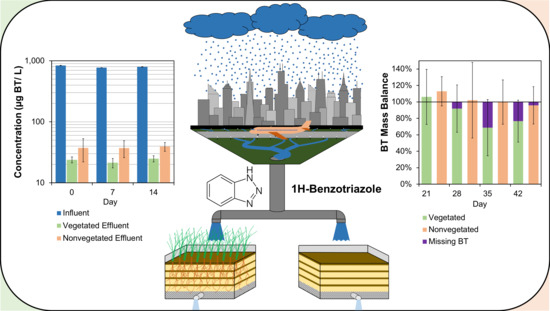
Benzotriazole Uptake and Removal in Vegetated Biofilter Mesocosms Planted with Carex praegracilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
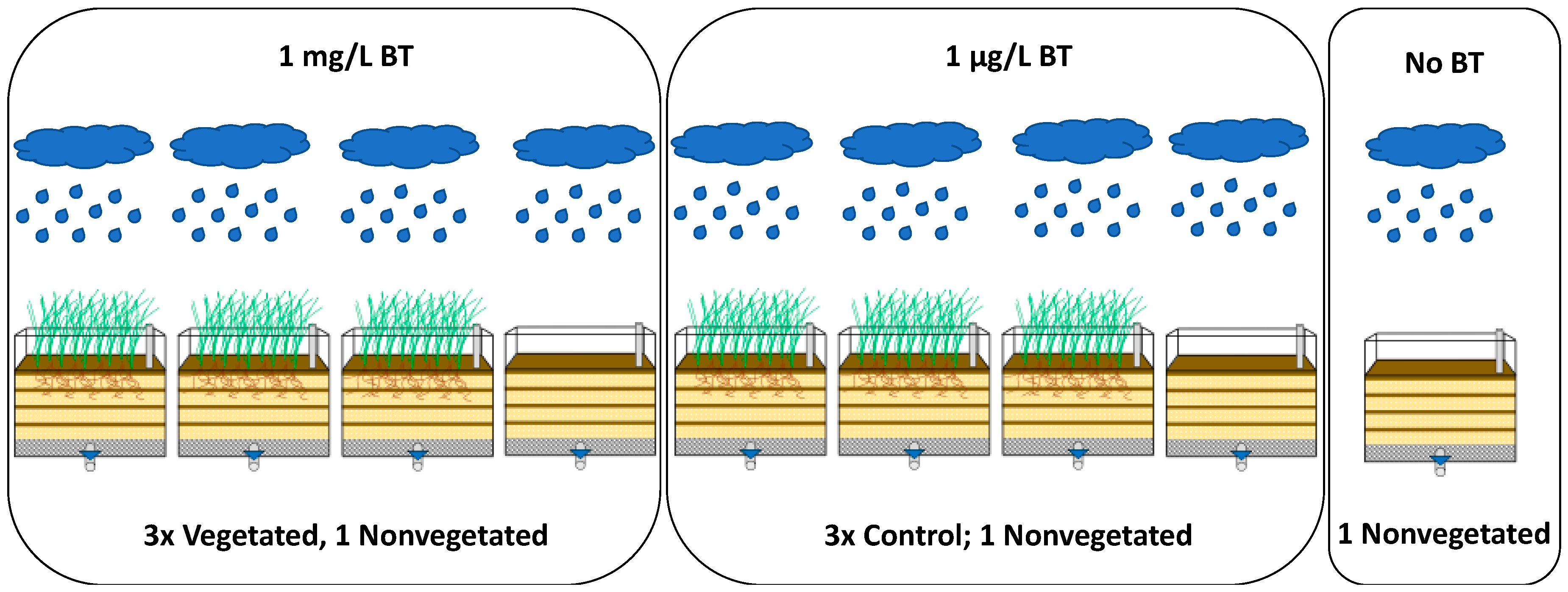
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling Plan
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Method for Pore Water, Influent, and Effluent
2.4.2. Method for C. praegracilis Tissue
2.4.3. Method for Geomedia
2.4.4. Mesocosm Deconstruction
2.4.5. LC-MS Analysis
2.5. Mass Balance and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
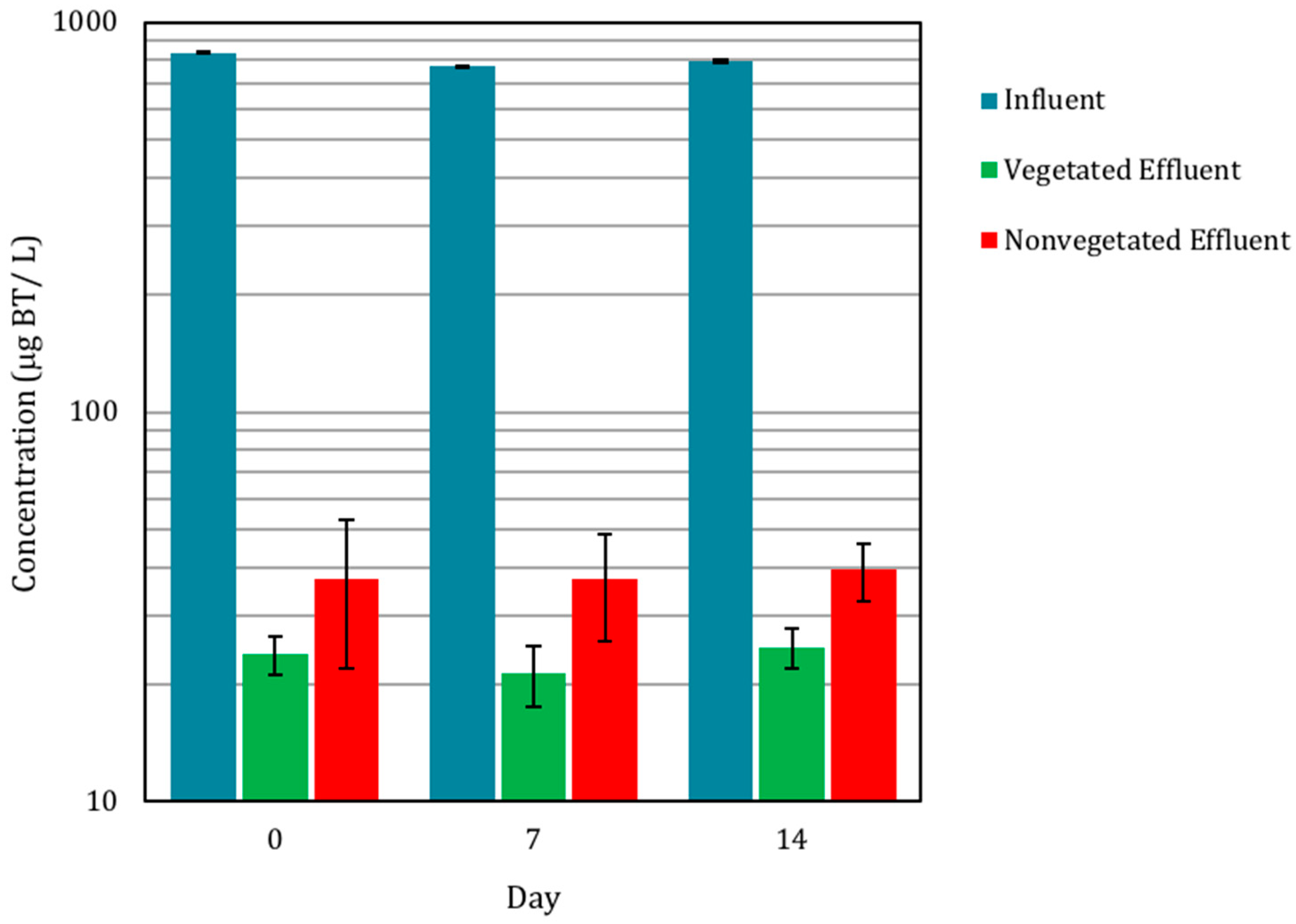
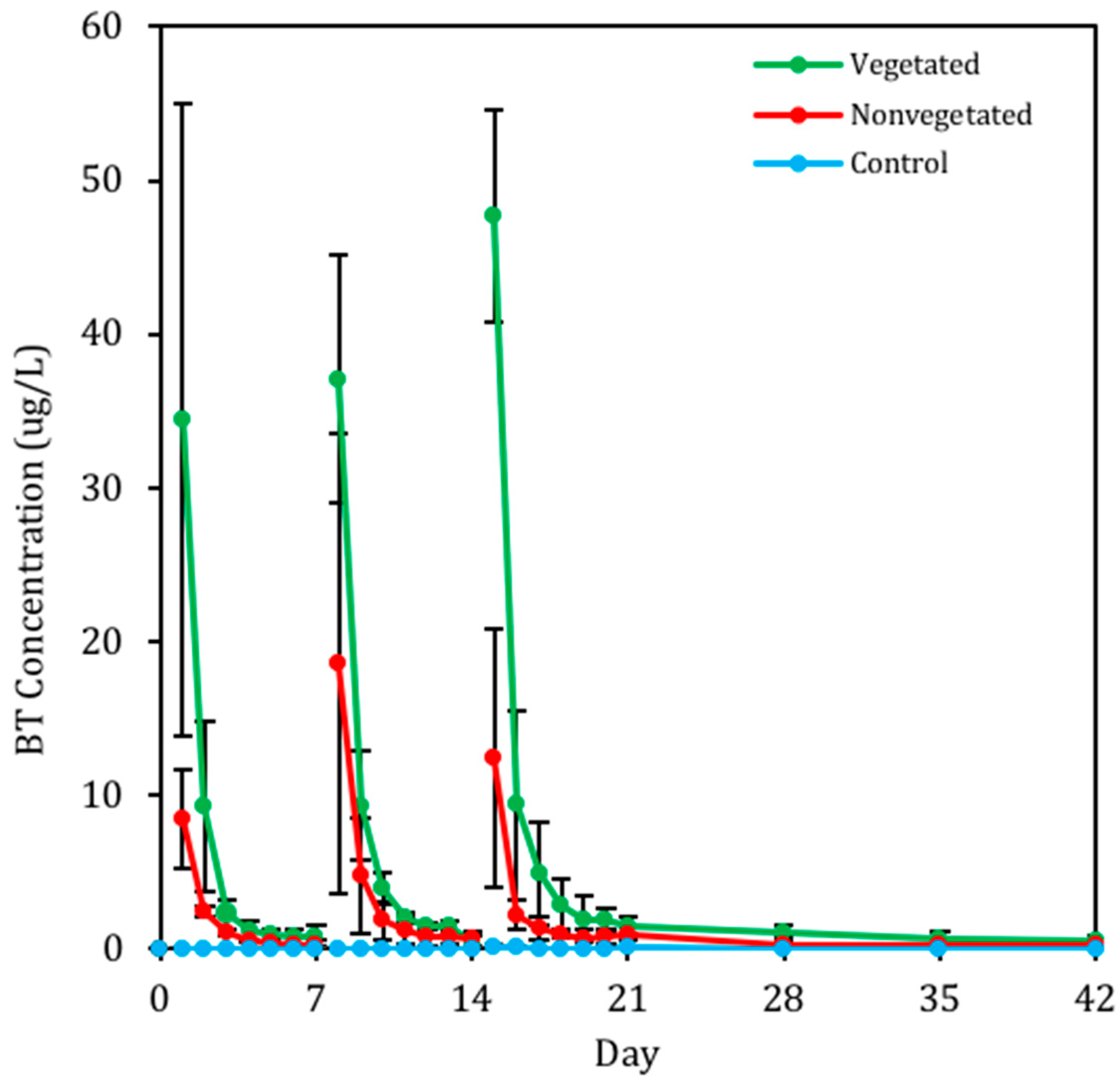
3.1. Biofilter Performance and C. praegracilis Growth
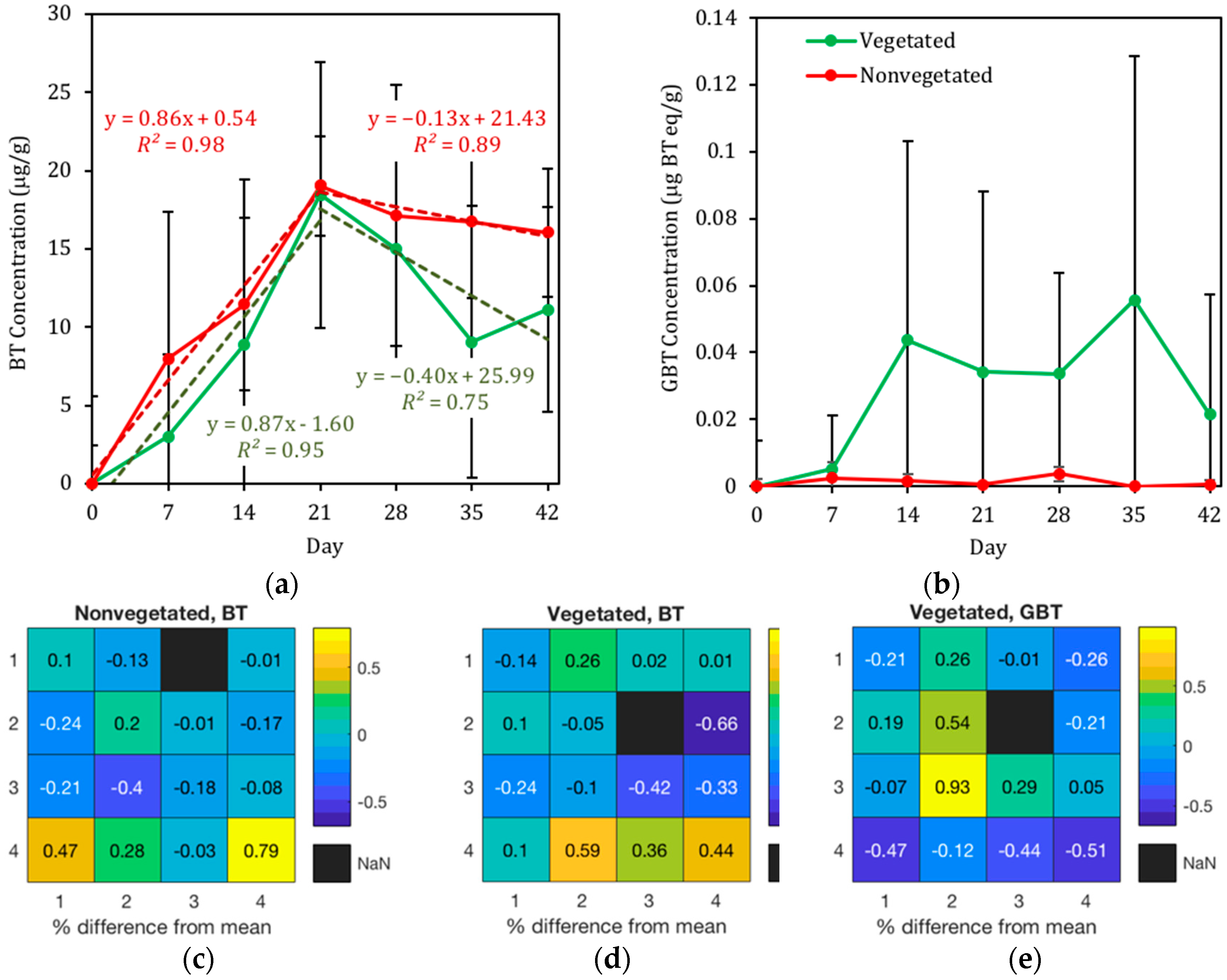
3.2. The Presence of BT and BT Metabolites in Biofilter Sinks
3.2.1. Presence of BT in Geomedia
3.2.2. Presence of BT in Pore Water
3.2.3. Presence of BT in C. praegracilis
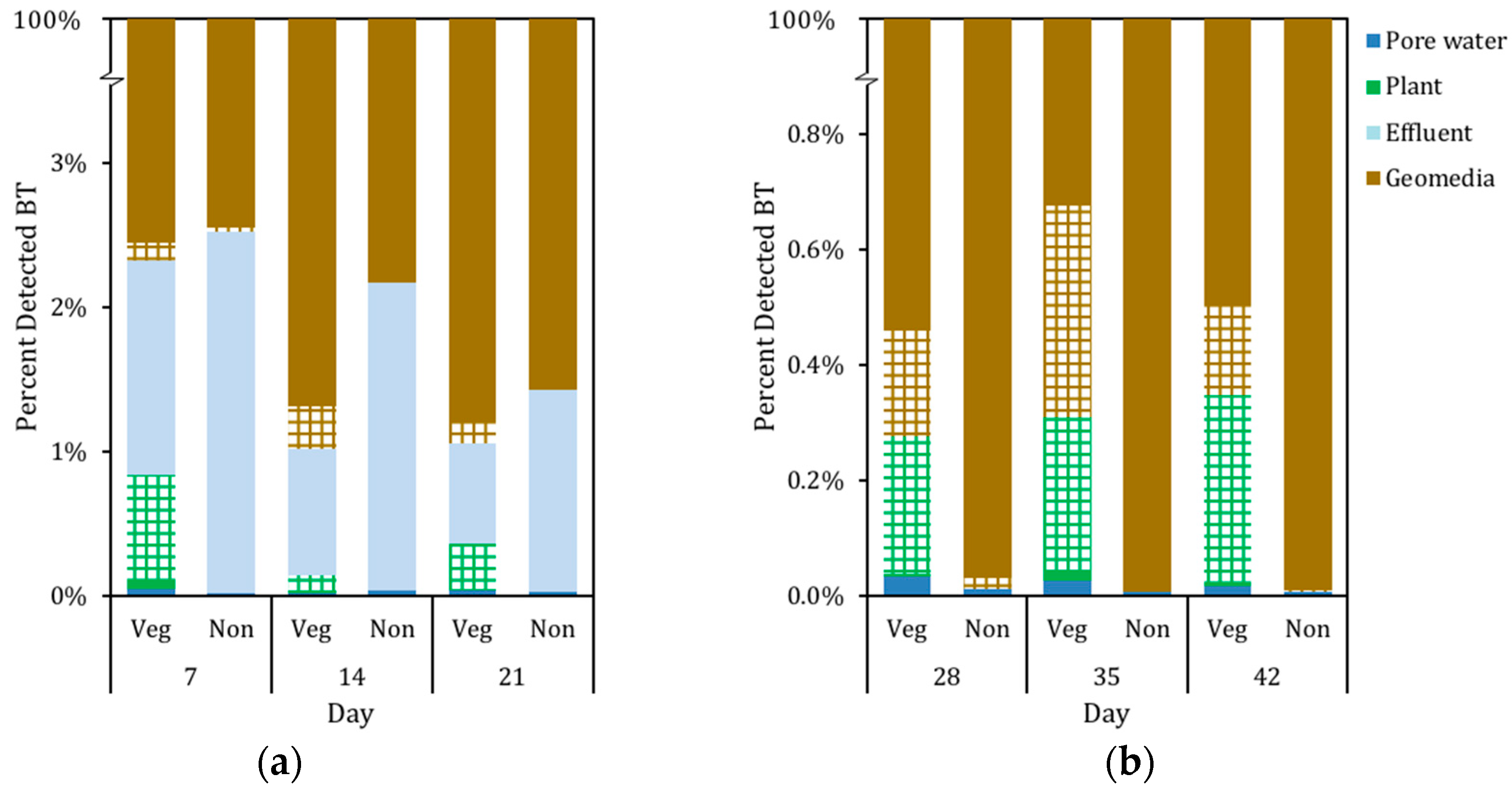
3.3. Mass Distribution of BT in System
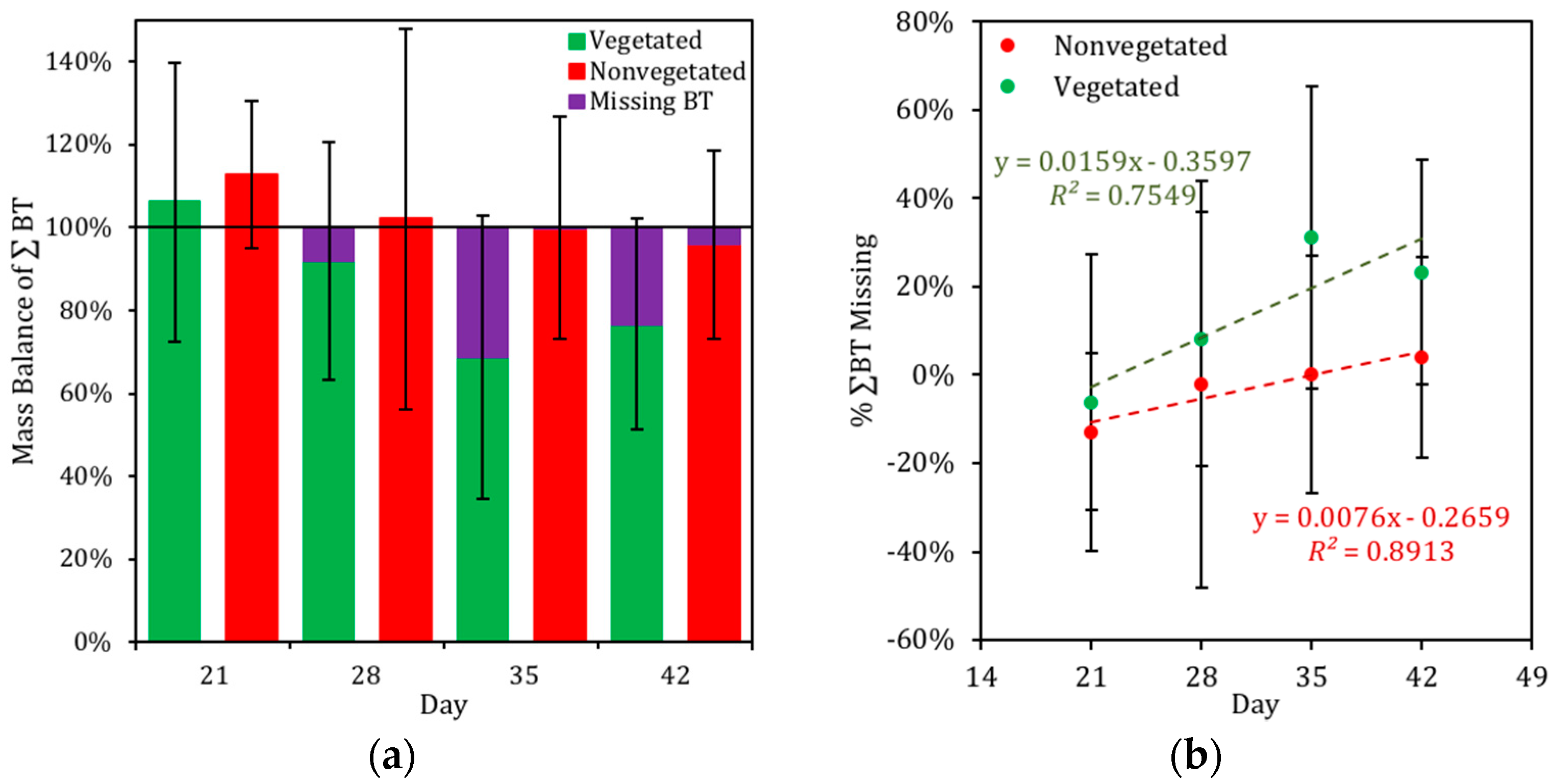
3.4. Mass Balance of BT in the Biofilter Mesocosms
4. Discussion
4.1. Biofilter Mesocosm Performance and C. praegracilis Growth
4.2. BT and BT Metabolites
4.3. Distribution of BT in Biofilter Mesocosms and Missing Sinks
4.4. Environmental Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| MRM Mass Transition | Q1 Mass [Da] | Q3 Mass [Da] | Declustering Potential [V] | Focusing Potential [V] | Entrance Potential [V] | Collision Energy [V] | Collision Cell Exit Potential [V] | Retention Time [min] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H-BT-1 | 119.951 | 65.110 | 51.000 | 240.000 | 10.000 | 31.000 | 4.000 | 5.58 |
| 1H-BT-2 | 119.951 | 92.127 | 51.000 | 240.000 | 10.000 | 25.000 | 6.000 | 5.58 |
| d4-BT-1 | 123.972 | 69.100 | 41.000 | 170.000 | 10.000 | 35.000 | 4.000 | 5.53 |
| d4-BT-2 | 123.972 | 96.000 | 41.000 | 170.000 | 10.000 | 27.000 | 6.000 | 5.53 |
