Abstract
Polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs), persistent environmental pollutants, are found in flue gas from incinerators. While air pollution control systems (APCSs) capture pollutants, the resulting sludge/fly ash (SFA) requires further treatment due to residual PCDEs and other harmful substances. This study investigated a hazardous waste thermal treatment system (HAWTTS) utilizing flameless combustion technology alongside a multistage APCS (scrubbers, cyclone demisters, bag houses). SFA from the APCS was recirculated for secondary combustion. PCDE levels were measured before and after each unit within the HAWTTS. The HAWTTS achieved a remarkable overall PCDE removal efficiency of 99%. However, the incinerator alone was less effective for low-chlorine PCDEs. Scrubbers and bag houses exhibited lower removal efficiencies (17.8% and 30.9%, respectively) due to the memory effect. Conversely, the cyclone demister achieved a high removal rate (98.2%). Following complete APCS treatment, PCDE emissions were significantly reduced to 1.02 ng/Nm3. While SFA still contained some PCDEs, the flameless combustion’s uniform temperature distribution enhanced combustion efficiency, minimizing overall PCDE emissions. This system demonstrates significant potential for mitigating PCDE pollution from incinerators. Further research could focus on optimizing treatment processes to address residual PCDEs in SFA.
1. Introduction
Polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs) are a class of synthetic halogenated aromatic compounds with the formula of C12H10−nClnO (n = 1–10), encompassing 209 potential congeners [1]. Their chlorine content (n = 1 to 10) resembles polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-furans (PCDFs). PCDEs find applications as hydraulic oils, electrical insulators, flame retardants, lubricants, and plasticizers [2]. They exhibit remarkable resistance to acids and oxidation, leading to high environmental persistence. Most PCDE congeners can travel long distances in the atmosphere or are adsorbed to particulate matter, accumulating in air, soil, and water [3]. Due to their lipophilic nature, PCDEs bioaccumulate in biological systems, particularly in marine and freshwater organisms [4,5]. Their extended half-life further promotes bioaccumulation up the food chain, with detection even in human adipose tissue [6]. Studies suggest PCDE exposure in mammals can lead to adverse effects like death, birth defects, stunted growth, tissue damage, reproductive problems, oxidative stress, immune system suppression, and hormonal disruption [7]. Therefore, controlling PCDE emissions is critical.
The primary sources of PCDEs are the industrial production of chlorophenols and chlorinated benzoic acids, as well as flue gas from the incinerator combustion of fly ash and municipal waste [8,9]. Incomplete combustion during initial stages (below 450 °C) promotes PCDE formation from chlorinated precursors like chlorobenzene and chlorophenol. Conversely, complete combustion at temperatures exceeding 800 °C minimizes PCDE formation [10]. Notably, environmental PCDE levels often surpass those of PCDFs [11]. Under natural conditions, PCDEs can degrade into PCDD/Fs, hydroxylated PCDEs, and chlorobenzene through photolysis and thermal decomposition [12]. Among these products, PCDD/Fs pose a greater toxicological threat [13]. Thermal decomposition exceeding 700 °C achieves near-complete degradation of PCDEs [14].
Waste incineration offers a significant advantage; it reduces waste mass and volume while recovering biomass energy in usable forms (solid, liquid, or gas) for generating power or heat [15]. Consequently, incineration remains the dominant method for waste management globally [16]. However, a crucial distinction exists; incineration can generate PBDE emissions, but effective combustion practices can significantly reduce PCDE emissions. Studies indicate that complete destruction of PCDDs/PCDFs occurs at incineration temperatures of 600 °C. Therefore, controlling dioxin and furan emissions from waste incineration primarily focuses on preventing their reformation in the flue gas [17]. Within the incinerator system, PCDE content exhibits a complex temperature dependence. At temperatures below 200 °C, PCDEs increase due to adhesion to ash surfaces and desorption from deposits within the furnace and flue gas pipes during initial heating. Between 200 °C and 800 °C, PCDE levels initially rise due to heterogeneous reactions involving precursor compounds (peaking around 250–400 °C). However, as temperatures surpass 800 °C, PCDE emissions become minimal, dropping to less than one-tenth of the peak concentration [9]. Flameless combustion (FC), also known by terms like moderate/intense low-oxygen dilution (MILD), high-temperature air combustion (HTAC), and flameless oxidation (FLOX), presents a promising alternative approach. FC offers several benefits, including reduced fuel consumption, a more stable combustion process with lower noise levels, and decreased emissions of NOx and CO [18]. The FC process ensures uniform distribution of reactants, temperature, and heat flux, leading to a wider combustion range, improved thermal efficiency, and enhanced combustion stability. While FC has been extensively studied with gaseous fuels [19], its application with solid biomass combustion requires further investigation.
Waste incineration generates a myriad of harmful pollutants, including acidic gases, heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), dioxins, and persistent organic compounds (POCs) [20]. To address these emissions, air pollution control devices (APCDs) are essential. Widely used APCDs include semidry scrubbers (SDSs), fabric filters (FFs), selective catalytic reduction (SCR), wet scrubbers (WSs), electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), spray dryer absorbers/bag filters (SDAs/BFs), and cyclone demisters (CYCDs) [21,22,23]. Venturi scrubbers, a type of wet scrubber, are commonly employed as the first stage for effectively absorbing acidic gases in flue gas. They also demonstrate high efficiency (around 90%) in capturing fine particulate matter (2.5 μm diameter) [24]. Cyclone demisters utilize inertial separation to remove larger particles (approximately 15 μm) with a 90% removal rate [25]. Bag filters excel at capturing heavy metals and PAHs present in flue gas, achieving an impressive fly ash removal efficiency of up to 99.5%. Notably, bag filters are often combined with activated carbon (AC) to further enhance adsorption efficiency [20]. Research indicates that spray dryer absorbers coupled with bag filters (SDAs/BFs) can achieve a PCDD/PCDF removal efficiency as high as 99% [23]. It is important to note that PCDEs can form on the surface of fly ash through non-homogeneous reactions involving precursor compounds [26]. Furthermore, PCDEs themselves can act as precursors for PCDD/PCDF formation [13]. Since APCDs effectively reduce PCDD/PCDF levels, further investigations into their removal efficacy for PCDEs are warranted. This research could lead to optimized APCD configurations for minimizing emissions of both PCDEs and PCDDs/PCDFs during waste incineration.
