Abstract
Hailfall is a severe local weather event that can cause great economic losses as well as the loss of people’s property; however, it is still difficult for domestic meteorological stations to comprehensively observe hail, and domestic independently developed hail observation instruments are still scarce. To help enable better automatic hail observations, a new independently developed hailstone disdrometer based on the acoustic principle, which can be used to measure the hailstone number and particle size and to calculate the corresponding equivalent liquid precipitation of hailstones, is proposed in this paper. The characteristics of hailstones were preliminarily analyzed using observation data from two hailstone disdrometers installed in Aksu, Xinjiang, where three hail events were observed via the hailstone disdrometer in the summer of 2023. By analyzing the development of deep convection clouds using the Fengyun 4A satellite-based cloud-top brightness temperature, and synoptic conditions based on the fifth-generation global climate reanalysis dataset produced by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (the ECMWF ERA5 dataset), the hail formation mechanism was investigated in detail for one hailfall event. Accurate hail observations are an important basis for understanding spatiotemporal hail variation. The hailstone disdrometer proposed in this study offers a useful approach for domestic hail observation to provide first-hand hail information for the inspection of weather modification effects and disaster prevention and reduction.
1. Introduction
As a kind of solid precipitation, hailstone is usually generated by strong convective clouds (i.e., hail clouds) and is composed of interlayers of transparent and opaque ice [1,2]. In general, hail is a kind of severe local weather that can cause great destruction and great losses to the economy and people’s property [3,4,5]. Natural hailstones exhibit a wide variety of shapes associated with their growth history, trajectory, and fall behavior through their parent storm [6]. The shape, size, and mass of hailstones affect their drag coefficient [1,7] and therefore also influence their fall speed, kinetic energy, and potential damage [8,9]. The National Weather Service defined hail size according to the maximum dimension threshold as “subsevere” (≤25 mm), “severe” (between 25 mm and 50 mm), or “significantly severe” (≥50 mm). Note that giant or gargantuan hail events have also been documented around the world [10,11]; for example, gargantuan hail was estimated to be 188–237 mm in the maximum dimension in Córdoba Province, Argentina, on 8 February 2018 [12].
To date, hail observations have included surface manual observations [13,14,15], ground-based hail pad networks [16,17,18] and radar remote sensing [19,20], satellite-based observations [21,22,23], and aerial-based observations [24,25]. Ground sensors for measuring the size distribution of hail can be separated into time-recording (e.g., hail disdrometers) and time-integrated measurements (e.g., hail pads). Time-recording instruments, such as optical disdrometers, are typically deployed as smaller networks or for field campaigns [26], since they are often expensive to fabricate and maintain. In contrast, time-integrated instruments, such as most commonly used hail pads, are relatively cheap and suitable for the long-term monitoring of hailfall [27,28,29]. The time-integrated technique for measuring hail size distribution is also developed by combining aerial imagery captured from a small unmanned aircraft with deep learning and computer vision feature extraction [30]. Due to the difficulty in measuring the commonly highly irregular shapes of natural hailstones, hailstones are usually represented as or assumed to be spheres or spheroids in model simulations [31,32] and radar- or satellite-based hailstone detection algorithms [33,34]. The advent of infrared laser scanning technology has made it possible to obtain high-resolution three-dimensional renderings of hailstone shapes, such as natural hailstone volume and surface area [35]. Among the remote sensing detection methods, weather radar measurements, which can provide echo characteristics with high temporal and spatial resolution to reflect the morphology, structure, and evolution characteristics of hail clouds, play important roles in hail identification and early warning. A weighing-type precipitation gauge is also widely used to measure precipitation forms, including hail [36]. In addition, hail detection and prediction may rely on the identification of atmospheric environmental conditions; for example, sounding data can provide statistical information on the characteristics of physical parameters, such as instability, water vapor, heat, and dynamic conditions, in the hail weather process and extract the physical threshold of hail occurrence [37,38,39].
In general, information on hail frequency and intensity is difficult to obtain due to the low occurrence probability of hailstorms at a certain location. Compared to the U.S. [40], hail in Europe tends to be less frequent and severe, mainly due to a different orientation of large-scale orography (i.e., the Alps) and related circulation patterns [41,42]. The spatial extent of an area affected by hail is usually smaller than 500 km2 in central Europe. It was reported for the U.S. that 80% of a large number of observed hailstones affected areas of even less than 40 km2, and the median affected area was 20.5 km2 [43]. China is one of the countries with the most severe hail in the world [15,44]. By using hail data from 2254 surface stations in China during the period of 1980–2015, it was found that hail frequency increased with station topography height, with a maximum of more than 30 events per year in the Tibetan Plateau and a minimum of less than 1 event per year in southern China, whereas the station’s averaged maximum hail diameter decreased with topography height [15]. Xinjiang Autonomous Region, located in Northwest China, is among the areas with a high incidence of hail disasters in China. Annual hail disasters have seriously influenced health and economic development in Xinjiang. Previous studies have indicated that the occurrence frequency of local hail clouds is generally similar to that of large-scale hail clouds in Xinjiang [45]. The Aksu region, an important production area for cotton and fruit in Xinjiang, is among the areas most severely affected by hail disasters [46,47].
Generally, hail is often affected by environmental factors, and regional terrain and is thus characterized by local and sudden occurrences and rapid occurrences, which makes the monitoring and early recognition of hail difficult in weather forecasting. Accurate observations of hail events are important for understanding spatiotemporal hail variations and can provide a reference for timely and accurate hail prediction, early warning, and hail prevention and mitigation. However, this precipitation type mainly affects certain zones, and China, especially its Northwest area, is particularly prone to heavy hailstone events. Measuring hailstones on the ground using in situ instruments is still challenging due to the localized nature of the phenomena and the lack of specific instruments dedicated to such observations at domestic meteorological stations. In this sense, the development of an automatic hail observation instrument is valuable and expected to enhance hail measurements. Based on this consideration, a new independently developed hailstone disdrometer is proposed in this paper that can measure the hailstone number and particle size and calculate the corresponding equivalent liquid precipitation. Moreover, the characteristics of hailstones were preliminarily analyzed based on measurements from two hailstone disdrometers installed in Aksu, Xinjiang. The hail formation mechanism was also investigated in detail for one hail process by combining satellite observations and reanalysis datasets. This paper is organized as follows. The introduction of the hailstone disdrometer, the retrieval method of the hailstone, and the field experiment and data used in this study are described in Section 2. The results of the characteristic analysis of the hailstone event and its formation mechanism are presented in Section 3, and the conclusions are summarized in Section 4.
