Responses of Water Fluxes and Water-Use Efficiency of Maize to Warming Based on Water Transformation Dynamical Processes Experimental Device (WTDPED) Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Water Transformation Dynamical Processes Experimental Device (WTDPED)
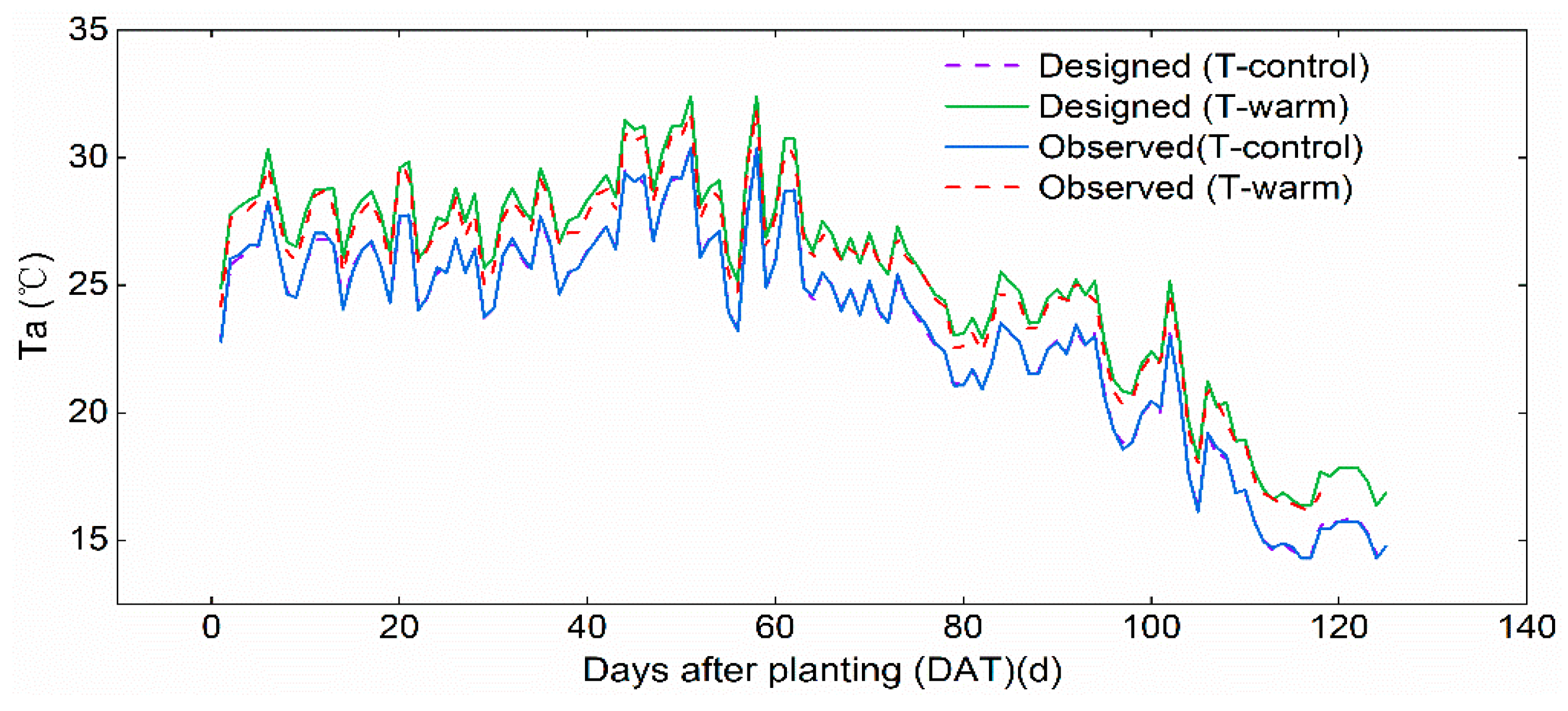
2.2. Experimental Design and Measurements
2.3. Water Balance Analysis
2.4. Estimation of Water-Use Efficiency (WUE) and WUEI
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
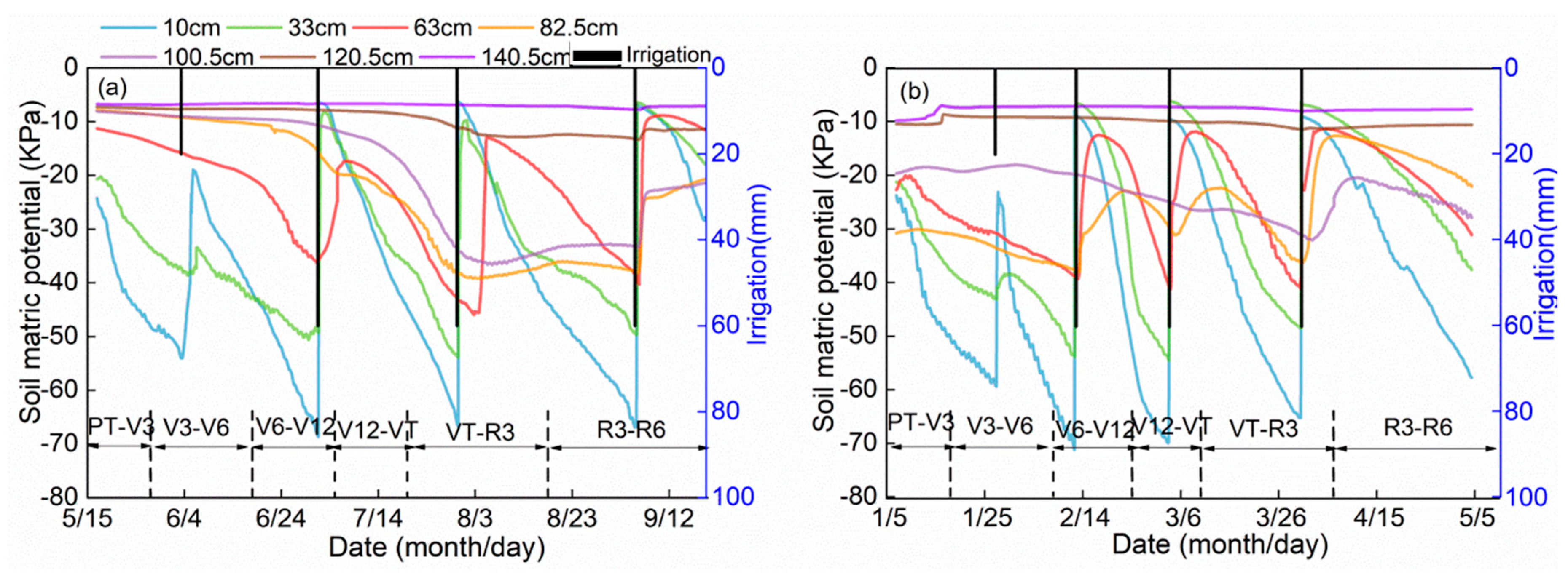
3.1. Temporal Variations in Soil Moisture Distribution
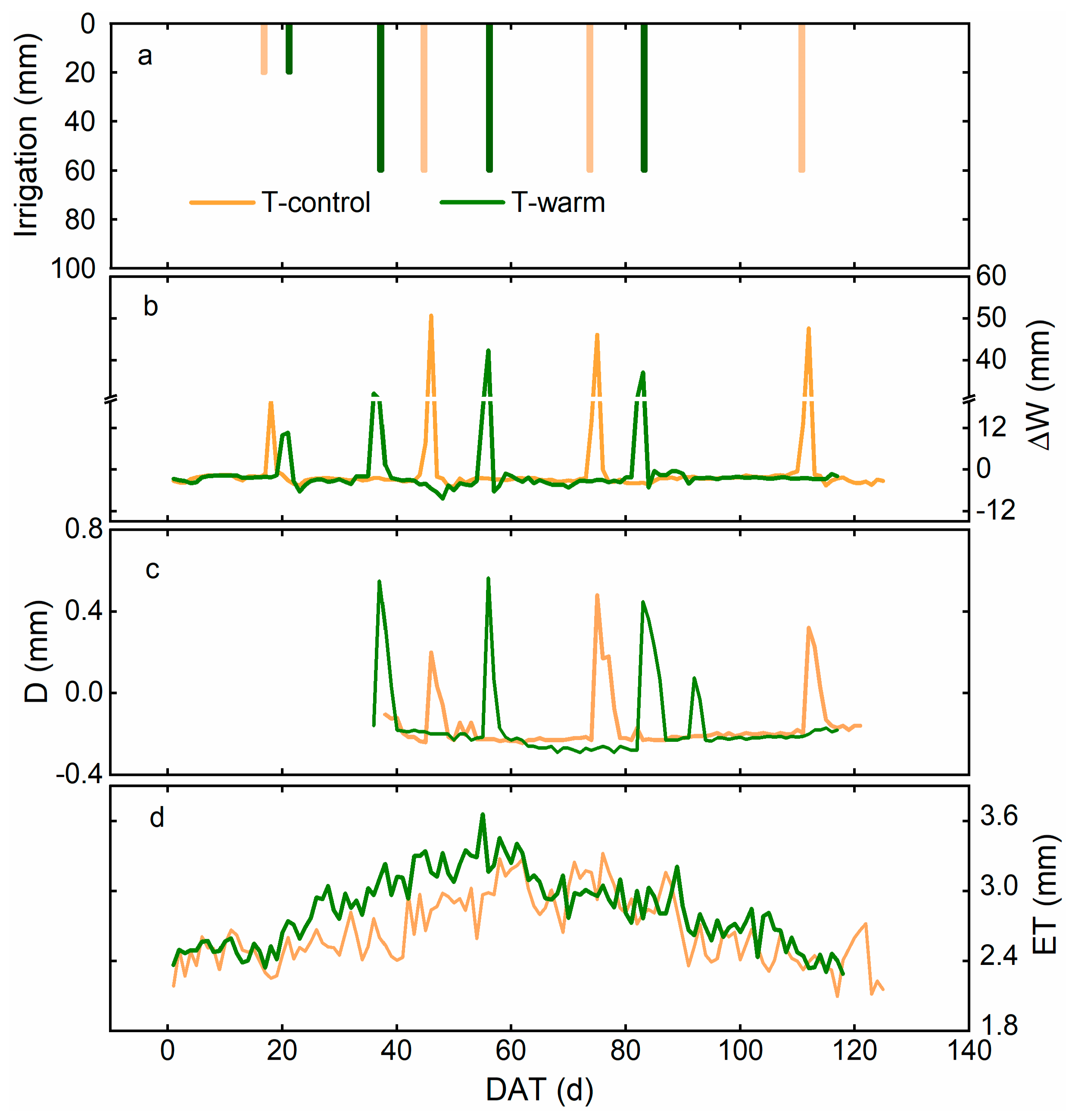
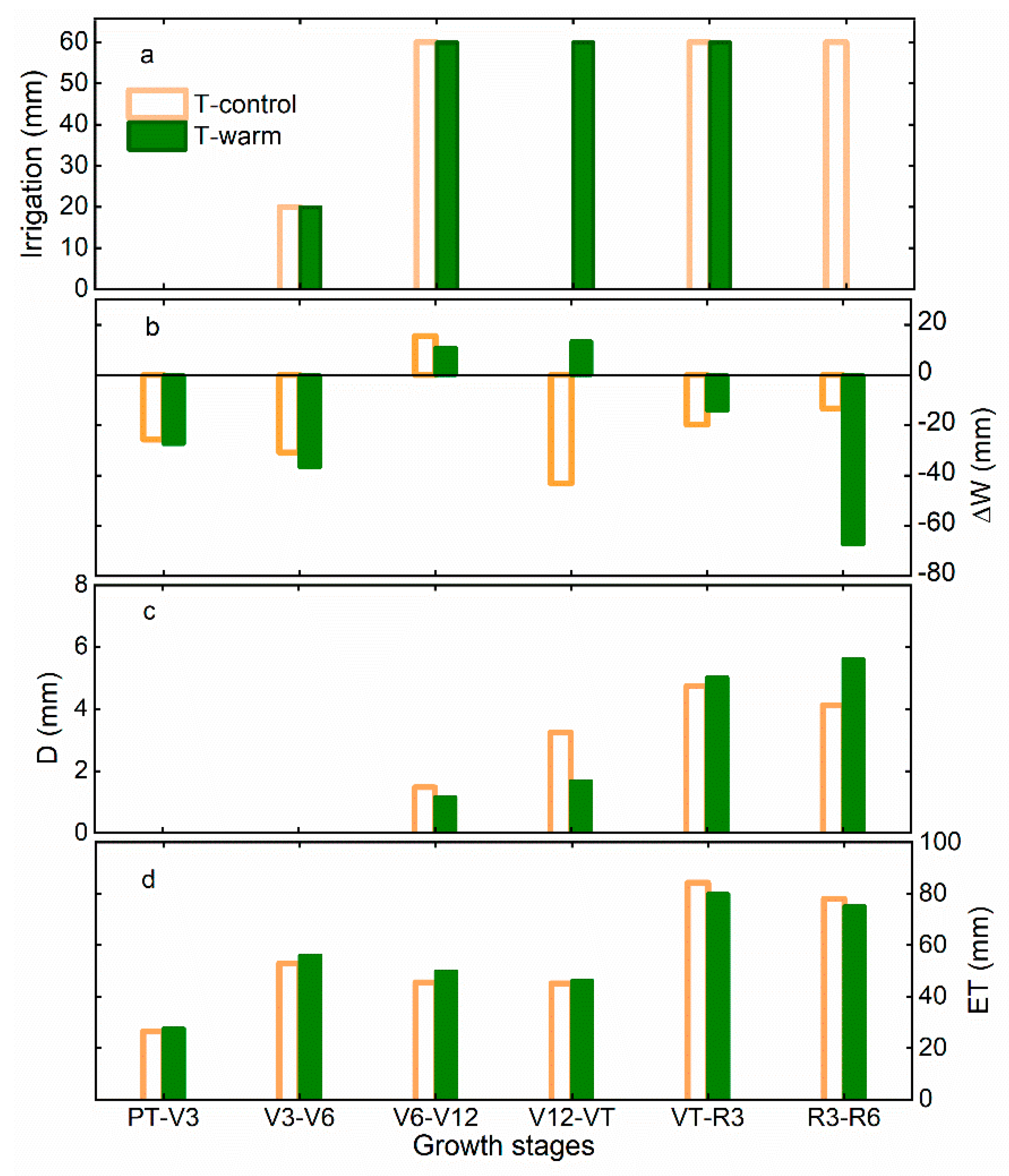
3.2. Temporal Variations in the Water Fluxes at Different Groundwater–Soil–Plant–Atmosphere Continuum (GSPAC) Interfaces
3.3. Temporal Variations in Maize Development and WUE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eitzinger, J.; Štastná, M.; Žalud, Z.; Dubrovský, M. A simulation study of the effect of soil water balance and water stress on winter wheat production under different climate change scenarios. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 61, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsten, A.; Vetter, T.; Vohland, K.; Krysanova, V. Impact of climate change on soil moisture dynamics in Brandenburg with a focus on nature conservation areas. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, F.; Pan, M.; Niel, T.V.; Wegehenkel, M. Hydrological processes in changing climate, land use and cover change. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 73, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, M.; Bao, A.; De M, P.; Feng, X.; Chen, X. Local climate change and the impacts on hydrological processes in an arid alpine catchment in Karakoram. Water 2017, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Das, S.; Ren, Q. Hydrological appraisal of climate change impacts on the water resources of the Xijiang Basin, South China. Water 2017, 9, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Kiem, A.S.; Babel, M.S.; Chu, S.T.; Chakma, B. Evaluation of climate change impacts and adaptation strategies for maize cultivation in the Himalayan foothills of India. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 596–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, A.; Pathak, H.; Singh, S.D.; Bhatia, A.; Harit, R.C.; Kumar, V. Growth, yield and quality of maize with elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide and temperature in north-west India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 218, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, M.S.; Deb, P.; Soni, P. Performance evaluation of AquaCrop and DSSAT-CERES for maize under different irrigation and manure application rates in the Himalayan region of India. Agric. Res. 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. Agriculture irrigation demand under present and future climate scenarios in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 60, 306–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, Z.; Guo, R. Regional crop yield, water consumption and water use efficiency and their responses to climate change in the North China Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 134, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 151, pp. 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rijsberman, F.; Swart, R. Targets and Indicators of Climate Change; Report of Working Group II of the Advisory Group on Greenhouse Gases; Stockholm Environmental Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, C.C.; Jaeger, J. Three views of two degrees. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, W. Water balance and migration for maize in an oasis farmland of northwest China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4829–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-asher, J.; Hoogenboom, G. Effect of high temperature on photosynthesis and transpiration of sweet corn (Zea mays L. var. rugosa). Photosynthetica 2008, 46, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ren, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, Z.; Fang, C. Responses of a rice-wheat rotation agroecosystem to experimental warming. Ecol. Res. 2013, 28, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, M.; Shen, R.; Qiu, S. Effects of artificial warming on the structural, physiological and biochemical changes of maize (Zea mays L.) leaves in northern China. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 2891–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizildeniz, T.; Mekni, I.; Santesteban, H.; Pascual, I.; Morales, F.; Irigoyen, J.J. Effects of climate change including elevated CO2 concentration, temperature and water deficit on growth, water status and yield quality of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) cultivars. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G. Keeping global warming within 1.5 °C reduces future risk of yield loss in the United States: A probabilistic modeling approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, L.; Hou, R.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Li, F.; Cheng, D.; Peng, Z.; Xu, M. Experimental warming enhances the carbon gain but does not affect the yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in the North China Plain. Flora 2018, 240, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchiola, D.; Nana, E.; Soncini, A. Impact of climate change scenarios on crop yield and water footprint of maize in the Po valley of Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalota, S.K.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, S.; Vashisht, B.B. Impact of climate change scenarios on yield, water and nitrogen-balance and -use efficiency of rice-wheat cropping system. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchiola, D. Impact of potential climate change on crop yield and water footprint of rice in the Po valley of Italy. Agric. Syst. 2015, 139, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Bai, J. Future projected changes in local evapotranspiration coupled with temperature and precipitation variation. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Evans, L.G.; Semenov, M.A.; Eckersten, H.; Iglesias, A. Comparison of wheat simulation models under climate change. I. Model calibration and sensitivity analyses. Clim. Res. 1996, 7, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J.; Tubiello, F.N. Global food security