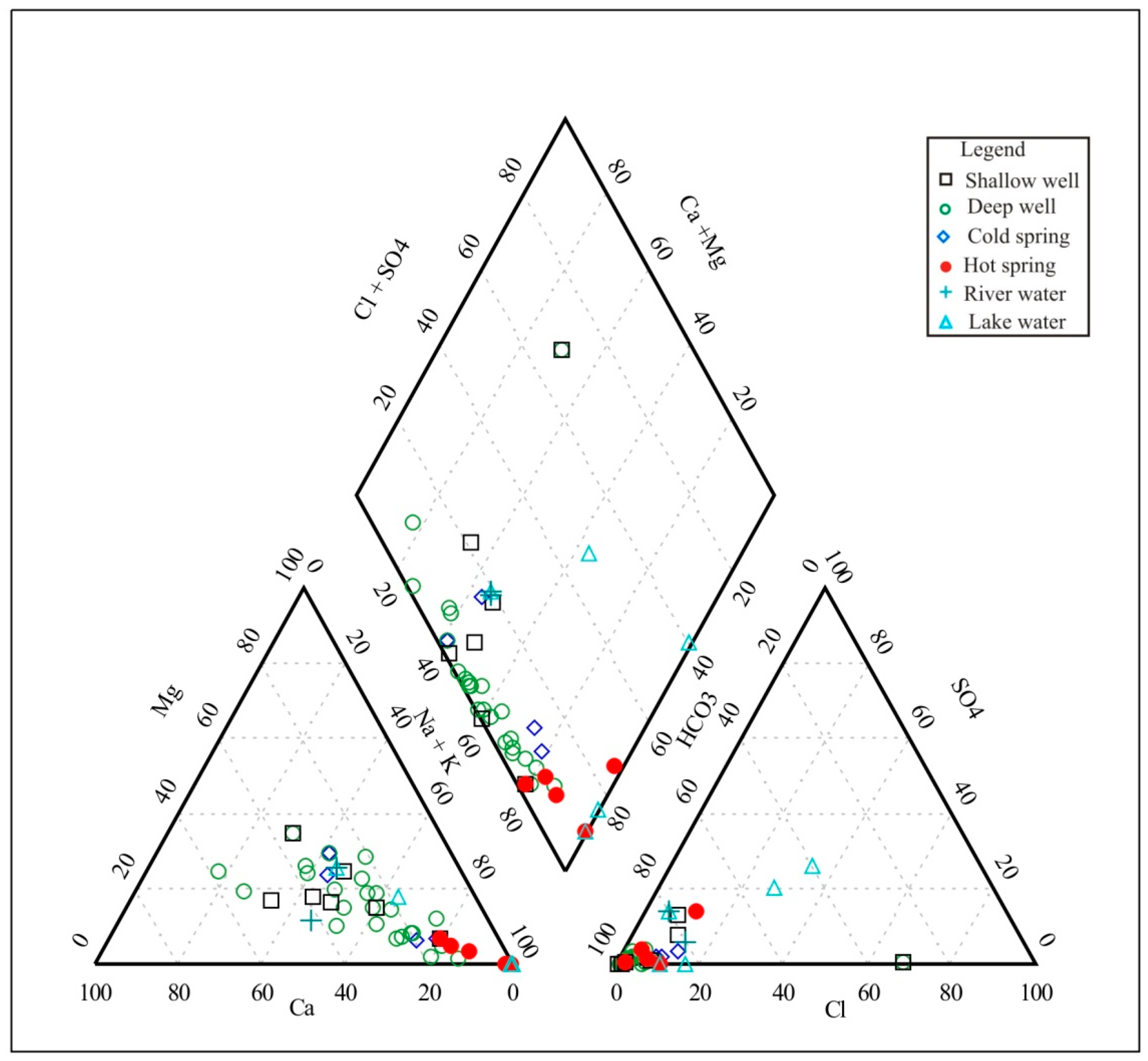
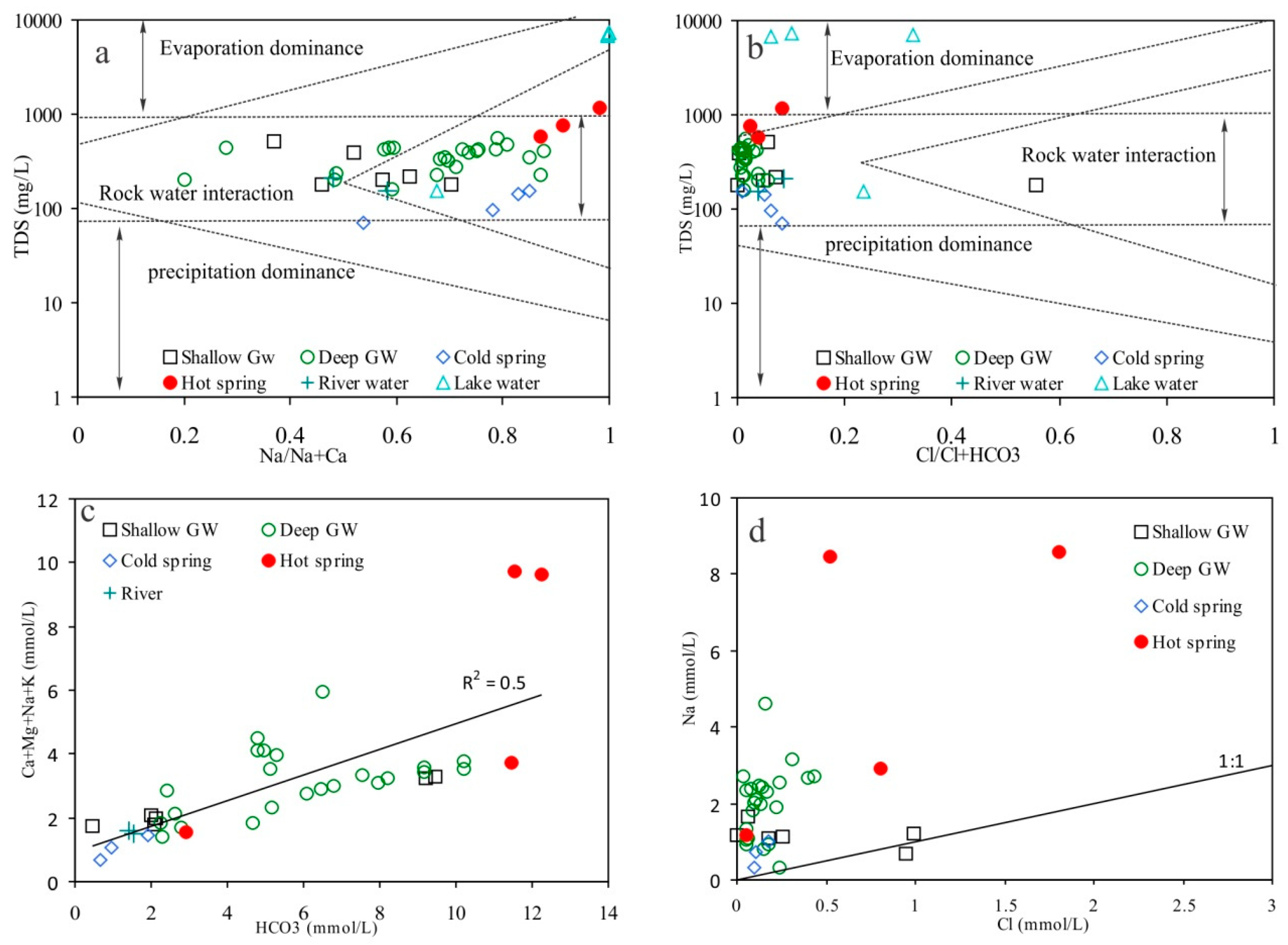
5.1. Hydrochemistry
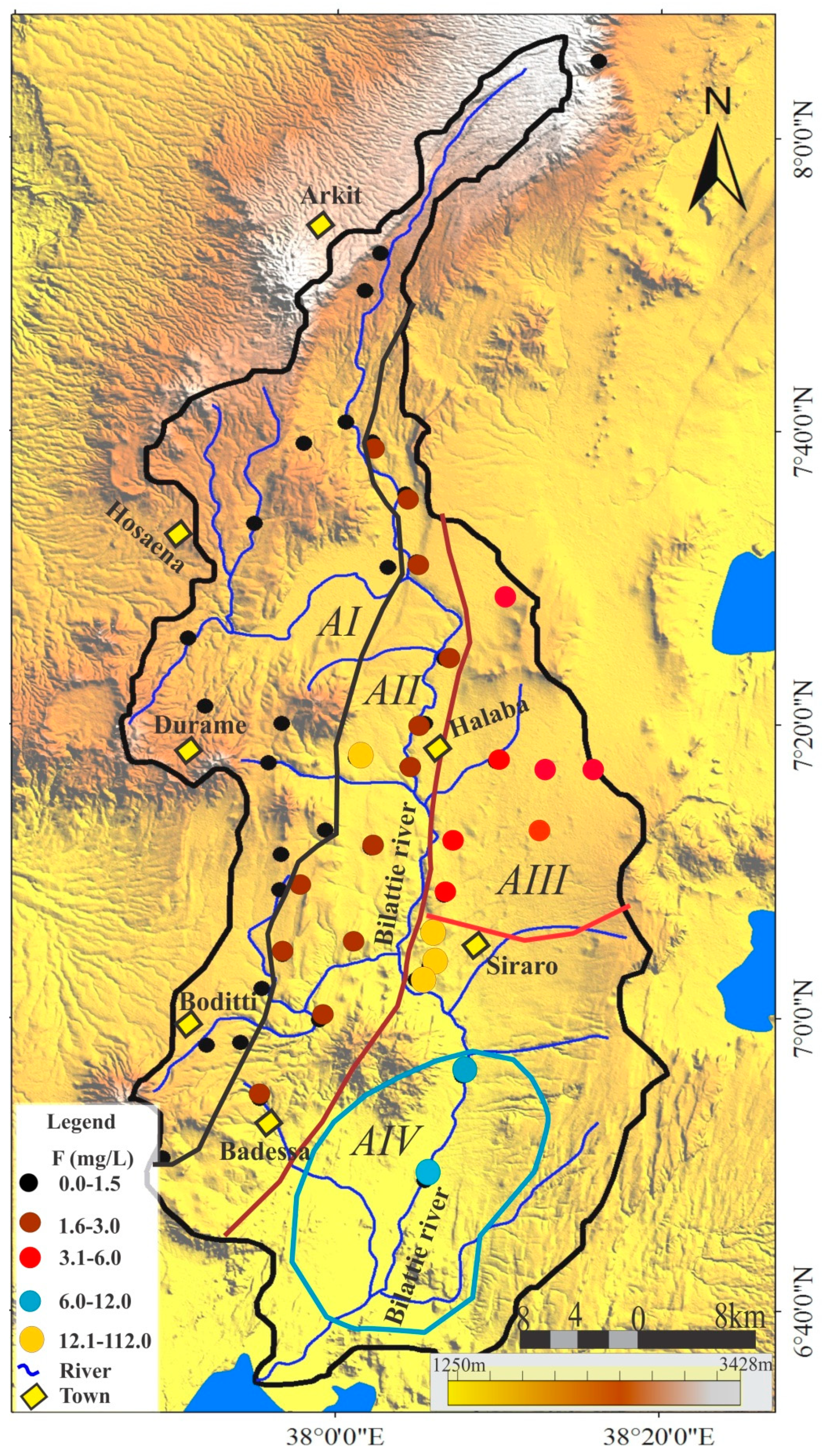
5.2. F− Concentrations
5.3. Spatial Distribution of Fluoride
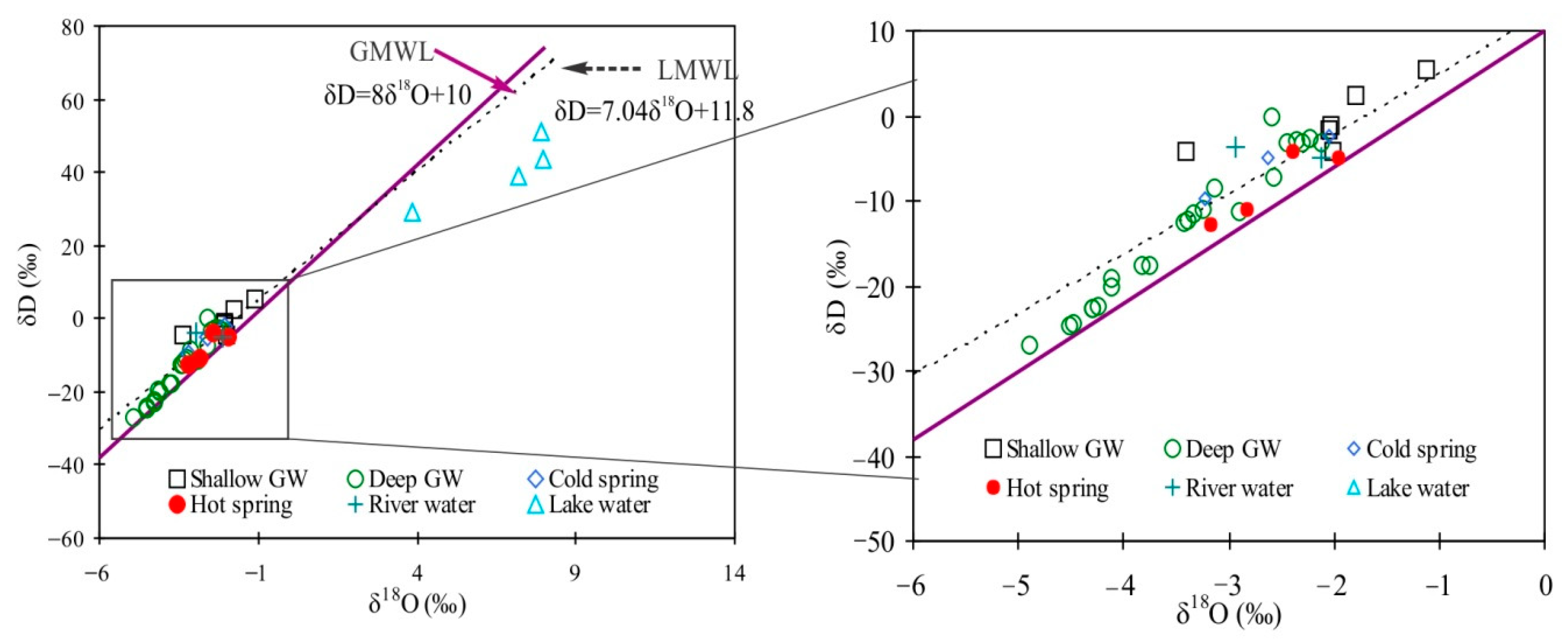
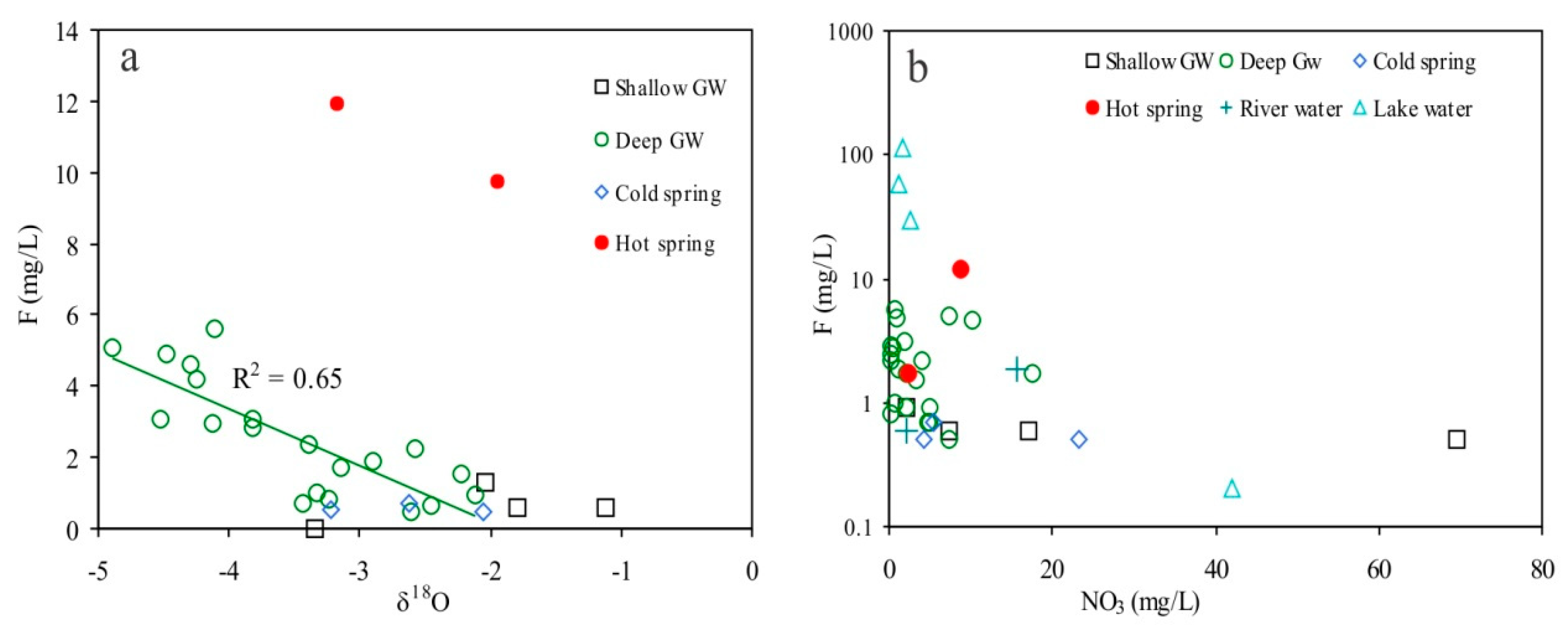
5.4. Stable Hydrogen (δD) and Oxygen (δ18O) Isotopes
6. Discussion
6.1. Mechanisms Controlling Groundwater Chemistry
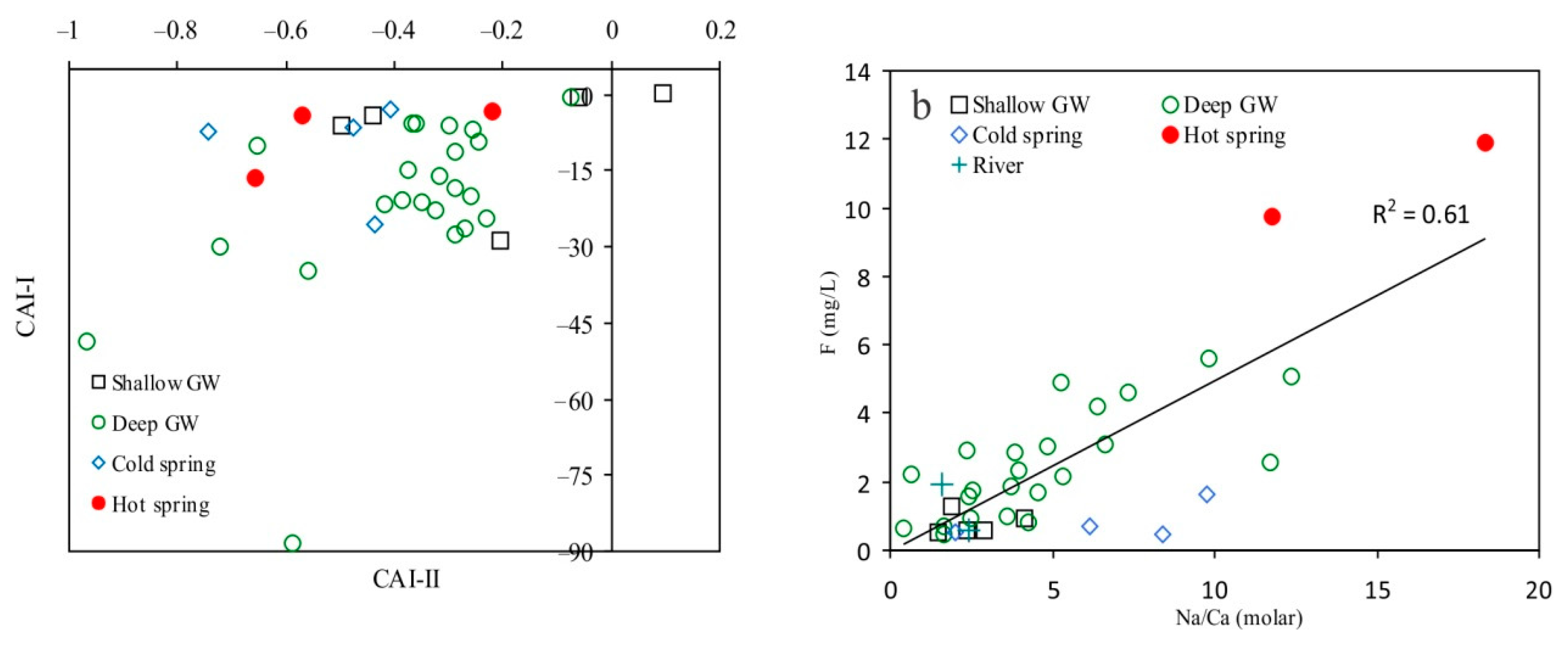
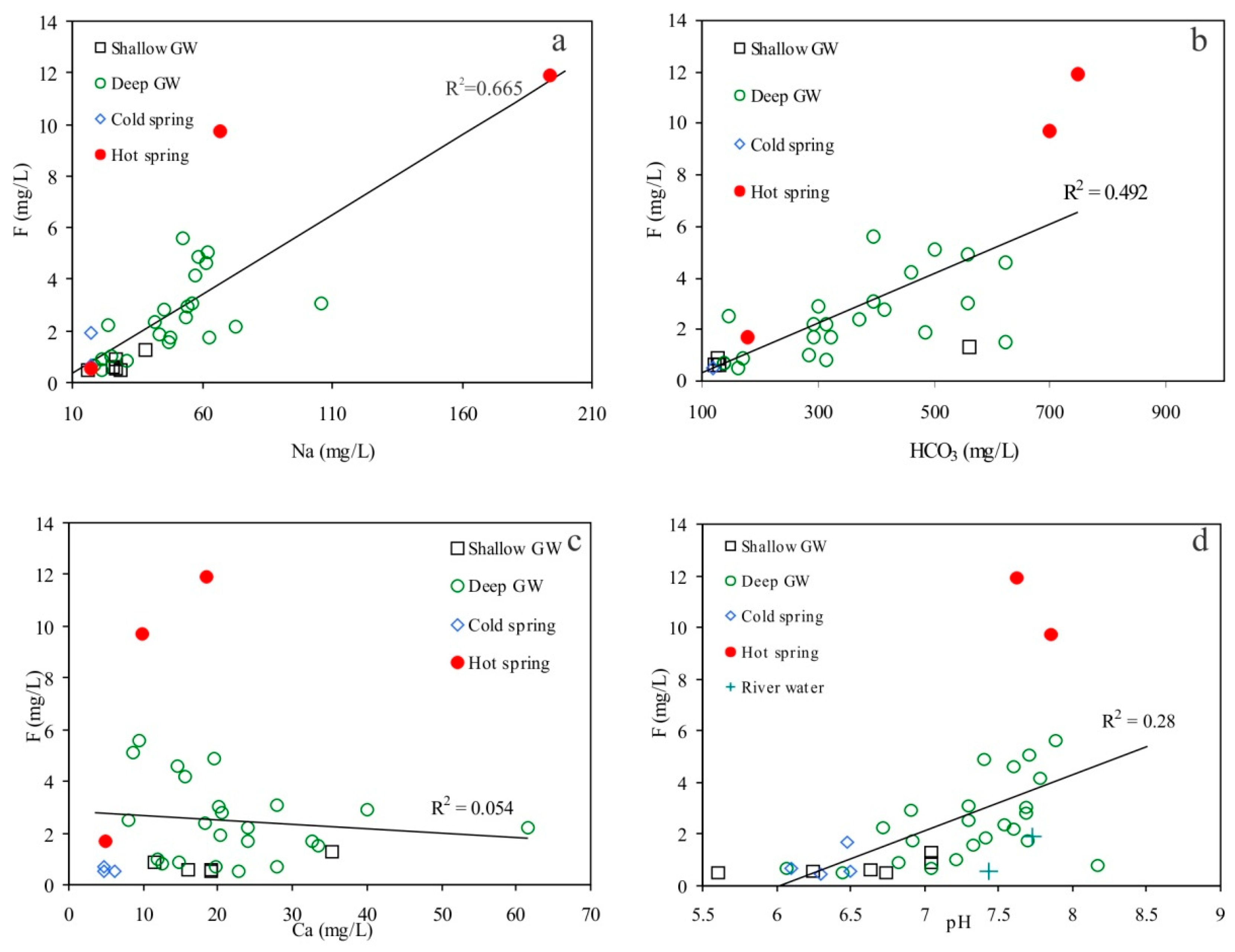
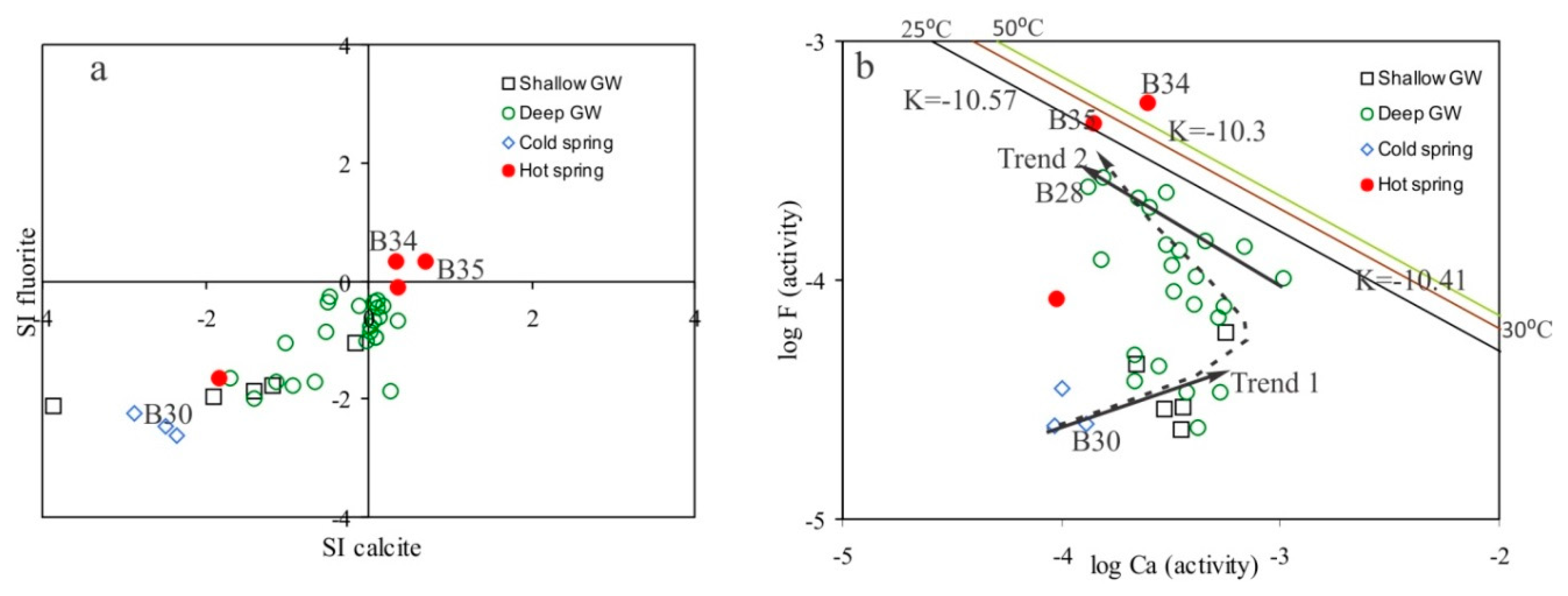
6.2. Genesis of High Fluoride Groundwater
6.3. Geochemical Modeling of Water Rock Interaction
6.4. Implication for Fluoride Geochemistry in Volcanic Aquifers
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dissanayake, C.B. The fluoride problem in the ground water of Sri Lanka — environmental management and health. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1991, 38, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Bianchini, G.; Beccaluva, L.; Tassinari, R. Geochemistry and water quality assessment of central Main Ethiopian Rift natural waters with emphasis on source and occurrence of fluoride and arsenic. J. Afr. Earth. Sci. 2010, 57, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoob, S.; Gupta, A.K. Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Review on the Status and Stress Effects. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 433–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kut, K.M.K.; Sarswat, A.; Srivastava, A.