Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
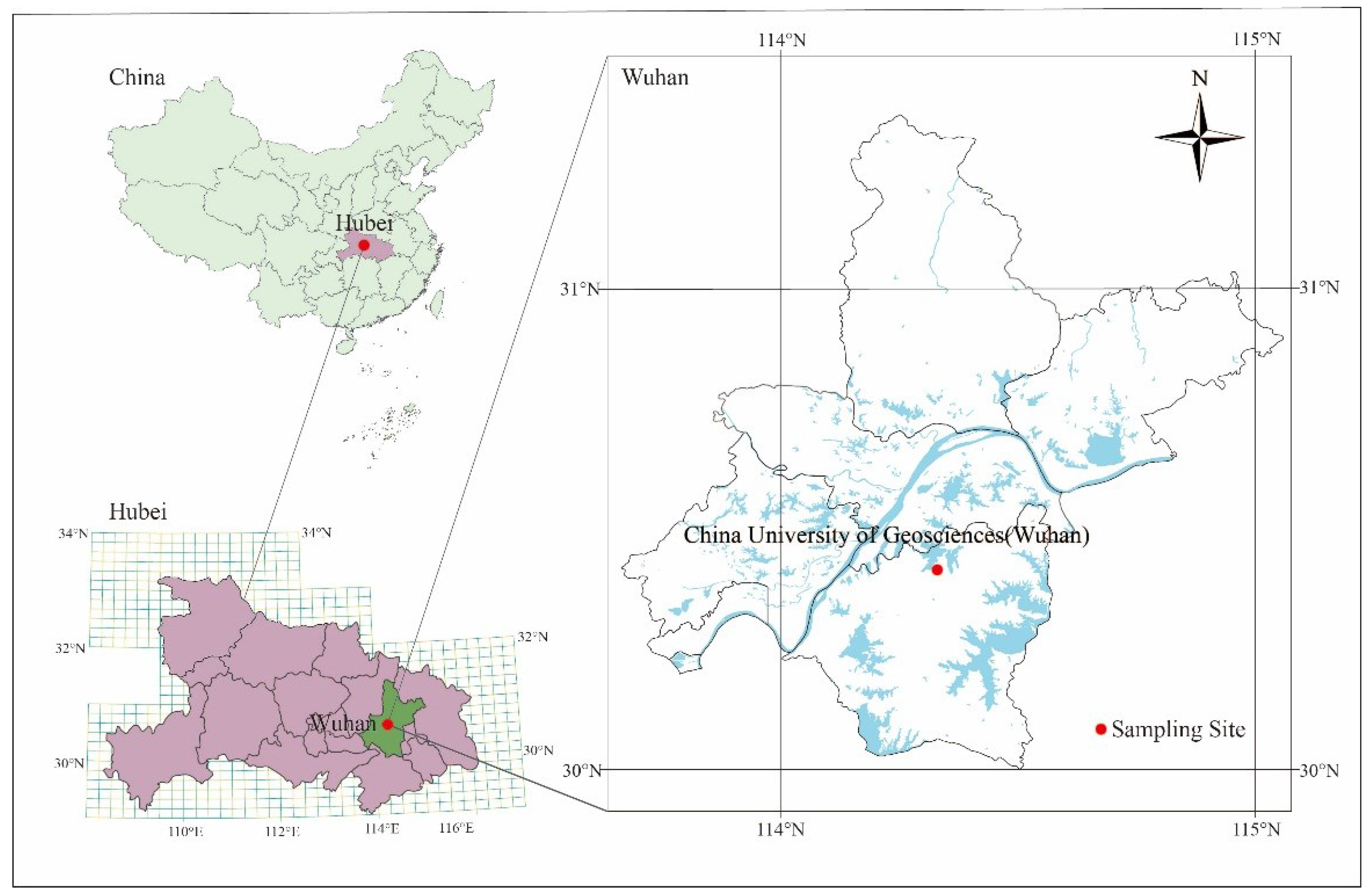
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Analysis Method
3. Results and Discussion
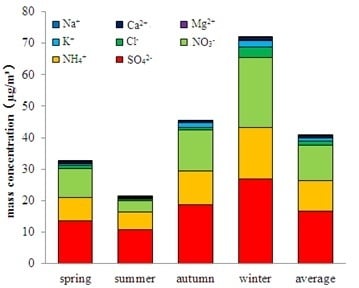
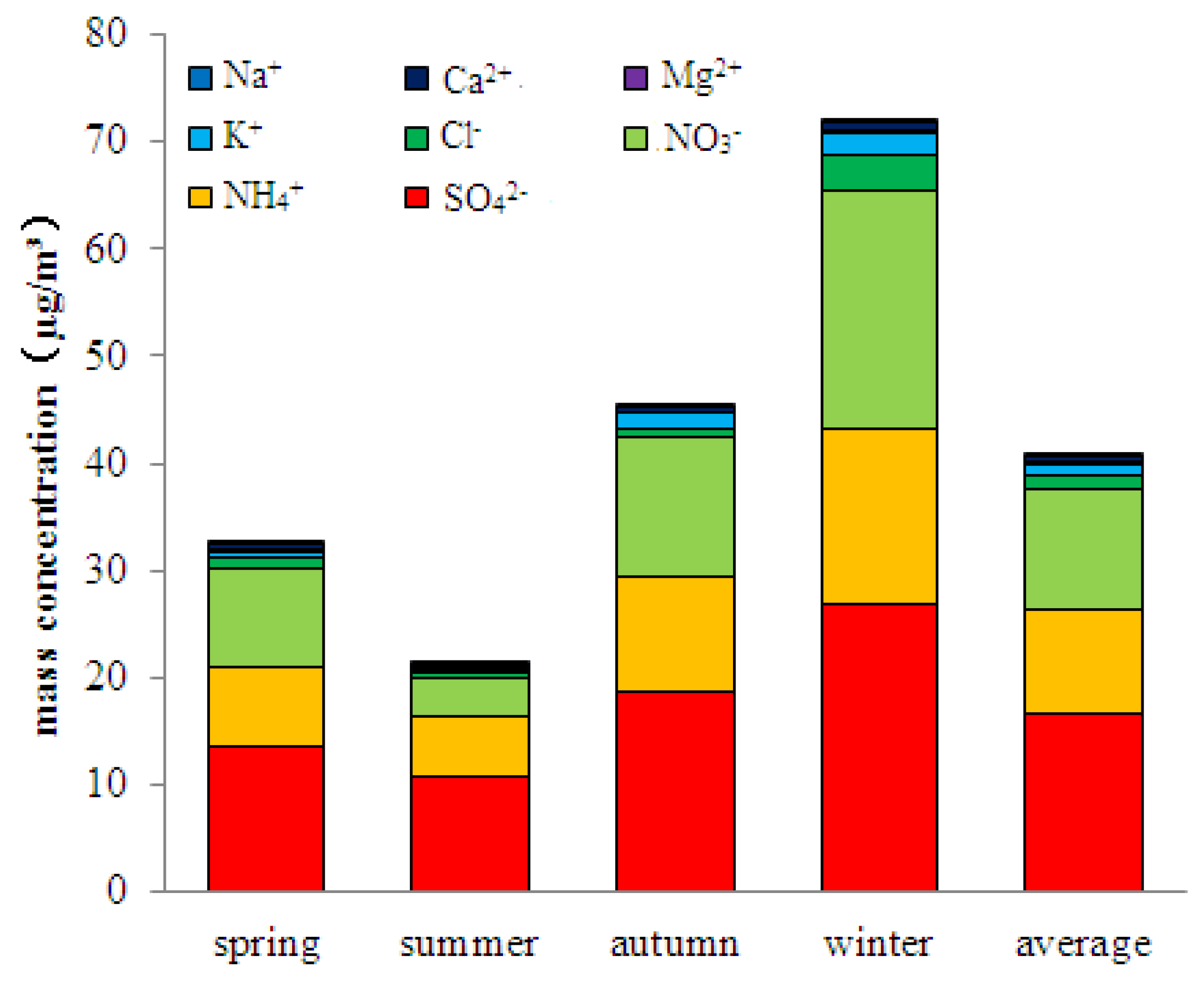
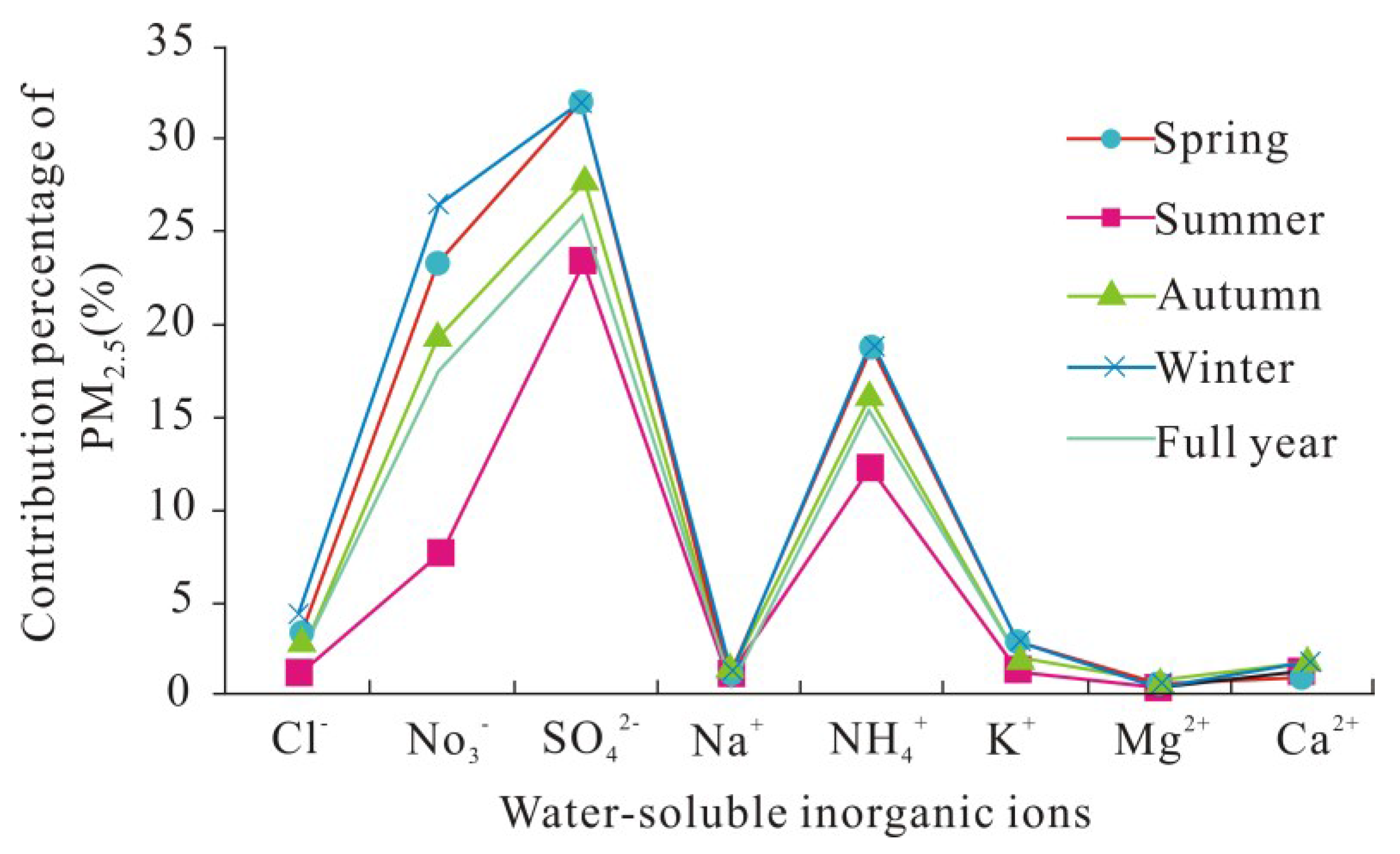
3.1. Concentration Level Analysis of PM2.5’s Water-Soluble Ions
3.2. Seasonal Variation Characteristics of Water-Soluble Ions
3.3. Concentration Equivalent Ratio Analysis of NO3−/SO42−
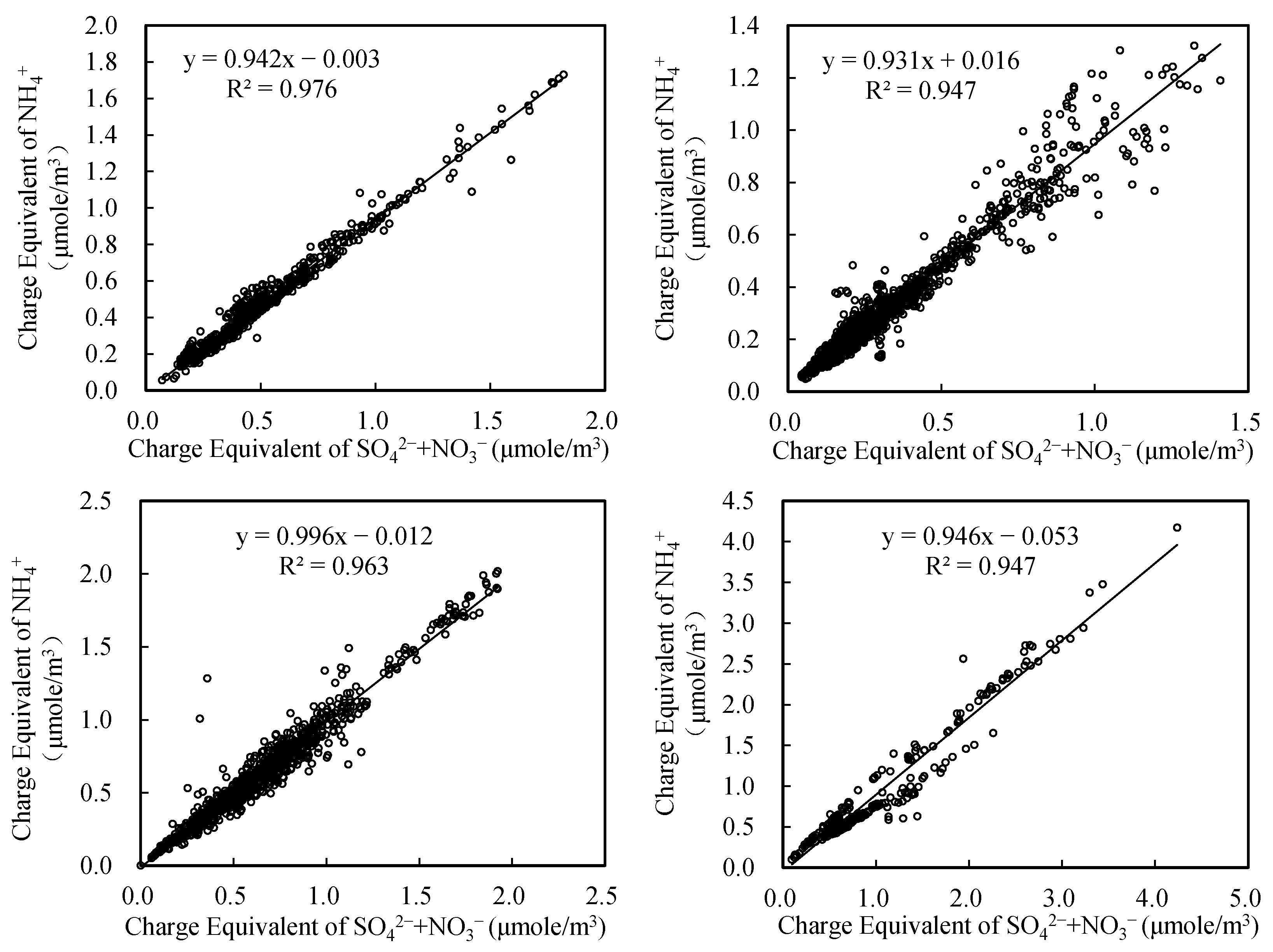
3.4. Charge Balance Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions
3.5. Correlation and Seasonal Difference Analysis of Water-Soluble Ions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, C.S.; Lee, C.G.; Liu, S.H.; Chang, J.C.; Yuan, C.; Yang, H.Y. Correlation of atmospheric visibility with chemical composition of Kaohsiung aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 82, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.H.; Wang, X.M.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, S.Z.; Chang, M.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Tu, Q.L. Long-term atmospheric visibility, sunshine duration and precipitation trends in South China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.R.; Foley, K.M. A nonlinear regression model estimating single source concentrations of primary and secondarily formed PM2.5. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3758–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.X.; Cheng, S.H.; Wang, X.F.; Nie, W.; Xu, P.J.; Gao, X.M.; Yuan, C.; Wang, W.X. Source identification and health impact of PM2.5 in a heavily polluted urban atmosphere in China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Qu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Han, T.T.; Gu, J.W.; Zhao, J.