Abstract
Climate change is expected to have an impact on various aspects of health, including mucosal areas involved in allergic inflammatory disorders that include asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis and anaphylaxis. The evidence that links climate change to the exacerbation and the development of allergic disease is increasing and appears to be linked to changes in pollen seasons (duration, onset and intensity) and changes in allergen content of plants and their pollen as it relates to increased sensitization, allergenicity and exacerbations of allergic airway disease. This has significant implications for air quality and for the global food supply.
1. Introduction
There is increasing evidence that climate change will result in more extreme weather events, including an increased frequency of severe droughts and extreme rainfall [1]. The global average surface temperature has increased over time, with observations indicating that it has increased by 0.74 °C over roughly the last century [1]. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has stated that most of the observed warming over the last 50 years is likely to have been due to the increase in greenhouse gas concentrations [1]. Greenhouse gas concentrations have been shown to have increased substantially over recent decades. Measurements made at the Mauna Loa observatory have shown that CO2 concentrations have risen from below 320 parts per million (ppm) in 1960 to greater than 380 ppm in 2010 [2].
Climate change can impact a wide range of environmental processes that have implications for human health. Many studies have demonstrated the impact climate change can have on increasing the ecological range of vectors for disease and other pests. For example, Triatoma bugs transmitting Chagas disease commonly occur in South and Central America, but can now be found north of the Mexican border in Texas [3]. Insect migration due to climate change has recently been noted in a retrospective review of three independent patient databases in Alaska. A Medicaid database of 132,000 Alaskans showed that the incident rate of allergic reactions to insect stings increased from 346 per 100,000 patients in 1999 to 455 per 100,000 patients in 2006. In the interior, sting rates per 100,000 patients increased from 260 a year in 1999 to an average of 437 a year between 2000 and 2006. Regionally, the team saw a sevenfold increase in stings in northern Alaska between 1999 and 2006. One of the potential conclusions was that the increasing annual and winter temperature correlated with the change in habitat, thus promoting exposure to stinging insects with a consequent surge in allergic reactions [4]. However, the impact of climate change on increasing ecological range is not limited to animals, but also includes plants. Invasive plant species have been shown to increase their ecological range as a result of the warming trends associated with climate change [1]. Occurring simultaneously with increasing ecological range, the impacts of climate change on allergic respiratory diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis via changes in aeroallergens such as pollen and mold spores have been emerging as one of the major impacts of climate change on public health [5,6]. In addition, there has been discussion of potential impacts of climate change on the allergen content of plants that are important to the food supply [7,8].
The most recent assessment of the IPCC [1] reported that climate change can result in pole-ward and upward shifts in ranges in plant species; such shifts are likely to be occurring in plant species that produce clinically important pollen. The IPCC concluded that there was “good evidence” that general warming affects the timing of the onset of allergenic pollen production, which may influence pollen abundance and/or potency [9]. Allergies that are associated with pollen result in a significant burden of disease among the population, especially asthmatics [10]. Climate change is a factor in allergic disease [5,11], but currently little is known about how climate change affects allergen development and few studies demonstrate its effects on allergen removal and concentrations.
2. Impacts of Climate Change on Allergenic Plants
2.1. Allergenic Plants
Allergenic grasses predominantly divide into two physiological groups, using the C3 and C4 photosynthetic pathways for carbon fixation. C3 grasses are referred to as “cool season” grasses, that include annuals such as wheat, rye, annual blue grass (annual meadow grass, Poa annua), and oat while perennial cool season grasses include orchard grass (cocksfoot, Dactylis glomerata), fescue (Festuca spp), Kentucky bluegrass and perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). The C4 grasses, also known as “warm season” grasses, have a photosynthetic pathway linked to specialized Kranz leaf anatomy that particularly adapts them to hot climates and an atmosphere low in carbon dioxide. The annual warm season C4 grasses include corn, Sudan grass, pearl millet, perennial big bluestem, Indian grass, Bermuda grass, and switch grass.