under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19703–19708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.R.; Taniguchi, M.; Kooi, H.; Gurdak, J.J.; Allen, D.M.; Hiscock, K.M.; Treidel, H.; Aureli, A. Beneath the surface of global change: Impacts of climate change on groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 532–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangle, L.A.; Gregg, J.W.; McDonnell, J.J. Rainfall seasonality and an ecohydrological feedback offset the potential impact of climate warming on evapotranspiration and groundwater recharge. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, R.; Gaudet, J.P.; Bariac, T. Preferential flow and solute transport in a large lysimeter, under controlled boundary conditions. J. Hydrol. 1999, 215, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, H.M.; Flury, M. Simulation of water flow and solute transport in free-drainage lysimeters and field soils with heterogeneous structures. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R.; Schwartz, R.C.; Casanova, J.J.; Heng, L.K. Soil water sensing for water balance, ET and WUE. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 104, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, D.; Veste, M.; Badorreck, A.; Freese, D. Evaluation of fast growing tree water use under different soil moisture regimes using wick lysimeters. iForest 2013, 6, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klammler, G.; Fank, J. Determining water and nitrogen balances for beneficial management practices using lysimeters at Wagna test site (Austria). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegehenkel, M.; Gerke, H.H. Water table effects on measured and simulated fluxes in weighing lysimeters for differently-textured soils. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Vera, U.M.; Siebers, M.H.; Drag, D.W.; Ort, D.R.; Bernacchi, C.J. Canopy warming caused photosynthetic acclimation and reduced seed yield in maize grown at ambient and elevated CO2. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 4237–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpp, C.; Nützmann, G.; Maciejewski, S.; Maloszewski, P. A comparative modeling study of a dual tracer experiment in a large lysimeter under atmospheric conditions. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Paredes, P.; Pereira, L.S. Simulation of the soil water balance of wheat using daily weather forecast messages to estimate the reference evapotranspiration. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghedifar, S.M.; Ziaei, A.N.; Ansari, H. Simulation of irrigation return flow from a Triticale farm under sprinkler and furrow irrigation systems using experimental data: A case study in arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroco, J.P.; Edwards, G.E.; Ku, M.S.B. Photosynthetic acclimation of maize to growth under elevated levels of carbon dioxide. Planta 1999, 210, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Vera, U.M.; Siebers, M.H.; Jaiswal, D.; Ort, D.R.; Bernacchi, C.J. Canopy warming accelerates development in soybean and maize, offsetting the delay in soybean reproductive development by elevated CO2 concentrations: Climate change impacts on crops development. Plant Cell Environ. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, K.Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.X.; Teng, N.J. The effect of experimental warming on leaf functional traits, leaf structure and leaf biochemistry in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.P.; Xu, M.; Hou, R.X.; Shen, R.C.; Qiu, S.; Ouyang, Z. Effects of experimental warming on stomatal traits in leaves of maize (zea may L.). Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 3095–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.P.; Lin, Z.H.; Mo, X.G.; Yang, C.L. Response of crop yield and water use efficiency to climate change in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, A.; Belova, T.; Florides, C.G.; Maulis, C.; Fischer, I.; Gell, G.; Birinyi, Z.; Ong, J.; Keeble-Gagnère, G.; Maharajan, A.; et al. Genome mapping of seed-borne allergens and immunoresponsive proteins in wheat. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yihdego, Y.; Salem, H.S.; Muhammed, H.H. Agricultural pest management policies during drought: Case studies in Australia and the state of Palestine. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2018, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Khalil, A. Groundwater resources assessment and impact analysis using a conceptual water balance model and time series data analysis: Case of decision making tool. Hydrology 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Webb, J.A. Comparison of evaporation rate on open water bodies: Energy balance estimate versus measured pan. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Date in T-Control Experiment | Date in T-Warm Experiment | Management Practices | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 May 2014 | 3 January 2015 | Irrigation | 100 mm |
| N, P2O5, K2O | 150, 150, 150 kg ha−1 * | ||
| 3 June 2014 | 27 January 2015 | Irrigation | 20 mm |
| N, P2O5, K2O | 100, 100, 100 kg ha−1 * | ||
| 1 July 2014 | 12 February 2015 | Irrigation | 60 mm |
| 30 July 2014 | 3 March 2015 | Irrigation | 60 mm |
| Urea | 300 kg ha−1 * | ||
| 5 September 2014 | 30 March 2015 | Irrigation | 60 mm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, S. Responses of Water Fluxes and Water-Use Efficiency of Maize to Warming Based on Water Transformation Dynamical Processes Experimental Device (WTDPED) Experiment. Water 2018, 10, 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111660
Wu Y, Ma Y, Song X, Yang L, Yang S. Responses of Water Fluxes and Water-Use Efficiency of Maize to Warming Based on Water Transformation Dynamical Processes Experimental Device (WTDPED) Experiment. Water. 2018; 10(11):1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111660
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yali, Ying Ma, Xianfang Song, Lihu Yang, and Shengtian Yang. 2018. "Responses of Water Fluxes and Water-Use Efficiency of Maize to Warming Based on Water Transformation Dynamical Processes Experimental Device (WTDPED) Experiment" Water 10, no. 11: 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111660
APA StyleWu, Y., Ma, Y., Song, X., Yang, L., & Yang, S. (2018). Responses of Water Fluxes and Water-Use Efficiency of Maize to Warming Based on Water Transformation Dynamical Processes Experimental Device (WTDPED) Experiment. Water, 10(11), 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111660