| GBT-1 | 281.900 | 119.900 | 23.000 | 200.000 | 10.000 | 25.000 | 10.000 | 4.49 |
| GBT-2 | 281.900 | 85.000 | 23.000 | 200.000 | 10.000 | 35.000 | 10.000 | 4.49 |
| M207-1 | 207.088 | 120.000 | 36.000 | 170.000 | 10.000 | 22.000 | 8.000 | 4.29 |
| M270-2 | 207.088 | 179.100 | 36.000 | 170.000 | 10.000 | 13.000 | 12.000 | 4.29 |
Appendix B
Appendix C
| Day | Vegetated | Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean 1 [g] | Mean 1 [g] | |||
| 0 | 3.52 | ±1.66 | 5.76 | ±3.76 |
| 7 | 3.56 | ±2.44 | 2.13 | ±0.69 |
| 14 | 3.02 | ±2.21 | 1.13 | ±0.07 |
| 21 | 2.17 | ±0.43 | 1.41 | ±0.71 |
| 28 | 1.24 | ±0.83 | 6.70 | ±3.37 |
| 35 | 5.09 | ±0.96 | 2.18 | ±0.72 |
| 42 | 2.47 | ±0.63 | 2.10 | ±0.66 |
| Mean | 3.01 | ±1.23 | 3.06 | ±2.22 |
| Day | Vegetated | Nonvegetated | Control | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean 1 [mL] | Mean 1 [mL] | Mean 1 [mL] | ||||
| 0 2 | 426 | ±136 | 232 | ±161 | 454 | ±157 |
| 0 3 | 43 | ±75 | 99 | ±99 | 66 | ±114 |
| 1 | 300 | ±147 | 257 | ±39 | 350 | ±220 |
| 2 | 199 | ±40 | 143 | ±135 | 220 | ±51 |
| 3 | 174 | ±146 | 555 | ±473 | 55 | ±50 |
| 4 | 196 | ±75 | 178 | ±58 | 392 | ±13 |
| 5 | 415 | ±13 | 219 | ±36 | 378 | ±26 |
| 6 | 138 | ±59 | 115 | ±103 | 198 | ±63 |
| 7 2 | 435 | ±60 | 155 | ±18 | 404 | ±91 |
| 7 3 | - | - | 260 | ±248 | - | - |
| 8 | 278 | ±97 | 170 | ±87 | 225 | ±45 |
| 9 | 268 | ±56 | 208 | ±118 | 258 | ±40 |
| 10 | 287 | ±79 | 242 | ±67 | 504 | ±55 |
| 11 | 489 | ±80 | 195 | ±75 | 300 | ±42 |
| 13 | 271 | ±89 | 318 | ±31 | 290 | ±15 |
| 14 2 | 580 | ±101 | 253 | ±83 | 473 | ±97 |
| 14 3 | 89 | ±154 | - | - | 216 | ±71 |
| 15 | 322 | ±121 | 271 | ±38 | 356 | ±67 |
| 16 | 355 | ±29 | 247 | ±97 | 324 | ±85 |
| 17 | 153 | ±19 | 68 | ±20 | 192 | ±60 |
| 18 | 286 | ±52 | 161 | ±24 | 283 | ±23 |
| 19 | 394 | ±73 | 290 | ±42 | 431 | ±160 |
| 20 | 227 | ±82 | 114 | ±58 | 245 | ±86 |
| 21 | 389 | ±75 | 163 | ±10 | 598 | ±270 |
