Performance of Earthworm-Enhanced Horizontal Sub-Surface Flow Filter and Constructed Wetland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
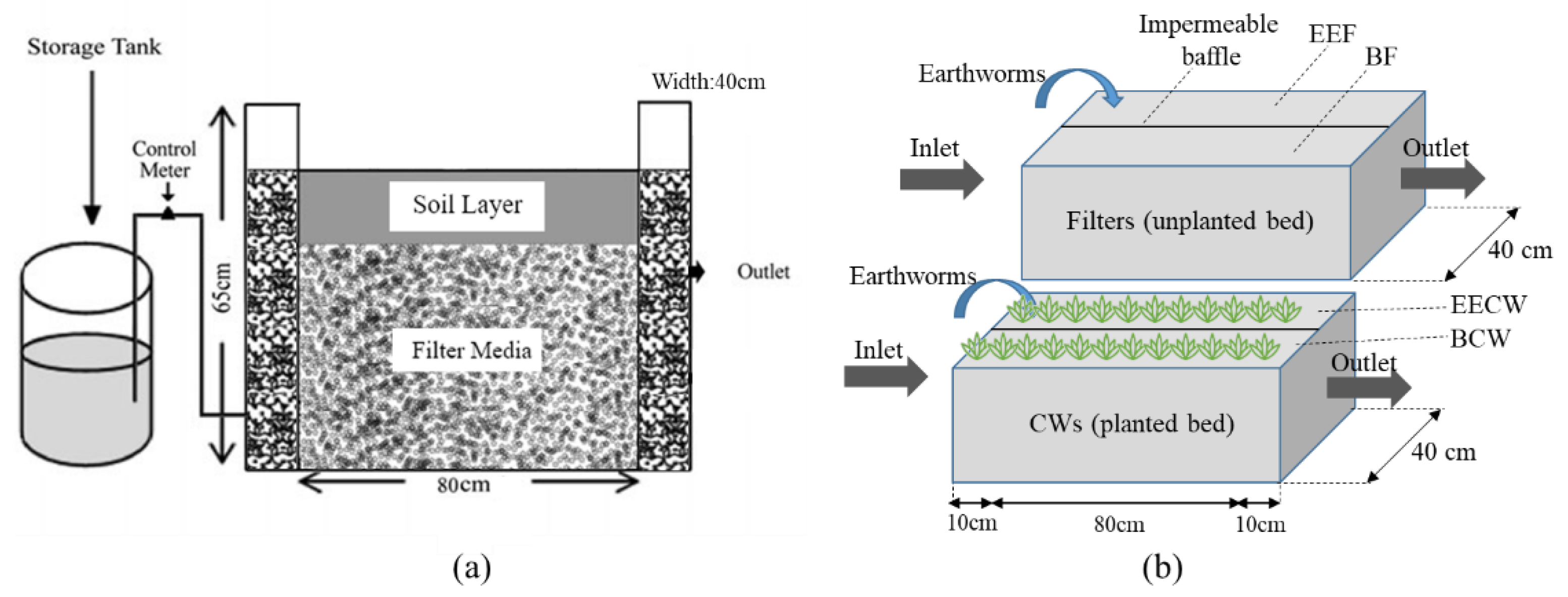
2.1. Experimental Units
2.2. Earthworm Selection and Placement
2.3. Chemicals and Experimental Water Quality
2.4. System Operation and Sampling
2.5. Sample Analysis
2.6. Characterization of Pollutant Removal Effect
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth and Distribution of Earthworms
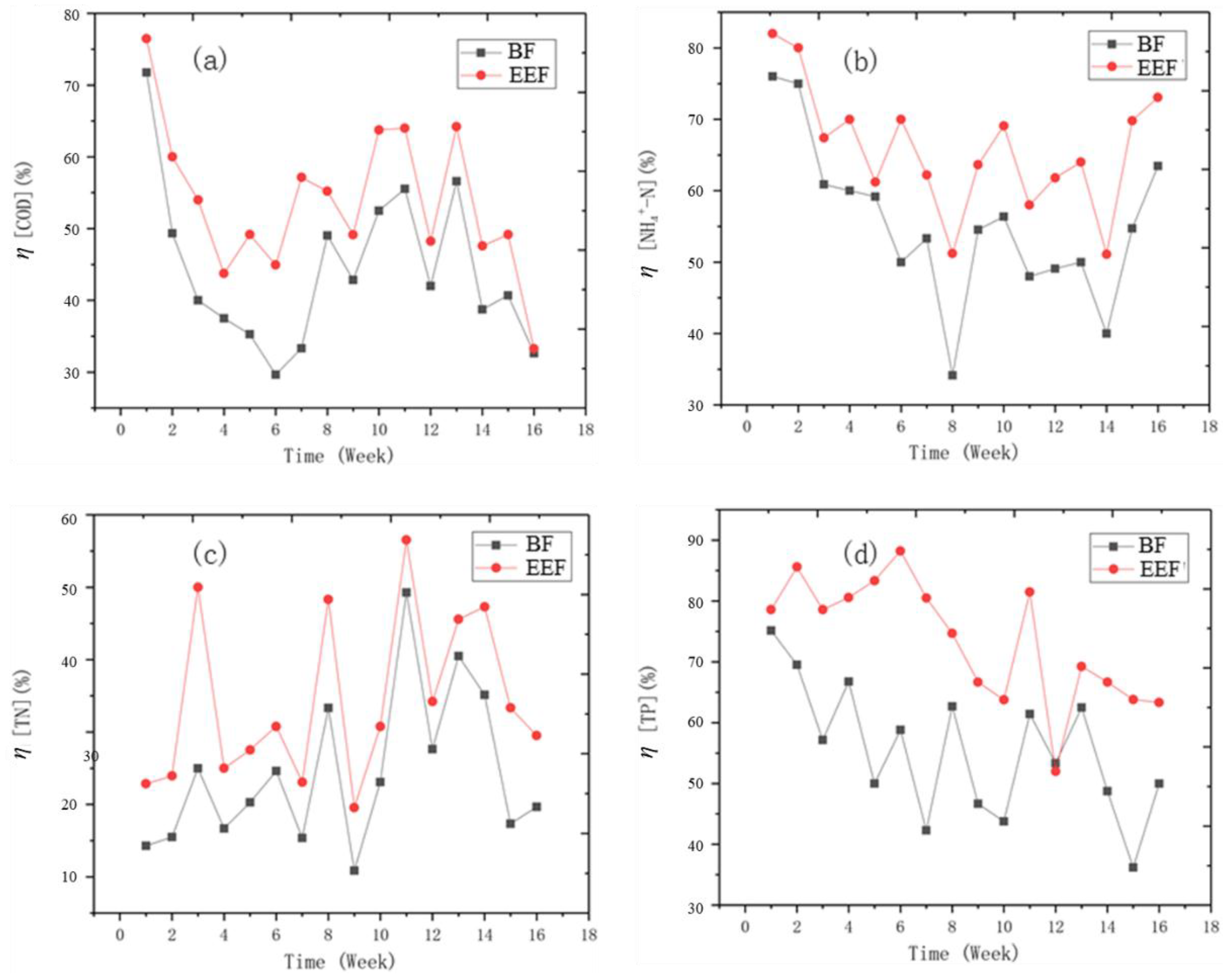
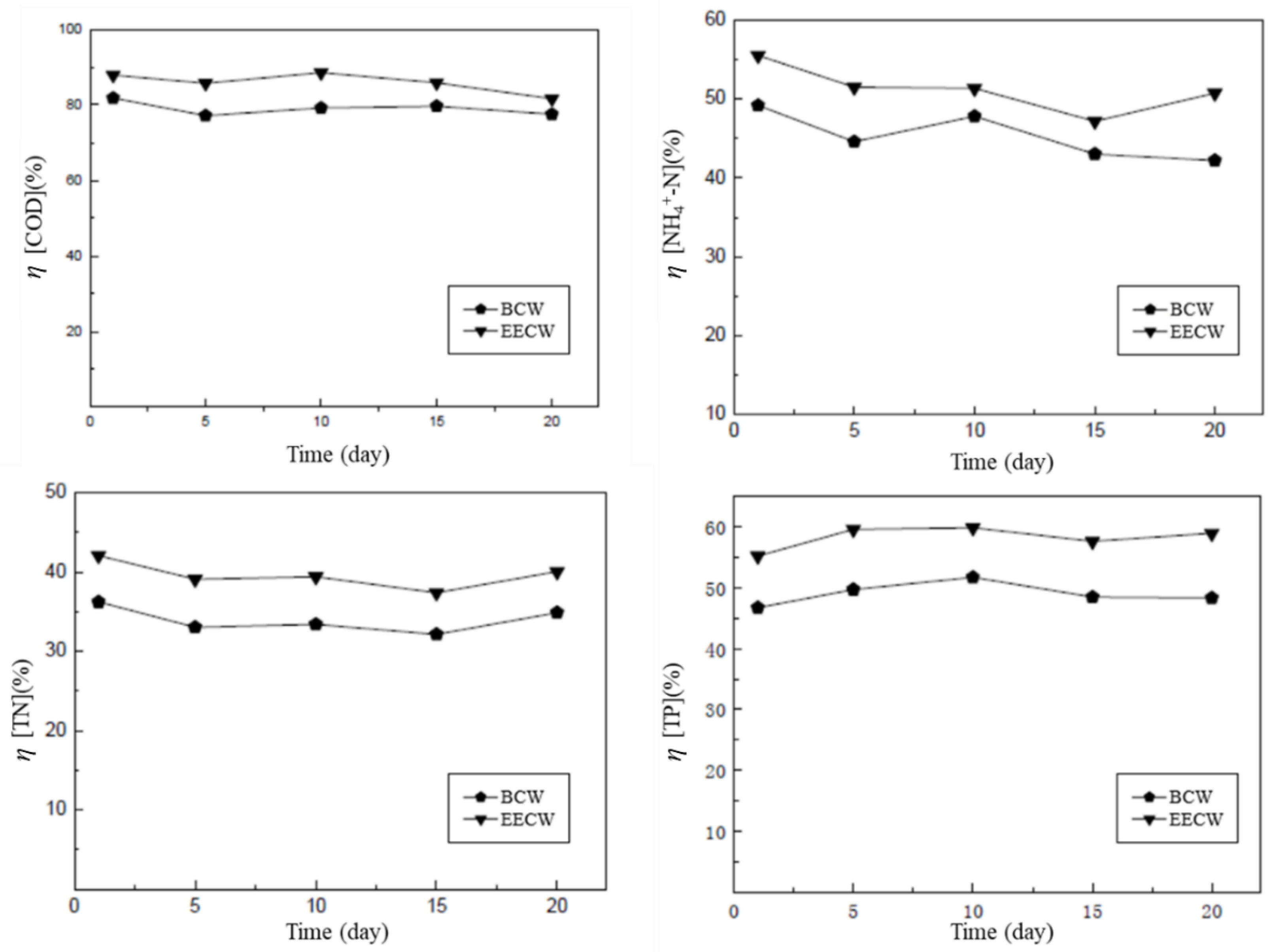
3.2. Pollutants Removal Effect of EEF and EECW
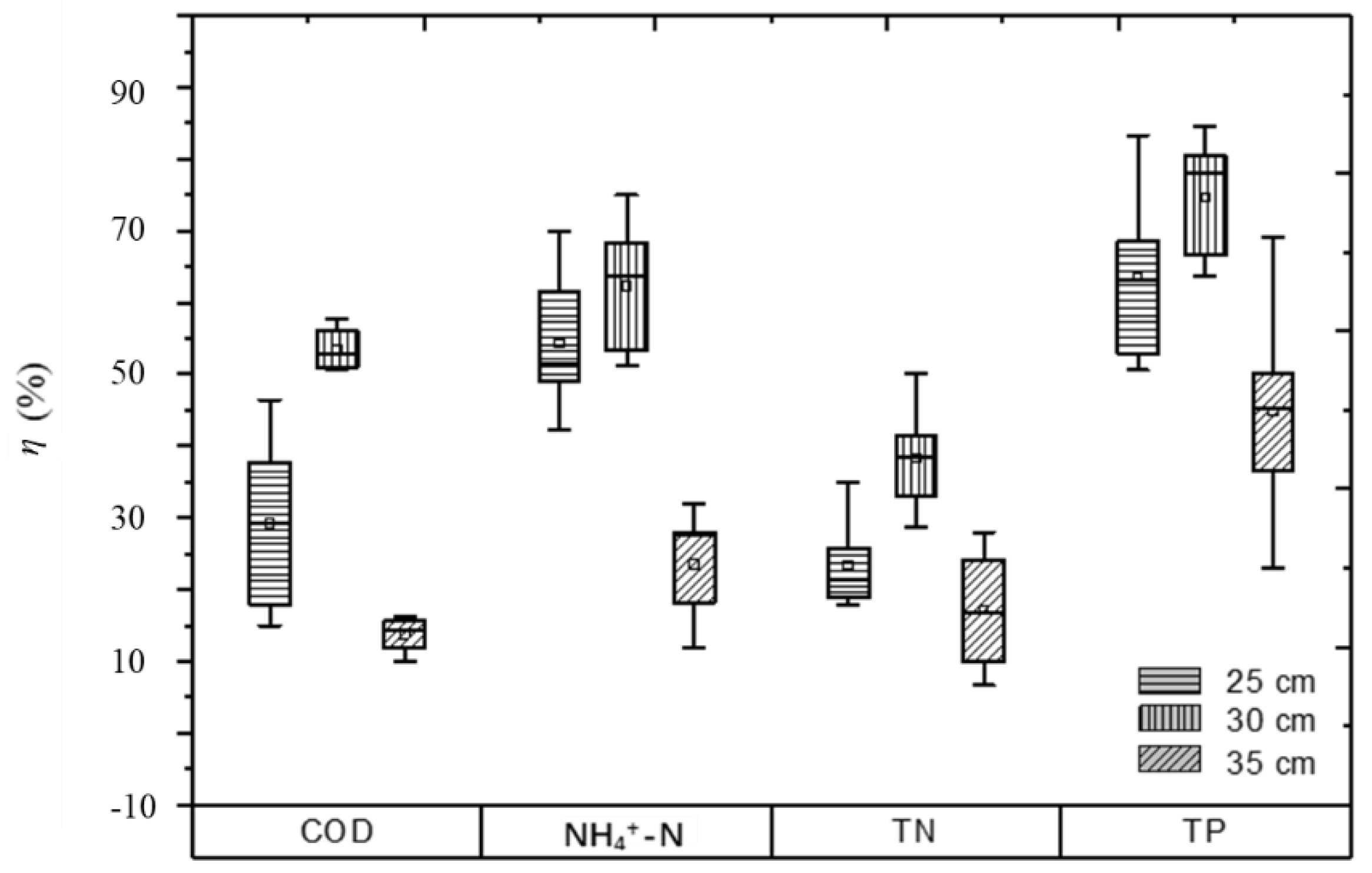
3.3. Influence of Water Level on EEF Performance
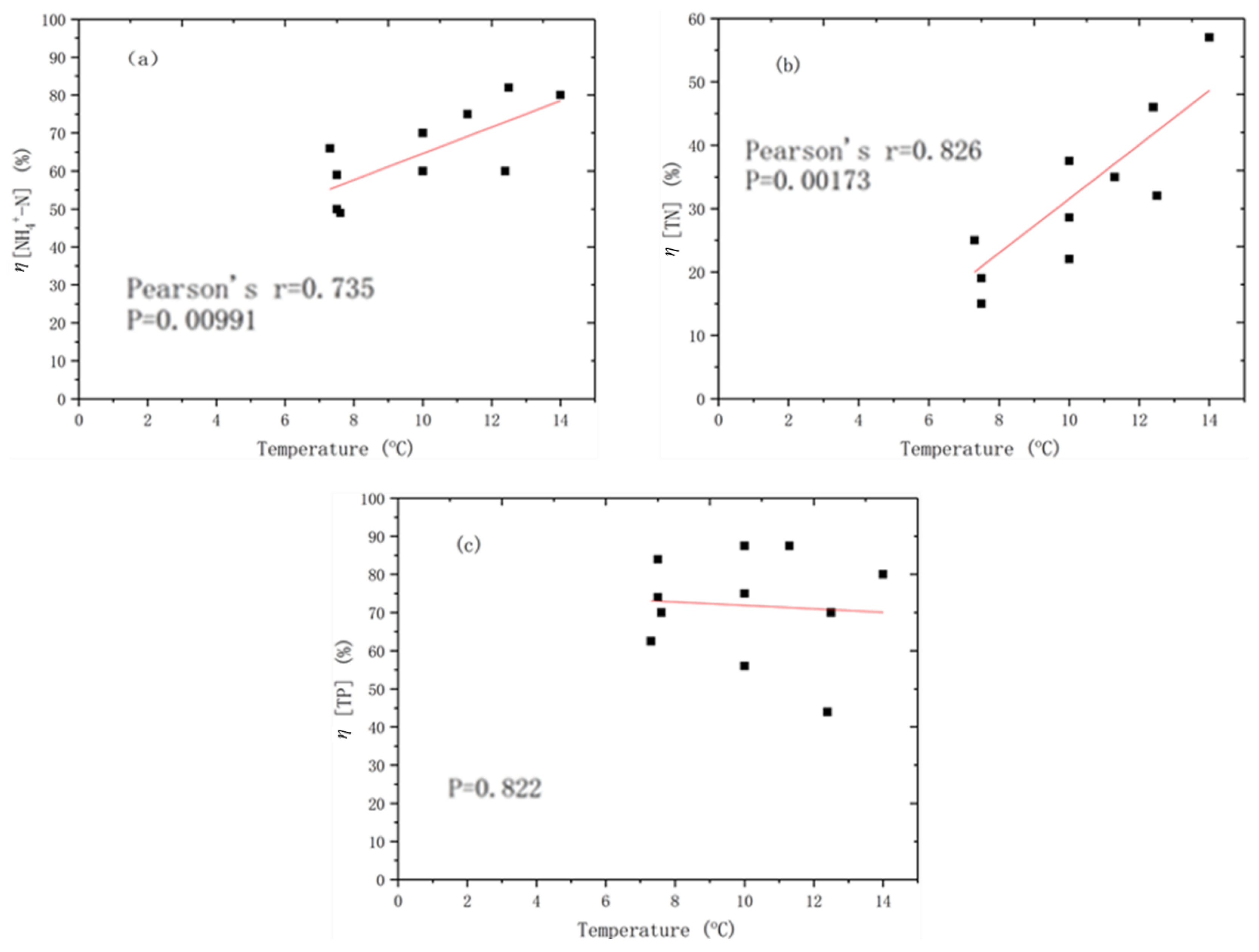
3.4. Influence of Temperature on EEF Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durgananda, S.C.; Saravanamuthu, V.; Huu-Hao, N.; Wang, G.S.; Hee, M. Biofilter in water and wastewater treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Ma, Y.F.; Zeng, M.; Li, L. Study on denitrification effect of non-reflux biofilter. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 316–322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.G. Study on the Effect of Bio-Filter and Constructed Wetlands Purifying Mariculture Effluent. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Starla, G.T.; Kumar, M. Biological filters and their use in potable water filtration systems in spaceflight conditions. Life Sci. Space Res. 2018, 17, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Mei, R.W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Study on Enhanced treatment of domestic sewage by a novel biological filter-constructed wetland coupling system. Technol. Water Treat. 