C3 plants typically respond better to atmospheric CO2 enrichment than do C4 plants in terms of increasing their rates of photosynthesis and biomass production. C3 plants utilize CO2 in their light independent photosynthesis to produce 3-phosphoglycerate. However, due to enzyme activity leading to photorespiration, C4 plants have developed a mechanism to efficiently deliver CO2 to the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase (RuBisCo enzyme). The enzyme system can enhance the ability of C4 plants to tolerate high temperature and water stress [12]. Thus, C4 plants may have a competitive advantage over plants possessing the common C3 pathway under conditions of drought and high temperatures that are projected to result from climate change. Many allergenic plants use the C4 system, including 550 out of 1,400 Chenopods, 250 of the 1,000 Amarathaceae species, Cynodon dactylon and members of the sedge (Cyperaceae) family, including daisies (Asteraceae).
Currently, there is debate about which type of plants will have the overall competitive advantage as a result of climate change [6]. Projected rising CO2 concentrations may allow C3 plants to out-compete C4 plants because of their ability to thrive in higher CO2 concentrations. This would displace C4 plants, thereby decreasing the biodiversity of certain ecosystems. However, a counter argument is that C4 plants will have better abilities to achieve longer term survival in drier conditions due to being able to cope better with water stress and higher temperatures [12]. An increase in C4 plants may result in ecosystems with more allergenic plant species.
Interestingly, plant physiologists have recently demonstrated that concurrent changes in precipitation, temperature, and CO2 levels may reduce the reproductive effectiveness of plants. This is particularly important for plants that have significant value as a food source. For example, several researchers have shown that increasing CO2 concentrations alone could enhance rice productivity, but Matsui and colleagues [13] showed that conditions simulating climate change, such as elevated temperatures together with increased CO2, resulted in an increase in pollen sterility of the indica rice plant and therefore could reduce the yield of rice crops worldwide. This has dramatic and significant impacts because many countries that rely heavily on rice as a food staple would be severely impacted by shortages. Other researchers have shown temperature increases that are projected to result from climate change also resulted in decreases in pollen germination of peanut and grain sorghum [14], cowpea [15], and sorghum [16] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Impact of increasing CO2 concentrations and temperature on various plant species.
| Common Name | Latin Name | Variables Temp. (day max/night min) °C; CO2 parts per million (ppm) | Location/Method | Observed Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peanut and grain sorghum | Arachis hypogaea; Sorghum bicolor | Temp.: 32/22, 36/26, 40/30, and 44/34 °C; CO2:350 and 700 ppm | Controlled laboratory facility in Gainesville, FL, USA; SPAR chamber with natural sunlight | Elevated temperature decreased germination in both species and elevated CO2 did not alter pollen longevity | [14] |
| Cowpea | Vigna unguiculata | Temp.: 30/22 and 38/30 °C; CO2: 360 and 720 ppm | Controlled laboratory facility in Mississippi, USA; SPAR chamber with natural sunlight | Elevated CO2 did not protect pollen from damage by elevated UV/temperature | [15] |
| Loblolly Pine | Pinus taeda L. | Temp.: ambient summer, not controlled; CO2: ambient and ambient plus 200 ppm | Outdoor plantation plots in North Carolina, USA with vertical CO2 delivery pipes on plot | Elevated CO2 resulted in increased pollen production and pollen production at younger ages and smaller tree sizes | [17] |
| Grain-sorghum | Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench | Temp.: 32/22, 36/26, 40/30 or 44/34 °C; CO2: 350 and 700 ppm | Controlled laboratory facility in Gainesville, FL, USA; SPAR chamber with natural sunlight | Temperature effects on reproductive processes is more severe at elevated CO2 concentrations | [16] |
| Soybean | Glycine max L. | Temp.: 30/22 and 38/30 °C; CO2: 360 and 720 ppm | Controlled laboratory facility in Mississippi, USA; SPAR chamber with natural sunlight | Elevated CO2 did not protect against damaging effects of increased UV-B | [18] |
| Ragweed | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Temp.: constant; CO2: 280, 370, and 600 ppm | Controlled laboratory facility in Maryland, USA; Chambers with artificial lights programmed for specific photon flux | Allergen content increases with elevated CO2 | [19] |
| Ragweed | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Temp.: constant 26/21 °C; CO2:~380 (ambient) and 700 ppm | Glasshouse with controls for CO2, temperature, and lighting (6 hours per day supplemental light) | Elevated CO2 increased pollen production, biomass, and flowered earlier | [20] |
