Biomass Burning Aerosols Observed in Northern Finland during the 2010 Wildfires in Russia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Instrumentation
2.1. Remote Sensing Measurements
2.1.1. PFR
2.1.2. Brewer
2.1.3. FTS
2.1.4. MODIS
2.1.5. AIRS
2.1.6. CALIOP
2.1.7. Ceilometers
2.2. In situ Measurements

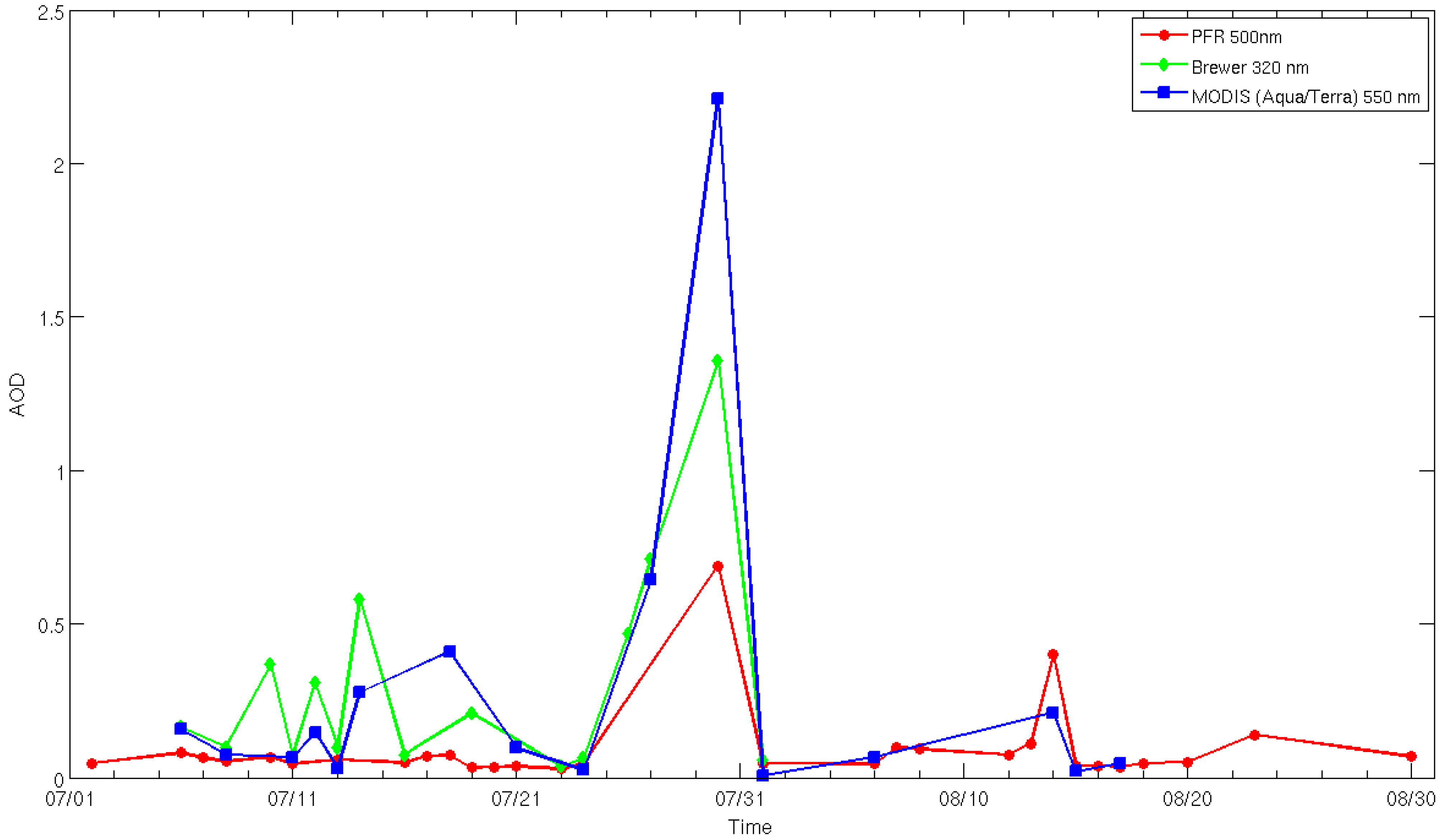
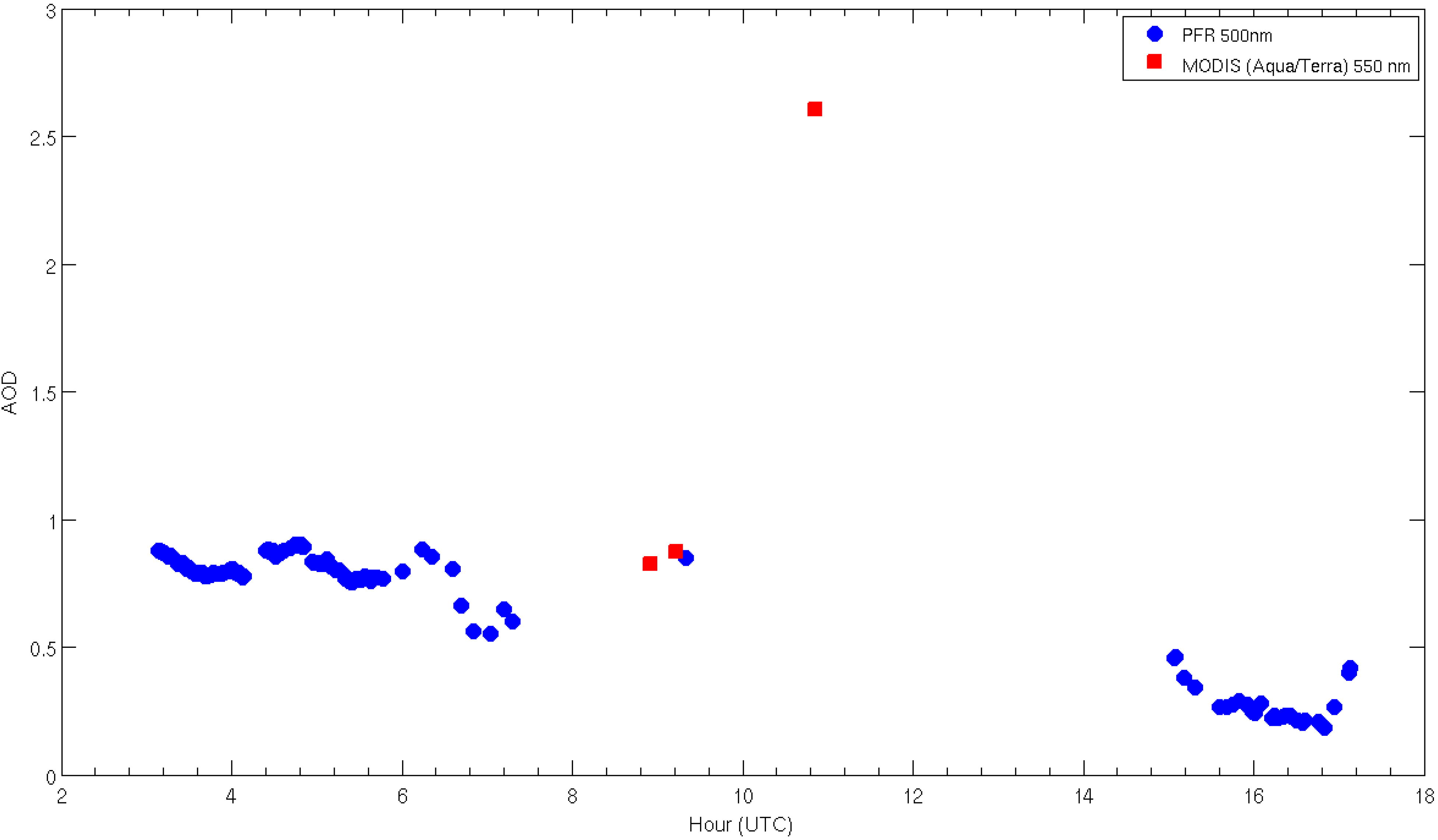
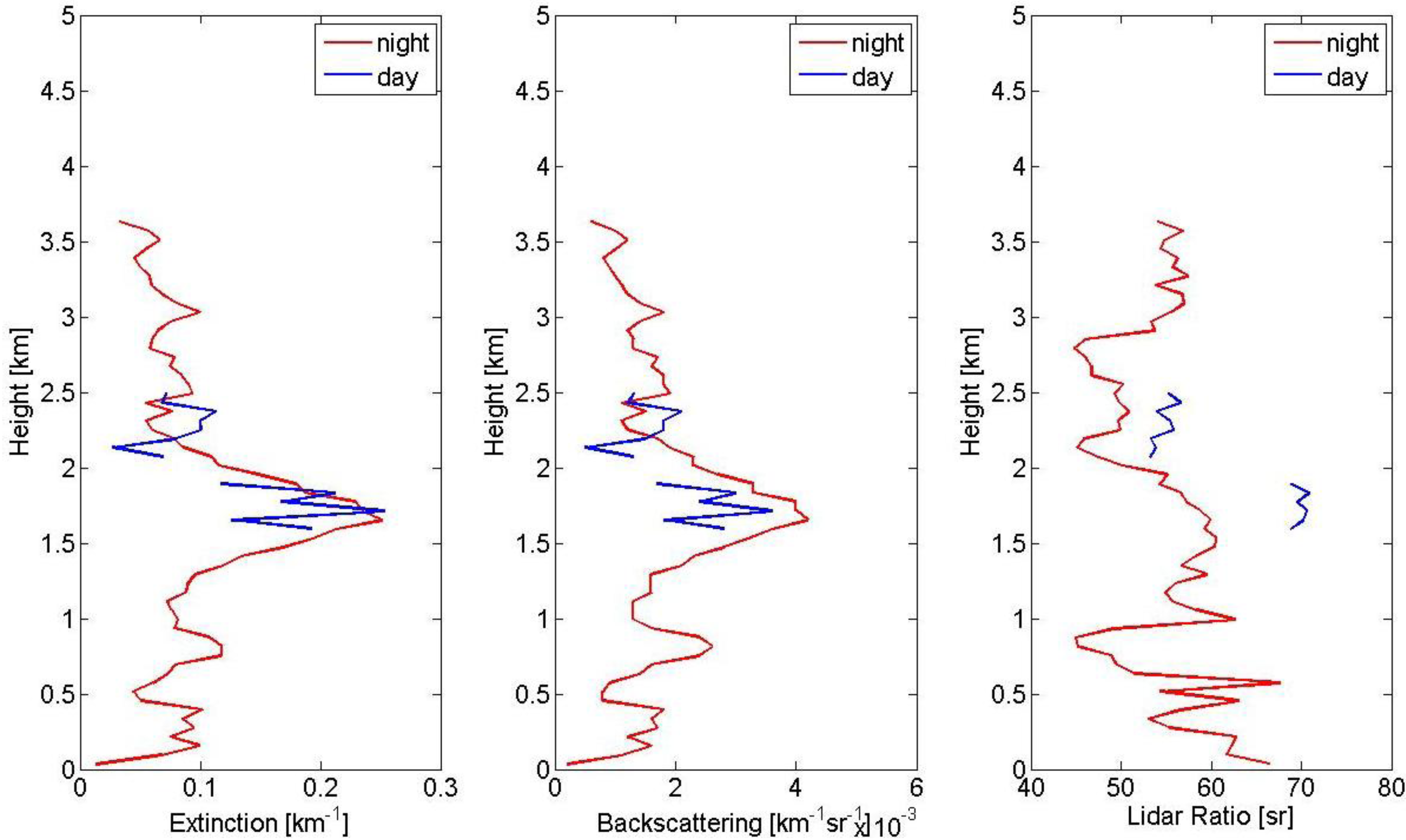
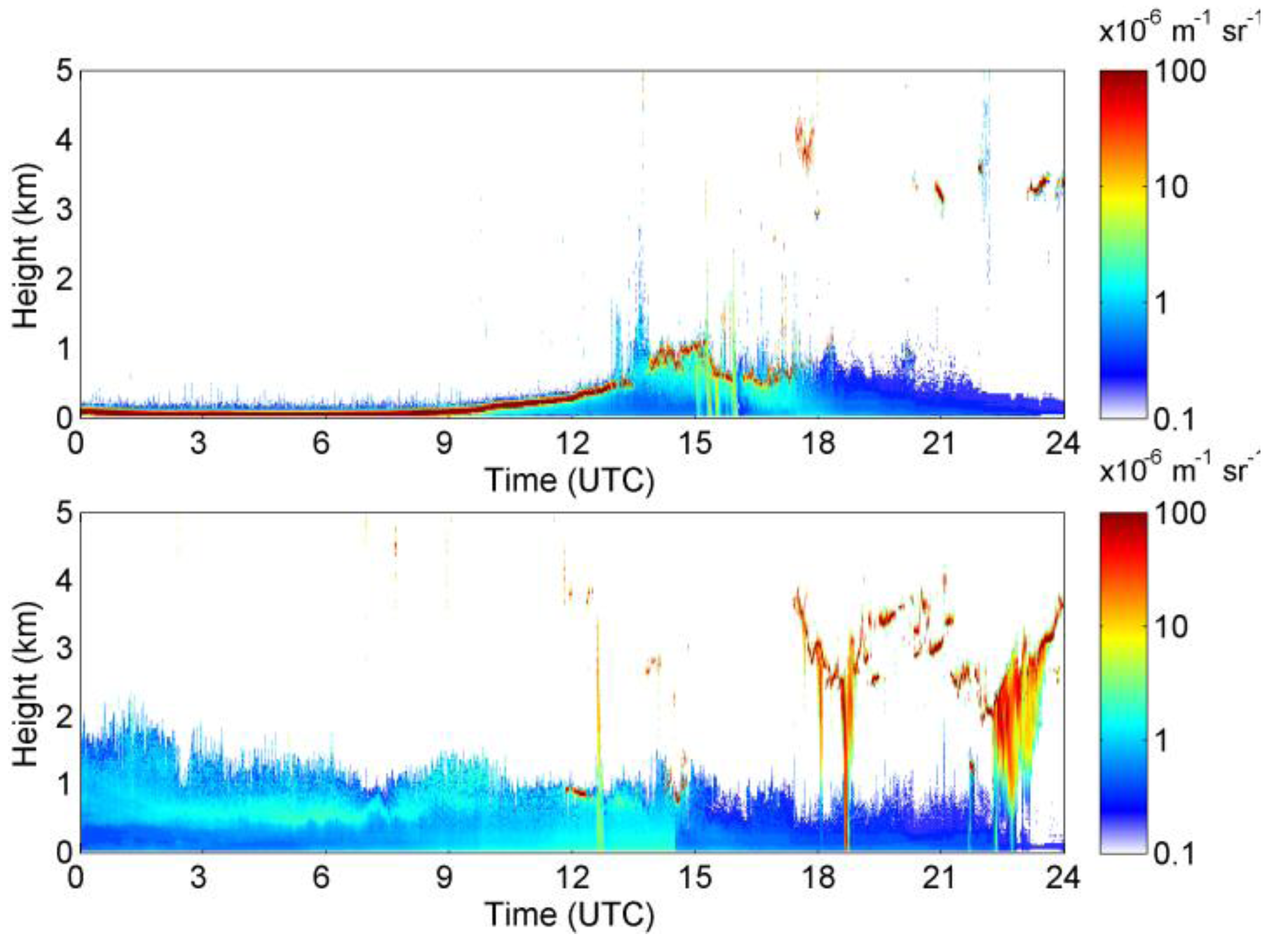
3. Results and Discussion
