Changes in Magnitude and Shifts in Timing of the Latvian River Annual Flood Peaks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Flood Seasonality
2.3.2. Trend Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Timing of Annual Qmax Peaks
3.1.1. Flood Seasonality Using Mathematical Calculations
3.1.2. Flood Seasonality Using Circular Statistics
3.1.3. Flood Seasonality Using Linear Mixed Effects Models
3.2. Trends in Annual Qmax (Mmax)
3.2.1. Magnitude
3.2.2. Timing
3.3. Relationship of Trends in Magnitude of Mmax and Changes in Timing of Qmax
4. Discussion
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bari, M.A.; Amirthanathan, G.E.; Woldemeskel, F.M.; Feikema, P.M. Changes in Magnitude and Shifts in Timing of Australian Flood Peaks. Water 2023, 15, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.W.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barrett, K.; Blanco, G.; et al. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin; BALTEX Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin. Springer London NetLibrary, Inc./Guildford Boulder: London, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-72786-6.
- Meier, H.E.M.; Kniebusch, M.; Dieterich, C.; Gröger, M.; Zorita, E.; Elmgren, R.; Myrberg, K.; Ahola, M.P.; Bartosova, A.; Bonsdorff, E.; et al. Climate Change in the Baltic Sea Region: A Summary. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2022, 13, 457–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellarin, A.; Burn, D.H.; Brath, A. Assessing the Effectiveness of Hydrological Similarity Measures for Flood Frequency Analysis. J. Hydrol. 2001, 241, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M.; Blöschl, G.; Merz, R.; Gutknecht, D. Linking Flood Frequency to Long-term Water Balance: Incorporating Effects of Seasonality. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 2004WR003439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matti, B.; Dahlke, H.E.; Dieppois, B.; Lawler, D.M.; Lyon, S.W. Flood Seasonality across Scandinavia—Evidence of a Shifting Hydrograph? Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4354–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G. On the Seasonality of Flooding across the Continental United States. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 87, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, C.; Nathan, R.; Peel, M.C. Trends in Global Flood and Streamflow Timing Based on Local Water Year. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre Zaffaroni, P.; Baldi, G.; Texeira, M.; Di Bella, C.M.; Jobbágy, E.G. The Timing of Global Floods and Its Association With Climate and Topography. