Observations of Gas-Phase Alkylamines at a Coastal Site in the East Mediterranean Atmosphere
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Site
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Method
2.4. Auxilary Observations
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Alkylamines Concentrations
3.2. Alkylamines Seasonality
3.3. Factor Analysis-Source Identification
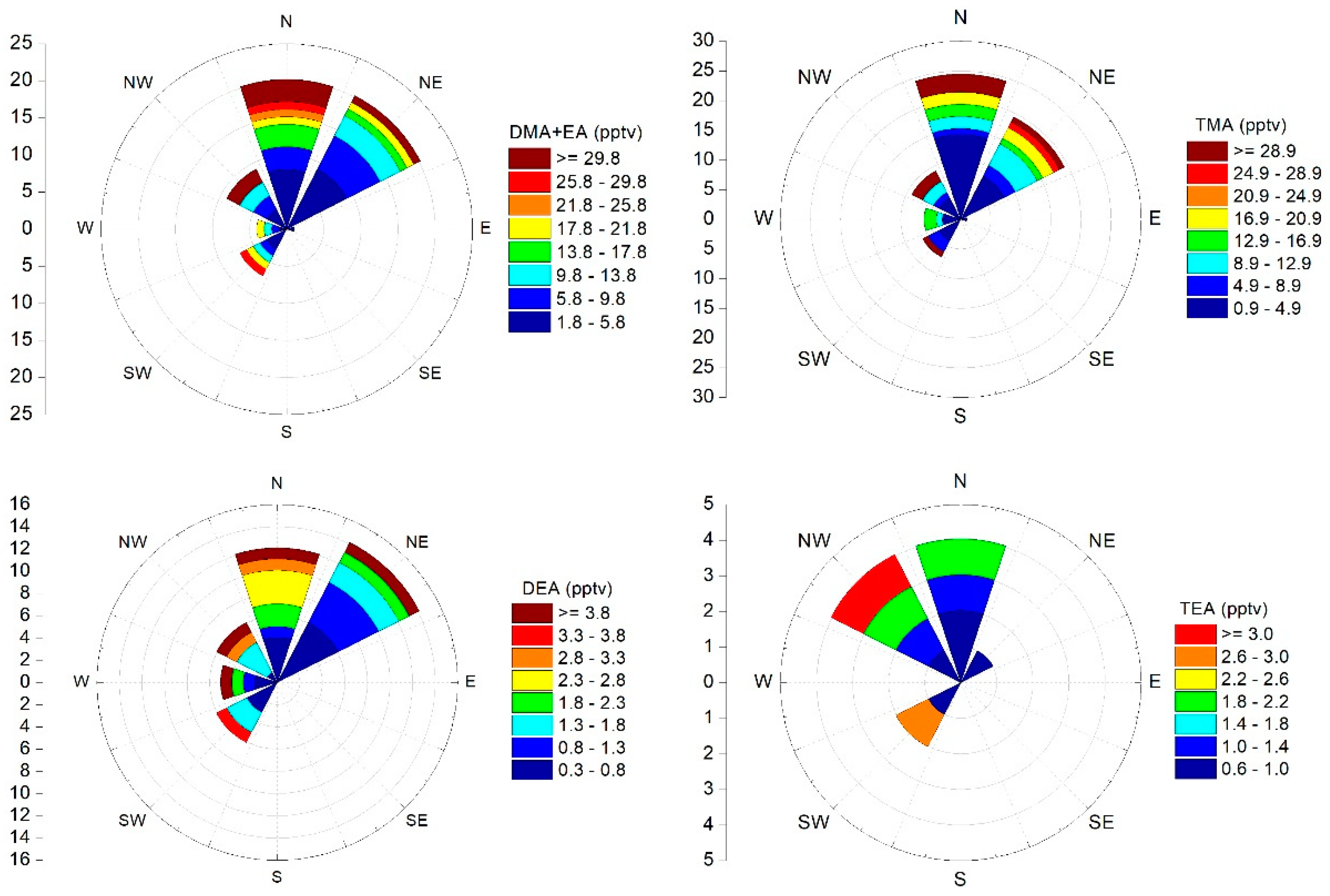
3.4. Air Masses Back Tranjectories Analysis
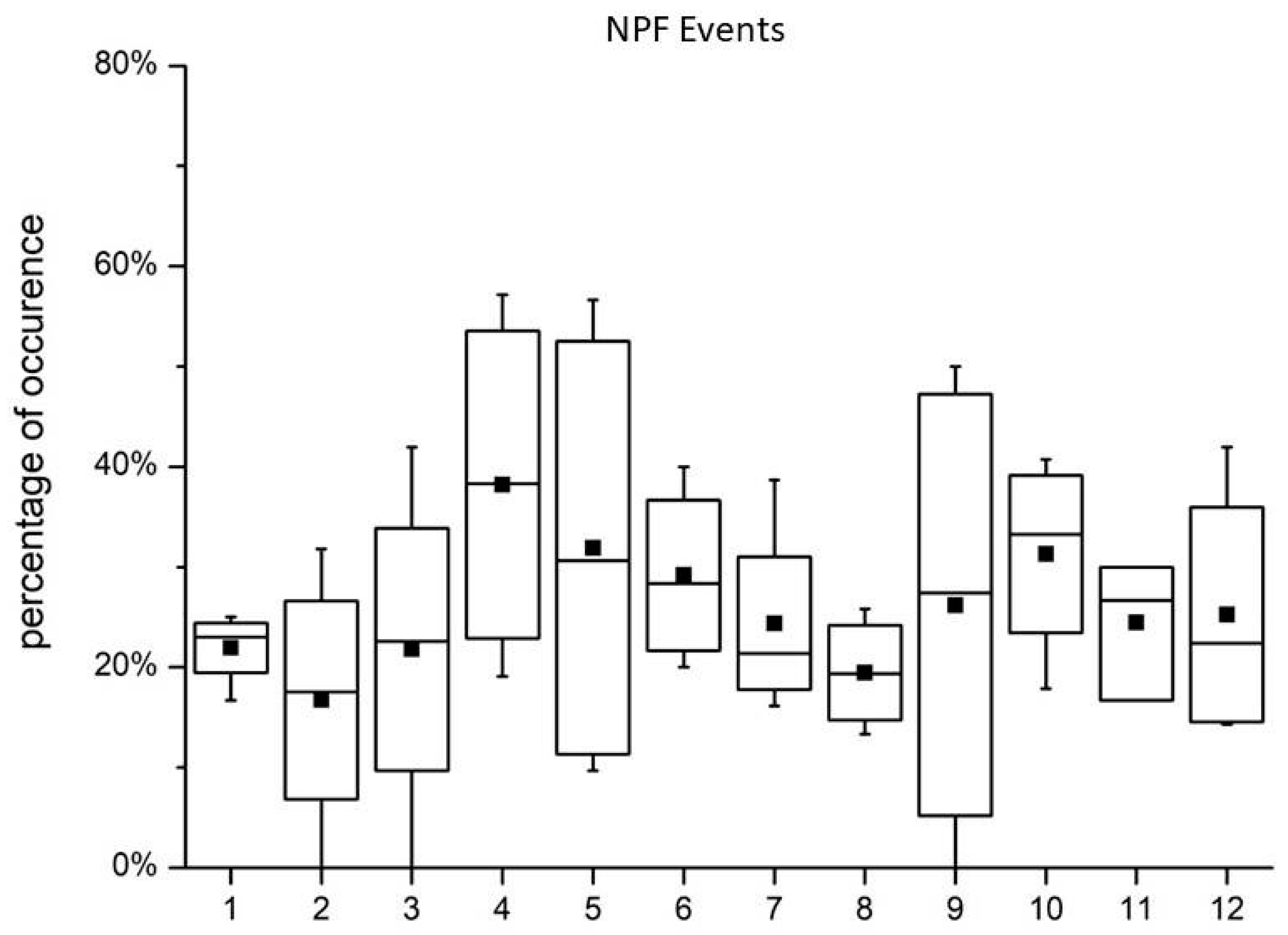
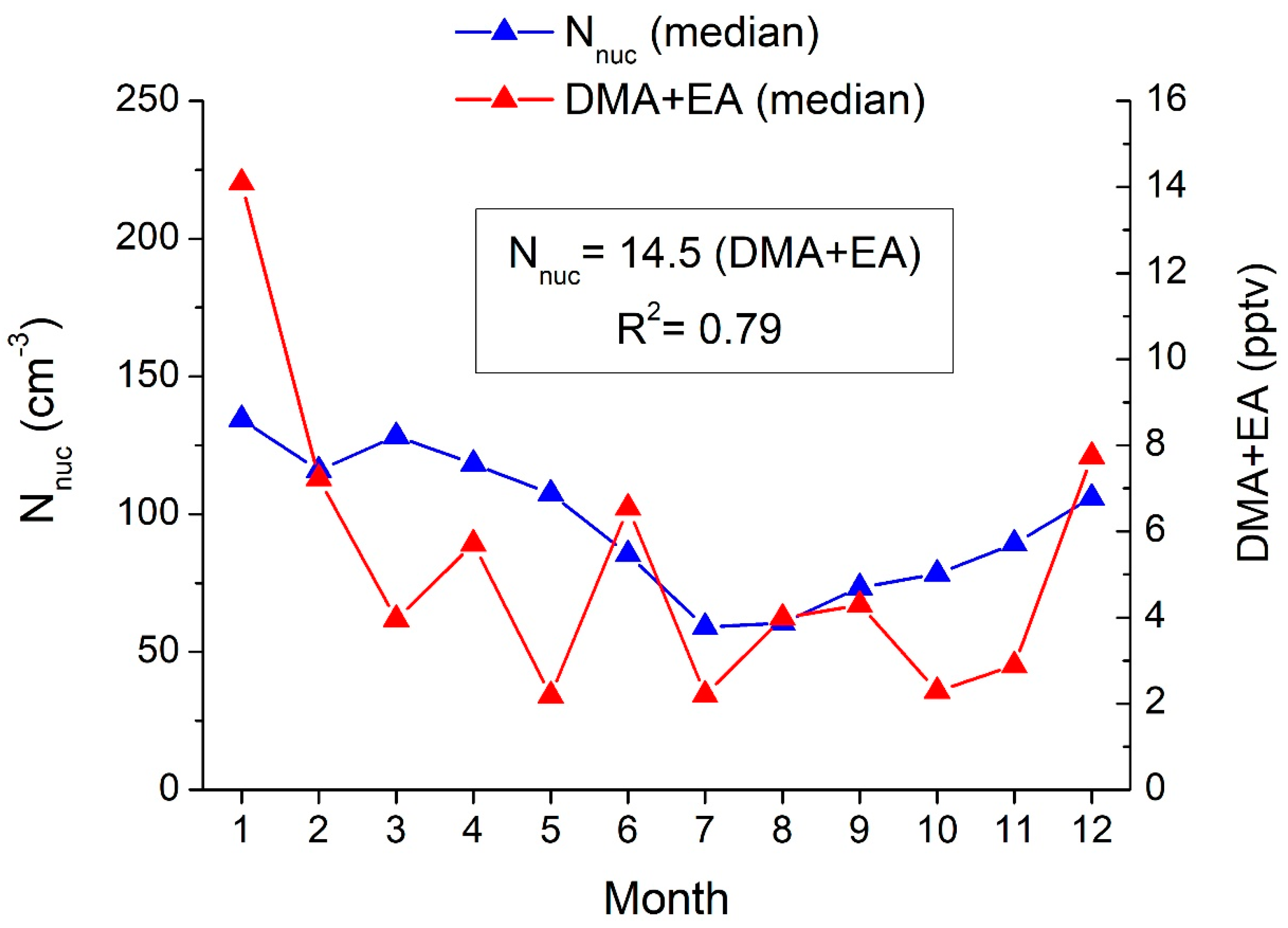
3.5. Alkylamines and NPF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornell, S.E.; Jickells, T.D.; Cape, J.N.; Rowland, A.P.; Duce, R.A. Organic Nitrogen Deposition on Land and Coastal Environments: A Review of Methods and Data. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2173–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, S.E. Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition: Revisiting the Question of the Importance of the Organic Component. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, A.; Murphy, S.M.; Hersey, S.; Gates, H.; Padro, L.T.; Nenes, A.; Brechtel, F.J.; Jonsson, H.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Comprehensive Airborne Characterization of Aerosol from a Major Bovine Source. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5489–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schade, G.W.; Crutzen, P.J. Emission of Aliphatic Amines from Animal Husbandry and Their Reactions: Potential Source of N2O and HCN. J. Atmos. Chem. 1995, 22, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Wexler, A.S. Atmospheric Amines—Part III: Photochemistry and Toxicity. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIOSH. Carcinogen List by National Institute for Occupational Safetyand Health (NIOSH). Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/cancer/npotocca.html (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Yu, F.; Luo, G. Modeling of Gaseous Methylamines in the Global Atmosphere: Impacts of Oxidation and Aerosol Uptake. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12455–12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, X.; Wexler, A.S.; Clegg, S.L. Atmospheric Amines—Part II. Thermodynamic Properties and Gas/Particle Partitioning. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Chan, C.K. Reactive Uptake of Dimethylamine by Ammonium Sulfate and Ammonium Sulfate-Sucrose Mixed Particles. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Sauerwein, M.; Chan, C.K. Hygroscopic and Phase Transition Properties of Alkyl Aminium Sulfates at Low Relative Humidities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 19789–19796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.P.; Chan, C.K. Role of the Aerosol Phase State in Ammonia/Amines Exchange Reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5755–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wexler, A.S.; Clegg, S.L. Atmospheric Amines—Part I. A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Neste, A.; Duce, R.A.; Lee, C. Methylamines in the Marine Atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1987, 14, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erupe, M.E.; Viggiano, A.A.; Lee, S.-H. The Effect of Trimethylamine on Atmospheric Nucleation Involving H2SO4. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4767–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulmala, M.; Petäjä, T.; Mönkkönen, P.; Koponen, I.K.; Dal Maso, M.; Aalto, P.P.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Kerminen, V.-M. On the Growth of Nucleation Mode Particles: Source Rates of Condensable Vapor in Polluted and Clean Environments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulmala, M.; Kontkanen, J.; Junninen, H.; Lehtipalo, K.; Manninen, H.E.; Nieminen, T.; Petäjä, T.; Sipilä, M.; Schobesberger, S.; Rantala, P.; et al. Direct Observations of Atmospheric Aerosol Nucleation. Science 2013, 339, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; McGraw, R.; Lee, S.-H. Effects of Amines on Formation of Sub-3 Nm Particles and Their Subsequent Growth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R. Getting to the Critical Nucleus of Aerosol Formation. Science 2010, 328, 1366–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Khalizov, A.; Wang, L.; Hu, M.; Xu, W. Nucleation and Growth of Nanoparticles in the Atmosphere. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1957–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtén, T.; Loukonen, V.; Vehkamäki, H.; Kulmala, M. Amines Are Likely to Enhance Neutral and Ion-Induced Sulfuric Acid-Water Nucleation in the Atmosphere More Effectively than Ammonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kürten, A.; Li, C.; Bianchi, F.; Curtius, J.; Dias, A.; Donahue, N.M.; Duplissy, J.; Flagan, R.C.; Hakala, J.; Jokinen, T.; et al. New Particle Formation in the Sulfuric Acid-Dimethylamine-Water System: Reevaluation of CLOUD Chamber Measurements and Comparison to an Aerosol Nucleation and Growth Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 845–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, J.; Schobesberger, S.; Kürten, A.; Ortega, I.K.; Kupiainen-Määttä, O.; Praplan, A.P.; Adamov, A.; Amorim, A.; Bianchi, F.; Breitenlechner, M.; et al. Molecular Understanding of Sulphuric Acid–Amine Particle Nucleation in the Atmosphere. Nature 2013, 502, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parshintsev, J.; Rönkkö, T.; Helin, A.; Hartonen, K.; Riekkola, M.