Hurricanes as a Major Driver of Coastal Erosion in the Mississippi River Delta: A Multi-Decadal Analysis of Shoreline Retreat Rates at Bay Champagne, Louisiana (USA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
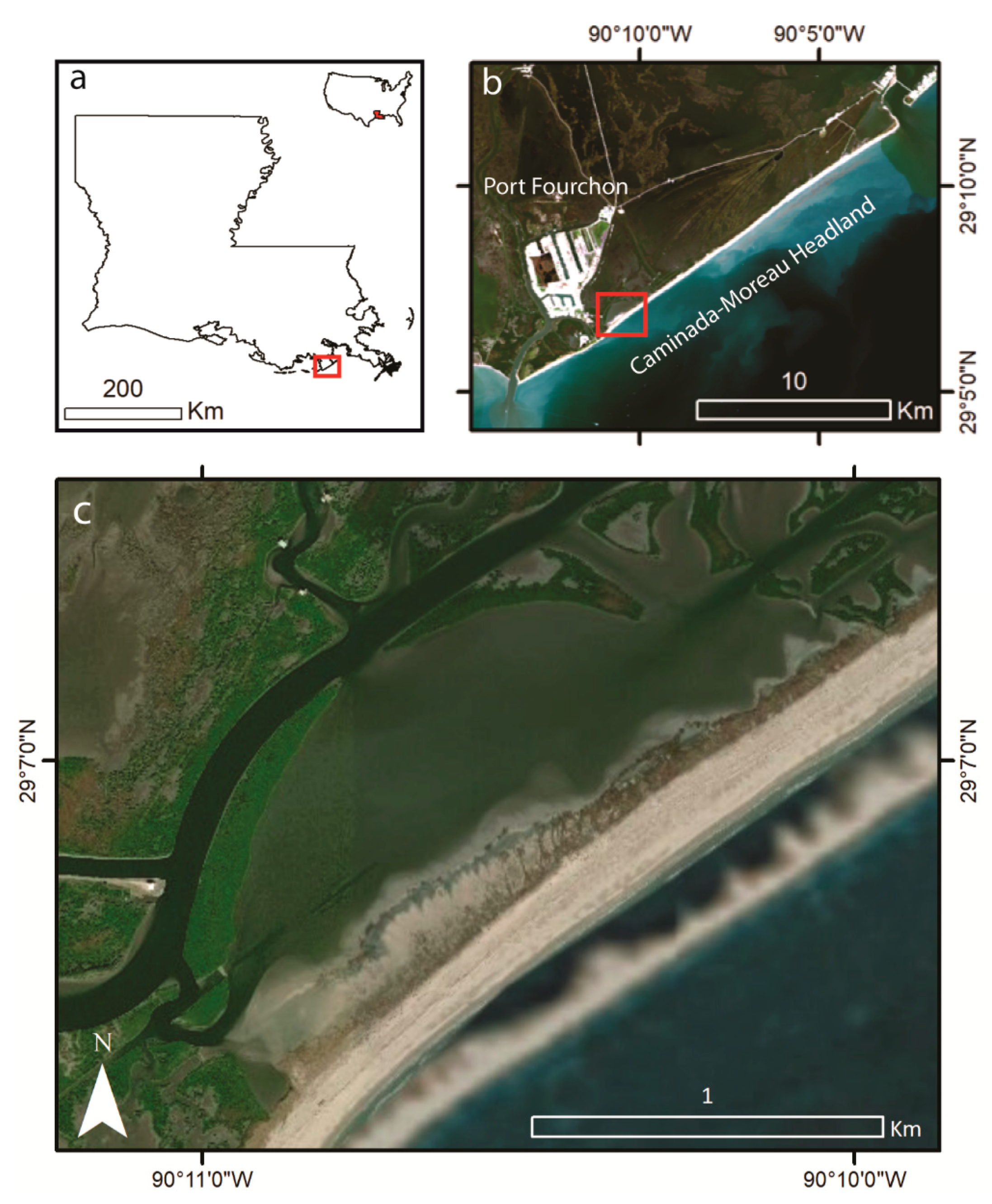
2. Study Region
Study Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Imagery
3.2. Methods
4. Results
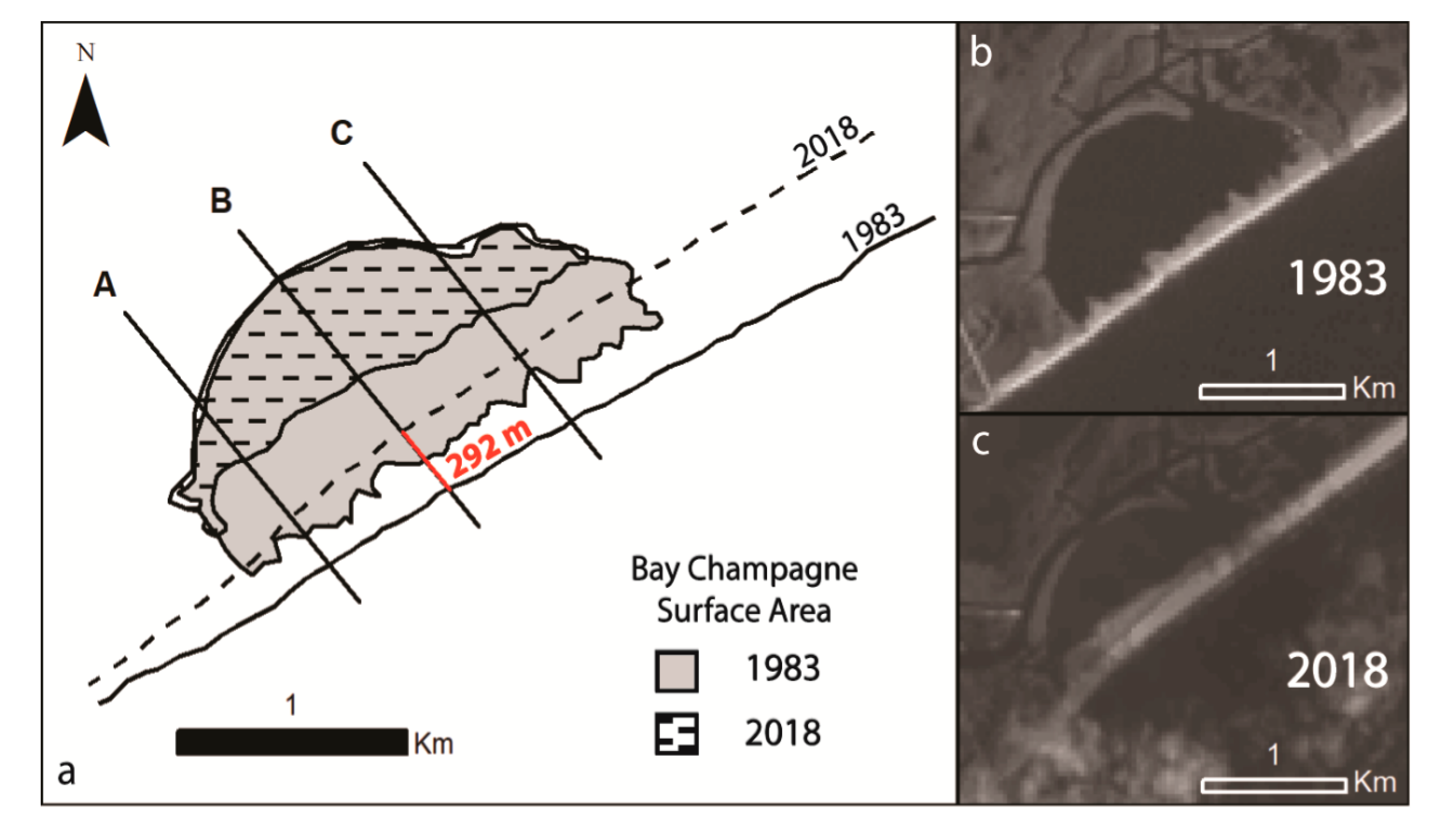
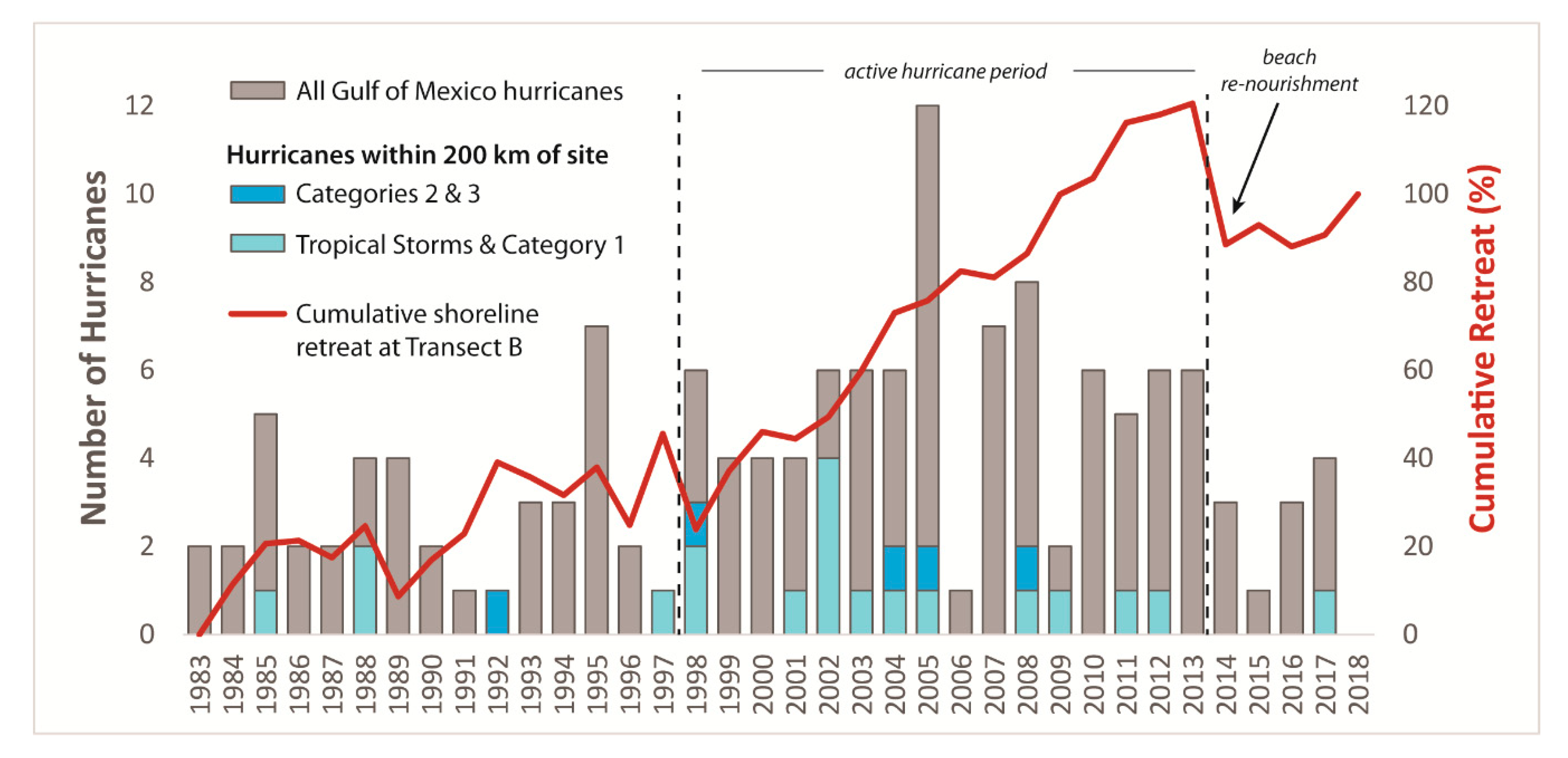
4.1. Decadal Retreat Rates
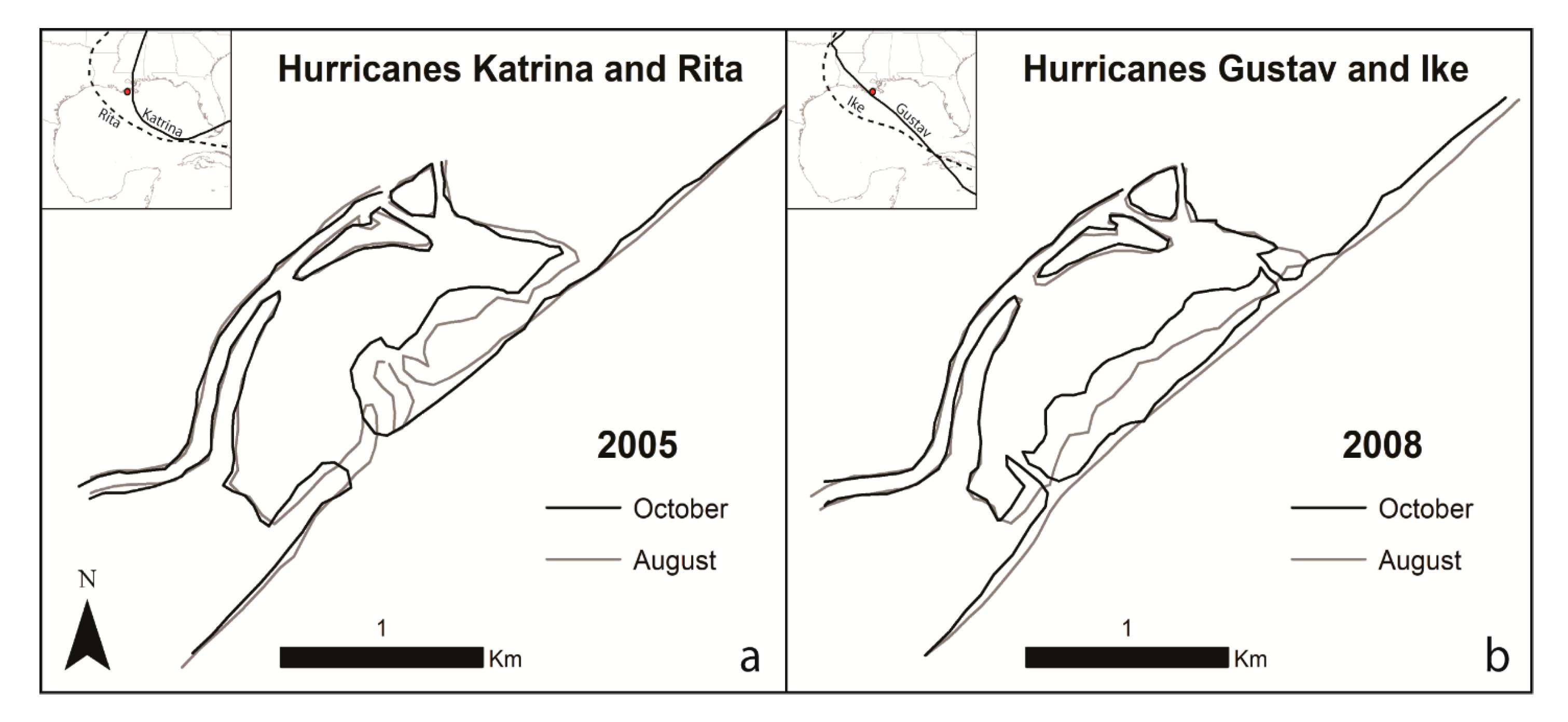
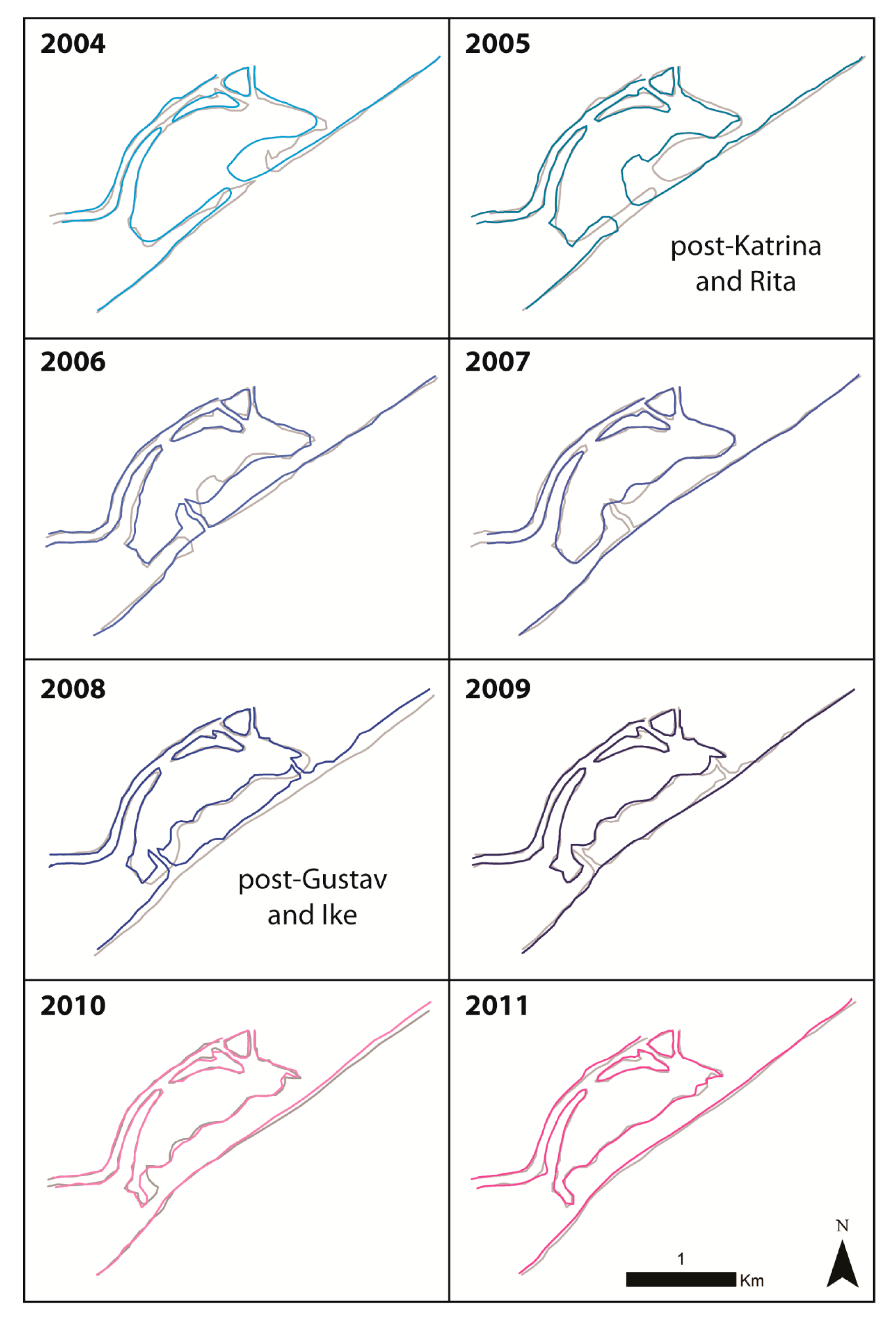
4.2. Case Studies–Hurricanes in 2005 and 2008
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Shoreline Retreat
5.2. Hurricane Impacts on Shoreline Retreat
5.3. Impacts of Individual Hurricanes on Shoreline Morphology
5.4. Persistence of Hurricane-Created Shoreline Features
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luijendijk, A.; Hagenaars, G.; Ranasinghe, R.; Baart, F.; Donchyts, G.; Aarninkhof, S. The state of the world’s beaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantamaneni, K. Coastal infrastructure vulnerability: An integrated assessment model. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A.J.; Overeem, I.; Hutton, E.W.H.; Hannon, M.T.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Day, J.; Vörösmarty, C.; Saito, Y.; Giosan, L.; et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantamaneni, K.; Du, X.; Aher, S.; Singh, R.M. Building blocks: A quantitative approach for evaluating