2. Instrument, Method, and Data
2.1. Components of the Hailstone Disdrometer
The hailstone disdrometer (model KT-HD) used in this paper, which was independently developed by Beijing Keytec Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), based on acoustic principles, can monitor the number of hailstones and retrieve their size distributions in real time. As shown in Figure 1a, the hardware of the hailstone disdrometer mainly includes a hail collection tray, a signal processor composed of a microphone device with signal processing capabilities, an image analyzer, and an anemometer. The aseismic design of the hardware can eliminate effects well by the vibration of the arms carrying the image analyzer and the anemometer. The hail collection tray is a three-layer structure, in which the upper and lower layers are stainless steel plates and the middle layer is filled with a nonrigid shock absorber material, which can effectively prevent resonance and which does not affect the clarity of sound signal transmission. The operating principle of the hailstone disdrometer is as follows. A hailstone impinges on the hail collection tray to generate sound signals, which are converted to voltage signals through high-resolution pulse detectors in the signal processor. The voltage signals are associated with the number and terminal velocity of hailstones (specified in Section 2.2). The data processing software (KT-HD software of version 1) combines voltage signals with wind measurements from anemometers to determine the hail number, hail size distribution, and corresponding equivalent liquid precipitation. In addition, an image analyzer deployed in a hailstone disdrometer is used to aid in hail identification. As shown in Table 1, a hail collection tray with a diameter of 20 cm and sampling area of 314 cm2 can detect hail for a diameter range of 5 mm~75 mm at 5 mm intervals with a frequency of 25 Hz, and the data are output at 1 min intervals; the maximum measuring range of the precipitation is 1200 mm/h. The system host of the hailstone disdrometer supports SDI-12 communication, RS232 serial port communication, Modbus RTURS485, FTP transmission, and cloud storage. Hailstone disdrometer software (KT-HD software of version 1) can display images of the observation site, the data communication status, the regional distribution of hail numbers, the hail size distribution, and the corresponding equivalent liquid precipitation. The hailstone disdrometer developed in this study can be used in the fields of severe weather process monitoring, weather modification effect assessment, disaster assessment, and disaster prevention and reduction.
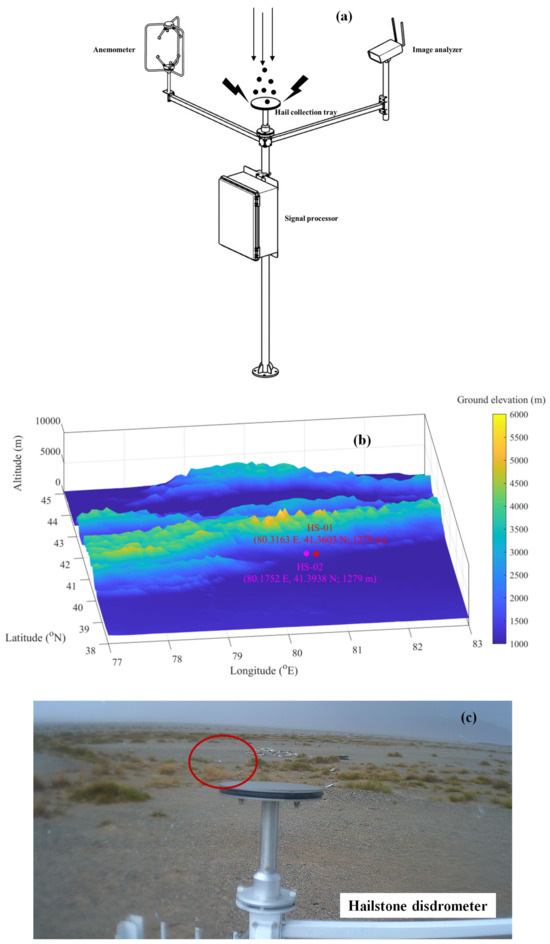
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the hailstone disdrometer (a) and the installation of two hailstone disdrometers in Aksu, Xinjiang (b). The color bar in (b) shows the ground elevation (m), and the longitude, latitude, and altitude of the two hailstone disdrometers (HS-01 and HS-02) are also noted. Field image provided by the image analyzer deployed on the hailstone disdrometer in Aksu, Xinjiang (c); the white particles in the red circle denote the falling hailstones.

Table 1.
Main technical parameters of the hailstone disdrometer.
2.2. Method of Hailstone Retrieval
When the hail hits the hail collection tray, the acoustic detector receives the acoustic signal and counts the hail. The diameter of the hail collection tray is 20 cm, which results in a relatively smaller sampling area of 314 cm2 and is expected to reduce the recounting caused by repeat hits from the same hail. Since the terminal velocity of a repeat hit by the same hail is significantly lower than that of its first hit, identifying and eliminating the recounting signal from the same hail are easy to do.
The retrieval of hail particle size distributions is based on two assumptions: hail is regarded as spherical, and the density of hail is assumed to be equivalent to the density of ice [32,48,49]; based on these assumptions, the hail particle size is derived from its relationship with the hail terminal velocity as follows. The theoretical calculation of the hail terminal velocity in still air relies on the following formula, which calculates the balance between gravity and drag forces [50,51,52]:
where m is the hail mass (kg). is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of Earth (in m s−2). is the cross-sectional area of the hail (m2). is the air density at the surface (kg m−3), which can be calculated from the surface temperature and pressure observed at the surface weather station. is the drag coefficient, which is related to the Reynolds number and is set as a constant parameter of 0.6 for spherical hailstones [53,54,55]. is the hail terminal velocity in still air (m/s).
and in Formula (1) are expressed as follows:
where is the diameter of the hail and is the density of ice.
