Spatially Heterogeneous Effects of Atmospheric Circulation on Greenland Ice Sheet Melting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
3. Results
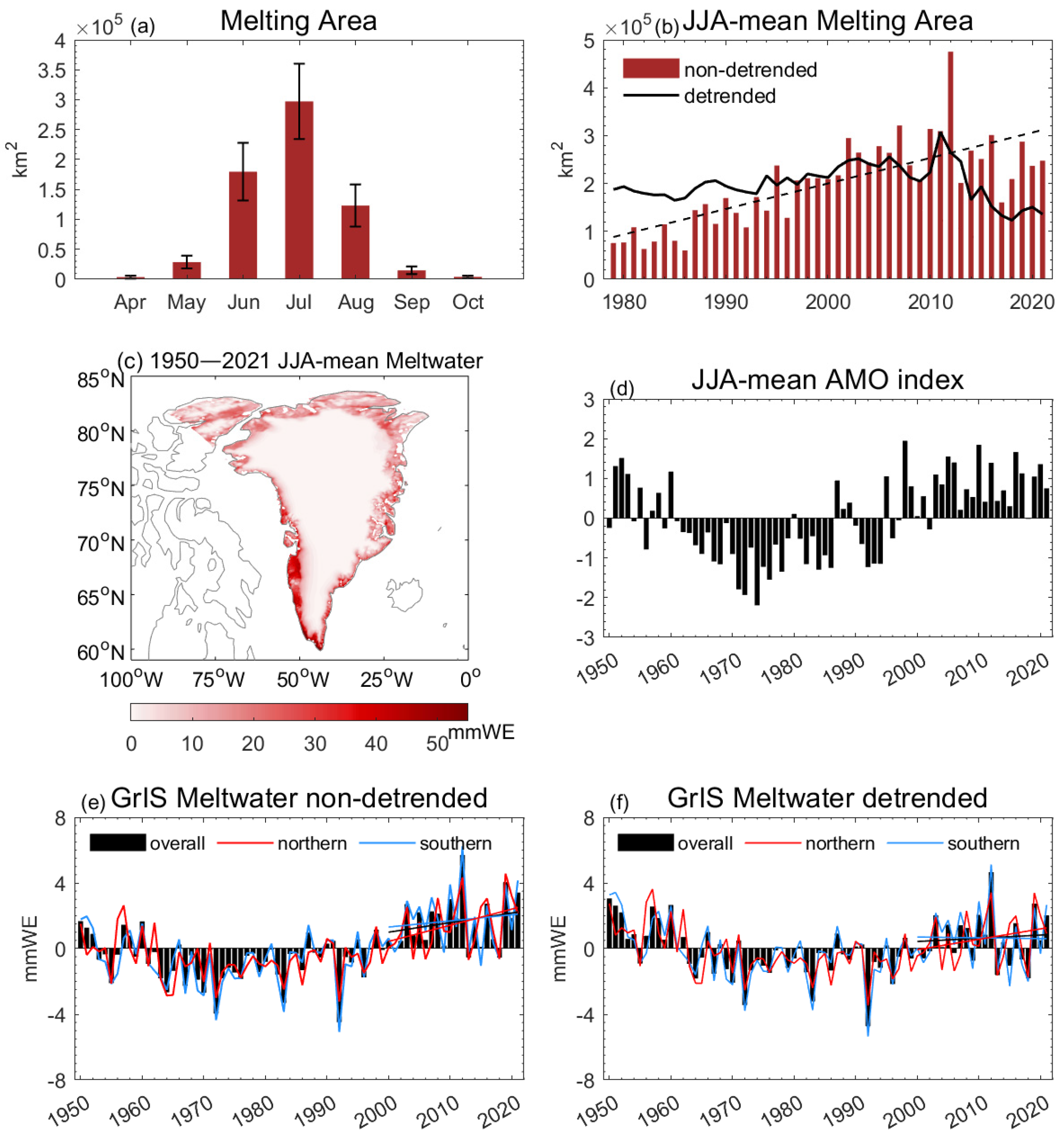
3.1. The Characteristics of GrIS Melting
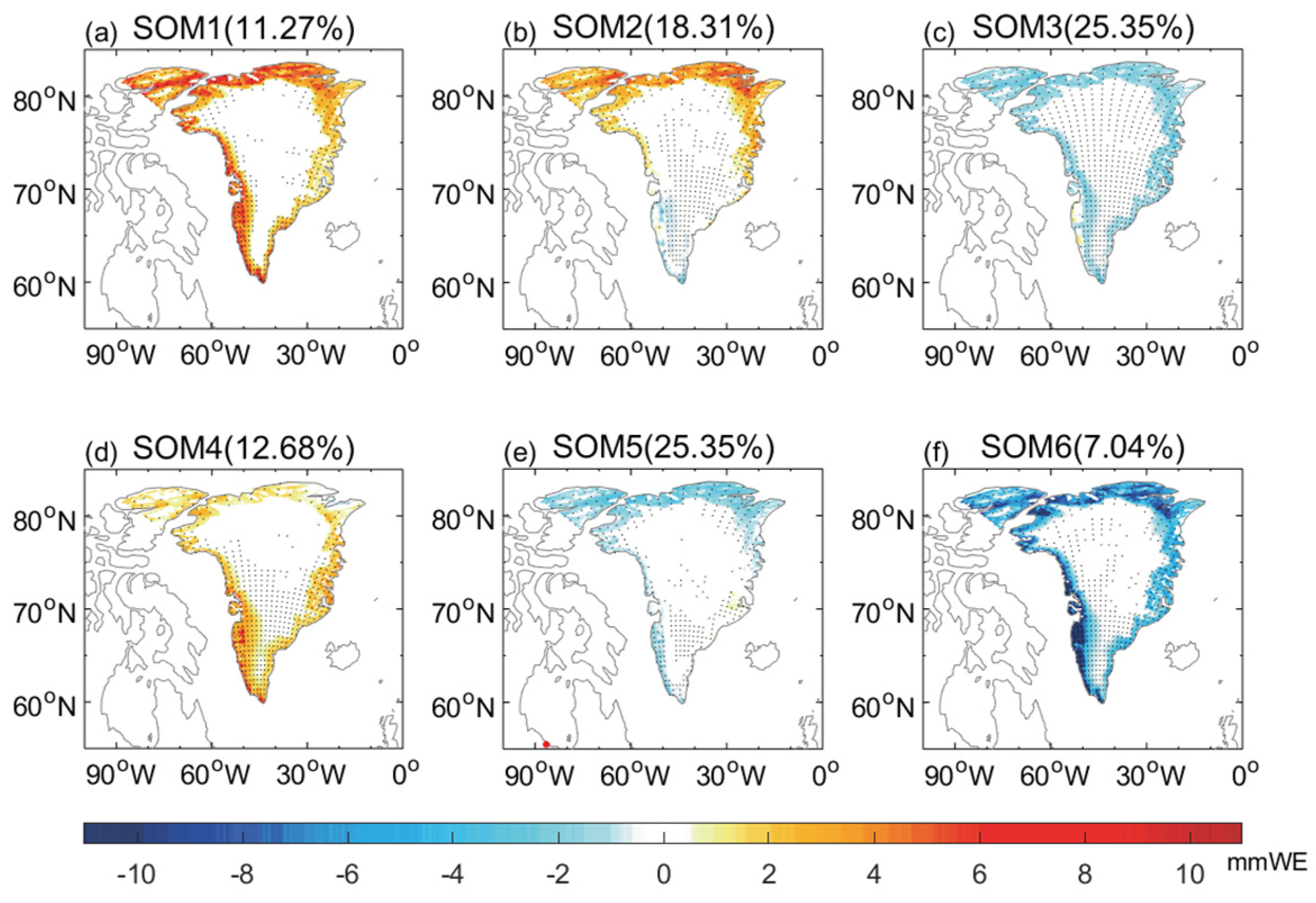
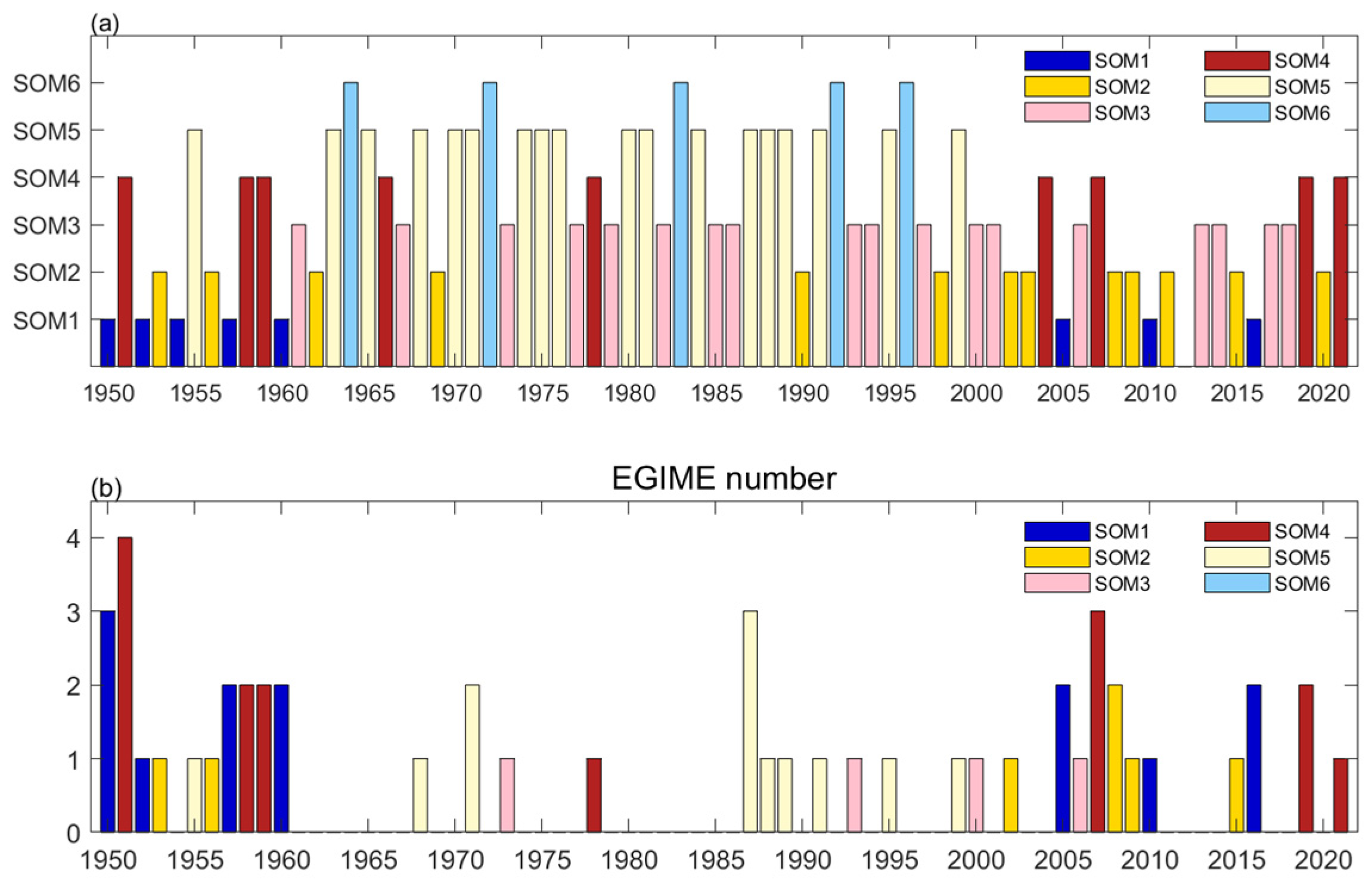
3.2. Impacts of Greenland Blocking on Extreme GrIS Melting Events for Different Modes
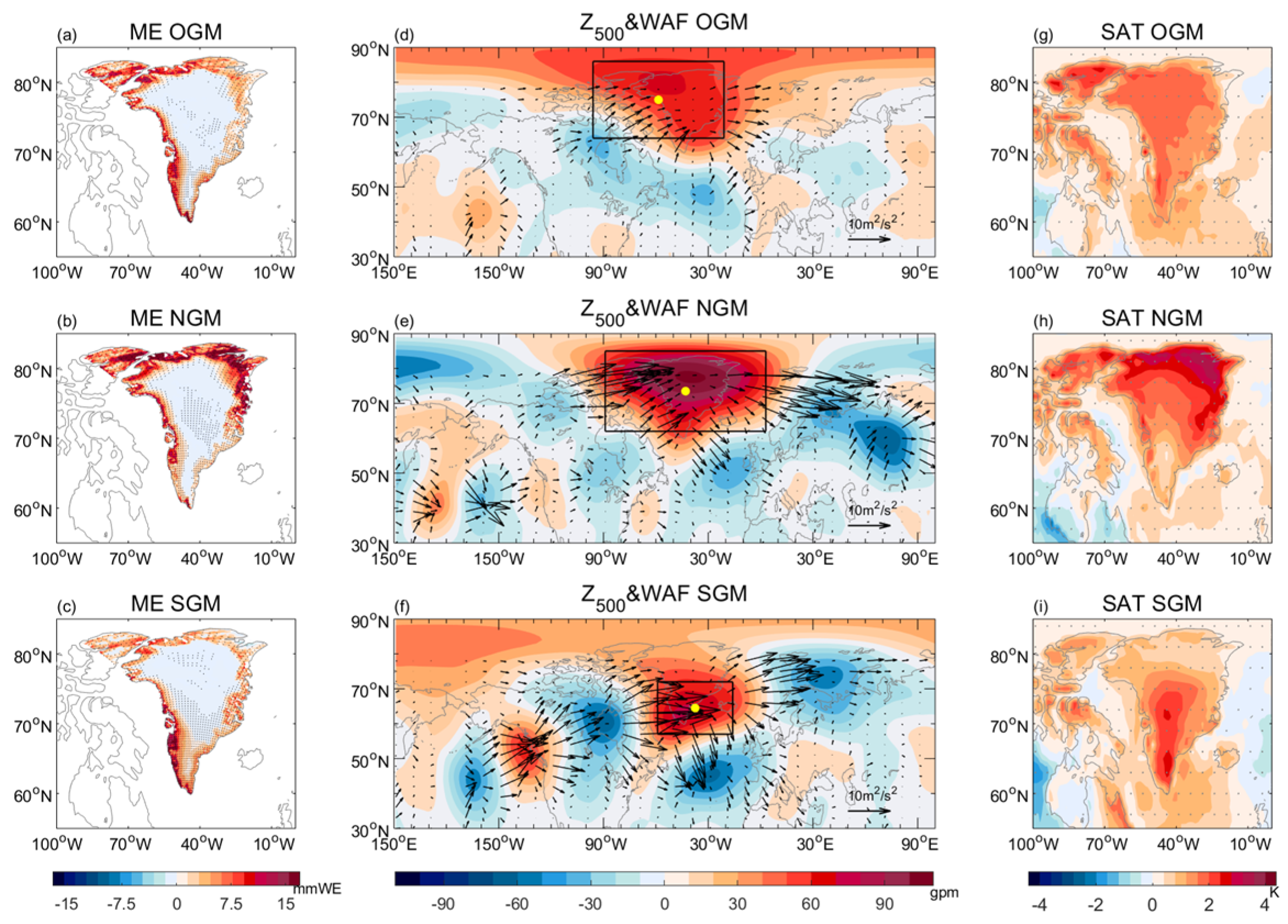
3.3. Evolution of Circulation during the Pre-Melting Period
3.4. The Influence of Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies over the Atlantic and Pacific and Zonal Wind
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GrIS | Greenland ice sheet |
| GB | Greenland blocking |
| AMO | Atlantic multidecadal oscillation |
| NAO | North Atlantic oscillation |
| EGIME | Extreme GrIS melting event |
| Z500 | Geopotential height at 500 hPa |
| SAT | Surface air temperature |
| SST | Sea surface temperature |
| U500 | Zonal winds at 500 hPa |
| V500 | Meridional winds at 500 hPa |
| SSHF | Surface-sensitive heat flux |
| SLHF | Surface-latent heat flux |
| SHF | Surface heat flux |
| ME | Meltwater production |
| SWDnet | Net downward shortwave radiation |
| LWUnet | Net upward longwave radiation |
| WAF | Wave activity flux |
| OGM | Overall GrIS melting |
| NGM | Northern GrIS melting |
| SGM | Southern GrIS melting |
| EB | European blocking |
| MEA | Mid-latitude East Atlantic |
| GNN | Greenland–Norskehavet–North sea |
| MEP | Mid-latitude East Pacific |
References
- Hanna, E.; Mernild, S.H.; Cappelen, J.; Steffen, K. Recent warming in Greenland in a long-term instrumental (1881–2012) climatic context: I. Evaluation of surface air temperature records. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 045404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straneo, F.; Heimbach, P. North Atlantic warming and the retreat of Greenland’s outlet glaciers. Nature 2013, 504, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mernild, S.H.; Hanna, E.; Yde, J.C.; Cappelen, J.; Malmros, J.K. Coastal Greenland air temperature extremes and trends 1890-2010: Annual and monthly analysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilton, D.J.; Jowett, A.; Hanna, E.; Bigg, G.R.; Broeke, M.R.V.D.; Fettweis, X.; Huybrechts, P. High resolution (1 km) positive degree-day modelling of Greenland ice sheet surface mass balance, 1870–2012 using reanalysis data. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- White, R.H.; Hilgenbrink, C.; Sheshadri, A. The Importance of Greenland in Setting the Northern Preferred Position of the North Atlantic Eddy-Driven Jet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 14126–14134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goelzer, H.; Nowicki, S.; Payne, A.; Larour, E.; Seroussi, H.; Lipscomb, W.H.; Gregory, J.; Abe-Ouchi, A.; Shepherd, A.; Simon, E.; et al. The future sea-level contribution of the Greenland ice sheet: A multi-model ensemble study of ISMIP6. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 3071–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machguth, H.; Rastner, P.; Bolch, T.; Mölg, N.; Sørensen, L.S.; Aðalgeirsdottir, G.; Van Angelen, J.H.; Van den Broeke, M.R.; Fettweis, X. The future sea-level rise contribution of Greenland’s glaciers and ice caps. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.L.; Fettweis, X.; Gagliardini, O.; Gillet-Chaulet, F.; Goelzer, H.; Gregory, J.M.; Hoffman, M.; Huybrechts, P.; Payne, A.J.; Perego, M.; et al. Effect of uncertainty in surface mass balance-elevation feedback on projections of the future sea level contribution of the Greenland ice sheet. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slangen, A.B.A.; Meyssignac, B.; Agosta, C.; Champollion, N.; Church, J.A.; Fettweis, X.; Ligtenberg, S.R.M.; Marzeion, B.; Melet, A.; Palmer, M.D.; et al. Evaluating Model Simulations of Twentieth-Century Sea Level Rise. Part I: Global Mean Sea Level Change. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 8539–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, S.; Lang, C.; Amory, C.; Kittel, C.; Delhasse, A.; Tedstone, A.; Fettweis, X. Greater Greenland Ice Sheet contribution to global sea level rise in CMIP6. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, F.; Ritz, C.; Hanna, E.; Asay-Davis, X.; DeConto, R.; Durand, G.; Favier, L.; Fettweis, X.; Goelzer, H.; Golledge, N.R.; et al. The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets under 1.5 degrees C global warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Comiso, J.C.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Shuman, C.A.; Box, J.E.; Koenig, L.S. Variability in the surface temperature and melt extent of the Greenland ice sheet from MODIS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Fettweis, X.; Mote, T.; Wahr, J.; Alexander, P.; Box, J.E.; Wouters, B. Evidence and analysis of 2012 Greenland records from spaceborne observations, a regional climate model and reanalysis data. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E.; Fettweis, X.; Mernild, S.H.; Cappelen, J.; Ribergaard, M.H.; Shuman, C.A.; Steffen, K.; Wood, L.; Mote, T.L. Atmospheric and oceanic climate forcing of the exceptional Greenland ice sheet surface melt in summer 2012. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullather, R.I.; Andrews, L.C.; Croteau, M.J.; Digirolamo, N.E.; Hall, D.K.; Lim, Y.; Loomis, B.D.; Shuman, C.A.; Nowicki, S.M.J. Anomalous circulation in July 2019 resulting in mass loss on the Greenland Ice Sheet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Fettweis, X. Unprecedented atmospheric conditions (1948–2019) drive the 2019 exceptional melting season over the Greenland ice sheet. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Mote, T.; Fettweis, X.; Hanna, E.; Jeyaratnam, J.; Booth, J.F.; Datta, R.; Briggs, K. Arctic cut-off high drives the poleward shift of a new Greenland melting record. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettweis, X.; Hanna, E.; Lang, C.; Belleflamme, A.; Erpicum, M.; Gallée, H. Brief communication “Important role of the mid-tropospheric atmospheric circulation in the recent surface melt increase over the Greenland ice sheet”. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajewicz, J.; Marshall, S.J. Variability and trends in anticyclonic circulation over the Greenland ice sheet, 1948–2013. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2842–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-K.; Schubert, S.D.; Nowicki, S.M.J.; Lee, J.N.; Molod, A.M.; Cullather, R.I.; Zhao, B.; Velicogna, I. Atmospheric summer teleconnections and Greenland Ice Sheet surface mass variations: Insights from MERRA-2. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhasse, A.; Fettweis, X.; Kittel, C.; Amory, C.; Agosta, C. Brief communication: Impact of the recent atmospheric circulation change in summer on the future surface mass balance of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 3409–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Harig, C.; Khan, S.A.; Brown, A.; Simons, F.J.; Willis, M.; Fettweis, X.; van den Broeke, M.R.; Madsen, F.B.; Kendrick, E.; et al. Accelerating changes in ice mass within Greenland, and the ice sheet’s sensitivity to atmospheric forcing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, S.; Tedstone, A.J.; Fettweis, X.; Bamber, J.L. Decreasing cloud cover drives the recent mass loss on the Greenland Ice Sheet. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, K.S.; Mote, T.L.; Fettweis, X. Atmospheric River Impacts on Greenland Ice Sheet Surface Mass Balance. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123, 8538–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylek, P.; Box, J.E.; Lesins, G. Global Warming and the Greenland Ice Sheet. Clim. Chang. 2004, 63, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E.; Huybrechts, P.; Steffen, K.; Cappelen, J.; Huff, R.; Shuman, C.; Irvine-Fynn, T.; Wise, S.; Griffiths, M. Increased Runoff from Melt from the Greenland Ice Sheet: A Response to Global Warming. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E.; Cappelen, J.; Fettweis, X.; Mernild, S.H.; Mote, T.L.; Mottram, R.; Steffen, K.; Ballinger, T.J.; Hall, R.J. Greenland surface air temperature changes from 1981 to 2019 and implications for ice-sheet melt and mass-balance change. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 1336–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, E.; Jones, J.M.; Cappelen, J.; Mernild, S.H.; Wood, L.; Steffen, K.; Huybrechts, P. The influence of North Atlantic atmospheric and oceanic forcing effects on 1900-2010 Greenland summer climate and ice melt/runoff. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 862–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, J.T.; Mote, T.L. Linking interannual variability in extreme Greenland blocking episodes to the recent increase in summer melting across the Greenland ice sheet. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1484–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.; Ummenhofer, C.C.; Kwon, Y.-O. North Atlantic Natural Variability Modulates Emergence of Widespread Greenland Melt in a Warming Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 9171–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ye, A.; Xiao, C. The temperature increase in Greenland has accelerated in the past five years. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2020, 194, 103297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, J.T.; Mote, T.L. Assessing the role of precursor cyclones on the formation of extreme Greenland blocking episodes and their impact on summer melting across the Greenland ice sheet. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 12357–12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.E.; Ballinger, T.J.; Euskirchen, E.S.; Hanna, E.; Mård, J.; Overland, J.E.; Tangen, H.; Vihma, T. Extreme weather and climate events in northern areas: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 209, 103324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollings, T.; Barriopedro, D.; Methven, J.; Son, S.-W.; Martius, O.; Harvey, B.; Sillmann, J.; Lupo, A.R.; Seneviratne, S. Blocking and its response to climate change. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, S.; Hall, D.K.; Shuman, C.A.; Worthen, D.L.; DiGirolamo, N.E. Greenland ice sheet melt from MODIS and associated atmospheric variability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, S.; Rhines, P.B.; Worthen, D.L. Atmospheric Blocking and Atlantic Multidecadal Ocean Variability. Science 2011, 334, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusbaumer, J.; Alexander, P.M.; LeGrande, A.N.; Tedesco, M. Spatial Shift of Greenland Moisture Sources Related to Enhanced Arctic Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 14723–14731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Shupe, M.D.; Turner, D.D.; Walden, V.P.; Steffen, K.; Cox, C.J.; Kulie, M.S.; Miller, N.B.; Pettersen, C. July 2012 Greenland melt extent enhanced by low-level liquid clouds. Nature 2013, 496, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, W.; Compo, G.P.; Ralph, F.M.; Shupe, M.D. Continental heat anomalies and the extreme melting of the Greenland ice surface in 2012 and 1889. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 6520–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.R.; Shupe, M.D.; Miller, N.B. Impact of Atmospheric Circulation on Temperature, Clouds, and Radiation at Summit Station, Greenland, with Self-Organizing Maps. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8895–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballinger, T.J.; Mote, T.L.; Mattingly, K.; Bliss, A.C.; Hanna, E.; van As, D.; Prieto, M.; Gharehchahi, S.; Fettweis, X.; Noël, B.; et al. Greenland Ice Sheet late-season melt: Investigating multiscale drivers of K-transect events. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennartz, R.; Shupe, M.D.; Turner, D.D.; Walden, V.P.; Steffen, K.; Cox, C.J.; Kulie, M.S.; Miller, N.B.; Pettersen, C. Extreme Greenland blocking and high-latitude moisture transport. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, e1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Flanner, M.G.; Dunn-Sigouin, E. Impacts of Greenland Block Location on Clouds and Surface Energy Fluxes over the Greenland Ice Sheet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fausto, R.S.; van As, D.; Box, J.E.; Colgan, W.; Langen, P.L.; Mottram, R.H. The implication of nonradiative energy fluxes dominating Greenland ice sheet exceptional ablation area surface melt in 2012. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mernild, S.H.; Mote, T.L.; Liston, G.E. Greenland ice sheet surface melt extent and trends: 1960–2010. J. Glaciol. 2011, 57, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, T.L. Greenland surface melt trends 1973–2007: Evidence of a large increase in 2007. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L22507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, K.S.; Turton, J.V.; Wille, J.D.; Noël, B.; Fettweis, X.; Rennermalm, K.; Mote, T.L. Increasing extreme melt in northeast Greenland linked to foehn winds and atmospheric rivers. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, B.; van de Berg, W.J.; Lhermitte, S.; Broeke, M.R.v.D. Rapid ablation zone expansion amplifies north Greenland mass loss. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw0123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preece, J.R.; Wachowicz, L.J.; Mote, T.L.; Tedesco, M.; Fettweis, X. Summer Greenland blocking diversity and its impact on the surface mass balance of the Greenland ice sheet. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawkwell, F.G.L.; Bamber, J.L. The impact of cloud cover on the net radiation budget of the Greenland ice sheet. Ann. Glaciol. 2002, 34, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullather, R.I.; Nowicki, S.M.J. Greenland Ice Sheet Surface Melt and Its Relation to Daily Atmospheric Conditions. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 1897–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. 1979 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus-climate.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels-preliminary-back-extension?tab=overview (accessed on 26 December 2021). [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.; Hersbach, H.; Berrisford, P.; Dahlgren, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1950 to 1978 (Preliminary Version). Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2020. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus-climate.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels-preliminary-back-extension?tab=overview (accessed on 26 December 2021).