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. A review of fluoride in african groundwater and local remediation methods. Groundwater Sustainable Dev. 2016, 2, 190–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Smedley, P.L. Fluoride in natural waters. In Essentials of Medical Geology: Revised Edition; Selinus, O., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 311–336. [Google Scholar]
- Kloos, H.; Haimanot, R.T. Distribution of fluoride and fluorosis in Ethiopia and prospects for control. Trop. Med. Int. Health 1999, 4, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekle-Haimanot, R.; Melaku, Z.; Kloos, H.; Reimann, C.; Fantaye, W.; Zerihun, L.; Bjorvatn, K. The geographic distribution of fluoride in surface and groundwater in Ethiopia with an emphasis on the Rift Valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayenew, T. The distribution and hydrogeological controls of fluoride in the groundwater of central Ethiopian rift and adjacent highlands. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekle-Haimanot, R.; Haile, G. Chronic alcohol consumption and the development of skeletal fluorosis in a fluoride endemic area of the ethiopian rift valley. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2014, 6, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondwossen, F.; Åstrøm, A.N.; Bjorvatn, K.; Bårdsen, A. The relationship between dental caries and dental fluorosis in areas with moderate- and high-fluoride drinking water in Ethiopia. Community Dentistry Oral Epidemiol. 