Abstract
Background: Air pollution leads to many adverse diseases, especially respiratory diseases and cardiac symptoms. However, it has not been studied the association between air pollution and influenza cases in Jinan City, especially during the outbreak of COVID-19; Methods: The data were obtained from China’s Disease Information System, and influenza cases during 2020–2021 in Jinan City were collected from it. We used the generalized additive Poisson model to measure the association between air pollutants and the daily influenza cases after adjusting for possible influence variables; Results: There were 4767 influenza cases. PM2.5 and PM10 on lag 0, lag 3, and lag 4 were significantly associated with an increased risk of influenza; gaseous pollutants (NO2 and SO2) led to higher risk than particulate matter pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10). There were no significant differences for sex subgroup analyses. Except for O3, the incidence risk of males and females was highest on lag 3 and lag 4. For the study of different age groups, influenza cases aged over 59 years had a slightly larger relative risk when exposed to all air pollutants (except O3) than the younger group; Conclusions: The overall number of influenza cases decreased in 2020–2021. PM2.5, SO2, CO, and NO2 were significantly associated with the risk of influenza during 2020–2021. Countermeasures should be developed according to the characteristics of influenza risk to prevent and control it.
1. Introduction
Influenza is an acute respiratory infectious disease, mainly caused by the influenza virus. The main clinical manifestations are sudden onset of fever, cough, headache, muscle and joint pain, sore throat, and runny nose. Most people recover from these symptoms within a week [1,2]. However, severe illness and death can also be caused by influenza, especially among high-risk groups, such as the very young, the elderly, pregnant women, health workers, and those with serious medical conditions [2].
Hospitalizations and deaths occur mainly in high-risk groups. Globally, influenza epidemics are estimated to cause about 3 million to 5 million severe cases and about 290,000 to 650,000 deaths associated with respiratory diseases each year according to the World Health Organization (WHO) [3]. China is also facing a serious situation. For example, there were about 2800 outbreaks of influenza according to the Emergency Public Reporting System (EPRS) from April 2005 to November 2013 [4]. Influenza epidemics not only affect health, but also can cause economic losses by depriving the productive workforce and burdening health services [5]. A decrease in the number of patients with influenza was the most significant among those with notifiable infectious diseases during the global COVID-19 pandemic, but influenza cases still come first according to the Global Incident Map [6].
Air pollution is the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical, or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere according to the World Health Organization [7]. Including PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, O3, and CO, some studies have shown air pollution is strongly associated with many respiratory diseases and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as asthma, acute respiratory distress syndrome, respiratory infection, and mental disorder, and many studies have confirmed the consistency of these results [8,9].
Influenza spreads easily and can spread rapidly. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, droplets containing the virus (i.e., infectious droplets) are spread into the air and spread up to one meter, and people around them become infected by inhaling these droplets. The virus can also be spread through direct contact with secretions (through contact with a contaminated host or surface) [10]. Studies have found that air pollution can not only make infected people sick by weakening the human immune system, but also carry microorganisms to directly infect people. Airborne pollution particles may provide “ondensation nuclei” to which virus droplets attach [11]. This suggests that the risk of influenza may be related to the concentration of pollutants.
Some studies have shown that as concentrations of pollutants rise, the risk of influenza increases. For example, studies have shown that short-term changes in ambient PM2.5 levels and other pollutants exposure are associated with an increased risk of influenza in Beijing and Wuhan, China [10,12]. There were significant seasonal differences between the cold season and the warm season [13]. ILI morbidity increases with the rising PM concentrations, for both PM2.5 and PM10 in Warsaw, Poland [14]. Song’s study showed five air pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO) are significantly positively correlated with the incidence of influenza, with the decreasing order of contribution to it: SO2 > CO > NO2 > PM2.5 > PM10 in China from 2004 to 2017 [15]. In the age subgroup analysis, people over the age of 25 were virtually unaffected by air pollutants in Nanjing, China [16]. Another study suggested that PM2.5 and PM10 have similar effects on clinical ILI and influenza incidence, while SO2 and NO2 on ILI and influenza are distinct [17]. Ambient PM2.5 may increase the risk of exposure to influenza in China, especially on cooler days [18].