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Jiang, Q.; Gao, Z.Q.; Hu, M.; et al. Chemical characteristics of size-resolved aerosols in winter in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Griffith, S.M.; Yu, X.; Lau, A.K.H.; Yu, J.Z. Effect of nitrate and sulfate relative abundance in PM2.5 on liquid water content explored through half-hourly observations of inorganic soluble aerosols at a polluted receptor site. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, W. Characteristics of PM1.0, PM2.5, and PM10, and Their Relation to Black Carbon in Wuhan, Central China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, K.; Sarin, M.M.; Tripathi, S.N. Temporal trends in atmospheric PM2.5, PM10, elemental carbon, organic carbon, water-soluble organic carbon, and optical properties: Impact of biomass burning emissions in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Xu, S.Y. Contamination characteristics and possible sources of PM10 and PM2.5 in different functional areas of Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugamsetty, B.; Wei, H.; Liu, C.N.; Awasthi, A.; Hsu, S.C.; Tsai, C.J.; Roam, G.D.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, C.F. Source characterization and apportionment of PM10, PM2.5 and PM0.1 by using positive matrix factorization. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, D.K.; Deb, M.K.; Tsai, Y.I.; Mkoma, S.L. Water soluble ions in PM2.5 and PM1 aerosols in Durg city, Chhattisgarh, India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.J.; Wang, H.L.; Shen, L.J.; Zhu, B.; Zou, J.N.; Gao, J.H.; Kang, H.Q. Characteristics of new particle formation events in Nanjing, China: Effect of water-soluble ions. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 108, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reff, A.; Bhave, P.V.; Simon, H.; Pace, T.G.; Pouliot, G.A.; Mobley, J.D.; Houyoux, M. Emissions inventory of PM2.5 trace elements across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5790–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueglin, C.; Gehrig, R.; Baltensperger, U.; Gysel, M.; Monn, C.; Vonmont, H. Chemical characterisation of PM2.5, PM10 and coarse particles at urban, near-city and rural sites in Switzerland. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Liu, B.X.; Zhang, D.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.N.; Liang, Y.P. Correlation, Seasonal and Temporal Variation of Water-soluble Ions of PM2.5 in Beijing during 2012–2013. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 768–773. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fann, N.; Lamson, A.D.; Anenberg, S.C.; Wesson, K.; Risley, D.; Hubbell, B.J. Estimating the national public health burden associated with exposure to ambient PM2.5 and ozone. Risk Anal. 2012, 32, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, S.S.; Shang, J.; Wilfrid, O.M.F.; Liu, X.G.; Tian, H.Z.; Boman, H. Impact of relative humidity and water soluble constituents of PM2.5 on visibility impairment in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, C. Research on the Coupling Coordination Relationship between Urbanization and the Air Environment: A Case Study of the Area of Wuhan. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.R.; Gong, W.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.M.; Lv, X.P.; Liu, J.; Fu, X.X.; Zhang, G. Ionic composition of submicron particles (PM1.0) during the long-lasting haze period in January 2013 in Wuhan, central China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.T.; Zhou, J.B.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, J.P.; Zhao, R.S. Seasonal Variations and Sources of Carboxylic Acids in PM2.5 in Wuhan, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Shen, Z.X.; Chow, J.C.; Waston, J.G.; Lee, S.C.; Tie, X.X.; Ho, K.F.; Wang, G.H.; Han, Y.M. Winter and summer PM2.5 chemical compositions in fourteen Chinese cities. J. Air Waste Manag. 2012, 62, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.W.; Cheng, H.R.; Lv, X.P.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, G. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of PM2.5 in Wuhan, central China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 518, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, H.R.; Wang, Z.W.; Lu, X.P. Characteristics of Water-soluble Ions in PM2.5 during Haze and Non-haze Periods in autumn in Wuhan. China Power Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 31–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, K.; Xu, C.; Tang, A.H.; Chen, J.M.; An, Z.S. The ion chemistry, seasonal cycle, and sources of PM2.5 and TSP aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.X.; Bai, Z.P.; Li, W.F.; Wu, L.P.; Liu, A.X.; Dong, H.Y.; Xie, Y.Y. Chemical composition of PM2.5 during winter in Tianjin, China. Particuology 2011, 9, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Chow, J.C.; Louie, P.K.K.; Cao, J.J.; Hai, X. Chemically-speciated on-road PM 2.5 motor vehicle emission factors in Hong Kong. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.M.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, R.J.; Lin, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.S.; Lin, M.; Cao, J.J.; Liu, S.X.; Wang, G.H. Impact of PM2.5 chemical compositions on aerosol light scattering in Guangzhou—The largest megacity in South China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhan City Environmental Monitoring Center. Wuhan City Environmental Quality Report. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lough, G.C.; Schauer, J.J.; Park, J.S.; Shafer, M.M.; Deminter, J.T.; Weinstein, J.P. Emissions of metals associated with motor vehicle roadways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimoto, R.; Duce, R.A.; Savoie, D.L.; Prospero, J.M.; Talbot, R.; Cullen, D.; Tomza, U. Relationships among aerosol constituents from Asia and the North Pacific during PEM-West A. J. Geophys. Res.-Atoms. 1996, 101, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Wang, Y.S.; Wen, T.X.; Liu, Q. Characterization of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 at Dinghu Mount. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 1232–1239. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Orsini, D.A.; Ma, Y.L.; Sullivan, A.; Sierau, B.; Baumann, K.; Weber, R.J. Refinements to the Particle-Into-Liquid Sampler (PILS) for ground and airborne measurements of water soluble aerosol composition. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wu, Z.J.; Slanina, J.; Lin, P.; Liu, S.; Zeng, M. Acidic gases, ammonia and water-soluble ions in PM2.5 at a coastal site in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6310–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Chan, C.K. Inter-particle and gas-particle interactions in sampling artifacts of PM2.5 in filter-based samplers. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Y.; Querol, X.; Zhuang, X.; Alastuey, A.; López, A.; Viana, M. Geochemical and statistical analysis of trace metals in atmospheric particulates in Wuhan, central China. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, S.; Shang, J.; Wilfrid, O.M.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Boman, J. Impact of relative humidity and water soluble constituents of PM2.5 on visibility impairment in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | Wuhan (This Study) | Wuhan [23] | Beijing [15] | Shanghai [24] | Tianjin [25] | Hongkong [26] | Guangzhou [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | urban | urban | urban & suburb | urban | urban | urban | urban |
| Time | 2013 | 2012 | 2012–2013 | 2003–2005 | 2008 | 2003 | 2012–2013 |
| Sampling sites | 1 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sample number | 52 | 21 | 519 | 202 | 19 | -- | 51 |
| PM2.5 | 65 | 120.91 | 89.8 | 94.6 | 144.6 | 49.3 | 76.8 |
| Cl− | 1.24 | 2.18 | 3.61 | 3 | 6.7 | 0.17 | 1.8 |
| NO3− | 11.28 | 25.61 | 20.3 | 6.32 | 16.6 | 0.79 | 7.8 |
| SO42− | 16.78 | 43.15 | 19.4 | 10.39 | 24.1 | 11.6 | 18.1 |
| NH4+ | 9.67 | 17.83 | 13.5 | 3.78 | 8.7 | 4.3 | 5.1 |
| Na+ | 0.24 | 0.75 | 1.19 | 0.57 | 3.4 | 0.26 | 2.2 |