2004, 32, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Kravchenko, J.; Atlaw, B.; McCornick, P.G.; Jeuland, M.; Merola, B.; Vengosh, A. Groundwater quality and its health impact: An assessment of dental fluorosis in rural inhabitants of the Main Ethiopian Rift. Environ. Int. 2012, 43, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Bianchini, G.; Beccaluva, L.; Ayenew, T.; Colombani, N. Hydrogeochemical study in the Main Ethiopian Rift: new insights to the source and enrichment mechanism of fluoride. Environ. Geol. 2008, 58, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaleb-Looie, S.; Moore, F.; Jafari, H.; Jacks, G.; Ozsvath, D. Hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwaters with excess fluoride concentrations from Dashtestan, South of Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, M.L.; Vieiro, A.P.; Machado, G. The fluoride in the groundwater of Guarani Aquifer System: The origin associated with black shales of Paraná Basin. Environ. Geol. 2007, 55, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, S.; Coutinho, R.; Cruz, J.V. Fluoride content in drinking water supply in Sao Miguel volcanic island (Azores, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamatha, P.; Rao, S.M. Geochemistry of fluoride rich groundwater in Kolar and Tumkur Districts of Karnataka. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 61, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, K. Geochemical characteristics of fluoride in groundwater of Gimcheon, Korea: Lithogenic and agricultural origins. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 63, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frencken, J.E. Endemic Fluorosis in Developing Countries, Causes, Effects and Possible Solutions; TNO Institute for Preventive Health Care: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Olaka, L.A.; Wilke, F.D.; Olago, D.O.; Odada, E.O.; Mulch, A.; Musolff, A. Groundwater fluoride enrichment in an active rift setting: Central Kenya Rift case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žáček, V.; Rapprich, V.; Šíma, J.; Škoda, R.; Laufek, F.; Legesa, F. Kogarkoite, Na3(SO4)F, from the Shalo hot spring, Main Ethiopian Rift: implications for F-enrichment of thermal groundwater related to alkaline silicic volcanic rocks. J. Geosci. 2015, 60, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Rivera, J.J.; Cardona, A.; Edmunds, W.M. Use of abstraction regime and knowledge of hydrogeological conditions to control high-fluoride concentration in abstracted groundwater: San Luis Potosí basin, Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, G.T.; Yun, S.T.; Mayer, B.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, J.S.; Kim, K.; Koh, Y.K. Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 385, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Mukherjee, S. Aqueous geochemistry of fluoride enriched groundwater in arid part of Western India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 2668–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, F. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, S.J.; Manoharan, V.; Hedley, M.J.; Loganathan, P. Fluoride: A review of its fate, bioavailability and risks of fluorosis in grazed-pasture systems in New Zealand. New Zealand J. Agric. Res. 2010, 43, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, P. The sources, pathway and preventive measures for fluorosis in Zhijin County, Guizhou, China. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Nayak, A.K.; Sharma, Y.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Sharma, D.K. Fluoride accumulation in soil and vegetation in the vicinity of brick fields. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molin, P.; Corti, G. Topography, river network and recent fault activity at the margins of the Central Main Ethiopian Rift (East Africa). Tectonophysics 2015, 664, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldegabriel, G.; Aronson, J.L.; Walter, R.C. Geology, geochronology and rift basin development in the central sector of the Main Ethiopia Rift. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1990, 102, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, G.; Sani, F.; Philippon, M.; Sokoutis, D.; Willingshofer, E.; Molin, P. Quaternary volcano-tectonic activity in the Soddo region, western margin of the Southern Main Ethiopian Rift. Tectonics 2013, 32, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, N.J.; Ebinger, C.J. Variations in the along-axis segmentation of the Afar Rift system. Tectonics 1996, 15, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.; Corti, G.; Innocenti, F.; Manetti, P.; Mazzarini, F.; Abebe, T.; Pecskay, Z. Evolution of the Main Ethiopian Rift in the frame of Afar and Kenya rifts