Random Forest-Based Retrieval of XCO2 Concentration from Satellite-Borne Shortwave Infrared Hyperspectral
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Processing
2.1.1. OCO-2 Satellite Data
2.1.2. MODIS MOD04 and MCD43A3 Data
2.1.3. TCCON XCO2 Data
2.1.4. Data Preprocessing
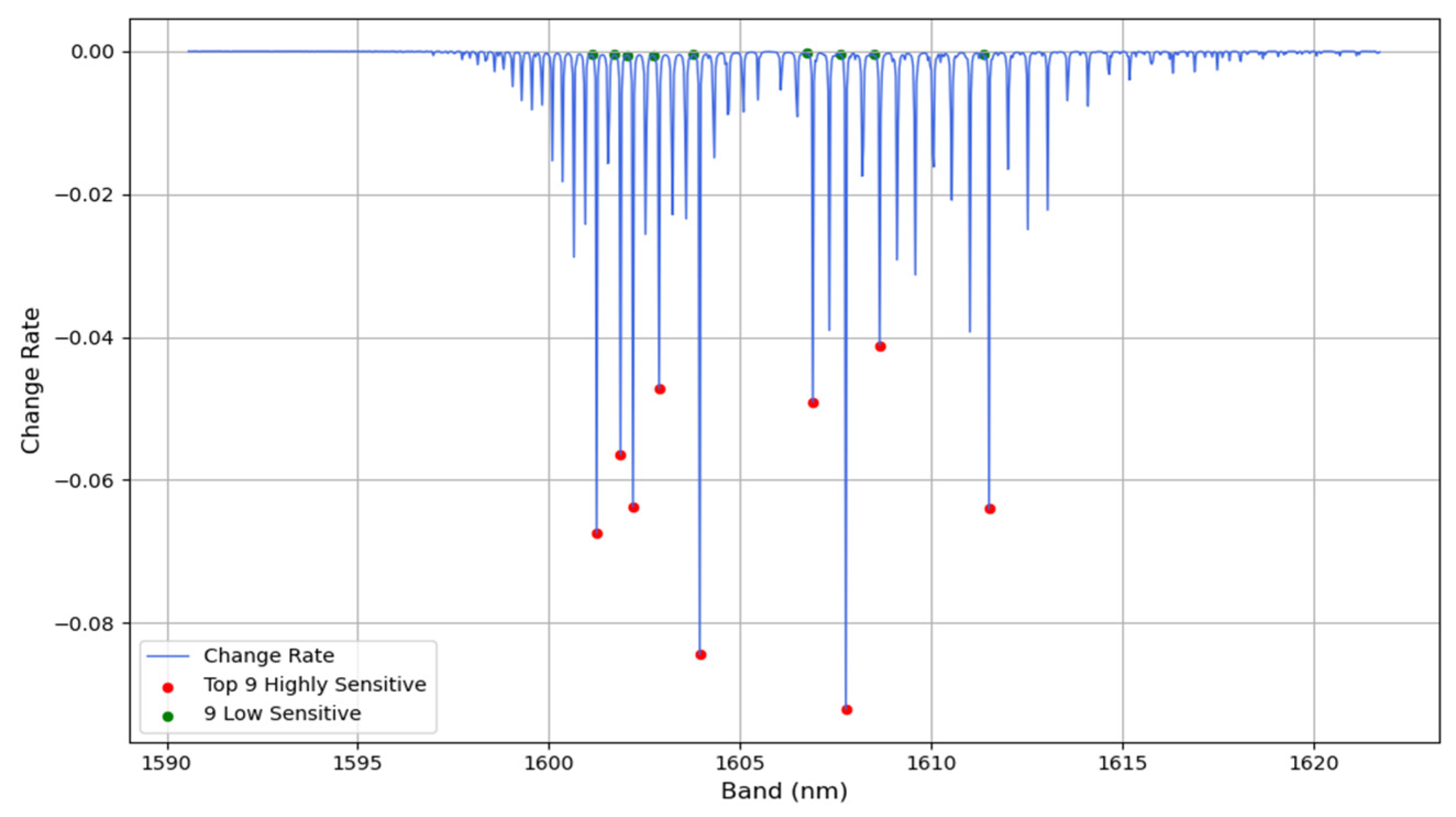
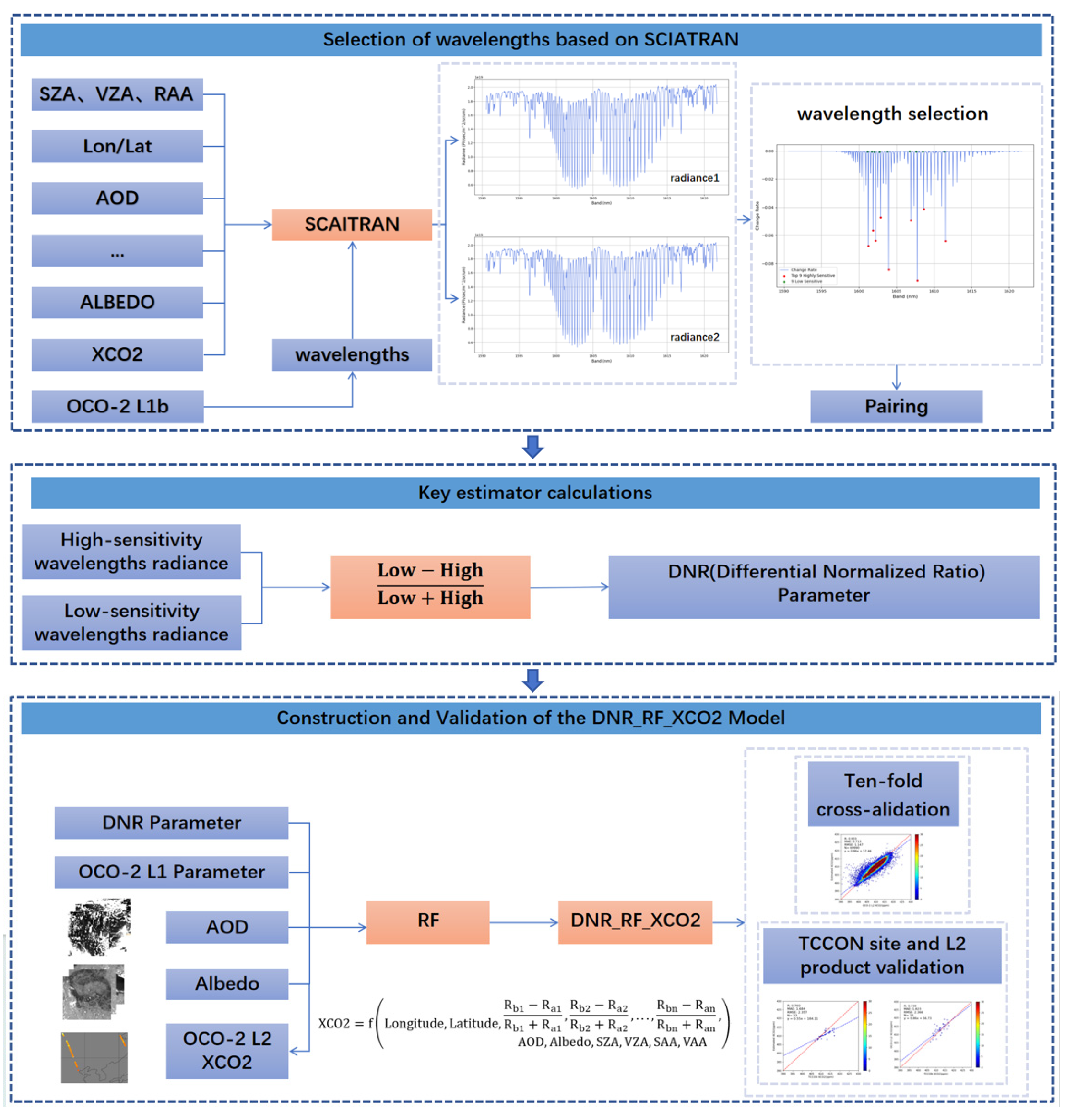
2.1.5. Retrieval Wavelength Selection
2.2. Model Dataset Construction
2.3. Model Description
3. Results
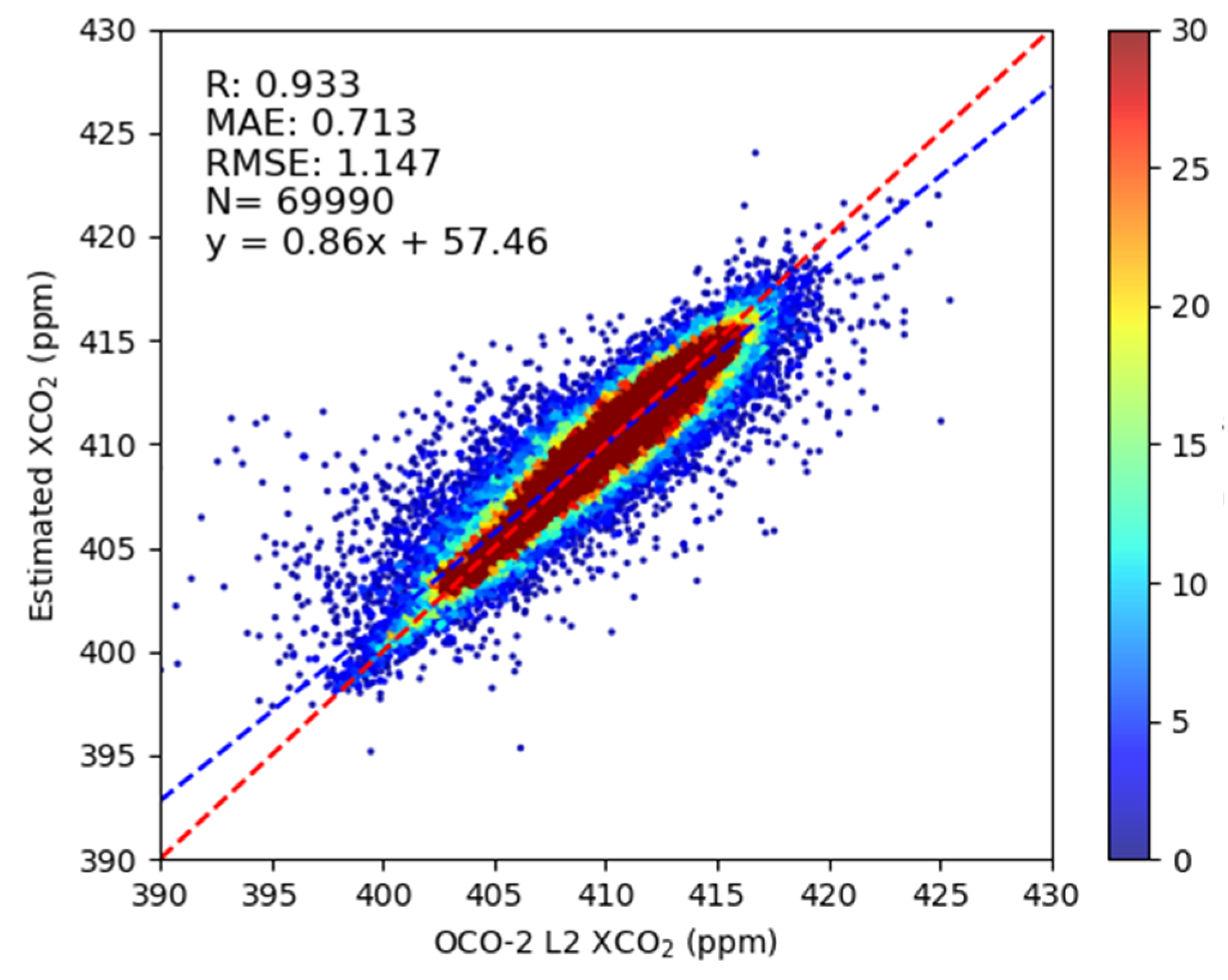
3.1. Model Accuracy Evaluation
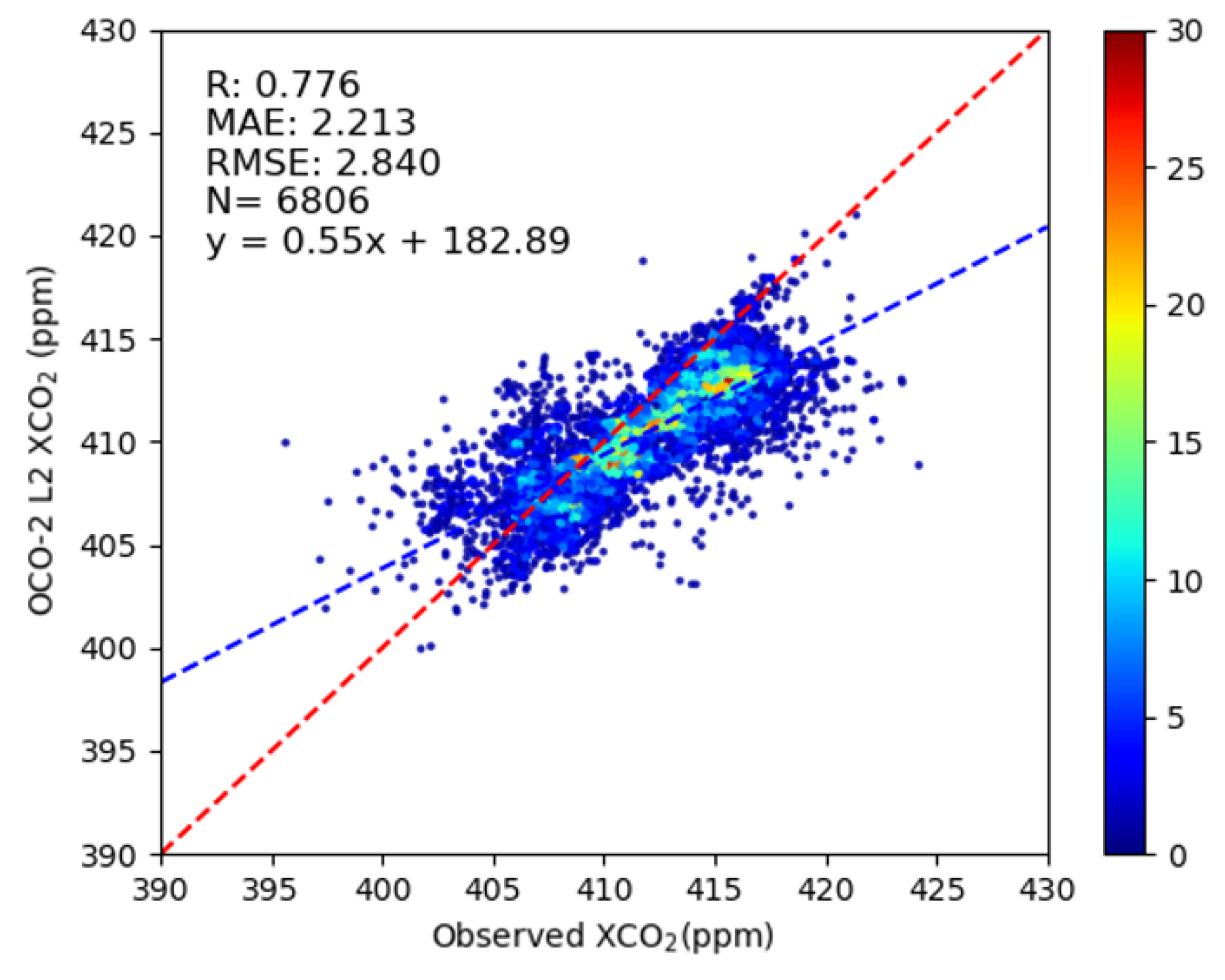
3.2. Retrieval Accuracy Evaluation
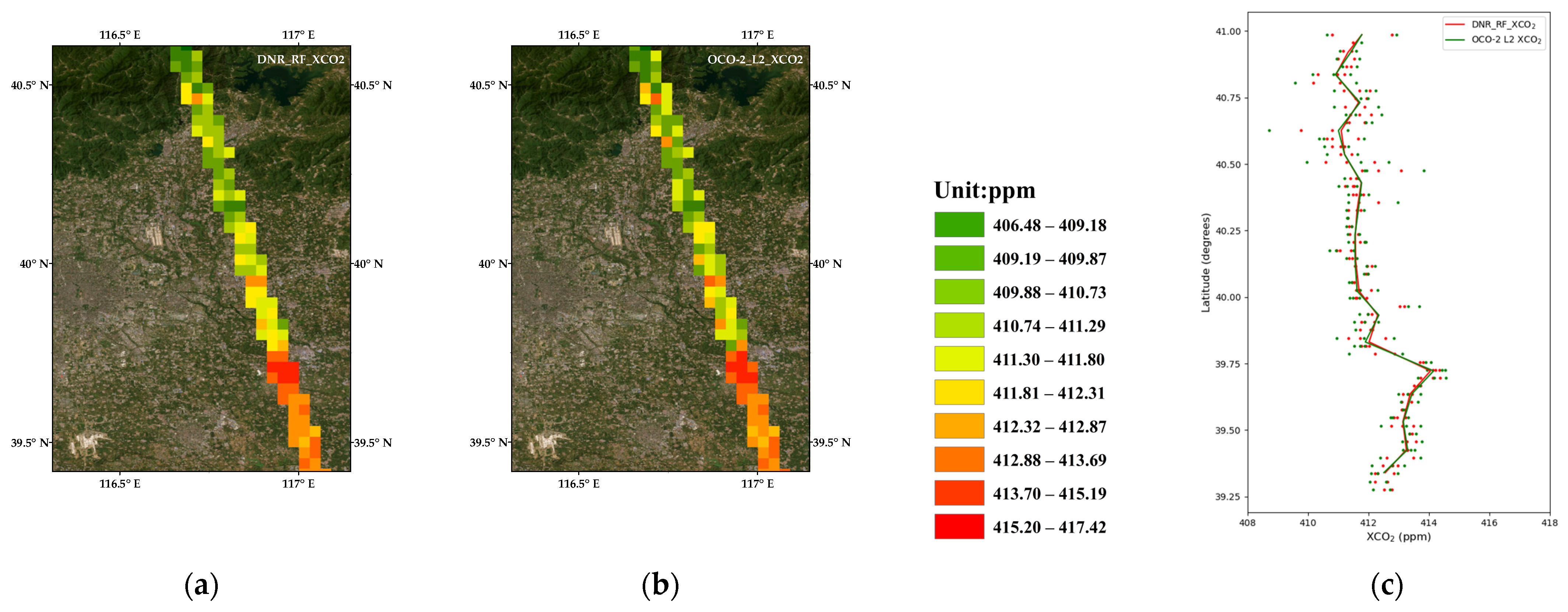
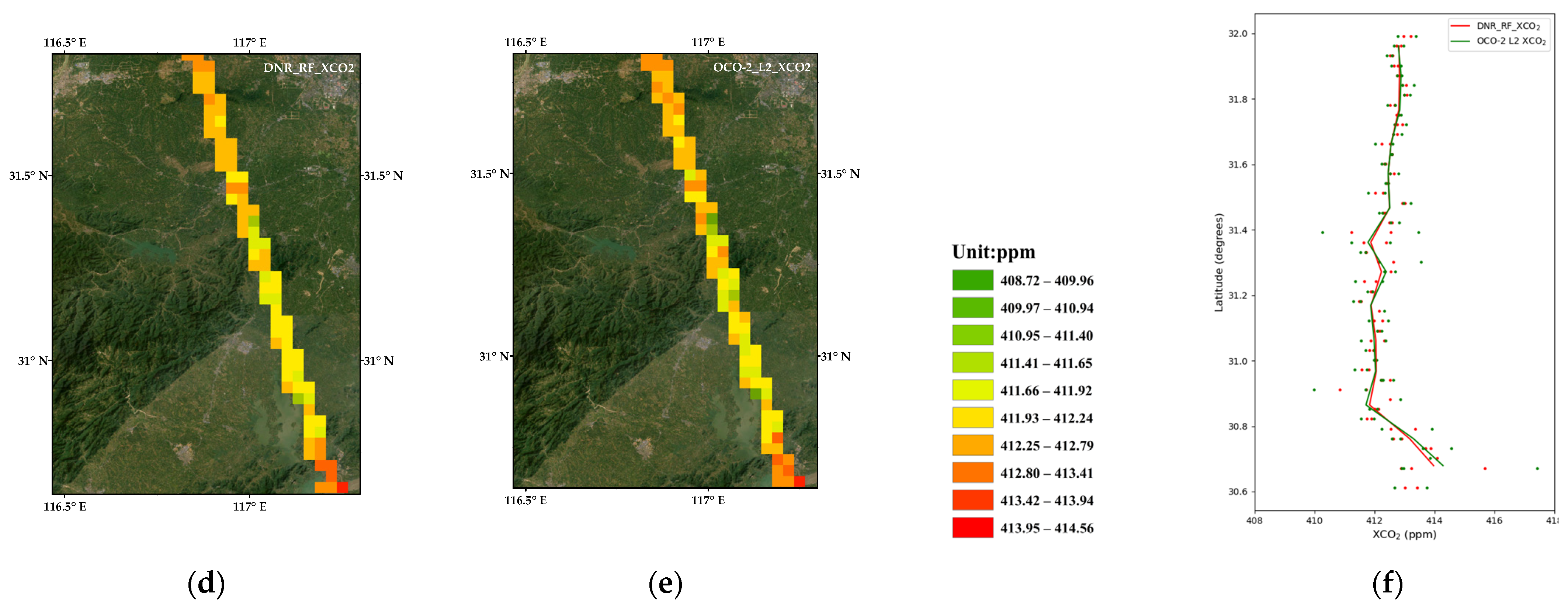
3.3. Spatiotemporal Extension Evaluation
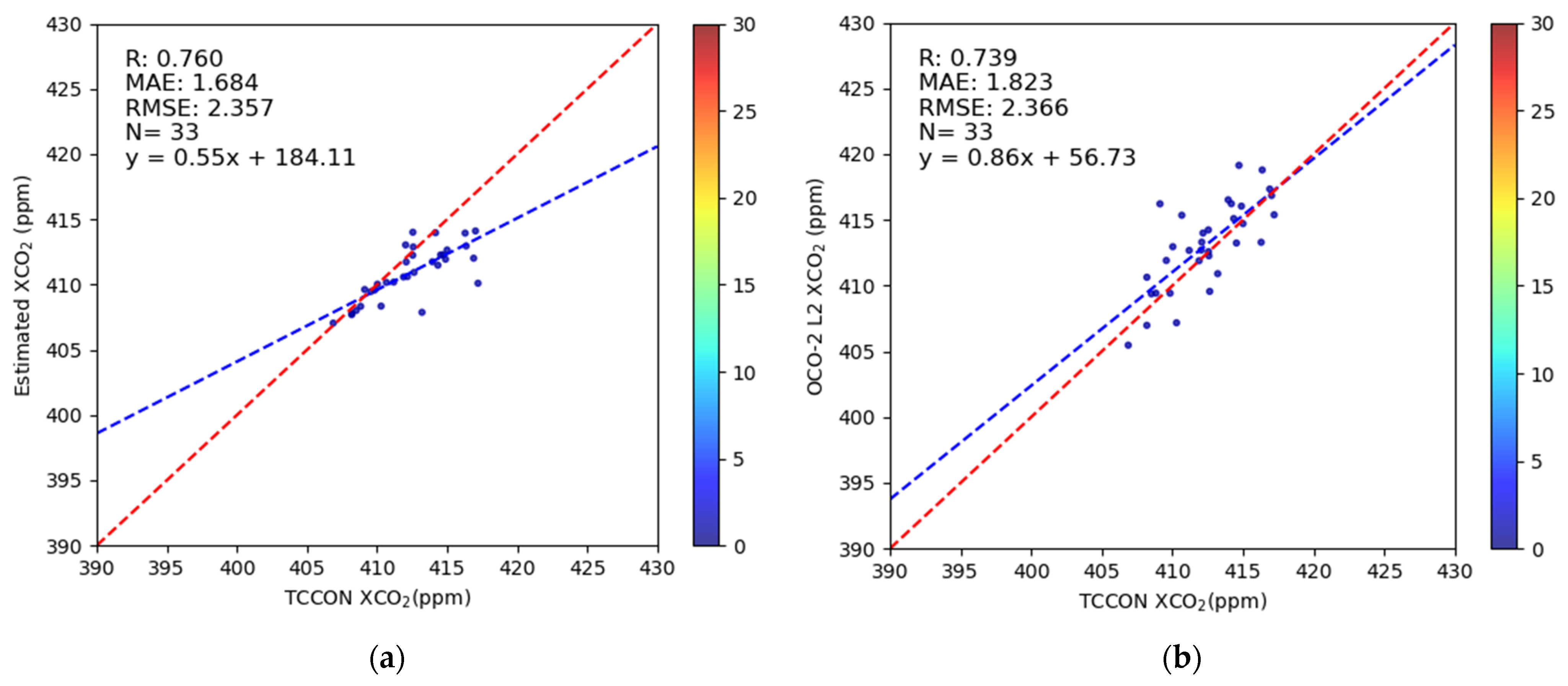
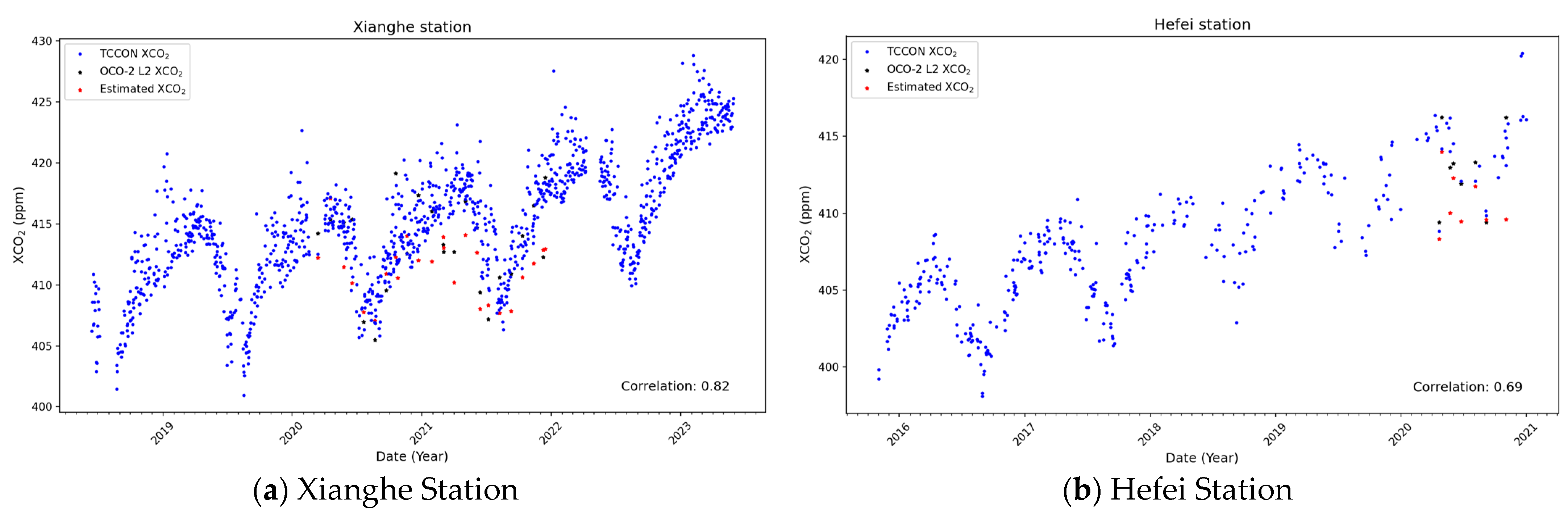
3.4. Analysis Based on TCCON Sites
3.5. Comparison of Results from Different Parameter Models
3.6. SHAP Interpretable Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The results show that it can effectively invert the atmospheric CO2 concentration, and the correlation with the TCCON ground station data when spatially and temporally migrated to different years is 0.760, indicating that this method has broad application prospects in improving the accuracy of CO2 concentration monitoring.
- (2)
- Compared with the existing OCO-2 satellite products, the retrieval method in this paper can significantly reduce systematic errors and demonstrates strong spatiotemporal adaptability, being able to accurately invert CO2 concentrations under different time and regional conditions, verifying its stability and reliability under various environmental conditions.
- (3)
- Future research can further optimize the retrieval model by adding more feature variables (such as climate patterns, other satellite data) and improve machine learning algorithms to further enhance retrieval accuracy. Combining more satellite data (such as GOSAT, TanSat, etc.) and ground station data can enhance the diversity of the training set, further improving the robustness and accuracy of the model. At the same time, further improving the model’s spatiotemporal migration capability, especially its performance under extreme climatic conditions, will be a key direction for the future.
- (4)
