Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Set Summary and Study Methods
2.1. Data
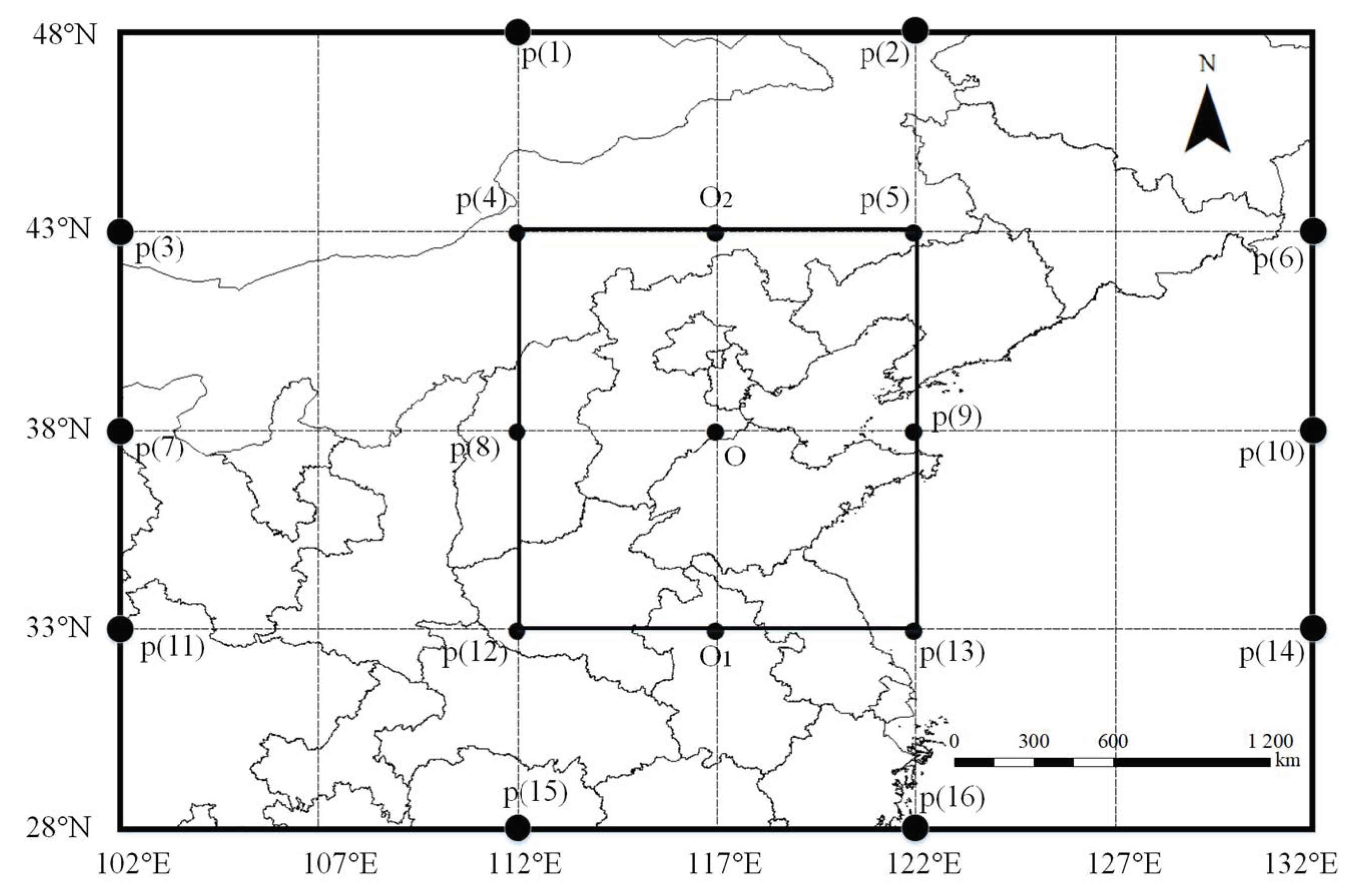
2.1.1. Meteorological Data
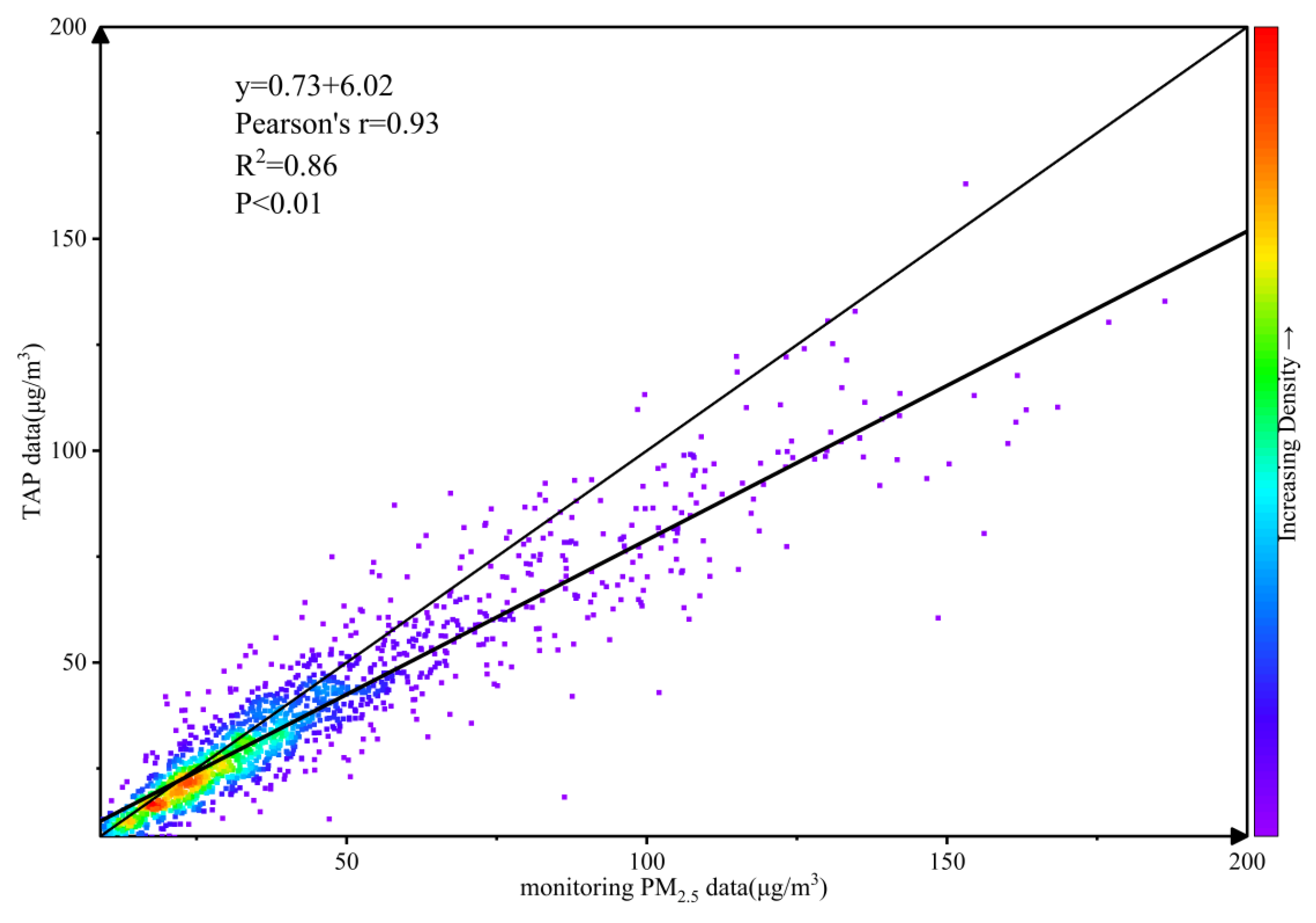
2.1.2. PM2.5 Data
2.2. Lamb-Jenkinson Objective Classification Method
2.3. PM2.5 Data Significance Test Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Spatiotemporal Differentiation of PM2.5 Concentration in the BTH Region
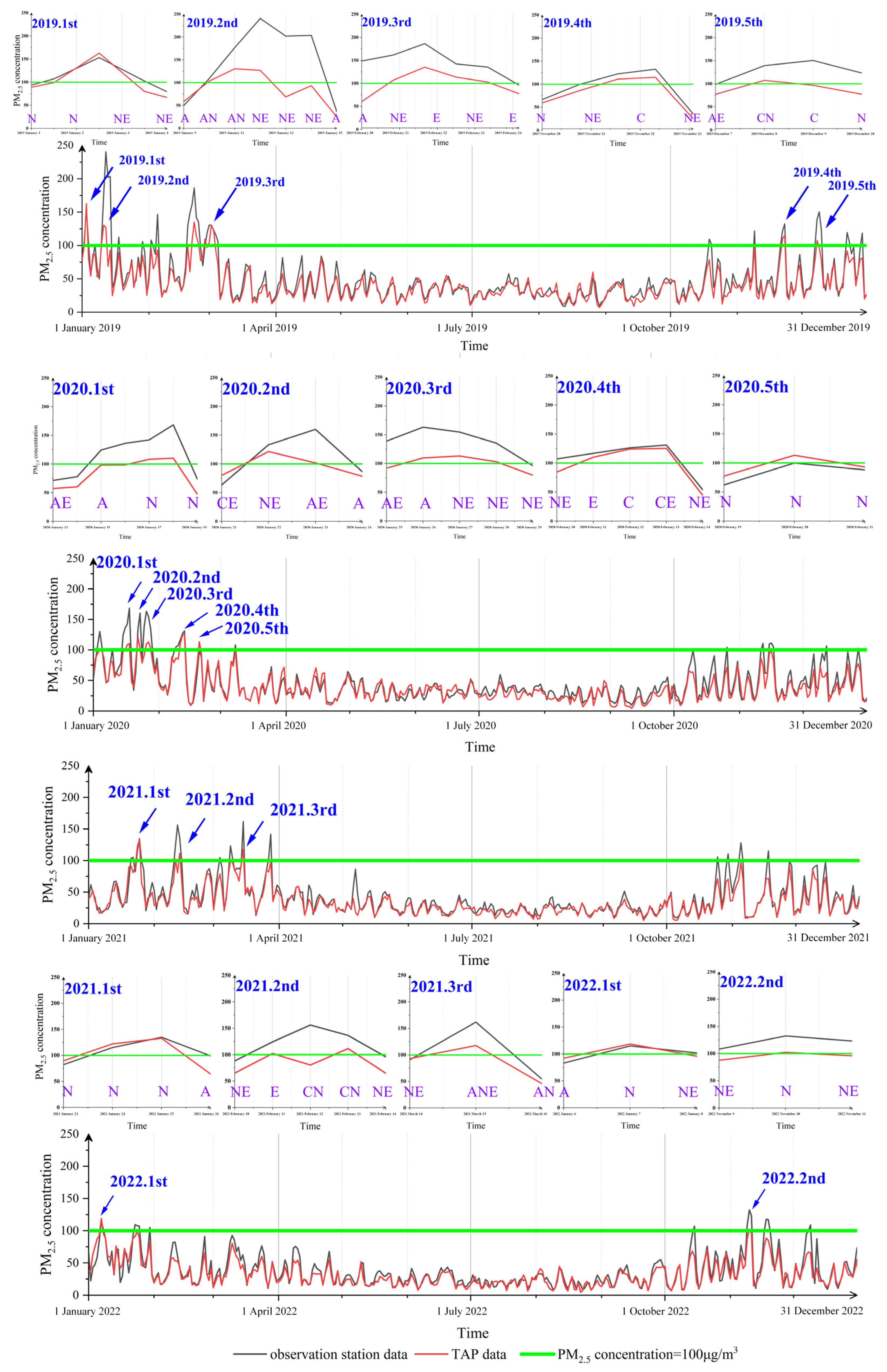
3.2. Variation of PM2.5 Concentration and Atmospheric Circulation in the Pollution Period
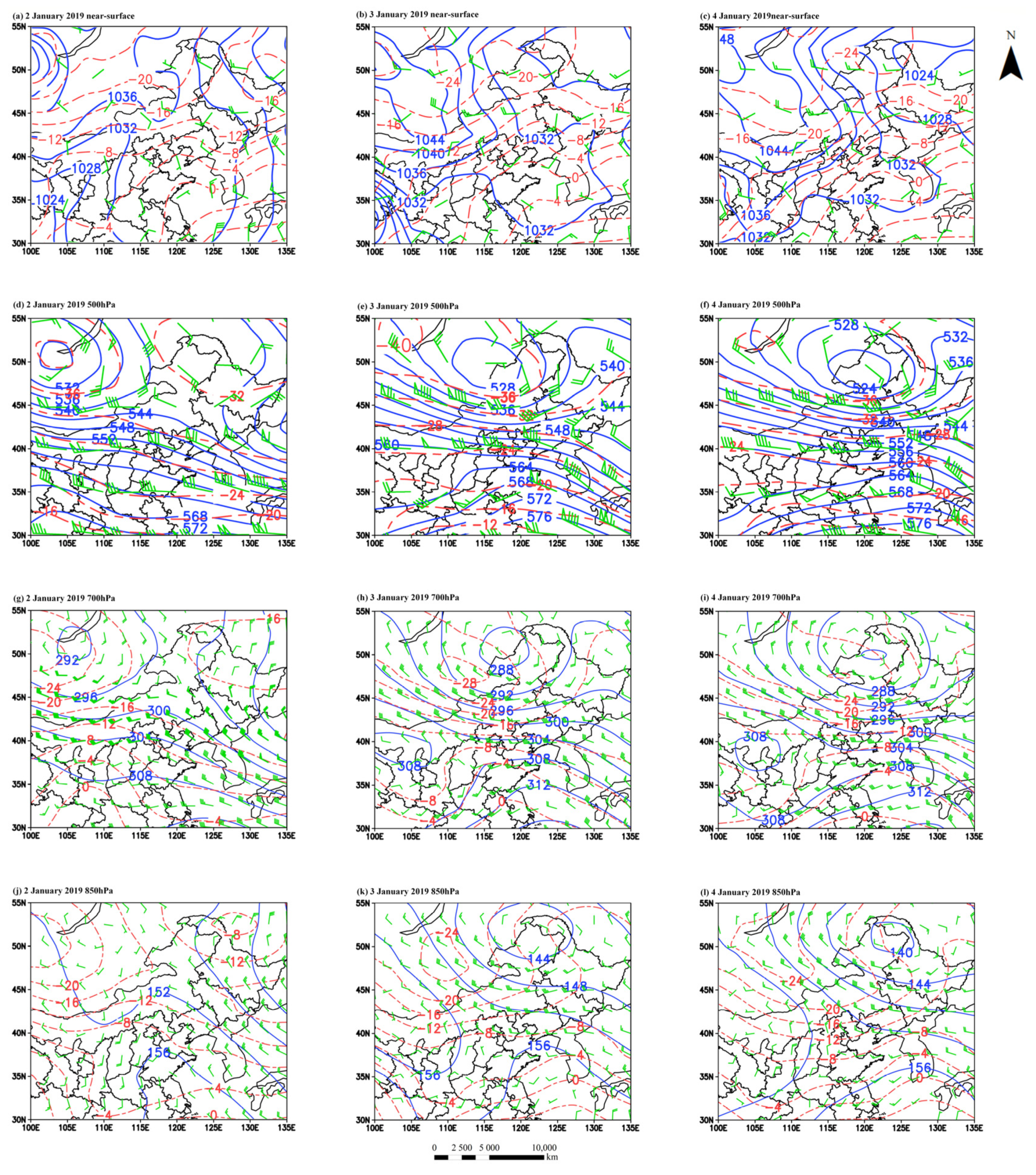
3.3. A Case Study of Circulation Situation under the Pollution Period
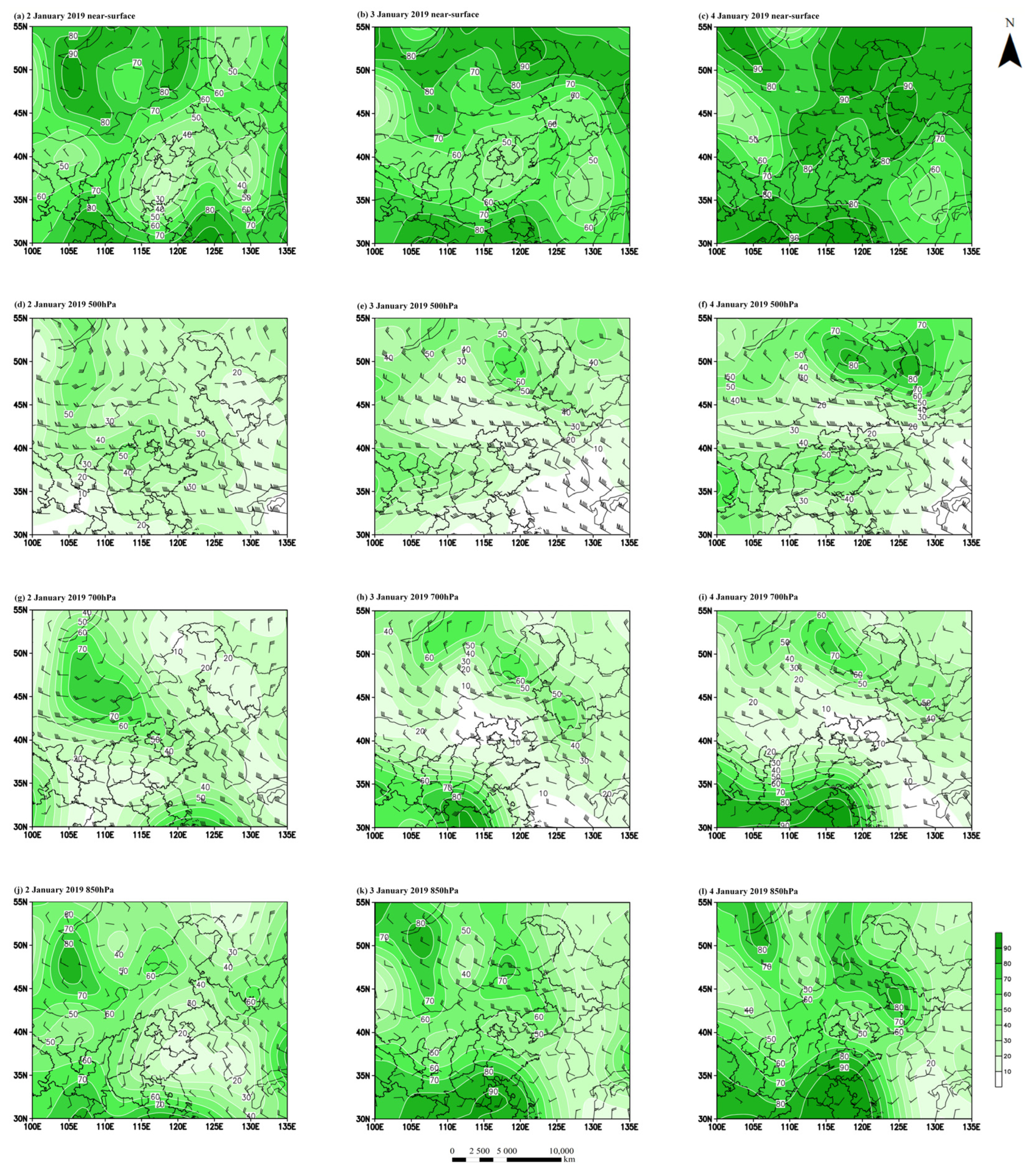
3.4. A Case Study of Physical Parameter Field under the Pollution Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, J.; Fan, S. The Impact of Synoptic Circulation on Air Quality and Pollution-Related Human Health in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Han, L.; Ding, A.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X. The Health Impacts of Aerosol-Planetary Boundary Layer Interactions on Respiratory and Circulatory Mortality. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 276, 119050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Duan, F.; Zhao, W. Changes in Air Quality and Drivers for the Heavy PM2.5 Pollution on the North China Plain Pre- to Post-COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Qiao, L.; Yao, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, W. Characteristics of Atmospheric Pollution in a Chinese Megacity: Insights from Three Different Functional Areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, L.; Nie, X.; Xiao, X. Meteorological Influences on Spatiotemporal