The incineration of municipal solid waste (MSW) generates various types of ash, including fly ash (SFA) captured by air pollution control devices (APCDs) and bottom ash remaining after combustion. SFA consists primarily of fine particles entrained in the flue gas, including unburned carbon, combustion products, and volatile components of salts and heavy metals released during high-temperature processing [27]. While the bulk composition of SFA is sulfate, aluminum silicate, and silicate minerals, it also contains concerning contaminants like heavy metals (cadmium, mercury, lead, zinc) and persistent organic pollutants (PAHs, PCBs, PCDDs, and PCDFs) [28]. Improper SFA management poses significant environmental risks and incurs high treatment or recovery costs [29]. Traditionally, incineration has been used for sludge treatment. However, single-stage incineration can inadvertently create PCDDs/PCDFs from inorganic chlorides and organic compounds present in the sludge. This occurs within the 250–400 °C range of heat recovery boilers, where metal chlorides (cupric chloride oxides and sulfates) in fly ash act as catalysts [30,31]. To address this concern, researchers are increasingly exploring the reintroduction of SFA into the incinerator for a secondary incineration process aimed at reducing harmful substances [32,33,34]. Reintroducing SFA alters the furnace’s temperature distribution and chemical composition, thereby modifying the combustion characteristics of the mixed fuel [35]. Prior studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of co-combusting MSW with SFA in reducing emissions of PAHs [36], HCl, NOx [37], PCDDs/Fs [38], and heavy metal Hg [39]. However, the impact of SFA recirculation on PCDE emissions remains understudied.
This study investigates the influence of non-flaming combustion and SFA co-incineration on PCDE emissions in hazardous waste thermal treatment systems (HAWTTSs). The HAWTTS employed here features a non-flaming combustion incinerator coupled with an air pollution control system (APCS) consisting of a venturi scrubber (SCB), a cyclonic demister (CYCD), and a bag filter (BH). Subsequently, the scrubber sludge, cyclone demister sludge, and bag house fly ash (SFA) are recirculated back into the incinerator. Previous research has demonstrated that this system can effectively remove NOx and CO produced during waste incineration, resulting in decreases in HCl and SO2 emissions by 81.8% and 38.8%, respectively [40]. It also reduces the emissions of PM10 and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with fine particles (FP-PAHs), achieving removal efficiencies of 99.9% for PM10 and 65.4% for FP-PAHs [41]. The total mass and toxic equivalent concentrations of PCDDs/Fs were reduced by 99.9% [42]. This study primarily explores the impact of the system on PCDE congeners. By measuring the mass concentrations of PCDE congeners at various points within the HAWTTS, the removal efficiencies of the incinerator and APCS for PCDE congeners are calculated. Additionally, the mechanisms by which flameless combustion and co-incineration with SFA affect PCDE congeners are analyzed, providing a foundation for further optimization of the HAWTTS.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. HAWTTS Overview
The hazardous waste thermal treatment system (HAWTTS) consists of an exothermic combustion system with a primary and secondary combustion chamber within the incinerator, along with air pollution control devices (APCDs). The primary chamber operates at 900 °C, while the secondary chamber reaches 1100 °C to ensure complete pollutant incineration. APCDs further reduce the emissions of persistent organic pollutants through physical capture and chemical degradation. Figure 1 illustrates the system layout and connection sequence. Detailed descriptions of each component follow.
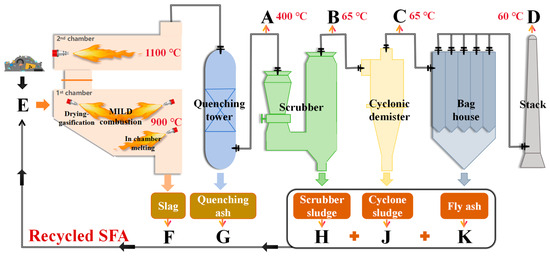
Figure 1.
Diagram of the HAWTTS system.
This hazardous waste thermal treatment system has the capacity to process 800 tons of organic waste and 400 tons of inorganic material annually, with a construction cost of approximately CNY 9.25 million. The operational costs include the consumption of diesel and natural gas as well as the post-treatment of bottom ash and fly ash. The system employs flameless combustion, resulting in higher temperatures in the primary combustion chamber and lower exhaust flow rates. Compared to traditional hazardous waste treatment systems (see [40]), it reduces diesel consumption by 25.8%, natural gas usage by 49.7%, and post-treatment costs by approximately 81.7%. This results in annual operational cost savings of about CNY 450,000, with a payback period of 20.5 months. In terms of greenhouse gas emissions, flameless combustion saves about 25% in energy consumption and reduces pollutant emissions, including CO2, by 50%. Research indicates that by 2030, adopting flameless combustion could save 68 billion liters/year of fuel oil and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 180 billion tons/year [43].
2.1.1. Flameless Combustion System
This system incorporates a modified primary chamber and the existing secondary chamber. The primary chamber is virtually divided into three zones: flameless oxidation (FO), water–gas shift reaction (WGSR), and in-chamber melting (ICM). The FO zone is established by continuous air-deficient mixing in the primary chamber’s center, achieved by an angled burner placement relative to the central axis. This asymmetric air–fuel mixing creates a double vortex flow within the combustion zone. An O2 sensor regulates the air and fuel flow rates for both burners to maintain dilution combustion (1–3% O2) at the inter-chamber connection. Flameless combustion generates heat that converts fully vaporized H2O and CO from the FO zone into syngas (CO2 + H2) through the WGSR. Water serves as an oxygen carrier within the primary chamber. Products from the WGSR are further combusted in the secondary chamber at temperatures exceeding 1050 °C. Heat from the flameless zone diffuses to a bed of material within the chamber, combined with a diffusion flame jet from a burner positioned on the bed. This combined heat melts the bottom ash produced during flameless combustion, forming slag (bed temperature > 850 °C). Smoke generated in the process is cooled using a quench tower. Table 1 summarizes the processing capacity and combustion details for each chamber. Refer to [40] for a more comprehensive discussion of the flameless combustion system.

Table 1.
Basic information of the primary and secondary combustion chambers.
2.1.2. Air Pollution Control System (APCS)
The APCS, as depicted in Figure 1, comprises a semidry spray catalytic quenching tower (1050–400 °C), a venturi wet scrubber (400–60 °C) (SCB), a cyclone demister (CYCD), and an activated carbon powder-filled bag house (BH) (~60 °C). This system effectively removes harmful substances before the flue gas exits through the stack. Table 2 presents the key operational details for each component. Upon entering the quenching tower from the incinerator, the flue gas undergoes water spraying to reduce its temperature from 950 °C to 400 °C. Subsequently, it enters the venturi scrubber where an alkaline solution neutralizes acidic gases and further lowers the temperature to 65 °C. A cyclone demister then efficiently removes water and large particles from the flue gas while maintaining its temperature. Before reaching the bag house, activated carbon powder (detailed specifications in Table 2) is introduced to adsorb organic pollutants within the flue gas. Finally, the purified flue gas is subject to fine-particle capture and removal by the bag house before discharge through the stack.