- We developed an integrated approach combining OCO-2 satellite spectral data, TCCON ground-based measurements, aerosol optical depth (AOD), and surface albedo, ultimately establishing the DNR_RF_XCO2 carbon dioxide retrieval model. The model validated its transferability over diverse regions (e.g., Xianghe and Hefei stations) and temporal scales (2019–2021), with consistent performance under varying climatic conditions (e.g., R = 0.776 in 2020). This establishes a reliable foundation for operational large-scale CO2 monitoring and supports methodological advancements for next-generation greenhouse gas satellites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, N.; Ju, W.; Jiang, F.; Yin, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. Satellite remote sensing for global stocktaking: Methods, progress and perspectives. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 26, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Che, K.; Cai, Z.; Yang, D.; Wu, L. Satellite remote sensing of greenhouse gases: Progress and trends. Natl. J. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Liu, Z.; Shao, P.; Ma, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Di, L.; Xia, M.; et al. A Review of Satellite-Based CO2 Data Reconstruction Studies: Methodologies, Challenges, and Advances. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Jiang, F.; Ju, W.; Chevallier, F.; Baker, D.F.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Johnson, M.S.; Philip, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Improved Constraints on the Recent Terrestrial Carbon Sink Over China by Assimilating OCO-2 XCO2 Retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD037773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, F.; He, W.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Ju, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sitch, S.; Walker, A.P.; et al. A Robust Estimate of Continental-Scale Terrestrial Carbon Sinks Using GOSAT XCO2 Retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL102815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Boesch, H.; Liu, Y.; Somkuti, P.; Cai, Z.; Chen, X.; Di Noia, A.; Lin, C.; Lu, N.; Lyu, D.; et al. Toward High Precision XCO2 Retrievals from TanSat Observations: Retrieval Improvement and Validation Against TCCON Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; van der A, R.J.; Stammes, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Lu, N.; Zhang, X.; Bi, Y.; Wang, P.; Fang, L. Carbon Dioxide Retrieval from TanSat Observations and Validation with TCCON Measurements. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.E.; O’Dell, C.W.; Baker, D.; Bruegge, C.; Chang, A.; Chapsky, L.; Chatterjee, A.; Cheng, C.; Chevallier, F.; Crisp, D.; et al. Evaluating the consistency between OCO-2 and OCO-3 XCO2 estimates derived from the NASA ACOS version 10 retrieval algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 3173–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ju, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Reconstructing annual XCO2 at a 1 km × 1 km spatial resolution across China from 2012 to 2019 based on a spatial CatBoost method. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.M.; Ju, W.; Tian, X.; Feng, S.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; et al. Regional CO2 fluxes from 2010 to 2015 inferred from GOSAT XCO2 retrievals using a new version of the Global Carbon Assimilation System. Atmos. Chem. Meas. 2021, 21, 1963–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, M.; He, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ju, W.; Chen, J.M. Global Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Flux Inferred from TanSat XCO2 Retrievals. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 2022, 9816536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, A.; Marion, R.; Briottet, X.; Foucher, P.-Y. Simultaneous retrieval of CO2and aerosols in a plume from hyperspectral imagery: Application to the characterization of forest fire smoke using AVIRIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6837–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Gu, X.; Yu, T. Applicability Analysis of Three Atmospheric Radiative Transfer Models in Nighttime. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Zhang, P.; Lu, N.; Zhang, W.; Ma, G.; Qi, C.; Liu, H. Carbon dioxide column-retrieval errors arising from neglecting the 3D scattering effect caused by sub-pixel low-level water clouds in the short-wave infrared band. Chin. J. Geophys. 2022, 65, 3759–3769. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, J.; Braverman, A.; Cressie, N.; Granat, R.; Gunson, M. Simulation-based uncertainty quantification for estimating atmospheric CO2 from satellite data. SIAM-ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2017, 5, 956–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yue, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Bai, W.; Meng, X. Retrieval and Validation of XCO2 from TanSat Target Mode Observations in Beijing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Ni, Q.; Cai, Z.; Langerock, B.; Nan, W.; Yang, Y.; Che, K.; Yang, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. CO2 in Beijing and Xianghe Observed by Ground-Based FTIR Column Measurements and Validation to OCO-2/3 Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xie, F.; Ren, T.; Zhao, C. Atmospheric CO2 retrieval from satellite spectral measurements by a two-step machine learning approach. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2022, 278, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Ren, T.; Zhao, C.; Wen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P.; Shiomi, K.; Morino, I. Fast retrieval of XCO2 over east Asia based on Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) spectral measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 3949–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, C. Machine Learning Model-Based Estimation of XCO2 with High Spatiotemporal Resolution in China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Song, S.; Li, Z. Estimation of the Concentration of XCO2 from Thermal Infrared Satellite Data Based on Ensemble Learning. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, A.; Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, L.S.; Acharya, P.K.; Dothe, H.; Matthew, M.W.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Chetwynd, J.H., Jr.; Richtsmeier, S.C.; Pukall, B.; et al. MODTRAN4 Radiative Transfer Modeling for Atmospheric Correction. In Optical Spectroscopic Techniques and Instrumentation for Atmospheric and Space Research III; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 3756. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, S.; Shephard, M.; Mlawer, E.; Delamere, J.; Iacono, M.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Boukabara, S.; Brown, P. Atmospheric radiative transfer modeling: A summary of the AER codes. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2005, 91, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guan, K.; Wang, Z.