| Ragweed | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Ambient observations with increased temp and CO2 | A transect that ran from Texas to Canada/ambient observations | Increased duration of ragweed pollen season | [21] |
| Ragweed | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Temp.: ambient; CO2: ambient | Central Croatia/ambient measurements of pollen levels | Increased duration of pollen season | [22] |
| Fireweed; also called Willowherb | Epilobium angustifolium | Temp.: ambient; CO2: 350 and 650 ppm | Polyethylene chamber within greenhouse with ambient sunlight and temperature. Also varied nutrient loading in soil and sunlight was supplemented by artificial lighting. Greenhouse located in France or Switzerland | No effect on pollen tube growth but significant effect on pollen germination probability. Some families increased and others decreased | [23] |
| Garden Nasturtium; also called Indian Cress or Monks Cress | Tropaeolum majus | Temp.: constant, 22/16 °C; CO2: ~380 and 760 ppm | Growth cabinets with artificial lighting located in Australia | Elevated CO2 increased nectar secretion rate but did not affect time to flowering, total number of flowers produced, pollen to ovule ratio | [24] |
| rice (cv IR72) | Oryza sativa | Temp.: ambient and ambient plus 4 °C; CO2: Ambient and ambient plus 300 ppm | Open-top chambers Los Banos, Philippines | Increased temperature and CO2 resulted in sterility among pollen grains (less germination) | [13] |
| field bean | Vicia faba L. | Temp.: 18 °C; CO2: 350 and 700 ppm | Climate and CO2 controlled rooms with artificial light | Increased CO2 increased number of flowers by 25%, and these flowers remained for 17% longer time compared to controls | [25] |
There has also been speculation that the overall allergenic content of important food products may be increasing as a result of climate change [7]. For example, peanut allergy is the most common cause of food-related death and it has been observed that the number of young children affected with peanut allergy doubled between 1997 and 2002, leading to speculation that climate change may be one factor contributing to this increase [8]. The issue of increasing food allergen content of important foodstuffs as a potentially serious consequence of climate change has become an additional complication of climate change that has not received enough attention [7].
2.2. Pollen and Aeroallergens
In the context of global climate change and associated increased CO2 concentrations and temperature, a number of future climate and air pollution scenarios project increases in concentrations of pollen, an extension of the pollen season, and an increase in the allergenicity of pollen [6].
The effects of climate changes on pollen and aeroallergens may be significant. First, it appears that plants produce a greater quantity of pollen under increased CO2 concentrations [26,27]. Studies found a significant increase in ragweed pollen production under an approximate doubling of the atmospheric CO2 concentration [19,26,27]. Table 1 summarizes findings indicating that pollen production of many common plants increased significantly with increasing temperature and CO2. The trends in pollen amount over time have been observed in some regions of the world and are summarized by Beggs [28]. Second, there is some evidence of significantly stronger allergenicity in pollen from trees grown at increased temperatures. Hjelmroos and his colleagues studied the heterogeneity of antigenic proteins and allergens within individual White birch (Betula pendula) trees in the Northern Hemisphere and found the pollens from the trees growing on the south side contain the greatest antigenic proteins [29]. Higher temperature on the south sides of trees probably partly contributed to the finding. A later study by Ahlholm and colleagues [30] assessed the quantity of the major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, produced by mountain birch, grown at two temperatures and discovered that the pollen from the mountain birch trees grown at higher temperatures had significantly stronger allergenicity [30]. Singer and colleagues [19] showed similar results in ragweed pollen where the pollen allergen Amb a 1 content increased with increasing CO2.
Finally, changes in climate appear to have changed the temporal and spatial distribution of pollen [6]. Many studies have indicated that the pollen season is beginning earlier in the year for a number of species in various parts of the world. Climate changes can advance phenological spring events, such as flowering by six days and delay of autumn events by five days, compared with the early 1960s [31]. These changes have been described most thoroughly in Europe and are summarized by Beggs [28].
