Abstract
The application of ultraviolet (UV) radiation to inhibit bacterial growth is based on the principle that the exposure of DNA to UV radiation results in the formation of cytotoxic lesions, leading to inactivation of microorganisms. Herein, we present the impacts of UV radiation on bacterial cultures’ properties from the biological, biochemical and molecular biological perspective. For experiments, commercial bacterial cultures (Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium) and isolates from patients with bacterial infections (Proteus mirabilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) were employed. The above-mentioned strains were exposed to UV using a laboratory source and to stratospheric UV using a 3D printed probe carried by a stratospheric balloon. The length of flight was approximately two hours, and the probe was enriched by sensors for the external environment (temperature, pressure and relative humidity). After the landing, bacterial cultures were cultivated immediately. Experimental results showed a significant effect of UV radiation (both laboratory UV and UV from the stratosphere) on the growth, reproduction, behavior and structure of bacterial cultures. In all parts of the experiment, UV from the stratosphere showed stronger effects when compared to the effects of laboratory UV. The growth of bacteria was inhibited by more than 50% in all cases; moreover, in the case of P. aeruginosa, the growth was even totally inhibited. Due to the effect of UV radiation, an increased susceptibility of bacterial strains to environmental influences was also observed. By using commercial tests for biochemical markers of Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, significant disparities in exposed and non-exposed strains were found. Protein patterns obtained using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry revealed that UV exposure is able to affect the proteins’ expression, leading to their downregulation, observed as the disappearance of their peaks from the mass spectrum.
1. Introduction
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a proven and effective method for the inactivation of microorganisms. It is not surprising that it has become a widely-used technology in facilities for wastewater treatment. The advantages of UV radiation are well known throughout the water industry, and technological advances have stimulated the interest in further research. UV disinfection is based on the ability to cause DNA damage, leading to the inhibition of vital cellular processes, such as transcription and replication, and ultimately, this may lead to the death of an organism [1,2,3]. DNA strongly absorbs UV-C (220–280 nm) with a maximum at 260 nm, resulting in the formation of lesions between adjacent nucleobases, primarily pyrimidines [4,5]. Two basic types of lesions may be formed as cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6–4 photoproducts. CPDs are the majority of lesions caused by UV-C radiation (approximately 75%), while the remaining 25% consists of photoproducts [3,6]. Areas in the stratosphere, where bacteria may be exposed to UV-C, are characterized as regions with a low temperature and a high degree of exposure to UV radiation, in particular highly biologically-harmful UV-C [7].
The occurrence of live bacteria and fungi in the stratosphere is of interest for researchers [8,9]. Recent studies have shown that bacteria can be isolated from the stratosphere at heights of 20 km [10] and 41 km [11], which also confirms the previous reports of the presence of stratospheric bacterial species [12]. Microbes are very abundant in soil, and some of them are adapted for dispersion [13]. While mixing to the border tropopause is limited, a wide range of mechanisms can carry aerosols (or biological cells) from the troposphere into the stratosphere. These mechanisms include the following: a volcanic eruption, Brewer–Dobson atmospheric circulation, dust storms, monsoons, electrostatic forces generated by cells and the starts of rockets [14].
Numerous microbes have evolved mechanisms to repair some UV-induced lesions, including CPDs and photoproducts [15]. Studies of these mechanisms brought results and conclusion based on these, and we can say that these are very well understood from the molecular perspective. Briefly, there are two main categories of repair of damaged DNA: photoreactivation and excision repair. Photoreactivation is an enzyme-mediated mechanism stimulated by the exposure of visible and/or near UV light. Excision is also an enzyme-mediated mechanism, but it is not evoked by the effects of radiation exposure only [3,15].
It is not known how long microbes may survive in the stratosphere, but many studies have shown that the period may vary within several months or even years [14,16]. Most of the stratospheric studies are focused on the characterization of microbes (i.e., the determination of species and the place of origin), while these do not address the other environmental issues, such as how long they can be viable in the stratosphere and/or how atmospheric and biological factors control the cell survival. Answers to these questions can provide a critical framework for understanding the patterns of microbial biogeography and the evolutionary implications of remote diversion through the routes in the upper atmosphere [17].
The aim of this study was to reveal the impacts of UV radiation on bacterial cultures from the biological, biochemical and molecular biological perspective. For experiments, commercial bacterial cultures (Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium) and isolates from patients with bacterial infections (Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) were employed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Atmospheric Conditions
Generally, 19 fundamental physical conditions classified into nine categories (a group of temperatures; precipitations; soils; wind; pressure, vapor and air; relative humidity; sunshine; cloudiness and group of phenomenon) are measured on climatological stations worldwide. These values are used for the processing of climatic characteristics and indicators. Measurements and observation on climatological stations are performed by classical methods through reading the device or observing the phenomenon daily at 7, 14 and 21 h, local time, measuring of precipitation and snow cover at 7 o’clock, whereas the occurrence of precipitation and significant weather events are recorded continuously.
During the flight, there were climatological measurements performed on the Earth’s surface of daily air temperatures, minimum, maximum and average air pressure and the amount of precipitation. Sunrise and sunset were also detected. All of these conditions during the transition of stratospheric balloon into the stratosphere could affect the final values of the experimental flight and are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Climatic data observed on the Earth’s surface before the start of the stratospheric flight.
| Date, Time and Place of Flight | Climatic Data on the Earth’s Surface | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 May 2015 Spisska Nova Ves 7:45 a.m.–9:45 a.m. | sunshine | daily air temperature | air pressure (hPa) | atmospheric precipitations | |||
| sunrise | sunset | / | daily minimum air pressure | daily maximum air pressure | average daily air pressure | / | |
| 4:18 | 18:47 | 13 °C | 980 | 1015 | 997 | 46 | |
During all of time spent by the stratospheric probe in the stratosphere, the temperature outside the probe, pressure and relative humidity were monitored (Figure 1). Temperature during the flight ranged from +10 to −60 °C. The highest temperature was observed at 15,000 meters above sea level. The pressure was lower with increasing altitude. When observing the relative humidity, a similar trend as in the case of pressure monitoring was observed.