However, the exposure−response relationships between studies and locations may differ, and the findings are not necessarily applicable to different areas with different socioeconomic statuses and air pollution levels. What’s more, none of these studies involved an infectious disease pandemic. Therefore, it is important to explore the effects of air pollutants on the risk of influenza during COVID-19.
The purpose of this study was to explore the short-term effects of air pollution on the risk of influenza in Jinan City during COVID-19 and to provide a scientific evaluation basis for influenza prevention and control in the context of normalized epidemic prevention and control.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
Jinan is the capital city of Shandong Province with a permanent population of 9,202,400. It covers an area of 10,244.45 km2 and is located between 36°01′ to 37°32′ north latitude and 116°11′ to 117°44′ east longitude. It belongs to the warm temperate continental monsoon climate zone, surrounded by mountains on three sides. It is characterized by four distinct seasons, including hot summer and cold winter, and abundant rainfall. In recent years, air quality in Jinan has gradually improved, but the situation is still not optimistic due to the rapid development of industry and the popularity of cars [19].
2.2. Data Collection
Influenza has been listed as a class C statutory reporting infectious disease by the National Infectious Disease Reporting System in China. In this study, we collected influenza cases from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2021, which were extracted from Disease Information System in China, with case information including onset date, gender, age, and residential address.
The concentrations of air pollutants, including PM2.5, PM10, SO2, CO, NO2, andO3, were collected between 1 January 2020 and 31 December 2021, from the Air Quality Online Monitoring and Analysis Platform of China (https://www.aqistudy.cn/) (accessed on 15 March 2022). Daily mean temperature, mean relative humidity, and mean wind speed of Jinan were obtained from the weather of the world (https://rp5.ru/) (accessed on 20 March 2022) during the study period.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The descriptive analysis method was used to describe the characteristics of air pollutants, influenza cases, and meteorological factors. We used the spearman correlation coefficient to measure the relationship between air pollutants and the paired data of air pollutants and meteorological factors. To reduce the effect of collinearity between pollutants, when the number is greater than 0.7, only one was included in the two-pollutant model.
Time series regression studies have been widely used in environmental epidemiology, especially in investigating the short-term associations between exposures and health outcomes [20]. Daily influenza cases, air pollutant concentrations, and meteorological parameters were merged by date to be analyzed with a time-series design. We fitted a Poisson regression in a generalized additive model and include the daily mean temperature, the relative humidity, the wind speed, public holidays, and days of the week as confounding covariates based on previous studies to adjust, and they were controlled by using natural spline smoothing functions. All analyses were performed using R statistical software (ver. 4.2.0) and SPSS(ver. 27.0). The GAM models were built using R package ‘mgcv’ (Wood, S.N. (2017). The constructed model is as follows:
where E () denotes the expected number of influenza cases on day t, Zt denotes the concentration of a pollutant on day t, β denotes the coefficient of exposure, ns denotes natural smoothing spline function, df denotes the degree of freedom, and DOW means “day of the week”.
There were two main models used to explore the short-term effects of air pollutants on influenza risk in this study. One was the single-day lag model (from the current day (lag 0) to the past 7th day (lag 7)), and the other was the multi-day lag model (lag 1–lag 7). We reported the associations’ results as the percent change and the 95% confidence interval (CI) in the count of daily influenza cases associated with a 1 μg/m3 increase in the air pollutant concentration. In addition, we did a further stratified analysis to explore the potential effect of modification by sex and age groups (0–6, 7–18, 19–59, and ≥60 years). We further tested the statistical significance of differences between effect estimates of the strata by calculating the 95% confidence intervals (CIs):
where Q1 and Q2 are the estimates for two categories, and SÊ1 and SÊ2 are their respective standard errors [21].