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR032968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.J.; Villarini, G. Recent Trends in U.S. Flood Risk. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 12428–12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, H.-Y.; Leung, L.R.; Guo, J.; Ran, Q.; Demissie, Y.; Sivapalan, M. Understanding Flood Seasonality and Its Temporal Shifts within the Contiguous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1997–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, N.; Palmer, R.N. Changing River Flood Timing in the Northeastern and Upper Midwest United States: Weakening of Seasonality over Time? Water 2020, 12, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, M.; Assani, A.A.; Landry, R.; Massicotte, P. Temporal Variability of the Magnitude and Timing of Winter Maximum Daily Flows in Southern Quebec (Canada). J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henstra, D.; Thistlethwaite, J. Climate Change, Floods, and Municipal Risk Sharing in Canada; Institute on Municipal Finance: Toronto, ON, CA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-7727-0974-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, M.S.; Burn, D.H.; O’Brien, N. Detection of Trends in Flood Magnitude and Frequency in Canada. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Arheimer, B.; Borga, M.; Brázdil, R.; Claps, P.; Kiss, A.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lang, M.; et al. Understanding Flood Regime Changes in Europe: A State-of-the-Art Assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2735–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediero, L.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Macdonald, N.; Kohnova, S.; Merz, B.; Vorogushyn, S.; Wilson, D.; Alburquerque, T.; Blöschl, G.; Bogdanowicz, E.; et al. Identification of Coherent Flood Regions across Europe by Using the Longest Streamflow Records. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; Boháč, M.; Bonacci, O.; Borga, M.; Burlando, P.; Castellarin, A.; Chirico, G.B.; et al. A European Flood Database: Facilitating Comprehensive Flood Research beyond Administrative Boundaries. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 370, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Parajka, J.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Merz, B.