2018, 44, 110–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Terry, L.G.; Summers, R.S. Biodegradable organic matter and rapid-rate biofilter performance: A review. Water Res. 2018, 128, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherpour, M.B.; Nikazar, M.; Welander, U.; Bonakdarpour, B.; Sanati, M. Effects of irrigation and water content of packings on alpha-pinene vapours biofiltration performance. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 24, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, Z.X.; Li, H.Z. The strengthening method of subsurface constructed wetland treating domestic sewage. Environ Sci. 2006, 27, 2432–2438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, T.; Risal, C.P.; Yanagimoto, R. Increase in the nitrogen content of soil by the introduction of earthworms into soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2005, 51, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Five decades of experience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenatu, A.; Seyoum, L.; Worku, M.; Helmut, K.; Erik, M. Organic matter and nutrient removal performance of horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands planted with Phragmites karka and Vetiveria zizanioide for treating municipal wastewater. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.S.; Chen, Z.B. Earthworm effects on biosolids characteristics in sludge treatment wetlands. Ecol. Engi. 2018, 118, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.B.; Hu, S.S.; Hu, C.X.; Huang, L.L.; Liu, H.B.; Vymazal, J. Preliminary investigation on the effect of earthworm and vegetation for sludge treatment in sludge treatment reed beds system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11957–11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Guan, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhao, X. Influence of earthworm Eisenia fetida on Iris pseudacorus’s photosynthetic characteristics, evapotranspiration losses and purifying capacity in constructed wetland systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, L.; Headley, T.; Pratt, K. Aspects of design, structure, performance and operation of reed beds—Eight years’ experience in Northeastern New South Wales, Australia. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, M.; Juliane, F. The influence of earthworms and organic additives on the biodegradation of oil contaminated soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 36, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirbes, L.; Thonart, P.; Haubruge, E. Microscale interactions between earthworms and microorganisms: A review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. 2012, 16, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.; Clarke, W.P.; Greenfield, P.F. The treatment of domestic wastewater using small-scale vermicompost filter beds. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 21, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Edwards, C.A.; Babenko, A.; Cannon, J.; Galvis, P.; Metzger, J.D. Influences of vermi-composts, produced by earthworms and microorganisms from cattle manure, food waste and paper waste, on the germination, growth and flowering of petunias in the greenhouse. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 39, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis-Lardy, L.; Brossard, M.; Lavelle, P.; Schouller, E. Phosphorus transformations in a ferralsol through ingestion by Pantoscolex corethrurus, a geophagous earthworm. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 1998, 34, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, A. Vermicompost as a strong buffer and natural adsorbent for reducing transition metals, BOD, COD from industrial effluent. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Specification of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment Engineering; Ministry of Environmental Protection of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.M. The Use and Cultivation of Earthworms; Wuzhou Press: Taipei, Taiwan, 1989; pp. 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, B.; Nadali, A.; Monireh, M.; Pooya, P. Compost leachate treatment by a pilot-scale subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 105, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sohair, I.A.; Mohamed, A.E.; Magdy, T.K.; Mohamed, S.H. Factors affecting the performance of horizontal flow constructed treatment wetland vegetated with Cyperus papyrus for municipal wastewater treatment. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Ye, Z. Metal accumulation and tolerance in wetland plant. Front. Biol. 2009, 4, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognetti, C.; Mazzarino, M.J.; Laos, F. Improving the quality of municipal organic waste compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.Y.; Luo, G.Y.; Zhou, J. Experimental study on earthworm and wastewater treatment. Chongqing Environ. Sci. 1998, 20, 12–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Z.; Wang, S.; Ye, J.F.; Xu, Z.X.; Jin, W. A practical method for the restoration of clogged rural vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment using earthworm. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.N.; Song, H.L.; Wang, G.F.; Jin, Q.; Xu, X.L.; Gao, Y.C. Enhanced removal of organic matter and nitrogen in a vertical-flow constructed wetland with Eisenia foetida. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 7460–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulc, T.; Slak, A.S. Performance of constructed wetland for highway runoff treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poe, A.C.; Piehler, M.F.; Thompson, S.P.; Paerl, H.W. Denitrification in a constructed wetland receiving agricultural runoff. Wetlands 2003, 23, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldheimer, G.; Bennerstedt, K. Facilities for treatment of stormwater runoff from highways. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Composition | Mean Concentration (mg/L) | Composition | Mean Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 278 | NaHCO3 | 111 |
| Starch | 278 | CaCl2 | 6 |
| Peptone | 28 | FeSO4·7H2O | 0.549 |
| Carbamide | 167 | KH2PO4 | 26.4 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 66 | MnSO4·7H2O | 6 |
| Index | COD (mg/L) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 360~516 | 40.2~57.9 | 56.3~79.2 | 2.27~4.13 | 7~8 |
| Technological Parameter | Experimental Condition 1 | Experimental Condition 2 | Experimental Condition 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water level (cm) | 35 | 30 | 25 |