| K+ | 1.08 | 2.96 | 1.05 | 0.63 | 0.9 | 0.67 | 0.9 |
| Mg2+ | 0.14 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 1 | 0.045 | -- |
| Ca2+ | 0.54 | 5.17 | 0.78 | 1.25 | 1.8 | 0.13 | -- |
| Year | 2013 | 2014 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sources | Emissions (t) | Percentage (%) | Emissions (t) | Percentage (%) |
| Total NOx emission | 147,100 | -- | 137,000 | -- |
| Total industrial NOx emission | 95,600 | 65.00 | 84,200 | 61.46 |
| Thermal power industry | 51,576 | 35.06 | 29,817 | 21.80 |
| Iron and steel industry | 9937 | 6.76 | 9661 | 7.05 |
| Cement industry | 7340 | 5.00 | 6580 | 4.80 |
| Vehicle exhaust emissions | 50,000 | 34.00 | 51,400 | 37.54 |
| Life source emissions | 1400 | 0.95 | 1300 | 0.95 |
| Centralized management facilities | 100 | 0.05 | 100 | 0.05 |
| -- | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NO3− | 0.401 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SO42− | 0.036 | 0.579 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Na+ | 0.458 ** | 0.337 ** | 0.396 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NH4+ | 0.276 ** | 0.882 ** | 0.859 ** | 0.371 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| K+ | 0.537 ** | 0.439 ** | 0.426 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.492 ** | 1 | -- | -- |
| Mg2+ | 0.152 ** | 0.082 * | 0.590 * | 0.473 ** | 0.001 | 0.269 ** | 1 | -- |
| Ca2+ | 0.085 * | −0.253 ** | 0.536 ** | 0.382 ** | −0.301 ** | 0.135 ** | 0.698 ** | 1 |
| -- | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NO3− | 0.668 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SO42− | 0.293 ** | 0.335 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Na+ | 0.173 ** | 0.423 ** | 0.159 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NH4+ | 0.582 ** | 0.611 ** | 0.686 ** | 0.441 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| K+ | 0.449 ** | 0.397 ** | 0.631 ** | 0.211 ** | 0.659 ** | 1 | -- | -- |
