Analysis of Extreme Rainstorms Associated with Tropical Cyclone Rammasun (2014) over Guangxi Province of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.2. Orographic Precipitation Equation
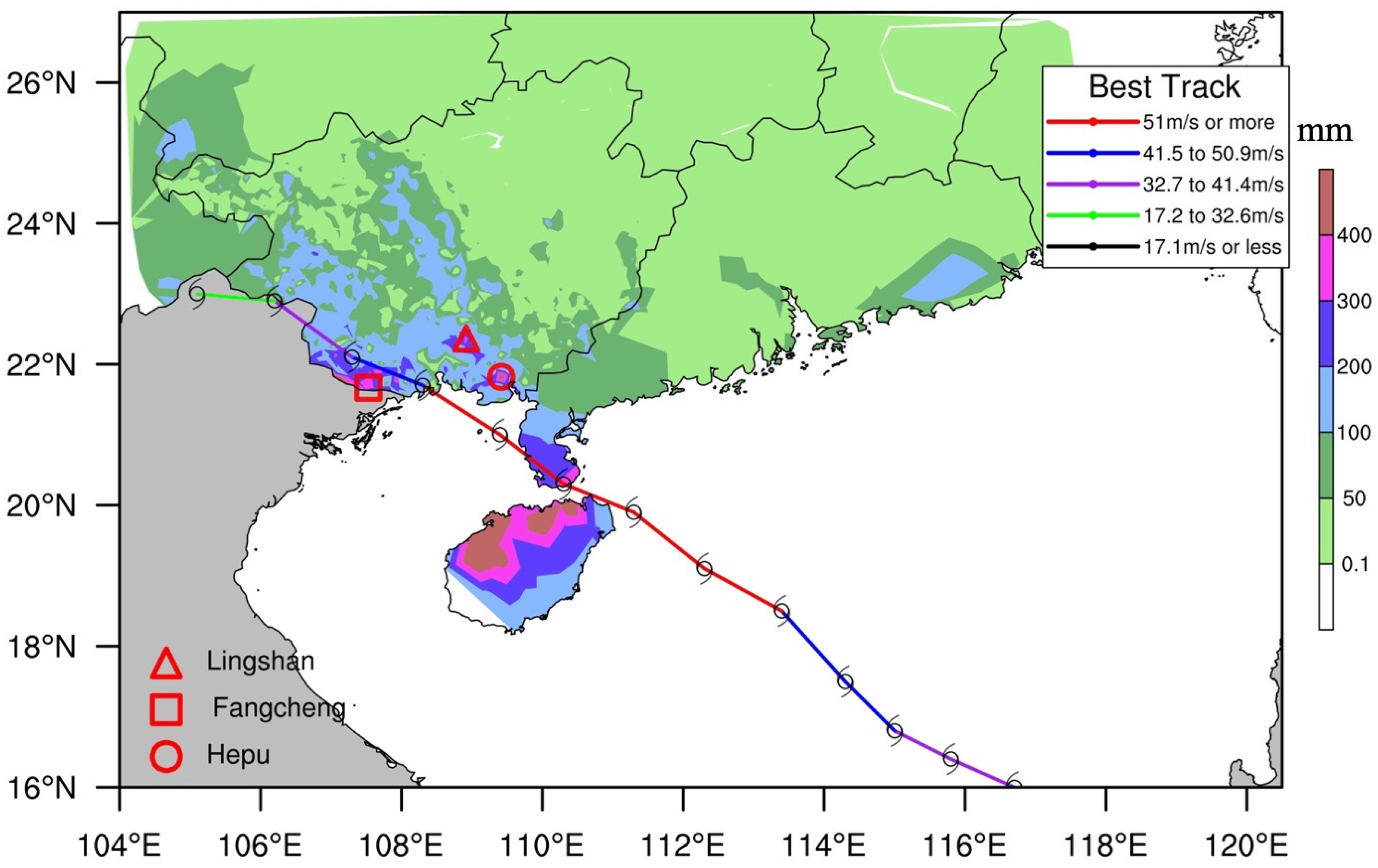
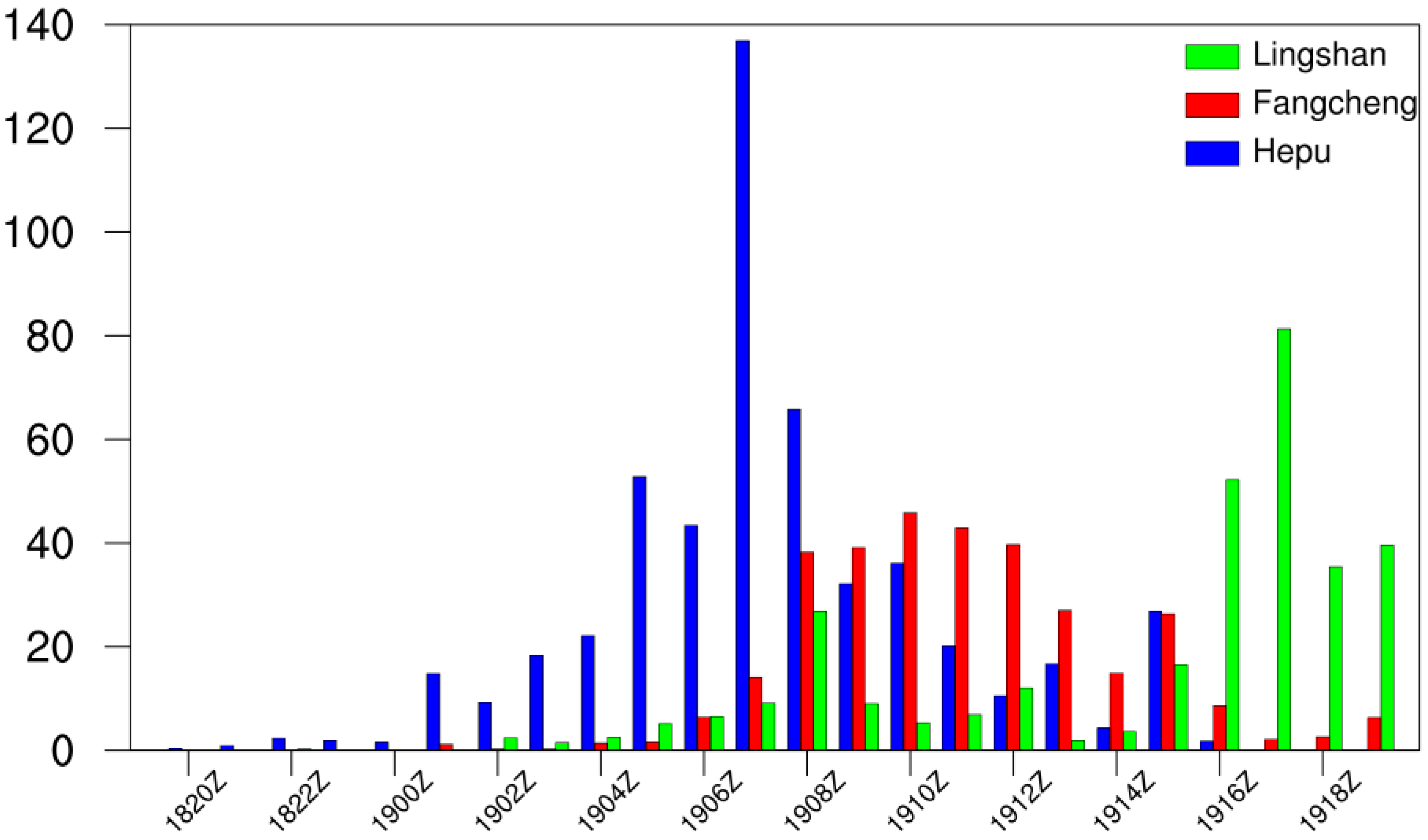
3. Overview of the Guangxi Rainstorms
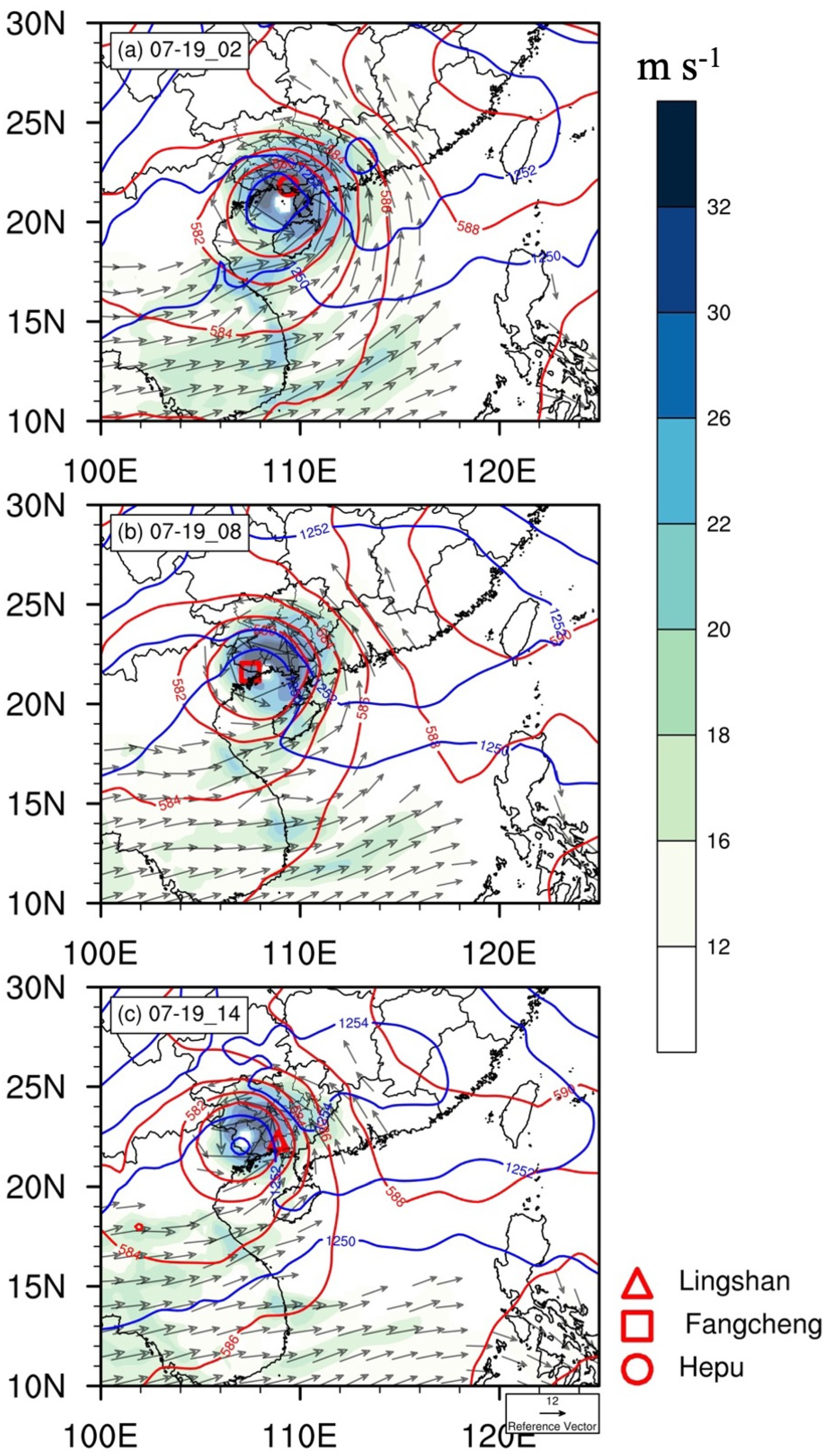
4. Synoptic Situation
5. Cause Analysis
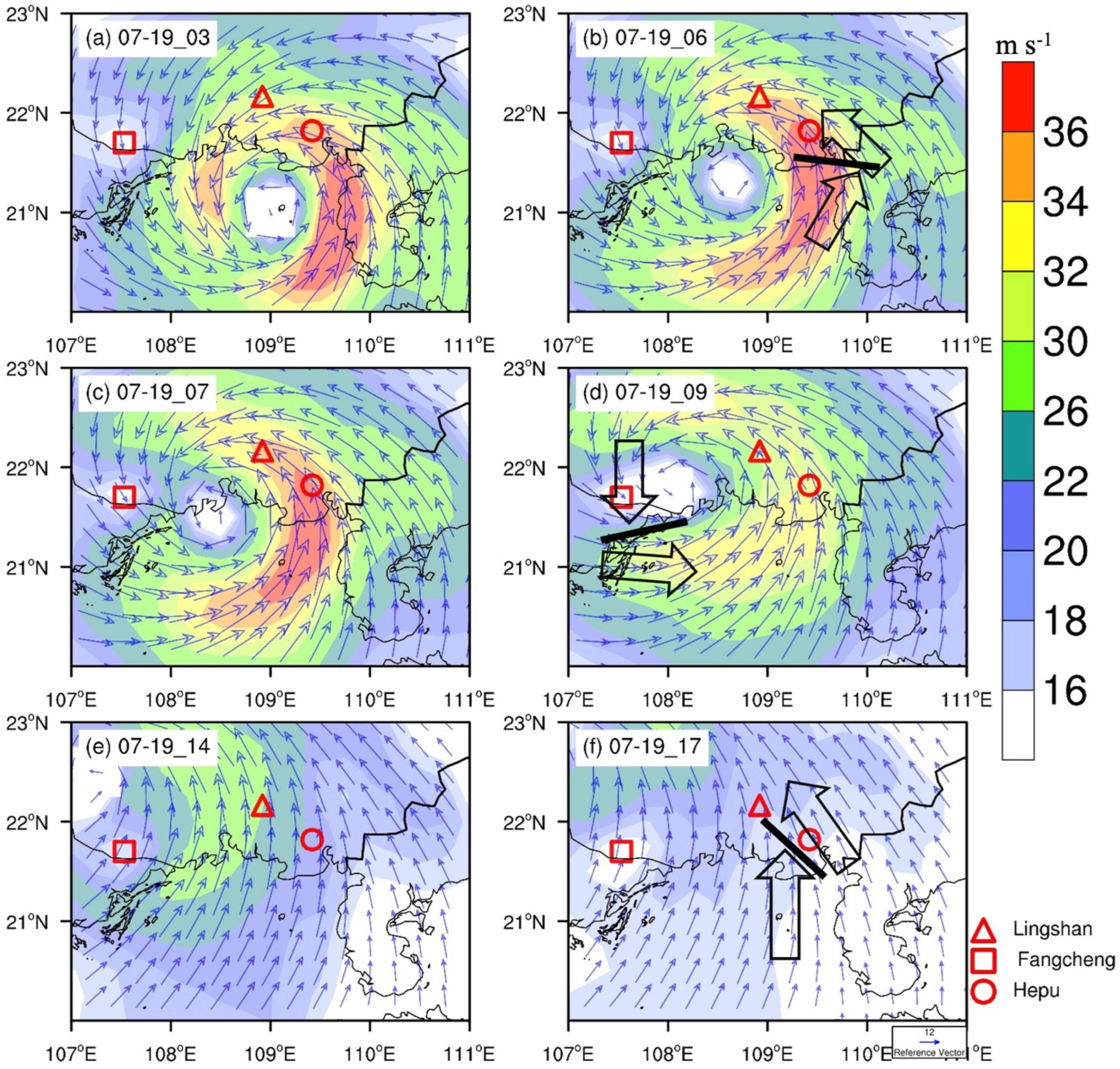
5.1. Low-Level Convergence
5.2. Radar-Observed Characteristics
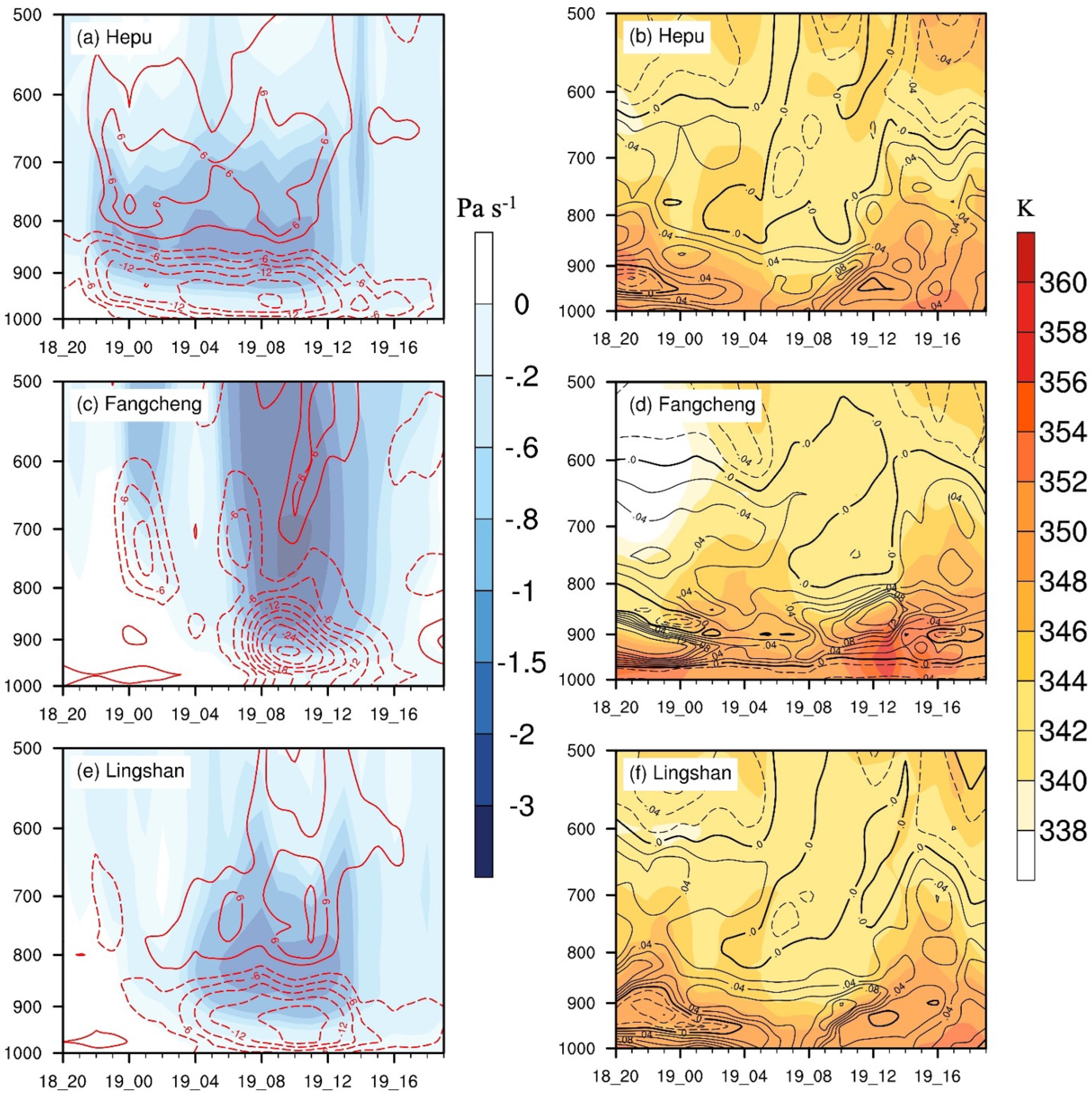
5.3. Vertical Motion and Thermal Condition
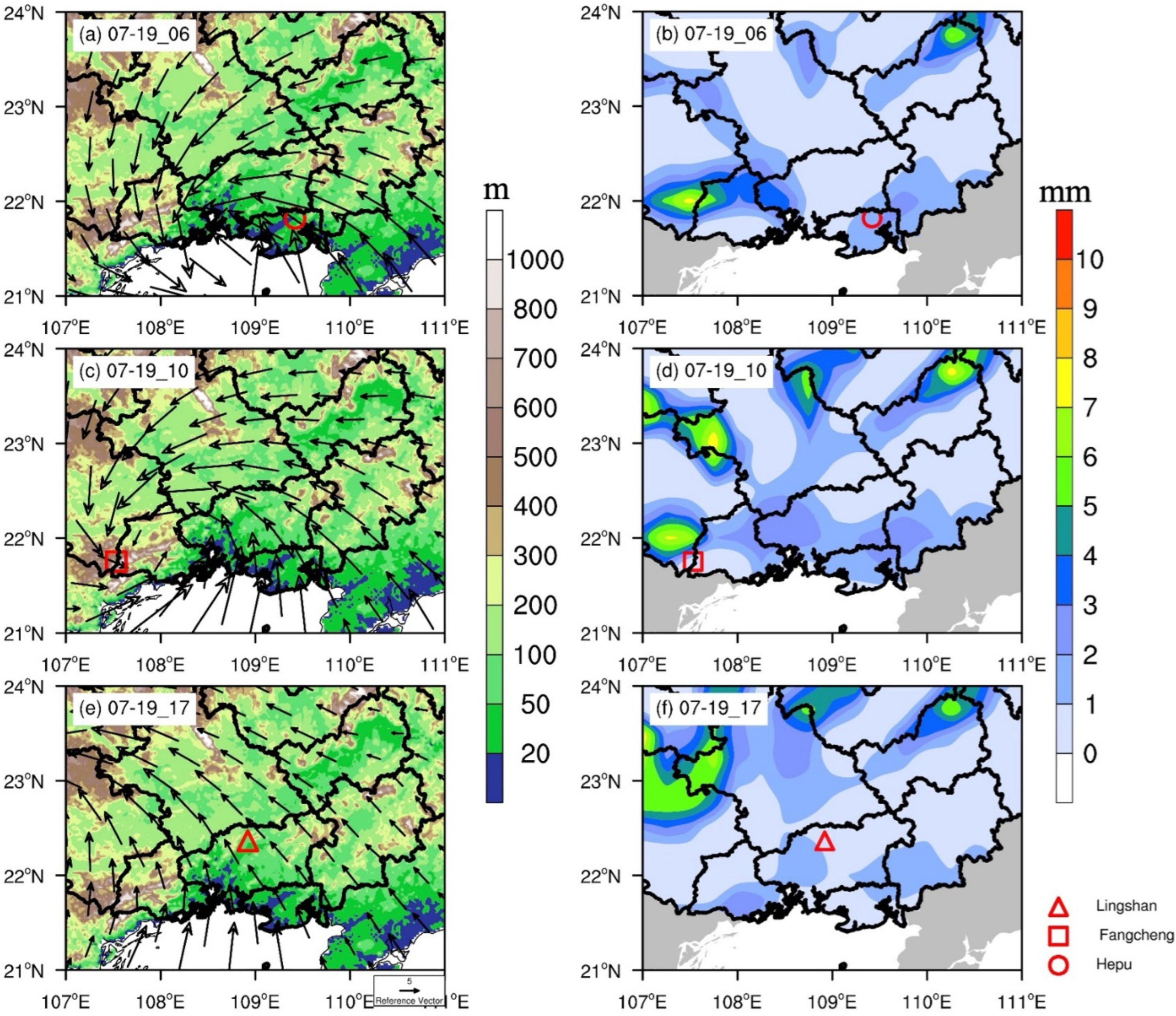
5.4. Discussion of Orographic Precipitation
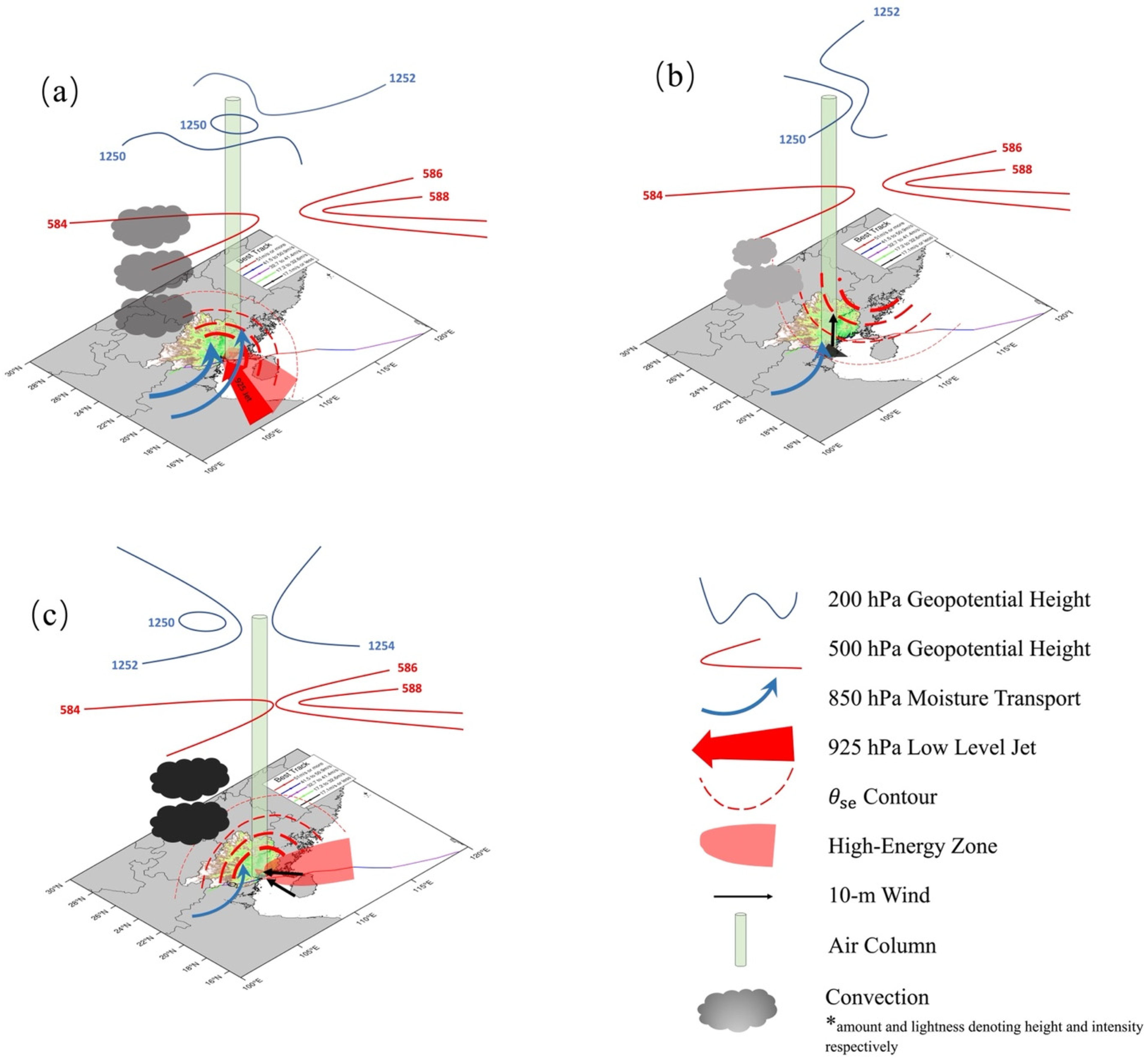
6. Conceptual Model and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Meng, Z. An overview on Tropical Cyclone Research Progress in China during the Past Ten Years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 25, 420–432. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Peng, T. Research Progress on Typhoon Heavy Rainfall in China for Last Ten Years. Meteorol. Mon. 2005, 31, 3–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Xu, Y. Assimilation of FY-3D MWHS-2 Radiances with WRF Hybrid-3DVAR System for the Forecast of Heavy Rainfall Evolution Associated with Typhoon Ampil. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2021, 149, 1419–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lü, H.; Shi, D.; Xia, C.; Dong, C. A Comparative Study of the Landfall Precipitation by Tropical Cyclones ARB 01 (2002) and Luban (2018) near the Arabian Peninsula. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y. Comparative analyses of the heavy rainfall associated with landfalling tropical cy-clones SOULIK (1307) and MARIA (1808) with similar routes. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, T. Composite analysis of precipitation intensity and distribution characteristics of western track land-fall typhoons over China under strong and weak monsoon conditions. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, H. Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Wang, Y. A diagnostic study on heavy rainfall induced by landfalling Typhoon Utor (2013) in South China: 2. Postlandfall rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12803–12819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, A. The impacts of Taiwan topography on the predictability of Typhoon Morakot’s rec-ord-breaking rainfall: A high-resolution ensemble simulation. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHart, J.C.; Houze, R.A. Orographic Modification of Precipitation Processes in Hurricane Karl (2010). Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ren, F.; Li, Y.; Qiu, W.; Ma, Z.; Cai, Q. Characteristics and Preliminary Causes of Tropical Cyclone Extreme Rainfall Events over Hainan Island. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Paul, S.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-W.; Tsuboki, K.; Lee, D.-I.; Lee, J.-S. Typhoon Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts by the 2.5 km CReSS Model in Taiwan: Examples and Role of Topography. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, C. Rainfall Reinforcement Associated with Landfalling Tropical Cyclones. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 3541–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lei, H.; Zheng, H. Precipitation characteristics of typhoon Lekima (2019) at landfall revealed by joint observations from GPM satellite and S-band radar. Atmos. Res. 2021, 260, 105714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L. Impact of the Monsoonal Surge on Extreme Rainfall of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, L. Diagnosis of previous conditions for typhoon rainstorm amplification in the north of east China with a conceptual model. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteorol. 