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; Bonacci, O.; Borga, M.; et al. Changing Climate Shifts Timing of European Floods. Science 2017, 357, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.; Blöschl, G. Spatial Patterns and Characteristics of Flood Seasonality in Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3883–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing Climate Both Increases and Decreases European River Floods. Nature 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, M.; Viglione, A.; Lun, D.; Hall, J.; Blöschl, G. Flood Trends in Europe: Are Changes in Small and Big Floods Different? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 1805–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, A.; Jalali Shahrood, A.; Ghadimi, S.; Alborz, M.; Patro, E.R.; Klöve, B.; Torabi Haghighi, A. A Century of Variations in Extreme Flow across Finnish Rivers. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 124027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintunen, K.; Kasvi, E.; Uvo, C.B.; Alho, P. Changes in the Discharge Regime of Finnish Rivers. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arheimer, B.; Lindström, G. Climate Impact on Floods: Changes in High Flows in Sweden in the Past and the Future (1911–2100). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas-Cordero, N.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Jamro, S.; Piniewski, M. Detection of Trends in Observed River Floods in Poland. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriauciuniene, J.; Meilutyte-Barauskiene, D.; Reihan, A.; Koltsova, T.; Lizuma, L.; Sarauskiene, D. Variability in Temperature, Precipitation and River Discharge in the Baltic States. Boreal Environ. Res. 2012, 17, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Klavins, M.; Briede, A.; Rodinov, V. Long Term Changes in Ice and Discharge Regime of Rivers in the Baltic Region in Relation to Climatic Variability. Clim. Chang. 2009, 95, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reihan, A.; Koltsova, T.; Kriauciuniene, J.; Lizuma, L.; Meilutyte-Barauskiene, D. Changes in Water Discharges of the Baltic States Rivers in the 20th Century and Its Relation to Climate Change. Hydrol. Res. 2007, 38, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apsite, E.; Bakute, A.; Elferts, D.; Kurpniece, L.; Pallo, I. Climate Change Impacts on River Runoff in Latvia. Clim. Res. 2011, 48, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latkovska, I.; Apsite, E.; Elferts, D.; Kurpniece, L. Forecasted Changes in the Climate and the River Runoff Regime in Latvian River Basins. Baltica 2012, 25, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apsite, E.; Rudlapa, I.; Latkovska, I.; Elferts, D. Changes in Latvian River Discharge Regime at the Turn of the Century. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 44, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavins, M.; Rodinov, V. Long-Term Changes of River Discharge Regime in Latvia. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reihan, A.; Kriauciuniene, J.; Meilutyte-Barauskiene, D.; Kolcova, T. Temporal Variation of Spring Flood in Rivers of the Baltic States. Hydrol. Res. 2012, 43, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarauskiene, D.; Kriauciuniene, J.; Reihan, A.; Klavins, M. Flood Pattern Changes in the Rivers of the Baltic Countries. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2015, 23, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avotniece, Z.; Rodinov, V.; Lizuma, L.; Briede, A.; Kļaviņš, M. Trends in the Frequency of Extreme Climate Events in Latvia. Baltica 2010, 23, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kalvane, G.; Kalvans, A.; Briede, A. Shifts of the Air Temperature in Latvia from 1991 to 2020. Folia Geogr. 2021, XIX, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvāns, A.; Kalvāne, G.; Zandersons, V.; Gaile, D.; Briede, A. Recent Seasonally Contrasting and Persistent Warming Trends in Latvia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2023, 154, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briede, A.; Apsīte, E.; Elferts, D.; Koļcova, T. Trends and Regime Shifts in Climatic Parameters and River Runoff in Latvia for the Period 1951–2020. In Proceedings of the XXXI Nordic Hydrological Conference: Hydrology and Water-related Ecosystems, Tallinn, Estonia, 15–18 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rimkus, E.; Briede, A.; Jaagus, J.; Stonevicius, E.; Kilpys, J.; Viru, B. Snow-Cover Regime in Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia and Its Relationship to Climatic and Geographical Factors in 1961–2015. Boreal Environ. Res. 2018, 23, 193–208. [Google Scholar]
- Apsīte, E.; Latkovska, I.; Kļaviņš, M.; Strautnieks, I.; Aigars, J.; Ruskule, A.; Veidemane, K. Surface waters. In Latvia, Land, Nature, Nation, State; Nikodemus, O., Kļaviņš, M., Krišjāne, Z., Zelčs, V., Eds.; The University of Latvia Press: Rīga, Latvia, 2018; pp. 273–321. ISBN 978-9934-18-297-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zīverts, A.; Strūbergs, J. Hydrological Calculations in LATVIA (Compact Disc); Latvian University of Agriculture Press: Jelgava, Latvia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Glazacheva, L. Hydrological Districts. The Elaboration of Methodology; The University of Latvia Press: Rīga, Latvia, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kļaviņš, M.; Rodinov, V.; Draveniece, A. Largescale Atmospheric Circulation Processes as a Driving Force in the Climatic Turning Points and Regime Shifts in the Baltic Region. In Climate Change in Latvia; Kļaviņš, M., Ed.; The University of Latvia Press: Rīga, Latvia, 2017; ISBN 9984-802-70-1. [Google Scholar]