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Zheng, T.; Townsend, P.A.; Liu, N.; Nafziger, E.; Masters, M.D.; Li, K.; et al. Airborne hyperspectral imaging of nitrogen deficiency on crop traits and yield of maize by machine learning and radiative transfer modeling. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Lei, L.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Rao, W.; Song, H.; Wu, C. Global land 1° mapping dataset of XCO2 from satellite observations of GOSAT and OCO-2 from 2009 to 2020. Big Earth Data 2023, 7, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, H.; Baker, D.; Connor, B.; Crisp, D.; Miller, C. Global Characterization of CO2 Column Retrievals from Shortwave-Infrared Satellite Observations of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 Mission. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 270–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunchala, R.K.; Patra, P.K.; Kumar, K.N.; Chandra, N.; Attada, R.; Karumuri, R.K. Spatio-temporal variability of XCO2 over Indian region inferred from Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO-2) satellite and Chemistry Transport Model. Atmos. Res. 2022, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-P.; Sun, L. Retrieval of Aerosol Optical Depth over Arid Areas from MODIS Data. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Boesch, H.; Lee, H.; Cho, C.; Goo, T.-Y. Impact of Aerosol Property on the Accuracy of a CO2 Retrieval Algorithm from Satellite Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, N.; He, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, L. Retrieving High-Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth from GF-4 PMS Imagery in Eastern China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wen, J.; Xiao, Q.; You, D.; Dou, B.; Lin, X.; Hueni, A. Accuracy Assessment on MODIS (V006), GLASS and MuSyQ Land-Surface Albedo Products: A Case Study in the Heihe River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ke, C.Q.; Fan, Y.; Shen, X.; Cai, Y. Estimating glacier mass balance in High Mountain Asia based on Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer retrieved surface albedo from 2000 to 2020. Int. J. Clim. 2022, 42, 9931–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.N.; Copland, L.; Hik, D.S. The accuracy of satellite-derived albedo for northern alpine and glaciated land covers. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tian, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Y. The Impact of Climate Change on the Surface Albedo over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, P.C.; Wang, S.P.; Guo, L.L.; Hu, L.Q. XCO2 satellite retrieval experiments in short-wave infrared spectrum and ground-based validation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Dilawar, A.; Guo, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Gemechu, T.M.; Zhang, X. Global Evaluation and Intercomparison of XCO2 Retrievals from GOSAT, OCO-2, and TANSAT with TCCON. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Rao, K.; Fang, R.; Yue, Y.; Xia, A. An improved band design framework for atmospheric pollutant detection and its application to the design of satellites for CO2 observation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2023, 309, 108712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Rozanov, V.; Rozanov, A.; Burrows, J.P. SCIATRAN software package (V4.6): Update and further development of aerosol, clouds, surface reflectance databases and models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 1511–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Huyan, Z. Sensitivity analysis of an XCO2 retrieval algorithm for high-resolution short-wave infrared spectra. Optik 2020, 209, 164502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, V.V.; Buchwitz, M.; Eichmann, K.-U.; de Beek, R.; Burrows, J.P. Sciatran—A new radiative transfer model for geophysical applications in the 240–2400 NM spectral region: The pseudo-spherical version. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 29, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganos, S.; Grippa, T.; Gadiaga, A.N.; Linard, C.; Lennert, M.; VanHuysse, S.; Mboga, N.; Wolff, E.; Kalogirou, S. Geographical random forests: A spatial extension of the random forest algorithm to address spatial heterogeneity in remote sensing and population modelling. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekulić, A.; Kilibarda, M.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Nikolić, M.; Bajat, B. Random Forest Spatial Interpolation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonlau, M.; Zou, R.Y. The random forest algorithm for statistical learning. Stata J. 2020, 20, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, E.; Veihelmann, B.; Buschmann, M.; Deutscher, N.M.; Feist, D.G.; Morino, I. On the consistency of methane retrievals using the Total Carbon Column Observing Network (TCCON) and multiple spectroscopic databases. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 2377–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Han, G.; Mao, F.; Xu, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, H.; Sun, T.; Gong, W. A Regional Spatiotemporal Downscaling Method for CO2Columns. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8084–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Liu, C. First TanSat CO2 retrieval over land and ocean using both nadir and glint spectroscopy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, J.L.; Miller, M.E.; Tooze, J.; Ip, E. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 134, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Gong, W.; Han, G.; Xiang, C. Comparison of Satellite-Observed XCO2 from GOSAT, OCO-2, and Ground-Based TCCON. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Meng, X.; Yang, X.; Tan, Q. Multi-scale carbon emission characterization and prediction based on land use and interpretable machine learning model: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Appl. Energy 2024, 360, 122819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Mei, Q.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y. A Spatial–Temporal Causal Convolution Network Framework for Accurate and Fine-Grained PM2.5 Concentration Prediction. Entropy 2022, 24, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Yang, B.; Brauer, M.; Zhang, K.M. Enhancing the Evaluation and Interpretability of Data-Driven Air Quality Models. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 246, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Cai, Z. A retrieval algorithm for TanSat XCO2 observation: Retrieval experiments using GOSAT data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, N.; Lei, L.; Zeng, Z.; Cai, B.; Yang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, C.; Nassar, R. Regional uncertainty of GOSAT XCO2 retrievals in China: Quantification and attribution. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1251–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


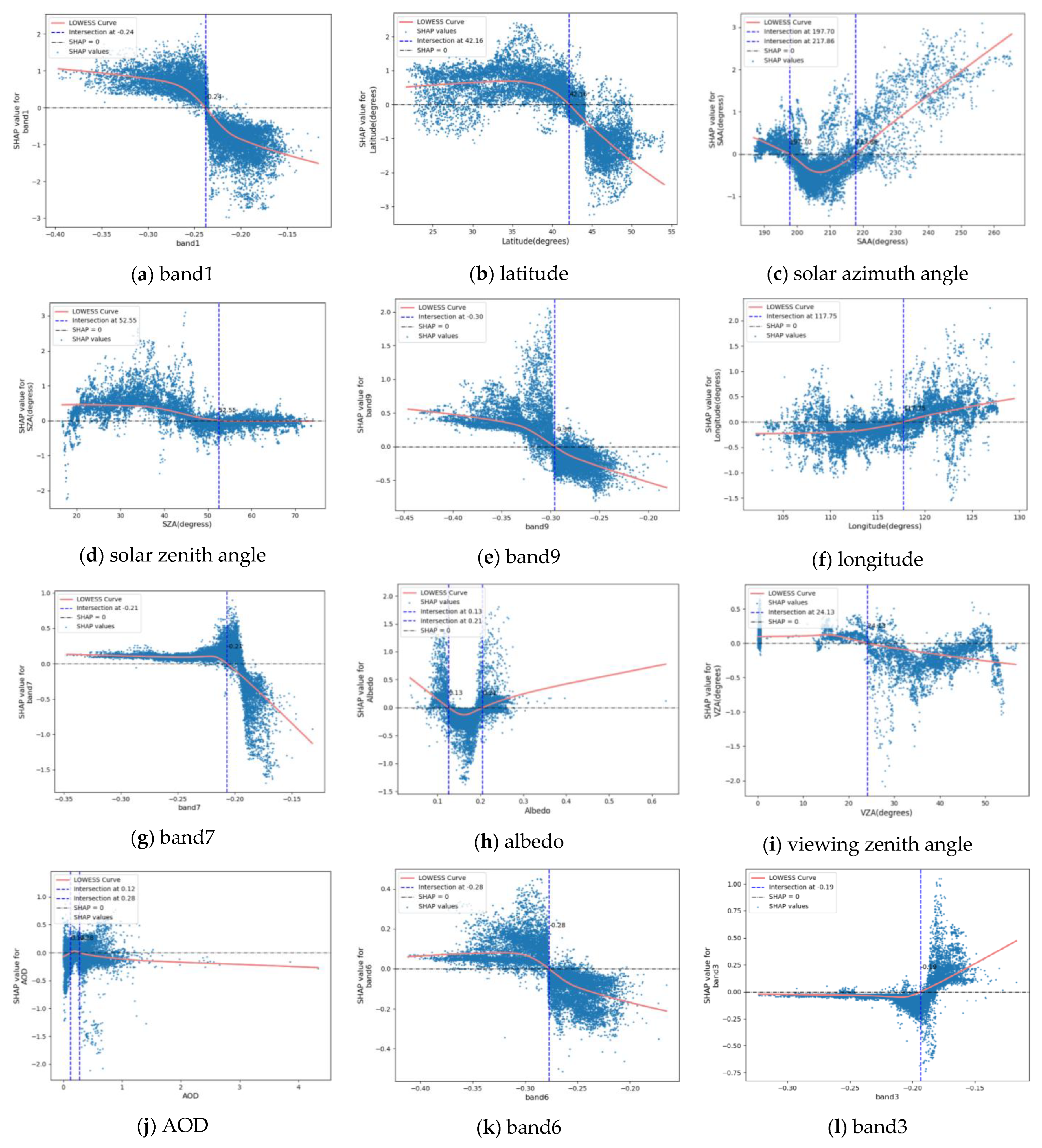
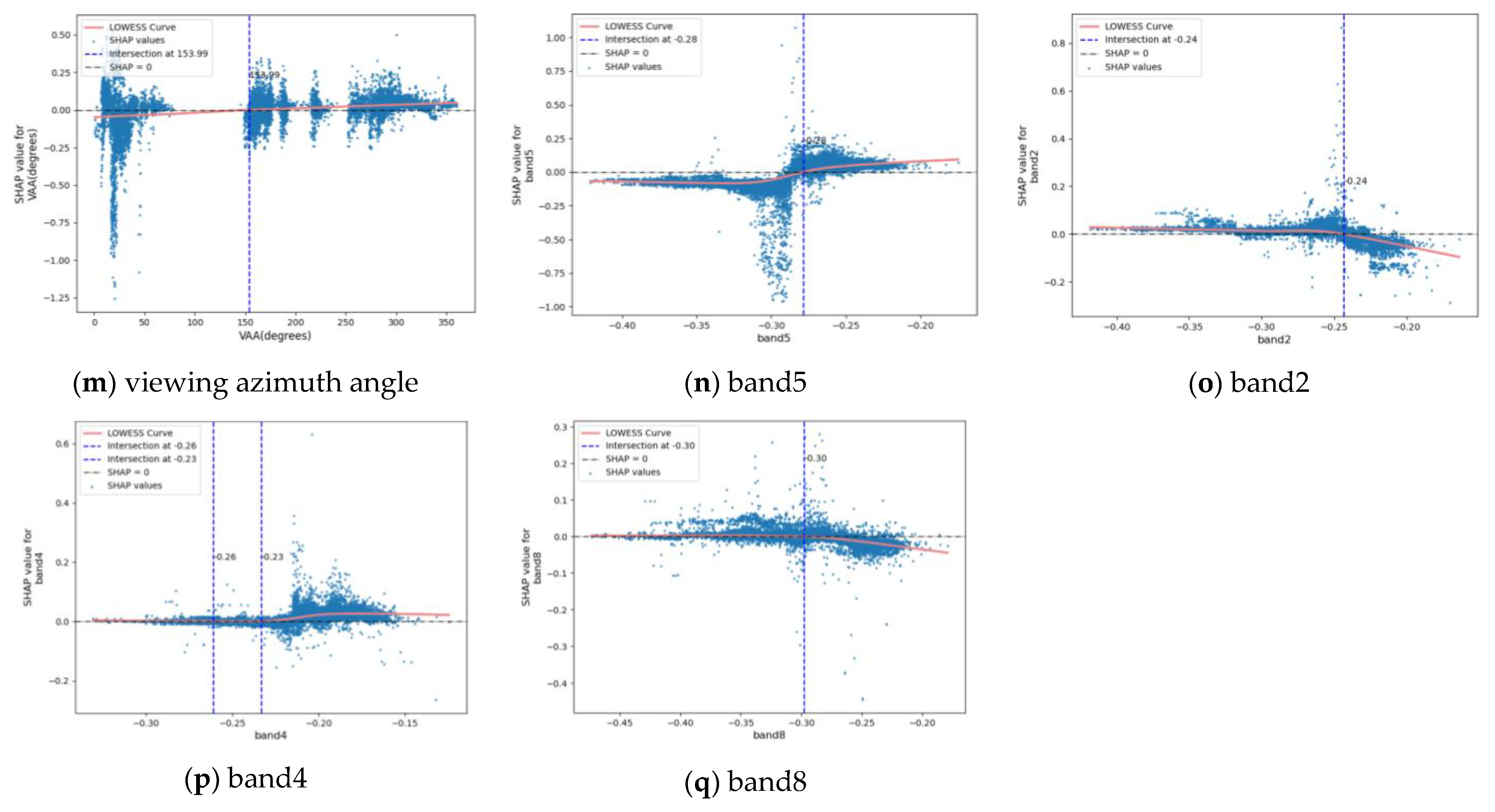
| Data Sources | Data | Units | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCO-2 L1b | Radiance | Ph/s/m2/sr/um | 1.29 km × 2.25 km | 16 day |