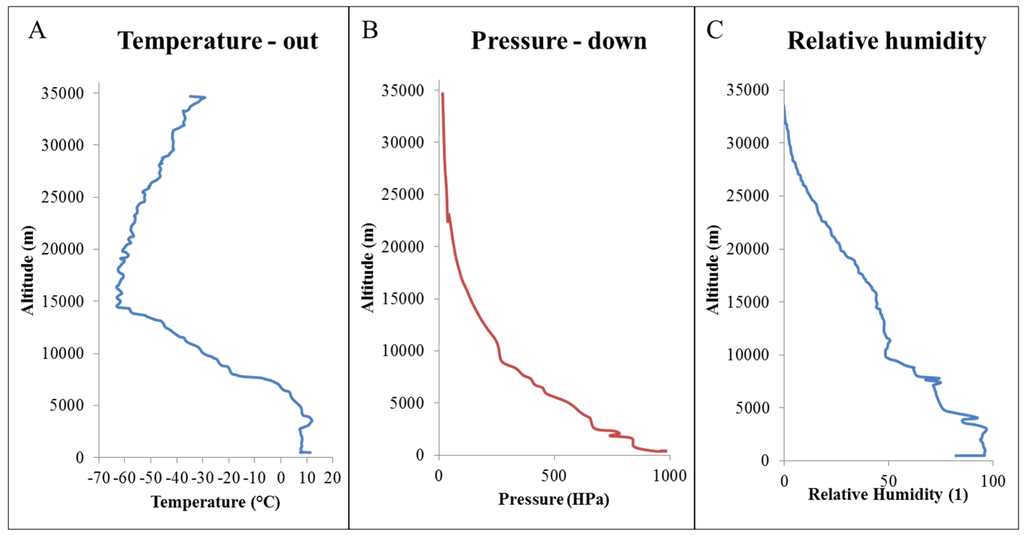
Figure 1.
Conditions observed during the flight of the stratospheric probe in the stratosphere: (A) temperature outside the stratospheric probe, (B) stratospheric pressure and (C) relative humidity.
2.2. Effects on Bacteria
The biological part of the experimental stratospheric flight was primarily focused on studying and the comparison of the effect of laboratory UV radiation (wavelength of 264 nm) and stratospheric UV radiation [18] on bacterial strains’ growth, their resistance to environmental externalities (antibiotics, and/or semimetal nanoparticles) and the protein composition of the bacterial cell wall. 3D printing was used as a technique for producing a probe bearing the bacteria, as this has already been used several times by us for the production platforms for the detection of nucleic bases, bacteria, viruses and others [18,19,20,21].
2.2.1. Growth Properties
The first part of the biological experimental study looked at the growth characteristics of bacteria. Lyophilized bacterial cultures were inoculated in cultivated media, which corresponded to the optimal conditions for bacterial growth by their compositions. Media inoculated with the tested bacterial cultures (E. coli, S. aureus, MRSA, S. typhimurium, P. mirabilis and P. aeruginosa) were immediately placed into the microtiter plate, and from the beginning of the inoculation, the absorbance values at intervals of half an hour were measured. Growth curves showing the progress of the lag phase, the exponential and stationary growth phase of bacteria are in Figure 2A–F for E. coli, S. aureus, MRSA, S. typhimurium, P. mirabilis and P. aeruginosa, respectively.
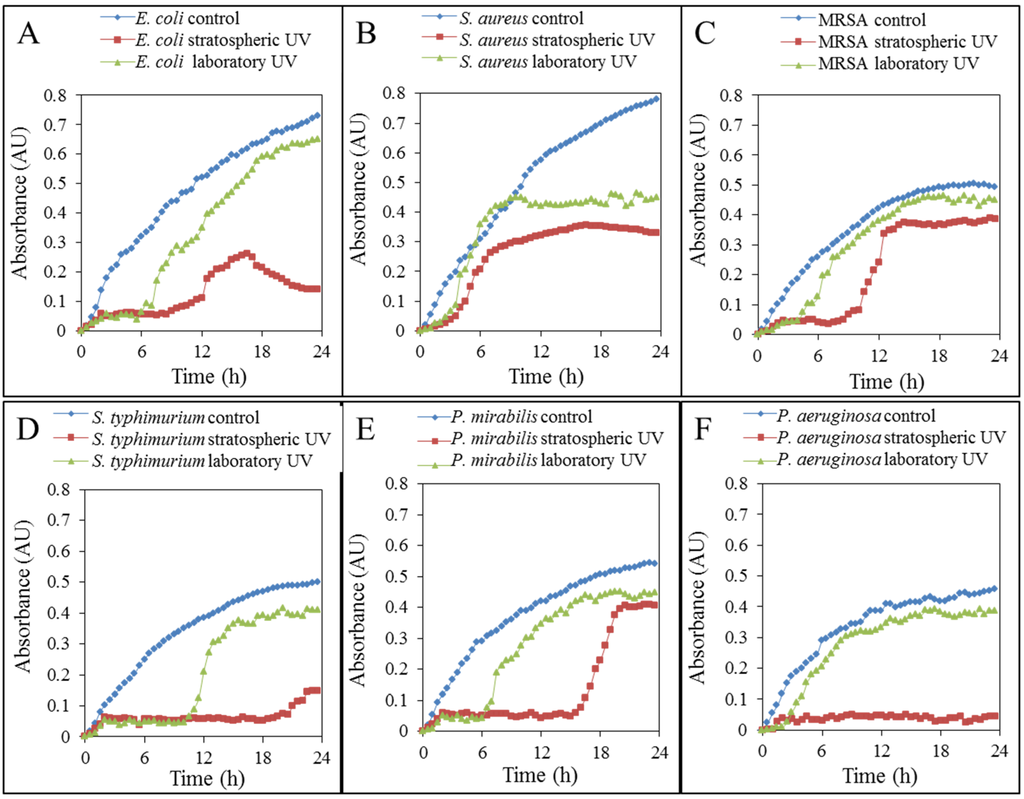
Figure 2.
Growth properties of the bacteria (A) E. coli, (B) S. aureus, (C) MRSA, (D) S. typhimurium, (E) P. mirabilis and (F) P. aeruginosa) without UV exposure, after exposure to laboratory UV and after sending the bacteria into the stratosphere on the surface of the stratospheric probe. Lyophilized bacterial cultures were after the landing of stratospheric probe immediately cultivated in GTY medium, and absorbance at 37 °C in half-hour intervals for 24 hours was measured.
In all tested bacterial cultures, the influence of UV radiation on the growth and reproduction of bacteria was determined, while the laboratory UV of a wavelength of 264 nm always caused lower growth inhibition than exposure to stratospheric UV. It can be therefore assumed that stratospheric UV radiation is more intense and harmful (Figure 2).
The influence of UV radiation of specific wavelengths on bacterial growth was observed in the study done by Poepping et al. [22], which observed the impact of single wavelengths and sequential wavelengths. Log inactivation values for single-wavelength and sequential wavelength exposures were representative of the amount of irradiation attributed to the ranges 225–235 nm and 275–285 nm for representative MP UV doses of 50, 100 and 150 mJ/cm2. Single-wavelength exposures at either 280 nm or 228 nm yielded the expected result in the increasing E. coli inactivation with the increasing dose of the irradiation. Two hundred eighty nanometer single-wavelength exposures resulted in higher E. coli inactivation levels than 228 nm for similar doses, similar to past research showing increased inactivation efficiency of 280 nm versus 228 nm [22].