- Stips, A.K.; Lilover, M. Yet Another Assessment of Climate Change in the Baltic Sea Area; Breakpoints in Climate Time Series: Rīga, Latvia, 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jaagus, J.; Sepp, M.; Tamm, T.; Järvet, A.; Mõisja, K. Trends and Regime Shifts in Climatic Conditions and River Runoff in Estonia during 1951–2015. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2017, 8, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesiński, D.; Marsz, A.A.; Sobkowiak, L.; Styszyńska, A. Response of Low Flows of Polish Rivers to Climate Change in 1987–1989. Water 2022, 14, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewsey, A.; Neuhäuser, M.; Rxton, G.D. Circular Statistics in R; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cunderlik, J.M.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Bobée, B. Determination of Flood Seasonality from Hydrological Records / Détermination de La Saisonnalité Des Crues à Partir de Séries Hydrologiques. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, C.; Lund, U. R Package “Circular”: Circular Statistics (Version 0.5-0). 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=circular (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Soft. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patakamuri, S.; O’Brien, N. Modifiedmk: Modified Versions of Mann Kendall and Spearman’s Rho Trend Tests_. R Package Version 1.6. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.Org/package=modifiedmk (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Abdul Aziz, O.I.; Burn, D.H. Trends and Variability in the Hydrological Regime of the Mackenzie River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birsan, M.-V.; Molnar, P.; Burlando, P.; Pfaundler, M. Streamflow Trends in Switzerland. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. On “Field Significance” and the False Discovery Rate. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team, R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-Project.Org/ (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Hagen, E.; Feistel, R. Climatic Turning Points and Regime Shifts in the Baltic Sea Region: The Baltic Winter Index (WIBIX) 1659–2002. Boreal Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 211–224. [Google Scholar]