-L. Determination of Atmospheric Amines by On-Fiber Derivatization Solid-Phase Microextraction with 2,3,4,5,6-Pentafluorobenzyl Chloroformate and 9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl Chloride. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1376, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieloaho, A.-J.; Hellén, H.; Hakola, H.; Manninen, H.E.; Nieminen, T.; Kulmala, M.; Pihlatie, M. Gas-Phase Alkylamines in a Boreal Scots Pine Forest Air. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellén, H.; Kieloaho, A.-J.; Hakola, H. Gas-Phase Alkyl Amines in Urban Air; Comparison with a Boreal Forest Site and Importance for Local Atmospheric Chemistry. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.L.; Perraud, V.; Gomez, A.; Arquero, K.D.; Ezell, M.J.; Finlayson-Pitts, B.J. Measurement of Gas-Phase Ammonia and Amines in Air by Collection onto an Ion Exchange Resin and Analysis by Ion Chromatography. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2733–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akyüz, M. Simultaneous Determination of Aliphatic and Aromatic Amines in Indoor and Outdoor Air Samples by Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2007, 71, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyüz, M. Simultaneous Determination of Aliphatic and Aromatic Amines in Ambient Air and Airborne Particulate Matters by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellegri, K.; Hanke, M.; Umann, B.; Arnold, F.; Kulmala, M. Measurements of Organic Gases during Aerosol Formation Events in the Boreal Forest Atmosphere during QUEST. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Y.; Kanawade, V.P.; de Gouw, J.A.; Guenther, A.B.; Madronich, S.; Sierra-Hernández, M.R.; Lawler, M.; Smith, J.N.; Takahama, S.; Ruggeri, G.; et al. Atmospheric Amines and Ammonia Measured with a Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer (CIMS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12181–12194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Lee, S.-H. Chemical Ionisation Mass Spectrometry for the Measurement of Atmospheric Amines. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanson, D.R.; McMurry, P.H.; Jiang, J.; Tanner, D.; Huey, L.G. Ambient Pressure Proton Transfer Mass Spectrometry: Detection of Amines and Ammonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8881–8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshour, N.A.; Carlson, K.K.; Melka, Y.A.; Hinz, S.; Panta, B.; Hanson, D.R. Amine Permeation Sources Characterized with Acid Neutralization and Sensitivities of an Amine Mass Spectrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3611–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sipilä, M.; Sarnela, N.; Jokinen, T.; Junninen, H.; Hakala, J.; Rissanen, M.P.; Praplan, A.; Simon, M.; Kürten, A.; Bianchi, F.; et al. Bisulfate – Cluster Based Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer for High-Sensitivity (< 100 PpqV) Detection of Atmospheric Dimethyl Amine: Proof-of-Concept and First Ambient Data from Boreal Forest. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4001–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kürten, A.; Bergen, A.; Heinritzi, M.; Leiminger, M.; Lorenz, V.; Piel, F.; Simon, M.; Sitals, R.; Wagner, A.C.; Curtius, J. Observation of New Particle Formation and Measurement of Sulfuric Acid, Ammonia, Amines and Highly Oxidized Organic Molecules at a Rural Site in Central Germany. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12793–12813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Khalizov, A.F.; Yao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Measurement of Atmospheric Amines and Ammonia Using the High Resolution Time-of-Flight Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, M.-Y.; Wang, X.-K.; Liu, Y.-J.; Chen, H.-F.; Zheng, J.; Nie, W.; Ding, A.-J.; Geng, F.-H.; Wang, D.-F.; et al. Detection of Atmospheric Gaseous Amines and Amides by a High-Resolution Time-of-Flight Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer with Protonated Ethanol Reagent Ions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14527–14543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemmilä, M.; Hellén, H.; Virkkula, A.; Makkonen, U.; Praplan, A.P.; Kontkanen, J.; Ahonen, L.; Kulmala, M.; Hakola, H. Amines in Boreal Forest Air at SMEAR II Station in Finland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6367–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VandenBoer, T.C.; Petroff, A.; Markovic, M.Z.; Murphy, J.G. Size Distribution of Alkyl Amines in Continental Particulate Matter and Their Online Detection in the Gas and Particle Phase. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4319–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VandenBoer, T.C.; Markovic, M.Z.; Petroff, A.; Czar, M.F.; Borduas, N.; Murphy, J.G. Ion Chromatographic Separation and Quantitation of Alkyl Methylamines and Ethylamines in Atmospheric Gas and Particulate Matter Using Preconcentration and Suppressed Conductivity Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1252, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzitzikalaki, E.; Kalivitis, N.; Panagiotopoulou, G.; Kanakidou, M. Observations of Alkylamines in the East Mediterranean Atmosphere. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Meteorology, Climatology and Atmospheric Physics COMECAP 2021, Ioannina, Greece, 26–29 September 2021; Bartzokas, A., Nastos, P., Eds.; Hellenic Meteorological Society: Ioannina, Greece, 2021; pp. 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalopoulos, N.; Stephanou, E.; Kanakidou, M.; Pilitsidis, S.; Bousquet, P. Tropospheric Aerosol Ionic Composition in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1997, 49B, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivitis, N.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kouvarakis, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Tzitzikalaki, E.; Kalkavouras, P.; Daskalakis, N.; Myriokefalitakis, S.; Bougiatioti, A.; Manninen, H.E.; et al. Formation and Growth of Atmospheric Nanoparticles in the Eastern Mediterranean: Results from Long-Term Measurements and Process Simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2671–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lelieveld, J.; Berresheim, H.; Borrmann, S.; Crutzen, P.J.; Dentener, F.J.; Fischer, H.; Feichter, J.; Flatau, P.J.; Heland, J.; Holzinger, R.; et al. Global Air Pollution Crossroads over the Mediterranean. Science 2002, 298, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampfl, M.; Mair, S.; Mayer, F.; Sedlbauer, K.; Breuer, K.; Niessner, R. Determination of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amines in Air by Direct or Diffusion Sampling Followed by Determination with Liquid Chromatography and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.P.; Chan, C.K. Displacement of Ammonium from Aerosol Particles by Uptake of Triethylamine. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, J.A.; Heaton, K.J.; Johnston, M.V. Reactive Uptake of Trimethylamine into Ammonium Nitrate Particles. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 4840–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources of Atmospheric Aerosol from Long-Term Measurements (5 years) of Chemical Composition in Athens, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Maso, M.; Kulmala, M.; Riipinen, I.; Wagner, R. Formation and Growth of Fresh Atmospheric Aerosols: Eight Years of Aerosol Size Distribution Data from SMEAR II, Hyytiälä, Finland. Boreal Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sciare, J.; d’Argouges, O.