coastal vulnerability. Water 2017, 9, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C. Human influence and the changing geomorphology of Mediterranean deltas and coasts over the last 6000 years: From progradation to destruction phase? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 139, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergillos, R.J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, C.; Millares, A.; Ortega-Sánchez, M.; Losada, M.A. Impact of river regulation on a Mediterranean delta: Assessment of managed versus unmanaged scenarios. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 5132–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergillos, R.J.; López-Ruiz, A.; Ortega-Sánchez, M.; Masselink, G.; Losada, M.A. Implications of delta retreat on wave propagation and longshore sediment transport-Guadalfeo case study (southern Spain). Mar. Geol. 2016, 382, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, S.; Connor, P.F., Jr.; Beall, A.; Fearnley, S.; Williams, S.J. Changes in Louisiana’s shoreline: 1855–2002. J. Coast. Res. 2005, SI 44, 7–39. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, S.; Ramsey, K.E. Relative sea-level rise in Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico: 1908–1988. J. Coast. Res. 1990, 6, 323–342. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, S.; Suter, J.R. Barrier island erosion and protection in Louisiana: A coastal geomorphological perspective. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1988, 38, 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, R.A.; Byrnes, M.R. Regional variations in shore response along barrier island systems of the Mississippi River delta plain: Historical change and future prediction. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 628–655. [Google Scholar]
- Kulp, M.; Penland, S.; Williams, S.J.; Jenkins, C.; Flocks, J.; Kindinger, J. Geologic framework, evolution, and sediment resources for restoration of the Louisiana coastal zone. J. Coast. Res. 2005, SI 44, 56–71. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, M.D.; Roberts, H.H. Drowning of the Mississippi delta due to insufficient sediment supply and global sea-level rise. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, K.E.; Penland, S.; Roberts, H.H. In Implications of accelerated sea-level rise on Louisiana coastal environments. In Proceedings of the Specialty Conference on Quantitative Approaches to Coastal Sediment Processes, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–27 June 1991; pp. 1207–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, J. Sediment dispersal trends of the Caminada-Moreau beach-ridge system. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1977, 27, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, L.; O’Brien, S.; Bethel, M.; Penland, S.; Kulp, M. Louisiana Barrier Island Comprehensive Monitoring Program (BICM) Volume 2: Shoreline Changes and Barrier Island Land Loss 