From the perspective of bacterial resistance, it is known that transparent water and high UV irradiance may maximize the penetration and effect of UV radiation. The study of Escudero et al. mainly deals with the identification of the microbial community composition in Aguas Calientes and with the testing of the UV and antibiotic resistances of some isolates to evaluate co-resistance mechanisms [23]. Both of the analyzed isolates show further inhibition with larger doses of UV-C radiation. Significant differences in survival after UV-C irradiation were observed. Higher survival was observed in Pseudomonas sp. compared to the other gamma Proteobacteria, both isolated from brine samples. Some recent studies point out that the base of the antibiotic resistance in some isolates is not mutagenesis, but the possible formation of multi-resistance to UV radiation [23].
2.2.2. Resistance
In terms of biological properties, the effect of UV radiation (laboratory and stratospheric) on the resistance of bacterial strains to environmental externalities, such as conventional antibiotic drugs or their alternative as selenium nanoparticles [24,25], was further monitored. It was shown that the exposure of UV significantly weakened the resistance of bacteria, and the application of antibiotic drugs or nanoparticles became more effective. When exposed to stratospheric UV, this effect on the bacteria was even higher in comparison to the laboratory UV (Table 2).

Table 2.
Resistance of bacterial cultures to antibiotic drugs or semimetal nanoparticles (1, erythromycin; 2, penicillin; 3, amoxicillin; 4, tetracycline; 5, lincomycin; and 6, selenium nanoparticles) without UV exposure, after exposure to laboratory UV and after exposure to stratospheric UV radiation. Bacterial cultures were exposed to commercial antibiotic drugs in Petri dishes for 24 hours in an incubator at 37 °C. The sizes of the resulting inhibition zones in millimeters indicate the level of the bacterial strains’ resistance to antibiotics. The lower the zone formation, the strain is described as more resistant.
| Bacterial Culture | Type of Exposure | The Size of The Inhibition Zone (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| ERY | PNC | AMX | TTC | LNC | SeNPs | ||
| S. aureus | control | 5 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| laboratory UV | 11 | 5 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 7 | |
| stratospheric UV | 11 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 12 | 7 | |
| MRSA | control | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| laboratory UV | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 8 | |
| stratospheric UV | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 9 | |
| E. coli | control | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| laboratory UV | 0 | 0 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 0 | |
| stratospheric UV | 0 | 0 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 6 | |
| S. typhimurium | control | 2 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| laboratory | 4 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | |
| stratospheric UV | 7 | 4 | 7 | 14 | 2 | 0 | |
| P. mirabilis | control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| laboratory UV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| stratospheric UV | 2 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | |
| P. aeruginosa | control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| laboratory UV | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| stratospheric UV | 2 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 3 | |
2.2.3. Biochemical Markers
Exposure to UV light causes significant biological and biochemical changes. UV radiation represents the most cytotoxic waveband of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface, causing several structural and physiological effects in organisms. Solar radiation elicits a complex chain of cellular events in microorganisms, which are not yet fully understood. The data for the role of UV-induced ROS in biological and biochemical damage to bacteria is rather scarce and mostly obtained indirectly from transcriptomic and proteomic studies reporting the induction of antioxidant defenses upon exposure of bacteria to UV-B radiation. The study of Santos et al. showed that the effects of ROS scavengers on biological and biochemical parameters were variable among the different tested isolates [26]. In this work, two G+ (Micrococcus sp. and Staphylococcus sp.) and two G− (Paracoccus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.) phylogenetically-distinct bacterial isolates were used. Referring to this fact, we confirmed that due to their cell wall characteristics, G+ bacteria have been proposed to be more resistant to UV radiation than G− strains.
Due to this, the changes in biochemical properties were performed by monitoring of the biochemical markers using commercial supplied tests. For the purposes of testing of G+ bacteria (S. aureus, MRSA), an assay for biochemical markers of staphylococci was used. The results of the observation of biochemical markers in G+ bacteria generally points to a very mild effect of UV radiation on the change in the biochemical properties of tested S. aureus and MRSA. In the case of bacterial culture S. aureus in all three cases of testing, the same results were observed; therefore, the influence of UV radiation is assessed as insignificant (Figure 3A). When testing the MRSA (Figure 3B), a strain, which is in many respects more resistant to environmental influences, exposed to laboratory UV compared to the control strain, changes in the fermenting of xylose (Figure 3Bb-2-B), maltose (Figure 3Bb-2-C), mannitol (Figure 3Bb-2-D), trehalose (Figure 3Bb-2-E), sucrose (Figure 3Bb-2-F), galactose, N-acetyl β-D-glucosamine (Figure 3Bb-2-G), xylitol (Figure 3Bb-3-A), raffinose (Figure 3Bb-3-B), arabinose (Figure 3Bb-3-C), cellobiose (Figure 3Bb-3-D), fructose (Figure 3Bb-3-E), ribose (Figure 3Bb-3-F), sorbitol (Figure 3Bb-3-H) and lactose (Figure 3Bb-3-H) were observed (Figure 3Bb). Stratospheric UV exposure in the case of the MRSA strain caused a change in ornithine (Figure 3Bc-1-F) and arginine fermentation (Figure 3Bc-1-G) only, which is shown in Figure 3Bc.
In contrast, testing of the biochemical changes in G- bacteria using a test for biochemical markers of Enterobacteriaceae demonstrated mild changes in laboratory exposure to UV radiation and significant changes in bacteria exposed to UV light in the stratosphere (Figure 4A–C). In the E. coli bacterial strain, substantial changes in biochemical parameters can be monitored, where the laboratory UV exposure to this strain caused the inability to ferment all of the components on the bottom of the wells in the biochemical assay (Figure 4Ab). A similar trend was observed in the E. coli bacterial strain exposed to the stratospheric UV, whereas the fermentation occurred in the case of ornithine (Figure 4Ab-1-E), lysine (Figure 4Ab-1-F), hydrogen sulfide (Figure 4Ab-1-G) and indole (Figure 4Ab-1-H).