| HRT (day) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Hydraulic load (cm/day) | 4.65 | 4.05 | 3.30 |
| Inflow discharge (L/h) | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.22 |
| Depth | Earthworm Number | Initial Mean Weight (g) | Final Mean Weight (g) | Growth Rate (%) | Earthworm Color | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 0~5 cm | 2 | 0.48 | 1.14 | 137.5 | Dark |
| 5~10 cm | 5 | 0.48 | 1.28 | 166.7 | Dark | |
| 10~15 cm | 6 | 0.48 | 1.62 | 237.5 | Light | |
| 15~20 cm | 7 | 0.48 | 2.07 | 331.3 | Light | |
| Gravel | 20~50 cm | 0 | —— | —— | —— | —— |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, R.P.; Fu, D.; Jia, J.; Wu, J. Performance of Earthworm-Enhanced Horizontal Sub-Surface Flow Filter and Constructed Wetland. Water 2018, 10, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101309
Singh RP, Fu D, Jia J, Wu J. Performance of Earthworm-Enhanced Horizontal Sub-Surface Flow Filter and Constructed Wetland. Water. 2018; 10(10):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101309
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Rajendra Prasad, Dafang Fu, Jing Jia, and Jiaguo Wu. 2018. "Performance of Earthworm-Enhanced Horizontal Sub-Surface Flow Filter and Constructed Wetland" Water 10, no. 10: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101309
APA StyleSingh, R. P., Fu, D., Jia, J., & Wu, J. (2018). Performance of Earthworm-Enhanced Horizontal Sub-Surface Flow Filter and Constructed Wetland. Water, 10(10), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101309