1800’s–2005; Pontchartrain Institute Report Study; Pontchartrain Institute: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, S.; Zganjar, C.; Westphal, K.A.; Connor, P.; List, J.; Williams, S.J. Shoreline Changes in the Caminada-Moreau Headland and Grand Isle—1887 to 1996 Lafourche and Jefferson Parishes, Louisiana; USGS Open File Report; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2003.
- Henry, K.M.; Twilley, R.R. Soil development in a coastal Louisiana wetland during a climate-induced vegetation shift from salt marsh to mangrove. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, S.; Ritchie, W. Short term morphological changes along the Caminada-Moreau coast, Louisiana. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1979, 29, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, S.; Suter, J.R.; Moslow, T.F. Inner-shelf shoal sedimentary facies and sequences: Ship Shoal, northern Gulf of Mexico. In Proceedings of the Modern and Ancient Shelf Clastics, 9th September, Core Workshop, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1986; pp. 73–123. [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt, N.T.; Flocks, J.G.; Hansen, M.; Kulp, M.; Reynolds, B. Bathymetric Survey of the Nearshore from Belle Pass to Caminada Pass, Louisiana: Methods and Data Report; U.S. Geological Survey Science Data Series 312; Reston, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mossa, J.; Penland, S.; Moslow, T.F. Coastal Structures in Louisiana’s Barataria