Abstract
Background: Hokkaido was the first Japanese prefecture to be affected by COVID-19. Since the beginning of the pandemic, the Japanese government has been publishing the information of each individual who was tested positive for the virus. Method: The current study analyzed the 1269 SARS-CoV-2 cases confirmed in Hokkaido in order to examine sex-based differences in symptomology and infectiveness, as well as the status of reinfections and the viral transmission networks. Results: The majority of asymptomatic patients were females and older. Females were 1.3-fold more likely to be asymptomatic (p < 0.001) while a decade of difference in age increased the likelihood of being asymptomatic by 1% (p < 0.001). The data contained information up to quaternary viral transmission. The transmission network revealed that, although asymptomatic patients are more likely to transmit the virus, the individuals infected by asymptomatic cases are likely to be asymptomatic (p < 0.001). Four distinct co-occurrences of symptoms were observed, including (i) fever/fatigue, (ii) pharyngitis/rhinitis, (iii) ageusia/anosmia, and (iv) nausea/vomiting/diarrhea. The presences of diarrhea (p = 0.05) as well as nausea/vomiting (p < 0.001) were predictive of developing dyspnea, i.e., severe disease. About 1% of the patients experienced reinfection. Conclusions: Sex and symptomatology appear to play important roles in determining the levels of viral transmission as well as disease severity.
1. Introduction
Infection by SARS-CoV-2 results in the development of mild to serious symptoms in most individuals, with severity being dependent on age and comorbidities [1,2,3]. However, there is mounting evidence that a significant number of infected individuals are asymptomatic [4,5]. An asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection refers to the situation where no clinical signs or symptoms, nor imaging abnormalities, are apparent in an individual who is confirmed to be infected with the virus by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) [6]. Given that asymptomatic patients appear to constitute a significant portion of infections [7], understanding the factors that are associated with being asymptomatic is important.
Japan has not been spared from the COVID-19 pandemic, and as of 18 January 2021, there have been 326,208 cases of the disease reported in the country [8]. Hokkaido was the first Japanese prefecture to be affected by COVID-19 with the first reported case being a tourist from Wuhan, China, a 40-year-old female who had the COVID-19 symptoms (fever, cough, fatigue, and pneumonia) on 26 January [8]. A State of Emergency was declared on 28 February when the number of cumulative confirmed cases reached 65. Issuance of a stay-at-home order, as well as the implementation of social distancing and active contact tracing measures called “cluster countermeasure” by the local government [9], resulted in a quick reduction in new cases by mid-March. With the disease seemingly under control, the government lifted the State of Emergency on 17 March. However, soon thereafter new cases began to surge again, particularly after the 3-day Equinox holiday between 20 and 22 March [10]. On 14 April, the government declared a State of Emergency for the second time. Although the State of Emergency was re-lifted on 25 May and the number of cases was no longer surging at the same rate, the prefecture remained designated as one “under special precautions” (Figure 1) [11].
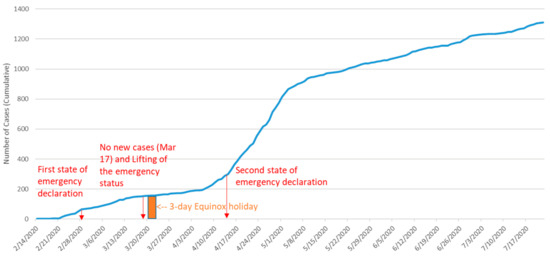
Figure 1.
The cumulative cases of COVID-19 patients in Hokkaido (14 February–22 July 2020). Sources: Author generated using the information from the following sources: http://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/hf/kth/kak/hasseijoukyou.htm [8]; https://time.com/5826918/hokkaido-coronavirus-lockdown/ [10]; http://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/ss/tuk/900brr/index2.htm#5sai-kaikyu [13]. (Accessed on 16 November 2021).
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak, the Japanese government has been publishing the information of each individual who was tested positive for the virus. The current study leveraged registry data from Hokkaido between mid-February and mid-July in order to investigate the viral transmission and clinical characteristics of COVID-19. The registry data published by the government were particularly detailed in the early stage of the pandemic, including the period covered under the current study. The data contain rich information about the transmission paths as a result of the government’s intensive contract tracing effort [9,12,13].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
We queried government registries for about a 5-month period between 14 February (the date when the first PCR positive case was identified in Hokkaido, excluding the tourist from Wuhan, China) and 22 July 2020. All COVID-19 cases confirmed by the local PHCs must be reported to the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare in Japan [12]. These PHCs also collect, record, and publish demographic, symptomatological, and epidemiologic information, such as transmission paths (likely infectors and infectees) and travel history, of the confirmed cases with informed consents [12]. Of the 1370 PCR-confirmed cases in Hokkaido during the study period, 1269 cases (93% including 674 females and 595 males) had comprehensive demographic and symptomatological information including sex; age (<10, 11–20, 21–30, 31–40, 41–50, 51–60, 61–70, 71–80, 81–90, 91–100, or >100); the city of residence or the testing site; the dates of PCR and the onset of symptoms; and symptoms experienced (if any).