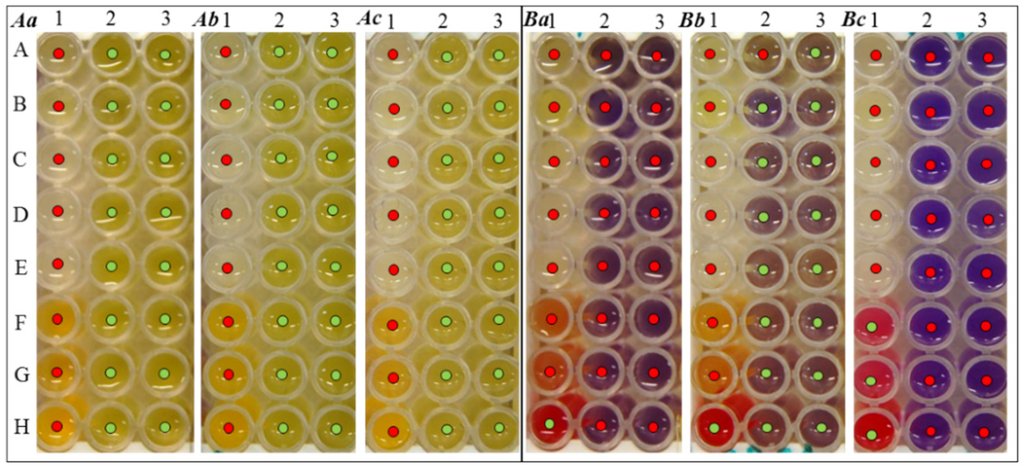
Figure 3.
Biochemical properties of tested G+ bacterial strains (A) S. aureus, and/or (B) MRSA. (a) without UV exposure, (b) after exposure to laboratory UV and (c) after stratospheric UV radiation. Biochemical changes were observed by biochemical markers after 24 hours of incubation in a thermostat at 37 °C. Legend: 1A, aesculin; 1B, phosphatase; 1C, β-glucosidase; 1D, β-glucuronidase; 1E, β galactosidase; 1F, ornithine; 1G, arginine; 1H, urease; 2A, mannose; 2B, xylose; 2C, maltose; 2D, mannite; 2E, trehalose; 2F, saccharose; 2G, galactose; 2H, N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine; 3A, xylitol; 3B, raffinose; 3C, arabinose; 3D, cellobiose; 3E, fructose; 3F, ribose; 3G, sorbitol; 3H, lactose.
Bacterial culture P. mirabilis showed a completely different trend in terms of the ability to ferment various substances. While the control culture without UV exposure was able to ferment ornithine (Figure 4Ba-1-E), lysine (Figure 4Ba-1-F), hydrogen sulfide (Figure 4Ba-1-G) and indole (Figure 4Ba-1-H), only, using exposure to laboratory UV, changes in the inability to ferment hydrogen sulfide (Figure 4Bb-1-G) were found. Significant changes in the biochemistry of bacteria compared to the control by exposure of UV from the stratosphere were observed. P. mirabilis bacteria after irradiation by stratospheric UV are able to ferment trehalose (Figure 4Bc-2-B), sucrose (Figure 4Bc-2-C), cellobiose (Figure 4Bc-2-D), adonitol (Figure 4Bc-2-E), inositol (Figure 4Bc-2-F), β-galactosidase (Figure 4Bc-2-G), phenylalanine (Figure 4Bc-2-H), raffinose (Figure 4Bc-3-C), melibiose (Figure 4Bc-3-D), rhamnose (Figure 4Bc-3-E), sorbitol (Figure 4Bc-3-F), aesculin (Figure 4Bc-3-G) and acetoin (Figure 4Bc-3-H). In contrast, this bacteria lose the ability to ferment ornithine (Figure 4Bc-1-E), lysine (Figure 4Bc-1-F), hydrogen sulfide (Figure 4Bc-1-G) and indole (Figure 4Bc-1-H), as in the previous cases.
A third tested bacterial culture of G- bacteria S. typhimurium exhibited the same biochemical parameters as E. coli. Changes during the exposure to laboratory UV radiation occurred in more than half of the components, such as ornithine (Figure 4Cb-1-E), sucrose (Figure 4Cb-2-C), cellobiose (Figure 4Cb-2-D), adonitol (Figure 4Cb-2-E), inositol (Figure 4Cb-2-F), β-galactosidase (Figure 4Cb-2-G), phenylalanine (Figure 4Cb-2-H), raffinose (Figure 4Cb-3-C), melibiose (Figure 4Cb-3-D), rhamnose (Figure 4Cb-3-E), sorbitol (Figure 4Cb-3-F), aesculin (Figure 4Cb-3-G) and acetoin (Figure 4Cb-3-H). After the exposure to stratospheric UV, S. typhimurium loses the ability to ferment nearly all components, except ornithine (Figure 4Cc-1-E), lysine (Figure 4Cc-1-F), hydrogen sulfide (Figure 4Cc-1-G) and indole (Figure 4Cc-1-H). Changes in biochemical properties were demonstrated in P. aeruginosa bacterial culture (Figure 4D).
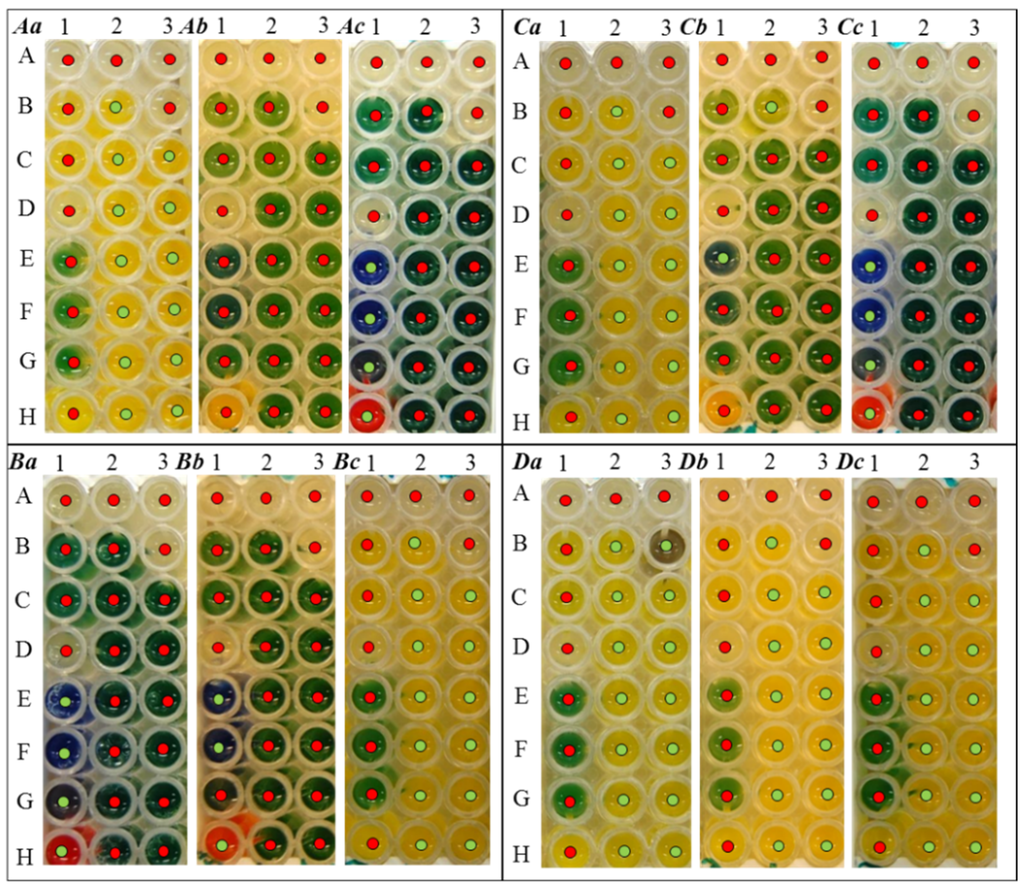
Figure 4.
