A Feasible Data-Driven Mining System to Optimize Wastewater Treatment Process Design and Operation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
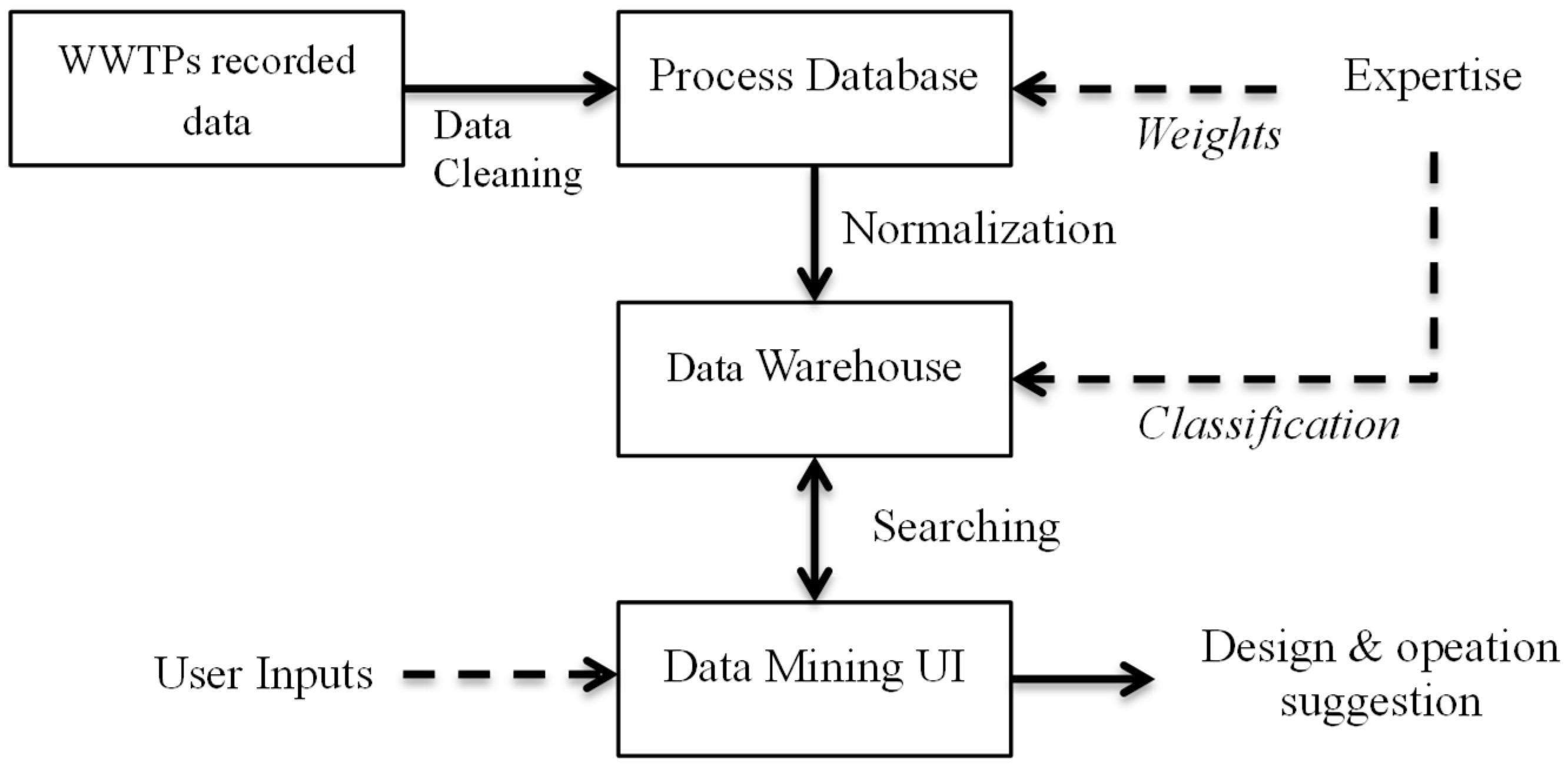
2.1. Protocol of Data Mining System
2.2. Data Collection and Cleaning
2.3. Data Warehouse Construction
Fact Sheet: F = {index, {WTPj|j = 1, …, 30}, {Ck|k = 1, …, 5}, {(t, yi)|i = 1, …, 6}}
Data warehouse: D = {F, {(t, PRm)|m = 1, …, 24}}
2.4. Data Mining
2.5. Web User Interface
2.6. Verification by Case Study
3. Results
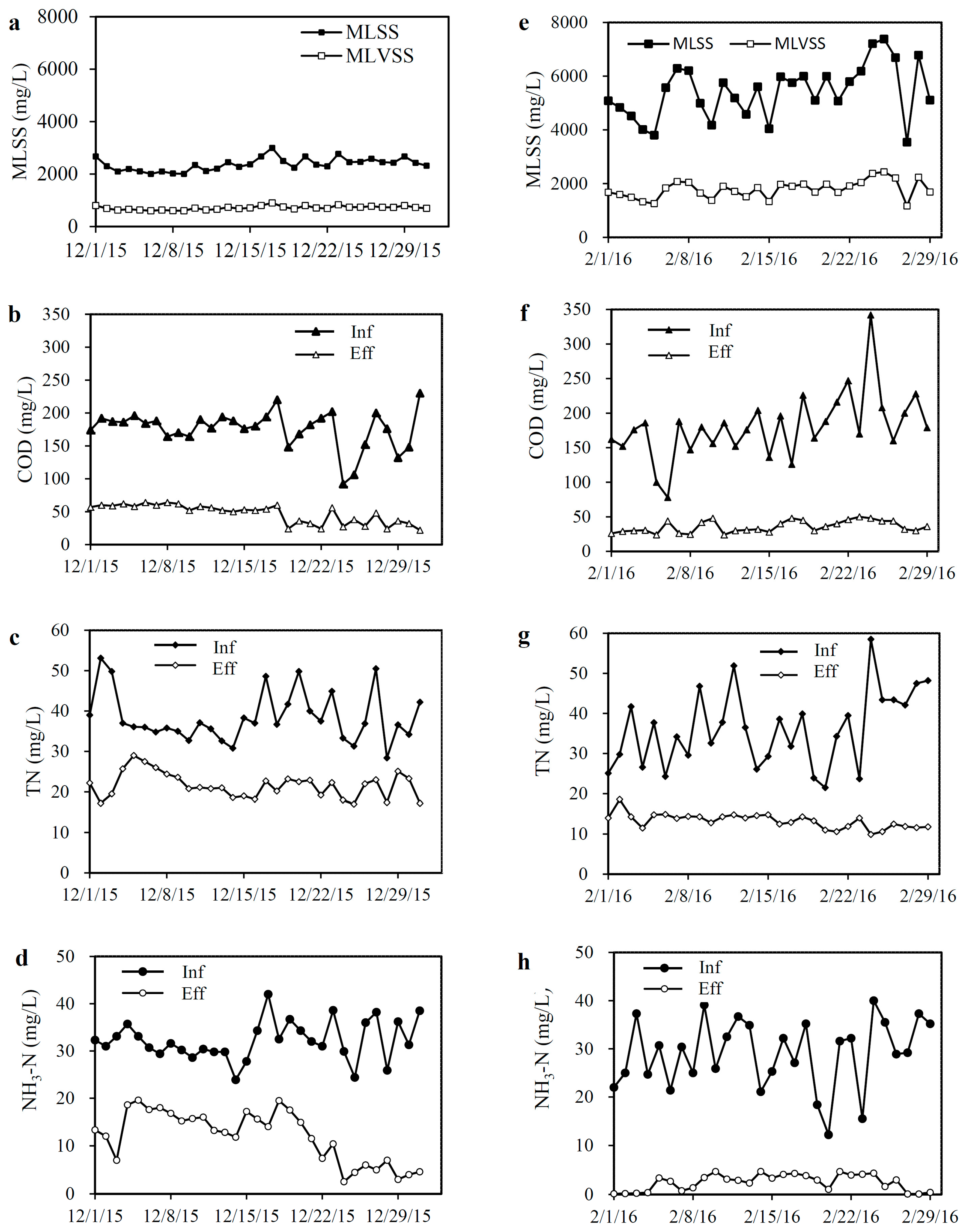
3.1. Data Collection and Cleaning
3.2. Data Warehouse and Analysis
3.3. Data Mining for Operational Optimization
3.4. Data Mining for Process Design
4. Discussion
4.1. Gaps between Scientific Knowledge and Practical Demands
4.2. Advances in the Data-Driven Models in WWTPs
4.3. Potential of Data Mining in the Control of WWTP
4.4. Challenges and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, W.N.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Jin, P.K.; Dzakpasu, M.; Yang, S.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Ao, D. Current status of urban wastewater treatment plants in China. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Liu, S. Energy for Conventional Water Supply and Wastewater Treatment in Urban China: A Review. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 1600016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong, Q.; Han-chang, S.; Miao, H. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in China: A Review. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 914110–914159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Du, X.; Li, K.; Zeng, S.; Bledsoe, B.P. Benchmarking sustainability of urban water infrastructure systems in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, G. Advancing Ica Technology by Eliminating the Constraints. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Park, T.J.; Ko, J.H. Instrumentation, control and automation for water and wastewater treatment and transport systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, J.; Siau, K. A review of data mining techniques. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2001, 1, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kusiak, A. Data mining: Manufacturing and service applications. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2006, 44, 4175–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovski, V.; Swain, M.; Kravtsov, V.; Niessen, T.; Wegener, D.; Kindermann, J.; Dubitzky, W. Grid-enabling data mining applications with DataMiningGrid: An architectural perspective. Future Gen. Comput. Syst. Int. J. Grid Comput. Theory Methods Appl. 2008, 24, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayward-Smith, V.J. Statistics to measure correlation for data mining applications. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2007, 51, 3968–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kusiak, A.; Zeng, Y.; Wei, X. Modeling and optimization of a wastewater pumping system with data-mining methods. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Modeling and analysis of pumps in a wastewater treatment plant: A data-mining approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Kusiak, A. Minimizing pump energy in a wastewater processing plant. Energy 2012, 47, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Kusiak, A. Data-driven minimization of pump operating and maintenance cost. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 40, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chang, N. Mining the fuzzy control rules of aeration in a submerged biofilm wastewater treatment process. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 20, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Verma, A.; Yang, K.; Mejabi, B. Wastewater treatment aeration process optimization: A data mining approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-del-Olmo, F.; Gaudioso, E.; Nevado, A. Autonomous Adaptive and Active Tuning Up of the Dissolved Oxygen Setpoint in a Wastewater Treatment Plant Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C-Appl. Rev. 2012, 42, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A.; Wei, X. A data-driven model for maximization of methane production in a wastewater treatment plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, M.; Gallop, J.R.; Lambert, S.C.; Healy, J.V. Experience with data mining for the anaerobic wastewater treatment process. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.; Gallop, J.R.; Lambert, S.C.; Lardon, L.; Healy, J.V.; Steyer, J. Data mining to support anaerobic WWTP monitoring. Control Eng. Pract. 2007, 15, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, K.; Rodriguez-Silva, G.; Rodriguez-Roda, I. Knowledge discovery with clustering based on rules by states: A water treatment application. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrossa, D.; Hansen, J.; Hernandez-Sancho, F.; Cornelissen, A.; Schutz, G.; Leopold, U. A data-driven methodology to support pump performance analysis and energy efficiency optimization in Waste Water Treatment Plants. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Kang, L.; Anderson, P.R. Predicting influent biochemical oxygen demand: Balancing energy demand and risk management. Water Res. 2018, 128, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Wei, X.; Kusiak, A. Predicting the total suspended solids in wastewater: A data-mining approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimi, H.; Mulas, M.; Corona, F.; Vahala, R. Data-derived soft-sensors for biological wastewater treatment plants: An overview. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 47, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerrenmatt, D.J.; Gujer, W. Data-driven modeling approaches to support wastewater treatment plant operation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 30, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-del-Olmo, F.; Gaudioso, E.; Dormido, R.; Duro, N. Energy and Environmental Efficiency for the N-Ammonia Removal Process in Wastewater Treatment Plants by Means of Reinforcement Learning. Energies 2016, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, L.; Garrido-Baserba, M.; Villez, K.; Olsson, G.; Cortes, U.; Poch, M. Transforming data into knowledge for improved wastewater treatment operation: A critical review of techniques. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 106, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanneau, S.; Recoules, L.; Durand, M.J.; Boukabache, A.; Picot, V.; Primault, Y.; Lakel, A.; Sengelin, M.; Barillon, B.; Thouand, G. Methods for assessing biochemical oxygen demand (BOD): A review. Water Res. 2014, 49, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Niu, Z.; Hu, H. Characteristics of water quality of municipal wastewater treatment plants in China: Implications for resources utilization and management. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, P.; Huang, X. Optimal Surface Aeration Control in Full-Scale Oxidation Ditches through Energy Consumption Analysis. Water 2018, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A.; Wei, X. Prediction of methane production in wastewater treatment facility: A data-mining approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2014, 216, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machon-Gonzalez, I.; Rodriguez-Iglesias, J.; Lopez-Garcia, H.; Castrillon-Pelaez, L.; Maranon-Maison, E. Knowledge extraction from a nitrification denitrification wastewater treatment plant using SOM-NG algorithm. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Yu, L. A novel nonlinear functional expansion based PLS (FEPLS) and its soft sensor application. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 161, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Qian, Y.; Tang, J. Diffusion of municipal wastewater treatment technologies in China: A collaboration network perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ville, N.; Le, H.M.; Schmidt, L.; Verbanck, M.A. Data-mining analysis of in-sewer infiltration patterns: Seasonal characteristics of clear water seepage into Brussels main sewers. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-del-Olmo, F.; Llanes, F.H.; Gaudioso, E. An emergent approach for the control of wastewater treatment plants by means of reinforcement learning techniques. Exp. Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, J.; Catarino, J. Sustainable value—An energy efficiency indicator in wastewater treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Shi, H. Understanding biofilm diffusion profiles and microbial activities to optimize integrated fixed-film activated sludge process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liang, P.; Yan, X.; Zuo, K.; Xiao, K.; Xia, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Reducing aeration energy consumption in a large-scale membrane bioreactor: Process simulation and engineering application. Water Res. 2016, 93, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torregrossa, D.; Hernandez-Sancho, F.; Hansen, J.; Cornelissen, A.; Popov, T.; Schutz, G. Energy saving in wastewater treatment plants: A plant-generic cooperative decision support system. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Liang, J.; Zhang, M. Seasonal artificial neural network model for water quality prediction via a clustering analysis method in a wastewater treatment plant of China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 3452–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Operation a | HRT (h) b | Effluent Water Quality (mg∙L−1) c | T % d | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORP | DO | MLSS | RS% | IR% | Ana | Ano | Oxic | COD | SS | TN | NH3-N | TP | ||