Contract tracing was administered by public health centers (PHCs) across the nation in order to retrospectively investigate all identifiable individuals who had had in-person contact with each confirmed case during the prior 14 days [13,14,15]. Individuals who were determined to have been in “close contact” with the confirmed cases were subjected to an “initial (PCR) screening test”, even when their source case (i.e., the infector) had no COVID-19 related symptoms [14]. The government defined the individuals who were in “close contact” as follows: (i) cohabitants of the confirmed cases; (ii) individuals who had spent long hours in an indoor setting (including a car and a flight) with confirmed cases; (iii) individuals who had provided (medical and nursing) care to the confirmed cases without adequate personal protective equipment; (iv) individuals who were likely to have been exposed to droplets or other body fluids of the confirmed cases; or (iv) individuals who had been within 1 m (6 feet) radius of the confirmed cases for a total of 15 min or more without protection [ibid]. Other individuals whose in-person contact with the confirmed cases did not meet the definition of “close contact” were requested to self-quarantine for 14 days and were guided to receive a test only if any COVID-19 related symptoms appeared during the monitoring period. Individuals who did not develop any symptoms during the monitoring period were, in general, not subject to the testing unless (i) they were in the occupations that involved high in-person interactions with COVID-19 patients or (ii) they were linked to a “cluster” [13,14,15]. Here, a “cluster” was defined as a group of five or more confirmed positive cases who were unrelated within themselves (i.e., no identifiable in-person interactions) but were traced back to a specific event or location [15].
Epidemiologic data, i.e., the viral transmission paths, were available for 371 cases. Some of these 371 cases were connected to multiple cases, indicating that they had multiple possibilities of exposure to infectors and/or infectees. For instance, all family members were more likely to be connected to each other, because, with the exception of the source family member who infected his/her family members, the specific transmission paths within the family are generally unknown. This also applied to the cases of “cluster” infections where a group of infectors/infectees emerged in one location, e.g., a nursing home.
2.2. Analysis
Clinical characteristics observed in female and male patients were compared using t-tests for continuous variables and chi-squared tests for nominal variables. Depending on the distribution of a continuous variable and the sample size of a nominal variable, Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney and Fisher’s exact tests were used to replace t-square and chi-square tests, respectively. Sex-adjusted clinical characteristics observed in age groups were also compared using t-squared/Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney and Chi-squared/Fisher’s exact tests.
Our data included PCR-positive COVID-19 patients without overt symptoms at the time of the laboratory-confirmed infection. While these cases may be pre-symptomatic, we have defined them as asymptomatic cases as suggested in the registry notes and to conform to the current guideline by WHO [16]. Our data also included a fraction of individuals who appeared in the registry twice, with notes indicating that these were “reinfection” cases. While our data did not contain enough evidence to determine whether these are truly reinfection cases or more likely to be reactivation or false-positive cases, the notes in the registry indicated that these patients had tested negative by PCR on two separate occasions before being discharged from the hospital (or hotel for asymptomatic patients) due to their first infection. In the absence of other evidence, including viral sequence data, we defined these cases as reinfections.
In order to identify factors correlated with asymptomatic cases, multivariate logistic regression was run with the absence of symptoms as the dependent variable. For the symptomatic cases, a supervised principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to assess the co-occurrence of symptoms. For each retained factor (i.e., a set of co-occurring symptoms), we estimated the factor score, which was subsequently used in multivariate logistic regression to identify the factor score correlated with the severity of COVID-19. Here, we defined severe cases by the presence of dyspnea. In order to visually inspect the patterns of viral transmissions, we constructed viral transmission networks using the records of the patients whose infectors or infectees were known in the registry. Network construction and visualization were conducted by using programming language R (R Core Team) and visualization software Gephi (v 0.9.2). All statistical analyses were performed in STATA (StataCorp, v14). For all analyses, statistical significance was defined by p ≤ 0.05 unless noted otherwise.