Biochemical properties of tested G- bacterial strains (A) E. coli, (B) P. mirabilis, (C) S. typhimurium and (D) P. aeruginosa. (a) without UV exposure, (b) after exposure to laboratory UV and (c) after stratospheric UV irradiation. Biochemical changes were observed by the observation of the biochemical markers of Enterobacteriaceae after 24 hours of incubation in a thermostat at 37 °C. Legend: 1A, malonate; 1B, Simmons citrate; 1C, arginine; 1D, urease; 1E, ornithine; 1F, lysine; 1G, hydrogen sulfide; 1H, indole; 2A, mannitol; 2B, trehalose; 2C, saccharose; 2D, cellobiose; 2E, adonitol; 2F, inositol; 2G, β galactosidase; 2H, phenylalanine; 3A, glucose; 3B, dulcitol; 3C, raffinose; 3D, melibiose; 3E, rhamnose; 3F, sorbitol; 3G, aesculin; 3H, acetoin.
2.2.4. Proteomic Analyses
Knowledge of the molecular effects of UV radiation on bacteria can contribute to a better understanding of the environmental consequences of enhanced UV levels associated with global climate changes and would help to optimize UV-based disinfection strategies. In the study of Santos et al., it was observed that the exposure to UV radiation caused an increase in methyl groups associated with lipids, lipid oxidation and also led to alterations in lipid composition, which were confirmed by gas chromatography [27]. Additionally, mid-infrared spectroscopy revealed the effects of UV radiation on protein conformation and protein composition, which were confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), oxidative damage to amino acids and changes in the propionylation, glycosylation and/or phosphorylation status of cell proteins [27].
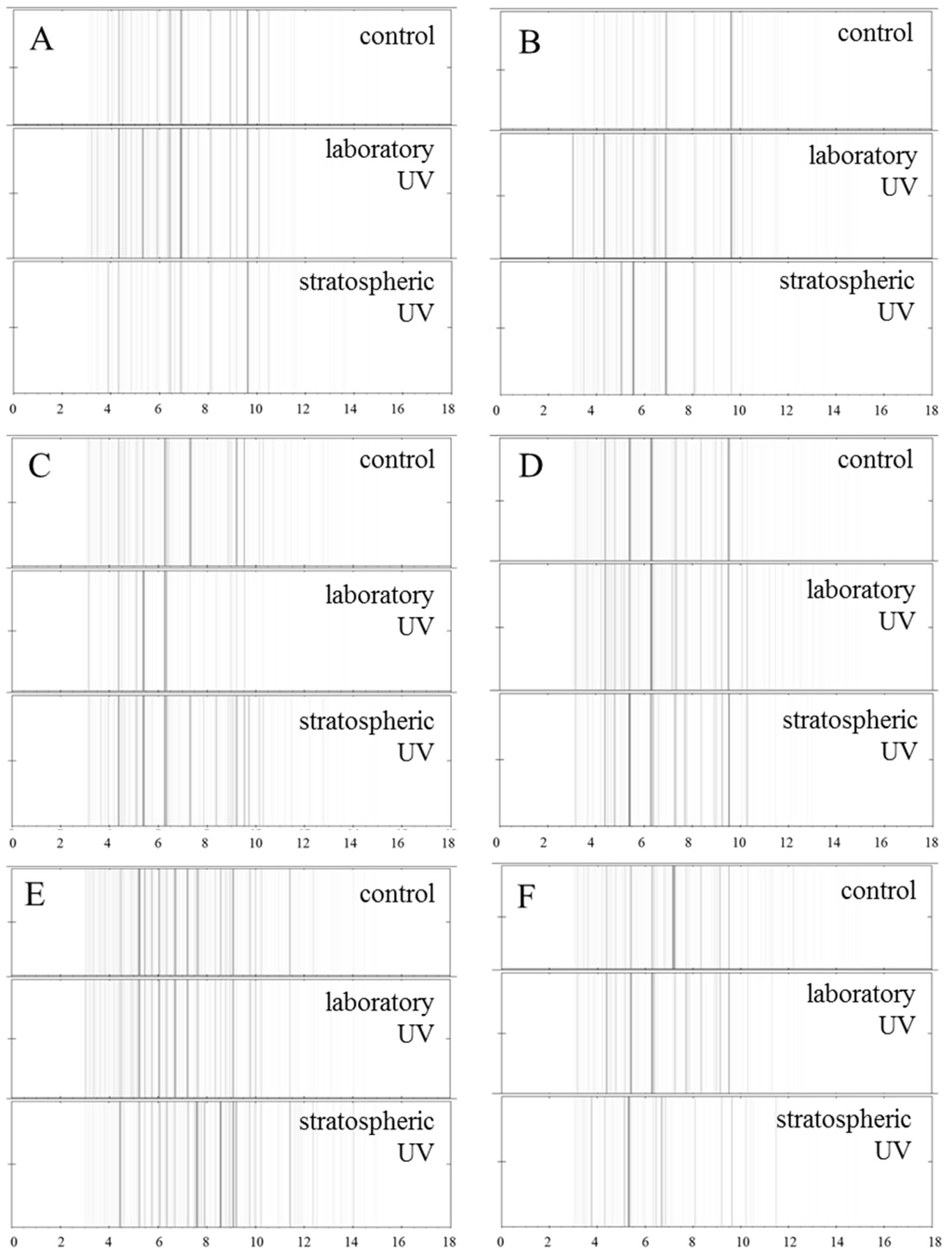
Figure 5.
Pseudo-gel view comparison of MALDI-TOF MS spectra of bacteria without UV exposure, after exposure to the laboratory and stratospheric UV as (A) S. aureus, (B) MRSA, (C) E. coli, (D) S. typhimurium, (E)P. mirabilis and (F) P. aeruginosa. Data were collected in the m/z range 2.000–20.000. For MALDI-TOF analysis, 1 µL of extract of each bacterial culture was used. The control samples were identified by MALDI BioTyperTM software.