propagation. Tectonics 2005, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, M.; Bonini, M.; Mazzuoli, R.; Abebe, B.; Piccardi, L.; Tortorici, L. Quaternary oblique extensional tectonics in the Ethiopian Rift (Horn of Africa). Tectonophysics 1998, 287, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, L.; Fisseha, S.; Bendick, R.; Reilinger, R.; McClusky, S.; King, R.; Solomon, T. Lithospheric strength and strain localization in continental extension from observations of the East African Rift. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugda, M.T. Crustal structure in Ethiopia and Kenya from receiver function analysis: Implications for rift development in eastern Africa. J. Geol. Soc. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebinger, C.J.; Yemane, T.; Woldegabriel, G.; Aronson, J.L.; Walter, R.C. Late eocene–recent volcanism and faulting in the southern main Ethiopian Rift. J. Geol. Soc. 1993, 150, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanettin, B.; Justin-Visentin, E.; Nicoletti, M.; Petrucciani, C. The Evolution of chencha escarpment and ganjule graben in Southern Ethiopin Rift. N. Jb. Geol. Palaont. Mh 1978, 473–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, S. Groundwater in Ethiopia.Features, Numbers and Opportunities; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alemayehu, T. Groundwater Occurrence in Ethiopia; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2006; Available online: https://docplayer.net/25281625-Groundwater-occurrence-in-ethiopia.html (accessed on 15 November 2016).