| Mg2+ | 0.101 ** | −0.089 ** | 0.469 ** | 0.067 * | −0.116 ** | 0.092 ** | 1 | -- |
| Ca2+ | 0.114 ** | 0.036 | 0.438 ** | 0.291 ** | 0.134 ** | 0.311 ** | 0.125 ** | 1 |
| -- | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NO3− | 0.552 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SO42− | 0.177 ** | 0.472 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Na+ | 0.184 ** | 0.331 ** | 0.224 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NH4+ | 0.488 ** | 0.846 ** | 0.821 ** | 0.214 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| K+ | 0.632 ** | 0.586 ** | 0.392 ** | 0.271 ** | 0.546 ** | 1 | -- | -- |
| Mg2+ | 0.111 ** | 0.235 ** | 0.441 * | 0.263 ** | 0.228 ** | 0.176 ** | 1 | -- |
| Ca2+ | −0.004 | 0.035 | 0.502 ** | 0.682 ** | 0.001 | 0.184 ** | 0.218 ** | 1 |
| -- | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NO3− | 0.365 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| SO42− | 0.486 ** | 0.846 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Na+ | 0.306 ** | 0.706 ** | 0.695 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| NH4+ | 0.474 ** | 0.925 ** | 0.941 ** | 0.696 ** | 1 | -- | -- | -- |
| K+ | 0.612 ** | 0.436 ** | 0.518 ** | 0.528 ** | 0.395 ** | 1 | -- | -- |
| Mg2+ | 0.331 ** | 0.021 | 0.141 * | 0.214 ** | −0.067 | 0.738 ** | 1 | -- |
| Ca2+ | −0.172 ** | 0.418 ** | 0.316 ** | 0.004 | −0.421 ** | −0.158 ** | 0.144 * | 1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, J.; Cheng, S. Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040049
Huang T, Chen J, Zhao W, Cheng J, Cheng S. Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ting, Juan Chen, Weituo Zhao, Jixiong Cheng, and Shenggao Cheng. 2016. "Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013" Atmosphere 7, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040049
APA StyleHuang, T., Chen, J., Zhao, W., Cheng, J., & Cheng, S. (2016). Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013. Atmosphere, 7(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7040049