- Fettweis, X.; Hofer, S.; Séférian, R.; Amory, C.; Delhasse, A.; Doutreloup, S.; Kittel, C.; Lang, C.; Van Bever, J.; Veillon, F.; et al. Brief communication: Reduction in the future Greenland ice sheet surface melt with the help of solar geoengineering. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 3013–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwerpen, R.M.; Tedesco, M.; Fettweis, X.; Alexander, P.; van de Berg, W.J. Assessing bare-ice albedo simulated by MAR over the Greenland ice sheet (2000–2021) and implications for meltwater production estimates. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 4185–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mote, T.L.; Anderson, M.R. Variations in snowpack melt on the Greenland ice sheet based on passive microwave measurements. J. Glaciol. 1995, 41, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-organized information of topologically correct features maps. Biol. Cybern. 1982, 43, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, R.A. On the three-dimensional propagation of stationary waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 1985, 42, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, D. North Atlantic Footprint of Summer Greenland Ice Sheet Melting on Interannual to Interdecadal Time Scales: A Greenland Blocking Perspective. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 1939–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, V.W.; Smith, L.C.; Rennermalm, A.K.; Forster, R.R.; Box, J.E. Greenland ice sheet albedo feedback: Thermodynamics and atmospheric drivers. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 821–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L.C.; Storelvmo, T.; Hofer, S.; Parfitt, R.; Ummenhofer, C.C. Importance of Orography for Greenland Cloud and Melt Response to Atmospheric Blocking. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 4187–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, M.; Charbit, S.; Ritz, C.; Khodri, M.; Ramstein, G. Quantifying ice-sheet feedbacks during the last glacial inception. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L24203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Clec’H, S.; Charbit, S.; Quiquet, A.; Fettweis, X.; Dumas, C.; Kageyama, M.; Wyard, C.; Ritz, C. Assessment of the Greenland ice sheet-atmosphere feedbacks for the next century with a regional atmospheric model coupled to an ice sheet model. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, D. Summer Russian heat waves and their links to Greenland’s ice melt and sea surface temperature anomalies over the North Atlantic and the Barents-Kara Seas. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Spatial Asymmetric Tilt of the NAO Dipole Mode and Its Variability. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Shang, X.; Chen, G.; Yu, L. Eddy covariance measurements of turbulent fluxes in the surf zone. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Cha, J.; Zhong, L.; Dai, A. A nonlinear multiscale interaction model for atmospheric blocking: The eddyblocking matching mechanism. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 1785–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

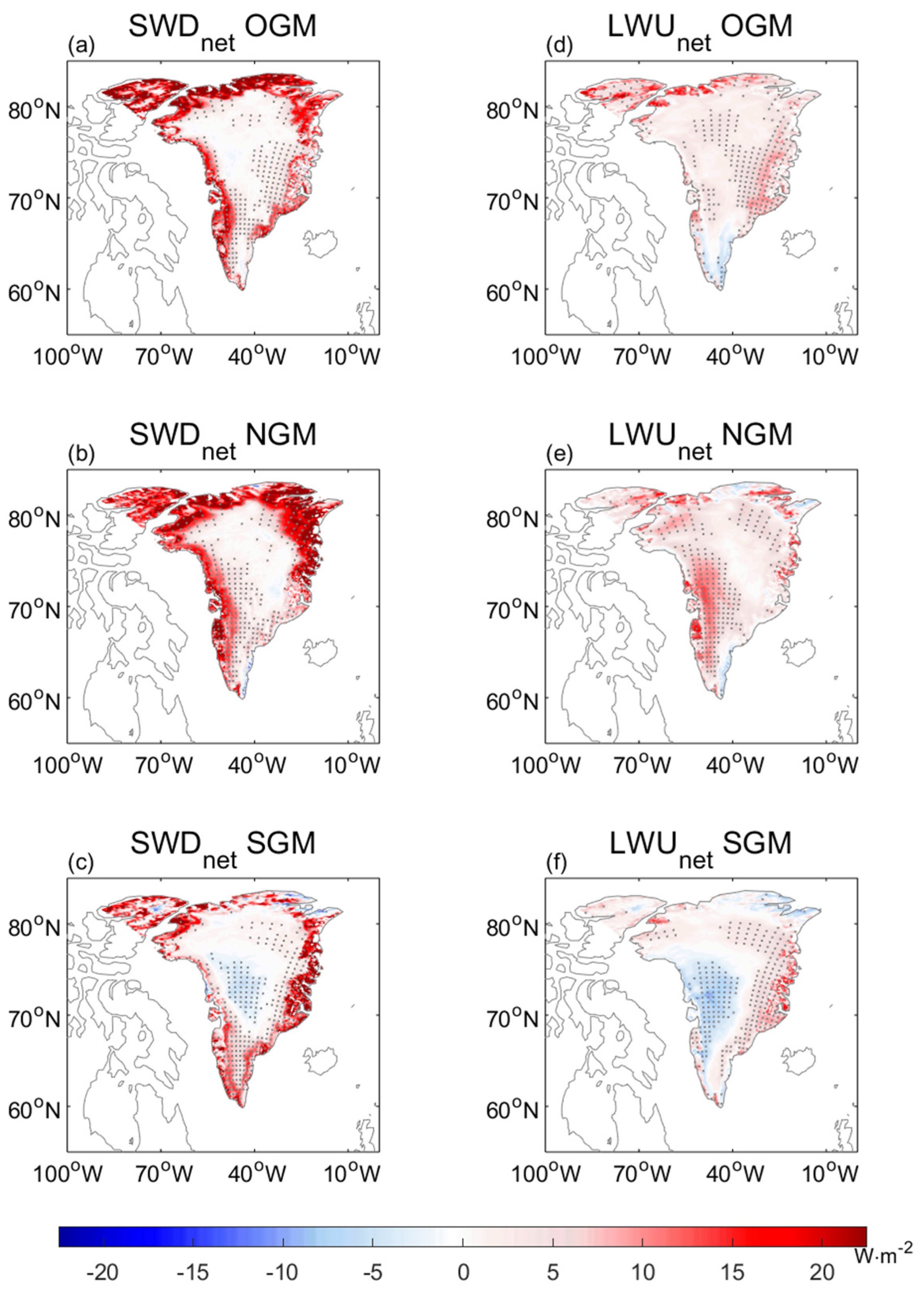

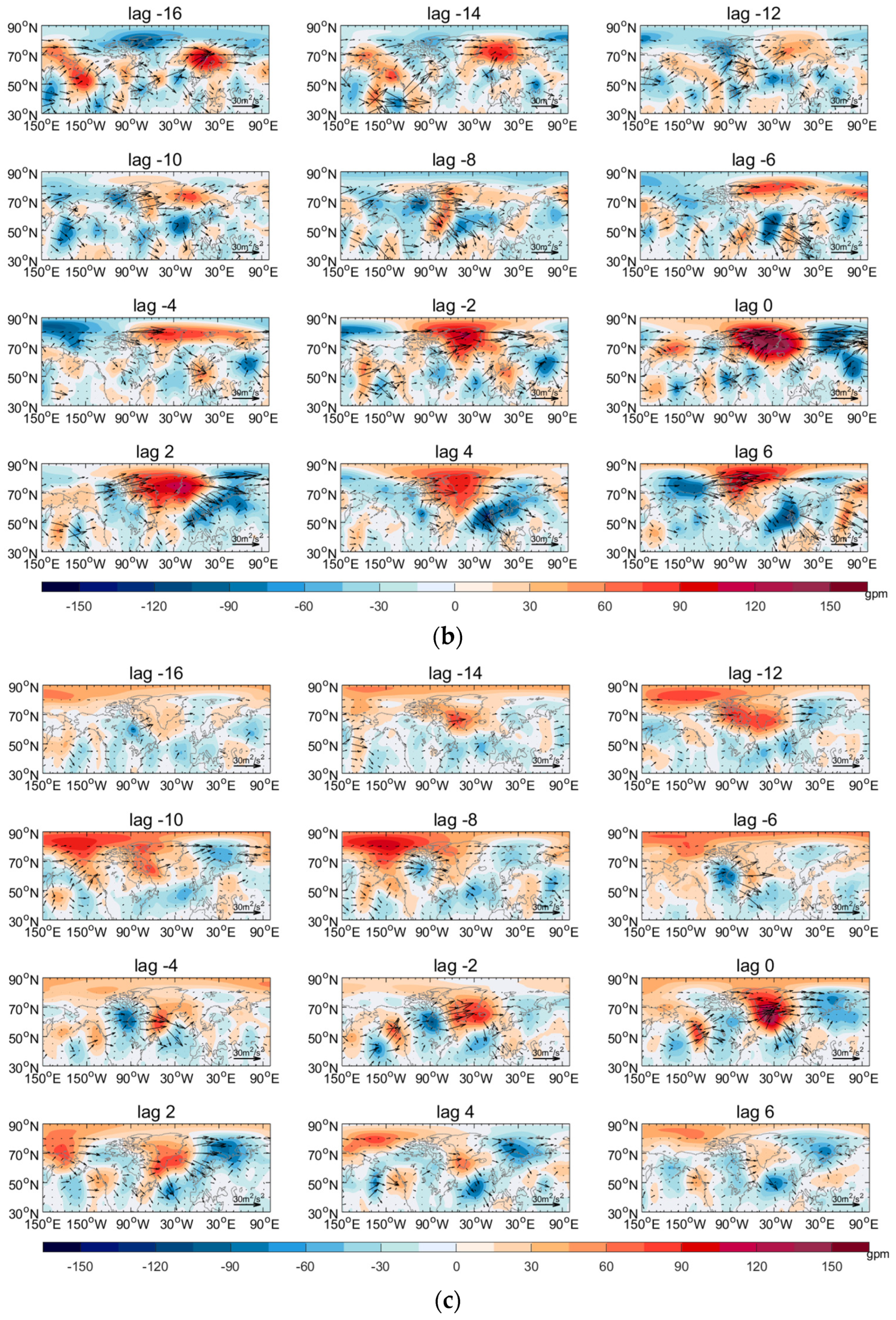
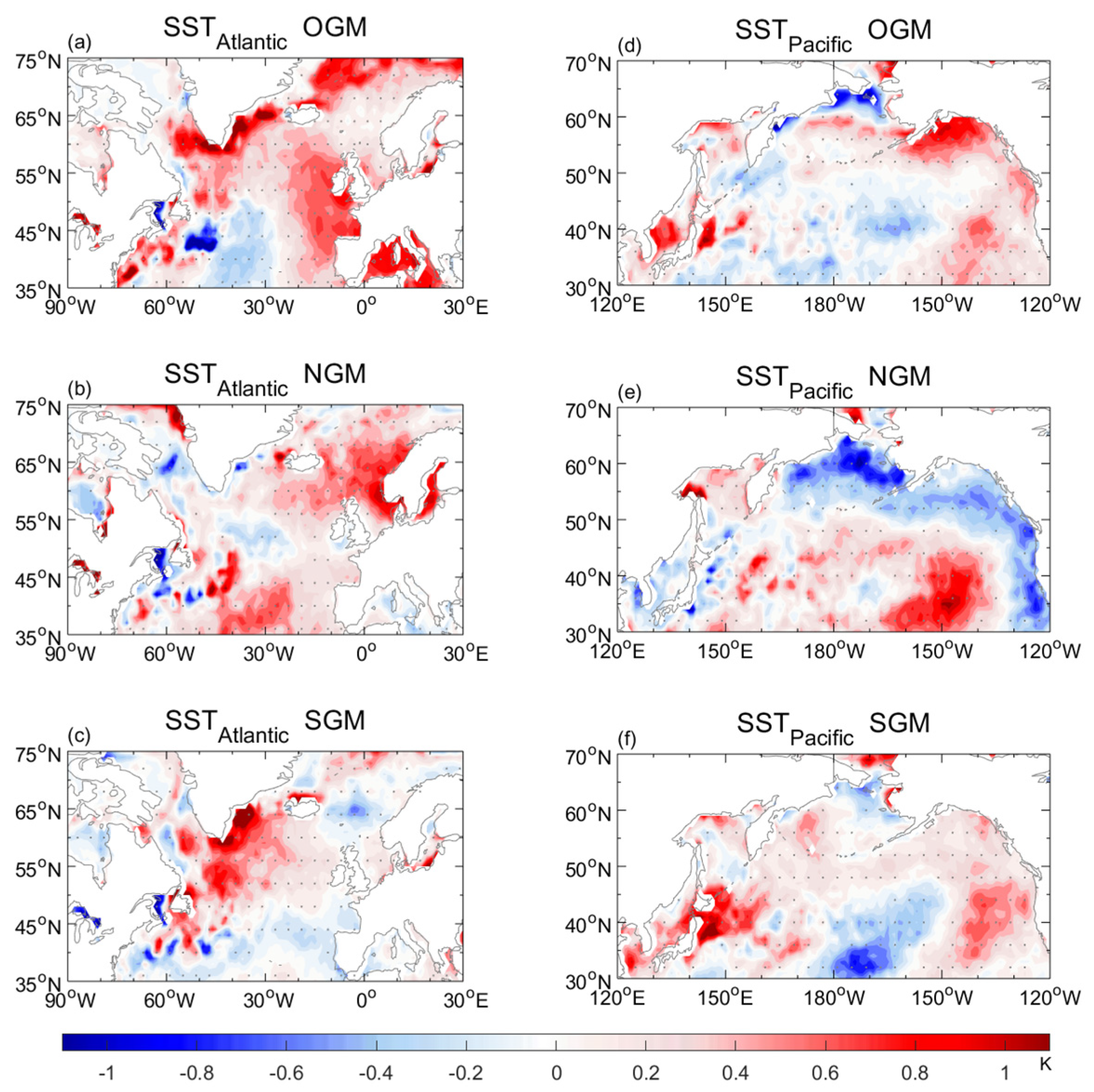
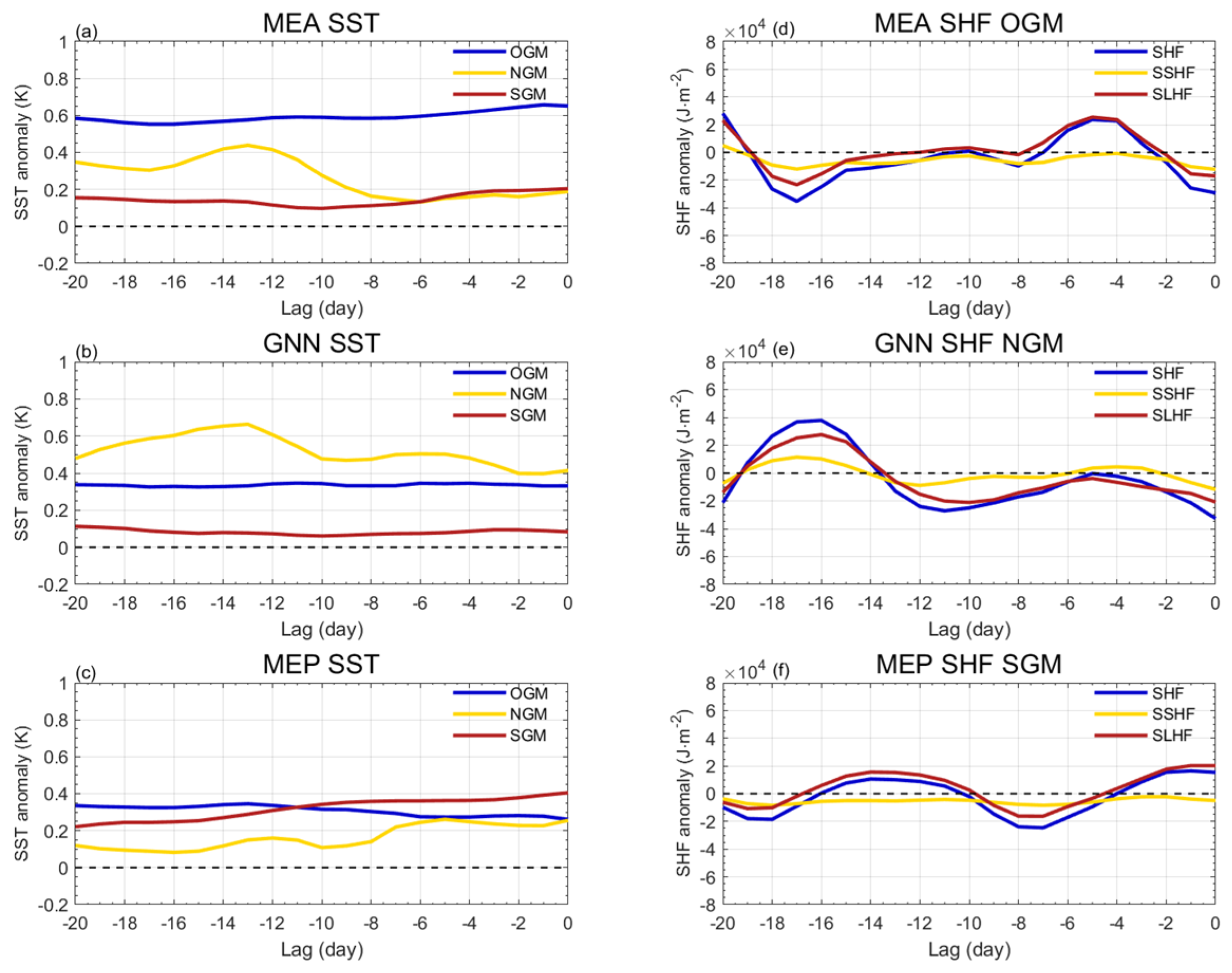


| Mode | Frequency | Duration (day) | Intensity (mmWE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OGM | 1.63 | 4.85 | 3.88 |
| NGM | 0.54 | 5.57 | 3.98 |
| SGM | 1.67 | 5.00 | 4.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Luo, D.; Chen, Y.; Ge, Y. Spatially Heterogeneous Effects of Atmospheric Circulation on Greenland Ice Sheet Melting. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010057
Wang H, Luo D, Chen Y, Ge Y. Spatially Heterogeneous Effects of Atmospheric Circulation on Greenland Ice Sheet Melting. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hejing, Dehai Luo, Yanan Chen, and Yao Ge. 2024. "Spatially Heterogeneous Effects of Atmospheric Circulation on Greenland Ice Sheet Melting" Atmosphere 15, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010057
APA StyleWang, H., Luo, D., Chen, Y., & Ge, Y. (2024). Spatially Heterogeneous Effects of Atmospheric Circulation on Greenland Ice Sheet Melting. Atmosphere, 15(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15010057