- Rimkus, E.; Kažys, J.; Butkutė, S.; Gečaitė, I. Snow Cover Variability in Lithuania over the Last 50 Years and Its Relationship with Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation. Boreal Environ. Res. 2014, 19, 337–357. [Google Scholar]
- Avotniece, Z. Characteristics and Long-Term Changes of Extreme Climate Events and Hazardous Hydrometeorological Phenomena in Latvia. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Latvia, Rīga, Latvia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Apsite, E.; Briede, A. Trends in River Runoff in Latvia for the Period 1951–2020. Folia Geogr. 2023, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaagus, J.; Briede, A.; Rimkus, E.; Sepp, M. Changes in Precipitation Regime in the Baltic Countries in 1966–2015. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birsan, M.-V.; Zaharia, L.; Chendes, V.; Branescu, E. Seasonal Trends in Romanian Streamflow. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4496–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilovich, I.S.; Loginov, V.F.; Groisman, P.Y. Changes of Hydrological Extremes in the Center of Eastern Europe and Their Plausible Causes. Water 2023, 15, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apsīte, E.; Nikodemus, O.; Brūmelis, G.; Lagzdiņš, A.; Elferts, D.; Rendenieks, Z.; Klints, L. Impact of Climate Variability, Drainage and Land-Cover Changes on Hemiboreal Streamflow. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 2558–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
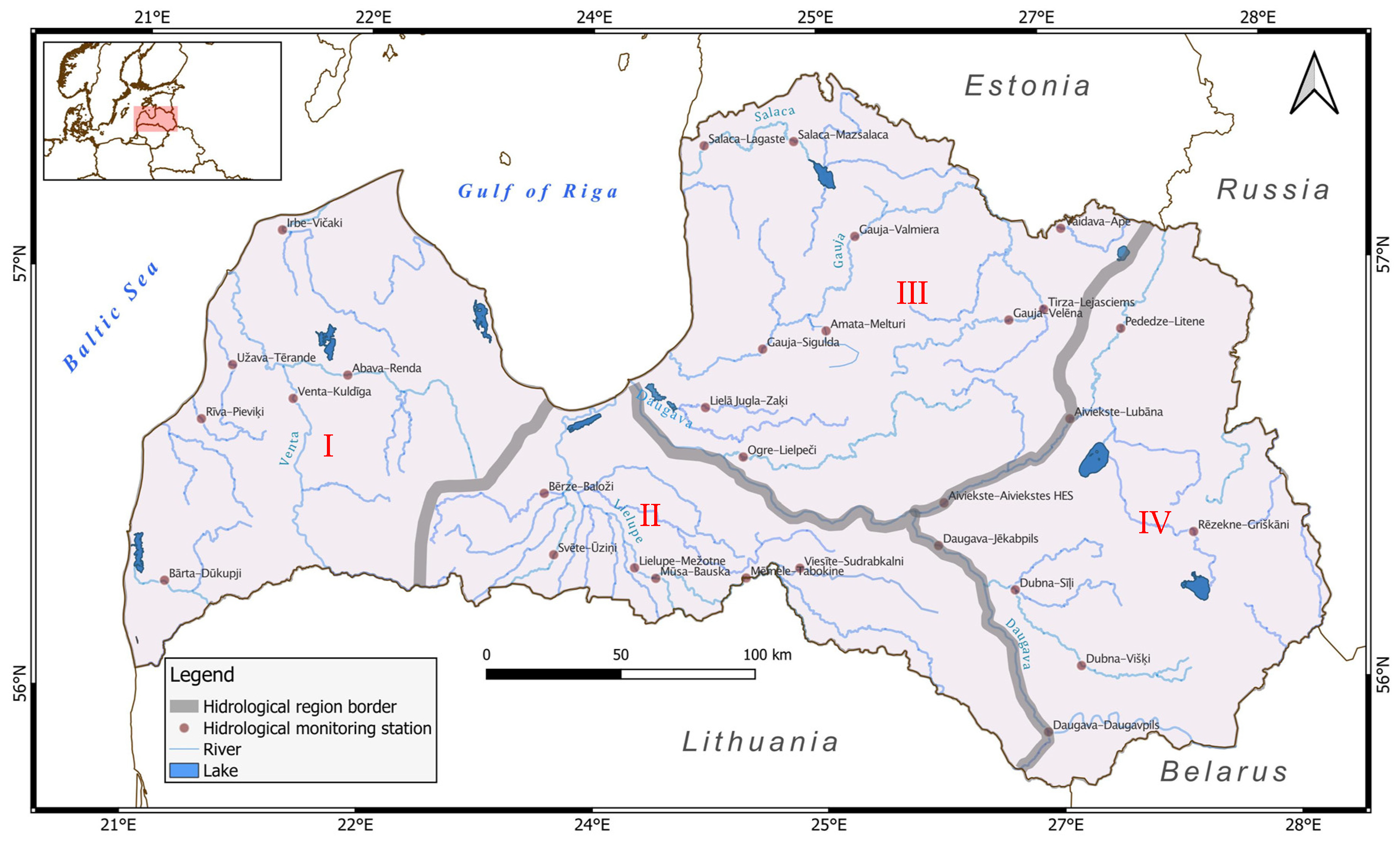
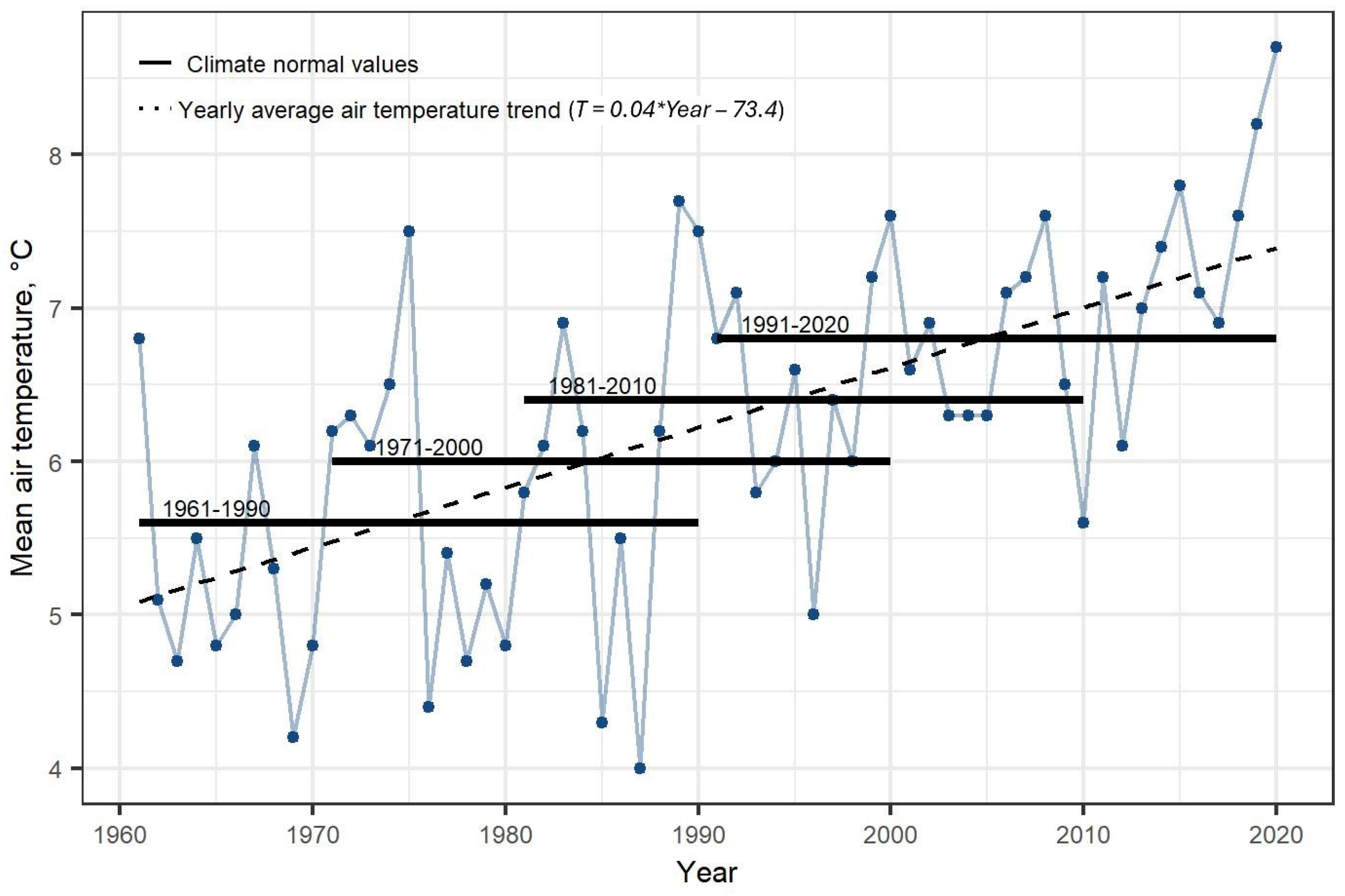

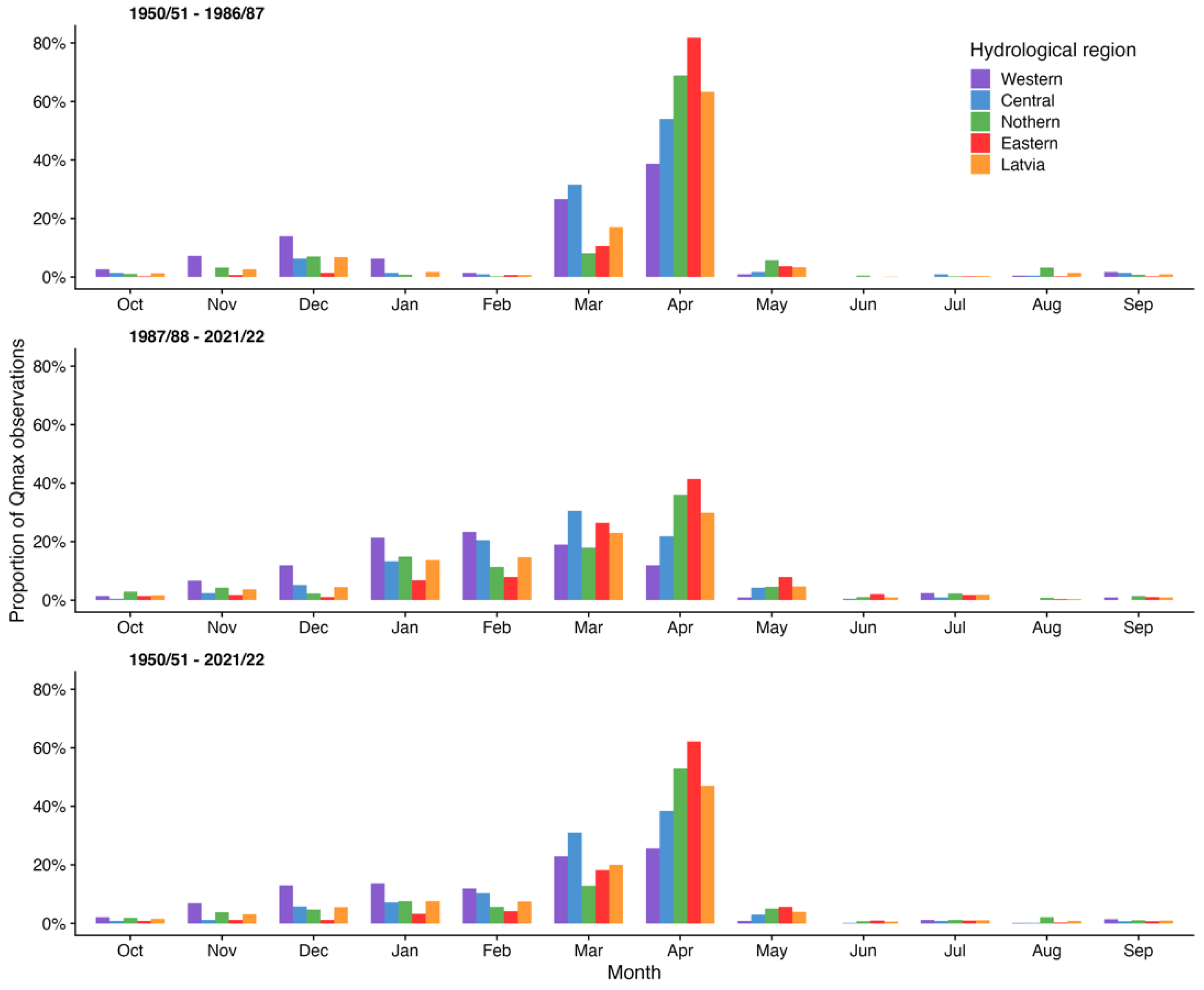



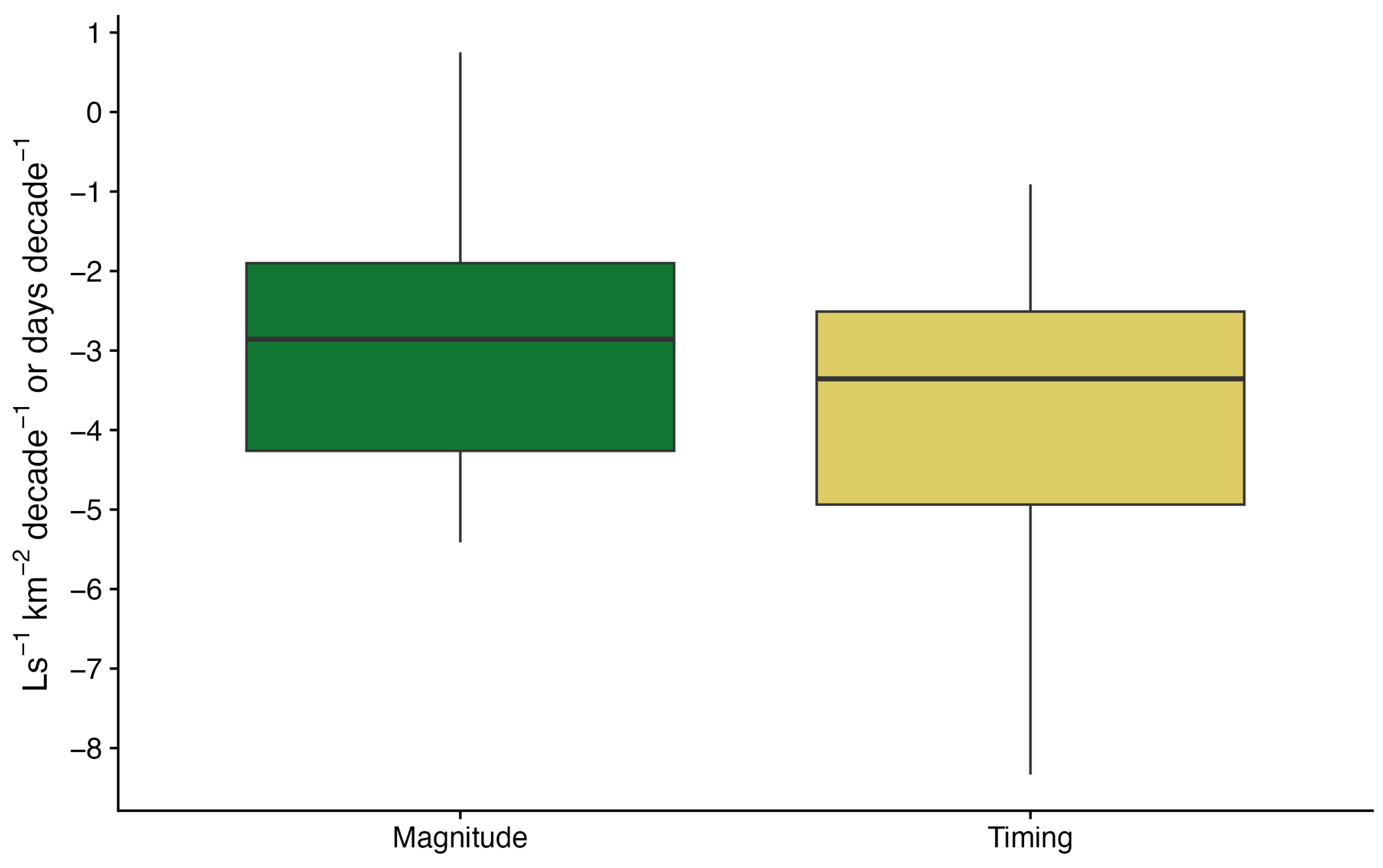
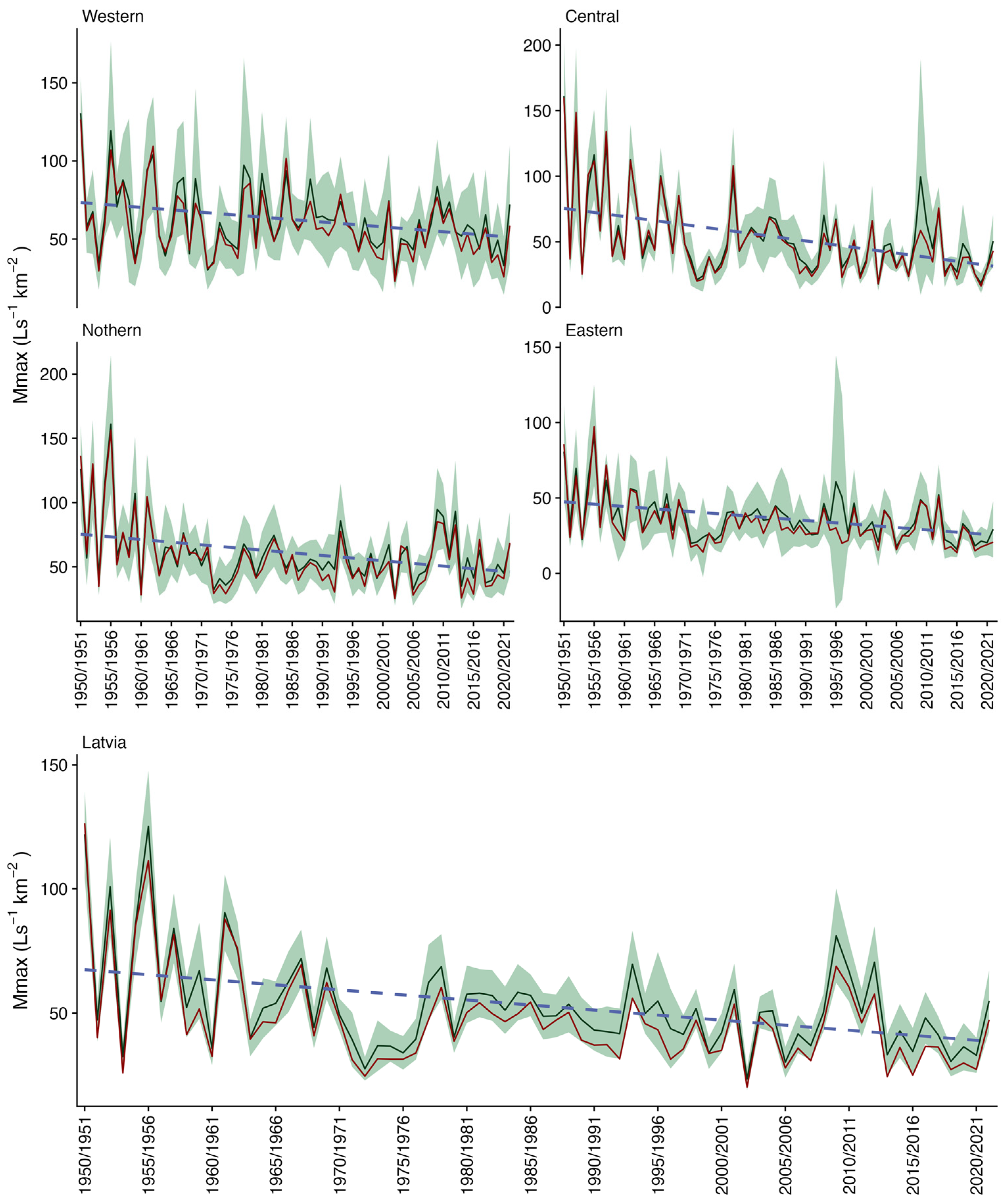
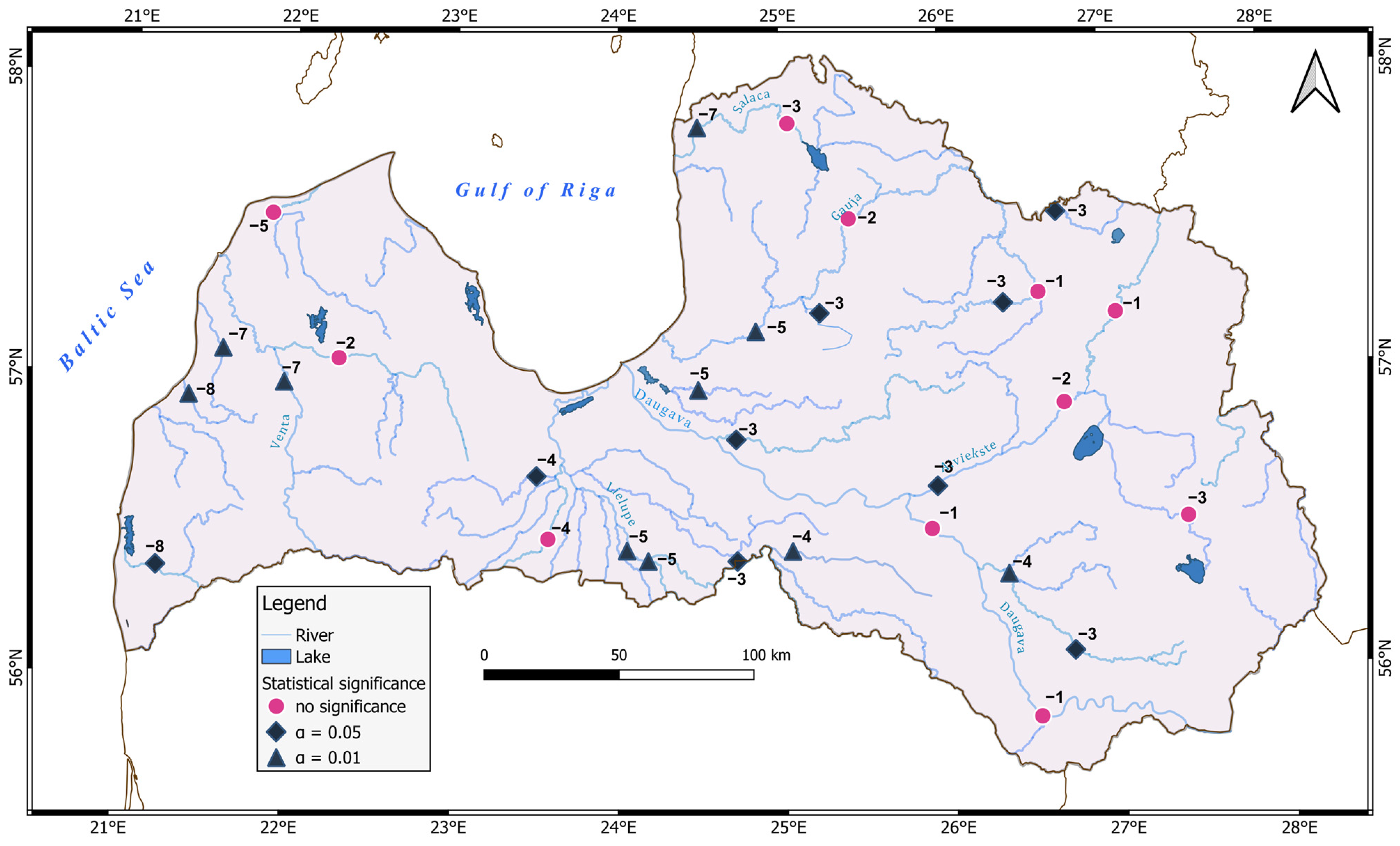

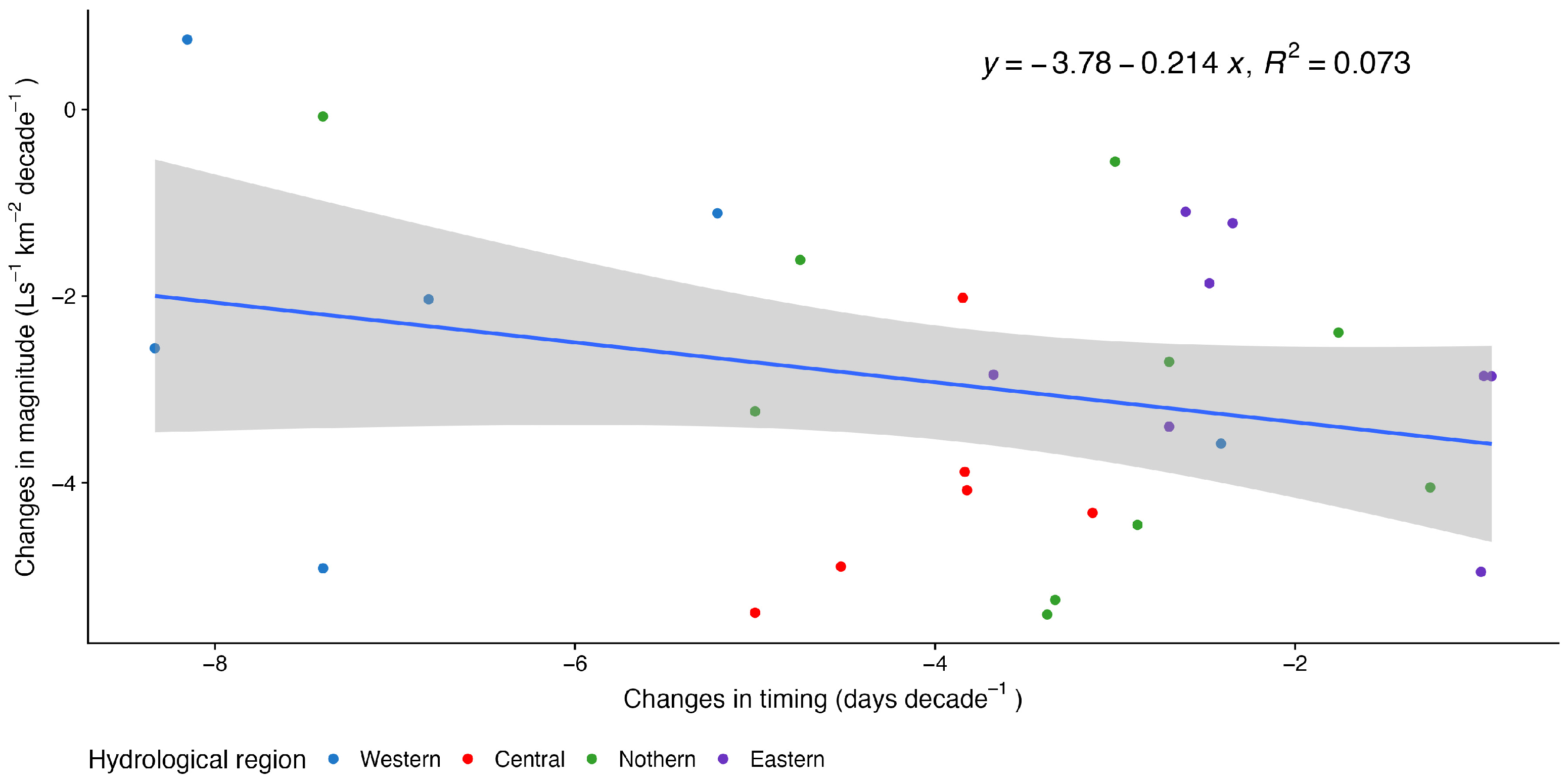
| Station | Number of Records | Missing Records (Number) | Missing Records (% of Total) | Minimal | Maximal | Mean | Median | SD | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abava Renda | 21,183 | 5115 | 19.45 | 0.7 | 281.4 | 14.2 | 7.6 | 18.1 | 3.7 |
| Aiviekste Aiviekstes HES | 24,106 | 2192 | 8.34 | 3.2 | 540.6 | 58.3 | 38.3 | 56.2 | 2.0 |
| Aiviekste Lubāna | 22,280 | 4018 | 15.28 | 1.6 | 301.0 | 41.9 | 28.1 | 40.4 | 1.9 |
| Amata Melturi | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 99.5 | 3.5 | 1.7 | 5.2 | 4.8 |
| Bārta Dūkupji | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 382.0 | 19.8 | 8.6 | 28.0 | 3.2 |
| Bērze Baloži | 22,645 | 3653 | 13.89 | 0.2 | 85.1 | 5.2 | 2.8 | 6.6 | 3.4 |