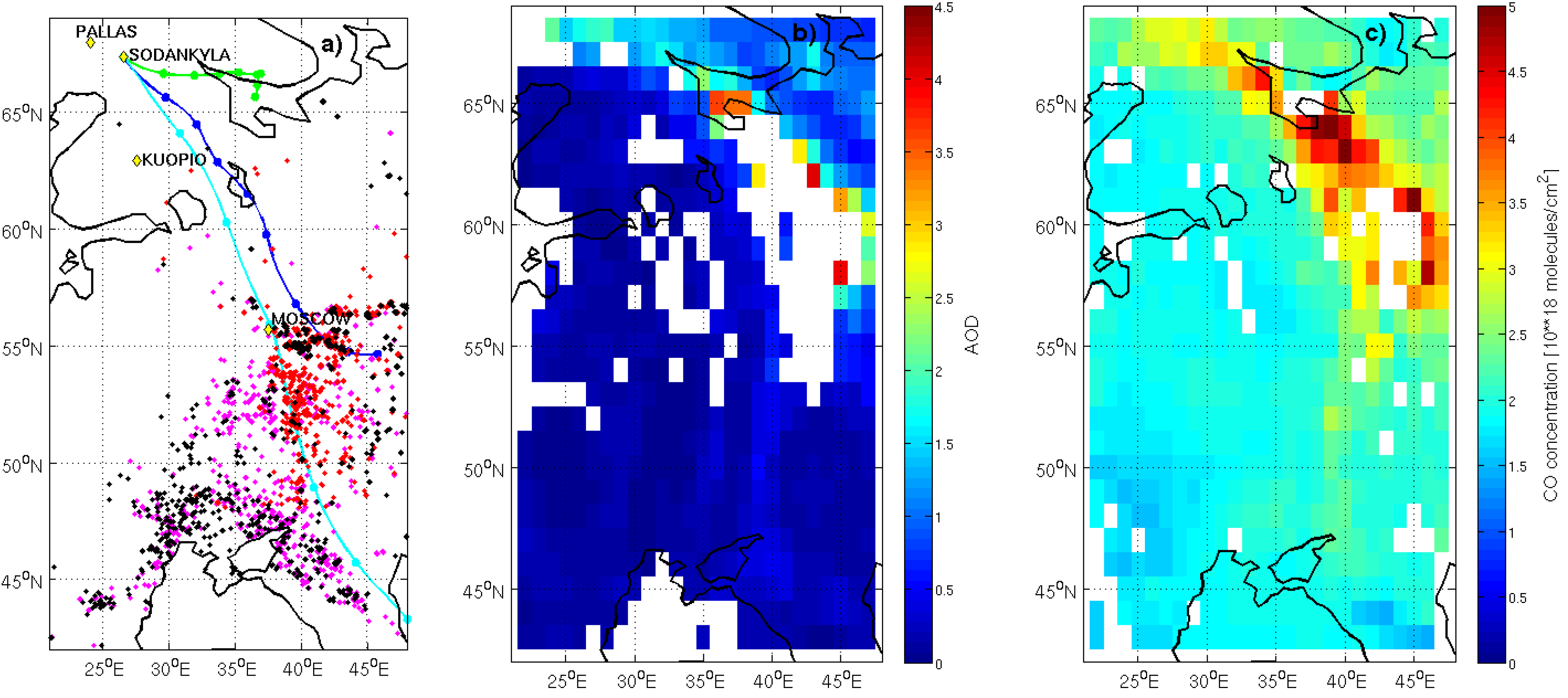
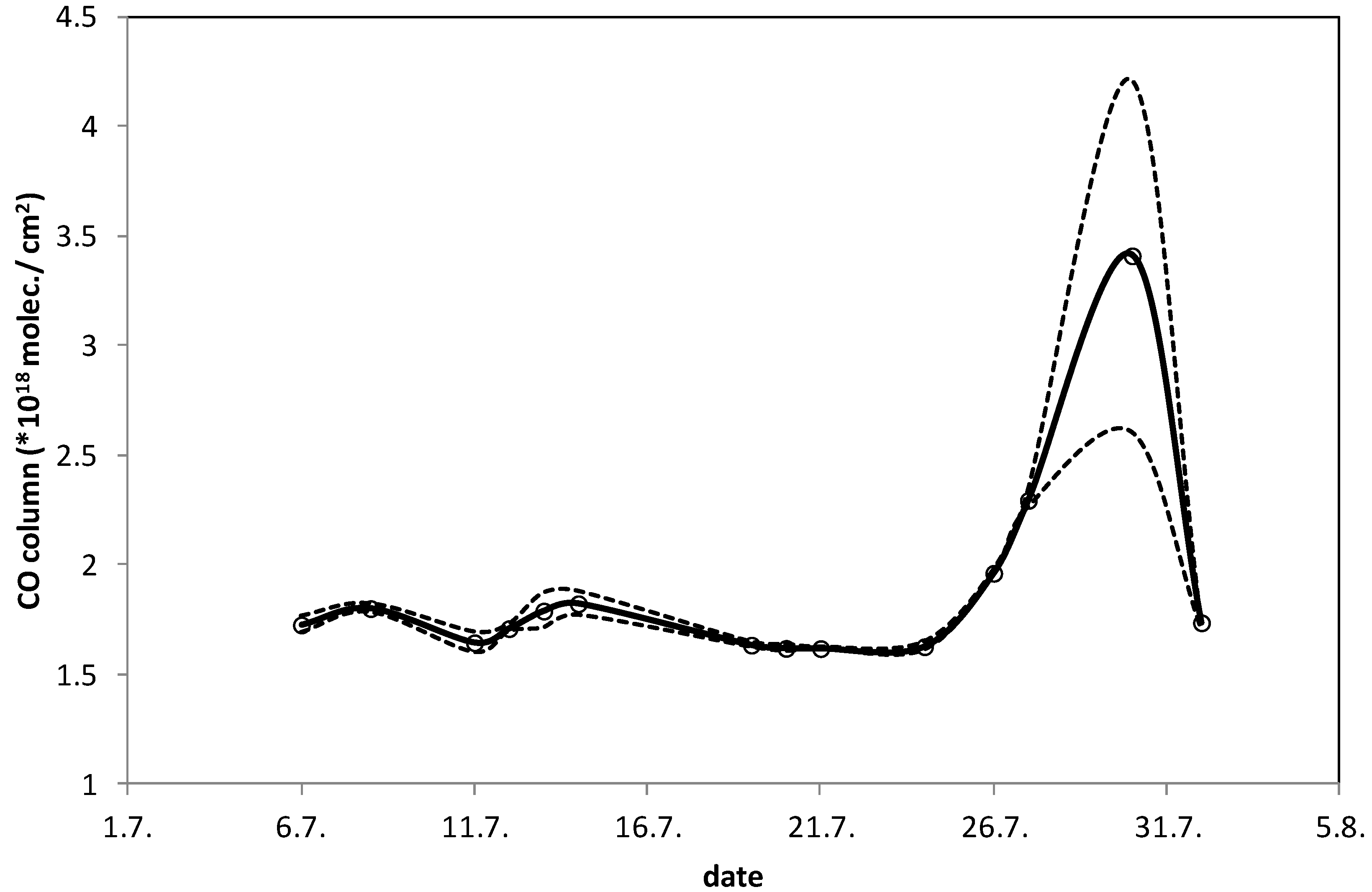
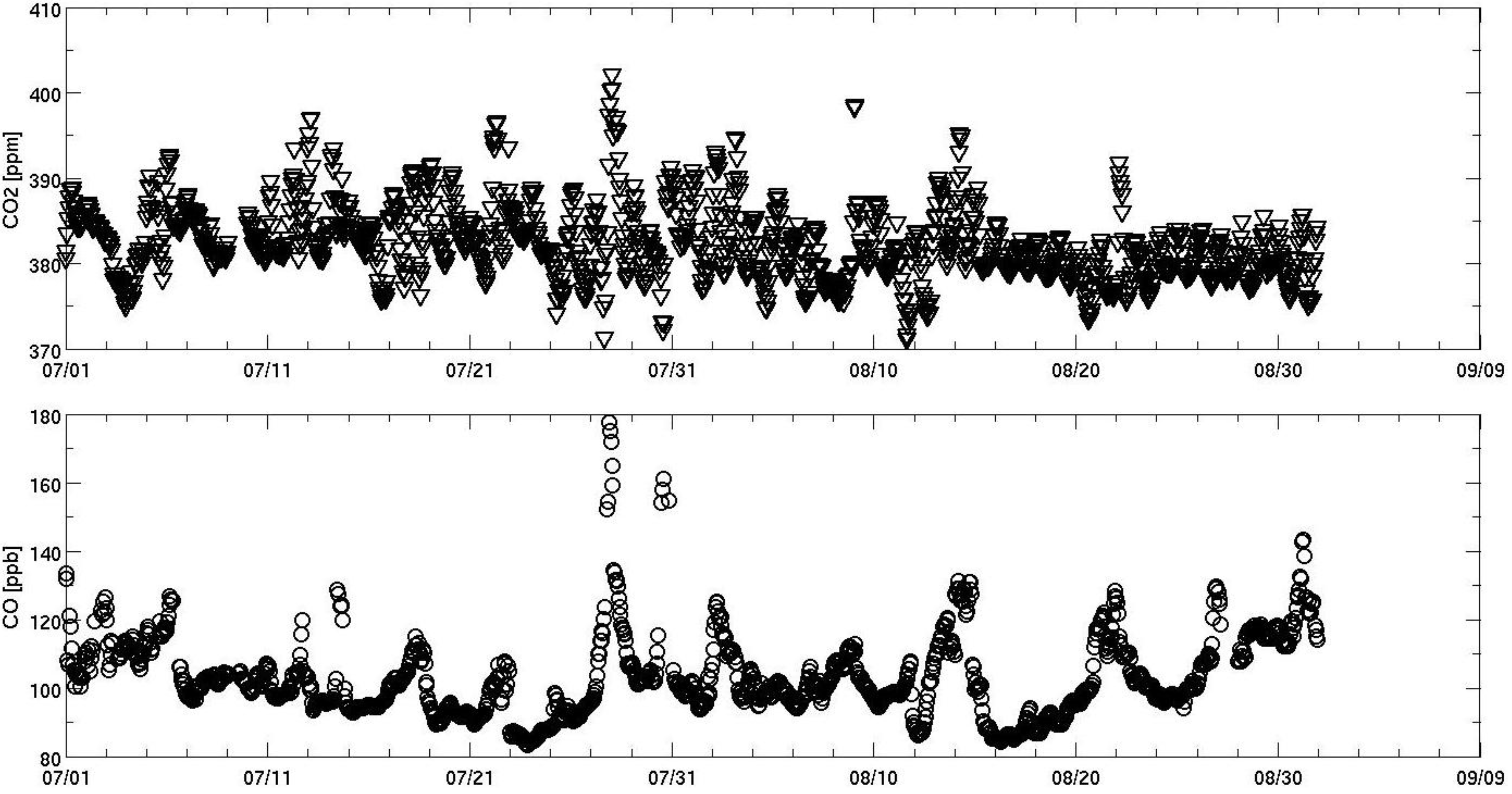
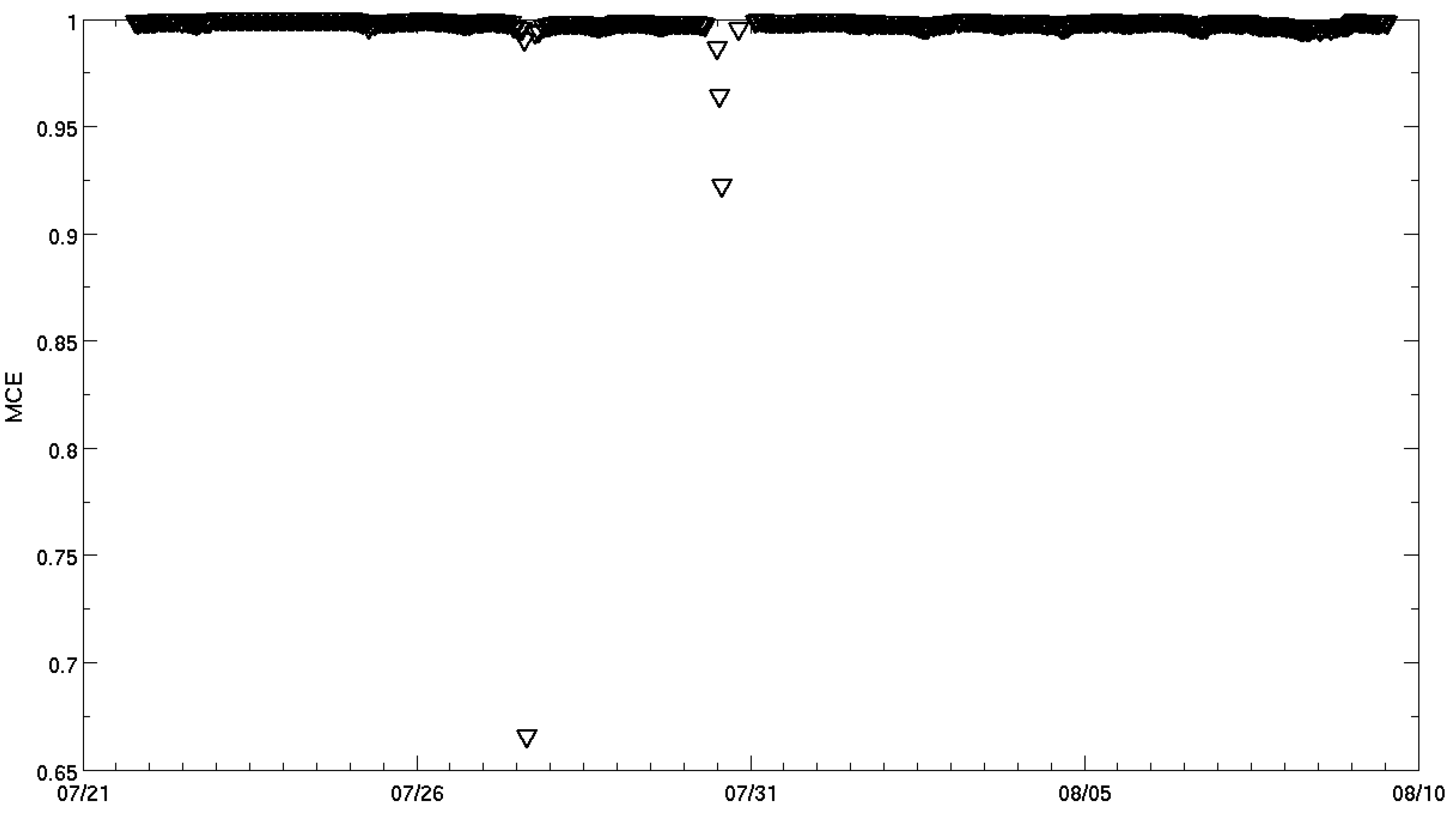
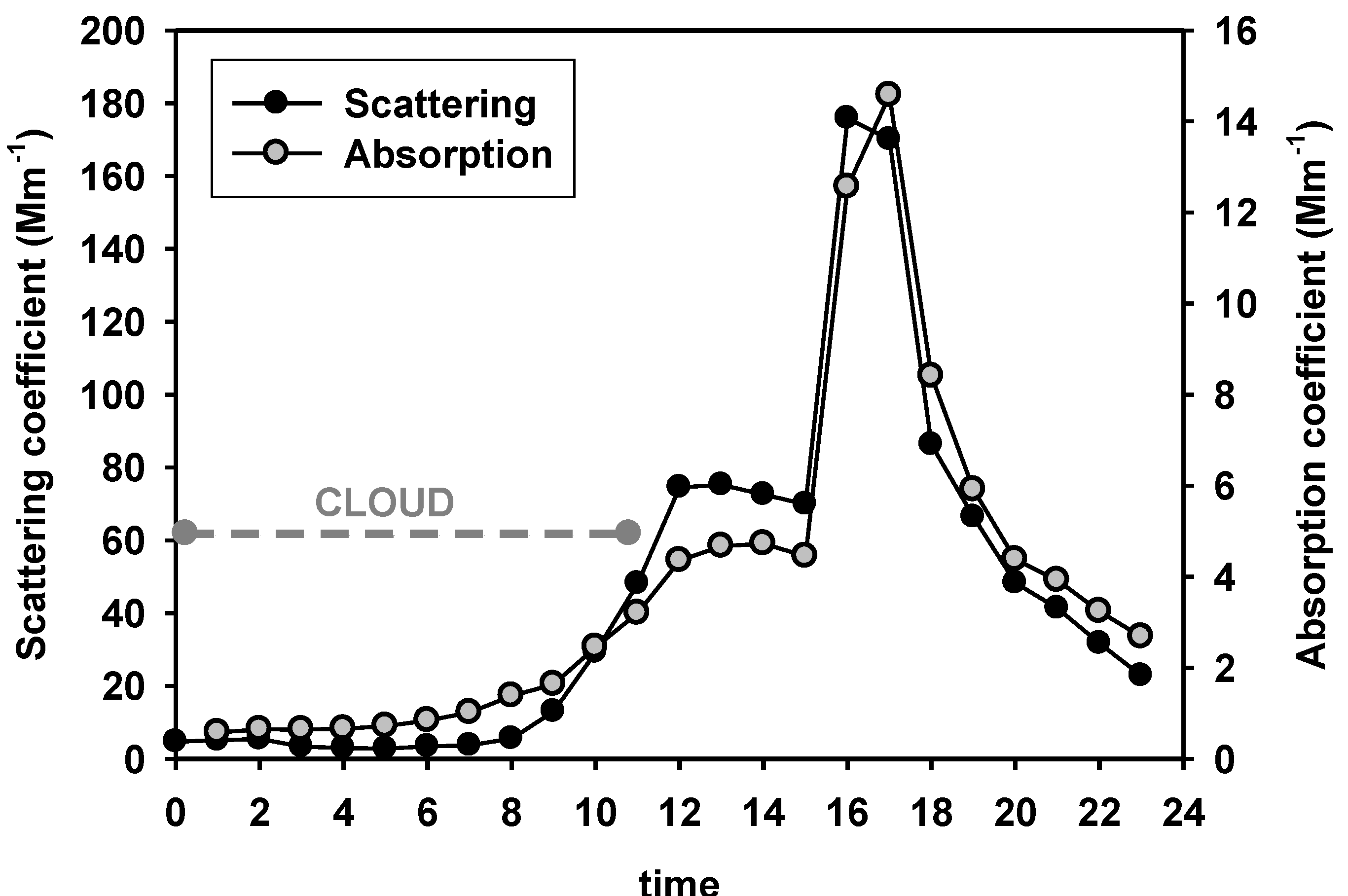
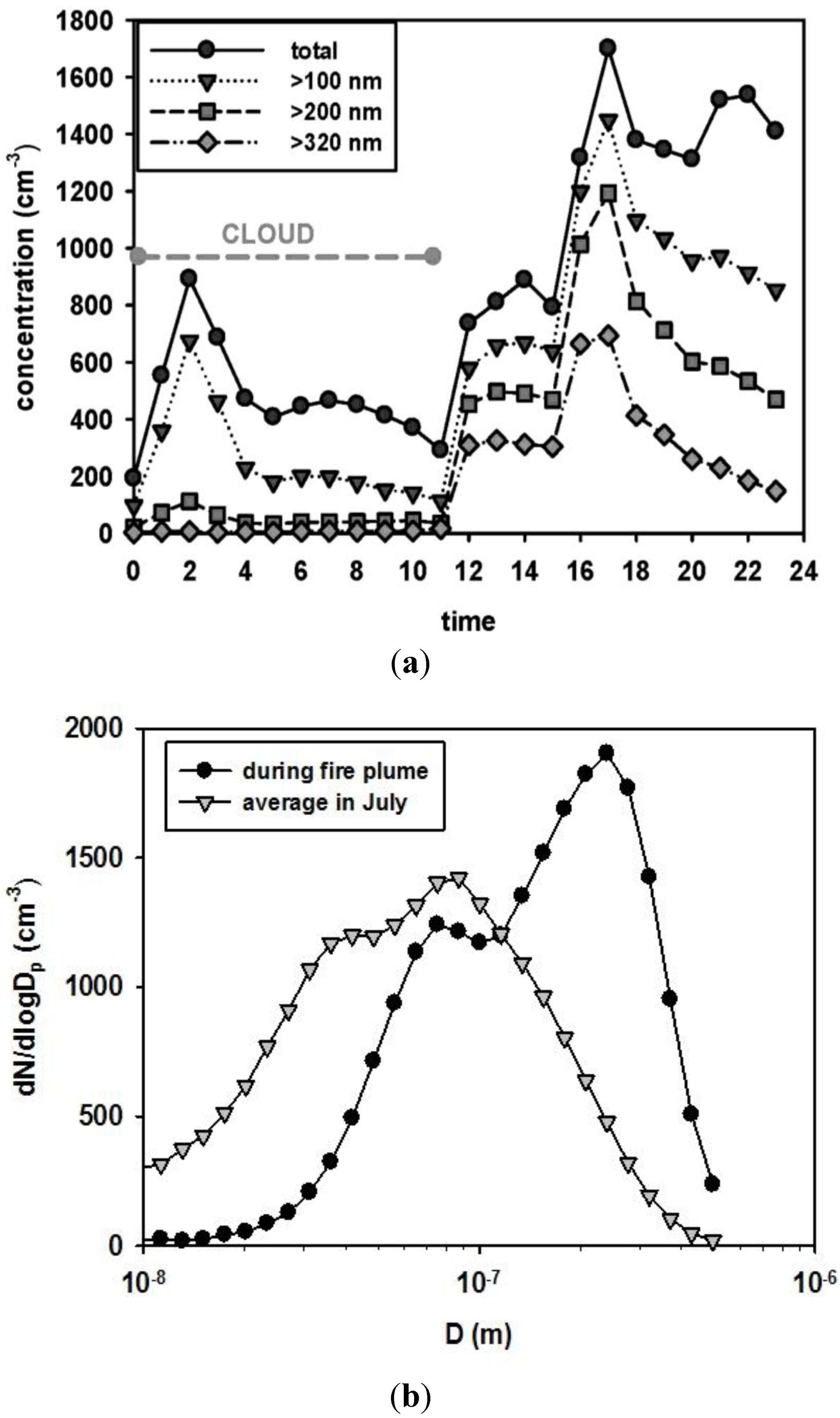
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The daily averaged optical thickness of aerosols increased fourfold, while MODIS AOD was as high as 4.5 for the thickest part of the plume. Cloud screening algorithms may classify thick smoke plumes as clouds.
- (2)
- CO column abundance increased by 100%. According to the FTS measurements, the peak column abundance on 30 July was 5.32 × 1018 molecules/cm2.
- (3)
- MCE values calculated from in situ CO and CO2 measurements indicated that the smoke plumes originated from flaming combustion (30 July) and smoldering peat combustion (27 July).
- (4)
- CALIOP and ceilometer measurements demonstrated that the smoke plume was located close to the surface, below 3 km, and the plume was not homogeneously mixed.