- Kebede, S.; Hailu, A.; Crane, E.; Ó Dochartaigh, B.É. Africa Groundwater Atlas: Hydrogeology of Ethiopia; British Geological Survey: Keyworth, UK, 2016; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenew, T.; Demlie, M.; Wohnlich, S. Hydrogeological framework and occurrence of groundwater in the Ethiopian aquifers. J. Afr. Earth. Sci. 2008, 52, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minissale, A.; Corti, G.; Tassi, F.; Darrah, T.H.; Vaselli, O.; Montanari, D.; Montegrossi, G.; Yirgu, G.; Selmo, E.; Teclu, A. Geothermal potential and origin of natural thermal fluids in the northern Lake Abaya area, Main Ethiopian Rift, East Africa. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 336, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-reaction, One-dimensional Transport and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999.
- Coetsiers, M.; Walraevens, K. Chemical characterization of the Neogene Aquifer, Belgium. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L.; Boudoukha, A. Geochemical evolution of groundwater in an alluvial aquifer: Case of El Eulma aquifer, East Algeria. J. Afr. Earth. Sci. 2012, 66, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; Taylor & Francis: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Tang, H.; Li, H.; Song, W.; Xie, G. The solubility of fluorite in Na-K-Cl solutions at temperatures up to 260 °C and ionic strengths up to 4 mol/kg H2O. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 82, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, N.; Back, W. The mass balance approach: application to interpreting the chemical evolution of hydrologic systems. Am. J. Sci. 1980, 280, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, L.N.; Parkhurst, D.L.; Thorstenson, D.C. Development of reaction models for ground-water systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kadi, A.I.; Plummer, L.N.; Aggarwal, P. NETPATH-WIN: An interactive user version of the mass-balance model, NETPATH. Ground Water 2011, 49, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IAEA. Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. The GNIP Database. Available online: https://nucleus.iaea.org/wiser (accessed on 15 November 2016).
- Elango, L.; Kannan, R. Chapter 11 Rock–water interaction and its control on chemical composition of groundwater. In Developments in Environmental Science; Sarkar, D., Datta, R., Hannigan, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 229–243. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.; Hao, Q.; Liu, H.; Hao, Z.; Meng, G.; Pei, Q.; Yan, H. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater in a long-term reclaimed water irrigation area, North China Plain. Water 2018, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, X.; Yin, S.; Pan, X.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y. Investigation of geochemical characteristics and controlling processes of groundwater in a typical long-term reclaimed water use area. Water 2017, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. Hydrogeochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater at Yuncheng Basin, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meybeck, M. Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am. J. Sci. 1987, 287, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeller, H. Geochemistry of Groundwater. In Groundwater Studies—An International Guide for Research and Practice; Brown, R.H., Konoplyantsev, A.A., Ineson, J., Kovalevsky, V.S., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1967; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jacks, G.; Bhattacharya, P.; Chaudhary, V.; Singh, K.P. Controls on the genesis of some high-fluoride groundwaters in India. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, J. Aqueous geochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater in Datong Basin, Northern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, P.D.; Ahmed, S.; Made, B.; Ledoux, E.; Gandolfi, J.M. Association of hydrogeological factors in temporal variations of fluoride concentration in a crystalline aquifer in India. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, B.K. Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride-containing ground waters in India. Ground Water 1975, 13, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Bianchini, G.; Beccaluva, L. Column elution experiments on volcanic ash: geochemical implications for the main Ethiopian Rift waters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 208, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žáček, V.; Rapprich, V.; Aman, Y.; Berhanu, B.; Čížek, D.; Dereje, K.; Erban, V.; Ezra, T.; Firdawok, L.; Habtamu, M.; et al. Explanation Booklet to the Set of Geoscience Maps of Ethiopia at A Scale 1:50,000: Sub-sheet 0738-D3 Shashemene; Czech Geological Survey: Prag, Czech Republic, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Furi, W.; Razack, M.; Abiye, T.A.; Ayenew, T.; Legesse, D. Fluoride enrichment mechanism and geospatial distribution in the volcanic aquifers of the Middle Awash basin, Northern Main Ethiopian Rift. J. Afr. Earth. Sci. 2011, 60, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeolog; CRC Press/Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sracek, O.; Hirata, R. Geochemical and stable isotopic evolution of the guarani aquifer system in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, D. Fluoride levels in the groundwater of the south-eastern part of Ranga Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, T.; Naseem, S.; Usmani, T.H.; Bashir, E.; Khan, F.A.; Bhanger, M.I. Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high fluoride groundwater in the Nagar Parkar area, Sindh, Pakistan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, T.; Leis, A.; Eisenhauer, A.; Dietzel, M. Multi-proxy approach (2H/H, 18O/16O, 13C/12C and 87Sr/86Sr) for the evolution of carbonate-rich groundwater in basalt dominated aquifer of Axum area, Northern Ethiopia. Chem. Erde Geochem. 2011, 71, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Shallow Groundwater | Deep Groundwater | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| Temperature | °C | 21.8 | 26.0 | 23.7 | 21.9 | 40.6 | 27.0 |