| Daugava Daugavpils | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 51.0 | 6230.0 | 443.7 | 262.0 | 511.6 | 3.4 |
| Daugava Jēkabpils | 23,010 | 3288 | 12.5 | 31.7 | 6923.0 | 504.5 | 306.4 | 570.6 | 3.4 |
| Dubna Sīļi | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 | 207.0 | 13.7 | 8.7 | 15.0 | 3.3 |
| Dubna Višķi | 24,515 | 1783 | 6.78 | −0.3 | 48.8 | 5.4 | 3.8 | 4.7 | 1.9 |
| Gauja Sigulda | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 6.1 | 870.0 | 72.6 | 49.3 | 67.6 | 3.5 |
| Gauja Valmiera | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 2.7 | 730.0 | 46.8 | 29.7 | 48.9 | 3.7 |
| Gauja Velēna | 23,741 | 2557 | 9.72 | −1.2 | 127.9 | 6.3 | 3.4 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| Irbe Vičaki | 24,837 | 1461 | 5.56 | 1.9 | 185.2 | 16.3 | 11.1 | 15.3 | 2.2 |
| Lielupe Mežotne | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 1680.0 | 54.3 | 24.9 | 85.5 | 5.4 |
| Lielā Jugla Zaķi | 25,850 | 448 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 126.0 | 6.6 | 3.6 | 8.2 | 3.5 |
| Mūsa Bauska | 26,175 | 123 | 0.47 | 0.6 | 924.0 | 24.4 | 9.3 | 44.0 | 6.4 |
| Ogre Lielpēči | 26,290 | 8 | 0.03 | 0.5 | 333.0 | 17.8 | 9.5 | 22.7 | 3.3 |
| Pededze Litene | 22,748 | 3550 | 13.5 | −7.7 | 301.9 | 8.7 | 4.3 | 14.7 | 7.6 |
| Rēzekne Griškāni | 25,033 | 1265 | 4.81 | 0.0 | 56.6 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 4.1 |
| Rīva Pieviķi | 21,781 | 4517 | 17.18 | −2.1 | 29.3 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 3.0 |
| Salaca Lagaste | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 400.1 | 32.5 | 23.6 | 30.2 | 2.4 |
| Salaca Mazsalaca | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 | 153.0 | 20.3 | 14.9 | 16.8 | 1.7 |
| Svēte Ūziņi | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 103.0 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 4.7 | 6.2 |
| Tabokine Mēmele | 26,297 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 684.0 | 19.9 | 9.7 | 31.7 | 5.6 |
| Tirza Lejasciems | 25,202 | 1096 | 4.17 | 0.1 | 101.0 | 4.3 | 2.2 | 6.4 | 5.0 |
| Užava Tērande | 21,947 | 4351 | 16.54 | 0.4 | 58.9 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 2.8 |
| Vaidava Ape | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 60.4 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 3.8 | 3.9 |
| Venta Kuldīga | 26,298 | 0 | 0 | 4.3 | 1300.0 | 67.9 | 35.6 | 88.7 | 3.6 |
| Viesīte Sudrabkalni | 18,202 | 8096 | 30.79 | 0.1 | 55.4 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 3.6 | 4.3 |
