Distribution and Genotyping of Aquatic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from the Puzi River and Its Tributaries Near Areas of Livestock Farming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
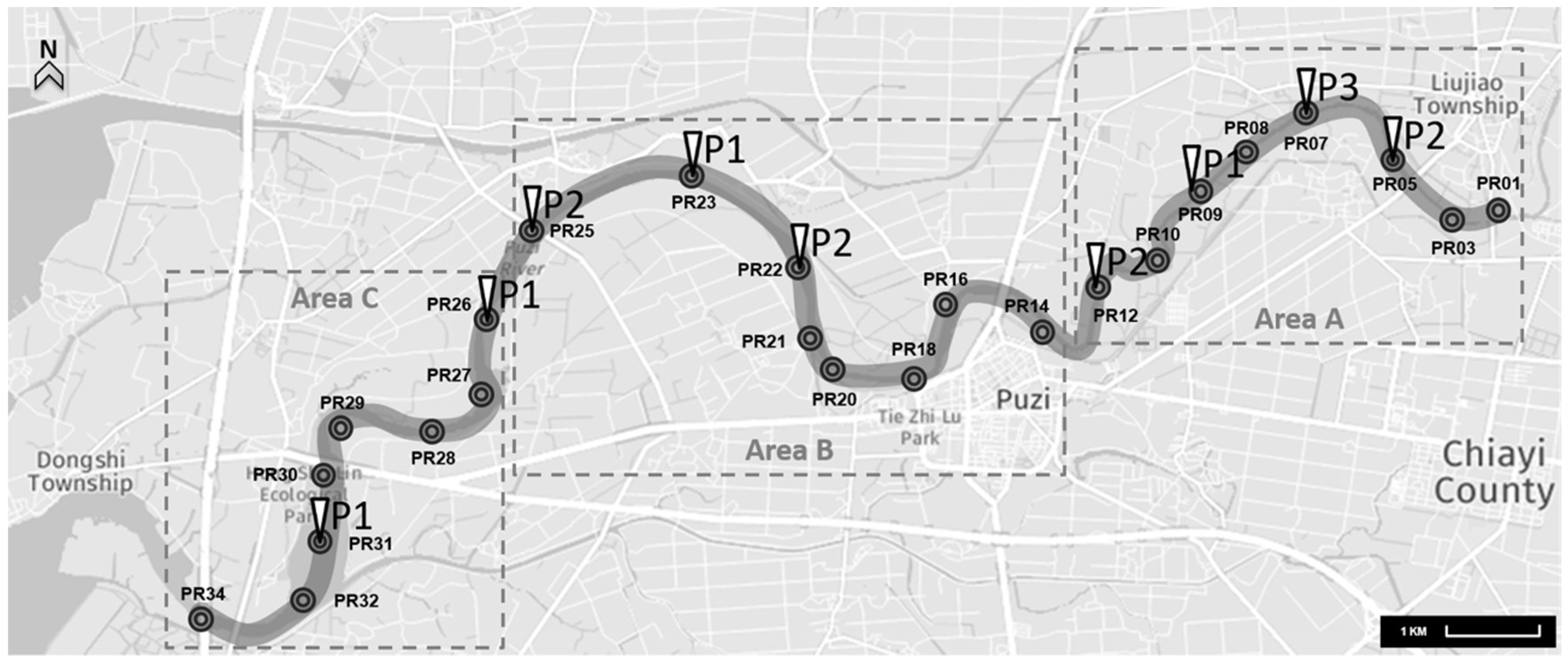
2.1. Collection and Concentration of Water Samples
2.2. Enrichment and Identification of A. baumannii
2.3. ERIC-PCR for A. baumannii
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility of A. baumannii
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Presence of A. baumannii in the Aquatic Environment
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
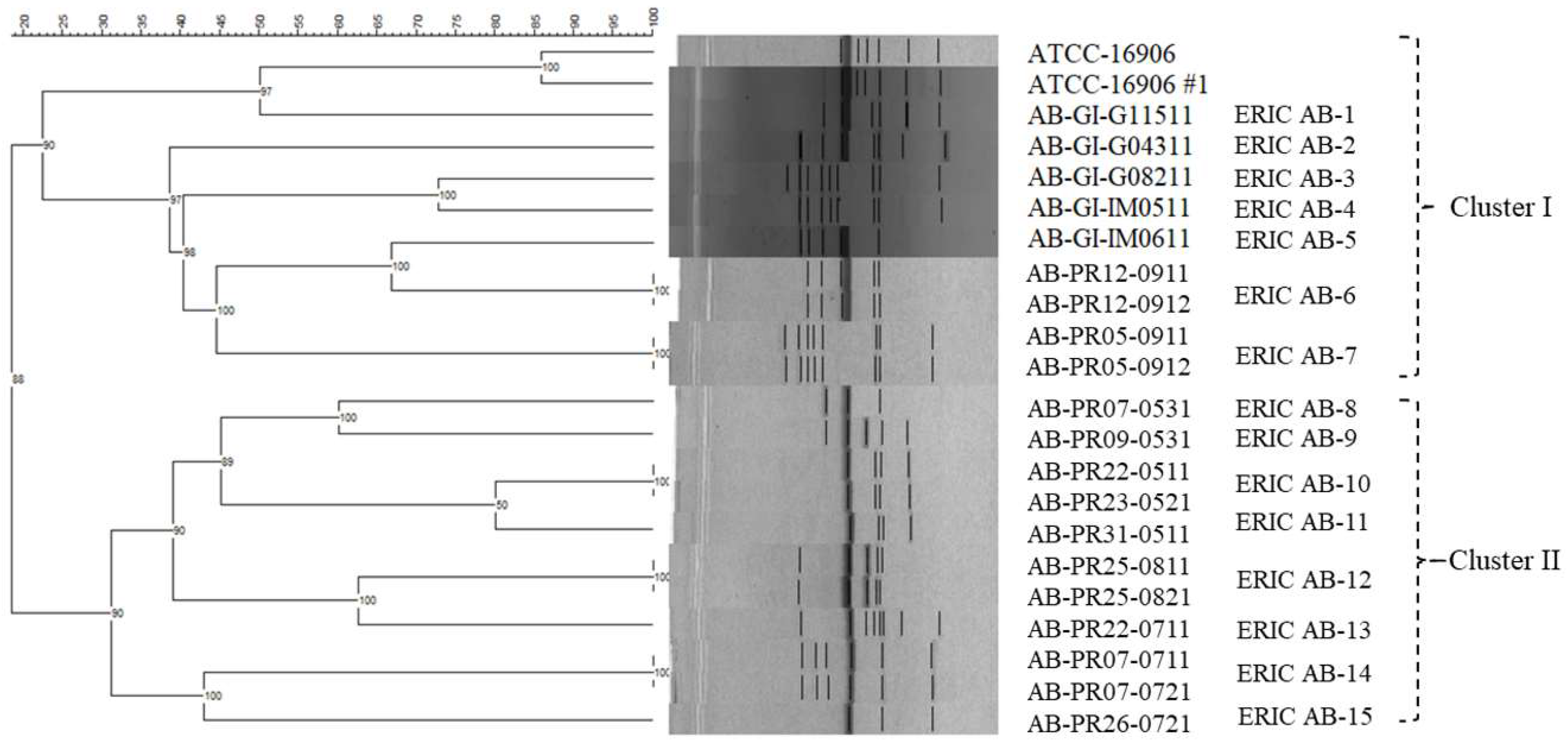
3.3. ERIC-PCR Fingerprint Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaei, N.; Aziemzadeh, M.; Bahador, A. Antimicrobial resistance profiles and genetic elements involved in carbapenem resistance in acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a referral hospital in Southern Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 5, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, A.; Vandyousefi, J.; Mirzaie, Z.; Ghafourian, S.; Kazemian, H.; Sadeghifard, N. Molecular analysis of the isolates of acinetobacter baumannii isolated from tehran hospitals using ERIC-PCR method. Mod. Med. Lab. J. 2016, 1, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Depascale, D.; Cleary, T.; Fajardo-Aquino, Y.; Kett, D.H.; Munoz-Price, L.S. Differential environmental contamination with acinetobacter baumannii based on the anatomic source of colonization. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2014, 42, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Z.; Zhang, J.-S.; Qiao, L. The acinetobacter baumannii group: A systemic review. World J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 4, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taitt, C.R.; Leski, T.; Stockelman, M.G.; Craft, D.W.; Zurawski, D.V.; Kirkup, B.C.; Vora, G.J. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in acinetobacter baumannii isolates taken from military treatment facilities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, A.; Snelling, A.; Heritage, J.; Hawkey, P. Exceptional desiccation tolerance of acinetobacter radioresistens. J. Hosp. Infect. 1998, 39, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, P.E.; Richet, H.; Weinstein, R.A. The epidemiology and control of acinetobacter baumannii in health care facilities. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, M.; Wilcox, M.; Parnell, P.; Green, D.; Keer, V.; Hawkey, P.; Evans, I.; Murphy, P. Role of environmental cleaning in controlling an outbreak of acinetobacter baumannii on a neurosurgical intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2004, 56, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Ortiz-Leyba, C.; Jimenez-Jimenez, F.; Barrero-Almodovar, A.; Garcia-Garmendia, J.; Bernabeu-Wittell, M.; Gallego-Lara, S.; Madrazo-Osuna, J. Treatment of multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) with intravenous colistin: A comparison with imipenem-susceptible vap. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartual, S.G.; Seifert, H.; Hippler, C.; Luzon, M.A.D.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Rodríguez-Valera, F. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of acinetobacter baumannii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4382–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou, G.; Cervero, G.; Dominguez, M.; Quereda, C.; Martinez-Beltran, J. PCR-based DNA fingerprinting (REP-PCR, AP-PCR) and pulsed-field GEL electrophoresis characterization of a nosocomial outbreak caused by imipenem-and meropenem-resistant acinetobacter baumannii. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, H.; Gerner-Smidt, P. Comparison of ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for molecular typing of acinetobacter isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vila, J.; Marcos, M.; De Anta, M.J. A comparative study of different pcr-based DNA fingerprinting techniques for typing of the acinetobacter calcoaceticus-A. Baumannii complex. J. Med. Microbiol. 1996, 44, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlowsky, J.A.; Draghi, D.C.; Jones, M.E.; Thornsberry, C.; Friedland, I.R.; Sahm, D.F. Surveillance for antimicrobial susceptibility among clinical isolates of pseudomonas aeruginosa and acinetobacter baumannii from hospitalized patients in the United States, 1998 to 2001. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.-E.; Vallenet, D.; Barbe, V.; Audic, S.; Ogata, H.; Poirel, L.; Richet, H.; Robert, C.; Mangenot, S.; Abergel, C. Comparative genomics of multidrug resistance in acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.; Kopterides, P. Risk factors for the isolation of multi-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii and pseudomonas aeruginosa: A systematic review of the literature. J. Hosp. Infect. 2006, 64, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, P.-R.; Teng, L.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-H.; Ho, S.-W.; Luh, K.-T. Pandrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii causing nosocomial infections in a university hospital, Taiwan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visca, P.; Seifert, H.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter infection—An emerging threat to human health. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karumathil, D.P.; Yin, H.-B.; Kollanoor-Johny, A.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Effect of chlorine exposure on the survival and antibiotic gene expression of multidrug resistant acinetobacter baumannii in water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francey, T.; Gaschen, F.; Nicolet, J.; Burnens, A.P. The role of acinetobacter baumannii as a nosocomial pathogen for dogs and cats in an intensive care unit. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2000, 14, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaneechoutte, M.; Devriese, L.A.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Lamote, B.; Deprez, P.; Verschraegen, G.; Haesebrouck, F. Acinetobacter baumannii-infected vascular catheters collected from horses in an equine clinic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4280–4281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, S.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Antimicrobial use and resistance in animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, S93–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widyasari-Mehta, A.; Hartung, S.; Kreuzig, R. From the application of antibiotics to antibiotic residues in liquid manures and digestates: A screening study in one european center of conventional pig husbandry. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerlin, P.; Travis, R.; Gyles, C.L.; Reid-Smith, R.; Janecko, N.; Lim, H.; Nicholson, V.; McEwen, S.A.; Friendship, R.; Archambault, M. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes of escherichia coli isolates from swine in ontario. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6753–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong Hoa, P.T.; Nonaka, L.; Hung Viet, P.; Suzuki, S. Detection of the SUL1, SUL2, and SUL3 genes in sulfonamide-resistant bacteria from wastewater and shrimp ponds of north vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAS) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Cai, Y.e.; Cheng, J.; Mou, S.; Yiqiang, L. Comparative study on the analytical performance of three waveforms for the determination of several aminoglycoside antibiotics with high performance liquid chromatography using amperometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1085, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butaye, P.; Devriese, L.A.; Haesebrouck, F. Antimicrobial growth promoters used in animal feed: Effects of less well known antibiotics on gram-positive bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, J.; Hashemi, F.B.; Bahador, A. Antibiotic resistance of acinetobacter baumannii in Iran: A systemic review of the published literature. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2015, 6, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.C.; Chou, M.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Wan, M.T.; Kuo, Y.J.; Chen, J.S.; Huang, T.Y.; Hsu, B.M. Seasonal distribution and genotyping of antibiotic resistant strains of listeria innocua isolated from a river basin categorized by ERIC-PCR. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.L.; Siu, L.K.; Wu, R.C.; Shaio, M.F.; Huang, L.Y.; Fung, C.P.; Lee, C.M.; Cho, W.L. Comparison of one-tube multiplex PCR, automated ribotyping and intergenic spacer (ITS) sequencing for rapid identification of acinetobacter baumannii. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, D.K.; Singh, M.; Singh, D.V.; Dubey, S.K. Virulence and genotypic characterization of listeria monocytogenes isolated from vegetable and soil samples. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, Approved Standard M7-A7, 7th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, D.M.; Khan, I.U.; Patidar, R.; Lapen, D.R.; Talbot, G.; Topp, E.; Kumar, A. Isolation and characterization of acinetobacter baumannii recovered from campylobacter selective medium. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.C.; Banerjee, S.N.; Jarvis, W.R.; System, N.N.I.S. Seasonal variation of acinetobacter infections: 1987–1996. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.W.; Leung, C.M.; Houang, E.T.S.; Ng, K.C.; Leung, C.B.; Leung, H.Y.; Cheng, A.F.B. Skin carriage of acinetobacters in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 2962–2967. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girlich, D.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. First isolation of the BLAOXA-23 carbapenemase gene from an environmental acinetobacter baumannii isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 578–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turano, H.; Gomes, F.; Medeiros, M.; Oliveira, S.; Fontes, L.C.; Sato, M.I.; Lincopan, N. Presence of high-risk clones of OXA-23-producing acinetobacter baumannii (ST79) and SPM-1-producing pseudomonas aeruginosa (ST277) in environmental water samples in Brazil. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 86, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gestal, M.C.; Zurita, J.; Gualpa, G.; Gonzalez, C.; Mino, A.P. Early detection and control of an acinetobacter baumannii multi-resistant outbreak in a hospital in quito, Ecuador. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygün, G.; Demirkiran, O.; Utku, T.; Mete, B.; Ürkmez, S.; Yılmaz, M.; Yaşar, H.; Dikmen, Y.; Öztürk, R. Environmental contamination during a carbapenem-resistant acinetobacter baumannii outbreak in an intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2002, 52, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, K.; Asai, S.; Ohshima, T.; Iwashita, H.; Ohashi, M.; Sasaki, M.; Kaneko, A.; Inokuchi, S.; Miyachi, H. Outbreak of drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii ST219 caused by oral care using tap water from contaminated hand hygiene sinks as a reservoir. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2015, 43, 1249–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.E.; Marchetti, D.P.; De Oliveira, L.M.; Gusatti, C.D.S.; Fuentefria, D.B.; Corcao, G. Presence of OXA-23-producing isolates of acinetobacter baumannii in wastewater from hospitals in Southern Brazil. Microbiol. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ece, G.; Erac, B.; Cetin, H.Y.; Ece, C.; Baysak, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility and clonal relation between acinetobacter baumannii strains at a tertiary care center in Turkey. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljindan, R.; Alsamman, K.; Elhadi, N. ERIC-PCR genotyping of acinetobacter baumannii isolated from different clinical specimens. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, H.; Halaji, M.; Taji, A.; Kazemian, H.; Shamsabadi, M.S.; Sisakht, M.T.; Ebrahim-Saraie, H.S. Molecular analysis of drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii isolates by ERIC-PCR. Meta Gene 2018, 17, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Date | Positive Samples | Total Samples | Detection Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 May | 5 | 24 | 20.8% |
| 14 June | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 14 July | 3 | 24 | 12.5% |
| 14 August | 1 | 24 | 4.2% |
| 14 September | 2 | 24 | 8.3% |
| 14 October | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 14 November | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 14 December | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 15 January | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 15 February | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 15 March | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| 15 April | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Total | 11 | 288 | 3.8% |
| Location | Sites | Positive Samples | Total Samples | Detection Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Puzi River | Area A (PR01-PR12) | 5 | 96 | 5.2% |
| Area B (PR14-PR25) | 4 | 96 | 4.2% | |
| Area C (PR26-PR34) | 2 | 96 | 2.1% | |
| Channels and tributaries | Livestock wastewater channels | 3 | 14 | 21.4% |
| Household wastewater channels | 0 | 3 | 0% | |
| Puzi River tributaries | 2 | 13 | 15.4% |
| Antibiotics Resistance Phenotype | Number | Resistant | Intermediate | Susceptible |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin | 20 | 0 | 0 | 20 (100%) |
| Cefepime | 20 | 0 | 0 | 20 (100%) |
| Gentamicin | 20 | 0 | 0 | 20 (100%) |