3. Results
3.1. Symptoms
No significant difference was observed in the mean age of male and female COVID-19 patients (54 vs. 53; p = 0.24). The most common symptom was fever, affecting 81% of females and 88% of males (Table 1). Fatigue and the presence of coughs were the next most common symptoms, each affecting around 40% of both females and males. Surprisingly, the number of female asymptomatic cases was nearly twice that of males (177 or 26% vs. 80 or 13%, p < 0.001). Analysis of age-related differences by sex (Table 2) indicated that headaches were more common in men and women between the ages of 20 and 40 (p < 0.001 for both men and women), whereas loss of taste was more common in men and women aged between 10 and 30 (p < 0.001 for both men and women). Body ache was less common among older patients (>59) (p < 0.001 for males and p = 0.01 for females). Although the number of patients who reported nausea/vomiting was small (n = 27), there was a significant statistical correlation between young age (10–19) and the presence of the symptoms for females (p = 0.05).

Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients.

Table 2.
Symptom by age and sex.
3.2. Reinfection
The data contained nine cases of reinfection, including four females ranging in age from 10 to 70 (one patient was 10 years old, one was 30 years old, one was 50 years old, and one was 70 years old) and four males ranging from 30 to 90 (one patient was 30, one patient was 40, one patient was 60, and one was 90) (Table 1). One person who experienced reinfection did not have complete data and was excluded from further analysis. After excluding this individual, reinfection cases made up approximately 1% of the total number of cases in both males and females. The duration between the confirmation of the first and second episodes of COVID-19 (both by PCR) ranged between 16 days and 42 days, with a mean of 29 (±9.6) days. One of the individuals, who was asymptomatic at the first PCR, was shown to be PCR positive again 41 days later, with fever as the only symptom of the disease. This individual had had two negative PCR tests in the period between the first PCR and the one 41 days later. As such, although it is possible that he had not completely cleared the virus and had a sub-PCR detectible viral load that spiked some 5 weeks later, it is also possible that he became reinfected by the virus. In the seven remaining cases, the symptoms of the first infection were generally similar to those of the second infection, as was the number of symptoms experienced.
3.3. Asymptomatic Patients
Table 3 summarizes the number of asymptomatic patients by age and sex. The majority of asymptomatic patients were females and older. Out of the 10 decadal age groups into which the patients were classified, there was a statistically significant difference in six of them between the number of asymptomatic males versus females (0 or 0% vs. 3 or 60%, p = 0.003, in ages 1–9; 4 or 8% vs. 19 or 25%, p = 0.002, in ages 20–29; 5 or 10% vs. 16 or 25%, p = 0.005, in ages 30–39; 4 or 5% vs. 16 or 18%, p = 0.001, in ages 50–59; 13 or 20% vs. 39 or 44%, p = 0.002, in ages 80–89; 5 or 22% vs. 25 or 48%, p = 0.003, in ages 90–99). Although the difference between asymptomatic females and males was not significant for every age group, the pattern was present in all of the groups, strongly suggesting that the observed differences are highly likely.

Table 3.
Asymptomatic patients by age and sex.
A subsequent logistic regression validated this observation. Females were 1.3-fold more likely to be asymptomatic than compared to males (Table 4, OR = 2.31, p < 0.001), while a decade of difference in age increased the likelihood of being asymptomatic by 1% (OR = 1.01, p < 0.001). Separately, we tested whether older females were more likely to be asymptomatic than older males by including the interaction term between female and age in the regression below, but this was statistically insignificant (p = 0.31).

Table 4.
Multivariate logistic regression for asymptomatic patients.
3.4. Viral Transmission
In our data, males were more likely to transmit the virus to at least one individual (122 or 21% vs. 88 or 13%, p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in the sex of the infectees (3.48 vs. 3.89, p = 0.60) (Table 1). In total, 371 cases were connected to at least one case in the registry. Of those, 210 patients infected at least one person, while the other 161 cases did not infect anyone else but were themselves infected by one of the 210 patients. Figure 2 depicts the networks of viral transmission. In the diagram, each patient is represented by a circle. The size of each circle represents the number of infections generated by the patient. The color of the circle represents the order (primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary) of the infections. The networks containing up to quaternary viral transmission. Of the 371 cases, 115 cases (31%) were primary, 212 cases (57%) were secondary, 40 cases (11%) were tertiary, and 4 cases (1%) were quaternary cases. There were 108 separate viral transmission networks. Most of these networks consisted of two patients (67 networks or 64%) while there was one network that involved 36 patients. The average network size was 3.44. Figure 3 represents the histogram of the network sizes.