| 1 | −37 | 2.9 | 3876 | 70 | 150 | 0.82 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 28 | 8 | 14.8 | 2.12 | 0.30 | 82 |
| 2 | −6 | 4.5 | 4228 | 70 | 150 | 0.79 | 3.5 | 7.8 | 24 | 7 | 13.9 | 3.82 | 0.23 | 81 |
| 3 | −96 | 2.9 | 4272 | 70 | 150 | 0.84 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 26 | 6 | 14.5 | 4.75 | 0.12 | 70 |
| 4 | −100 | 6.6 | 4562 | 70 | 150 | 0.80 | 3.6 | 8.2 | 26 | 6 | 14.5 | 4.75 | 0.12 | 64 |
| 5 | −59 | 4.6 | 4130 | 70 | 150 | 0.79 | 3.5 | 7.8 | 32 | 8 | 11.3 | 2.20 | 0.22 | 49 |
| Time a | Operation | HRT (h) | Effluent Water Quality (mg∙L−1) | T % | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORP | DO | MLSS | RS% | IR% | Ana | Anox | Oxic | COD | SS | TN | NH3-N | TP | ||
| Sum | −175 | 3.4 | 3960 | 70 | 150 | 0.80 | 3.6 | 8.2 | 22 | 6 | 11.2 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 81 |
| −174 | 4.1 | 4340 | 70 | 150 | 0.82 | 3.7 | 8.9 | 22 | 6 | 11.2 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 75 | |
| −144 | 3.1 | 4230 | 70 | 150 | 0.83 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 24 | 7 | 14.2 | 0.72 | 0.29 | 71 | |
| −180 | 3.2 | 4790 | 70 | 150 | 0.82 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 27 | 8 | 14.0 | 1.40 | 0.25 | 69 | |
| −188 | 3.6 | 3770 | 70 | 150 | 0.85 | 3.9 | 8.6 | 21 | 8 | 14.6 | 0.79 | 0.31 | 59 | |
| Win | −10 | 5.6 | 4550 | 70 | 150 | 0.81 | 3.6 | 8.2 | 22 | 8 | 12.2 | 1.12 | 0.20 | 83 |
| −5 | 2.7 | 4820 | 70 | 150 | 0.82 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 24 | 7 | 13.6 | 2.54 | 0.22 | 82 | |
| −50 | 4.2 | 4930 | 70 | 150 | 0.81 | 3.7 | 8.9 | 23 | 8 | 14.2 | 1.76 | 0.22 | 73 | |
| −5 | 3.3 | 4920 | 70 | 150 | 0.84 | 3.8 | 8.6 | 22 | 8 | 12.2 | 1.12 | 0.20 | 72 | |
| −14 | 4.4 | 4360 | 70 | 150 | 0.79 | 3.5 | 7.8 | 19 | 7 | 12.5 | 0.41 | 0.20 | 67 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Shi, H. A Feasible Data-Driven Mining System to Optimize Wastewater Treatment Process Design and Operation. Water 2018, 10, 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101342
Qiu Y, Li J, Huang X, Shi H. A Feasible Data-Driven Mining System to Optimize Wastewater Treatment Process Design and Operation. Water. 2018; 10(10):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101342
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Yong, Ji Li, Xia Huang, and Hanchang Shi. 2018. "A Feasible Data-Driven Mining System to Optimize Wastewater Treatment Process Design and Operation" Water 10, no. 10: 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101342
APA StyleQiu, Y., Li, J., Huang, X., & Shi, H. (2018). A Feasible Data-Driven Mining System to Optimize Wastewater Treatment Process Design and Operation. Water, 10(10), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101342