2.4. Sensitivity Analyses
We conducted a sensitivity analysis of the model in two ways. First, we adjusted each pollutant (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3) using the two-pollutant model. Second, we checked whether the estimates were robust for the changes in the degrees of freedom for the calendar time (6–10 per year), the temperature (3–6), the humidity (3–6), and the wind speed (3–6) separately.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
Table 1 shows the results of the descriptive analysis. From 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2021, a total of 4767 influenza cases were detected in Jinan City, of which 2548 were males and 2219 were females. There were 329 cases more males than females. According to age groups, the patients aged 0–6 years accounted for 44.37%. It was the highest proportion of influenza cases, which was followed by the 7–18-year-old group.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of outpatient visits of influenza cases in Jinan City from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2021.
Figure 1 shows the time series distribution of daily influenza cases and air pollutant concentrations. The concentrations of SO2, NO2, PM10, and PM2.5 increased significantly from November to February every year, the number of influenza cases peaked in the first three months of 2020 and the last three months of 2021, and a small peak appeared from April to July of 2021. However, during the same period, O3 concentration was in a downward trend. The fluctuation of the number of influenza cases was almost consistent with the fluctuation of pollutant concentration, except for O3.
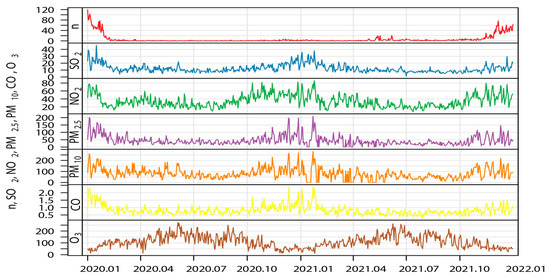
Figure 1.
The distributions of air pollutants concentration and daily influenza cases number in Jinan, China, during 2020–2021.
Table 2 shows that the daily average of pollutant concentration in Jinan during the study period. The reference limits of pollutant concentration given by China’s environmental protection authorities were divided into two levels, as shown in Table 3. PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 concentrations all reached the second-level national indicators of China, and CO and SO2 concentrations reached the first-level concentration limits of China, but except SO2, and other pollutants’ concentrations did not reach the pollutant concentration guidelines provided by the World Health Organization.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of air pollutants and meteorological factors in Jinan, China, from 2020 to 2021.

Table 3.
The reference limits of pollutant concentration given by China’s environmental protection authorities.
3.2. Spearman Correlation Coefficients Analysis
Table 4 shows the correlations between air pollutants and meteorological parameters during 2020–2021. We used r = 0.700 as the reference value for strong correlation. As can be seen from the table regarding PM10 and PM2.5 (r = 0.848, p < 0.001), CO, and NO2 (r = 0.757, p < 0.001), there was a strong correlation between the two pollutants, while O3 concentration had a weak correlation with other pollutants and meteorological factors.

Table 4.
Spearman correlation between daily air pollutant concentrations and the meteorological parameters during 2020–2021.
3.3. Single and Multi-Day Pollutant Model Analysis
Figure 2 shows the results of the single pollutant model. The results show that exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 had a significant effect on the incidence of influenza at lag 0, lag 3, and lag 4. SO2 and NO2 concentrations had a significant relationship with the increased risk of influenza at lag 2, lag 3, and lag 4. Generally, gaseous pollutants (NO2 and SO2) were associated with a higher risk of influenza cases than gaseous pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10). For CO, a rise of 1 mg/m3 increased the influenza cases by about 1.3469% (95% CI: 1.2074–1.5024). In the cumulative-day lag model of a single pollutant, we found that PM2.5, PM10, SO2, and CO all reached the peak at lag 3, lag 4, and lag 5. With the increase of cumulative lag days for NO2, the incidence risk was increased, while for O3 concentration, the relationship was opposite, with the increase of lag days and cumulative lag days, the risk of O3 for influenza decreased.