From Formulas (1)–(3), the diameter of the hail can be calculated as follows:
By using Formula (4), the hail terminal velocity in still air can be calculated for hail of different sizes; based on these calculations, we conducted simulation experiment and laboratory impact tests using artificially made frozen ice balls (instead of unavailable natural hailstones) [56] to reach the hail collection tray. The signal processor extracts the acoustic pulse amplitude of the ice ball’s impact from the acoustic signal through the high-resolution pulse detector, which is related to the terminal velocity of the ice ball. The signal processor then converts the acoustic pulse amplitude into a voltage signal, thereby establishing a functional relation between the terminal velocity and the voltage signal in the laboratory test atmospheric environment as follows:
where is the voltage signal (mV) and is the calculated terminal velocity in still air (m/s).
The voltage signal generated by the impact of hail on a hail collection tray can be detected in field experiments, based on which the hail terminal velocity corresponding to the laboratory test atmospheric environment can be obtained using the above Formula (5). However, the differences between the atmospheric environment in laboratory tests and field experiments, including differences in air density and wind field, will result in differences in hail terminal velocity between the two types of atmospheric environments. It is necessary to modify the hail terminal velocity by correcting the air density and wind field. The surface air density, which is related to the surface atmospheric pressure and temperature, can be calculated from the following formula:
where is the air density at the surface (kg m−3). is the surface atmospheric pressure (Pa). is the gas constant, and is the surface atmospheric temperature (K). The air density in the laboratory test is assumed to be , and the corresponding hail terminal velocity is . The air density in the field experiment is assumed to be , and the corresponding hail terminal velocity is . By using Formula (1), we can obtain the following formula:
From Formula (7), the hail terminal velocity after correcting the air density is then expressed as follows:
The atmospheric pressure and temperature are assumed to be and , respectively, in the laboratory test, and are assumed to be and , respectively, in the field experiment. By using Formula (6), we can obtain the following formula:
According to Formulas (8) and (9), the hail terminal velocity after correcting the air density is calculated as follows:
A three-dimensional ultrasonic anemometer deployed in a hailstone disdrometer is used to measure the wind field and modify the hail terminal velocity derived from the above Formula (10) [52], based on which the hail particle size can be calculated using Formula (4). For the size of hailstones, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) recommends a maximum dimension of >5 mm as the cutoff to distinguish hail from graupel [57]. The hail particle size in this study is divided into 15 bins, which include 14 bins at 5 mm intervals for diameters between 5 and 75 mm (i.e., bin1: 5–10 mm; bin2: 10–15 mm; …; bin14: 70–75 mm), and all the hail particles with diameters >75 mm are classified into the fifteenth bin (bin15).
The calculation of the equivalent liquid precipitation for a single hail is as follows:
where is the equivalent precipitation of a single hail, and are the densities of ice and water, respectively, and is the area of the hail collection tray. The accumulation of equivalent precipitation in all hailstones within a certain time (such as within one minute) is calculated as follows:
where is the total number of hailstones detected within a certain time.
2.3. Field Experiment and Data
In 2023, two hailstone disdrometer stations (HS-01 and HS-02) with a distance of 12.35 km were established in Aksu, Xinjing (Figure 1b,c). Three hail events observed using these two instruments in summer were analyzed in this study. The surface meteorological conditions provided by four surface weather stations around the two hailstone disdrometers, i.e., the Y5948, Y5979, Y8703, and 51629 surface weather stations, which had distances of 0.01 (12.36) km, 3.98 (16.11) km, 4.47 (12.65) km, and 12.17 (14.02) km from the HS-01 (HS-02) hailstone disdrometer, respectively, were used to aid in the hail analysis. The Fengyun 4A satellite-based cloud-top brightness temperature [58] was employed to display the development of deep convection clouds during the hail process. The data have a horizontal resolution of approximately 4 km at 1 h intervals. Moreover, the synoptic context of the hail event is shown by an hourly fifth-generation global climate reanalysis dataset produced by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (the ECMWF ERA5 dataset), with a horizontal grid spacing of 0.25° × 0.25° and 37 vertical levels [59].
3. Results
3.1. Hail Characteristics Observed using the Hailstone Disdrometer in Aksu, Xinjiang
As shown in Figure 2, three hail events were observed using the acoustic hailstone disdrometer installed in Aksu, Xinjiang, in the summer of 2023, i.e., on 29 June, 6 July, and 27 July. Due to drastic temporal and spatial variations in hail occurrence, hailstone events were simultaneously observed at two hailstone disdrometer stations (HS-01 and HS-02) on 29 June, while hail was observed only at one hailstone disdrometer station (HS-02) on 6 July and 27 July. The duration of the hail process on 29 June was ~28 min, which was longer than that of the other two processes on 6 July and 27 July (both hail events lasting for ~20 min). In addition, the peak in hailstone number on 29 June was ~70 per minute, which was also greater than that during the other two hail events (~60 per minute) on 6 July and 27 July. Overall, the hailfall process on 29 June was slightly stronger than the other two processes. In general, summer hail events should readily occur in the afternoon (such as the two hailfall events on 6 July and 27 July), when the upward movement caused by thermal circulation and dynamic forcing is conducive to triggering a strong convective system, which facilitates hail cloud formation and hail generation [15,60]. However, among the three processes observed using the acoustic hailstone disdrometer in this study, relatively stronger hail occurred in the evening of 29 June, and the formation mechanism of this hail process is further analyzed in Section 3.2.
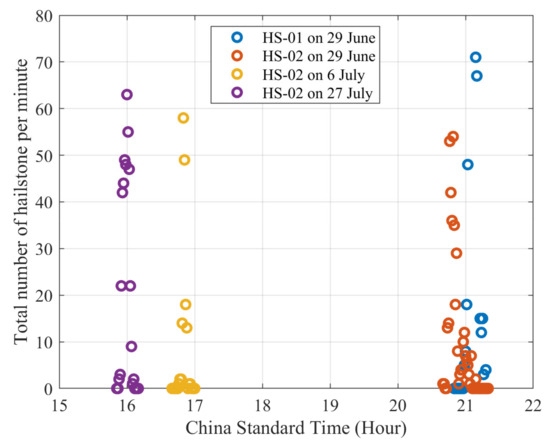
Figure 2.
