Effect of Biochar and Straw Application on Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Eutric Regosols with Different pH in Sichuan Basin: A Mesocosm Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurements of Gas Emissions
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
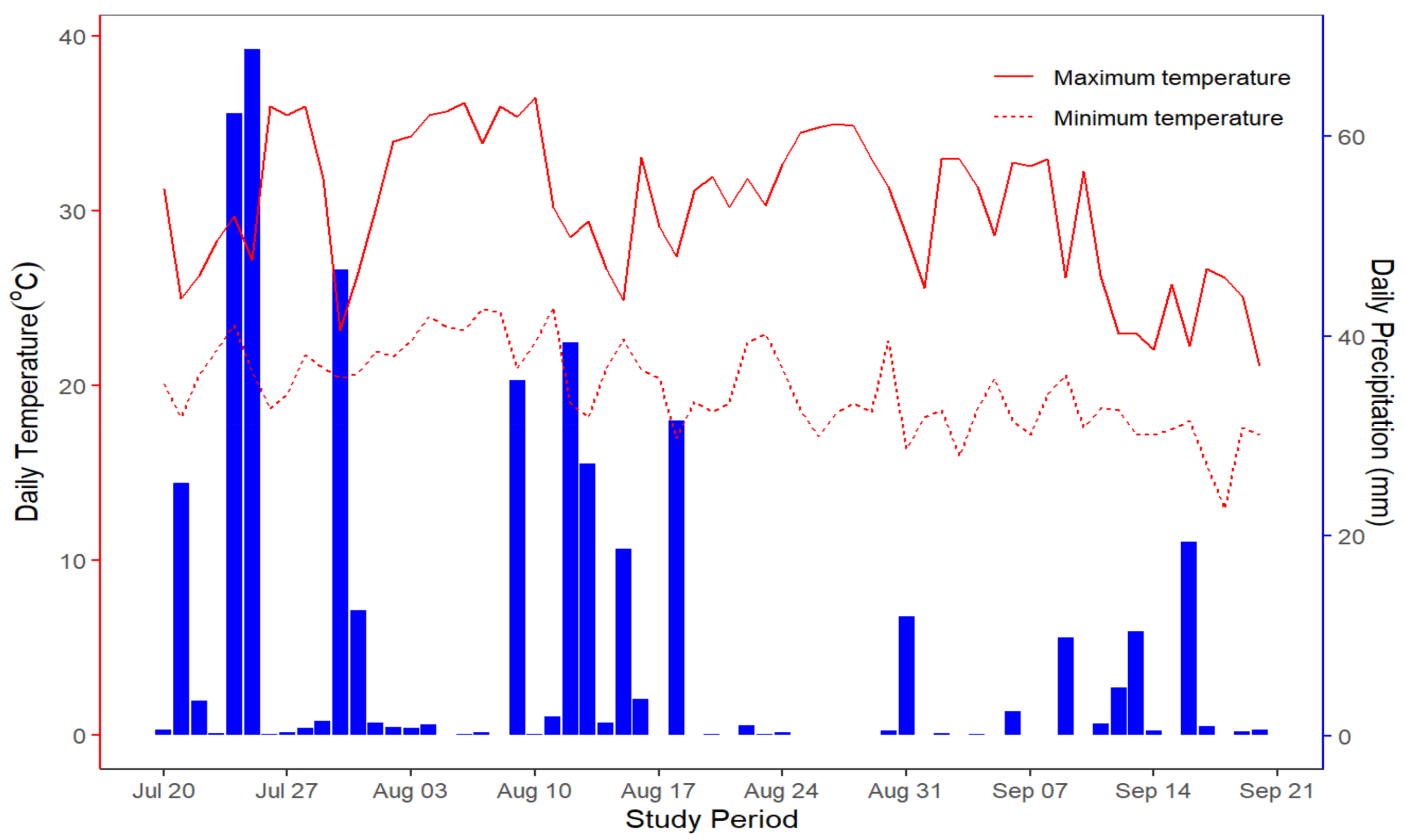
3.1. Precipitation and Air Temperature at the Experimental Site
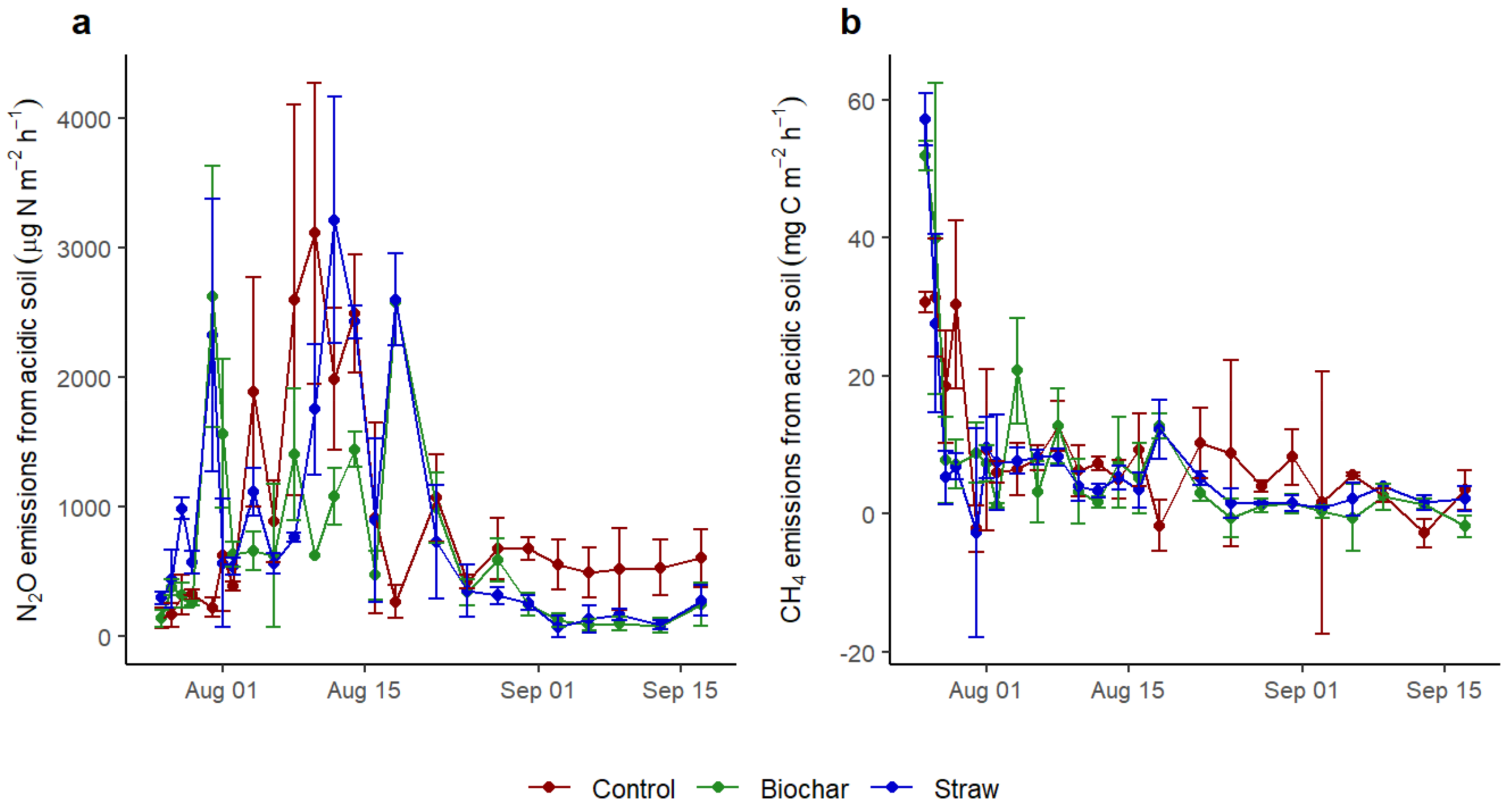
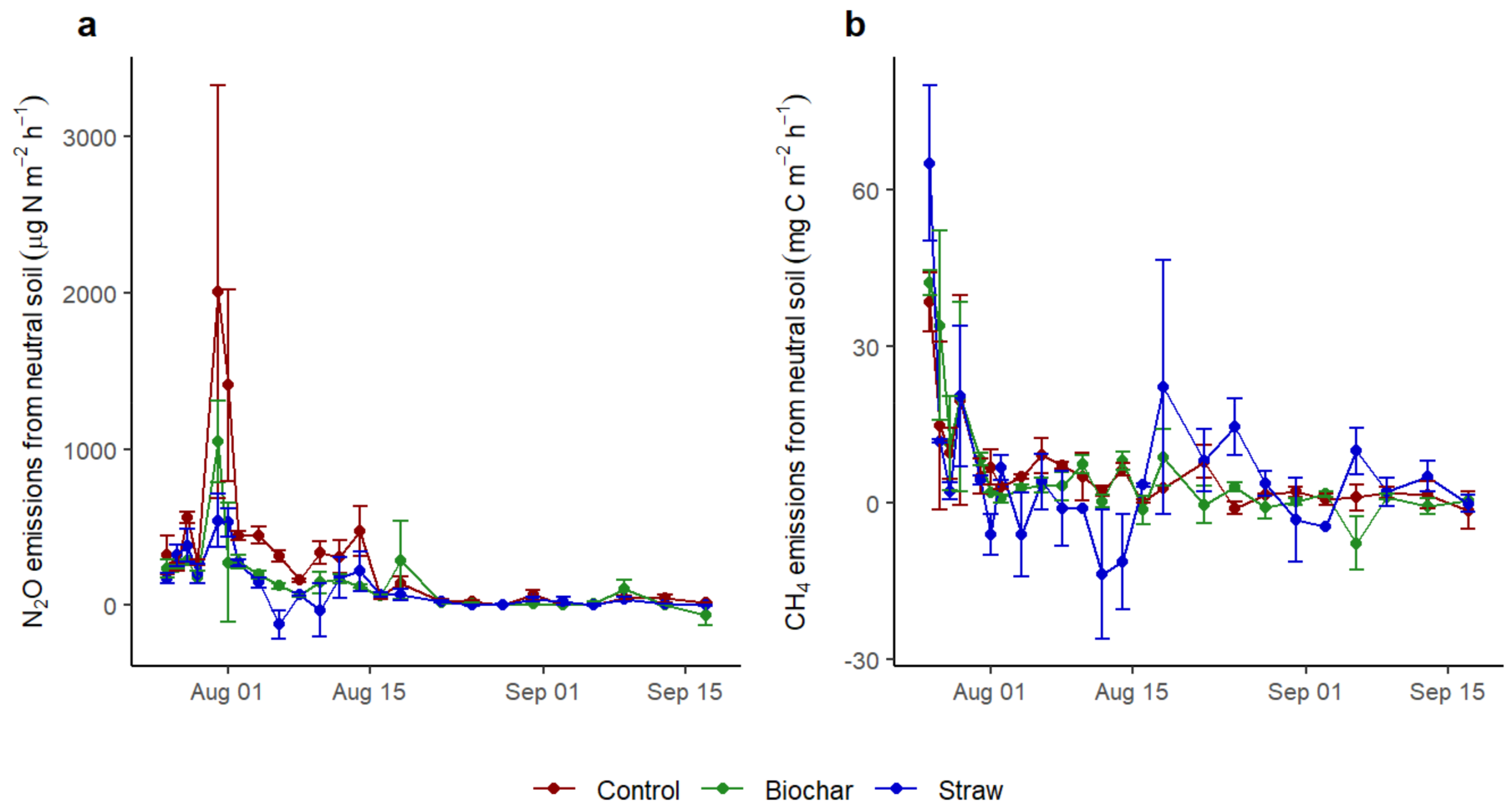
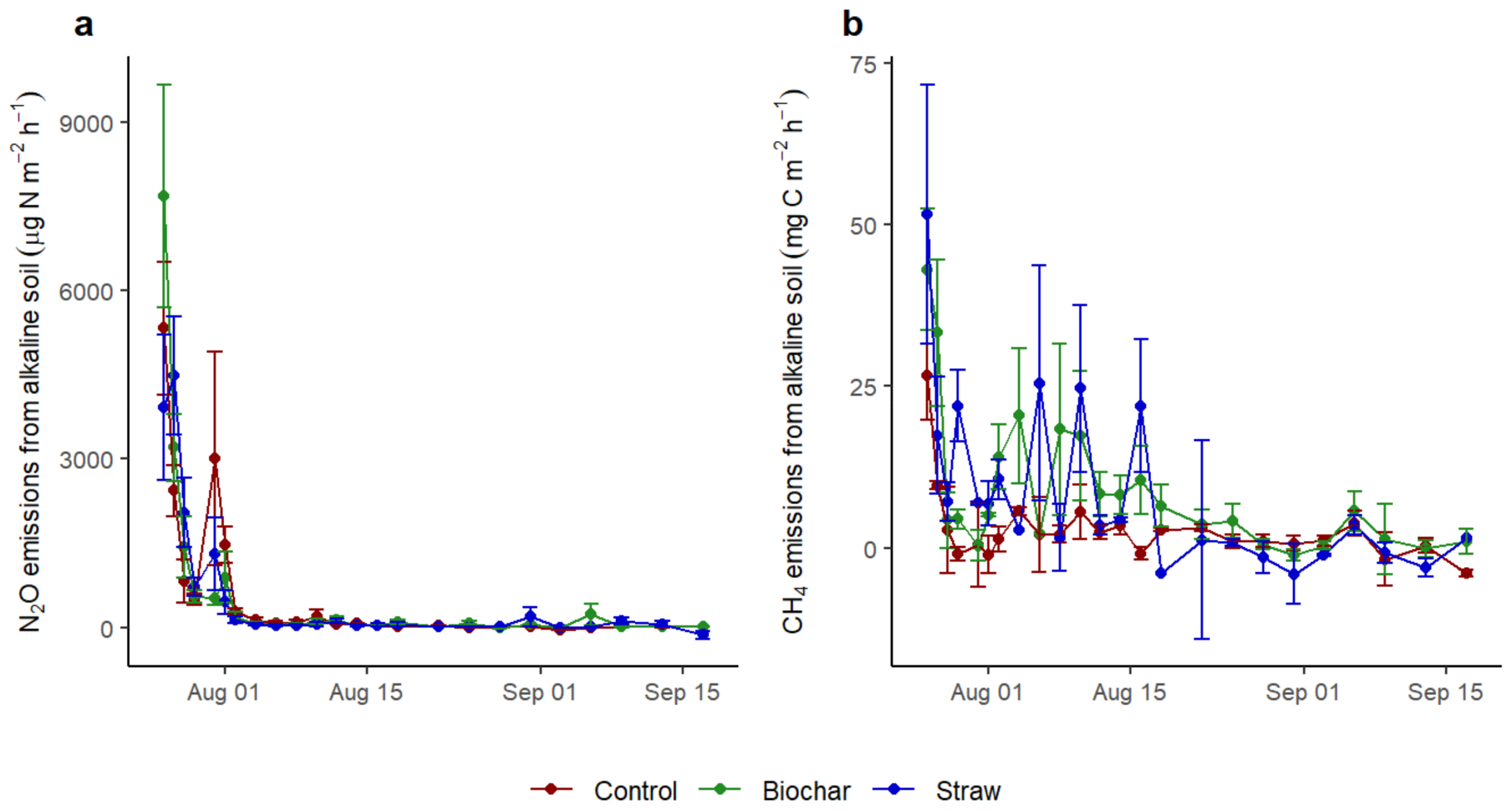
3.2. The CH4 and N2O Fluxes of Soils Influenced by Application of Straw and Biochar
3.3. Relationship of N2O and CH4 Emissions with Soil Factors in Soils of Different pH under Biochar and Straw
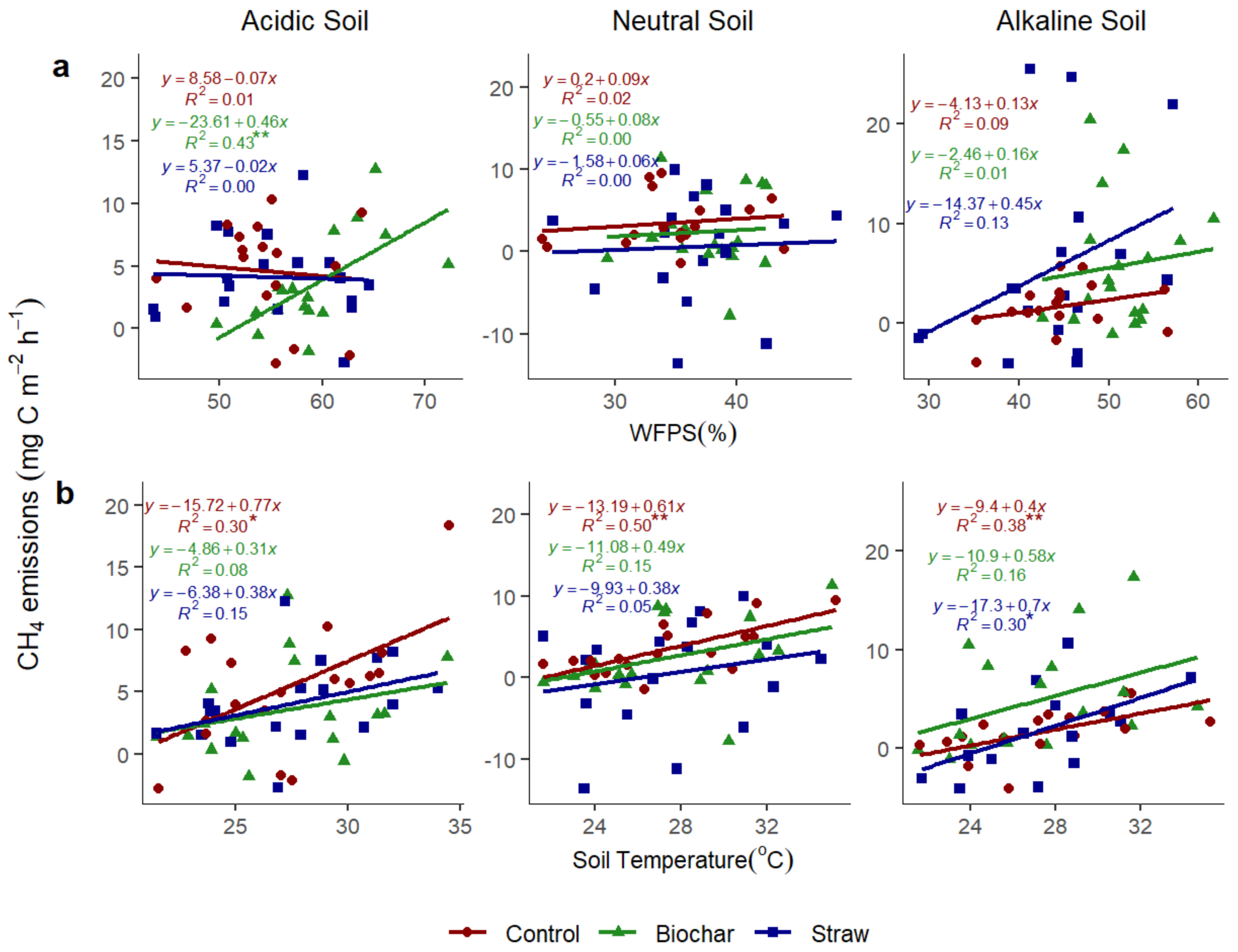
3.3.1. Relationship of N2O to WFPS and Soil Temperature
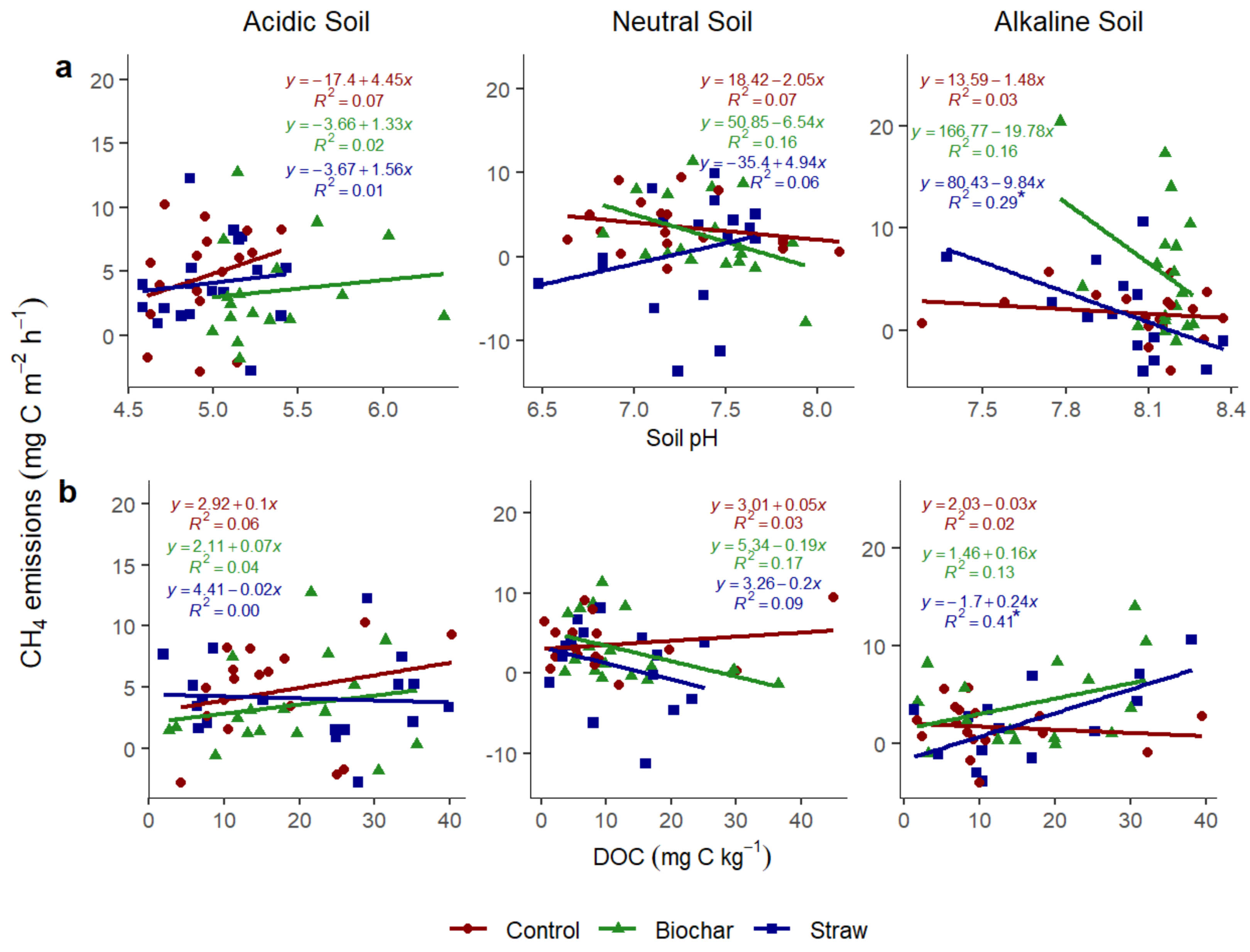
3.3.2. Relationship of N2O with Soil pH and Soil Dissolved Organic Carbon
3.3.3. Relationship of N2O with Soil Ammonium-N and Soil Nitrate-N
3.3.4. Relationship of CH4 with Soil Water-Filled Pore Space and Soil Temperature
3.3.5. Relationship of CH4 with Soil pH and Soil Dissolved Organic Carbon
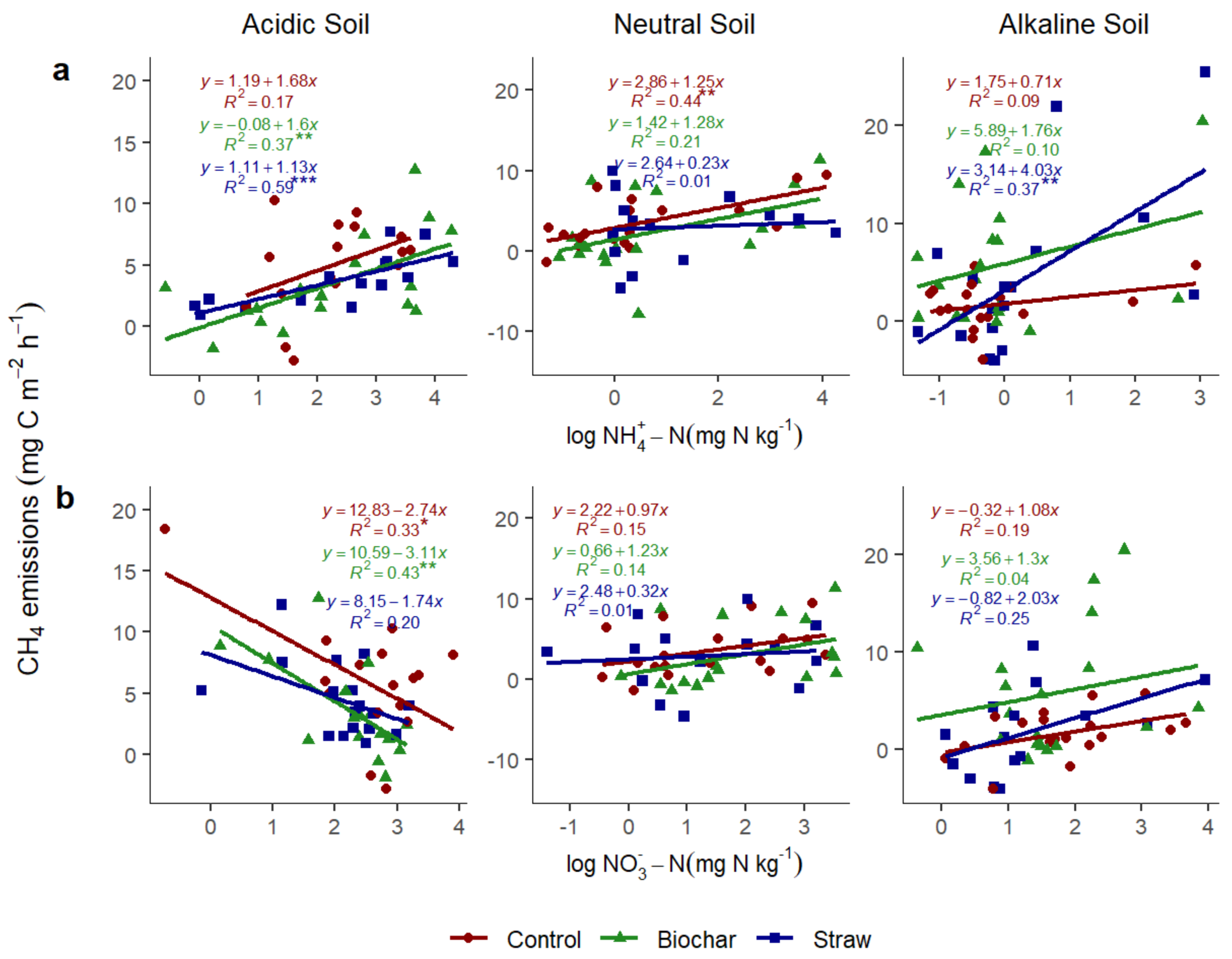
3.3.6. Relationship of CH4 with Soil Ammonium N and Soil Nitrate N
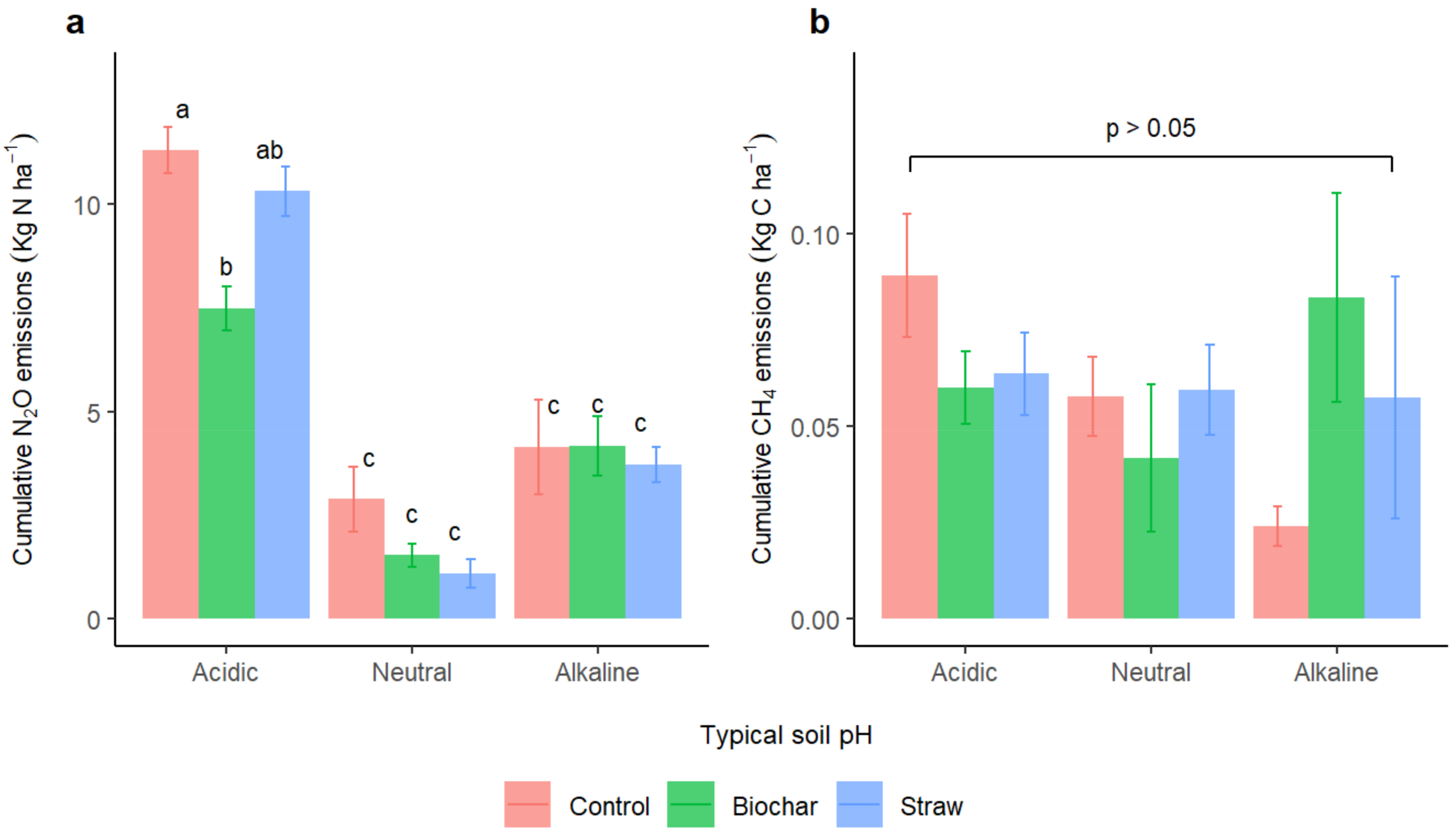
3.4. Contributions of Different Treatments to Soil Properties Following the Packed Soil Column Experiment
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Biochar and Straw Addition on N2O Emissions
4.2. Effect of Biochar and Straw Input on the CH4 Fluxes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, P.; Fang, C. A warm response by soils. Nature 2010, 464, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Bustamante, M.; Ahammad, H.; Clark, H.; Dong, H.; Elsiddig, E.A.; Haberl, H.; Harper, R.; House, J.; Jafari, M.; et al. Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use (AFOLU). In Climate Change. Mitigation of Climate Change; Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Farahani, E., Kadner, S., Seyboth, K., Adler, A., Baum, I., Brunner, S., Eickemeier, P., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. (Eds.) Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wuebbles, D.J.; Hayhoe, K. Atmospheric methane and global change. Earth Sci. Rev. 2002, 57, 177–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W. Nitrous oxide (N2O): The dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century. Science 2009, 326, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Giltrap, D. Determining optimum nitrogen input rate and optimum yield-scaled nitrous oxide emissions: Theory, field observations, usage, and limitations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuo, P.K.; Cadisch, G.; Albrecht, A.; Palm, C.A.; Verchot, L. Potential of agroforestry for carbon sequestration and mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions from soils in the tropics. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2005, 71, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Jabro, J.D.; Stevens, W.B. Soil carbon dioxide emission and carbon content as affected by irrigation, tillage, cropping system, and nitrogen fertilization. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.C.; Griffiths, B.S.; Topp, C.F.; Wheatley, R.; Walker, R.L.; Rees, R.M.; Watson, C.A.; Gordon, H.; Hallett, P.D.; McKenzie, B.M.; et al. Seasonal nitrous oxide emissions from field soils under reduced tillage, compost application or organic farming. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. World crop residues production and implications of its use as a biofuel. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, C.; Yu, X.; Lai, T.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; et al. Long-term effects of organic amendments on the rice yields for double rice cropping systems in subtropical China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Han, X.; Ru, S.; Cardenas, L.; Rees, R.M.; Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Meng, F. Crop straw incorporation interacts with N fertilizer on N2O emissions in an intensively cropped farmland. Geoderma 2019, 341, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wu, W.L.; Meng, F.Q.; Smith, P.; Lal, R. Increase in soil organic carbon by agricultural intensification in northern China. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, B.; Lu, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, Z. Straw incorporation strategy on cereal crop yield in China. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xu, C.; Dungait, J.A.; Bol, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Meng, F. Straw incorporation increases crop yield and soil organic carbon sequestration but varies under different natural conditions and farming practices in China: A system analysis. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, R.; Machado, S.; Rhinhart, K. Long-term crop residue and nitrogen management effects on soil profile carbon and nitrogen in wheat–fallow systems. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Dungait, J.A.; Xu, X.; Bol, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W. Coupled incorporation of maize (Zea mays L.) straw with nitrogen fertilizer increased soil organic carbon in Fluvic Cambisol. Geoderma 2017, 304, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, K.A.; Baggs, E.M. Do combined applications of crop residues and inorganic fertilizer lower emission of N2O from soil? Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Deng, A.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W. Impacts of cropping practices on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions from rice fields in China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková, B.; Hruby, J.; Dovrtel, J.; Dostál, O. Effects of different organic amendment on winter wheat yields under long-term continuous cropping. Plant Soil Environ. 2003, 49, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Xu, R.K.; Qian, W.; Wang, R.H. Comparison of the ameliorating effects on an acidic ultisol between four crop straws and their biochars. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J. A handful of carbon. Nature 2007, 447, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Jung, S.C.; Ryu, C.; Jeon, J.K.; Shin, M.C.; Park, Y.K. Production and utilization of biochar: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulyett, J.; Sakrabani, R.; Kibblewhite, M.; Hann, M. Impact of biochar addition on water retention, nitrification and carbon dioxide evolution from two sandy loam soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalus, K.; Koziel, J.A.; Opaliński, S. A review of biochar properties and their utilization in crop agriculture and livestock production. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Xie, D.; Ni, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ci, E.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Reduced mineral fertilization coupled with straw return in field mesocosm vegetable cultivation helps to coordinate greenhouse gas emissions and vegetable production. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Cheng, H.; Yue, S.; Li, S. Effects of biochar application on CO2 emissions from a cultivated soil under semiarid climate conditions in Northwest China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, V.; Saha, B.K.; Ruysschaert, G.; Boeckx, P. Effect of different biochar and fertilizer types on N2O and NO emissions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Walkiewicz, A.; Bieganowski, A.; Oenema, O.; Nosalewicz, M.; He, C.; Yuming, Z.; Hu, C. Biochar promotes the reduction of N2O to N2 and concurrently suppresses the production of N2O in calcareous soil. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.J.; Bertram, J.E.; Ray, J.L.; Condron, L.M.; O’Callaghan, M.; Sherlock, R.R.; Wells, N.S. Unweathered wood biochar impact on nitrous oxide emissions from a bovine-urine-amended pasture soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M. Soil microbial sources of nitrous oxide: Recent advances in knowledge, emerging challenges and future direction. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: How well do we understand the processes and their controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarin, M.W.K.; Khaliq, M.A.; Fan, L.; Xie, D.; Tayyab, M.; Chen, L.; He, T.; Rong, J.; Zheng, Y. Divergent consequences of different biochar amendments on carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from the red soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Senbayram, M.; Zang, H.; Ugurlar, F.; Aydemir, S.; Brüggemann, N.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Blagodatskaya, E. Effect of biochar origin and soil pH on greenhouse gas emissions from sandy and clay soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 129, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbayram, M.; Saygan, E.P.; Chen, R.; Aydemir, S.; Kaya, C.; Wu, D.; Bladogatskaya, E. Effect of biochar origin and soil type on the greenhouse gas emission and the bacterial community structure in N ertilized acidic sandy and alkaline clay soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Bao, Y.; Nan, H.; Xiong, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Tillage pedogenesis of purple soils in southwestern China. J. Mount. Sci. 2009, 6, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Zheng, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Nitrous oxide emissions and nitrate leaching from a rain-fed wheat-maize rotation in the Sichuan Basin, China. Plant Soil 2013, 362, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Brüggemann, N.; Bergmann, J.; Wang, Y.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. N2O and CH4 emissions, and NO3− leaching on a crop-yield basis from a subtropical rain-fed wheat–maize rotation in response to different types of nitrogen fertilizer. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Bo, Z.; Fuhong, K. Reducing interflow nitrogen loss from hillslope cropland in a purple soil hilly region in southwestern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 93, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shen, F.; Tian, D.