Table 2.
Basic information of the purification equipment in the APCS.
2.2. Experimental Design
Previous studies have documented the presence of toxic substances, such as PCDDs/Fs, in incinerator ash and sludge, including bottom ash, quenching tower ash, sludge, and fly ash. Research suggests that sludge generated by SCBs and CYCDs, as well as fly ash collected by the BH, exhibits elevated concentrations of these harmful substances [28,44]. Conversely, higher temperatures within the incinerator promote the degradation of pollutants like PCDDs/Fs, PCBs, and HCBs in bottom ash and quenching tower ash [45].
In this study, to effectively reduce the emission of hazardous pollutants and mitigate the adverse impact of excessive inorganic material on the calorific value of the incinerator, we adopted an innovative recycling strategy. This involved reintroducing by-products generated during the combustion process—sludge from the SCB and CYCD, along with fly ash from the BH—back into the incinerator. These materials were mixed with the raw feed and subjected to secondary combustion to further decompose organic pollutants and stabilize inorganic components through pyrolysis and combustion reactions.
To ensure the accuracy of the data and the reliability of the experimental results, sampling points were established at several critical locations once the system reached a stable operational state. These included the feed inlet point E, where the initial state of the mixed raw materials and recycled substances was primarily monitored; the quench tower bottom ash outlet G and the incinerator bottom ash outlet F, used to measure the solid-phase PCDE content in the residues post-combustion; and the sludge points H and J from the SCB and CYCD, where both liquid- and solid-phase PCDE concentrations were analyzed to assess the effectiveness of the washing and dust-removal processes in pollutant reduction. Additionally, solid-phase PCDE measurements were conducted at the fly ash point K from the BH to evaluate the efficacy of bag house dust-removal technology in controlling the toxic components in fly ash. Sampling and measurements were also carried out at the SCB inlet A, CYCD inlet B, BH inlet C, and the stack exit D to monitor the distribution and concentration changes of solid- and gaseous-phase PCDEs, thus providing a comprehensive assessment of the entire incineration system’s environmental emission control effectiveness.
Once the system achieved stable operation, the concentrations of PCDEs at each sampling point were observed to remain consistent over time. Consequently, samples were collected thrice at the aforementioned sampling points. Subsequently, the collected data were processed to remove outliers and averaged. The resulting data are presented in Section 3. This study hypothesizes that the distribution of PCDE congeners in the SFA mirrors that found in the PCDEs produced by the SCB, CYCD, and BH.
It is noteworthy that variations in operational conditions (such as temperature, oxygen supply, and waste load), the composition of waste, the use of chemical agents, the maintenance status of the system, and external environmental conditions could potentially influence the measurement results of PCDE congeners. However, existing research indicates that under strictly controlled experimental conditions, the impact of these variables on PCDE emissions is marginal [46]. Therefore, this study does not discuss these potentially influencing factors.
2.3. PCDE Measurement
There is currently no standardized method for quantifying polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and furans (PCDDs/Fs). This study adopted the detection approach employed by Yang et al. [9]. The targeted PCDE congeners included CDE-28, -77, -99, -141, -180, and -209. Sample preparation followed the standard PCDD/F analysis procedure with specific modifications for PCDE analysis.
Prior to analysis, a known amount of 13C-labeled internal standard (IS) solution was added to each sample to monitor recovery during the analytical process. Samples then underwent 24 h Soxhlet extraction. The resulting extracts were concentrated using N2 gas stream evaporation before being transferred to vials. Subsequently, the samples underwent acidic silica gel column cleaning (20 mL hexane eluent) and transfer onto an alumina column. Sequential elution involved 20–30 mL of hexane followed by 25 mL of DCM/hexane (40/60 v/v). The collected eluate was further purified using gaseous N2 (purity > 99.99 vt%) until reaching a near-dry state. Finally, the injection recovery standard (RS, L-CDE #61, 2,3,4,5-tetrachloro [13C12] diphenyl ether) was incorporated into the internal standard (IS) solution, and the combined volume was adjusted to 10 μL for instrumental analysis.
A high-resolution gas chromatograph interfaced with a high-resolution mass spectrometer (HRGC/HRMS) was employed for quantitative analysis of the target compounds. The GC section consisted of an Agilent/HP 6890 high-resolution gas chromatograph equipped with an automatic sampler (CTC Analytics Dual System), a non-fraction sampler (injection temperature 250 °C), and a silica gel capillary column (DB-5HT, L = 60 m, ID = 0.25 mm, film thickness = 0.25 μm). Helium served as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The temperature program began at 100 °C (held for 4 min), followed by a ramp of 40 °C per minute to 200 °C (held for 3.5 min), and a final ramp of 10 °C per minute to reach 325 °C (held for 2.5 min).
The MS component was a Micromass/Auto spec Ultima high-resolution mass spectrometer equipped with an electron impact (EI+) source operating in positive mode. Selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode was used with a resolution set to 10,000. The electron energy was set to 35 eV, and the source temperature was maintained at 250 °C.
2.4. Calculation of PCDE Congener Removal Efficiency and Net Emissions
To evaluate the effectiveness of SFA reintroduction into the incinerator for PCDE removal, this study calculates the removal efficiencies of PCDE congeners within the incinerator, APCDs, and the entire HAWTTS system. The removal efficiency of PCDE congeners by the incinerator is calculated using Formula (1):
In this formula, ‘i’ represents various PCDE isomers, and ‘m’ denotes the mass concentration of PCDEs at corresponding locations within the HAWTTS. The incinerator feedstock enters at point E and includes raw materials along with SFA from scrubber sludge (point H), cyclone sludge (point J), and fly ash (point K). The incinerator output consists of slag exiting at point F, quenching ash exiting at point G, and flue gas discharged from the cold stripping tower at point A.
The removal efficiency of PCDE congeners by the APCDs is calculated using Formula (2):
The input of the APCDs is the flue gas at point A, and the output is the flue gas at point D. The removal efficiency of PCDE congeners by the entire HAWTTS is shown in Formula (3):
The HAWTTS system processes the incinerator input and produces three outputs: flue gas exiting at point D, bottom ash exiting at point F, and quenching sludge exiting at point G.
In addition to determining the overall removal efficiency for the entire system, we also calculate the removal efficiency achieved by each individual device within the APCS for PCDE congeners. Formulas (4)–(6) present the removal efficiencies for the SCB, CYCD, and BH, respectively:
where ‘f’ represents the mass concentration of PCDE congeners in the flue gas at various points (A, B, C, and D). The SCB receives flue gas input at point A and produces flue gas exiting at point B; the CYCD receives flue gas input at point B and produces flue gas exiting at point C; and the BH receives flue gas input at point C and produces flue gas exiting at point D.