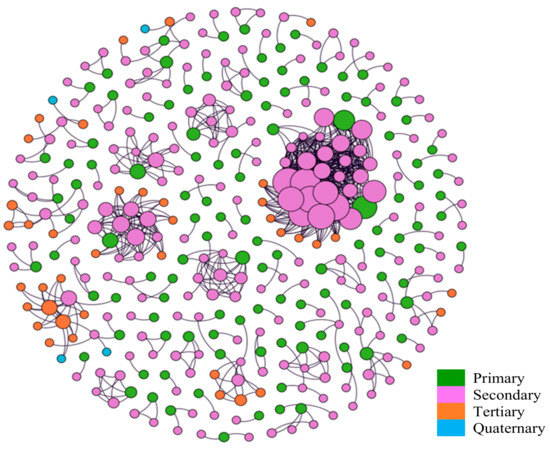
Figure 2.
Viral transmission networks and the order of infections.
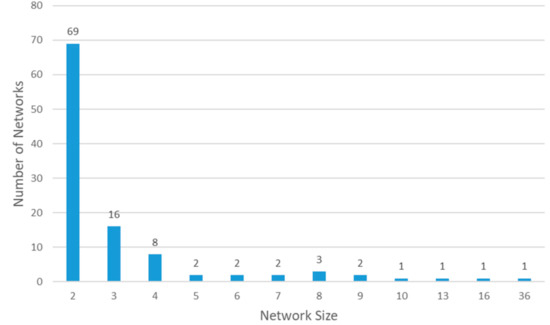
Figure 3.
Histogram: network size of viral transmission.
Figure 4 and Figure 5 present the age and the sex group that each case belongs to in the networks. The diagrams show no discernable patterns in terms of age and sex distributions in the networks, indicating that viral transmission occurred across age and sex groups regardless of the presence or absence of symptoms.
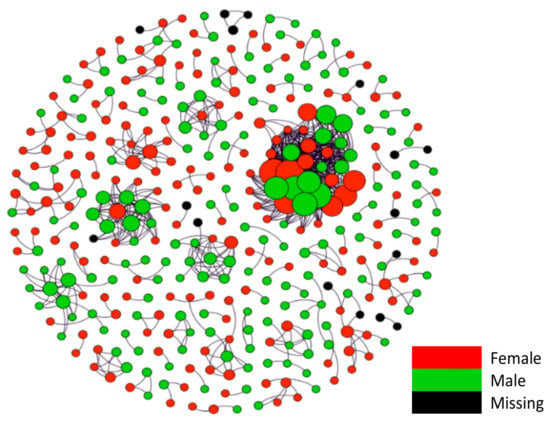
Figure 4.
Viral transmission networks by sex.
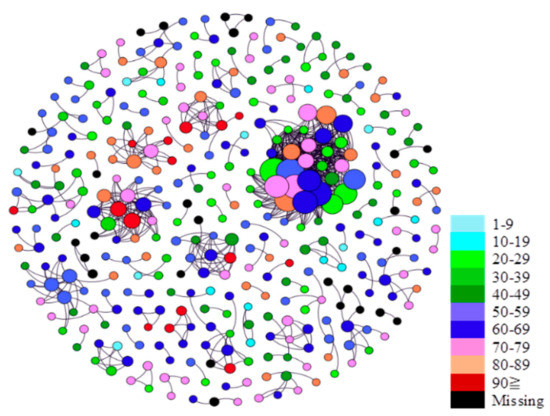
Figure 5.
Viral transmission networks by age.
Figure 6 present the asymptomatic status that each case belongs to in the networks. In the diagram, red circles correspond to asymptomatic cases, and blue circles correspond to symptomatic cases. The diagram suggests that although asymptomatic patients transmit the virus to others at a higher level, the infected individuals are also likely to be asymptomatic. This finding was confirmed by using descriptive statistics, which indicated that only 13% (n = 39) of the individuals who were infected by symptomatic patients ended up being asymptomatic, whereas 53% (n = 41) of the individuals who were infected by asymptomatic patients ended up being asymptomatic (p < 0.001).