Although there is evidence of a trend toward increasing annual pollen production in some European species over the last 30 years, research to date for the most part has not revealed major long-term trends in pollen production in the United States. However, early studies in the United States revealed variable results with some downward trends [32]. Despite the mixed evidence regarding past trends, recent studies suggest that future climate change could affect the timing and severity of the pollen season. For example, several recent studies have demonstrated earlier pollination (0.84 days per year) of trees compared to grasses or weeds [33] and longer pollination seasons [34]. Recent studies have also observed that over the last 18 years the pollen season has increased by four days in the Northeastern United States [35,36,37].
2.3. Mold Spores
Whereas a number of pollen types have been examined in relation to meteorological variables, few studies have examined the potential impacts of climate change on allergenic fungal species. A significant work conducted by Corden and Millington [38] examined long-term trends of Alternaria spore concentrations in Derby, UK from 1970 to 1998. The seasonal Alternaria spore concentrations showed a distinct upward trend over this period and a trend for an earlier seasonal start [38,39]. Increased atmospheric concentrations of some mold-spore types were found to be associated with increased temperature and humidity [40,41]. Ziska and Beggs [6] have also speculated about the impact of climate change on Alternaria spore exposure. Maximum mold concentrations were observed to occur earlier than normal in the year following the warm wet conditions of the 1997–1998 El Niño event [42] and perhaps the timing of mold counts could have also been affected by climate change [42].
3. Allergic Effects on Human Populations
The association between biological aerosols, such as pollen and fungal spores, and a host of allergic disorders has been well documented. Aeroallergen exposure is directly associated with two principal allergic diseases: allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and asthma. Biological aerosols could interact with chemical air pollutants to produce an interactive effect that may compound the risk of asthma exacerbation [43]. Some researchers have argued that this interaction may actually promote the development of asthma [44]. As a result of climate change, increased allergen exposures may act synergistically with pollutant exposures, such as diesel exhaust particles, to increase the rate of primary allergic sensitization to the allergen in atopic individuals [45] and enhance allergic response and subsequently increase allergic respiratory disease in the upcoming years [44]. For example, diesel exhaust particles can disrupt pollen particles upon physical contact, leading to the release of paucimicronic particles that may contain allergenic proteins [46,47,48]. Studies have suggested that an increase in hospital visits for asthma could be expected from anthropogenic pollutants alone, biological aerosols alone, and a heightened severity in admissions when anthropogenic and biological aerosols are both present [43,44,45].
Warmer average temperatures have been associated with an increase of asthma prevalence [49,50,51]. An increase in mean temperature of 1 °C was associated with an increase in asthma prevalence of almost 1% in a New Zealand study [49]. The Mediterranean climate was associated with an increase in prevalence of asthma attacks and asthma-like symptoms in young adults living in 13 areas from two different Italian climatic regions [50]. A prospective study found that exercise-induced asthma was aggravated in birch pollen allergic asthmatics when compared with non-birch pollen allergic asthmatics because of the warmer and more humid weather in the pollen season in spring [52]. A study in Italy also supported the relationship between higher annual mean temperatures and asthma-like symptoms [51].
There are several potential mechanisms by which climate change might affect allergic disease. First, longer pollen seasons may increase the duration of human exposure to aeroallergens and may thus increase allergic sensitization. Second, longer pollen seasons may increase the duration of allergy symptoms in individuals with allergic disease. Finally, higher atmospheric pollen counts may increase the severity of allergic symptoms [5,11]. Over the past half a century, allergic rhinitis appears to be increasing in the United States and globally with the prevalence increasing from 10 to 30%, coincident with climate changes [53]. This also coincides with the prevalence of allergic sensitization that was described as part of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III (1988–1994), which showed that 26.2% of the USA population was sensitized to ragweed, 27.5% of the USA population was sensitized to indoor allergens associated with dust mites, and another 26.9% were sensitized to the aeroallergens of perennial rye grass [54]. The increase in the USA studies represented almost a 10% increase in a relatively short period of time from the prior population study in NHANES II (1976–1980) [54].