| 22 | 397 | ±236 | 254 | ±78 | 250 | ±22 |
| 25 | 616 | ±163 | 418 | ±113 | 511 | ±26 |
| 26 | 330 | ±70 | 343 | ±84 | 293 | ±57 |
| 27 | 378 | ±17 | 60 | ±104 | 368 | ±19 |
| 28 | 260 | ±72 | 59 | ±51 | 293 | ±28 |
| 29 | 300 | ±66 | 147 | ±131 | 225 | ±35 |
| 32 | 837 | ±72 | 370 | ±115 | 779 | ±123 |
| 33 | 316 | ±73 | 133 | ±19 | 243 | ±71 |
| 35 | 568 | ±54 | 307 | ±15 | 757 | ±425 |
| 36 | 75 | ±27 | 90 | ±75 | 77 | ±20 |
| 39 | 674 | ±176 | 416 | ±74 | 339 | ±230 |
| 40 | 180 | ±49 | 172 | ±23 | 243 | ±23 |
| 41 | 605 | ±181 | 226 | ±81 | 469 | ±174 |
| 42 | 255 | ±36 | 150 | ±89 | 262 | ±46 |
| Mean | 329 | ±182 | 212 | ±113 | 324 | ±168 |
References
- LeFevre, G.H.; Paus, K.H.; Natarajan, P.; Gulliver, J.S.; Novak, P.J.; Hozalski, R.M. Review of Dissolved Pollutants in Urban Storm Water and Their Removal and Fate in Bioretention Cells. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Q. A Review of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems Considering the Climate Change and Urbanization Impacts. Water 2014, 6, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Taylor, S.L. The influence of urban density and drainage infrastructure on the concentrations and loads of pollutants in small streams. Environ. Manag. 2004, 34, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clary, J.; Urbonas, B.; Jones, J.; Strecker, E.; Quigley, M.; O’Brien, J. Developing, evaluating and maintaining a standardized stormwater BMP effectiveness database. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhillips, L.; Goodale, C.; Walter, M.T. Nutrient Leaching and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Grassed Detention and Bioretention Stormwater Basins. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Hunt, W.F.; Traver, R.G.; Clar, M. Bioretention Technology: Overview of Current Practice and Future Needs. J. Environ. Eng.