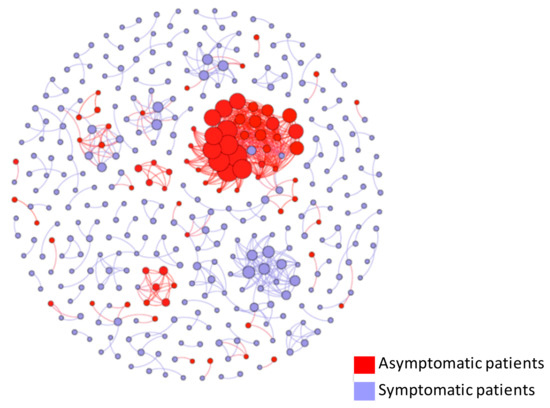
Figure 6.
Viral transmission networks by asymptomatic status.
Table 5 summarizes the results of a multivariate logistic regression that identifies the determinants of viral transmission. Male patients were 82% more likely to transmit the virus regardless of being symptomatic and asymptomatic (OR = 1.82, p < 0.001). Asymptomatic patients were 81% more likely to transmit the virus (OR = 1.81, p = 0.02). Patients with pneumonia were 54% less likely to transmit the virus (OR = 0.46, p = 0.02), possibly due to being in the hospital. Additionally, the time between PCR and the onset of symptoms was positively associated with the likelihood of viral transmission (5% greater likelihood, OR = 1.05, p < 0.001).

Table 5.
Multivariate logistic regression for viral transmission.
3.5. Severity
Principal component analysis identified six unique factors with an eigenvalue that is equal to or larger than one. Among those, we observed four distinct viral transmission networks of co-occurring symptoms. Specifically, we observed the co-occurrence of fever and fatigue (F1); pharyngitis and rhinitis (F2); loss of taste and smell (F3); and diarrhea/nausea/vomiting (F4). The factor scores estimated for these four factors were then used to identify the determinants of severity in multivariate logistic regression. Interestingly, the presence of diarrhea/nausea/vomiting was predictive of developing dyspnea, i.e., severe disease (OR = 1.58, p < 0.001). Severe disease, as defined by dyspnea, was also more prevalent in males (OR = 1.84, p < 0.005). To confirm this result, we performed concomitant logistic regression with dyspnea as the outcome dependent variable and male, diarrhea, and nausea/vomiting as explanatory variables. Two separate regressions were run to avoid multicollinearity, one with diarrhea and male, another with nausea/vomiting, and male as explanatory variables (Table 6). Here, being a male was a risk factor for having dyspnea with similar coefficients in the two regressions (OR = 1.59, p = 0.02; OR = 1.71, p = 0.01). Experiencing diarrhea increased the likelihood of developing dyspnea by 82% (OR = 1.82, p = 0.05) while experiencing nausea/vomiting increased the likelihood of developing dyspnea by 373% (OR = 4.73, p < 0.001). From the notes provided with the data, diarrhea and nausea/vomiting tended to be symptoms experienced in the early stage of the disease while dyspnea was observed at the later stage, indicating that early stage GI infections may result in a severe case of the disease.

Table 6.
Multivariate logistic regression for severity determinants.
4. Discussion
The current study analyzed data from 1269 (674 females and 595 males) individuals who were PCR-positive for SARS-CoV-2. Some of our findings confirmed the observations of previous studies: Fever was the most prevalent symptom, with 81% females and 88% of male subjects showing it. Fatigue and cough were the next most prevalent symptoms with approximately 40% of female and male patients possessing them. These findings are reported in prior studies including the one by Larsen and colleagues [17]. Our study additionally identified the four sets of co-occurring symptoms including (i) fever and fatigue; (ii) pharyngitis and rhinitis; (iii) ageusia (loss of taste) and anosmia (loss of smell); and (iv) nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. With dyspnea as an indicator of severity, our results suggested that severe disease was more frequently observed in patients who had nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. This interesting correlation may be due to the higher level of viremia and subsequent multi-organ infection, including the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The presence of nausea and vomiting suggests that upper GI involvement and that of diarrhea, lower GI infection, both are consistent with a disseminated disease as a result of viremia. Moreover, males were more susceptible to developing severe disease, although it is unknown whether or not this sex difference is hormonally driven. One study from China reports a similar finding. Tian et al. reviewed data from 15 clinical studies and case reports to investigate the GI features of COVID-19 in adult and pediatric patients [18]. They report that the proportion of patients with GI symptoms was higher among severe patients than in non-severe patients. Another single-hospital study from Wuhan, China, analyzed data from 206 patients with mild disease and GI symptoms. The study reports that these patients are more likely to have a positive test result for viral RNA in stool and to have a longer duration before viral clearance. The results of both these studies are consistent with our findings and suggest that GI symptoms may be suggestive of more disseminated diseases, although treatments, including antibiotics, and corticosteroids could also have an impact on the gastrointestinal mucosa and result in GI symptoms. The presence of GI symptoms in younger individuals has been observed previously [19,20,21], and it is speculated that a weaker respiratory immune response in this age group may be the reason for their mild respiratory symptoms when compared to adults [18]. The presence of anosmia and ageusia suggests that the virus affects the olfactory epithelium, as well as taste buds, both of which have cilia that act as the receptors for specific molecules that we taste and smell, respectively.