The hailfall process on 29 June was observed simultaneously using two hailstone disdrometers (HS-01: blue; HS-02: brown), and the hailfall process was observed using the HS-02 hailstone disdrometer on 6 July (yellow) and 27 July (purple).
Figure 3 shows the diurnal evolution of surface temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, and precipitation on 29 June, which was observed at four surface weather stations (Y5948, Y5979, Y8703, and 51629) around the hail disdrometer. The four surface weather stations concurrently experienced a sharp decrease in temperature when hail occurred, of which the maximum temperature decrease reached ~10 °C at Station Y5948 (Figure 3a). Moreover, the relative humidity increased significantly, with a magnitude of >40%, at the four surface weather stations (Figure 3b). The wind speed also increased rapidly at four surface weather stations, especially when it suddenly increased to 12 m/s at Station Y5948 (Figure 3c). After the hailfall, precipitation was observed at four surface weather stations, and the maximum precipitation exceeded 2 mm at Stations Y5948 and Y5979 (Figure 3d). According to synoptic principles, the abovementioned rapid changes in surface meteorological parameters are consistent with the characteristics of hail events. The variation trends in the equivalent liquid precipitation derived from the two hailstone disdrometers generally agreed (Figure 3e), although the occurrence period of the peak equivalent liquid precipitation was slightly different due to the temporal discrepancy in hail overpassing between the two stations. Moreover, the variation pattern of the hailstone disdrometer-retrieved equivalent liquid precipitation was generally consistent with the precipitation observed using the automatic rain gauge at two surface weather stations (Y5948 and Y5979) close to the HS-01 hailstone disdrometer, which indicates that the hailstone disdrometer can be used to reasonably evaluate the equivalent liquid precipitation of hail. Due to the spatial variation in hail systems, much less precipitation was observed at the other two surface weather stations (Y8703 and 51629), which are relatively far from the HS-01 hailstone disdrometer.
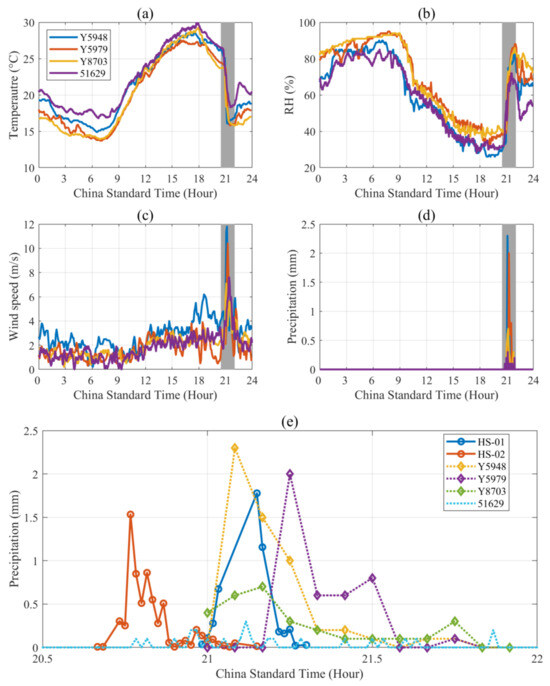
Figure 3.
Diurnal evolution of temperature (a), relative humidity (b), wind speed (c), and precipitation (d) on 29 June observed at four surface weather stations (Y5948: blue; Y5979: red; Y8703: yellow; and 51629: purple) around the hailstone disdrometers; the gray area denotes the periods with hail detected by the hailstone disdrometer. (e) Equivalent liquid precipitation derived from the two hailstone disdrometers (HS-01: solid blue; HS-02: solid brown) and observed using the automatic rain gauge at four surface weather stations (Y5948: dashed yellow; Y5979: dashed purple; Y8703: dashed green; and 51629: dashed blue).
Figure 4 shows the statistics for the number and particle size of hailstones from the three hailfall events in Aksu, Xinjiang, in the summer of 2023. The maximum number of hailstones was ~70 per minute (Figure 4a), with an average hail number and a standard deviation of 20.1 ± 21.0 per minute. The probabilistic statistical analysis showed that the hail number was mostly <10 per minute (Figure 4b), with an occurrence frequency of 48%. In addition, 13% of the hail numbers exhibited a secondary occurrence peak at 40–50 per minute. The main data characteristics of hail observations are summarized in Table 2. Although the hail particle size exhibited certain variations among the different observational samples, the hail particle size was generally <20 mm and was primarily distributed between 5 and 10 mm for the hail samples (Figure 4c), which was generally consistent with the results of Zhang et al. [60] based on hail data from surface stations in China for the period of 1980–2015. Zhang et al. [60] also indicated that severe hail (with a maximum hail diameter ≥20 mm; 5.32% of all cases) mainly occurred along the edge of the plain near mountainsides and was most likely to develop in the afternoon.
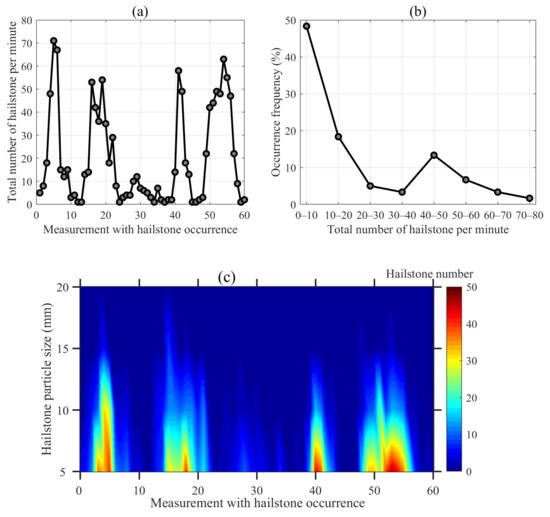
Figure 4.
The statistics of the total number of hailstones per minute (a), the occurrence frequency at different number intervals (b), and the distributions of hailstone numbers in each bin of hailstone particle sizes (c) during the three hail events in Aksu, Xinjiang, in the summer of 2023.