| Imipenem | 20 | 0 | 0 | 20 (100%) |
| Ampicillin-sulbactam | 20 | 0 | 0 | 20 (100%) |
| Sulphamethoxazole/Trimethoprim | 20 | 0 | 4 (20%) | 16 (80%) |
| Tetracycline | 20 | 1 (5%) | 2 (10%) | 17 (85%) |
| No. | Code of Strains | Antibiotics Resistance Phenotype | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIP | FEP | G | I | SAM | SXT | T | ||
| 1 | ATCC-16906 | S | S | S | S | S | R | I |
| 2 | A. baumannii-PR07-0531 | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| 3 | A. baumannii-PR09-0531 | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| 4 | A. baumannii-PR21-0511 | S | S | S | S | S | I | I |
| 5 | A. baumannii-PR23-0521 | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| 6 | A. baumannii-PR31-0511 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 7 | A. baumannii-PR07-0711 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 8 | A. baumannii-PR07-0721 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 9 | A. baumannii-PR22-0711 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 10 | A. baumannii-PR26-0721 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 11 | A. baumannii-PR25-0811 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 12 | A. baumannii-PR25-0821 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 13 | A. baumannii-PR05-0911 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 14 | A. baumannii-PR05-0912 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 15 | A. baumannii-PR12-0911 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 16 | A. baumannii-PR12-0912 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 17 | A. baumannii-GI-IM0511 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 18 | A. baumannii-GI-IM0611 | S | S | S | S | S | S | I |
| 19 | A. baumannii-GI-G04311 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 20 | A. baumannii-GI-G08211 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 21 | A. baumannii-GI-G11511 | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, H.-C.; Chou, M.-Y.; Shih, Y.-J.; Huang, T.-Y.; Yang, P.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Hsu, B.-M. Distribution and Genotyping of Aquatic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from the Puzi River and Its Tributaries Near Areas of Livestock Farming. Water 2018, 10, 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101374
Tsai H-C, Chou M-Y, Shih Y-J, Huang T-Y, Yang P-Y, Chiu Y-C, Chen J-S, Hsu B-M. Distribution and Genotyping of Aquatic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from the Puzi River and Its Tributaries Near Areas of Livestock Farming. Water. 2018; 10(10):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101374
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Hsin-Chi, Ming-Yuan Chou, Yi-Jia Shih, Tung-Yi Huang, Pei-Yu Yang, Yi-Chou Chiu, Jung-Sheng Chen, and Bing-Mu Hsu. 2018. "Distribution and Genotyping of Aquatic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from the Puzi River and Its Tributaries Near Areas of Livestock Farming" Water 10, no. 10: 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101374
APA StyleTsai, H.-C., Chou, M.-Y., Shih, Y.-J., Huang, T.-Y., Yang, P.-Y., Chiu, Y.-C., Chen, J.-S., & Hsu, B.-M. (2018). Distribution and Genotyping of Aquatic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from the Puzi River and Its Tributaries Near Areas of Livestock Farming. Water, 10(10), 1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101374