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, S. Partitioning biochar properties to elucidate their contributions to bacterial and fungal community composition of purple soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. Nitrous oxide emissions as influenced by amendment of plant residues with different C:N ratios. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, Y.; Pan, G.; Hussain, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. Effect of biochar amendment on maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions from a soil organic carbon poor calcareous loamy soil from Central China Plain. Plant Soil 2012, 351, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Ge, T.; Davey, L.J.; Wu, J. Contrasting effects of straw and straw-derived biochar amendments on greenhouse gas emissions within double rice cropping systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.F.; Jun, M.E.N.G.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhang, W.M.; Cheng, X.Y.; Chen, W.F. Effects of straw and biochar addition on soil nitrogen, carbon, and super rice yield in cold waterlogged paddy soils of North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.; Sjöstrom, J. Optimizing the experimental design of soil columns in saturated and unsaturated transport experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 115, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Wang, T.; Bergmann, J.; Brüggemann, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Kuang, F. Nitrate leaching, direct and indirect nitrous oxide fluxes from sloping cropland in the purple soil area, southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Venterea, R.T.; Follett, R.F. Chamber-based trace gas flux measurements. In Sampling Protocols; Follett, R.F., Ed.; USDA-Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yuesi, W.; Yinghong, W. Quick measurement of CH4, CO2 and N2O emissions from a short-plant ecosystem. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Pokharel, P.; Chang, S.X.; Zhou, P.; Niu, H.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Biochar application increased methane emission, soil carbon storage and net ecosystem carbon budget in a 2-year vegetable–rice rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of combined biochar and organic fertilizer on nitrous oxide fluxes and the related nitrifier and denitrifier communities in a saline-alkali soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, X.; Qiao, Y.; Hou, X.; Xing, B. Carbon dioxide emission from black soil as influenced by land-use change and long-term fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 40, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cai, Z. The effect of growing soybean (Glycine max. L.) on N2O emission from soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Bai, R.; Di, H.J.; Mo, L.Y.; Han, B.; Zhang, L.M.; He, J.Z. Differentiated mechanisms of biochar mitigating straw-induced greenhouse gas emissions in two contrasting paddy soils. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.H. Measurement of field capacity water. In Soil Sampling, Preparation, and Analysis; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kachurina, O.M.; Zhang, H.; Raun, W.R.; Krenzer, E.G. Simultaneous determination of soil aluminum, ammonium-and nitrate-nitrogen using 1M potassium chloride extraction. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R. Rstudio: Integrated Development for R. Rstudio. Rstudio Team (2020). Rstudio: Integrated Development for R. Rstudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. PBC. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: ‘ggplot2′ Based Publication Ready Plots (R Package Version 0.4.0) [Computer Software]. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Dai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Muhammad, N.; Yu, X.; Xiao, K.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. The effects and mechanisms of soil acidity changes, following incorporation of biochars in three soils differing in initial pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol Pereira, E.I.; Léchot, J.; Feola Conz, R.; da Silva Cardoso, A.; Six, J. Biochar enhances nitrous oxide reduction in acidic but not in near-neutral pH soil. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Qin, H.; Yuan, Q.; Fan, F.; Wu, J. Microbial mechanisms in the reduction of CH4 emission from double rice cropping system amended by biochar: A four-year study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yi, H.; Zhang, X.; Su, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X. Biochar Mitigates Greenhouse Gas Emissions from an Acidic Tea Soil. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, S.D.; McNamara, N.P.; Reay, D.S.; Whitaker, J. The effect of biochar addition on N2O and CO2 emissions from a sandy loam soil–the role of soil aeration. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 51, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, Y.; Toyota, K.; Okazaki, M. Effects of charcoal addition on N2O emissions from soil resulting from rewetting air-dried soil in short-term laboratory experiments. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.R.; Levy-Booth, D.; Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J. Different soil moisture control of net methane oxidation and production in organic upland and wet forest soils of the pacific coastal rainforest in Canada. Can. J. For. Res. 2017, 47, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Q.; Wolf, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Brüggemann, N.; Lin, S. Effects of increasing precipitation and nitrogen deposition on CH4 and N2O fluxes and ecosystem respiration in a degraded steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. Geoderma 2013, 192, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Muhammad, A.; Huang, G. Emission mechanism and reduction countermeasures of agricultural greenhouse gases—A review. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Roig, A.; Hanley, K.; Enders, A.; Lehmann, J. Biochar and denitrification in soils: When, how much and why does biochar reduce N2O emissions? Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Jeffery, S.; Roig, A.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A. Biochar’s role in mitigating soil nitrous oxide emissions: A review and meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.; Morris, S.; Downie, A.; Berger, E.; Rust, J.; Scheer, C. Influence of biochars on flux of N2O and CO2 from Ferrosol. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Duvall, M.; Sohi, S.P. Localisation of nitrate in the rhizosphere of biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.J.; Hutchinson, G.L.; Fehsenfeld, F.C. NOx and N2O emissions from soil. Glob. Biogeochem Cycles 1992, 6, 351–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.J.; Kiese, R.; Wolf, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Effects of soil temperature and moisture on methane uptake and nitrous oxide emissions across three different ecosystem types. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3205–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, T.E.; Patterson, C.J.; Reay, D.S.; Anderson, P.; Peshkur, T.A.; Sohi, S.P. Biochar diminishes nitrous oxide and nitrate leaching from diverse nutrient sources. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, E.; Six, J. Biochar does not mitigate field-scale N2O emissions in a Northern California vineyard: An assessment across two years. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lee, X.; Theng, B.K.; Wang, B.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Q. Effect of biochar addition on short-term N2O and CO2 emissions during repeated drying and wetting of an anthropogenic alluvial soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, Y.O.; Ding, W. Investigation of greenhouse gas emissions from the soil amended with rice straw biochar. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 2016, 20, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, L.; Jin, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Zou, J. Linking N2O emission from biochar-amended composting process to the abundance of denitrify (nirK and nosZ) bacteria community. AMB Express 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ding, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J. Biochar improved rice yield and mitigated CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy field under controlled irrigation in the Taihu Lake Region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Hu, R.; Tang, S.; Shaaban, M.; Zhang, W.; Shen, H.; Xu, M. Nitrous oxide emissions in response to straw incorporation is regulated by historical fertilization. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Iqbal, J.; Hu, R.; Shaaban, M.; Cai, J.; Chen, X. Nitrous oxide emissions from yellow brown soil as affected by incorporation of crop residues with different carbon-to-nitrogen ratios: A case study in central China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Dendooven, L.; Goulding, K.W.T. Quantitative assessment of soil nitrate disappearance and N2O evolution during denitrification: Nitrate disappearance during denitrification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; White, R.E.; Roger, B.P.; Tillman, R.W. Measuring denitrification activity in soils under pasture: Optimizing conditions for the short-term denitrification enzyme assay and effect of soil storage on denitrification activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Dong, D.; Deng, H.; Strong, P.J.; Wang, H.; Wu, W. Insight into the effects of biochar on manure composting: Evidence supporting the relationship between N2O emission and denitrifying community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7341–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R.; Halvorson, A.D.; Reule, C.A.; Liu, X.J. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in irrigated cropping systems in northeastern Colorado. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, C.; Grace, P.R.; Rowlings, D.W.; Kimber, S.; Van Zwieten, L. Effect of biochar amendment on the soil-atmosphere exchange of greenhouse gases from an intensive subtropical pasture in northern New South Wales, Australia. Plant Soil 2011, 345, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askaer, L.; Elberling, B.; Friborg, T.; Jørgensen, C.J.; Hansen, B.U. Plant-mediated CH4 transport and C gas dynamics quantified in-situ in a Phalaris arundinacea-dominant wetland. Plant Soil 2011, 343, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.J.; McDowell, W.H.; Silver, W.L. When wet gets wetter: Decoupling of moisture, redox biogeochemistry, and greenhouse gas fluxes in a humid tropical forest soil. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Crowley, D. Effect of biochar amendment on yield and methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a rice paddy from Tai Lake plain, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Gong, M. Effects of biochar application on soil methane emission at different soil moisture levels. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, R.C.; Allen, D.E.; Livesley, S.J.; Richards, G. Magnitude and biophysical regulators of methane emission and consumption in the Australian agricultural, forest, and submerged landscapes: A review. Plant Soil 2008, 309, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Tu, C.; Amonette, J.E.; Cadisch, J.W.Y.; Hu, S. Impact of biochar application on nitrogen nutrition of rice, greenhouse-gas emissions and soil organic carbon dynamics in two paddy soils of China. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Chávez, Á.; Díaz-Rojas, M.; del Rosario Cárdenas-Aquino, M.; Dendooven, L.; Luna-Guido, M. Greenhouse gas emissions from a wastewater sludge-amended soil cultivated with wheat (Triticum spp. L.) as affected by different application rates of charcoal. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelier, P.L.; Laanbroek, H.J. Nitrogen as a regulatory factor of methane oxidation in soils and sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Lü, F.; He, P.; Shao, L. Response of methanotrophs and methane oxidation on ammonium application in landfill soils. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.F.; Hong, Z.H.A.O.; Lü, Y.Z.; Fei, L.U.; Wang, X.K. The effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on methane and nitrous oxide emission/uptake in Chinese croplands. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnecker, J.; Bowles, T.; Hobbie, E.A.; Smith, R.G.; Grandy, A.S. Substrate quality and concentration control decomposition and microbial strategies in a model soil system. Biogeochemistry 2019, 144, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Statistical Yearbook. 2019. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2019/indexeh.htm (accessed on 22 February 2021).



| Parameters | pH | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | Total C (g kg−1) | Total N (g kg−1) | NH4+-N (mg N l−1) | NO3−-N (mg N l−1) | DOC (mg C l−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic soil | 4.69 | 24.09 ± 1.07 | 43.85 ± 0.86 | 32.06 ± 1.93 | 7.12 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 5.05 ± 0.08 | 8.46 ± 1.23 | 13.32 ± 0.06 |
