Inundated Areas Extraction Based on Raindrop Photometric Model (RPM) in Surveillance Video
Abstract
:1. Introduction
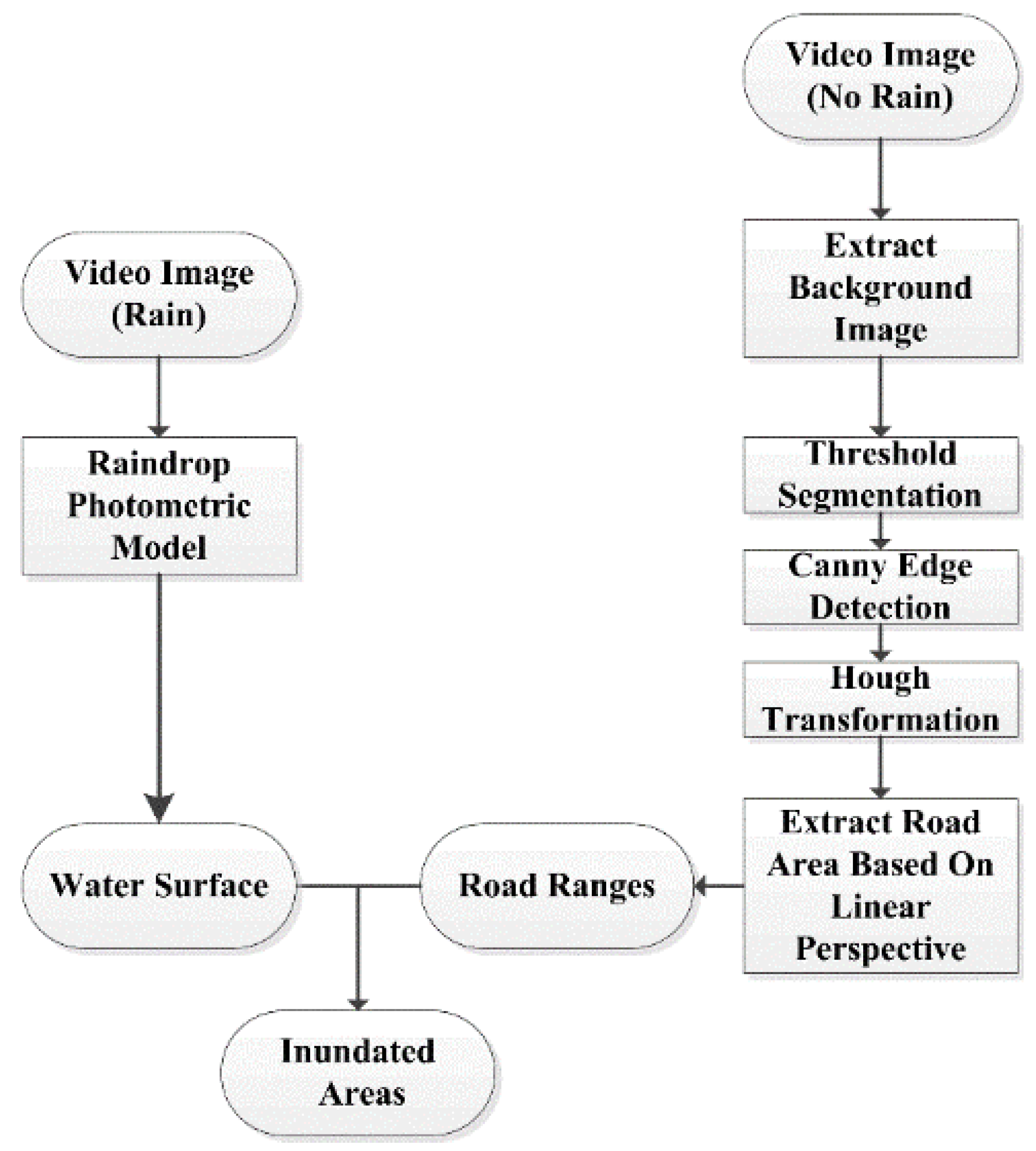
2. Methods
2.1. Raindrop Photometric Model (RPM)
2.2. Water Surface Extraction Based on the RPM
2.3. Inundated Areas Refinement with Spatial Constrained Information
2.3.1. Video Background Image Extraction
2.3.2. Road Range Extraction Based on Linear Perspective Features
3. Experiment and Discussion
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Experimental Results
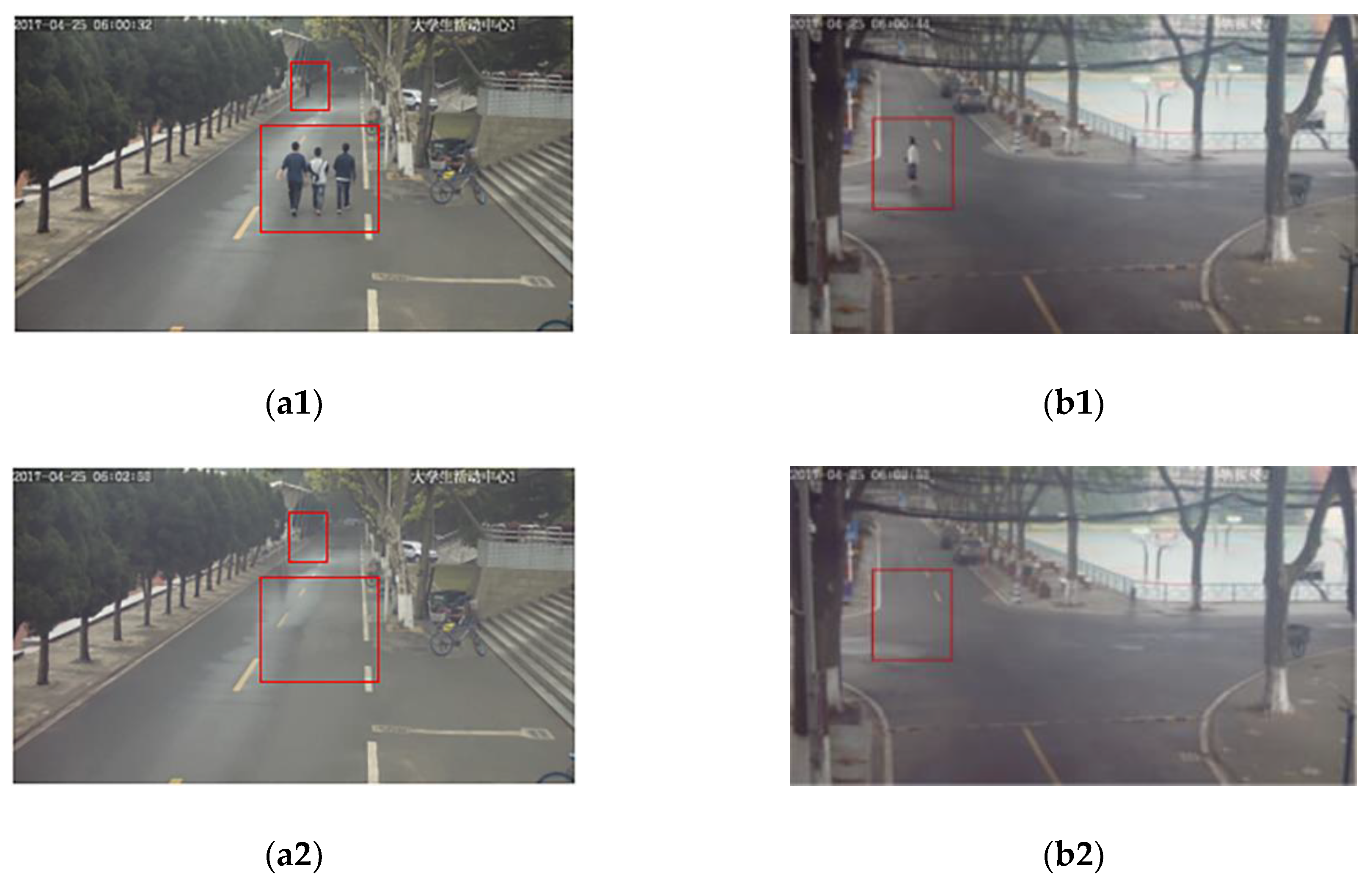
3.2.1. Road Range Extraction
3.2.2. Inundated Area Extraction based on RPM
3.3. Discussion
3.3.1. Discernibility Analysis
3.3.2. Comparison of Spectral Classification
3.3.3. Precision Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ziegler, A.D. Water management: Reduce urban flood vulnerability. Nature 2012, 481, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.B.; Zhou, H.L.; Zhang, H.; Du, G.M.; Zhou, J.H. Urban flood risk warning under rapid urbanization. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelfaut, K.; Pannemans, B.; Craats, I.V.D.; Krywkow, J.; Mysiak, J.; Cools, J. Bringing flood resilience into practice: The FREEMAN project. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Cao, L.D.; Pu, R.L. Progresses on monitoring and assessment of flood disaster in remote sensing. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 45, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Y.; Lei, X.H.; Liao, W.H.; Shang, Y.Z. Analysis of changes in flood regime using a distributed hydrological model: A case study in the Second Songhua River basin, China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dottori, F.; Todini, E. Testing a simple 2D hydraulic model in an urban flood experiment. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 1301–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Y.; Ao, T.Q.; Yu, H.J.; Huang, G.R.; Li, X.D. A Coupled 1D-2D Hydrodynamic Model for Urban Flood Inundation. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mark, O.; Weesakul, S.; Apirumanekul, C.; Aroonnet, S.B.; Djordjević, S. Potential and limitations of 1D modelling of urban flooding. J. Hydrol. 2004, 299, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.S.; Evans, B.; Djordjević, S.; Savić, D.A. Multi-layered coarse grid modelling in 2D urban flood simulations. J. Hydrol. 2012, 470–471, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.P.; Liu, C.; Peng, S.F. Progress on Assessment and Regionalization of Flood Risk. Prog. Geogr. 2007, 26, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.R.; Wang, S.L. Research on Flood Risk Assessment Model at Regional Scale. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Engineering Applications, Zhangjiajie, China, 6–7 November 2013; pp. 472–478. [Google Scholar]