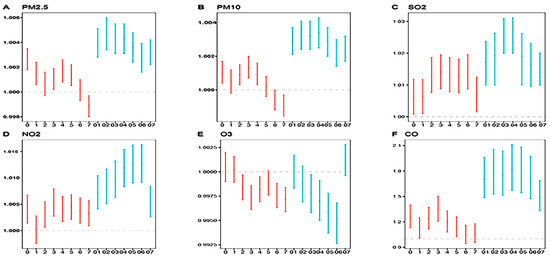
Figure 2.
Percent changes and estimated relative risks (RRs) of daily influenza for a 1 μg/m3 (CO concentration: 1 mg/m3) increase of pollutant concentrations at lag 0–lag 7 and lag 1–lag 7 during 2020–2021. Notes: the red color indicates single-day model results; the green color indicates muti-day model results.
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
This study further explored the subgroup analysis by sex and age in the single-day lag model. As shown in Figure 3, there were no statistically significant differences in the comparison for sex subgroup analyses. At lag 0 of exposure to each pollutant, the influenza incidence risk of females was higher than that of male when the pollutant concentration increased, and the incidence risk of male was higher than that of females at lag 1 and lag 2, except for O3. Except for O3, the incidence risk of males and females was highest on lag 3 and lag 4.
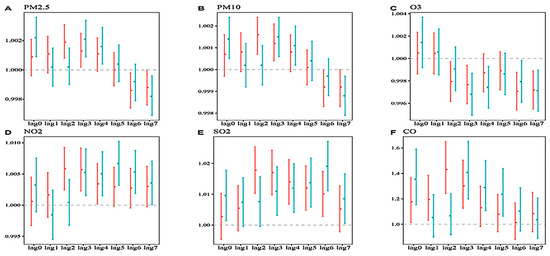
Figure 3.
Percent changes and estimated relative risks (RRs) of different sexes for a 1 μg/m3 (CO concentration: 1 mg/m3) increase of pollutant concentrations at lag 0–lag 7 during 2020–2021. Notes: the red color indicates male results; the green color indicates female results.
Supplementary Table S1 shows the relative risk of different age groups under a single-day lag model for exposure to different pollutant concentrations. For the 0–6-year-old group and 7–18-year-old group, the model results suggest that air pollutant concentrations exerted significative influence on influenza cases in Jinan City, especially the first four days after exposure (lag 0–lag 3); in the 19–59-year-old group, at lag 4–lag 7, the increases of NO2 and CO concentrations had a significant impact on the risk of influenza incidence; in the above 59-year-old group, at lag 3–lag 5, PM10, NO2, and CO concentrations exhibited significant effects for each 1 μg/m3 (CO concentration: 1 mg/m3) rise in pollutants. Generally, the groups aged above 59 years with influenza had slightly larger relative risks when exposed to PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, and CO than the younger groups. See Supplementary Materials for the full form (Supplementary Table S1).
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
The sensitivity analysis results are shown in Supplementary Tables S2 and S3. The association between pollutant concentration levels and influenza cases did not change with different degrees of freedom for the time, the temperature, and the relative humidity (3–6). In the two-pollutant models (Supplementary Table S4), the risk estimates of pollutants in influenza cases were not much change after adjusting for other pollutants. As a result, the results of sensitivity analyses illustrated the robustness of our study.
4. Discussion
The overall number of influenza cases in Jinan from 2020 to 2021 was lower than in previous years [22]. Some studies have shown that the number of influenza cases during the global COVID-19 pandemic has greatly reduced due to the prevention and control of the COVID-19 pandemic. These studies also suggest that the decline in the number of influenza cases may be related to the prevention and control measures during the COVID-19 pandemic [23,24,25]. Since the outbreak of COVID-19, Jinan City has forced masks in public places. In the first half of 2020, schools started online classes, and some public places were closed. Many people are staying at home. This has the potential to affect the time people are exposed to pollutants and the overall reduction of influenza diseases. Experts contend social distancing, wearing masks, diligent hand washing, and some other measures taken to mitigate COVID-19, which may help prevent influenza and reduce the cases of influenza [16,25,26].
