Analysis of Precipitation Process and Operational Precipitation Enhancement in Panxi Region Based on Cloud Parameters Retrievals from China’s Next−Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellite FY−4A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Multispectral Analysis Method with RGB Composite Image
2.3. Cloud Microphysical Characteristics Analysis Based on T−Re Contours
2.4. Analysis of Satellite Retrieval Products
3. Weather Background and Aircraft Operation Description
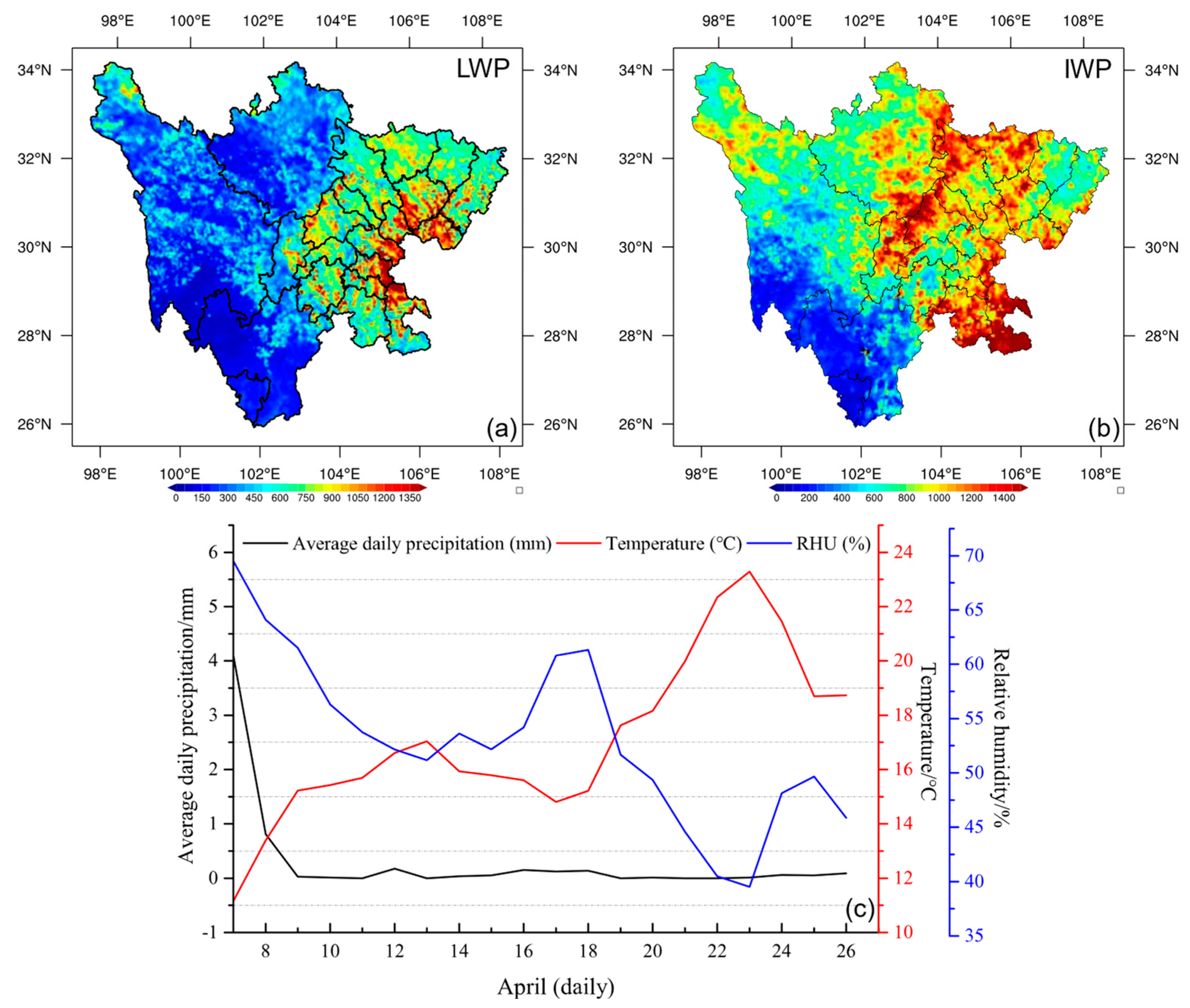
3.1. Analysis of Weather Background
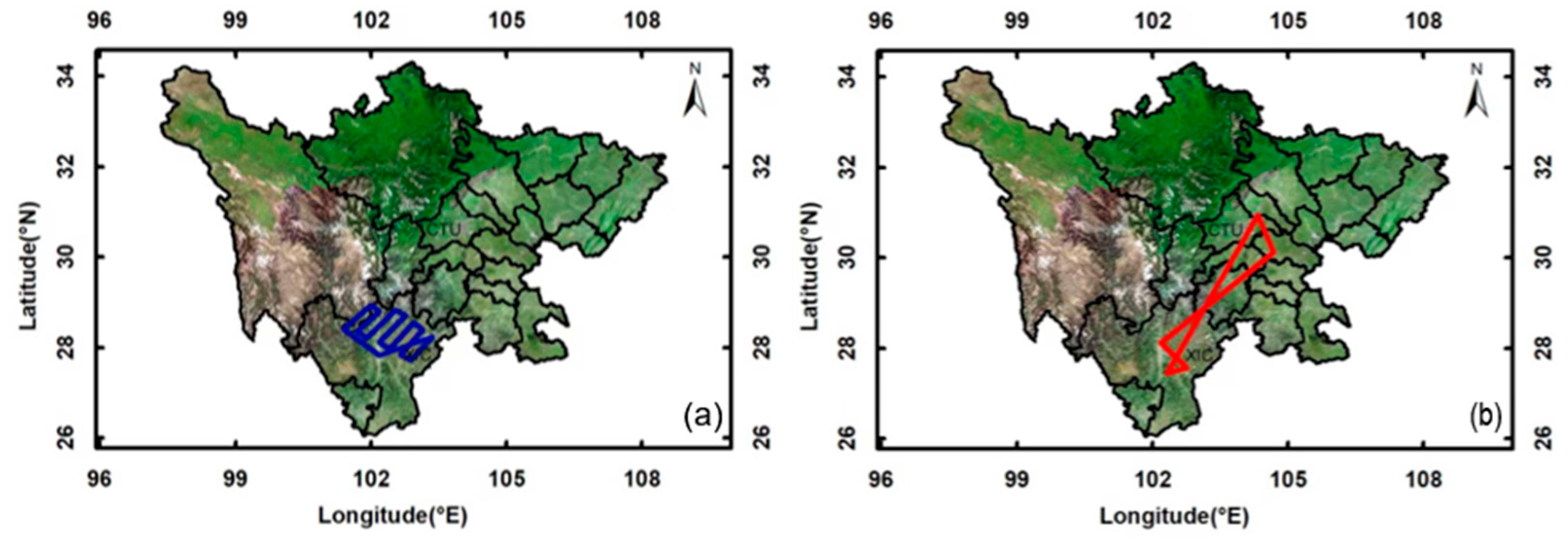
3.2. Aircraft Operation
4. Analysis of Cloud Parameters
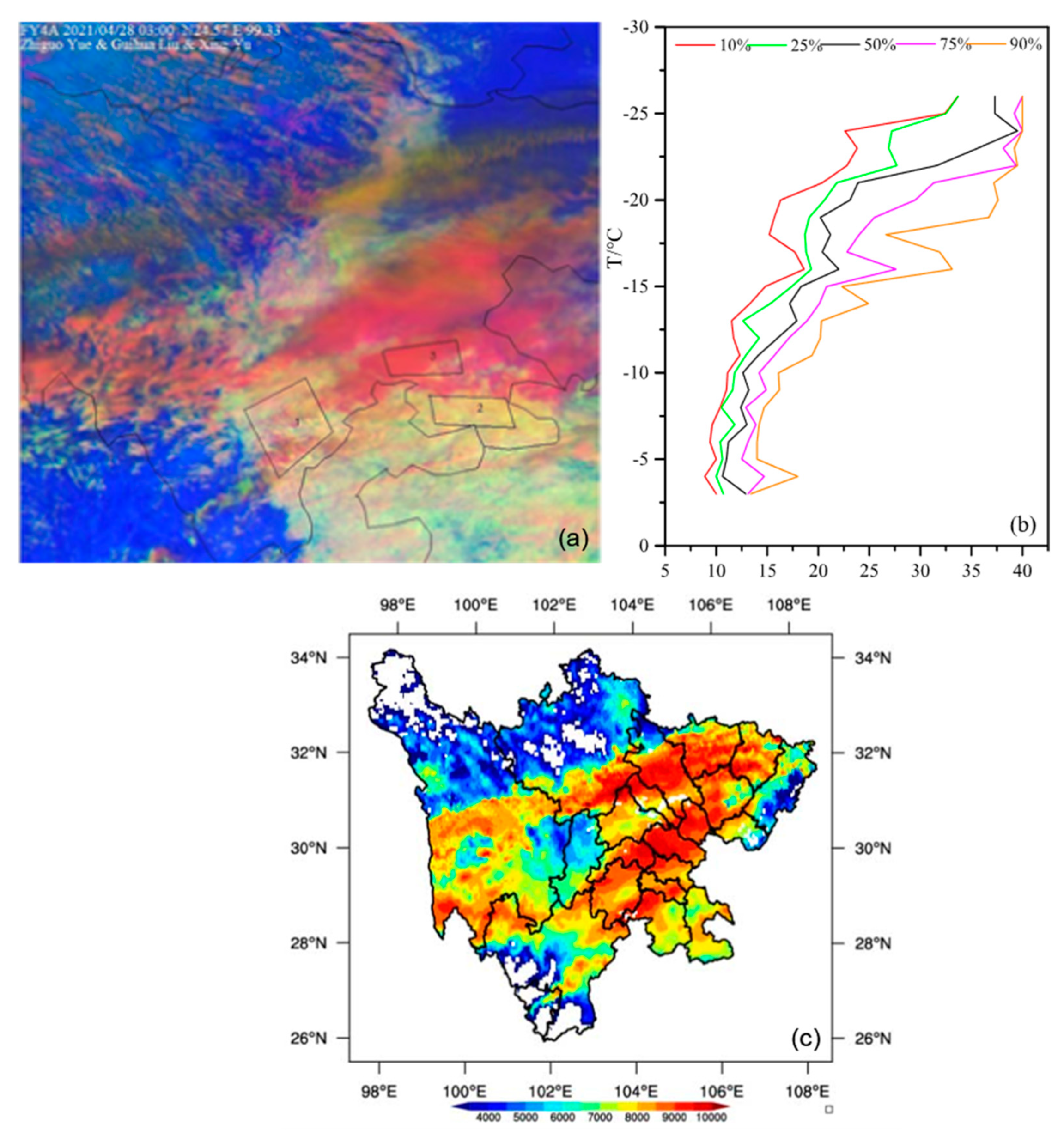
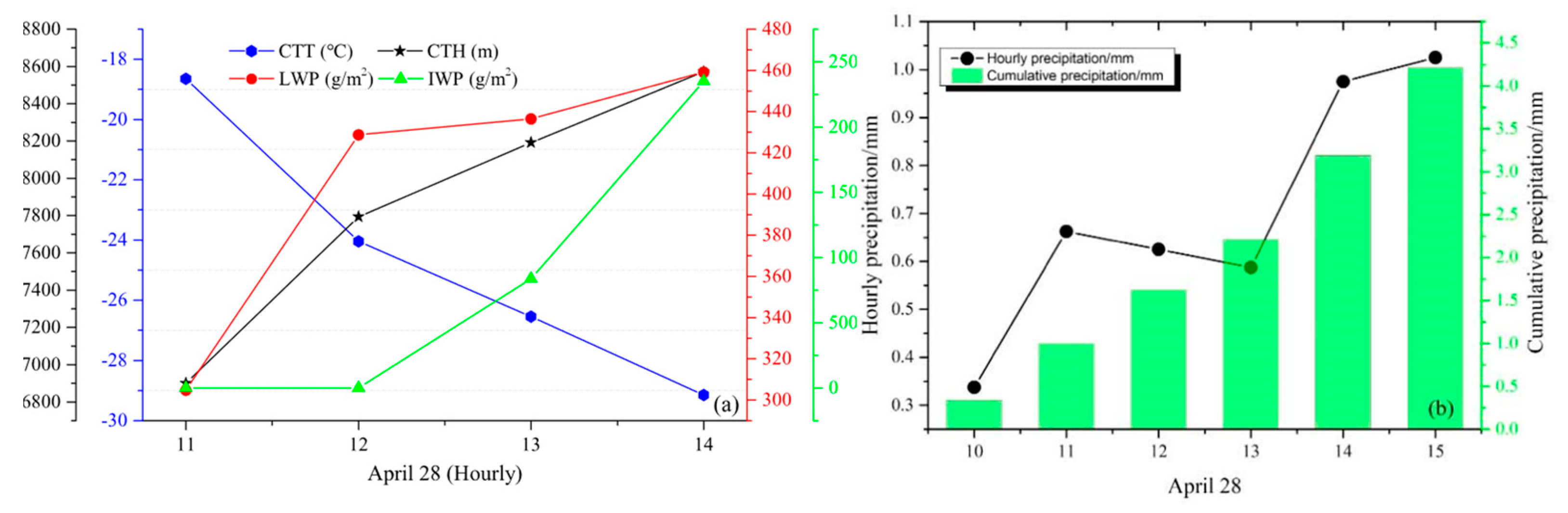
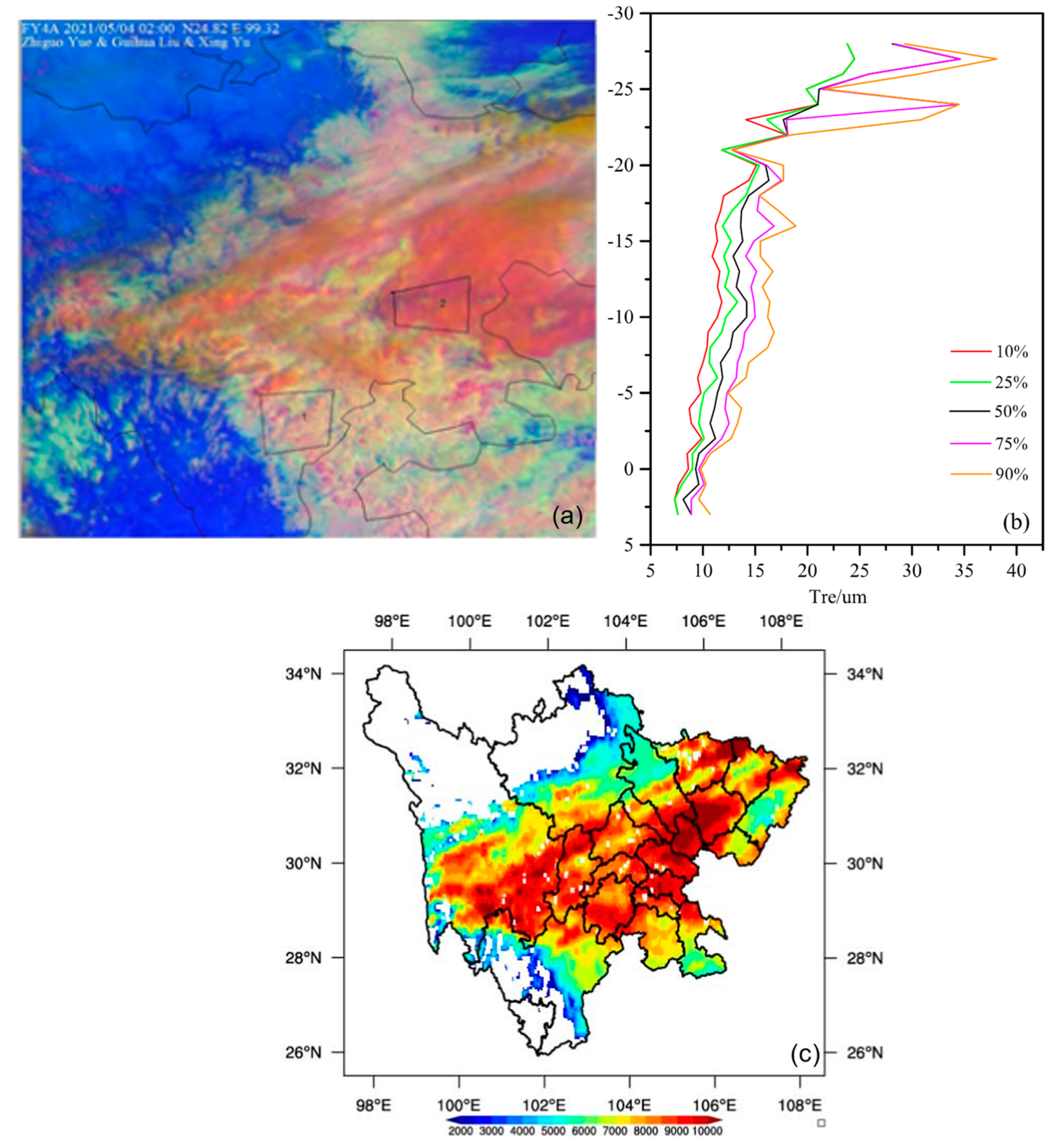
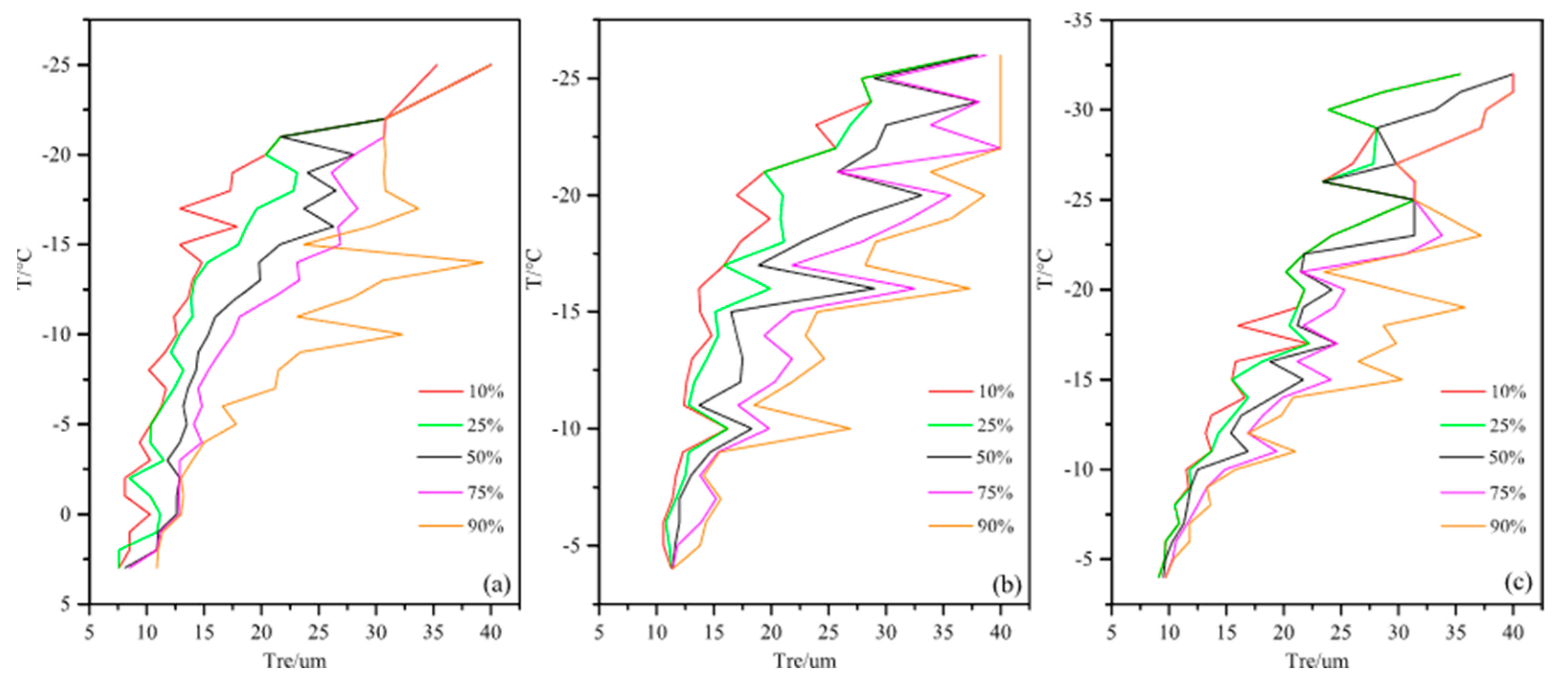
4.1. The First Flight
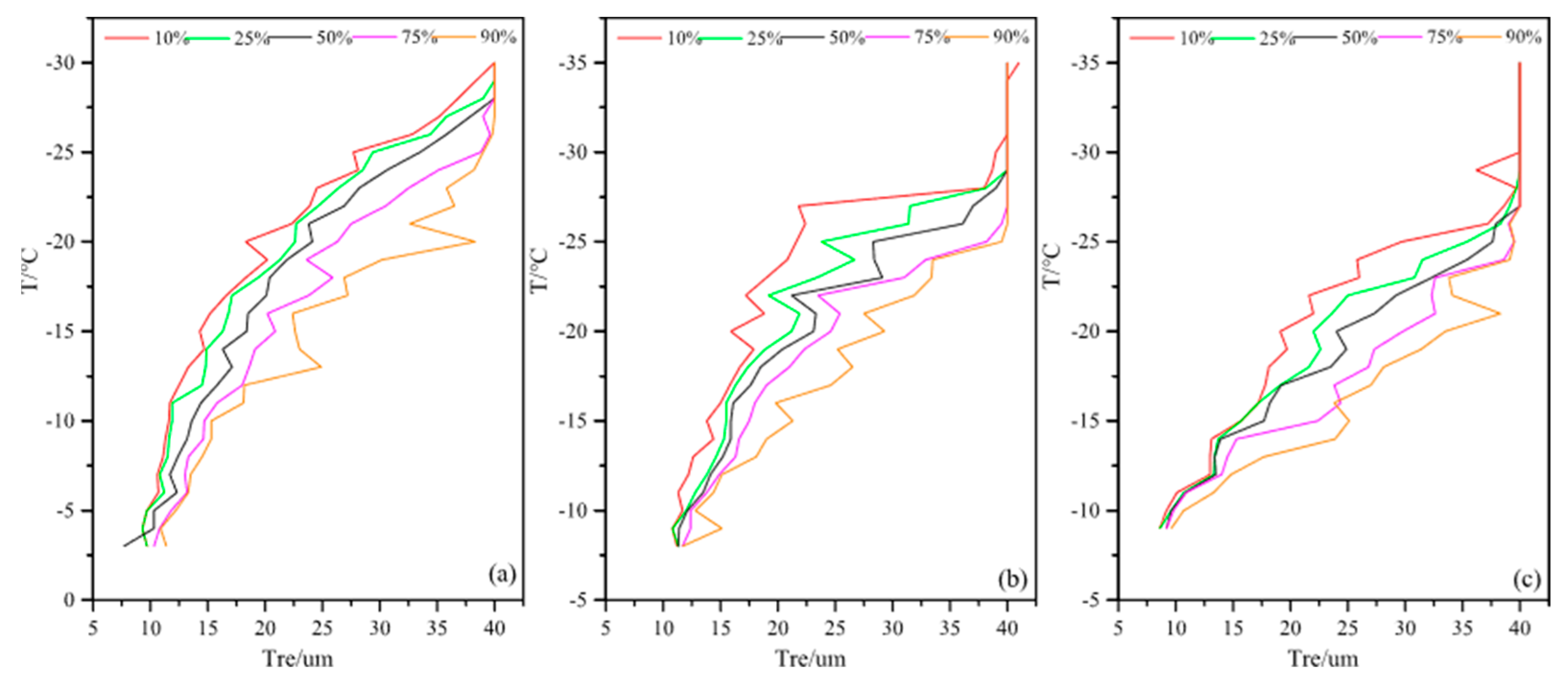
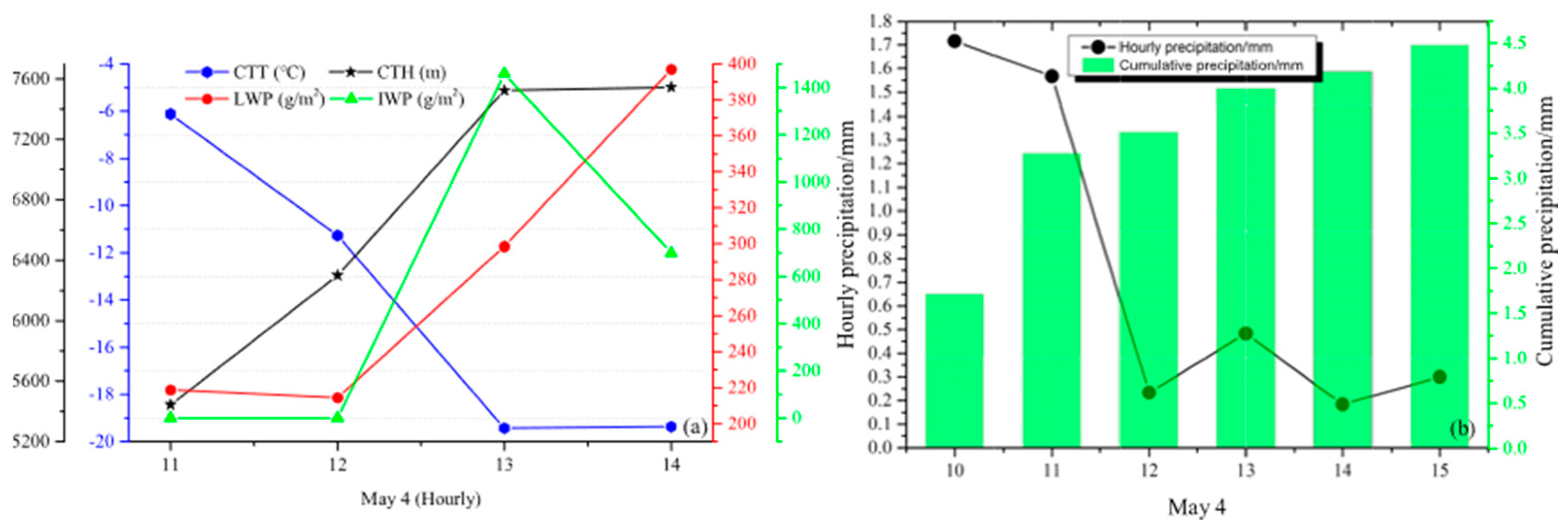
4.2. The Second Flight
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Rosenfeld, D.; Xu, X.H. Analysis of satellite observed microphysical signatures of cloud seeding tracks in supercooled layer clouds. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2006, 66, 622–630. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.P.; Li, P.R.; Shen, D.D.; Li, Y.Y.; Feng, Q.J. Evolution of Microphysical Characteristic Parameters of Stratiform Mixed Clouds in Summer and Artificial Precipitation Enhancement. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2017, 33, 126–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D. A new cloud and aerosol layer detection method based on micropulse lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6788–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.E.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J.; Nazarov, A. On the analysis of a cloud seeding dataset over Tasmania. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.E.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J. On a Natural Environment for Glaciogenic Cloud Seeding. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, A.; Fu, Y. Linkage between the vertical evolution of clouds and droplet growth modes as seen from FY-4A AGRI and GPM DPR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.N.; Zhu, Y.N.; Liu, G.H.; Dai, J.; Yue, Z.G. Seeding condition of precipitation enhancement revealed by multiple spectral data of satellite I: Convective clouds. Clim. Environ. Res. 2012, 17, 747–757. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Wu, K.; Wei, T.; Wang, L.; Shu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xia, H. Cloud Seeding Evidenced by Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Rosenfeld, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Li, J. The Evolution of an AgI Cloud-Seeding Track in Central China as Seen by a Combination of Radar, Satellite, and Disdrometer Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fu, J.; Cui, Y.; Dong, X.; Mai, R.; Xu, F. Response of Mixed-Phase Cloud Microphysical Properties to Cloud-Seeding Near Cloud Top Over Hebei, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 865966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Zheng, J.F.; Ruan, Z.; Cui, Z.H.; Hu, Z.Q.; Wu, S.H.; Wu, Y.H. The preliminary analyses of the cloud properties over the Tibetan Plateau from the field experiments in clouds precipitation with the various radars. Acta Meteor Sin. 2015, 73, 635–647. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liu, L.P.; Zhai, X.C. The comparison of cloud base observations with Ka-band solid-state transmitter-based millimeter wave cloud radar and ceilometer in summer over Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 41, 659–672. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Sun, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Peng, M.; Zhu, H. Aircraft Observation of a Two-Layer Cloud and the Analysis of Cold Cloud Seeding Effect. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 855813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Liu, G.; Geng, W. FY-4A Satellite Based Cloud Microphysical Variation Analysis of Airborne Cloud Seeding Operations in Sichuan Basin. The International Archives of Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Liang, P. Advances in satellite passive microwave remote sensing of cloud liquid water. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 67, 331–341. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Luo, J.; Liang, J.; Wang, B.; Tian, W.; Chen, X. Comparisons of AGRI/FY-4A Cloud Fraction and Cloud Top Pressure with MODIS/Terra Measurements over East Asia. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmus, D.A.; Rooyen, R.V. A.; Rooyen, R.V. A satellite survey of cloud cover and water vapor in northwest Africa and southern Spain. In SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering; SPIE: Bellingham, WC, USA, 2006; Volume 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cai, B.; Sun, L. Comparison of Vertical Structure Between Precipitation Cloud and Non-Precipitation Cloud Based on CloudSat Data over Northeast China. Meteorol. Mon. 2017, 43, 1374–1382. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Rodier, S.; Xu, K.; Sun, W.; Huang, J.; Lin, B.; Zhai, P.; Josset, D. Occurrence, liquid water content and fraction of supercooled water clouds from combined CALIOP/IIR/MODIS measurements. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00H34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lensky, I.M.; Rosenfeld, D.; Rosenfeld, D. The time-space exchangeability of satellite retrieved relations between cloud top temperature and particle effective radius. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.; Rosenfeld, D.; Liu, G.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hashimshoni, E.; Xu, X.; Hui, Y.; Lauer, O. Automated Mapping of Convective Clouds (AMCC) thermodynamical, microphysical, and CCN properties from SNPP/VIIRS satellite data. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hashimshoni, E.; Pöhlker, M.L.; Jefferson, A.; Pöhlker, C.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yue, Z.; et al. Satellite retrieval of cloud condensation nuclei concentrations by using clouds as CCN chambers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5828–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Fischman, B.; Zheng, Y.; Goren, T.; Giguzin, D. Combined satellite and radar retrievals of drop concentration and CCN at convective cloud base, Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Shou, Y. Channel simulation for FY-4 AGRI. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS 2011, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Gao, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, J. A Cloud Classification Method Based on a Convolutional Neural Network for FY-4A Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huo, J.; Lyu, D.; Wang, X. Assessment of FY-4A and Himawari-8 Cloud Top Height Retrieval through Comparison with Ground-Based Millimeter Radar at Sites in Tibet and Beijing. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1334–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Reliability Evaluation of the Joint Observation of Cloud Top Height by FY-4A and HIMAWARI-8. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.Q. Evaluation of Spatial and Temporal Changes of Drought Vulnerability in Panxi Region. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Guo, X.L. Characteristics of convective cloud and precipitation during summer time at Naqu over Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Lensky, I.M. Spaceborne sensed insights into precipitation formation processes in continental and maritime cloud. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 245–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Yu, X.; Dai, J.; Xu, X.H.; Yue, Z.G. A case study of the conditions for topographic cloud seeding based on the retrieval of satellite measurements. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2011, 69, 363–369. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chen, B.J.; Yin, Y. Cloud Precipitation Physics; Meteorological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 86–87, 326–327.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Lin, D.; Wu, F. Analysis of Precipitation Process and Operational Precipitation Enhancement in Panxi Region Based on Cloud Parameters Retrievals from China’s Next−Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellite FY−4A. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060922
Guo X, Lin D, Wu F. Analysis of Precipitation Process and Operational Precipitation Enhancement in Panxi Region Based on Cloud Parameters Retrievals from China’s Next−Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellite FY−4A. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060922
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaomei, Dan Lin, and Fan Wu. 2023. "Analysis of Precipitation Process and Operational Precipitation Enhancement in Panxi Region Based on Cloud Parameters Retrievals from China’s Next−Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellite FY−4A" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060922
APA StyleGuo, X., Lin, D., & Wu, F. (2023). Analysis of Precipitation Process and Operational Precipitation Enhancement in Panxi Region Based on Cloud Parameters Retrievals from China’s Next−Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellite FY−4A. Atmosphere, 14(6), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14060922