-ASCE 2009, 135, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sample, D.J.; Bell, C.; Guan, Y.T. Review and Research Needs of Bioretention Used for the Treatment of Urban Stormwater. Water 2014, 6, 1069–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muerdter, C.P.; Wong, C.K.; LeFevre, G.H. Emerging investigator series: The role of vegetation in bioretention for stormwater treatment in the built environment: Pollutant removal, hydrologic function, and ancillary benefits. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 592–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Hurley, S.E.; Wemple, B.C. Effects of different soil media, vegetation, and hydrologic treatments on nutrient and sediment removal in roadside bioretention systems. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 112, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycewicz-Borecki, M.; McLean, J.E.; Dupont, R.R. Nitrogen and phosphorus mass balance, retention and uptake in six plant species grown in stormwater bioretention microcosms. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Davis, A.P. A unified look at phosphorus treatment using bioretention. Water Res. 2016, 90, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratieres, K.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Zinger, Y. Nutrient and sediment removal by stormwater biofilters: A large-scale design optimisation study. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.W.; Song, K.G.; Cho, J.W.; Kim, T.G.; Ahn, K.H. Removal of nitrogen by a layered soil infiltration system during intermittent storm events. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rycewicz-Borecki, M.; McLean, J.E.; Dupont, R.R. Bioaccumulation of copper, lead, and zinc in six macrophyte species grown in simulated stormwater bioretention systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water quality improvement through bioretention: Lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Cao, Y.P.; Rippy, M.A.; Afrooz, A.; Grant, S.B. Indicator