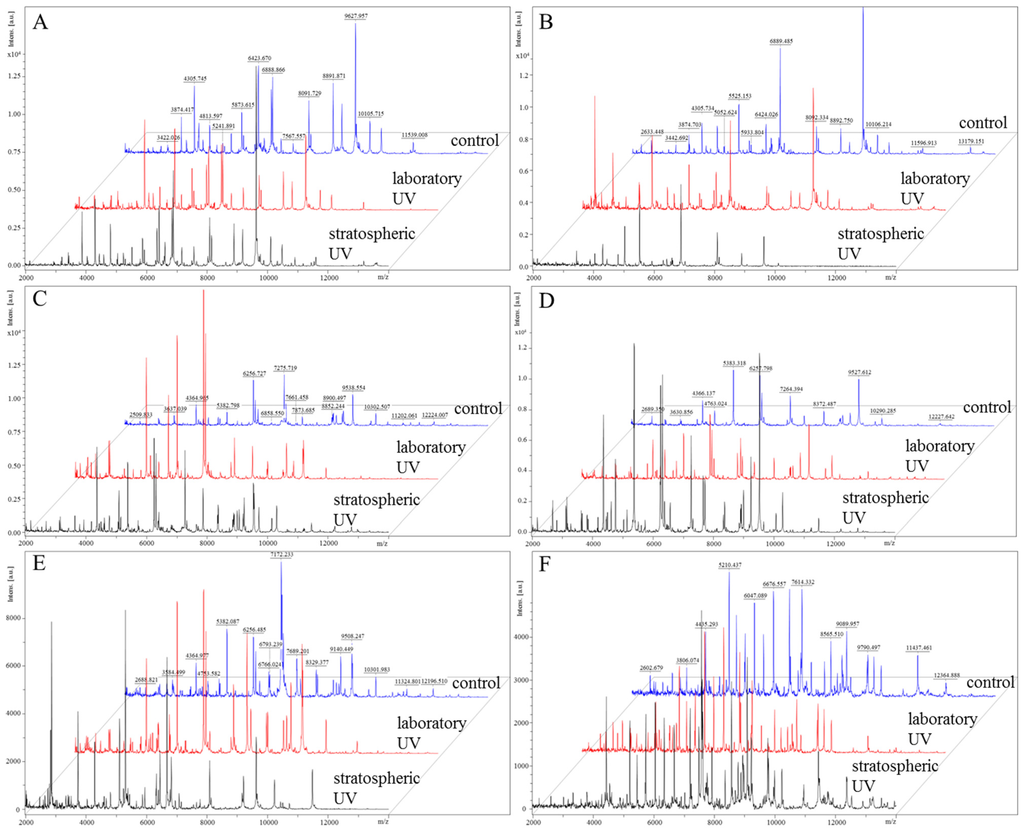
Figure 6.
Comparison of MALDI-TOF MS spectra of bacteria without UV exposure, after exposure to the laboratory and stratospheric UV: (A) S. aureus; (B) MRSA; (C) E. coli; (D) S. typhimurium; (E) P. mirabilis; and (F) P. aeruginosa. Data were collected in the m/z range 2.000–20.000. For MALDI-TOF analysis, 1 µL of extract of each bacterial culture was used. The control samples were identified by MALDI BioTyperTM software.
In the last experiment, the effect of UV radiation on the protein structure in the bacterial cell wall was evaluated [28]. This experiment revealed the influence of UV radiation on the structure and composition of bacteria; however, the intensities of the protein peaks of each tested culture were evaluated as a pseudo gel view (Figure 5). The mass spectra were also compared in a “stacked” view (Figure 6).
The differences of protein peak intensities between experimental groups exposed to UV irradiation in the laboratory and in the stratosphere were significant in all bacterial samples. In a closer view, the most significant differences were observed in MRSA (Figure 5B and Figure 6B), E. coli (Figure 5C and Figure 6C) and P. mirabilis (Figure 5E and Figure 6E). In the case of MRSA (Figure 5B), the peak intensities under stratospheric UV irradiation were lower, and some peaks disappeared within the m/z range from 10 to 14 m/z (10,487, 10,907, 11,597 and 13,179 m/z). Similar effect was also observed in the sample of P. mirabilis (Figure 5E), where peaks of 7246, 7690, 8329, 8898 and 9509 m/z disappeared. On the contrary, in the sample of E. coli (Figure 5C), peaks at 10,141, 10,696 and 11,202 m/z were observed with the lowest intensities in the mass spectrum under laboratory UV irradiation.
For better comparison, a dendrogram from the mass spectra based on the measurement of each bacterial sample (Figure 7) was also created, which showed that the protein profiles of P. mirabilis and MRSA were affected the most after stratospheric UV irradiation. It can be concluded that UV irradiation has an effect on bacterial protein expression. Stratospheric UV irradiation has a higher influence on protein expression than laboratory UV irradiation in most cases. This is probably caused by different conditions in the stratosphere, where other types of radiation with higher intensity than in the laboratory are also present.
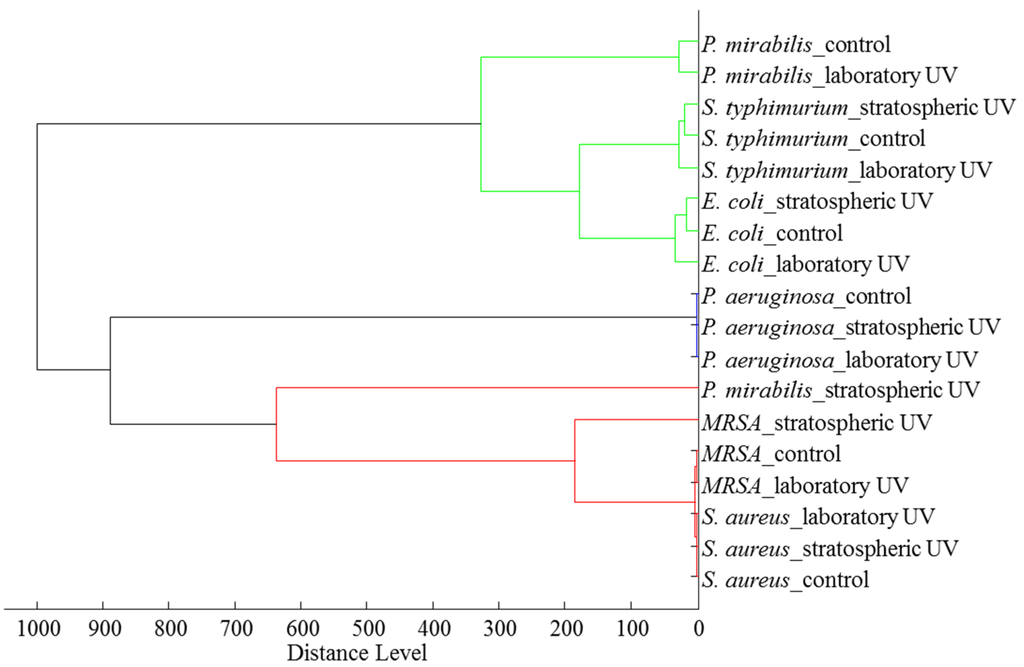
Figure 7.