- (5)
- The scattering and absorption coefficients were almost 20 times larger in the smoke plume than in typical conditions.
- (6)
- The total concentration of the aerosols did not change much. However, the number of particles larger than 320 nm increased 14-fold.
- (7)
- During the transport of the plume from eastern to northern Finland, the scattering coefficient, black carbon concentration, and total number concentration decreased 0.5%/h, 1.5%/h and 2.0%/h, respectively.
Acknowledgments
References
- Barriopedro, D.; Fischer, E.M.; Luterbacher, J.; Trigo, R.M.; Garcia-Herrera, R. The hot summer of 2010: Redrawing the temperature record map of Europe. Science 2011, 332, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, J.C.; Douglass, A.R.; da Silva, A.; Torres, O.; Levy, R.; Duncan, B.N. NASA A-Train and Terra observations of the 2010 Russian wildfires. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9287–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Xue, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Guang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, L.; Hou, T.; He, X.; et al. Integration of remote sensing data and surface observations to estimate the impact of the Russian wildfires over Europe and Asia during August 2010. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 3771–3791. [Google Scholar]
- Yurganov, L.N.; Rakitin, V.; Dzhola, A.; August, T.; Fokeeva, E.; George, M.; Gorchakov, G.; Grechko, E.; Hannon, S.; Karpov, A.; et al. Satellite- and ground-based CO total column observations over 2010 Russian fires: Accuracy of top-down estimates based on thermal IR satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7925–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Levy, R.; DaSilva, A.M.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Chubarova, N.E.; Semutnikova, E.; Cohen, A.J. Satellite-based estimates of ground-level fine particulate matter during extreme events: A case study of the Moscow fires in 2010. Atmos. Env. 2011, 45, 6225–6232. [Google Scholar]
- Konovalov, I.B.; Beekmann, M.; Kuznetsova, I.N.; Yurova, A.; Zvyagintsev, A.M. Atmospheric impacts of the 2010 Russian wildfires: Integrating modelling and measurements of an extreme air pollution episode in the Moscow region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10031–10056. [Google Scholar]
- Warneke, C.; Froyd, K.D.; Brioude, J.; Bahreini, R.; Brock, C.A.; Cozic, J.; de Gouw, J.A.; Fahey, D.W.; Ferrare, R.; Holloway, J.S.; et al. An important contribution to springtime Arctic aerosol from biomass burning in Russia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L01801. [Google Scholar]
- Barnaba, F.; Angelini, F.; Curci, G.; Gobbi, G.P. An important fingerprint of wildfires on the European aerosol load. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10487–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portin, H.J.; Mielonen, T.; Leskinen, A.; Arola, A.; Pärjälä, E.; Romakkaniemi, S.; Laaksonen, A.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Komppula, M. Biomass burning aerosols observed in Eastern Finland during the Russian wildfires in summer 2010—Part 1: In-situ aerosol characterization. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Mielonen, T.; Portin, H.J.; Komppula, M.; Leskinen, A.; Tamminen, J.; Ialongo, I.; Hakkarainen, J.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Arola, A. Biomass burning aerosols observed in Eastern Finland during the Russian wildfires in summer 2010—Part 2: Remote sensing. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Stohl, A.; Berg, T.; Burkhart, J.F.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Forster, C.; Herber, A.; Hov, Ø.; Lunder, C.; McMillan, W.W.; Oltmans, S.; et al. Arctic smoke—Record high air pollution levels in the European Arctic due to agricultural fires in Eastern Europe in spring 2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrli, C. Calibrations of filter radiometers for determination of atmospheric optical depth. Metrologia 2000, 37, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Yoon, S.-C.; Dutton, E.G.; Kim, J.; Wehrli, C.; Holben, B.N. Global surface-based sun photometer network for long-term observations of column aerosol optical properties: Intercomparison of aerosol optical depth. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2008, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlund, T.; Landelius, T.; Josefsson, W. Comparison and uncertainty of aerosol optical depth estimates derived from spectral and broadband measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-screening and quality control algorithms for AERONET database. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Ozone Services Inc. (IOS). 2012. Available online: http://www.io3.ca (accessed on 30 October 2012).
- de La Casinière, A.; Cachorro, V.; Smolskaia, I.; Lenoble, J.; Sorribas, M.; Houet, M.; Massot, O.; Antón, M.; Vilaplana, J.M. Comparative measurements of total ozone amount and aerosol optical depth during a campaign at El Arenosillo, Huelva, Spain. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 3399–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenco, F.; Santacesaria, V.; Bais, A.F.; Balis, D.; di Sarra, A.; Papayannis, A.; Zerefos, C. Optical properties of tropospheric aerosols determined by lidar and spectrophotometric measurements (photochemical activity and solar ultraviolet radiation campaign). Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 6875–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.; Henriques, D. Use of Brewer ozone spectrophotometer for aerosol optical depth measurements on ultraviolet region. Adv. Space Res. 2000, 25, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheymol, A.; de Backer, H. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth in the UV-B at Uccle from Brewer ozone measurements over a long time period 1984-2002. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108((D24)), 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazadzis, S.; Bais, A.; Kouremeti, N.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Garane, K.; Blumthaler, M.; Schallhart, B.; Cede, A. Direct spectral measurements with a Brewer spectroradiometer: Absolute calibration and aerosol optical depth retrieval. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 1691–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröbner, J.; Meleti, C. Aerosol optical depth in the UVB and visible wavelength from Brewer spectrophotometer direct irradiance measurements: 1991-2002. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D09202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheymol, A.; de Backer, H.; Josefsson, W.; Stuebi, R. Comparison and validation of the aerosol optical depth obtained with the Langley plot method in the UV-B from Brewer Ozone Spectrophotometer measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheymol, A.; Gonzalez Sotelino, L.; Lam, K.S.; Kim, J.; Fioletov, V.; Siani, A.M.; de Backer, H. Intercomparison of Aerosol Optical Depth from Brewer Ozone spectrophotometers and CIMEL sunphotometers measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinsland, C.P.; Mahieu, E.; Zander, R.; Jones, N.B.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Goldman, A.; Anderson, J.; Russell, J.M., III.; Demoulin, P.; Notholt, J.; et al. Long-term trends of inorganic chlorine from ground-based infrared solar spectra: Past increases and evidence for stabilization. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigouroux, C.; de Mazière, M.; Demoulin, P.; Servais, C.; Hase, F.; Blumenstock, T.; Kramer, I.; Schneider, M.; Mellqvist, J.; Strandberg, A.; et al. Evaluation of tropospheric and stratospheric ozone trends over Western Europe from ground-based FTIR network observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 6865–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunch, D.; Toon, G.C.; Blavier, J.-F.L.; Washenfelder, A.; Notholt, J.; Connor, B.J.; Griffith, D.W.T.; Sherlock, V.; Wennberg, P.O. The total carbon column observing network. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 2087–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Barnes, W.L.; Maymon, P.W.; Montgomery, H.E.; Ostrow, H. MODIS, advanced facility instrument for studies of the Earth as a system. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1989, 27, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar]
- Goddard Space Flight Center, Level 1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (LAADS Web). 2012. Available online: http://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/data/search.html (accessed on 30 October 2012).