| Longitude | degrees | |||
| Latitude | degrees | |||
| Solar zenith angle (SZA) | degrees | |||
| View zenith angle (VZA) | degrees | |||
| Solar azimuth angle (SAA) | degrees | |||
| View azimuth angle (VAA) | degrees | |||
| OCO-2 L2 | XCO2 | ppm | 1.29 km × 2.25 km | 16 day |
| MOD04_3 km | Aerosol optical depth (AOD) | - | 3 km | 1 day |
| MCD43A3 | Albedo | - | 500 m | 1 day |
| Model | n_Estimators | Max_Depth | R | MAE (ppm) | RMSE (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 220 | 100 | 0.933 | 0.713 | 1.147 |
| XGBoost | 143 | 9 | 0.929 | 0.768 | 1.182 |
| LightGBM | 442 | 163 | 0.840 | 1.222 | 1.731 |
| Model | Model Radiance Parameters | Model Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Highly sensitive | |
| Model 2 | Highly sensitive + Low sensitive | |
| Model 3 | Low sensitive/Highly sensitive | |
| Model 4 | (Low sensitive − Highly sensitive)/(Low sensitive + Highly sensitive) |
| Model | Ten-Fold Cross-Validation in 2019 | Retrieval Results in 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | MAE | RMSE | R | MAE | RMSE | |
| Model 1 | 0.932 | 0.715 | 1.151 | 0.736 | 2.419 | 2.944 |
| Model 2 | 0.933 | 0.723 | 1.151 | 0.764 | 2.360 | 2.801 |
| Model 3 | 0.933 | 0.723 | 1.151 | 0.682 | 2.599 | 3.253 |
| Model 4 | 0.933 | 0.713 | 1.147 | 0.776 | 2.213 | 2.840 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Han, Z. Random Forest-Based Retrieval of XCO2 Concentration from Satellite-Borne Shortwave Infrared Hyperspectral. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030238
Zhang W, Wang Z, Li T, Li B, Li Y, Han Z. Random Forest-Based Retrieval of XCO2 Concentration from Satellite-Borne Shortwave Infrared Hyperspectral. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030238
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenhao, Zhengyong Wang, Tong Li, Bo Li, Yao Li, and Zhihua Han. 2025. "Random Forest-Based Retrieval of XCO2 Concentration from Satellite-Borne Shortwave Infrared Hyperspectral" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030238
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, Z., Li, T., Li, B., Li, Y., & Han, Z. (2025). Random Forest-Based Retrieval of XCO2 Concentration from Satellite-Borne Shortwave Infrared Hyperspectral. Atmosphere, 16(3), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030238