Moreove, consistent with prior findings [4,22], a significant number (~20%) of infected patients were found to be asymptomatic carriers in our study. Interestingly, however, there were significantly more female asymptomatic patients than males in our study. There are a handful of prior studies suggesting this. Williamson and colleagues analyzed COVID-19 death records in the UK and reported that men had a significantly higher risk of mortality with an HR of 1.59 [23]. Yang et al. studied 78 patients in Wuhan, China, and reported that being female and younger increased the likelihood of being asymptomatic [24]. Additionally, a meta-analysis by Kronbichler et al. demonstrated that while abnormal radiological findings could be observed in a large proportion of asymptomatic patients, asymptomatic patients with normal radiological findings were more likely to be female and younger [25]. Although it is currently unclear why females are more likely to be asymptomatic, a hormonal effect on T-cells may be involved. This possibility is supported by Wu et al., who reported that pregnant women are more likely to be asymptomatic [26]. In this study, four out of eight pregnant women were asymptomatic before delivery but became symptomatic after delivery, suggesting that the change in hormones and immune system during the pregnancy may play a role in the onsets of symptoms.
In contrast to Yang et al. and Kronbichler et al., our data did not suggest that younger (female) patients were more likely to be asymptomatic. Rather, our data demonstrated that the likelihood of being asymptomatic increased with age in the Hokkaido population. In relation to this, in a study of 98 PCR-positive COVID-19 patients, Takahashi and colleagues observed differences in T cell responses and innate immune cytokine levels in male and female patients, respectively, that correlated with progression to more severe disease. Their patient population, however, did not have a broad age distribution, nor was an assessment of initial symptoms included in their analysis [27]. As such, no conclusions about age and the presence or absence of symptoms could be reached.
The observations by Wu et al., and Takahashi et al., potentially suggest that sex hormones may be involved in the differences between disease manifestation in male and female COVID-19 patients. A recent hypothesis by Roche and Roche [28] and Garvin et al. [29], suggesting a role for the interconnected bradykinin and renin-angiotensin system (RAS), offers a plausible explanation for the observed sex-dependent differences. Estrogen is known to downregulate angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which not only catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II but also breaks down bradykinin [30]. Thus, a decrease in estrogen levels after menopause could result in higher levels of ACE and lower levels of bradykinin in tissues, resulting in a less intense inflammatory response and a reduction in the risk of a “bradykinin storm” triggered by SARS-CoV2. As bradykinin is pro-inflammatory, the lower levels may explain our observations. Moreover, enhanced angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) immunostaining activity during pregnancy has been reported in animal studies [31,32]. Bradykinin (BK-1-9 or BK) and its active metabolite [des-Arg9]-BK (BK-1-8 or DABK) bind to two different G protein-coupled receptors: the B1 receptor (BKB1R), for which its main ligand is DABK, and the B2 receptor (BKB2R), for which its ligand is BK. ACE2 has been shown to inactivate DABK by cleaving a single terminal amino acid from the peptide [33]. Inhibition of BKB1R activity decreases pulmonary neutrophil infiltration following LPS exposure and decreases the influx of neutrophils in response to endotoxin [33]. The elevated levels of ACE2 during pregnancy [34] may result in lower DABK levels and, thus, explain why pregnant women are more likely to be asymptomatic [20] or show mild symptoms.
As expected, asymptomatic patients in our study were more likely to transmit the virus in our study. Interestingly, however, these patients who became infected by asymptomatic patients were also likely to be asymptomatic. This may be the result of a lower viral load in asymptomatic individuals. Luo and colleagues also observed that transmission risk increased with the severity of the disease, suggesting a higher viral load in patients with more severe symptoms [35]. Other studies, however, have found similar viral loads in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients, although the number of patients analyzed was small [23]. Unfortunately, in our study, no viral samples were available; therefore, it was impossible to determine the possible effect of viral load or the presence of variants in explaining asymptomatic to asymptomatic transmissions. The length of time between PCR testing and the onset of symptoms was also positively associated with the transmission in our study, presumably due to the maintenance of social contacts during this period. Furthermore, male patients were 82% more likely to transmit the virus, regardless of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. This may be either due to a higher viral load in males or more likely due to behavioral or physical differences in the anatomy of the upper respiratory tract, including the mouth, which may result in a greater release of the virus in droplets or aerosol.