| pH | - | 5.6 | 7.1 | - | 6.1 | 8.2 | - |
| EC | µS/cm | 197.0 | 633.0 | 400.6 | 232.0 | 770.0 | 490.9 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 25.5 | 38.2 | 29.1 | 7.0 | 106.0 | 46.6 |
| K+ | mg/L | 6.9 | 16.7 | 10.1 | 4.3 | 19.0 | 11.7 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 4.1 | 10.1 | 7.7 | 0.6 | 20.5 | 7.3 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 11.4 | 48.3 | 24.8 | 8.0 | 61.6 | 22.1 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 2.3 | 35.1 | 17.3 | 1.2 | 15.3 | 5.5 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 0.1 | 74.9 | 14.5 | 0.0 | 16.6 | 4.0 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 26.8 | 577.1 | 257.3 | 136.9 | 622.6 | 359.2 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 2.1 | 69.5 | 20.0 | 0.2 | 17.6 | 3.7 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 5.6 | 2.5 |
| SiO2 | mg/L | 31.9 | 54.6 | 38.4 | 47.3 | 77.0 | 64.0 |
| δ18O | - | −3.4 | −1.1 | −2.1 | −4.9 | −2.1 | −3.5 |
| δD | - | −4.3 | 5.3 | −0.6 | −27.1 | −2.7 | −13.9 |
| Cold Spring | Hot Spring | ||||||
| Temperature | °C | 20.1 | 22.5 | 21.6 | 32.8 | 81.0 | 48.0 |
| pH | - | 6.1 | 6.5 | - | 6.5 | 8.5 | - |
| EC | µS/cm | 112.0 | 198.0 | 144.7 | 202.0 | 1262.0 | 840.3 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 7.1 | 23.3 | 15.8 | 27.2 | 197.7 | 121.5 |
| K+ | mg/L | 4.0 | 10.7 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 39.7 | 21.6 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 1.0 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 4.1 | 2.1 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 4.8 | 6.1 | 5.2 | 3.5 | 18.4 | 9.2 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 3.6 | 6.2 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 64 | 28.2 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 1.0 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 106 | 35.0 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 40.3 | 117.7 | 72.0 | 178.4 | 747.9 | 541.6 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 4.2 | 23.2 | 11.0 | 2.4 | 8.9 | 5.7 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 57.4 | 20.2 |
| SiO2 | mg/L | 33.4 | 34.7 | 34.1 | 67.17 | 70.2 | 68.7 |
| δ18O | - | −3.2 | −2.1 | −2.6 | −3.18 | −1.9 | −2.6 |
| δD | - | −9.7 | −2.4 | −5.6 | −12.73 | −4.1 | −8.2 |
| River | Lake | ||||||
| Temperature | °C | 23 | 24 | 23.5 | 23.6 | 27.8 | 26.0 |
| pH | - | 7.4 | 7.7 | - | 6.97 | 10.1 | - |
| EC | µS/cm | 83.2 | 219 | 151.1 | 187 | 26300.0 | 11846.8 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 17.0 | 17.2 | 17.1 | 15 | 4250 | 2541.3 |
| K+ | mg/L | 7.2 | 10.3 | 8.8 | 23 | 282 | 126.8 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 3.1 | 6.4 | 4.8 | 0.5 | 4.3 | 2.1 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 12.2 | 18.7 | 15.5 | 2.4 | 17.6 | 8.6 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 3.6 | 8.2 | 5.9 | 11.4 | 611.4 | 307.6 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 4.9 | 12.8 | 8.8 | 1.1 | 652.5 | 168.3 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 86.3 | 93.9 | 90.1 | 37.1 | 4114.0 | 2110.3 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 2.1 | 15.6 | 8.9 | 1.2 | 42.0 | 11.9 |
| F− | mg/L | 0.6 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 112.0 | 50.2 |
| δ18O | - | −2.9 | −2.1 | −2.5 | 3.88 | 8.0 | 6.7 |
| δD | - | −4.9 | −3.7 | −4.3 | 28.81 | 51.1 | 40.5 |
| Phase | Plagioclase | Biotite | Calcite | Fluorite | Ca-Na | CO2 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B30–B25 | 0.14721 | 0.05082 | 1.60339 | 0.04117 | 1.1576 | 2.75896 |
| B30–B20 | 0.10979 | 0.07604 | 1.39587 | 0.03485 | 1.02302 | 2.32185 |
| B30–B35 | 0.19637 | 0.0184 | 2.44832 | 0.13105 | 2.3787 | 3.01156 |
| B30–B28 | 0.25325 | −0.02664 | 2.04245 | 0.06825 | 2.00979 | 1.96745 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haji, M.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Qin, D.; Guo, Y. Geochemical Evolution of Fluoride and Implication for F− Enrichment in Groundwater: Example from the Bilate River Basin of Southern Main Ethiopian Rift. Water 2018, 10, 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121799
Haji M, Wang D, Li L, Qin D, Guo Y. Geochemical Evolution of Fluoride and Implication for F− Enrichment in Groundwater: Example from the Bilate River Basin of Southern Main Ethiopian Rift. Water. 2018; 10(12):1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121799
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaji, Muhammed, Dongdong Wang, Lu Li, Dajun Qin, and Yi Guo. 2018. "Geochemical Evolution of Fluoride and Implication for F− Enrichment in Groundwater: Example from the Bilate River Basin of Southern Main Ethiopian Rift" Water 10, no. 12: 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121799
APA StyleHaji, M., Wang, D., Li, L., Qin, D., & Guo, Y. (2018). Geochemical Evolution of Fluoride and Implication for F− Enrichment in Groundwater: Example from the Bilate River Basin of Southern Main Ethiopian Rift. Water, 10(12), 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121799