Dendrogram from the mass spectra of bacteria without UV exposure and after exposure to the laboratory and stratospheric UV. Mass spectra were collected in the m/z range 2.000–20.000. For MALDI-TOF analysis, 1 µL of extract of each bacterial culture was used. The dendrogram was created in MALDI BioTyperTM.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals
The chemicals used in this study were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) in ACS purity (meets the requirements of American Chemical Society (ACS)) unless noted otherwise. Deionized water was prepared using reverse osmosis equipment Aqual 25 (Brno, Czech Republic). Deionized water was further purified by using a Milli-Q Direct QUV apparatus equipped with a UV lamp. The resistance was 18 MΩ. The pH was measured using pH meter WTW inoLab (Weilheim, Germany).
3.2. Lyophilization of Bacterial Cultures
Lyophilization was performed using a Lyophilizer Christ Alpha 1-2 (SciQuip Ltd., Shropshire, United Kingdom). For lyophilization of bacterial cultures, 1 mL of the sample was used in each case.
3.3. The Experimental Conditions
Bacterial cultures for the full stratospheric flight were always prepared in three groups. The first group was the control culture without exposure to UV radiation. The second group of the bacterial culture was exposed to laboratory UV light of a wavelength of 264 nm. The last group of bacterial cultures was sent into the stratosphere by a stratospheric probe attached to its surface (exposed to UV from the stratosphere; temperature: −60 °C).
Exposure of Bacterial Cultures to UV Radiation in the Stratosphere
Lyophilized bacterial cultures were transported by stratospheric balloon to a height of 40 km above sea level. After landing, the samples were immediately transported to the laboratory, where the bacterial cultures were recultivated in GTY (glucose, tryptone, yeast extract) nutrient medium and subsequently tested.
3.4. Measurement of Climatic Conditions
Within the project, sunrise and sunset were recorded, and using the climatological measurements, the daily air temperatures, minimal, maximal and average air pressure and amount of precipitation were monitored, as well. During the stratospheric flight, temperature outside the probe, pressure and relative humidity were detected.
3.5. Cultivation of Bacterial Species
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) were obtained from the Czech Collection of Microorganisms, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University in Brno, Czech Republic. Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) were obtained by isolation from smears, which were collected from infected wounds of patients. Isolated strains were cultivated using selective agars (blood agar; blood agar with 10% NaCl; blood agar with amikacin; Endo agar) and identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. The experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of Trauma hospital in Brno and done with the agreement of patients. A smear was sampled by rolling motion at the site of skin puncture using a sterile swab sampler. All tested bacteria were cultivated as pure strains in non-selective broth (GTY = glucose, tryptone, yeast extract), and these were cultivated for 24 hours on a shaker at 130 rpm and 37 °C. The bacterial culture was diluted by cultivation medium to OD600 = 0.1 for the following experiments.
3.5.1. Determination of Growth Curves
The procedure for the evaluation of bacterial culture growth before and after UV exposure was carried out in accordance to our previously published study [29].
3.5.2. Determination of Bacterial Strain Resistance to Antibiotic Drugs
Petri dishes with GTY agar were coated with the tested bacterial cultures diluted to OD600 = 0.1. On the surface of the plates with the bacterial cultures, antibiotic commercial discs were placed containing the following drugs: erythromycin, penicillin, amoxicillin, tetracycline or lincomycin and a disc with selenium nanoparticles. These dishes were incubated in a thermostat for 24 hours at 37 °C.
3.6. Mass Spectrometry
The following extraction protocol and sample preparation was based on MALDI BioTyper 3.0 User Manual Revision 2, whereas a similar extraction method was used also in [30]. One colony of bacterial cultures was re-suspended in 300 µL of deionized water, and 900 µL of ethanol was added. After centrifugation at 14,000× g for 2 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the obtained pellet was air-dried. The pellet was then dissolved in 25 µL of 70% formic acid (v/v) and 25 µL of acetonitrile and mixed. The samples were centrifuged at 14,000× g for 2 min, and 1 µL of the clear supernatant was spotted in duplicate onto the MALDI target (MTP 384 target polished steel plate; Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) and air-dried at room temperature. Then, each spot was overlaid with 1 µL of saturated α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (HCCA) matrix solution in organic solvent (50% acetonitrile and 2.5% trifluoroacetic acid, both v/v) and air-dried completely prior to MALDI-TOF MS measurement on UltrafleXtreme MS (Bruker). Spectral data were taken in the m/z range of 2.000 Da–20.000 Da, and each was a result of the accumulation of at least 1000 laser shots obtained from ten different regions of the same sample spot. Spectra with peaks outside the allowed average were not considered. Modified spectra were loaded into the MALDI BioTyper™ 3.1 Version (Bruker Daltonics GmbH, Bremen, Germany).
4. Conclusions
The presented study showed the significant effect of UV radiation (laboratory UV and UV from the stratosphere region) on the growth, behavior and structure of bacterial cultures. Bacteria exposed to UV radiation from the stratosphere were part of the probe surface, which was sent into the stratosphere. It was shown that these cultures become more sensitive to adverse environmental influences with stronger and more intensive action of UV radiation in the stratosphere, whereas their growth was significantly inhibited and their basic structural characteristics were changed. Even a short-term effect of UV radiation significantly modulates the protein composition and behavior of microorganisms, and therefore, it can be assumed that just the UV at a time when the atmosphere was not as effective as today accelerated the development of the desirable characteristics of organisms and thus participated in the management of the development of life as we know it today.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from STRATO-NANOBIOLAB CZ/FMP.17A/0436 is highly acknowledged. The authors wish to express their thanks to Radek Chmela for the perfect technical cooperation.
Author Contributions
Dagmar Chudobova tested the effect of UV radiation on the biological activity and growth properties of the tested microorganisms and prepared the manuscript. Kristyna Cihalova tested the effect of UV radiation on the ability to form resistance to antibiotics of the tested microorganisms and participated in the preparation of the manuscript. Pavlina Jelinkova tested the effect of UV radiation on the biochemical properties of the tested microorganisms and participated in the preparation of the figures. Jan Zitka designed and manufactured the stratospheric probe using 3D printing. Lukas Nejdl participated in the 3D printing, the preparation of samples for microbiological measurements and participated in the preparation of the manuscript. Roman Guran tested the effect of UV radiation on the proteomic profiles of the tested microorganisms. Martin Klimanek cooperated in the coordination of the flight and the design of the study. Vojtech Adam participated in the design of the study and in the drafting of the manuscript. Rene Kizek participated in the design and coordination of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interests.