Of significant interest is the presence of nine cases of COVID-19 reinfection in the study population. Earlier evidence in smaller-scale retrospective clinical studies suggested that reinfection by the coronavirus is possible. Ye and colleagues studied 55 COVID-19 patients with pneumonia, out of which 9% had a second episode of COVID-19 [36]. Case reports from China (n = 2) [37] and Italy (n = 1) [38] also confirmed this. In our study, the prevalence of the virus reinfection was 1%, significantly smaller than that reported in Ye et al. Due to the aforementioned limitation regarding the availability of viral samples, it is unclear whether these cases of reinfection were caused by the same variant of SARS-CoV-2 or a different one. The data, however, suggest that in most reinfection cases in the current study, the symptoms of the first infection were similar to those of the second, raising the possibility that the first and second infection episodes were caused by different variants of the virus.
Finally, the current study is a retrospective secondary data analysis; thus, some of the relevant information, particularly the patients’ data on comorbidities, were not available in a consistently analyzable fashion. The authors were also unable to ensure either the accuracy or the completeness of the data. In this sense, some of the results, especially the findings concerning viral transmission networks, are subject to systematic bias if contact tracing was performed disproportionately in specific cases or cohorts. While the most up-to-date guideline published by the Japanese government still requests that all individuals who were in “close contact” with the confirmed cases be subject to an “initial (PCR) screening test” [14], the level of compliance with such a guideline is unknown, especially in light of the recent resurge in COVID-19 cases in the country. That being said, we believe that the guideline was adhered to in Hokkaido in the period between February and July and that further investigations on the patterns of viral transmissions and symptomology in the networks are warranted. Such investigations are deemed particularly valid as new variants of the virus continue to emerge.
5. Conclusions
The likelihood of being asymptomatic increases with age and sex (women and older individuals are more likely to be asymptomatic). Asymptomatic patients are more likely to transmit the virus and also to generate asymptomatic cases. Reinfection by the virus is likely.
Author Contributions
M.-H.L.—cleaned and co-organized the data and performed network analysis. A.B.S.—cleaned and co-organized the data and performed network analysis. A.A.—co-designed the study, contextualized the results, and analyzed the medical aspects of the data. N.K.—co-designed the study, accessed and organized the prefecture data, and performed the statistical analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially funded by National Science Foundation, USA (EAGER: ISN:/1838306).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available by emailing nkoizumi@gmu.edu.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanella, A.; Antonelli, M.; Cabrini, L.; Castelli, A.; Cereda, D.; Coluccello, A.; Foti, G.; Fumagalli, R.; et al. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefan, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Schulze, M.B.; Ludwig, D. Obesity and impaired metabolic health in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Yao, L.; Wei, T.; Tian, F.; Jin, D.Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, M. Presumed Asymptomatic Carrier Transmission of COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 323, 1406–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothe, C.; Schunk, M.; Sothmann, P.; Bretzel, G.; Froeschl, G.; Wallrauch, C.; Zimmer, T.; Thiel, V.; Janke, C.; Guggemos, W.; et al. Transmission of 2019-nCoV Infection from an Asymptomatic Contact in Germany. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, S.; Ma, K. A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 54, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, A.; Yi, B.; Ding, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, G. The epidemiological characteristics of infection in close contacts of COVID-19 in Ningbo city. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 667–671. [Google Scholar]
- Health and Welfare Department, Health and Safety Bureau Community Health Division. New Corona: Occurrence in Hokkaido. 2020. Available online: http://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/hf/kth/kak/hasseijoukyou.htm (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Oshitani, H. Cluster-Based Approach to Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Response in Japan, from February to April 2020. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, A. This Japanese Island Lifted Its Coronavirus Lockdown Too Soon and Became a Warning to the World. 2020. Available online: https://time.com/5826918/hokkaido-coronavirus-lockdown/ (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Sapporo. About Emergency Measures. 2020. Available online: http://www.city.sapporo.jp/2019n-cov/kinkyujitai.html (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Furuse, Y.; Sando, E.; Tsuchiya, N.; Miyahara, R.; Yasuda, I.; Ko, Y.K.; Saito, M.; Morimoto, K.; Imamura, T.; Shobugawa, Y.; et al. Clusters of Coronavirus Disease in Communities, Japan, January–April 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Saito, T.; Oshitani, H. Roles of Public Health Centers and Cluster-Based Approach for COVID-19 Response in Japan. Health Secur. 2021, 19, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases. Guidelines for Conducting an Active Epidemiological Survey on Patients with Coronavirus Infection. 