This study provided that exposure to PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO significantly increased the risk of influenza. Several studies have shown that elevated concentrations of air pollutants are associated with an increased risk of influenza, which is consistent with our findings [10,13,27]. However, Liu et al. suggested that SO2 and NO2 were not associated with ILI [17], which was inconsistent with our results. In the cumulative-day lag model of a single pollutant, for O3, with the increase of lag days and cumulative lag days, the risk of O3 for influenza decreased. The increase in O3 concentration had little effect on the correlation of influenza incidence in our study. Conversely, one study found that exposure to O3 significantly increased the incidence of influenza in both the single-and multiday lag models [13]. One study reveals that O3 exposure can either suppress or enhance immune responsiveness. Most studies indicate that continuous O3 exposure leads to an early (days 0–3) impairment of immune responsiveness followed, with continued exposures, by a form of adaptation to O3 that results in a re-establishment of the immune response [28]. This might be a reason why an increase in O3 concentration positively affects influenza.
This study shows that the increase of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO concentrations had a strong correlation with influenza cases at lag 0 and lag 2−lag 4. However, one study in Nanjing reported the results that only concentrations within three days before visiting the hospital might be associated with increased influenza cases for all analyzed air pollutants [16]. In a study about the association between air pollution and the daily number of consultations due to upper respiratory tract infections in general outpatient clinics in Hong Kong, the lag times ranged from lag 0 to lag 3 [29]. One study showed that exposure to SO2, NO2, and O3 has a significant effect on the incidence of influenza at lag 0, lag 1, and lag 2 and lag 0–1 and lag 0–2 in Wuhan [17]. Overall, the results of our study showed that influenza visits were 1–2 days later than in other studies. Hospitals are high-risk places for infectious diseases. Since the outbreak of COVID-19, some people are reluctant to go to hospitals for mild diseases, because they are worried about being infected. Another reason is that in Jinan, people need nucleic acid test results to go to hospitals, and the waiting process for nucleic acid test results will also affect the time of seeking medical treatment.
Gaseous pollutants (NO2 and SO2) had a higher impact on the risk of influenza than the other particulate matter pollutants in our study. The study by Liu et al. suggested that SO2 and NO2 were not correlated with ILI [17], which was opposite to our results. One of the reasons is that exposure to NO2 reduces the capacity of macrophages to engulf the virus and leads to a decrease in the inactivation of macrophage-dependent invasive pathogens and thus seriously aggravating inflammation. The NO2-exposed people would be more susceptible to influenza infections [30].
In the age subgroup analysis, the finding that the elderly had a higher risk than other age groups may be related their weakened immune systems. However, some studies show that for air pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, CO, and SO2), people aged 25–59 were shown to have a higher risk of ILI compared with the other age groups, such as a study of the short-term effects of PM2.5 on ILI in Beijing [12]. During their study period, people over the age of 25, who are the main working group, were exposed to the outside environment for a longer period and thus had a higher risk of exposure to pollutants [22]. Since January 2020, Jinan City in Shandong Province has required residents to wear masks in public. Preschool children and the elderly are not the main outdoor activists, so time of wearing masks is relatively short. The important thing is that epidemiology studies have demonstrated that children and the elderly are more likely to be affected because of their weak immune systems under bad circumstances of air quality [8,31].
There is no consensus on the effects of air pollutants on influenza for many reasons, such as regional differences, population specificities (herd susceptibility and age−sex composition), and a component of the complicated mixture (the proportions of NO2, SO2, and O3 in air pollutants), also including different analysis methods, demographic characteristics, sources of pollutants and even some social policies. These associations need to be analyzed and confirmed in further studies.