The impact of temperature on seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis in a Taiwanese pediatric population during 1995–1996 demonstrated that increased diagnosis of allergic rhinitis correlated with high non-summer (September–May) aeroallergen exposure in both male and female children [55]. Similarly, a Canadian study of allergies found statistically significant associations between medical consultations for allergic rhinitis and pollen levels, where an increase in medical consultations was observed for several days after high pollen levels were measured [56]. These analyses of medical care for allergic rhinitis have led some researchers to estimate that allergic rhinitis will increase 40% by 2050 due to the increase in annual temperatures associated with climate change [53].
Several studies have utilized hospital-based data to demonstrate various relationships in time trends between ambient pollen levels and hospital-based health care utilization. In particular, studies in Australia [57], Canada [58], NJ, USA [59], and Spain [60] have all shown that pollen levels are associated with an increase in emergency department visits or hospital admissions for asthma. The number of asthma-related hospital admissions and emergency department visits allow for an assessment of the effect of climate change on the presence of respiratory ailments. For example, in the mid-Atlantic region of the United States the typical number of asthma-related hospital admissions varies over time and neural network models suggest that defined peaks will occur during mid-Winter through the mid-Spring and in the early fall [61]. These models also suggest, in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, a low number of asthma hospital admissions in the summer [61]. This same trend can also be observed with state health department data on actual hospital admissions [62] (Figure 1).
Of course, these trends will vary by geographical region and their associated seasonal patterns. Using specific neural network modeling techniques that can make predictions from large multidimensional datasets, researchers in Baltimore, Maryland were able to create models of asthma admissions numbers based on past hospital admissions discharge data [61]. Similar temporal peaks were observed by a multi-year study conducted in Greece, where March was the peak of hospital admissions and August had the minimum number of admissions [63]. These researchers hypothesized that the spring peak is related to tree and grass pollen, whereas the second peak in the early autumn months of September and October is related to a high rate of respiratory infections transmitted among children starting the school year. The seasonality of asthma admissions has also been observed by Green and colleagues [64], who postulated that allergens and viruses may have a synergistic effect on the exacerbation of asthma symptoms and may correlate with adult asthma admissions.
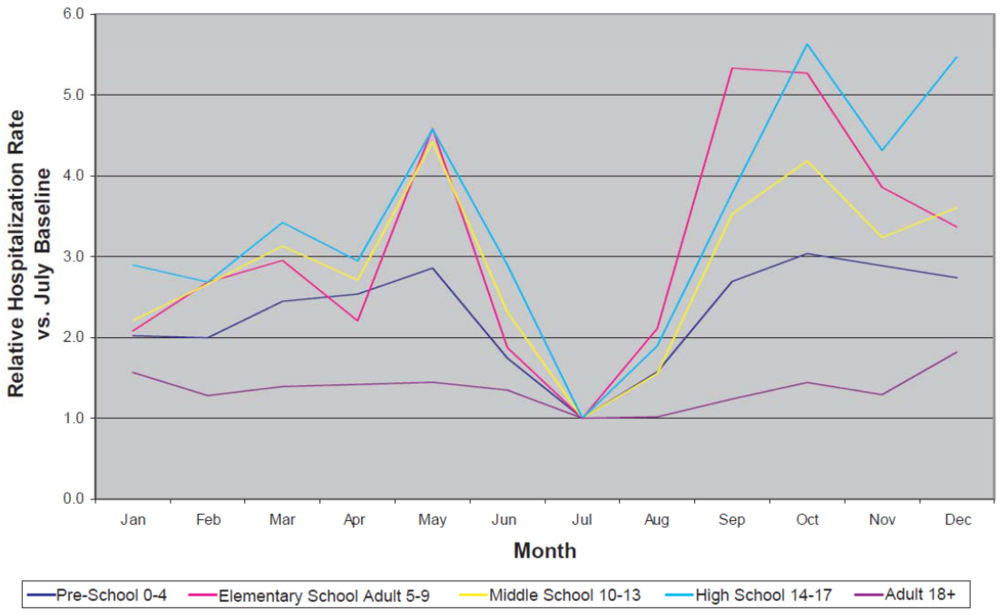
Figure 1.
Seasonal trends in asthma hospitalization related to the presence of aeroallergens. Source: New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services, 2003–2004; NJ Hospital Discharge file (UB-92) ICD-9-CM code: Asthma 493.0–493.9 as the primary diagnosis [62].