and Pathogen Removal by Low Impact Development Best Management Practices. Water 2016, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Torkelson, A.A.; Dodd, H.; Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B. Engineering Solutions to Improve the Removal of Fecal Indicator Bacteria by Bioinfiltration Systems during Intermittent Flow of Stormwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasena, G.I.; Shirdashtzadeh, M.; Li, Y.L.; Deletic, A.; Hathaway, J.M.; McCarthy, D.T. Retention and survival of E. coli in stormwater biofilters: Role of vegetation, rhizosphere microorganisms and antimicrobial filter media. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diblasi, C.J.; Li, H.; Davis, A.P.; Ghosh, U. Removal and Fate of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Pollutants in an Urban Stormwater Bioretention Facility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, N.; Leatherbarrow, J.E.; Yee, D.; McKee, L.J. Removal Efficiencies of a Bioretention System for Trace Metals, PCBs, PAHs, and Dioxins in a Semiarid Environment. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedoldi, D.; Chebbo, G.; Pierlot, D.; Kovacs, Y.; Gromaire, M.C. Impact of runoff infiltration on contaminant accumulation and transport in the soil/filter media of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 904–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Central Coast Low Impact Development Initiative. LID Plant Guidance for Bioretention; Central Coast Water Board: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stachel, B.; Holthuis, J.U.; Schulz, W.; Seitz, W.; Weber, W.H.; Tegge, K.T.; Dobner, I. Treatment Techniques and Analysis of Stormwater Run-off from Roads in Hamburg, Germany. In Xenobiotics in the Urban Water Cycle: Mass Flows, Environmental Processes, Mitigation and Treatment Strategies; FattaKassinos, D., Bester, K., Kummerer, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2010; Volume 16, pp. 445–461. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, A.; Fries, E. Occurrence of benzotriazoles in the rivers Main, Hengstbach, and Hegbach (Germany). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulej, A.M.; Polkowska, Z.; Astel, A.; Namiesnik, J. Analytical procedures for the determination of fuel combustion products, anti-corrosive compounds, and de-icing compounds in airport runoff water samples. Talanta 2013, 117, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, M.D.; McKinley, A.J.; Patterson, B.M.; Reeder, A.Y. Benzotriazoles in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Their Occurrence, Toxicity, Degradation and Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Ying, G.G.; Shareef, A.; Kookana, R.S. Biodegradation of three selected benzotriazoles in aquifer materials under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 151, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, A.; Fries, E. Seasonal source influence on river mass flows of benzotriazoles. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giger, W.; Schaffner, C.; Kohler, H.P.E. Benzotriazole and tolyltriazole as aquatic contaminants. 1. Input and occurrence in rivers and lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7186–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeland, A.; Oetken, M.; Kiss, A.; Fries, E.; Oehlmann, J. Acute and chronic toxicity of benzotriazoles to aquatic organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillard, D.A.; Cornell, J.S.; Dufresne, D.L.; Hernandez, M.T. Toxicity of benzotriazole and benzotriazole derivatives to three aquatic species. Water Res. 2001, 35, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.F.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Zha, J.M.; Wang, Z.J. Brain quantitative proteomic responses reveal new insight of benzotriazole neurotoxicity in female Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Aquatic Toxicol. 