Net emissions (qnet) were used to quantify the total PCDE emissions from the HAWTTS, as shown in Formula (7):
where qout represents the output of PCDE congeners from the HAWTTS, while qin denotes the input of PCDE congeners. The HAWTTS input includes PCDEs present in the raw material (point E) and SFA (scrubber sludge at point H, cyclone sludge at point J, and fly ash at point K). The output comprises PCDEs exiting at points D, F, and G, as illustrated by Formula (8):
The net emission serves as an indicator of the HAWTTS’s effectiveness in mitigating PCDE congeners. A negative qnet value signifies a successful reduction in PCDE emissions by the HAWTTS, whereas a positive qnet value indicates that the HAWTTS is not effectively eliminating PCDEs and may even be contributing to their increased release.
3. Results and Discussion
Table 3 presents the mass concentration of PCDE congeners at each measurement point within the HAWTTS system. A comprehensive analysis will be conducted to evaluate the influence of incineration, the APCS, and the overall HAWTTS on the removal efficiency of individual PCDE congeners.

Table 3.
PCDE mass concentrations among the units in the HAWTT system.
3.1. PCDE Congeners in Incinerators
3.1.1. Input of PCDE Congeners
PCDEs entering the incinerator originate primarily from two sources: the waste feedstock (point E) and the sludge and fly ash generated by the SCB, CYCD, and BH, collectively referred to as SFA (feedback = E + SFA). Figure 2 depicts the proportions and mass concentrations of PCDE congeners in both the feedstock and SFA. Recirculating SFA is the dominant source of PCDEs in the feedback stream, with a mass concentration of 938.80 ng/kg, accounting for 97.82% of the total PCDE content. The solid waste feedstock contains a significantly lower mass concentration of PCDE congeners (20.86 ng/kg), representing only 2.18% of the total. Due to its low water solubility [3], no detectable levels of PCDEs are found in liquid wastewater samples.
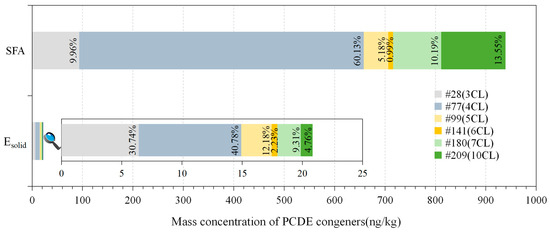
Figure 2.
Proportion and mass concentration of PCDE congeners in the incinerator input.
Previous studies have shown that fly ash exhibits higher concentrations of heavy metals like mercury, lead, cadmium, and volatile organics compared to bottom ash [44,47]. During the initial drying stage in the incinerator, rapid evaporation removes water content from the waste. High temperatures in this stage cause low-boiling-point organic compounds to volatilize and react with oxygen, forming water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). This process can create localized areas with limited oxygen (hypoxic zones) and generate incomplete combustion products (PICs) [48,49].
In subsequent combustion stages, a significant portion of the chlorine in the waste is released as HCl. This HCl can partially react with oxygen to form H2O and Cl2. At elevated temperatures, PICs undergo chlorination with Cl2, resulting in the formation of chlorobenzene, chlorophenol, and polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) precursors—all crucial for generating PCDEs. Studies have shown that chlorobenzene and chlorophenol can condense to form highly chlorinated polychlorinated biphenyl ether compounds within specific temperature ranges (300–450 °C) [50].
Furthermore, to ensure the stable operation of large-scale incinerators, the de novo synthesis of dominant compounds leads to a significant fraction of dioxins being adsorbed onto fly ash surfaces, contributing to its elevated dioxin content. Apart from de novo synthesis, there is another potential pathway for dioxin formation in fly ash: the low-temperature catalytic generation of gaseous precursors with similar structures as dioxins [51]. PCDEs, acting as important precursors for PCDDs/Fs, exhibit a high affinity for particulate-matter surfaces. Hence, fly ash also contains substantial PCDE content. Consequently, recycling and recombusting SFA is crucial for reducing pollutant levels. It is important to note that due to their strong hydrophobic properties, neither raw materials nor wastewater derived from SFA contain PCDEs.
Among the PCDE congeners present in feedstocks and SFA, tetrachlorodiphenyl ether (CDE #77(4CL)) is the most prevalent. It constitutes 40.8% of the total PCDEs in solid waste feedstocks and 60.1% in SFA, accounting for 59.7% of the overall feedback stream. In solid feedstocks, lower chlorinated CDE congeners are more prevalent, with the following ranking order: #77(4CL) > #28(3CL) > #99(5CL) > #180(7CL) > #209(10CL) > #141(6CL). In SFA, following the dominance of CDE #77(4CL), the second-highest congener is CDE #209(10CL), followed by CDE #180(7CL). This observation suggests that high-chlorinated PCDDs are more prevalent in SFA compared to feedstocks due to their propensity to accumulate in sediments [52].
3.1.2. Output of PCDE Congeners
The incinerator output consists of three components: bottom ash (F) discharged from the incinerator’s base, quenching tower slag (G), and flue gas (A) emitted from the quenching tower. This section examines PCDE congeners in these outputs. Figure 3 illustrates the proportions and mass concentrations of PCDEs found in ash (F), slag (G), and flue gas (A). Notably, no PCDE congeners were detected in quenching tower slag (G). Point A represents a mixture of particulate matter (solid phase) and gaseous components within the flue gas.
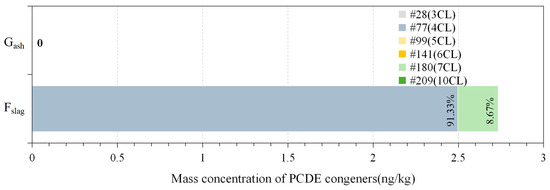
Figure 3.
The proportion and mass concentration of PCDE congeners at each point in the incinerator output.
Compared to the feedstock, the mass concentration of PCDEs in the flue gas is significantly lower, indicating thermal decomposition at high incineration temperatures. The bottom ash (F) exhibits a PCDE mass concentration of 2.73 ng/kg, reflecting reduced pollutant generation due to complete combustion at temperatures exceeding 800 °C. Furthermore, flameless combustion technology reduces the formation of localized rich-oxygen or rich-fuel zones, thereby decreasing the production of harmful gases and volatile compounds, which in turn lowers the overall generation of PCDEs [53]. Additionally, flameless combustion maximizes the utilization of fuel and oxygen, reducing the generation of unburned carbon and other combustion by-products [54]. It also diminishes the temperature gradients within the combustion chamber and enhances combustion efficiency [55,56]. Consequently, the concentration of PCDEs post-incinerator has been reduced to a minimal level.