1996, 19, 130–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Ye, Z. Analysis of atmospheric circulation characteristics of regional rainstorm reinforcement associ-ated with typhoons making landfall in northern Fujian and southern Zhejiang. Torrential Rain Disasters 2018, 37, 246–256. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Lee, W.-C.; Bell, M. A Squall-Line-Like Principal Rainband in Typhoon Hagupit (2008) Observed by Airborne Doppler Radar. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 2733–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, K.; Lee, W.-C.; Zhang, F. Microphysical and Kinematic Structure of Convective-Scale Elements in the Inner Rainband of Typhoon Matmo (2014) After Landfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6549–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Chan, J.C.L. Recent increase in extreme intensity of tropical cyclones making landfall in South China. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Su, B.; Wang, Y.; Fischer, T.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Chao, G.; Wang, R.; Jiang, T. Economic sector loss from influential tropical cyclones and relationship to associated rainfall and wind speed in China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 169, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cai, Q.; Cheng, S. Characteristics on intensity and precipitation of super typhoon Rammasun (1409) and reason why it rapidly intensified offshore. Torrential Rain Disasters 2014, 33, 333–341. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Ren, F.; Ma, Z.; Cai, Q. Rainfall characteristic and cause comparison of two track-similar tropical cyclones in 2014. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 1305–1320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Yao, X. Comparative analysis of moisture and helicity during extraordinary storms caused by two typhoons in different seasons. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2017, 33, 375–385. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, A.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Qi, L. Rammasun Intensification in Near Sea and Induced Abnormal Rainstorm in Guangxi. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 653–668. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Yao, C.; Luo, X.; Sun, H. A Comparative Study on the Offshore Intensification of Supertyphoon Rammasun (2014) and Typhoon Rumbia (2013): The Role of Summer Monsoon. Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Q.; Ma, S.; Xu, J.; Dai, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. The development of consideration of typhoon forecast operation of Central Meteoro-logical Center. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 10–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. An overview of the China Meteorological Administration tropical cyclone data-base. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2014, 31, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B. The Influence of Mountains on the Atmosphere. Adv. Geophys. 1979, 21, 87–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qian, H.; Luo, L.; Yu, H. A study of terrain correction method on typhoon precipitation based on ECMWF fore-casts. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2019, 77, 674–685. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, C. Research progress on abrupt intensification of heavy rainfall and super heavy rainfall associated with landfalling tropical cyclones. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2009, 25, 495–502. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, F.; Zhang, G.J.; Ramanathan, V.; Leung, L.R. Trends in surface equivalent potential temperature: A more comprehensive metric for global warming and weather extremes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117832119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.H. Observation and Mechanism Analysis for a Record-Breaking Heavy Rainfall Event over Southern China in August 2018. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 44, 695–715. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ding, Y. Introduction to Typhoons in the Western Pacific; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.; Dong, J.; Du, H. Climatic analysis on typhoon rainfall of east china and affecting factors of the precipitation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2005, 16, 402–407. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hu, B. The Effect of Terrain on Landing Typhoon 0604 Bilis. Torrential Rain Disasters 2007, 26, 97–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Ren, F.; Liu, A.; Huang, Z. Climatic variation features of typhoon precipitation influencing fujian for the past 46 years. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2008, 24, 411–416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-L. Effects of Orography on the Generation and Propagation of Mesoscale Convective Systems in a Two-Dimensional Conditionally Unstable Flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 3817–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.B.; Schafer, P.; Kirshbaum, D.; Regina, E. Orographic Enhancement of Precipitation inside Hurricane Dean. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liang, X.-Z. Improving US extreme precipitation simulation: Dependence on cumulus parameterization and underlying mechanism. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1325–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, C.; Sun, L.; Hou, J.; Lu, W. Analysis of Extreme Rainstorms Associated with Tropical Cyclone Rammasun (2014) over Guangxi Province of China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020320
Lan Y, Xiao Z, Yao C, Sun L, Hou J, Lu W. Analysis of Extreme Rainstorms Associated with Tropical Cyclone Rammasun (2014) over Guangxi Province of China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020320
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Yufeng, Zhixiang Xiao, Cai Yao, Lei Sun, Junxing Hou, and Weiping Lu. 2023. "Analysis of Extreme Rainstorms Associated with Tropical Cyclone Rammasun (2014) over Guangxi Province of China" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020320
APA StyleLan, Y., Xiao, Z., Yao, C., Sun, L., Hou, J., & Lu, W. (2023). Analysis of Extreme Rainstorms Associated with Tropical Cyclone Rammasun (2014) over Guangxi Province of China. Atmosphere, 14(2), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020320