Bight; Louisiana Geological Survey: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, W.; Penland, S. Rapid dune changes associated with overwash processes on the deltaic coast of south Louisiana. Mar. Geol. 1988, 81, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Tides and Currents. Relative Sea Level Trend 8761724-Grand Isle, Louisiana. Available online: https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/sltrends/sltrends_station.shtml?id=8761724 (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Meckel, T.; ten Brink, U.S.; Williams, S.J. Current subsidence rates due to compaction of Holocene sediments in southern Louisiana. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Kent, J.; Lam, N.S.-N.; Cai, H.; Qiang, Y.; Li, K. Evaluating land subsidence rates and their implications for land loss in the lower Mississippi River basin. Water 2016, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, I.Y.; FitzGerald, D.M.; Stone, G.W. The impact of physical processes along the Louisiana coast. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 44, 72–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, W.; Penland, S. Cyclical changes in the coastal dunes of southern Louisiana. J. Coast. Res. 1988, 3, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Moeller, C.C.; Huh, O.K.; Roberts, H.H.; Gumley, L.E.; Menzel, W.P. Response of Louisiana coastal environments to a cold front passage. J. Coast. Res. 1993, 9, 434–447. [Google Scholar]
- Siadatmousavi, S.M.; Jose, F. Winter storm-induced hydrodynamics and morphological response of a shallow transgressive shoal complex: Northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.; Penland, S. Washover of deltaic barriers on Louisiana coast. AAPG Bull. 1981, 65, 1682. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, N.D.; Hammack, A.B. Impacts of winter storms on circulation and sediment transport: Atchafalaya-Vermilion Bay region, Louisiana, USA. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 996–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Kobashi, D.; Jose, F.; Stone, G. In Impacts of fluvial fine sediments and winter storms on a transgressive shoal, off south-central Louisiana, USA. J. Coast Res. Gold Coast Aust. 2007, 50, 858–862. [Google Scholar]
- Safak, I.; Sheremet, A.; Allison, M.A.; Hsu, T.J. Bottom turbulence on the muddy Atchafalaya shelf, Louisiana, USA. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115, C12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.W.; Henderson, K.G. Cold front variability in the southern United States and the influence of atmospheric teleconnection patterns. Phys. Geogr. 2003, 24, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, G.W.; Grymes, J.M., III; Dingler, J.R.; Pepper, D.A. Overview and significance of hurricanes on the Louisiana coast, USA. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 656–669. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, S.; Debusschere, K.; Westphal, K.A.; Suter, J.R.; McBride, R.A.; Reimer, P.D. The 1985 hurricane impacts on the Isles Dernieres, Louisiana: A temporal and spatial analysis of the coastal geomorphic changes. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1989, 39, 455–470. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchette, T.; Liu, K.-B.; Qiang, Y.; Lam, N. Wetland accretion rates along coastal Louisiana: Spatial and temporal variability in light of Hurricane Isaac’s impacts. Water 2016, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, J.; Crozier, C.; DeLaune, R. Roles and patterns of hurricane sedimentation in an estuarine marsh landscape. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R.; Reed, D.J.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Steyer, G.D.; Boumans, R.M.; Lynch, J.C.; McNally, D.; Latif, N. The influence of Hurricane Andrew on sediment distribution in Louisiana coastal marshes. J. Coast. Res. 1995, 21, 280–294. [Google Scholar]
- Greater Lafourche Port Commission. Port Fourchon-Port Facts. Available online: http://portfourchon.com/seaport/port-facts/ (accessed on 17 June 2018).
- Penland, S.; Boyd, R.; Nummedal, D.; Roberts, H. Deltaic barrier development on the Louisiana coast. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1981, 31, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Coastal Engineering Consultants Inc. Caminada Headland Beach and Dune Restoration (BA-45) Completion Report; Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2015.