The absence of PCDEs in the quenching tower slag (G) is likely attributed to the high temperature and rapid cooling employed during the quenching process. This effectively inhibits PCDD/F formation or promotes their decomposition. Studies have shown that quenching slag at temperatures above 400 °C results in a PCDD/F content only 1/300th of that observed with gradual cooling below 200 °C [57]. Rapid quenching is also an effective measure to prevent the generation of hazardous compounds [58]. Interestingly, among the PCDE congeners detected in the bottom ash (F), CDE #77(4CL) constitutes approximately 91.33% of the total, with CDE #180(7CL) accounting for the remaining fraction. Notably, CDE congeners #28, #99, #141, and #209 were not detected in the bottom ash. A detailed analysis of the flue gas from point A will be discussed in Section 3.2.1.
3.2. Distribution of PCDE Congeners in the APCS
3.2.1. Mass Concentration of PCDE Congeners in APCS Flue Gas
Figure 4 presents the concentrations of PCDEs and their congeners at sampling points A (inlet of SCB), B (inlet of CYCD), C (inlet of HB), and D (outlet of the stack). Despite PCDEs’ low vapor pressure and poor volatility [59], the high fly ash concentration in recycled SFA promotes the condensation and aggregation of gaseous PCDEs. Consequently, the gaseous PCDE content exceeds the solid content at each point.
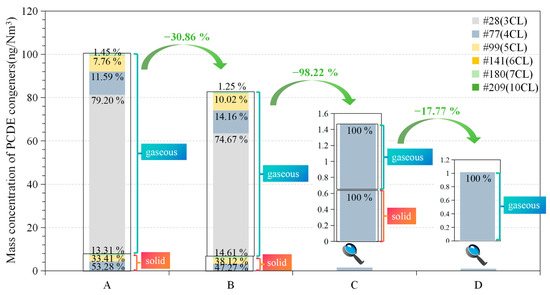
Figure 4.
The mass concentration of PCDEs at each point in the APCS and the removal efficiency of PCDEs by the SCB, CYCD, and BH.
Across all APCS sampling points, a higher proportion of low-chlorine CDE congeners is observed, particularly for gaseous PCDEs. High-chlorine CDEs are almost absent due to their lower volatility compared to their low-chlorine counterparts [3]. Notably, the flue gas at point A does not contain CDE #141 and #209; these congeners will not be synthesized after passing through various treatment systems and are therefore absent in subsequent sampling points.
The significant amount of PCDE congeners in the smoke emitted from the quenching tower (point A) is attributed to the gradual cooling process. As the smoke leaves the furnace and undergoes heat exchange with the external environment, low-temperature heterogeneous reactions on solid surfaces catalyze the formation of precursors, unburned carbon, and certain transition metal compounds [60]. These precursors include organic compounds with structures similar to PCDDs/Fs but lacking chlorination, phenol and chlorophenol, benzene and chlorobenzene, and short-chain aromatic hydrocarbons [61]. These precursors can potentially be resynthesized into PCDEs. Additionally, PCDEs’ stable chemical properties allow them to remain gaseous at higher temperatures. Consequently, during the smoke’s cooling process within the quenching tower, these gaseous pollutants are not effectively condensed or adsorbed onto slag particles, leading to their persistence at high concentrations within the smoke.
Figure 4 illustrates the remarkable reduction in various pollutants achieved by utilizing SCBs. Extensive research indicates that SCBs can reduce PCDD/F emissions by 97.6% [40], PM10 emissions by 97.6% [62], and PM10 bound-PAH emissions by 84.8% [42]. However, in this study, the removal efficiency of SCBs for PCDEs and its congeners is only 17.8%. This disparity can be attributed to the ‘memory effect’ in wet scrubbers. Persistent organic pollutants can be delayed in emission due to mechanisms like impaction, interception, or gravity within flue gas delivery lines and air pollution control systems [63]. These pollutants may become adsorbed or desorbed on the surface of the plastic packaging materials used in SCBs or be entrapped within washing solutions or fine particles [64].
While traversing through the scrubber, semivolatile organic compounds (SVOCs) in the gas phase can undergo condensation or adsorption, converting them into solid phases or encapsulating them within liquid-water films [65]. However, due to their lipophilic nature, PCDEs tend to remain in the gaseous form or adhere to the internal surfaces of scrubbers, reducing their removal efficiency during washing procedures [66]. Additionally, their hydrophobic properties hinder effective dissolution in scrubber water, leading to lower capture and elimination rates. Notably, there is a slight increase observed in CDE #99 concentration after passing through the SCB, which can be attributed to the de novo synthesis occurring within SCBs [67]. Figure 4 illustrates that the concentrations of low-chlorinated CDEs in the inlet and outlet flue gases of the SCB are significantly higher than those of high-chlorinated CDEs. This is attributed to the higher volatility of low-chlorinated CDEs compared to high-chlorinated ones. During combustion and emission processes, volatile compounds more readily transition from the combustion zone into the flue gas. Additionally, due to their higher molecular weights and lower volatility, high-chlorinated CDEs are more likely to deposit within the equipment during adsorption and capture processes.
The removal efficiency of the CYCD for PCDEs and their congeners is impressive, reaching 98.2%. This can be attributed to the strong centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotating air stream within the cyclone. This force effectively separates larger particles containing adsorbed PCDEs. Additionally, under specific conditions, cyclone collectors can remove gaseous pollutants through adsorption or condensation mechanisms [68]. Studies have shown that combining cyclone collectors with subsequent treatment technologies like activated carbon adsorption and bag filters can significantly enhance PCDD/F removal efficiencies in waste incinerator flue gas treatment systems [69]. Notably, the CYCD achieves complete removal of CDE congeners #28, #99, and #180.
The removal efficiency of the bag house (BH) for PCDEs and their congeners is 30.86%, with a 100% removal efficiency for particulate-bound congeners. This efficiency is attributed to the high porosity of the filter material used in the BH and the large filter surface area, which optimize air velocity and increase the opportunity for contact between the particles and the filter medium, thus effectively capturing fine particles. Research has found that the BH achieves a removal rate for fine particles exceeding 99% [70]. However, the negative gas-phase removal efficiency (−23.0%) indicates the re-entrainment of pollutants due to the memory effect observed in bag houses. This effect occurs when gaseous pollutants adsorbed onto aged filter bags are released back into the gas stream. Li’s research confirms this phenomenon, reporting negative removal efficiencies for PCDDs/Fs attributable to the memory effect [71].