Variation of PM2.5 Concentrations in Atmospheric Pollution Transmission Channel Cities of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Cui, X.; He, J.; Liu, D. A Modeling Study of PM2.5 Transboundary Transport during a Winter Severe Haze Episode in Southern Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Rong, B.; Zhang, N.; Chu, C. Long-Term Health Impacts Attributable to PM2.(5) and Ozone Pollution in China’s Most Polluted Region during 2015–2020. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 321, 128970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Park, T.-W.; Deng, Y. Quantifying the Relationship between Extreme Air Pollution Events and Extreme Weather Events. Atmos. Res. 2017, 188, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.Q.; Moelders, N. Investigations on Meteorological Conditions for Elevated PM2.5 in Fairbanks, Alaska. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Gao, H.; Luo, K.; Fan, J. Analysis and Accurate Prediction of Ambient PM2.5 in China Using Multi-Layer Perceptron. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 232, 117534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Yin, Z. Future Atmospheric Circulations Benefit Ozone Pollution Control in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei with Global Warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Dong, W.; Yan, D.; Guo, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chou, J.; Zhu, X.; Wen, X. Relative Contributions of Urbanization and Greenhouse Gases Concentration on Future Climate over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 1085–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, N.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, B.; Meng, N.; Feng, T. Impacts of Local Circulations on the Wintertime Air Pollution in the Guanzhong Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flocas, H.; Kelessis, A.; Helmis, C.; Petrakakis, M.; Zoumakis, M.; Pappas, K. Synoptic and Local Scale Atmospheric Circulation Associated with Air Pollution Episodes in an Urban Mediterranean Area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 95, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnucci, R.H.; Richman, M.B. Can Principal Component Analysis Provide Atmospheric Circulation or Teleconnection Patterns? Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, R.; Beck, C.; Philipp, A.; Demuzere, M.; Ustrnul, Z.; Cahynova, M.; Kysely, J.; Tveito, O.E. Classifications of Atmospheric Circulation Patterns Recent Advances and Applications. In Trends and Directions in Climate Research; Gimeno, L., GarciaHerrera, R., Trigo, R.M., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume 1146, pp. 105–152. ISBN 978-1-57331-732-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Du, H.; Cheng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. Influence of Meteorological Conditions on the Air Quality during the 2022 Winter Olympics in Beijing. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 987272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Wu, L.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, D. Impact of Synoptic Weather Types on Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations in Guangzhou, China. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Karlsson, P.E.; Gu, Y.; Chen, D.; Grennfelt, P. Synoptic Weather Types and Long-Range Transport Patterns for Ozone Precursors during High-Ozone Events in Southern Sweden. Ambio 2009, 38, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Cheng, C.; Li, M.; Zheng, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. The Influence of Synoptic Weather Patterns on Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Ozone Pollution Across Pearl River Delta of Southern China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD037121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Yan, Z.; Chen, D.; Fu, C. Comparison between Two Statistical Downscaling Methods for Summer Daily Rainfall in Chongqing, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3781–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Liao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Song, T.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, D.; et al. Quantifying the Impact of Synoptic Circulation Patterns on Ozone Variability in Northern China from April to October 2013–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14477–14492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Jia, S.; Wu, L.; Zhong, B.; Liao, W.; Chang, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Nitrogen Wet Deposition in Different Weather Types in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H. British Isles Weather Types and a Register of the Daily Sequence of Circulation Patterns. In Geophysical Memoirs; H.M. Stationery Office: London, UK, 1972; Volume 116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Gao, W.; Song, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. Exploring the Regional Pollution Characteristics and Meteorological Formation Mechanism of PM2.5 in North China during 2013-2017. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, S.; Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Song, A.; Bai, Y.; Ling, Z.; et al. Effectiveness of Emission Control in Reducing PM2.5 Pollution in Central China during Winter Haze Episodes under Various Potential Synoptic Controls. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 3143–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, N.; Zou, S.; Yoshino, H.; Yanagi, U.; Yu, C.W.; Qu, H. Indoor Environmental Conditions in Schoolchildren’s Homes in Central-South China. Indoor Built Environ. 2020, 29, 956–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chi, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, R.; Wang, X. Analysis of the Spatial Characteristics and Driving Forces Determining Ecosystem Quality of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 12555–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Li, T.; Che, H. Modeling Study of PM2.5 Pollutant Transport across Cities in China’s Jing-Jin-Ji Region during a Severe Haze Episode in December 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5803–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Geng, G.; Cheng, J.; Liang, F.; Li, R.; Meng, X.; Xue, T.; Huang, X.; Kan, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Evaluation of Gap-Filling Approaches in Satellite-Based Daily PM2.5 Prediction Models. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, T.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Peng, Y.; et al. Tracking Air Pollution in China: Near Real-Time PM2.5 Retrievals from Multisource Data Fusion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12106–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Geng, G.; Xue, T.; Liu, S.; Cai, C.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Tracking PM2.5 and O-3 Pollution and the Related Health Burden in China 2013-2020. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6922–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Separating Emission and Meteorological Contributions to Long-Term PM2.5 Trends over Eastern China during 2000–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9475–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Guo, B.; Zhang, B.; Che, H.; Zhang, X. Classification of the Circulation Patterns Related to Strong Dust Weather in China Using a Combination of the Lamb-Jenkinson and k-Means Clustering Methods. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liao, H.; Hu, J.; Li, N. Severe Particulate Pollution Days in China during 2013-2018 and the Associated Typical Weather Patterns in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the Yangtze River Delta Regions. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R. Effects of Atmospheric Circulations on the Interannual Variation in PM2.5 Concentrations over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in 2013-2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7667–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Evident Differences of Haze Days between December and January in North China and Possible Relationships with Preceding Climate Factors. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Socioeconomic Drivers of Urban Air Quality in China. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


(Directional Flow Class) | (Rotational Flow Class) | (Mixed Class) | and (Undefined) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N(north),NE(northeast) E(east),SE(southeast) S(south),SW(southwest) W(west),NW(northwest) | A(anticyclonic), C(cyclonic) | ANE(anticyclonic northeast), CNE(cyclonic northeast) | UD(Undefined) |
| Type (Day) | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 24 | 23 | 24 | 14 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 16 | 30 | 38 | 22 | 34 |