4. Conclusions
This review described how climate change will likely have a significant impact on public health through effects mediated by allergens. The significant impact on the human population includes significant increases in allergic diseases, visits to health care providers, and visits to the hospital as a result of asthma exacerbation and adverse allergic reactions to foods. Climate change may likely and paradoxically cause both food shortages because of damage resulting in decreased pollen viability and yet at the same time increase the public health impact of allergic diseases by causing more pollen to be produced for longer periods of time and also increase the allergenic potential of these bioaerosols. The increase in allergen potential is one of the many significant public health hazards resulting from climate change. Several adaption strategies have been described by Beggs [65]. Health care providers and public health professionals must plan to address the increasing burden of allergic diseases in the years to come.
Acknowledgments
The publication is supported in part by a grant from the USEPA, EPA RD-83454701-0 Studies of Impacts Climate-Allergic Airway Disease. The authors would like to thank the reviewers of this manuscript for their assistance.
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2007.
- Tans, P.; Keeling, R. Trends in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Available online: http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/mlo.html#mlo_full (accessed on7 January 2012).
- Beard, C.; Pye, G.; Steurer, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Campman, R.; Peterson, T.; Ramsey, J.; Wirtz, R.; Robinson, L. Chagas disease in a domestic transmission cycle, Southern Texas, US. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, J.G.; Gessner, B.D.; McLaughlin, J.B.; Sikes, D.S.; Foote, J.T. Increasing insect reactions in Alaska: Is this related to changing climate? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2009, 30, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, P.J.; Bambrick, H.J. Is the global rise of asthma an early impact of anthropogenic climate change? Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziska, L.H.; Beggs, P.J. Anthropogenic climate change and allergen exposure: The role of plant biology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, P. Climate change and plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, P.; Walczyk, N. Impacts of climate change on plant food allergens: A previously unrecognised threat to human health. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2008, 1, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2007.
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI). Allergy Statistics (1996–2006). 2008. Available online: http://www.aaaai.org/about-the-aaaai/newsroom/allergy-statistics.aspx#Allergy_Statistics (accessed on 23 Feburary 2012).
- Gamble, J.L.; Reid, C.E.; Post, E.; Sacks, J. Review of the Impacts of Climate Variability and Change on Aeroallergens and Their Associated Effects; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 91, EPA/600/R-06/164F. [Google Scholar]
- Wand, J.K.; Midgley, G.F.; Jones, M.H.; Curtis, P.S. Responses of wild C4 and C3 grass (Poaceae) species to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration: A meta-analytic test of current theories and perceptions. Glob. Change Biol. 1999, 5, 723–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Namuco, O.; Ziska, L.; Horie, T. Effects of high temperature and CO2 concentration on spikelet sterility in indica rice. Field Crops Res. 1997, 51, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.V.; Boote, K.J.; Allen, L.H. Longevity and temperature response of pollen as affected by elevated growth temperature and carbon dioxide in peanut and grain sorghum. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 70, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Kakani, V.G.; Surabhi, G.K.; Reddy, K.R. Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.) genotypes response to multiple abiotic stresses. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 100, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.V.; Boote, K.J.; Allen, L.H. Adverse high temperature effects on pollen viability, seed-set, seed yield and harvest index of grain-sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] are more severe at elevated carbon dioxide due to higher tissue temperatures. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 139, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeau, S.L.; Clark, J.S. Pollen production by Pinus taeda growing in elevated atmospheric CO2. Funct. Ecol. 2006, 20, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koti, S.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, V.R.; Kakani, V.G.; Zhao, D. Interactive effects of carbon dioxide, temperature, and ultraviolet-B radiation on soybean (Glycine max L.) flower and pollen morphology, pollen production, germination, and tube lengths. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, B.; Ziska, L.; Frenz, D.; Gebhard, D.; Straka, J. Increaseing Amb a 1 content in common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) pollen as a function of rising atmospheric CO2 concentration. Funct. Plant Biol. 2005, 32, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.A.; Wayne, P.M.; Macklin, E.A.; Muilenberg, M.L.; Wagner, C.J.; Epstein, P.R.; Bazzaz, F.A. Interaction of the onset of spring and elevated atmospheric CO2 on ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) pollen production. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 865–869. [Google Scholar]