2016, 181, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeFevre, G.H.; Muller, C.E.; Lo, R.J.X.; Luthy, R.G.; Sattely, E.S. Rapid Phytotransformation of Benzotriazole Generates Synthetic Tryptophan and Auxin Analogs in Arabidopsis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10959–10968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.O.D.; BlakeKalff, M.M.A.; Davies, T.G.E. Detoxification of xenobiotics by plants: Chemical modification and vacuolar compartmentation. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkleij, J.A.C.; Golan-Goldhirsh, A.; Antosiewisz, D.M.; Schwitzguebel, J.P.; Schroder, P. Dualities in plant tolerance to pollutants and their uptake and translocation to the upper plant parts. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 67, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flasinski, M.; Hac-Wydro, K. Natural vs synthetic auxin: Studies on the interactions between plant hormones and biological membrane lipids. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwanski, E.R.; Last, R.L. Tryptophan biosynthesis and metabolism–biochemical and molecular-genetics. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.L.; Nason, S.L.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Pedersen, J.A. Root Uptake of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Product Ingredients. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeFevre, G.H.; Lipsky, A.; Hyland, K.C.; Blaine, A.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Luthy, R.G. Benzotriazole (BT) and BT plant metabolites in crops irrigated with recycled water. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attachment H. Bioretention/Biofiltration Design Criteria; Order No. R4-2012-0175, NPDES PERMIT No. CAS004001; (MS4) Discharge Within the Coastal Watersheds of Los Angeles County: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2012.