The results of our study could deepen the understanding of the relationship between air pollutants and the risk of influenza during 2020–2021. However, several limitations exist in our study. Firstly, the monitoring stations for air pollutants and meteorological were not distributed according to the settlements, and the data from only one monitoring station were used in this study. For example, residents living far away from the monitoring station may have a larger difference in the concentration of exposed pollutants from the monitoring point. In addition, some patients may not immediately seek medical assistance, which will affect the true number of cases in a day. This may be responsible for possible autocorrelation of cases. Third, during the study period, most people aged 18–59 years in Jinan City received the COVID-19 vaccine, and some children received the influenza vaccine. We did not have data on vaccination and socioeconomic status and thus could not control for these confounders, and our ability to examine their effect modification was limited. Fourth, this study collected data only from Jinan City for the last two years, and the results are also not easy to generalize for broader regions.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our study found that concentrations of air pollutants, especially PM2.5, SO2, CO, and NO2, had significant associations with the risk of influenza during the COVID-19 epidemic. The higher the concentration, the higher the risk. Especially, people aged 0–7 and above 59 were shown to have a higher risk on influenza. These findings can provide more epidemiological evidence for studying the influence of air pollution and can serve as a basis for future policymaking regarding air pollution and infectious diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos14010053/s1. Table S1: Relative risk for outpatient visits of influenza cases by air pollutants in various age groups; Table S2: Estimates of pollutants on hospital visits for influenza when changing the degrees of freedom (df) for short-term trends; Table S3: Estimates of pollutants on hospital visits for influenza when changing the degrees of freedom (df, 3–6) for short-term trends of the temperature, the humidity, and the wind speed; Table S4: Percentage change (95% CI) in hospital visits for influenza per 1 μg/m3 increase in concentrations of pollutant using the two-pollutant model.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C. and Z.S.; methodology, Z.L.; software, F.C. and T.H.; formal analysis, T.H.; resources, X.G. and W.W.; data curation, W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, F.C. and T.H.; writing—review and editing, F.C. and Z.L.; visualization, F.C. and B.W.; supervision, X.G. and W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this paper can be provided by Weiru Wang (jncdcwwr@jn.shandong.cn).
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Jinan Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interest that could inappropriately influence the contents of this manuscript.
Abbreviations
| PM2.5 | particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter less than 2.5 μg |
| PM10 | particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter less than 10 μg |
| NO2 | nitrogen dioxide |
| SO2 | sulfur dioxide |
| O3 | ozone |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| ILI | influenza-like illness |
| RR | relative risk |
| CI | confidence interval |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
References
- Brenner, F.; Marwan, N.; Hoffmann, P. Climate impact on spreading of airborne infectious diseases: Complex network based modeling of climate influences on influenza like illnesses. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top 2017, 226, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seasonal Influenza. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal) (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Seasonal Influenza. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/influenza-seasonal#tab=tab_2 (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Chen, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Bai, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Transmissibility of the Influenza Virus during Influenza Outbreaks and Related Asymptomatic Infection in Mainland China, 2005-2013. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Feng, S.; Chen, T.; Yang, J.; Lau, Y.C.; Peng, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Wong, J.Y.T.; Qin, Y.; et al. Burden of influenza-associated outpatient influenza-like illness consultations in China, 2006-2015: A population-based study. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2020, 14, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disease Outbreaks. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news (accessed on 4 June 2022).
- Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/air-pollution#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Hahad, O.; Lelieveld, J.; Birklein, F.; Lieb, K.; Daiber, A.; Munzel, T. Ambient Air Pollution Increases the Risk of Cerebrovascular and Neuropsychiatric Disorders through Induction of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Bing, R.; Kiang, J.; Bashir, S.; Spath, N.; Stelzle, D.; Mortimer, K.; Bularga, A.; Doudesis, D.; Joshi, S.S.; et al. Adverse health effects associated with household air pollution: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and burden estimation study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1427–e1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, J.J.; Deng, Z.H.; Du, J.; Xie, M.Z.; Wang, X.R.; Liu, Y.; Cui, F.; et al. Air pollutants and outpatient visits for influenza-like illness in Beijing, China. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooryanarain, H.; Elankumaran, S. Environmental Role in Influenza Virus Outbreaks. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2015, 3, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Impact of ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure on the risk of influenza-like-illness: A time-series analysis in Beijing, China. Env. Health 2016, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Liu, S. Short-term effects of ambient air pollution on the incidence of influenza in Wuhan, China: A time-series analysis. Env. Res. 2021, 192, 110327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner-Cendrowska, K.; Broede, P. Impact of biometeorological conditions and air pollution on influenza-like illnesses incidence in Warsaw. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 65, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Qian, S.; Wang, S. Spatio-temporal Differentiation in the Incidence of Influenza and Its Relationship with Air Pollution in China from 2004 to 2017. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, F. Acute effects of air pollution on influenza-like illness in Nanjing, China: A population-based study. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-X.; Li, Y.; Qin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Hu, M.; Wang, X.-L.; Zheng, X. Effects of air pollutants on occurrences of influenza-like illness and laboratory-confirmed influenza in Hefei, China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Williams, G.; Huxley, R.; Ren, H.; Cao, W.; Guo, Y. The impact of ambient fine particles on influenza transmission and the modification effects of temperature in China: A multi-city study. Env. Int. 2017, 98, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, H.; Feng, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Ning, E. The impacts of road traffic on urban air quality in Jinan based GWR and remote sensing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Time-series studies of particulate matter. Annu Rev. Public Health 2004, 25, 247–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, N.; Gentleman, J.F. On judging the significance of differences by examining the overlap between confidence intervals. Am. Stat. 2001, 55, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wu, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T. The short-term effects of air pollutants on influenza-like illness in Jinan, China. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Gomez, R.E.G.; Hong, K.; Yum, S.; Jang, J.; Chun, B.C. Changing influenza activity in the Southern hemisphere countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, S.; Diwadkar, A.R.; Dudley, J.W.; O’Brien, J.; Dvorin, D.; Kenyon, C.C.; Himes, B.E.; Hill, D.A.; Henrickson, S.E. COVID-19 Pandemic-Related Reductions in Pediatric Asthma Exacerbations Corresponded with an Overall Decrease in Respiratory Viral Infections. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2022, 10, 91–99.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, N.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, S. The Effect of Coronavirus 2019 Disease Control Measures on the Incidence of Respiratory Infectious Disease and Air Pollutant Concentrations in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Int. J. Env. Res Public Health 2022, 19, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, S.J.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Budd, A.P.; Brammer, L.; Sullivan, S.; Pineda, R.F.; Cohen, C.; Fry, A.M. Decreased Influenza Activity During the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, Australia, Chile, and South Africa, 2020. Mmwr-Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 3681–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Hu, X.; Xue, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Gong, Y.; Nie, S. Short-term impact of air pollutants on influenza-like illness in Yichang City. Chin. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 2018, 35, 879–884, 891. [Google Scholar]
- Jakab, G.J.; Spannhake, E.W.; Canning, B.J.; Kleeberger, S.R.; Gilmour, M.I. The Effects of Ozone on Immune Finction. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tam, W.W.S.; Wong, T.W.; Ng, L.; Wong, S.Y.S.; Kung, K.K.L.; Wong, A.H.S. Association between Air Pollution and General Outpatient Clinic Consultations for Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Hong Kong. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciencewicki, J.; Jaspers, I. Air pollution and respiratory viral infection. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-Y.; Chau, T.-T. An Association between Air Pollution and Daily Outpatient Visits for Respiratory Disease in a Heavy Industry Area. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).