| Neutral soil | 7.12 | 8.37 ± 0.21 | 38.72 ± 0.89 | 52.91 ± 0.69 | 11.23 ± 0.06 | 1.05 ± 0.01 | 1.38 ± 0.54 | 5.87 ± 1.16 | 12.49 ± 2.28 |
| Alkaline soil | 8.32 | 30.82 ± 0.31 | 51.76 ± 1.87 | 17.42 ± 2.13 | 14.84 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 11.14 ± 0.01 | 7.29 ± 3.18 |
| Biochar | 10.11 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 420.32 ± 5.49 | 12.73 ± 0.66 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Straw | 6.28 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 315.25 ± 2.05 | 11.2 ± 1.32 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Soil Types | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic Soil | Neutral Soil | Alkaline Soil | |||||||
| Treatment | Treatment | Treatment | |||||||
| Soil Properties | Control | Biochar | Straw | Control | Biochar | Straw | Control | Biochar | Straw |
| Soil pH | 5.15 ± 0.087 cd | 5.39 ± 0.071 c | 4.90 ± 0.038 d | 7.41 ± 0.074 b | 7.42 ± 0.109 b | 7.27 ± 0.142 b | 8.14 ± 0.104 a | 8.02 ± 0.027 a | 8.07 ± 0.029 a |
| Soil NH4-N | 3.85 ± 1.96 | 0.415 ± 0.183 | 2.23 ± 1.14 | 0.88 ± 0.28 | 0.61 ± 0.16 | 1.06 ± 0.29 | 1.05 ± 0.32 | 1.24 ± 0.47 | 0.81 ± 0.11 |
| Soil NO3-N | 12.7 ± 1.76 b | 5.21 ± 2.88 ab | 7.93 ± 2.28 ab | 3.54 ± 2.32 ab | 1.14 ± 0.59 a | 2.61 ± 0.98 ab | 4.24 ± 2.72 ab | 5.02 ± 2.49 ab | 3.14 ± 1.71 ab |
| Soil DOC | 17.4 ± 10.6 | 24.3 ± 11.5 | 18.4 ± 6.1 | 14.5 ± 6.7 | 18.0 ± 8.6 | 14.9 ± 4.9 | 19.4 ± 9.0 | 24.4 ± 8.1 | 16.4 ± 5.5 |
| Soil WFPS | 50.5 ± 4.26 b | 44.7 ± 5.02 ab | 49.4 ± 3.82 ab | 34.5 ± 1.18 ab | 33.7 ± 2.00 ab | 30.9 ± 3.48 a | 40.1 ± 1.42 ab | 45.6 ± 1.65 ab | 34.8 ± 7.78 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntacyabukura, T.; Uwiringiyimana, E.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, B.; Harerimana, B.; Nambajimana, J.d.D.; Nsabimana, G.; Nsengumuremyi, P. Effect of Biochar and Straw Application on Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Eutric Regosols with Different pH in Sichuan Basin: A Mesocosm Study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060729
Ntacyabukura T, Uwiringiyimana E, Zhou M, Zhang B, Zhu B, Harerimana B, Nambajimana JdD, Nsabimana G, Nsengumuremyi P. Effect of Biochar and Straw Application on Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Eutric Regosols with Different pH in Sichuan Basin: A Mesocosm Study. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(6):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060729
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtacyabukura, Tite, Ernest Uwiringiyimana, Minghua Zhou, Bowen Zhang, Bo Zhu, Barthelemy Harerimana, Jean de Dieu Nambajimana, Gratien Nsabimana, and Pascal Nsengumuremyi. 2021. "Effect of Biochar and Straw Application on Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Eutric Regosols with Different pH in Sichuan Basin: A Mesocosm Study" Atmosphere 12, no. 6: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060729
APA StyleNtacyabukura, T., Uwiringiyimana, E., Zhou, M., Zhang, B., Zhu, B., Harerimana, B., Nambajimana, J. d. D., Nsabimana, G., & Nsengumuremyi, P. (2021). Effect of Biochar and Straw Application on Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Eutric Regosols with Different pH in Sichuan Basin: A Mesocosm Study. Atmosphere, 12(6), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12060729