- Meesuk, V.; Vojinovic, Z.; Mynett, A.E.; Abdullah, A.F. Urban flood modelling combining top-view LiDAR data with ground-view SfM observations. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 75, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Shafiee, M.; Pirasteh, S. Maximum flood prone area mapping using RADARSAT images and GIS: Kelantan river basin. Int. J. Geoinform. 2009, 5, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, M.; Akhtar, M.; Muhammad, S.; Paras, S.; Rahmatullah, J. Techniques of Remote Sensing and GIS for flood monitoring and damage assessment: A case study of Sindh province, Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2012, 15, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Guo, H.; Schlegel, I.; Tuan, V.Q.; Li, X.; Dech, S. Varying Scale and Capability of Envisat ASAR-WSM, TerraSAR-X Scansar and TerraSAR-X Stripmap Data to Assess Urban Flood Situations: A Case Study of the Mekong Delta in Can Tho Province. Remote. Sens. 2013, 5, 5122–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.L.; Liu, D.S. Blending MODIS and Landsat images for urban flood mapping. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2014, 35, 3237–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D.; Mason, D.C. A change detection approach to flood mapping in urban areas using very high-resolution microwave remote sensing imagery. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 22–27 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Trigg, M.A.; Michaelides, K.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D. Surface water connectivity dynamics of a large scale extreme flood. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.M.; Sado, K. Development Priority Map for Flood Countermeasures by Remote Sensing Data with Geographic Information System. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.T.; Xu, Z.X.; Bo, P.; Liu, L. Flood risk zoning in China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 43, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.L.; Du, Z.Q.; Zhu, Q. Adaptive Water Level Correction Algorithm for Flooding Analysis. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2013, 42, 546–553. [Google Scholar]
- Cristani, M.; Raghavendra, R.; Bue, A.D.; Murino, V. Human behavior analysis in video surveillance: A Social Signal Processing perspective. Neurocomputing 2013, 100, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Agrawal, A. A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis. Comput. 2013, 29, 983–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Dong, H.Y.; Joo, Y.H. Fast and robust algorithm of tracking multiple moving objects for intelligent video surveillance systems. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2011, 57, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantrigo, J.J.; Hernández, J.; Sánchez, A. Multiple and variable target visual tracking for video-surveillance applications. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Yang, J.C.; Chen, Y.H. A Real Time Video Processing Based Surveillance System for Early Fire and Flood Detection. In Proceedings of the Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Warsaw, Poland, 1–3 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, S.W.; Wu, J.H.; Lin, F.P.; Hsu, C.H. Cyber Surveillance for Flood Disasters. Sensors 2015, 15, 2369–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borges, P.V.K.; Mayer, J.; Izquierdo, E. A probabilistic model for flood detection in video sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, M.J.P.S.; Ruiz, C.R., Jr. A Flood Detection and Warning System Based on Video Content Analysis; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, K.; Nayar, S.K. Detection and Removal of Rain from Videos. In Proceedings of the EEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, K.; Nayar, S.K. When does a camera see Rain. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barnum, P.C.; Narasimhan, S.; Kanade, T. Analysis of Rain and Snow in Frequency Space. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 86, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderara, S.; Piccinini, P.; Cucchiara, R. Vision based smoke detection system using image energy and color information. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2011, 22, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.Q.; Wang, L.S.; Tan, T.N.; Maybank, S. A real-time object detecting and tracking system for outdoor night surveillance. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, D.B.; Liao, Q.M.; University, T. Image defogging: A survey. J. Image Graph. 2011, 16, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.P.; Li, H.; Qi, Y.Y.; Leow, W.K.; Ng, T.K. Rain Removal in Video by Combining Temporal and Chromatic Properties. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–12 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X. The rain drops are measured and get rid of the method to study in the video picture. Microcomput. Appl. 2007, 12, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.X.; Dou, Y.L.; Tian, T.; Zhou, J.L.; Yu, S.S. A robust foreground segmentation method by temporal averaging multiple video frames. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Audio, Shanghai, China, 7–9 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.L.; Hong, C. Image Denoising Based on Adaptive Filtering and Multi-frame Averaging Filtering. Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Comput. Intell. 2009, 3, 523–526. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.M.; Chang, W.H.; Wang, S.B.; Liu, C.S. An Efficient Histogram-Based Method for Background Modeling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing, Information and Control, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 7–9 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Z.; Suter, D. A novel robust statistical method for background initialization and visual surveillance. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Hyderabad, India, 13–16 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.J.; Xin, Y.H. Combined continuous frame difference with background difference method for moving object detection. Acta Photonica Sin. 2014, 43, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.X. Approach for road detection based on video image. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 1, 324–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, A.H.S.; Yung, N.H.C. Lane detection by orientation and length discrimination. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2000, 30, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.K.C.; Sahoo, P.K. A gray-level threshold selection method based on maximum entropy principle. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.P.; Li, G.Y.; Bao, Y. Improvement of grayscale image 2D maximum entropy threshold segmentation method. Int. Conf. Logist. Syst. Intell. Manag. 2010, 1, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, P.V.C. Method and Means for Recognizing Complex Patterns. U.S. Patent US3069654A, 18 December 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, LI.; Bao, F.; Qiao, G. Lane Detection Method Based on Two-Dimensional Renyi’s Entropy from MMS Images. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2013, 1, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Razier, P.; Kumar, L. Comparative assessment of the measures of thematic classification accuracy. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2006, 107, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Location 1 | Location 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Start time | 6:00 (non-water) 12:00 (wet) 18:20 (inundated) | |
| Duration | 30 s (each video) | |
| Weather | Cloudy (non-water) Heavy rain (wet and inundated) | Cloudy (non-water) Heavy rain (wet and inundated) |
| Traffic | Light (non-water) Heavy (wet and inundated) | Light (non-water) Medium (wet and inundated) |
| Image clarity | Clear | Medium |
| Inundation size | Large | Small |
| The Results of the Proposed Method | The Results of Supervised Classification | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | APA | AUA | Kappa | OA | APA | AUA | Kappa | |
| Location 1 | 79.04% | 68.81% | 78.54% | 0.7898 | 75.04% | 62.95% | 71.05% | 0.7404 |
| Location 2 | 78.86% | 60.34% | 74.84% | 0.7787 | 74.42% | 60.49% | 67.42% | 0.7235 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Gao, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, N. Inundated Areas Extraction Based on Raindrop Photometric Model (RPM) in Surveillance Video. Water 2018, 10, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101332
Lv Y, Gao W, Yang C, Wang N. Inundated Areas Extraction Based on Raindrop Photometric Model (RPM) in Surveillance Video. Water. 2018; 10(10):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101332
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yunzhe, Wei Gao, Chen Yang, and Ning Wang. 2018. "Inundated Areas Extraction Based on Raindrop Photometric Model (RPM) in Surveillance Video" Water 10, no. 10: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101332
APA StyleLv, Y., Gao, W., Yang, C., & Wang, N. (2018). Inundated Areas Extraction Based on Raindrop Photometric Model (RPM) in Surveillance Video. Water, 10(10), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101332