Table 2.
Main data characteristics of hail observations in Aksu, Xinjiang.
3.2. Synoptic Analysis of Hail Formation on 29 June 2023
As shown by the distribution of the Fengyun 4A satellite-based cloud-top brightness temperature (TBB) in Figure 5, a strong convection system induced hail in the Aksu area on the southern slope of the Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang on 29 June 2023. The areas with a TBB less than 241 K (−32 °C) in Figure 5 indicate the development of deep convection clouds. A hailstone disdrometer was used to detect hail in Aksu at approximately 13 UTC (~21:00 China Standard Time in Figure 3), before which convective clouds began to develop near the hailstone disdrometer at 11 UTC, approximately 30–40 km at the horizontal scale (Figure 5a). At 12–13 UTC (Figure 5b,c), deep convective clouds developed rapidly and increased to approximately 200 km around the hailstone disdrometer. At 15 UTC (Figure 5d), a convective band formed along the mountain from the northeast toward the southwest, and the horizontal scale extended to approximately 400 km.
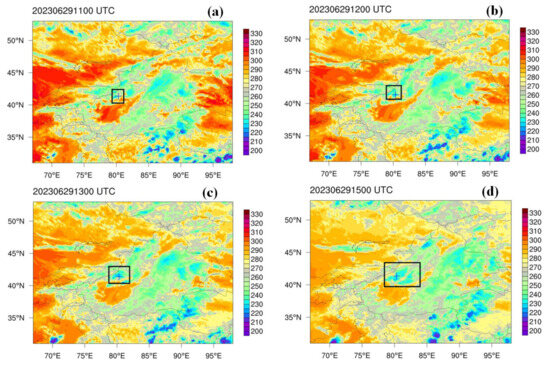
Figure 5.
Distribution of the Fengyun 4A satellite-based TBB (unit K) at 11 UTC (a), 12 UTC (b), 13 UTC (c), and 15 UTC (d) on 29 June 2023. The black crosses mark the HS-01 hailstone disdrometer, and the black rectangles denote the development of deep convective clouds.
Figure 6 shows the 200 hPa weather conditions derived from the ECMWF ERA5 dataset on 29 June 2023, which indicate an east—west-oriented high-altitude jet during convective cloud development. At 06 UTC (Figure 6a), there were multiple jet cores in Xinjiang and its surrounding areas, with the highest wind speed reaching ~42 m/s between 35 and 40° N over western Xinjiang. In addition, there was also a weak jet near 45° N. The convective clouds developed between the two jets and were located on the left side of the entrance area of the southerly jet. At 12 UTC (Figure 6b), the westerly jet moved eastward and strengthened. A significant high-level divergence area (blue contour line in Figure 6c) appeared near the hailfall regions, which was conducive to the development of upward motion. Figure 7 shows the 500 hPa weather situation on 29 June 2023, and there was a cutoff vortex near 60° N in the high-latitude region. Xinjiang was under the influence of the westerly flow at the bottom of the vortex. A shortwave trough appeared over the Tarim Basin in southern Xinjiang, and the hailfall areas were under the control of northwest airflow. At 700 hPa, a vortex system was distributed along the terrain on the southern slope of the Tianshan Mountains (Figure 8a). Under its influence, a westward jet formed in the middle of the Tarim Basin. Given that the hailfall area on 29 June 2023 was mainly located on the side of the vortex system near the mountain, the basin jet should have had little influence on this hail event. The convergence of the wind field near the hailfall area was not significant, and there was only a small-scale local water vapor convergence center (Figure 8b), which provided water vapor conditions for the development of convection clouds. The water vapor convergence mechanism of hailstorms in Xinjiang may be complex and associated with complicated terrain; thus, additional detailed investigations of the wind field structure based on high-resolution observation data are needed in the future.
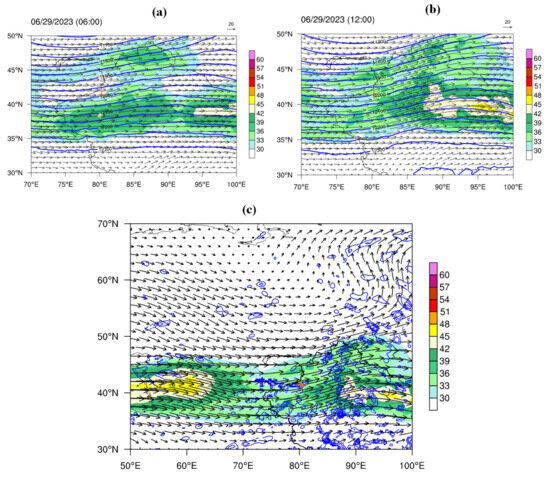
Figure 6.
Wind field (arrows, unit: m/s) and geopotential height (blue contours, unit: gpm) at 200 hPa on 29 June 2023: (a) 06 UTC and (b) 12 UTC. (c) Horizontal divergence larger than zero (blue contours) near the high-level jet stream at 12 UTC. The shaded areas denote wind speeds >30 m/s, and the brown crosses mark the HS-01 hailstone disdrometer.
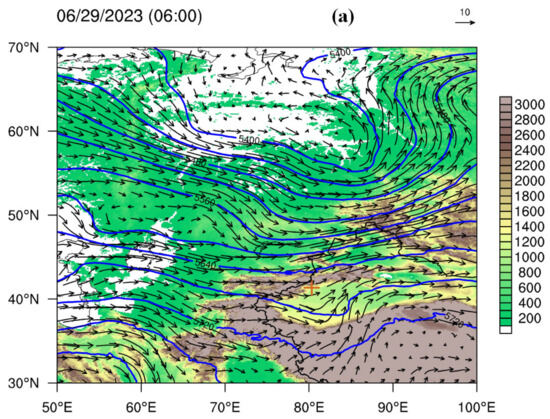
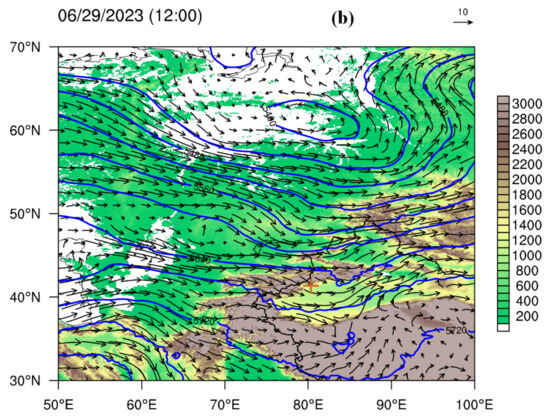
Figure 7.