| AE | 6 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| AN | 14 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 25 |
| ANE | 17 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 8 | 9 |
| C | 4 | 3 | 14 | 8 | 16 | 26 | 27 | 19 | 9 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| CE | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| CN | 3 | 8 | 4 | 14 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 14 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| CNE | 0 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 11 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| E | 6 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 10 | 6 | 5 |
| N | 29 | 25 | 31 | 34 | 46 | 30 | 21 | 35 | 36 | 27 | 34 | 27 |
| NE | 21 | 14 | 21 | 15 | 9 | 12 | 25 | 14 | 12 | 13 | 20 | 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, S.; Wu, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tian, B.; Yu, Y.; Ma, N.; Ji, P.; Zhang, B. Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060942
Gu S, Wu S, Yang L, Hu Y, Tian B, Yu Y, Ma N, Ji P, Zhang B. Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060942
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Shijie, Shuai Wu, Luoqi Yang, Yincui Hu, Bing Tian, Yan Yu, Ning Ma, Pengsong Ji, and Bo Zhang. 2023. "Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060942
APA StyleGu, S., Wu, S., Yang, L., Hu, Y., Tian, B., Yu, Y., Ma, N., Ji, P., & Zhang, B. (2023). Synoptic Weather Patterns and Atmospheric Circulation Types of PM2.5 Pollution Periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Atmosphere, 14(6), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060942