2021. Available online: https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/images/epi/corona/COVID19-02-210108.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Japan Epidemiological Association. Guide on Active Epidemiological Investigation for Public Health Nurses in Response to COVID-19 in Japan. 2020. Available online: https://jeaweb.jp/covid/links/guide_0421.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- World Health Organization. Clinical Management of COVID-19: Interim Guidance, 27 May 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, J.R.; Martin, M.R.; Martin, J.D.; Kuhn, P.; Hicks, J.B. Modeling the Onset of Symptoms of COVID-19. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Rong, L.; Nian, W.; He, Y. Review article: Gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of faecal transmission. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Mo, X.; Hu, Y.; Qi, X.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Ton, S. Epidemiological characteristics of 2143 pediatric patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in China. Pediatrics 2020, 58, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiang, R.; Song, H.; Shu, S.; Chen, L.; Liang, L.; Zhou, J.; You, L.; et al. Detection of COVID-19 in Children in Early January 2020 in Wuhan, China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1370–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Shao, J.; Guo, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, D. Clinical and CT features in pediatric patients with COVID-19 infection: Different points from adults. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abduljali, J.M.; Abduljali, B.M. Epidemiology, genome and clinical features of the pandemic SARS-CoV-2: A recent view. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 35, 100672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gui, X.; Xiong, Y. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Asymptomatic vs. Symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2010182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Kresse, D.; Yoon, S.; Lee, K.H.; Effenberger, M.; Shin, J.I. Asymptomatic patients as a source of COVID-19 infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W.; Xia, J. Clinical Manifestation and Laboratory Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnant Women. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, T.; Ellingson, M.K.; Wong, P.; Israelow, B.; Lucas, C.; Klein, J.; Silva, J.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Tokuyama, M.; et al. Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes. Nature 2020, 588, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J.A.; Roche, R. A hypothesized role for dysregulated bradykinin signaling in COVID-19 respiratory complications. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7265–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, M.R.; Alvarez, C.; Miller, J.I.; Prates, E.T.; Walker, A.M.; Amos, B.K.; Mast, A.; Justice, A.; Aronow, B.; Jacobson, D. Author response: A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm. Elife 2020, 9, e59177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnihan, K.; Senanayake, P.; Li, P.; Ferrario, C. Bi-directional actions of estrogen on the renin-angiotensin system. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1999, 32, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, J.C. Sex and the renin-angiotensin system: Inequality between the sexes in response to RAS stimulation and inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1220–R1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brosnihan, K.B.; Neves, L.A.; Joyner, J.; Averill, D.B.; Chappell, M.C.; Sarao, R.; Penninger, J.; Ferrario, C.M. Enhanced Renal Immunocytochemical Expression of ANG-(1-7) and ACE2 During Pregnancy. Hypertension 2003, 42, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sodhi, C.P.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Prindle, T.; Fulton, W.B.; Wang, S.; McCray, P.B., Jr.; Chappell, M.; Hackam, D.J.; Jia, H.; et al. Attenuation of pulmonary ACE2 activity impairs inactivation of des-Arg9 bradykinin/BKB1R axis and facilitates LPS-induced neutrophil infiltration. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L17–L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, M.S.; Strawn, W.B.; Groban, L.; Yamaleyeva, L.M.; Chappell, M.C.; Horta, C.; Atkins, K.; Firmes, L.; Gurley, S.B.; Brosnihan, K.B. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Deficiency Is Associated with Impaired Gestational Weight Gain and Fetal Growth Restriction. Hypertension 2011, 58, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Liu, D.; Liao, X.; Wu, X.; Jing, Q.; Zheng, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Bi, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Contact Settings and Risk for Transmission in 3410 Close Contacts of Patients With COVID-19 in Guangzhou, China. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Pan, Z.; Pan, Y.; Deng, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Clinical characteristics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 reactivation. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e14–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravioli, S.; Ochsner, H.; Lindner, G. Reactivation of COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of two cases. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e72–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loconsole, D.; Passerini, F.; Palmieri, V.O.; Centrone, F.; Sallustio, A.; Pugliese, S.; Grimaldi, L.D.; Portincasa, P.; Chironna, M. Recurrence of COVID-19 after recovery: A case report from Italy. Infection 2020, 48, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).