Wind field (arrows, unit: m/s) and geopotential height (blue contours, unit: gpm) at 500 hPa on 29 June 2023: (a) 06 UTC and (b) 12 UTC, with shaded terrain.
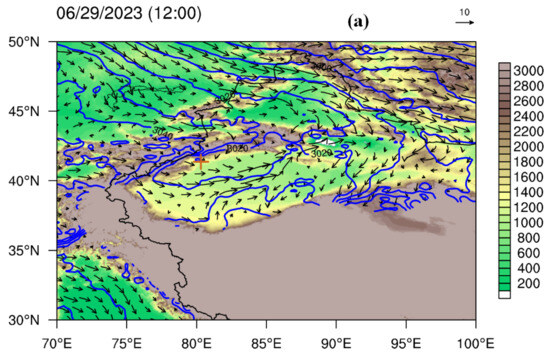
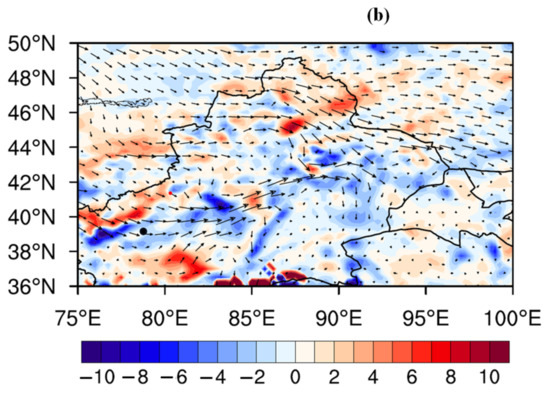
Figure 8.
(a) Wind field (arrows, unit: m/s) and geopotential height (blue contours, unit: gpm) at 700 hPa at 12 UTC on 29 June 2023, with shaded terrain. (b) Water vapor flux divergence (shaded area) at 700 hPa, with red dot indicating the HS-01 hailstone disdrometer.
A favorable environment for deep convection development is shown in Figure 9. This result indicated that a high-value center of precipitable water (PW) formed in the Tarim Basin, with a PW value of approximately 22 mm, which was a moist atmosphere for the commonly dry air environment in southern Xinjiang. There were multiple high-value centers of convective available potential energy (CAPE) around the hailfall area, approximately 400 J/kg, to provide unstable conditions for convection development. The heights of the −20 °C layer and the 0 °C layer and their distances are important parameters for generating hail and were thus investigated. The heights of the −20 °C layer and the 0 °C layer were 7.1 km and 4.4 km, respectively, with a distance of <3 km, which satisfied the local conditions for hail formation. In addition, the 0–6 km vertical wind shear velocity across the hailfall areas reached approximately 12 m/s, which also provided a favorable shear environment for the development of hail clouds.
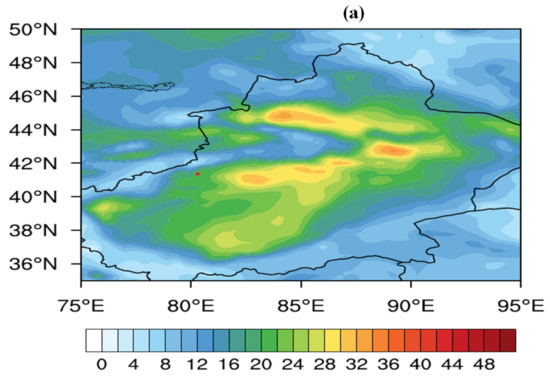
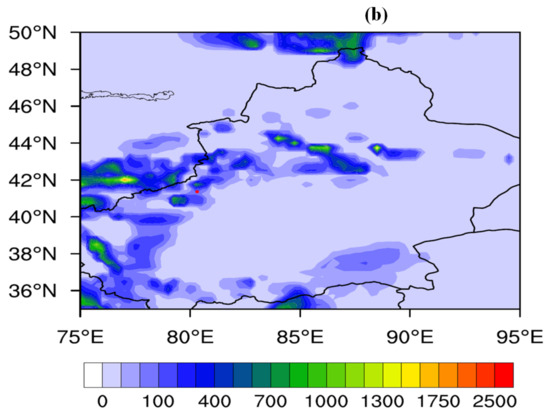
Figure 9.
Atmospheric precipitation (PW; unit: mm) (a) and convective available potential energy (CAPE; J/kg) (b) at 06 UTC on 29 June 2023. The red dots mark the HS-01 hailstone disdrometer.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
To enable better automatic hail observation, this study presents a new independently developed hailstone disdrometer based on the acoustic principle. In 2023, two hailstone disdrometers were installed in Aksu, Xinjiang, and three hail events were observed that were accompanied by rapid changes in surface meteorological parameters. The maximum hail number measured by the hailstone disdrometer was ~70 per minute, with an average hail number and a standard deviation of 20.1 ± 21.0 per minute during the three hail events. The probabilistic statistical analysis indicated that the hail number was mostly <10 per minute, with an occurrence frequency of 48%; the hail number also displayed a secondary occurrence peak of 13% at 40–50 per minute. The hail particle size was generally <20 mm and was primarily distributed between 5 and 10 mm for hail samples. In general, the trends in the variations in the equivalent liquid precipitation derived from the two hailstone disdrometers agreed, although the occurrence periods of the peak equivalent liquid precipitation were slightly different due to the temporal discrepancy in hail overpassing locations between the two hailstone disdrometers. Moreover, the variation pattern of the hailstone disdrometer-retrieved equivalent liquid precipitation was generally consistent with the measurements from the automatic rain gauge at the surface weather stations, which indicated that the hailstone disdrometer could reasonably evaluate the equivalent liquid precipitation of hail. The hail formation mechanism was also investigated in detail for one hail process by analyzing the development of deep convection clouds using the Fengyun 4A satellite-based cloud-top brightness temperature and synoptic conditions based on the ECMWF ERA5 dataset.