In conclusion, the air pollution control system (APCS) primarily relies on the CYCD for the efficient removal of most PCDE congeners. Following APCS treatment, PCDE levels in the flue gas are significantly reduced to negligible amounts. At point D, the particle-phase concentration is zero, while the gas-phase concentration is a mere 1.02 ng/kg with only CDE #77(4CL) detected. This demonstrates the high efficiency of the APCS in eliminating pollutants.
3.2.2. Mass Concentration of PCDE Congeners in Recirculated SFA
Figure 5 presents the distribution and mass concentrations of PCDE congeners in the sludge or fly ash (SFA) generated by the APCS. Consistent with PCDEs’ hydrophobic nature, no PCDE congeners were detected in the wastewater from either scrubber sludge (point H) or cyclone demister sludge (point J).
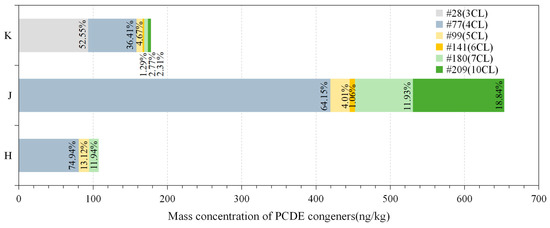
Figure 5.
The mass concentration and proportion of PCDE congeners at each point in SFA.
As shown in Figure 5, the PCDE content at points H, J, and K (fly ash from the bag filter) is 107 ng/kg, 654 ng/kg, and 178 ng/kg, respectively, accounting for 11.44%, 69.6%, and 18.9% of the total PCDEs in SFA. Scrubber sludge (point H) exhibits the lowest content of both PCDEs and their congeners, while CYCD sludge (point J) demonstrates the highest concentration. Additionally, cyclone demister sludge contains a wider variety of PCDE congeners compared to scrubber sludge. This is primarily due to the cyclone demister utilizing high-velocity air flows to generate centrifugal forces that separate particulate matter. This physical separation method is particularly effective in capturing larger or heavier particles, among which high-chlorinated CDEs, due to their larger molecular weights and higher propensity for deposition, tend to accumulate in heavier particles. In contrast, scrubbers trap both particles and gas-phase pollutants using liquid sprays. The removal mechanism in scrubbers primarily relies on dissolution or adsorption. During this washing process, some PCDEs may become diluted within the liquid medium or undergo chemical reactions. This can explain the relatively lower quantity and diversity of PCDEs found in scrubber sludge.
3.3. Removal Efficiency and Net Emissions of PCDE Congeners by the HAWTTS
Figure 6 illustrates the input, output, and net emissions of PCDE congeners within the HAWTTS system. The total input is 960 ng/kg. As this input mirrors the incinerator’s feedstock, Section 3.2.1 (refer to Figure 6) details the specific proportions of each CDE in the total input. The overall PCDE output is a mere 3.75 ng/kg, with CDE #77(4CL) constituting 93.7% and CDE #180(7CL) constituting 6.31%. No other CDE congeners were detected in the output. Notably, the HAWTTS demonstrates a significant net PCDE emission reduction of −956 ng/kg, highlighting its effectiveness in removing PCDEs.
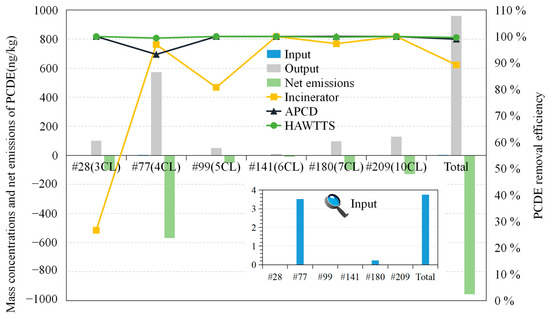
Figure 6.
The input, output, and net emissions of PCDEs in the HAWTTS and the removal efficiency of the incinerator, APCS, and HAWTTS.
Figure 6 also presents the removal efficiencies of the incinerator, air pollution control system (APCS), and HAWTTS. Removal efficiencies vary significantly across different PCDE congeners (ranging from 26.68% to 100%). Notably, CDE #28(3CL), with low chlorine content, exhibits a removal efficiency of only 26.68%. In contrast, other chlorinated CDE congeners demonstrate removal efficiencies exceeding 80%. Due to the limited research on PCDEs compared to the well-studied PCDDs/Fs with analogous properties [72], we can draw insights from PCDD/F studies [22,73] to explain this phenomenon. The higher volatility of low-chlorinated PCDEs at high temperatures facilitates their transition from solid to gaseous phases during combustion, leading to capture by flue gas treatment systems. Conversely, highly chlorinated PCDEs, with lower volatility due to their increased chlorine content, remain predominantly in solid waste due to their greater stability and hydrophobicity. It is important to note that the incinerator achieves complete removal of CDE #141(6CL) and CDE #209(10CL). On the other hand, the APCS exhibits high removal efficiencies for all PCDE congeners (>93%; ranging from 93.21% to 100%), with the specific reasons discussed in Section 3.2.1. Notably, the HAWTTS achieves over a 99% reduction for all tested PCDE congeners (ranging from 99.61% to 100%). These findings underscore the effectiveness of the HAWTTS in mitigating PCDE congener emissions.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated a hazardous air pollutant treatment train system (HAWTTS) employing flameless combustion and a three-stage air pollution control system (APCS) consisting of a scrubber, a cyclone demister, and a bag filter. The SFA generated from the APCS is reintroduced into the incinerator for secondary incineration. PCDE congener concentrations were measured at key points throughout the system during stable operation. These measurements allowed for the calculation of removal efficiencies for each device. The HAWTTS achieved a remarkable removal efficiency for PCDE congeners, ranging from 99.61% to 100%. This effectiveness can be attributed to the combined strategies employed:
- Flameless combustion: This technology promotes uniform temperature distribution and complete combustion, minimizing PCDE formation in the slag. Additionally, the high-temperature, rapid-cooling quenching process further prevents PCDE presence in the bottom slag. Flameless combustion also addresses challenges like high moisture content in raw materials and carbon adhesion during SFA recovery.
- Air pollution control system: While the incinerator demonstrates variable removal efficiencies due to volatility differences among PCDEs, the APCS effectively compensates for this by achieving high removal efficiencies (93.21% to 100%). Notably, the cyclone demister (CYCD) exhibits exceptional performance, reaching complete removal for CDE congeners #28, #99, and #180.
The high fly ash content in the recirculated SFA system facilitates the condensation and aggregation of gaseous PCDEs. Compared to the feedstock, SFA exhibits a higher concentration and diversity of PCDE congeners due to strong adsorption on particle surfaces. Importantly, no PCDEs were detected in the SFA wastewater due to their hydrophobic nature. However, the scrubber (SCB) and bag filter (BH) exhibited lower removal efficiencies (17.8% and 30.9%, respectively) due to the ‘memory effect’.