| Region | 1950/51–1986/87 | 1987/88–2021/22 | 1950/51–2021/22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western | April/39% | February/23% | April/26% |
| Central | April/54% | March/30% | April/38% |
| Northern | April/69% | April/36% | April/53% |
| Eastern | April/82% | April/41% | April/62% |
| Latvia | April/63% | April/30% | April/47% |
| Region | R | p-Value | Day | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950/51–1986/87 | ||||
| Western | 0.67 | <0.0001 | 154 | 3 March |
| Central | 0.88 | <0.0001 | 180 | 29 March |
| Northern | 0.81 | <0.0001 | 188 | 6 April |
| Eastern | 0.97 | <0.0001 | 192 | 10 April |
| Latvia | 0.90 | <0.0001 | 181 | 30 March |
| 1987/88–2021/22 | ||||
| Western | 0.79 | <0.0001 | 128 | 5 February |
| Central | 0.87 | <0.0001 | 156 | 5 March |
| Northern | 0.76 | <0.0001 | 163 | 12 March |
| Eastern | 0.87 | <0.0001 | 177 | 26 March |
| Latvia | 0.86 | <0.0001 | 158 | 7 March |
| 1950/51–2021/22 | ||||
| Western | 0.71 | <0.0001 | 140 | 17 February |
| Central | 0.86 | <0.0001 | 168 | 17 March |
| Northern | 0.77 | <0.0001 | 176 | 25 March |
| Eastern | 0.91 | <0.0001 | 185 | 3 April |
| Latvia | 0.86 | <0.0001 | 170 | 19 March |
| Region | Average Day/Date | Differences between Periods | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950/51–1986/87 | 1987/88–2021/22 | in Days | p-Value | |
| Western | 153/2 March | 135/12 February | −18 | 0.002 |
| Central | 179/28 March | 154/3 March | −25 | <0.0001 |
| Northern | 184/2 April | 163/12 March | −21 | <0.0001 |
| Eastern | 191/9 April | 179/28 March | −12 | 0.0002 |
| in Latvia | 179/28 March | 160/9 March | −19 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apsīte, E.; Elferts, D.; Lapinskis, J.; Briede, A.; Klints, L. Changes in Magnitude and Shifts in Timing of the Latvian River Annual Flood Peaks. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091139
Apsīte E, Elferts D, Lapinskis J, Briede A, Klints L. Changes in Magnitude and Shifts in Timing of the Latvian River Annual Flood Peaks. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(9):1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091139
Chicago/Turabian StyleApsīte, Elga, Didzis Elferts, Jānis Lapinskis, Agrita Briede, and Līga Klints. 2024. "Changes in Magnitude and Shifts in Timing of the Latvian River Annual Flood Peaks" Atmosphere 15, no. 9: 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091139
APA StyleApsīte, E., Elferts, D., Lapinskis, J., Briede, A., & Klints, L. (2024). Changes in Magnitude and Shifts in Timing of the Latvian River Annual Flood Peaks. Atmosphere, 15(9), 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091139