- Ziska, L.; Knowlton, K.; Rogers, C.; Dalan, D.; Tierney, N.; Elder, M.A.; Filley, W.; Shropshire, J.; Ford, L.B.; Hedberg, C.; et al. Recent warming by latitude associated with increased length of ragweed pollen season in central North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4248–4251. [Google Scholar]
- Peternel, R.; Culig, J.; Srnec, L.; Mitić, B.; Vukusić, I.; Hrga, I. Variation in ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) pollen concentration in central Croatia, 2002–2003. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2005, 12, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, C.; Mignot, A.; Stocklin, J. Genetic variation in the response of pollen germination to nutrient availability and elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations in Epilobium angustifolium. Int. J. Plant Sci. 1999, 160, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, J.; Hughes, L. Nectar production and floral characteristics of Tropaeolum majus L. grown in ambient and elevated carbon dioxide. Ann. Bot. 1999, 84, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.; Awmack, C.; Clark, S.; Williams, I.; Mills, V. Nectar and flower production in Vicia faba L. (field bean) at ambient and elevated carbon dioxide. Apidologie 1997, 28, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziska, L.H.; Caulfield, F. Rising CO2 and pollen production of common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia), a known allergy-inducing species: Implications for public health. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 2000, 27, 893–898. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, P.M.; Foster, S.; Connolly, J.; Bazzaz, F.; Epstein, P.R. Production of allergenic pollen by ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) is increased in CO2-enriched atmospheres. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002, 88, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, P.J. Impacts of climate change on aeroallergens: Past and future. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelmroos, M.; Schumacher, M.; van Hage-Hamsten, M. Heterogeneity of pollen proteins within individual Betula pendula trees. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1995, 108, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlholm, J.U.; Helander, M.; Savolainen, J. Genetic and environmental factors affecting the allergenicity of birch (Betula pubescens ssp. czerepanovii [Orl.] Hamet-Ahti) pollen. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1998, 28, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.R.; Post, E.; Convey, P.; Menzel, A.; Parmesan, C.; Beebee, T.J.C.; Fromentin, J.-M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bairlein, F. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 2002, 416, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Bielory, L.; Diaz, C. Aeroallergen prevalence in New Jersey. New Jersey Med.: J. Med. Soc. New Jersey 1988, 85, 503–505. [Google Scholar]
- Clot, B. Trends in airborne pollen: An overview of 21 years of data in Neuchatel (Switzerland). Aerobiologica 2003, 19, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minckley, T.; Whitlock, C. Spatial variation of modern pollen in Oregon and southern Washington, USA. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2000, 112, 97–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, C.I.; Isukapalli, S.S.; Bielory, L.J.; Georgopoulos, P.G. A novel modeling system for estimating pollen emissions: Application to North East US. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, S231. [Google Scholar]
- Witkowska, R.; Benincasa, P.; Bielory, L. Grass pollen trends in New York metropolitan area. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, S92. [Google Scholar]
- Milks, C.; Weiss, M.; Zhao, C.; Diaz, C.; Bielory, L. Emergency Room Asthma Visits (EDVA) lag behind pollen counts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 464, S121. [Google Scholar]
- Corden, J.; Millington, W. The long-term tredns and seasonal variation of the aeroallergen Alternaria in Derby, UK. Aerobiologia 2001, 17, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulimood, T.B.; Corden, J.M.; Bryden, C.; Sharples, L.; Nasser, S.M. Epidemic asthma and the role of the fungal mold Alternaria alternata. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katial, R.K.; Zhang, Y.; Jones, R.H.; Dyer, P.D. Atmospheric mold spore counts in relation to meteorological parameters. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1997, 41, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutt, C.; Levetin, E. Correlation of spring spore concentrations and meteorological conditions in Tulsa, Oklahoma. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2001, 45, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freye, H.B.; King, J.; Litwin, C.M. Variations of pollen and mold concentrations in 1998 during the strong El Niño event of 1997-1998 and their impact on clinical exacerbations of allergic rhinitis, asthma, and sinusiti. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2001, 22, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno, P.M.; Brito, F.F.; Martínez, C.; Tobías, A.; Suárez, L.; Guerra, F.; Galindow, P.A.; Gómez, E. Decompensation of pollen-induced asthma in two towns with different pollution levels in La Mancha, Spain. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, M.I.; Jaakkola, M.S.; London, S.J.; Nel, A.E.; Rogers, C.A. How exposure to environmental tobacco smoke, outdoor air pollutants, and increased pollen burdens influences the incidence of asthm. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, M.A. The effect of air pollution on asthma and allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008, 8, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devalia, J.L.; Rusznak, C.; Davies, R.J. Allergen/irritant interaction—Its role in sensitization and allergic disease. Allergy 1998, 53, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, P.R. Climate change and human health. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1433–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartra, J.; Mullol, J.; del Cuvillo, A.; Davila, I.; Ferrer, M.; Jauregui, I.; Montoro, J.; Sastre, J.; Valero, A. Air pollution and allergens. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 17, S3–S8. [Google Scholar]
- Hales, S.; Lewis, S.; Slater, T.; Crane, J.; Pearce, N. Prevalence of adult asthma symptoms in relation to climate in New Zealand. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marco, R.; Poli, A.; Ferrari, M.; Accordini, S.; Giammanco, G.; Bugiani, M.; Villani, S.; Ponzio, M.; Bono, R.; Carrozzi, L.; et al. The impact of climate and traffic-related NO2 on the prevalence of asthma and allergic rhinitis in Italy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanolin, M.E.; Pattaro, C.; Corsico, A.; Bugiani, M.; Carrozzi, L.; Casali, L.; Dallari, R.; Ferrari, M.; Marinoni, A.; Migliore, E.; et al. The role of climate on the geographic variability of asthma, allergic rhinitis and respiratory symptoms: results from the Italian study of asthma in young adults. Allergy 2004, 59, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, J.; Lindqvist, A.; Laitinen, L.A. Seasonal variability of exercise-induced asthma especially outdoors. Effect of birch pollen allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1989, 19, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R. Climate change blamed for rise in hay fever. Nature 2005, 434, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbes, S.J., Jr.; Gergen, P.J.; Elliott, L.; Zeldin, D.C. Prevalences of positive skin test responses to 10 common allergens in the US population: Results from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Shaw, C.K.; Su, H.J.; Lai, J.S.; Ko, Y.C.; Huang, S.L.; Sung, F.C.; Guo, Y.L. Climate, traffic-related air pollutants and allergic rhinitis prevalence in middle-school children in Taiwan. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, M.C.; Garneau, M.; Fortier, I.; Guay, F.; Louis, J. Relationship between climate, pollen concentrations of Ambrosia and medical consultations for allergic rhinitis in Montreal, 1994–200. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, I.C.; Johnston, F.H. Respiratory hospital admissions were associated with ambient airborne pollen in Darwin, Australia, 2004–2005. Clin. Exp.Allergy 2007, 37, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.E.; Cakmak, S.; Judek, S.; Coates, F. Tree pollen and hospitalization for asthma in Urban Canada. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 146, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lm, W.; Schneider, D. Effect of weed pollen on children’s hospital admissions for asthma during the fall season. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2005, 60, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobías, A.; Galán, I.; Banegas, J.; Aránguez, E. Short term effects of airborne pollen concentrations on asthma epidemic. Thorax 2003, 58, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, D.; Nelson, R.; Levine, E.; Weiss, S.; Bollinger, M.E.; Blaisdell, C. Predicting paediatric asthma hospital admissions and ED visits. Neural Comput. Appl. 2003, 12, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services (NJDHSS), Asthma in NJ Update 2006; NJDHSS: Trenton, NJ, USA, 2006.
- Nastos, P.; Paliastos, A.; Anthracopoulos, M.; Roma, E.; Priftis, K. Outdoor particulate matter and childhood asthma admissions in Athens, Greece: A time-series study. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Custovic, A.; Sanderson, G.; Hunter, J.; Johnston, S.L.; Woodcock, A. Synergism between allergens and viruses and risk of hospital admission with asthma: Case-control study. BMJ 2002, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, P.J. Adaptation to impacts of climate change on aeroallergens and allergic respiratory diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3006–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).