The hailstone disdrometer proposed in this study can detect solid precipitation (the hail), and, therefore, can be used as an effective supplement to surface measurements, such as laser raindrop spectrometers and weighing rain gauges. Moreover, this method ought to be useful for replenishing traditional manual observations and providing 24 h of uninterrupted measurements; moreover, comprehensive hail data can be obtained to provide a beneficial basis for the assessment of hail disasters. In this study, the hailstone size was derived from the hailstone terminal velocity based on two assumptions of the hailstone: a spherical shape and the density of ice. Direct in situ measurements of the terminal velocities and shapes of natural hailstones are sparse at present. The advent of new technologies, such as 3-D scanning and printing, has fostered new experimental research using printed hailstones placed in a vertical wind tunnel to evaluate the aerodynamics and tumbling of hail [35], which may help assess and improve the hail retrieval methods used in this study. In addition, the observation period of the hailstone disdrometer was relatively short at present in Aksu, Xinjiang, and the hail characteristics were preliminarily analyzed based on three hail events observed using hailstone disdrometers; therefore, the results presented in this study still need to be evaluated with longer time series of observational samples. Hail events are common in strong convective cloud systems, and China is one of the countries with the most severe hail events worldwide. As a next step, additional hailstone disdrometer stations need to be established to better monitor the long-term distribution and variations in hail to provide first-hand hail information for the assessment of weather modification effects and disaster prevention and reduction. More in-depth statistics will be collected with the accumulation of a longer time series of observational datasets in the future. Furthermore, as a next step, the comparison of the acoustic disdrometers proposed in this study with the other observation techniques available (such as laser optical disdrometer and 3-D scanning and printing) may help assess the uncertainty of the retrieval method in this study.
Author Contributions
Data curation, writing—original draft, review, and editing, Y.L., X.M., J.K., S.Z., Y.F., H.F., X.W., D.C., S.J., N.L., L.R., K.Z. and J.Z.; conceptualization, Y.L. and S.J.; instrument development, retrieval method, and methodology, X.M., S.R., S.J. and J.L.; supervision, Y.L. and S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant No. 2022D01A294), Scientific research subject to the Zhejiang Meteorological Service (Grant No. 2022YB31), the Basic Scientific Program of the Institute of Atmospheric Physics supporting the 14th Five-Year Plan (Grant No. 7-224151), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42293321 and 41875183).
Data Availability Statement
The data of Fengyun 4A satellite-based cloud-top brightness temperature are available at http://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/PortalSite/Data/Satellite.aspx (accessed on 10 December 2023). The ECMWF ERA5 data are obtained from https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/datasets/reanalysis-datasets/era5 (accessed on 10 December 2023). The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
Shiqi Ren, Shengjie Jia, Jia Li are employees of Beijing Keytec Technology Co., Ltd. The company had no roles in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the articles. The paper reflects the views of the scientists and not the company.
References
- Allen, J.T.; Giammanco, I.M.; Kumjian, M.R.; Punge, H.J.; Zhang, Q.; Groenemeijer, P.; Kunz, M.; Ortega, K. Understanding hail in the Earth system. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2019RG000665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.B.; Dore, J.E.; Leslie, D.; Lyons, W.B.; Sands, D.C.; Priscu, J.C. Biological ice nucleation initiates hailstone formation. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 12186–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.M.; Pogorzelski, W.H.; Giammanco, I.M. Evaluating hail damage using property insurance claims data. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2015, 7, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, K.; Karl, T.; Brooks, H.; Kossin, J.; Lawrimore, J.; Arndt, D.; Bosart, L.; Changnon, D.; Cutter, S.L.; Doesken, N.; et al. Monitoring and understanding trends in extreme storms: State of knowledge. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2013, 94, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.J. Hail: Mechanisms, monitoring, forecasting, damages, financial compensation systems, and prevention. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedd, L.; Kumjian, M.R.; Giammanco, I.; Brown-Giammanco, T.; Maiden, B.R. Hailstone shapes. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 78, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.P.; Agarwal, L.; Sinha, N.K. Drag on nonspherical particles: An evaluation of available methods. Powder Technol. 1999, 101, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punge, H.J.; Bedka, K.M.; Kunz, M.; Werner, A. A new physically based stochastic event catalog for hail in Europe. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 1625–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.; Szakáll, M.; Jost, A.; Giammanco, I.; Wright, R. A comprehensive observational study of graupel and hail terminal velocity, mass flux, and kinetic energy. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojorlie, K.L.; Doering, S.; Fowle, M.A. The record-breaking Vivian, South Dakota hailstorm of 23 July 2010. J. Oper. Meteor. 2013, 1, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, A.; Burgess, D.W.; Seimon, A.; Allen, J.T.; Snyder, J.C.; Bluestein, H.B. Rapid-scan radar observations of an Oklahoma tornadic hailstorm producing giant hail. Weather Forecast. 2018, 33, 1263–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Gutierrez, R.; Soderholm, J.S.; Nesbitt, S.W.; Maldonado, P.; Luna, L.M.; Marquis, J.; Bowley, K.A.; Imaz, M.A.; Salio, P. Gargantuan Hail in Argentina. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 101, E1241–E1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.F.; Laflin, J.M.; Cavanaugh, D.E.; Sanders, K.J.; Currens, S.R.; Pullin, J.I.; Cooper, D.T.; Deroche, D.R.; Leighton, J.W.; Fritchie, R.V.; et al. High-resolution hail observations: Implications for NWS warning operations. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 1101–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Zou, T.; Lin, J.; Kong, H.; Ren, Z. Decreased hail size in China since 1980. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, T.; Lin, J.; Kong, H.; Ren, Z. Climatology of hail frequency and size in China, 1980–2015. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2018, 57, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaiotti, D.; Gianesini, E.; Stel, F. Heuristic considerations pertaining to hailstone size distributions in the plain of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. Atmos. Res. 2001, 57, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessens, J.; Berthet, J.L.; Sanchez, J.L. A point hailfall classification based on hailpad measurements: The ANELFA scale. Atmos. Res. 2007, 83, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioutas, M.; Meaden, T.; Webb, J. Hail frequency, distribution and intensity in Northern Greece. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, R.; Schiesser, H.H.; Aller, D. Hailfall: The relationship between radar-derived hail kinetic energy and hail damage to buildings. Atmos. Res. 2002, 63, 177–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Richardson, Y.P.; Meyer, T.; Kosiba, K.A.; Wurman, J. Resonance scattering effects in wet hail observed with a dual-X-band-frequency, dual-polarization Doppler on Wheels on radar. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2018, 57, 2713–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punge, H.J.; Bedka, K.M.; Kunz, M.; Reinbold, A. Hail frequency estimation across Europe based on a combination of overshooting top detections and the ERA-INTERIM reanalysis. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, K.; Battaglia, A.; Lang, T.J.; Cecil, D.J.; Tanelli, S.; Tridon, F. Hail-detection algorithm for the GPM core observatory satellite sensors. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2017, 56, 1939–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedka, K.; Allen, J.; Punge, H.; Kunz, M. A long-term overshooting convective cloud top detection database over Australia derived from MTSAT Japanese advanced meteorological imager observations. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2018, 57, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, W.R. Observations in hailstorms using the T-28 aircraft system. J. Appl. Meteor. 1976, 15, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, P.R.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Detwiler, A.G.; Wilkinson, J.M. Normalized hail particle size distributions from the T-28 storm-penetrating aircraft. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2019, 58, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler-Mang, M.; Schön, D.; Landry, M. Characteristics of a new automatic hail recorder. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.B.; Matson, R.J.; Crow, E.L. The Hailpad: Materials, Data Reduction and Calibration. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1979, 19, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cifelli, R.; Doesken, N.; Kennedy, P.; Carey, L.D.; Rutledge, S.A.; Gimmestad, C.; Depue, T. The Community Collaborative rain, hail, and snow network. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, E.A.; Friedrich, K.; Ellis, S.M.; Burgess, D.W. Comparison of Disdrometer and X-Band Mobile Radar Observations in Convective Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 2414–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderholm, J.S.; Kumjian, M.R.; McCarthy, N.; Maldonado, P.; Wang, M. Quantifying hail size distributions from the sky—Application of drone aerial photogrammetry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.J.; Kumjian, M.R. The impact of vertical wind shear on hail growth in simulated supercells. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 641–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumjian, M.R.; Lombardo, K. A hail growth trajectory model for exploring the environmental controls on hail size: Model physics and idealized tests. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 2765–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Kumjian, M.R.; Ganson, S.M.; Khain, A.P. Polarimetric radar characteristics of melting hail. Part I: Theoretical simulations using spectral microphysical modeling. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2849–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, K.L.; Krause, J.M.; Ryzhkov, A.V. Polarimetric radar characteristics of melting hail. Part III: Validation of the algorithm for hail size discrimination. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2016, 55, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giammanco, I.M.; Maiden, B.R.; Estes, H.E.; Brown-Giammanco, T.M. Using 3D laser scanning technology to create digital models of hailstones. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2017, 98, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, S.; Levizzani, V.; Anagnostou, E.; Bauer, P.; Kasparis, T.; Lane, J.E. Precipitation: Measurement, remote sensing, climatology and modeling. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperuelo, M.; Llasat, M.C.; López, L.; García-Ortega, E.; Sánchez, J.L. Study of 11 September 2004 hailstorm event using radar identification of 2-D systems and 3-D cells. Adv. Geosci. 2006, 7, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhi, J.; Zhang, C. Cause analysis of a strong hail weather in Kashi area in June 2013. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2014, 8, 19–26, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Seeley, J.; Romps, D. The effect of global warming on severe thunderstorms in the United States. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2443–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changnon, S.A. Increasing major hail losses in the U.S. Clim. Chang. 2009, 96, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, H.E.; Lee, J.W.; Craven, J.P. The spatial distribution of severe thunderstorm and tornado environments from global reanalysis data. Atmos. Res. 2003, 67–68, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punge, H.J.; Kunz, M. Hail observations and hailstorm characteristics in Europe: A review. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176–177, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changnon, S.A. The scales of hail. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1977, 16, 626–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prein, A.F.; Holland, G.J. Global estimates of damaging hail hazard. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2018, 22, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Ma, L.; Cai, R. The overview of study on hailstorm in Xinjiang. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2023, 17, 10–17, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y.; Feng, H. Study on spatio-temporal pattern of hail disaster in China mainland from 1950 to 2009. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2015, 36, 83–92, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Luo, J.; Qu, L. The spatial-temporal distribution and radar echo signatures of hail in Aksu, Xinjiang. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2021, 15, 81–88, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Schleusener, R.A.; Jennings, P.C. An energy method for relative estimates of hail intensity. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1960, 41, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.A.; Ludlam, F.H.; Macklin, W.C. The density and structure of hailstones. Q. J. R. Met. Soc. 1963, 89, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Bergström, H. An auxiliary tool to determine the height of the boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteor. 2005, 115, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, X.; Teng, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, X.; Li, J.; et al. A novel method for estimating the vertical velocity of air with a descending radiosonde system. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieling, C.; Smith, M.; Beruvides, M. Review of impact factors of the velocity of large hailstones for laboratory hail impact testing consideration. Geosciences 2020, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, A.S. Weather Modification by Cloud Seeding; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Gokhale, N.R. Hailstorms and Hailstone Growth, 1st ed.; State University of New York Press: Albany, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Bian, J.; Brown, W.O.; Cole, H.; Grubišić, V.; Young, K. Vertical air motion from T-REX radiosonde and dropsonde data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E44 Committee. Test Method for Determining Resistance of Photovoltaic Modules to Hail by Impact with Propelled Ice Balls 2019; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Technical Regulations: Volume II—Meteorological Service for International Air Navigation, 2018th ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, FengYun-4. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Climatology of hail in China: 1961–2005. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2008, 47, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).