- Acker, J.G.; Leptoukh, G. Online analysis enhances use of NASA earth science data. Eos. Trans. AGU 2007, 88, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.K.; Ilavajhala, S.; Wong, M.M.; Justice, C.O. Fire information for resource management system: Archiving and distributing MODIS active fire data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, H.H.; Chahine, M.T.; Gautier, C.; Goldberg, M.D.; Kalnay, E.; McMillin, L.M.; Revercomb, H.; Revercomb, P.W.; Revercomb, W.L.; Revercomb, D.H.; et al. AIRS/AMSU/HSB on the Aqua mission: Design, science objectives, data products, and processing systems. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote 2003, 41, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, M.T.; Pagano, T.S.; Aumann, H.H.; Atlas, R.; Barnet, C.; Blaisdell, J.; Chen, L.; Divakarla, M.; Fetzer, E.J. AIRS: Improving weather forecasting and providing new data on greenhouse gases. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2006, 87, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA, Giovanni, AIRS Online Visualization and Analysis. 2012. Available online: http://gdata.1.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/daac-bin/G3/gui.cgi?instance_id=AIRS_Level3Daily (accessed on 30 October 2012).
- Winker, D.M.; Pelon, J.; McCormick, M.P. The CALIPSO mission: Spaceborne lidar for observation of aerosols and clouds. Proc. SPIE 2003, 4893, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan, M.; Young, S.; Winker, D.; Powell, K.; Omar, A.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Hostetler, C. Fully automated analysis of space-based lidar data: An overview of the CALIPSO retrieval algorithms and data products. Proc. SPIE 2004, 5575, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial performance assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisala Oyj, Ceilometer CT25K: User’s Guide; Vaisala Oyj: Vantaa, Finland, 2002.
- Emeis, S.; Münkel, C.; Vogt, S.; Müller, W.J.; Schäfer, K. Atmospheric boundary-layer structure from simultaneous SODAR, RASS and ceilometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eresmaa, N.; Karppinen, A.; Joffre, S.M.; Räsänen, J.; Talvitie, H. Mixing height determination by ceilometers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakka, J.; Aalto, T.; Aaltonen, V.; Aurela, M.; Hakola, H.; Komppula, M.; Laurila, T.; Lihavainen, H.; Paatero, J.; Salminen, K.; Viisanen, Y. Overview of the atmospheric research activities and results at Pallas GAW station. Boreal Env. Res. 2003, 8, 365–384. [Google Scholar]
- Aaltonen, V.; Lihavainen, H.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Komppula, M.; Hatakka, J.; Eneroth, K.; Kulmala, M.; Viisanen, Y. Measurements of optical properties of atmospheric aerosols in Northern Finland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, A.-P.; Kolmonen, P.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Virkkula, A.; Leskinen, A.; Komppula, M.; Hatakka, J.; Burkhart, J.; Stohl, A.; Aalto, P.; et al. Aerosol black carbon at five background measurement sites over Finland, a gateway to the Arctic. Atmos. Env. 2011, 45, 4042–4050. [Google Scholar]
- Komppula, M.; Lihavainen, H.; Hatakka, J.; Paatero, J.; Aalto, P.; Kulmala, M.; Viisanen, Y. Observations of new particle formation and size distributions at two different heights and surroundings in subarctic area in northern Finland. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.E.; Radke, L.F. Fire in the Environment: The Ecological, Atmospheric, and Climatic Importance of Vegetation Fires; Dahlem Workshop Reports; Environmental Sciences Research Report 13; Crutzen, P.J., Goldammer, J.G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chischester, UK, 1993; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, J.S.; Koppmann, R.; Eck, T.F.; Eleuterio, D.P. A review of biomass burning emissions part II: Intensive physical properties of biomass burning particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 799–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. Description of the HYSPLIT_4 Modeling System. NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL ARL-224; NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1997; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D. HYSPLIT—HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model. Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 30 October 2012).
- Rolph, G.D. Real-time Environmental Applications and Display sYstem (READY). Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov (accessed on 30 October 2012).
- Iinuma, Y.; Brüggemann, E.; Gnauk, T.; Müller, K.; Andreae, M.O.; Helas, G.; Parmar, R.; Herrmann, H. Source characterization of biomass burning particles: The combustion of selected European conifers, African hardwood, savanna grass, and German and Indonesian peat. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Eck, T.F.; Christopher, S.A.; Koppmann, R.; Dubovik, O.; Eleuterio, D.P.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, E.A.; Zhang, J. A review of biomass burning emissions part III: Intensive optical properties of biomass burning particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 827–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komppula, M.; Lihavainen, H.; Kerminen, V.; Kulmala, M.; Viisanen, Y. Measurements of cloud droplet activation of aerosol particles at a clean subarctic background site. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D06204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mielonen, T.; Aaltonen, V.; Lihavainen, H.; Hyvärinen, A.-P.; Arola, A.; Komppula, M.; Kivi, R. Biomass Burning Aerosols Observed in Northern Finland during the 2010 Wildfires in Russia. Atmosphere 2013, 4, 17-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4010017
Mielonen T, Aaltonen V, Lihavainen H, Hyvärinen A-P, Arola A, Komppula M, Kivi R. Biomass Burning Aerosols Observed in Northern Finland during the 2010 Wildfires in Russia. Atmosphere. 2013; 4(1):17-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleMielonen, Tero, Veijo Aaltonen, Heikki Lihavainen, Antti-Pekka Hyvärinen, Antti Arola, Mika Komppula, and Rigel Kivi. 2013. "Biomass Burning Aerosols Observed in Northern Finland during the 2010 Wildfires in Russia" Atmosphere 4, no. 1: 17-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4010017
APA StyleMielonen, T., Aaltonen, V., Lihavainen, H., Hyvärinen, A.-P., Arola, A., Komppula, M., & Kivi, R. (2013). Biomass Burning Aerosols Observed in Northern Finland during the 2010 Wildfires in Russia. Atmosphere, 4(1), 17-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4010017