- Grebel, J.E.; Charbonnet, J.A.; Sedlak, D.L. Oxidation of organic contaminants by manganese oxide geomedia for passive urban stormwater treatment systems. Water Res. 2016, 88, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebel, J.E.; Mohanty, S.K.; Torkelson, A.A.; Boehm, A.B.; Higgins, C.P.; Maxwell, R.M.; Nelson, K.L.; Sedlak, D.L. Engineered Infiltration Systems for Urban Stormwater Reclamation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Hydrologic and pollutant removal performance of stormwater biofiltration systems at the field scale. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virahsawmy, H.K.; Stewardson, M.J.; Vietz, G.; Fletcher, T.D. Factors that affect the hydraulic performance of raingardens: Implications for design and maintenance. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korasick, D.A.; Enders, T.A.; Strader, L.C. Auxin biosynthesis and storage forms. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, A.W.; Bartel, B. Auxin: Regulation, action, and interaction. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, N.; Doucette, W.J.; White, J.C. Investigating differences in the root to shoot transfer and xylem sap solubility of organic compounds between zucchini, squash and soybean using a pressure chamber method. Chemosphere 2015, 130, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatidou, G.; Oursouzidou, M.; Stefanatou, A.; Stasinakis, A.S. Removal mechanisms of benzotriazoles in duckweed Lemna minor wastewater treatment systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felis, E.; Sochacki, A.; Magiera, S. Degradation of benzotriazole and benzothiazole in treatment wetlands and by artificial sunlight. Water Res. 2016, 104, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acero, J.L.; Benitez, F.J.; Real, F.J.; Rodriguez, E. Degradation of selected emerging contaminants by UV-activated persulfate: Kinetics and influence of matrix constituents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 201, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, H.H. Bioaccumulation and metabolic fate of sewage sludge derived organic xenobiotics in plants. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 185, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchi, T.; Maor, Y.; Tadmor, G.; Shenker, M.; Chefetz, B. Irrigation of Root Vegetables with Treated Wastewater: Evaluating Uptake of Pharmaceuticals and the Associated Human Health Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9325–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reemtsma, T.; Miehe, U.; Duennbier, U.; Jekel, M. Polar pollutants in municipal wastewater and the water cycle: Occurrence and removal of benzotriazoles. Water Res. 2010, 44, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, B.A.; Vignola, M.; Edgehouse, K.; Werner, D.; Higgins, C.P. Organic Carbon Amendments for Enhanced Biological Attenuation of Trace Organic Contaminants in Biochar-Amended Stormwater Biofilters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9184–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henner, P.; Bredoire, F.; Tailliez, A.; Coppin, F.; Pierrisnard, S.; Camilleri, V.; Keller, C. Influence of root exudation of white lupine (Lupinus albus L.) on uranium phytoavailability in a naturally uranium-rich soil. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 190, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, C.D.; Richardson, A.E.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Mezeli, M.M.; Brown, L.K.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Darch, T.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Shand, C.A.; Stutter, M.I.; et al. Phosphorus acquisition by citrate- and phytase-exuding Nicotiana tabacum plant mixtures depends on soil phosphorus availability and root intermingling. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 163, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffner, A.; Hoffland, E.; Temminghoff, E.J.M. Bioavailability of zinc and phosphorus in calcareous soils as affected by citrate exudation. Plant Soil 2012, 361, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabas, S.; Saavedra-Mella, F.; Huynh, T.; Kopittke, P.M.; Carter, S.; Huang, L.B. Metal uptake and organic acid exudation of native Acacia species in mine tailings. Aust. J. Bot. 2017, 65, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Hou, D.Y.; Dai, Y.; Lu, H.L.; Yan, C.L. Effects of root exudates on the mobility of pyrene in mangrove sediment water system. Catena 2018, 162, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Li, Q.J.; Luo, B.; Chen, X.Y. Ex planta phytoremediation of trichlorophenol and phenolic allelochemicals via an engineered secretory laccase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilon-Smits, E. Phytoremediation. In Annual Review of Plant Biology; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 56, pp. 15–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.L.; Wang, X.Z.; He, X.J.; Zhang, S.B.; Liang, R.B.; Shen, J. Effects of root exudates on denitrifier gene abundance, community structure and activity in a micro-polluted constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.A.; Guthrie, E.A.; Walton, B.T. Bioremediation in the Rhizosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wang, S.N.; Xie, H.J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J. Influence of Artificial Root Exudates on Triclosan Removal in Soil under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions. Clean-Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendahl, I.; Siemens, J.; Groeneweg, J.; Linzbach, E.; Laabs, V.; Herrmann, C.; Vereecken, H.; Amelung, W. Dissipation and Sequestration of the Veterinary Antibiotic Sulfadiazine and Its Metabolites under Field Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5216–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, K.E.; Huang, X.D.; Glick, B.R.; Greenberg, B.M. Phytoremediation and rhizoremediation of organic soil contaminants: Potential and challenges. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeFevre, G.H.; Hozalski, R.M.; Novak, P.J. The role of biodegradation in limiting the accumulation of petroleum hydrocarbons in raingarden soils. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6753–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blecken, G.T.; Zinger, Y.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D.; Viklander, M. Impact of a submerged zone and a carbon source on heavy metal removal in stormwater biofilters. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pritchard, J.C.; Cho, Y.-M.; Ashoori, N.; Wolfand, J.M.; Sutton, J.D.; Carolan, M.E.; Gamez, E.; Doan, K.; Wiley, J.S.; Luthy, R.G. Benzotriazole Uptake and Removal in Vegetated Biofilter Mesocosms Planted with Carex praegracilis. Water 2018, 10, 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111605
Pritchard JC, Cho Y-M, Ashoori N, Wolfand JM, Sutton JD, Carolan ME, Gamez E, Doan K, Wiley JS, Luthy RG. Benzotriazole Uptake and Removal in Vegetated Biofilter Mesocosms Planted with Carex praegracilis. Water. 2018; 10(11):1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111605
Chicago/Turabian StylePritchard, James Conrad, Yeo-Myoung Cho, Negin Ashoori, Jordyn M. Wolfand, Jeff D. Sutton, Margaret E. Carolan, Eduardo Gamez, Khoa Doan, Joshua S. Wiley, and Richard G. Luthy. 2018. "Benzotriazole Uptake and Removal in Vegetated Biofilter Mesocosms Planted with Carex praegracilis" Water 10, no. 11: 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111605
APA StylePritchard, J. C., Cho, Y.-M., Ashoori, N., Wolfand, J. M., Sutton, J. D., Carolan, M. E., Gamez, E., Doan, K., Wiley, J. S., & Luthy, R. G. (2018). Benzotriazole Uptake and Removal in Vegetated Biofilter Mesocosms Planted with Carex praegracilis. Water, 10(11), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111605