References
- Mone, M.J.; Volker, M.; Nikaido, O.; Mullenders, L.H.F.; van Zeeland, A.A.; Verschure, P.J.; Manders, E.M.M.; van Driel, R. Local UV induced DNA damage in cell nuclei results in local transcription inhibition. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.A.; Bounty, S.; Linden, K.G. Long-range quantitative PCR for determining inactivation of adenovirus 2 by ultraviolet light. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1854–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.P.; Hader, D.P. UV-induced DNA damage and repair: A review. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Douki, T.; Ravanat, J.L. Oxidatively generated base damage to cellular DNA. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Sage, E.; Douki, T. Ultraviolet radiation-mediated damage to cellular DNA. Mutat. Res. 2005, 571, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douki, T. The variety of UV-induced pyrimidine dimeric photoproducts in DNA as shown by chromatographic quantification methods. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 1286–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasinghe, C. The universe: A cryogenic habitat for microbial life. Cryobiology 2004, 48, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaji, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Suresh, K.; Reddy, G.S.N.; Dutt, C.B.S.; Wainwright, M.; Narlikar, J.V.; Bhargava, P.M. Bacillus aerius sp nov., Bacillus aerophilus sp nov., Bacillus stratosphericus sp nov and Bacillus altitudinis sp nov., isolated from cryogenic tubes used for collecting air samples from high altitudes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Griffin, D.W.; Schuerger, A.C. Stratospheric microbiology at 20 km over the Pacific Ocean. Aerobiologia 2010, 26, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.W. Terrestrial microorganisms at an altitude of 20,000 m in Earth’s atmosphere. Aerobiologia 2004, 20, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, M.; Wickramasinghe, N.C.; Narlikar, J.V.; Rajaratnam, P.; Perkins, J. Bacteria in the stratosphere-confirmation of viable but non-cultureable forms. In Instruments, Methods, and Missions for Astrobiology VII; Hoover, R.B., Rozanov, A.Y., Eds.; Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering: Bellingham, USA, 2004; Vol. 5163, pp. 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Imshenetsky, A.A.; Lysenko, S.V.; Kazakov, G.A. Upper boundary of biosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papke, R.T.; Ward, D.M. The importance of physical isolation to microbial diversification. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Griffin, D.W.; McPeters, R.D.; Ward, P.D.; Schuerger, A.C. Microbial survival in the stratosphere and implications for global dispersal. Aerobiologia 2011, 27, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, F. Light and dark in chromatin repair: Repair of UV-induced DNA lesions by photolyase and nucleotide excision repair. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 6585–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, N.C.; Stewart, M.; Granger, D.; Guzik, T.G.; Christner, B.C. A method for sampling microbial aerosols using high altitude balloons. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 107, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudin, V.; Khatattov, B. Introduction to atmospheric chemistry and constituent transport. In Data Assimilation; Lahoz, M., Khattatov, B., Eds.; Springer-Verlag Berlin: Berlin, France, 2010; pp. 409–430. [Google Scholar]
- Chudobova, D.; Cihalova, K.; Skalickova, S.; Zitka, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Milosavljevic, V.; Hynek, D.; Kopel, P.; Vesely, R.; Adam, V.; et al. 3D-printed chip for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus labeled with gold nanoparticles. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heger, Z.; Zitka, J.; Cernei, N.; Krizkova, S.; Sztalmachova, M.; Kopel, P.; Masarik, M.; Hodek, P.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V.; et al. 3D-printed biosensor with poly (dimethylsiloxane) reservoir for magnetic separation and quantum dots-based immunolabeling of metallothionein. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejcova, L.; Nejdl, L.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Zurek, M.; Matousek, M.; Hynek, D.; Zitka, O.; Kopel, P.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. 3D printed chip for electrochemical detection of influenza virus labeled with CdS quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachova, J.; Tmejova, K.; Kopel, P.; Korabik, M.; Zitka, J.; Hynek, D.; Kynicky, J.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. A 3D microfluidic chip for electrochemical detection of hydrolysed nucleic bases by a modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors 2015, 15, 2438–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poepping, C.; Beck, S.E.; Wright, H.; Linden, K.G. Evaluation of DNA damage reversal during medium-pressure UV disinfection. Water Res. 2014, 56, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero, L.; Chong, G.; Demergasso, C.; Farias, M.E.; Cabrol, N.A.; Grin, E.; Minkley, E.; Yu, Y. Investigating microbial diversity and UV radiation impact at the high-altitude Lake Aguas Calientes, Chile. In Instruments, Methods, and Missions for Astrobiology X; Hoover, R.B., Levin, G.V., Rozanov, A.Y., Davies, P.C.W., Eds.; Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering: Bellingham, USA, 2007; Vol. 6694, pp. 236–245. [Google Scholar]
- Chudobova, D.; Dostalova, S.; Blazkova, I.; Michalek, P.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Sklenar, M.; Nejdl, L.; Kudr, J.; Gumulec, J.; Tmejova, K.; et al. Effect of ampicillin, streptomycin, penicillin and tetracycline on metal resistant and non-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3233–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudobova, D.; Cihalova, K.; Dostalova, S.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Tmejova, K.; Kopel, P.; Nejdl, L.; Kudr, J.; Gumulec, J.; et al. Comparison of the effects of silver phosphate and selenium nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus growth reveals potential for selenium particles to prevent infection. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 351, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Henriques, I.; Almeida, A.; Correia, A.; Cunha, A. Contribution of reactive oxygen species to UV-B-induced damage in bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2012, 117, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Moreirinha, C.; Lopes, D.; Esteves, A.C.; Henriques, I.; Almeida, A.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Delgadillo, I.; Correia, A.; Cunha, A. Effects of UV radiation on the lipids and proteins of bacteria studied by mid-infrared spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6306–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudobova, D.; Dostalova, S.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Guran, R.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Tmejova, K.; Krizkova, S.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. The effect of metal ions on Staphylococcus aureus revealed by biochemical and mass spectrometric analyses. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 170, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudobova, D.; Nejdl, L.; Gumulec, J.; Krystofova, O.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Kynicky, J.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Kopel, P.; Babula, P.; Adam, V.; et al. Complexes of silver(I) ions and silver phosphate nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid and/or chitosan as promising antimicrobial agents for vascular Grafts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13592–13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, S.; Freiwald, A.; Maier, T.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Kostrzewa, M.; Geider, K. Classification and identification of bacteria by mass spectrometry and computational analysis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).