Overall, the findings demonstrate the well-designed nature of the HAWTTS. The combination of flameless combustion technology, SFA recirculation, and a multistage APCS effectively reduces PCDE emissions to negligible levels. This study highlights the potential of the HAWTTS for mitigating PCDE emissions from waste incineration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-L.L.; methodology, S.-L.L. and L.-L.D.; software, S.-L.L. and L.-L.D.; formal analysis, J.-L.W. and C.-E.H.; data curation, L.-L.D. and J.-L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-L.L. and L.-L.D.; writing—review and editing, J.-L.W. and C.-E.H.; supervision, S.-L.L. and M.-J.S.; project administration, M.-J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan under the grant number 113-2222-E-006-001, as well as the Environmental Resource and Management Research Center, National Cheng Kung University, under the grant number H113-A01.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We also appreciate Tzu-Ying Wu, Ya-Jing Fu, and Kun-Hui Lin for their technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AC(I) | activated carbon (injection) |
| APCDs | air pollution control devices |
| APCS | air pollution control system |
| BHs | bag houses |
| CYCDs | cyclone demisters |
| FLOX | flameless oxidation |
| HAWTTS | hazardous waste thermal treatment system |
| HTAC | high-temperature air combustion |
| INC | incinerator |
| MILD | moderate or intense low-oxygen dilution |
| PAHs | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PCBs | polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PCDEs | polychlorinated diphenyl ethers |
| PCDDs/Fs | polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans |
| PCDFs | polychlorinated dibenzo-p-furans |
| SCBs | scrubbers |
| SFA | sludge and/or fly ash |
References
- Wu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R. Polychlorinated Diphenyl Ethers in the Environment: A Review and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koistinen, J. Polychlorinated Diphenyl Ethers (PCDE); Anthropogenic Compounds Part K; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 3, pp. 157–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kurz, J.; Ballschmiter, K. Vapour pressures, aqueous solubilities, Henry’s law constants, partition coefficients between gas/water (Kgw), n-octanol/water (Kow) and gas/n-octanol (Kgo) of 106 polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDE). Chemosphere 1999, 38, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, J.L.; Rogerson, P.F.; Norwood, C.B. A polychlorinated dibenzofuran and related compounds in an estuarine ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1981, 15, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimi, A.; Huestis, S.; Metcalfe, C. Chlorinated diphenyl ethers in Great Lakes fish and their environmental implication. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1994, 13, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.T.; Kennedy, B.; LeBel, G.L. Chlorinated diphenyl ethers in human adipose tissue. Part 2. Chemosphere 1991, 23, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinosa, E.O.; Odjadjare, E.E.; Chigor, V.N.; Igbinosa, I.H.; Emoghene, A.O.; Ekhaise, F.O.; Igiehon, N.O.; Idemudia, O.G. Toxicological profile of chlorophenols and their derivatives in the environment: The public health perspective. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 460215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, J.; Ballschmiter, K. Isomer-Specific Determination of 79 Polychlorinated Diphenyl Ethers (Pcde) in Cod-Liver Oils, Chlorophenols and in a Fly Ash. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1995, 351, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Lin, S.-L.; Lin, T.-C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Wang, L.-C.; Chang-Chien, G.-P. Emissions of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers from a municipal solid waste incinerator during the start-up operation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheruiyot, N.K.; Yang, H.-H.; Wang, L.-C.; Lin, C.-C. Feasible and effective control strategies on extreme emissions of chlorinated persistent organic pollutants during the start-up processes of municipal solid waste incinerators. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huestis, S.; Sergeant, D. Removal of chlorinated diphenyl ether interferences for analyses of PCDDs and PCDFs in fish. Chemosphere 1992, 24, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hao, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, J. Theoretical investigations on direct photolysis mechanisms of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altarawneh, M.; Dlugogorski, B.Z. Mechanisms of transformation of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers into polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Chemosphere 2014, 114, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, R.; Rappe, C.; Buser, H.R. Formation of polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) from the pyrolysis of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers. Chemosphere 1980, 9, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelnuor, A.; Wahid, M.; Hosseini, S.E.; Saat, A.; Saqr, K.M.; Sait, H.H.; Osman, M. Characteristics of biomass in flameless combustion: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Song, J.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Geng, P.; Qu, B.; Lin, L. Preferential policies promote municipal solid waste (MSW) to energy in China: Current status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Ogada, T. Sewage sludge combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 55–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, W.; Yang, W.; Narayanan, K.; Von Schéele, J. Flameless oxyfuel combustion for fuel consumption and nitrogen oxides emissions reductions and productivity increase. J. Energy Inst. 2007, 80, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A.; Abuelnuor, A.A.A. Biogas flameless combustion: A review. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 388, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Jin, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, M. Experimental study on flue gas purifying of MSW incineration using in-pipe jet adsorption techniques. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Zhong, Z.-P.; Jin, B.-S.; Huang, Y.-J.; Xiao, R. Experimental study on the removal of PAHs using in-duct activated carbon injection. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, S.; Yan, J. Effect of different air pollution control devices on the gas/solid-phase distribution of PCDD/F in a full-scale municipal solid waste incinerator. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sam-Cwan, K.; Hwan, J.S.; Il-Rok, J.; Ki-Hun, K.; Myung-Hee, K.; Jae-Hyung, K.; Jun-Heung, Y.; Seung-Jin, K.; Jae-Cheon, Y.; Dong-Hee, J. Removal efficiencies of PCDDs/PCDFs by air pollution control devices in municipal solid waste incinerators. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehlow, J. Air pollution control systems in WtE units: An overview. Waste Manag. 2015, 37, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, G.H.; Li, R.; Liang, K.Y. Control particulate and metals HAPs. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1997, 93, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, M.; Liu, W.; Gao, L.; Su, G.; Zhang, B. Mechanism of polychlorinated diphenyl ether formation on a simulated fly ash surface. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermo, P.; Cariati, F.; Pozzi, A.; Demartin, F.; Tettamanti, M.; Collina, E.; Lasagni, M.; Pitea, D.; Puglisi, O.; Russo, U. The analytical characterization of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash: Methods and preliminary results. Fresenius’ J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 365, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajwan, K.; Paramasivam, S.; Alva, A.; Adriano, D.; Hooda, P. Assessing the feasibility of land application of fly ash, sewage sludge and their mixtures. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 8, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Gianoncelli, A.; Struis, R.P.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Review of fly ash inertisation treatments and recycling. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgroe, J.D. Control of dioxin, furan, and mercury emissions from municipal waste combustors. J. Hazard. Mater. 1996, 47, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, T.; Hagenmaier, H.; Hartmann, E.; Römer, R.; Siefert, H. Einfluss des Schwefels auf die Dioxin-und Furanbildung bei der Klärschlammverbrennung. VGB Kraftwerkstechnik 1992, 72, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, D.; Feng, P.; Hao, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S. Municipal sewage sludge incineration and its air pollution control. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Ma, X. Simulation of co-incineration of sewage sludge with municipal solid waste in a grate furnace incinerator. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, B.M.; Namieśnik, J.; Konieczka, P. Review of sewage sludge management: Standards, regulations and analytical methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Ma, X.; Dai, M.; Fang, S. Co-combustion of paper sludge in a 750 t/d waste incinerator and effect of sludge moisture content: A simulation study. Fuel 2018, 217, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Qin, L.; Ye, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Yao, H. Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from coal and sewage sludge co-combustion in a drop tube furnace. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liao, Y.; Xia, Y.; Ma, X. Combustion characteristics of co-combusted municipal solid wastes and sewage sludge. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zheng, J.; Yuan, X.; Song, H.; Peng, J.; Ren, M. Characterization and mass balance of PCDD/Fs during the co-combustion of sewage sludge in a grate-type municipal solid waste incineration. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, W. Behaviour of mercury during Co-incineration of sewage sludge and municipal solid waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Wu, J.-L.; Lin, K.C.; Wu, H.; Guo, Z.; Tu, C.-W. A novel flameless oxidation and in-chamber melting system coupled with advanced scrubbers for a laboratory waste plant. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, S.-L.; Wu, J.-L.; Huang, S.-W.; Song, M. Enhanced mitigation of inhalable particles and fine particle-bound PAHs from a novel hazardous waste-power plant candidate. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Wu, J.-L.; Chen, W.-H.; Wu, H.; Tang, W. Ultra-low PCDD/F emissions and their particle size and mass distribution in a hazardous waste treatment system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.; Gupta, A.K.; Mochida, S. High temperature air combustion (HiTAC): How it all started for applications in industrial furnaces and future prospects. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Urano, S.; Takatsuki, H. Leaching behavior of PCBs and PCDDs/DFs from some waste materials. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, L.; Marklund, S. Thermal degradation of PCDD/F, PCB and HCB in municipal solid waste ash. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Ni, Y.-W.; Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, Q. Influence of variation in the operating conditions on PCDD/F distribution in a full-scale MSW incinerator. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, M.; Takeda, N.; Miura, S. The behaviour of heavy metals and phosphorus in an ash melting process. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhuo, X.; Luo, Z.; Cheng, Q. Modeling Analysis and Research on the Evaporation System of a Multisource Organic Solid Waste Incinerator. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, D.M. Solids drying: Basics and applications. Chem. Eng. 2014, 121, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, M.; Liu, W.; Ma, X.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, B. Formation of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers from condensation of chlorophenols with chlorobenzenes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2008, 15, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B. Degradation technologies and mechanisms of dioxins in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Feng, M.; Qin, L.; Shi, J.; Cheng, D. Polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs) in surface sediments, suspended particulate matter (SPM) and surface water of Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Buekens, A.; Li, X. Dioxins from biomass combustion: An overview. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Hasegawa, T.; Katsuki, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Morita, M. High Temperature Air Combustion: From Energy Conservation to Pollution Reduction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, M.; Benticha, H.; Sassi, M. Detailed chemical modelling of a flameless combustion turbine for pollution prevention. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 32, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, H.; Toporov, D.; Förster, M.; Kneer, R. On the influence of the char gasification reactions on NO formation in flameless coal combustion. Combust. Flame 2009, 156, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Lee, K.-L.; Wu, J.-L.; Cheruiyot, N.K. Effects of a quenching treatment on PCDD/F reduction in the bottom ash of a lab waste incinerator to save the energy and cost incurred from post-thermal treatment. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, Y.-I.; Wu, Z.-L.; Kuo, Y.-M. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran (PCDD/F) emission behavior during incineration of laboratory wastes. Part 2: PCDD/F profiles and characteristics of output materials. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Yuan, X.; Schramm, K.-W.; Kettrup, A. QSPR models for physicochemical properties of polychlorinated diphenyl ethers. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 305, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuppurainen, K.; Halonen, I.; Ruokojärvi, P.; Tarhanen, J.; Ruuskanen, J. Formation of PCDDs and PCDFs in municipal waste incineration and its inhibition mechanisms: A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 1493–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, I.; Van Caneghem, J.; Vandecasteele, C. Indication of PCDD/F formation through precursor condensation in a full-scale hazardous waste incinerator. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2014, 16, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Tang, W.; Wu, J.-L.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Wang, C.-L.; Chen, W.-H. Particulate PCDD/F size distribution and potential deposition in respiratory system from a hazardous waste thermal treatment process. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, J.; Majumdar, D. Memory effect driven emissions of persistent organic pollutants from industrial thermal processes, their implications and management: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 119, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.-I.; Lee, D.-H.; Osako, M.; Kim, S.-C. The prediction of PCDD/DF levels in wet scrubbers associated with waste incinerators. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-H.; Lu, I.-C.; Huang, P.-W.; Wu, Y.-J.; Whang, L.-M. Biological treatment of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)-containing wastewaters from wet scrubbers in semiconductor industry. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyytikäinen, M.; Hirva, P.; Minkkinen, P.; Hämäläinen, H.; Rantalainen, A.-L.; Mikkelson, P.; Paasivirta, J.; Kukkonen, J.V. Bioavailability of sediment-associated PCDD/Fs and PCDEs: Relative importance of contaminant and sediment characteristics and biological factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, R.V.; Eiceman, G.A.; Long, Y.T.; Collins, M.C.; Lu, M.Q. Mechanism of chlorination of aromatic compounds adsorbed on the surface of fly ash from municipal incinerators. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Peng, X. Separation performance of new type of multi-stage axial cyclone used as demister in power plant emission system. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.H.; Chang, M.B. Evaluation of PCDD/F congener partition in vapor/solid phases of waste incinerator flue gases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Hao, J.; Duan, L.; Tang, X.; Ning, P.; Li, X. Fine particle and trace element emissions from an anthracite coal-fired power plant equipped with a bag-house in China. Fuel 2008, 87, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-W.; Wang, L.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Yang, X.-Y.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Wu, E.M.-Y. Influence of memory effect caused by aged bag filters on the stack PCDD/F emissions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutzinger, O. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Part, A. Air Pollution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-C. Dechlorination and destruction of PCDDs/PCDFs in fly ashes from municipal solid waste incinerators by low temperature thermal treatment. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).