- Whitehurst, C.A.; Self, R. Sediment Transport and Erosion in the Fourchon Area of Lafourche Parish; NTRS: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Naquin, J.D.; Liu, K.-B.; McCloskey, T.A.; Bianchette, T.A. Storm deposition induced by hurricanes in a rapidly subsiding coastal zone. J. Coast. Res. 2014, SI 70, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.-B.; Li, C.; Bianchette, T.A.; McCloskey, T.A.; Yao, Q.; Weeks, E. Storm deposition in a coastal backbarrier lake in Louisiana caused by Hurricanes Gustav and Ike. J. Coast. Res. 2011, SI 64, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, R.C. In Using Arcmap to extract shorelines from Landsat TM and ETM+ data. In Proceedings of the 32nd ESRI International Users Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, R.A.; Barras, J.A. Hurricane impacts on coastal wetlands: A half-century record of storm-generated features from southern Louisiana. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, S.; Roberts, H.; Williams, S.; Sallenger, A., Jr.; Cahoon, D.R.; Davis, D.W.; Groat, C. Coastal land loss in Louisiana. Gulf Coast Assoc. Geol. Soc. Trans. 1990, 40, 685–699. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnley, S.M.; Miner, M.D.; Kulp, M.; Bohling, C.; Penland, S. Hurricane impact and recovery shoreline change analysis of the Chandeleur Islands, Louisiana, USA: 1855 to 2005. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, K.-B.; Ryu, J. Multi-proxy characterization of Hurricanes Rita and Ike storm deposits in the Rockefeller Wildlife Refuge, southwestern Louisiana. J. Coast. Res. 2018, SI 85, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, S.; Suter, J.R.; Sallenger, A.H., Jr.; Williams, S.J.; McBride, R.A.; Westphal, K.E.; Reimer, P.D.; Jaffe, B.E. Morphodynamic signature of the 1985 hurricane impacts on the northern Gulf of Mexico. In Coastal Zone’89, Proceedings of the Sixth Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management, the Omni Hotel, Charleston, SC, USA, 11–14 July 1989; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 4220–4234. [Google Scholar]
- Elsner, J.B.; Kossin, J.P.; Jagger, T.H. The increasing intensity of the strongest tropical cyclones. Nature 2008, 455, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarini, G.; Vecchi, G.A. Projected increases in North Atlantic tropical cyclone intensity from CMIP5 models. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Holland, G.J.; Curry, J.A.; Chang, H.-R. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 2005, 309, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-level rise and its impact on coastal zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmstorf, S. A semi-empirical approach to projecting future sea-level rise. Science 2007, 315, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Shoreline Retreat Rates (m/yr) by Decade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transects | ||||
| A | B | C | Average | |
| 1980s | 8.41 | 7.15 | 8.46 | 8.01 |
| 1990s | 8.12 | 8.67 | 9.09 | 8.62 |
| 2000s | 17.69 | 17.11 | 18.51 | 17.77 |
| 2010s | −8.39 | −1.53 | 0.01 | −3.30 |
| OVERALL: | 7.29 | 8.74 | 9.86 | 8.63 |
| 1983–2013 | 11.49 | 12.35 | 13.90 | 12.58 |
| Retreat Rate (m/yr) by Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | Average | |
| Quiet (1983–1997) | 4.22 | 4.72 | 5.00 | 4.65 |
| Stormy (1998–2013) | 19.88 | 20.53 | 23.43 | 21.28 |
| Quiet (2015–2018) | 4.74 | 8.50 | 1.05 | 4.76 |
| OVERALL: | 9.61 | 11.25 | 9.83 | 10.23 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dietz, M.E.; Liu, K.-b.; Bianchette, T.A. Hurricanes as a Major Driver of Coastal Erosion in the Mississippi River Delta: A Multi-Decadal Analysis of Shoreline Retreat Rates at Bay Champagne, Louisiana (USA). Water 2018, 10, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101480
Dietz ME, Liu K-b, Bianchette TA. Hurricanes as a Major Driver of Coastal Erosion in the Mississippi River Delta: A Multi-Decadal Analysis of Shoreline Retreat Rates at Bay Champagne, Louisiana (USA). Water. 2018; 10(10):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101480
Chicago/Turabian StyleDietz, Marianne E., Kam-biu Liu, and Thomas A. Bianchette. 2018. "Hurricanes as a Major Driver of Coastal Erosion in the Mississippi River Delta: A Multi-Decadal Analysis of Shoreline Retreat Rates at Bay Champagne, Louisiana (USA)" Water 10, no. 10: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101480
APA StyleDietz, M. E., Liu, K.-b., & Bianchette, T. A. (2018). Hurricanes as a Major Driver of Coastal Erosion in the Mississippi River Delta: A Multi-Decadal Analysis of Shoreline Retreat Rates at Bay Champagne, Louisiana (USA). Water, 10(10), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101480