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Gaimoz, C.; Dolgorouky, C.; Bonnaire, N.; Favez, O.; Bonsang, B.; Gros, V. Large Contribution of Water-Insoluble Secondary Organic Aerosols in the Region of Paris (France) during Wintertime. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D22203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sintermann, J.; Neftel, A. Ideas and Perspectives: On the Emission of Amines from Terrestrial Vegetation in the Context of New Atmospheric Particle Formation. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 3225–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Mapping Gaseous Amines, Ammonia, and Their Particulate Counterparts in Marine Atmospheres of China’s Marginal Seas: Part 1—Differentiating Marine Emission from Continental Transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021, 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Weschler, C.J.; Bekö, G.; Wargocki, P.; Lucic, G.; Williams, J. Human Ammonia Emission Rates under Various Indoor Environmental Conditions. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the International Society of Indoor Air Quality & Climate (Indoor Air 2020), Online, 1–4 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke, P.; Schleibinger, H. Indoor Air Pollution, The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 64, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, O.; Skjøth, C.; Reis, S.; Bleeker, A.; Harrison, R.; Cape, J.N.; Fowler, D.; Skiba, U.; Simpson, D.; Jickells, T.; et al. Governing Processes for Reactive Nitrogen Compounds in the European Atmosphere. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 4921–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Draxler, R.; Hess, G. An Overview of the HYSPLIT_4 Modeling System for Trajectories, Dispersion, and Deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]


| DMA+EA | TMA | DEA | TEA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 124 | 124 | 124 | 124 |
| Number of samples above LOD | 80 | 84 | 54 | 13 |
| Average (pptv) | 7.8 ± 12.0 | 7.5 ± 12.4 | 1.1 ± 3.5 | 0.6 ± 0.4 |
| LOD (pptv) | 1.7 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Maximum value (pptv) | 78.0 | 69.5 | 37.5 | 3.1 |
| Author | Place | Type | Period | M | DMA+EA | TMA | DEA | TEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akyüz et al. [27] | Zonguldak, Turkey | Urban | May–Sep. 2004–2005 | M1 | 2.18 a,b | 0.83 a | ||
| Akyüz et al. [27] | Zonguldak, Turkey | Urban | Oct.–Apr. 2005–2006 | M1 | 2.96 a,b | 0.62 a | ||
| Akyüz et al. [28] | Zonguldak, Turkey | Urban | May–Sep. 2006–2007 | M1 | 1.77 ± 0.99 a,b | 1.62 ± 0.77 a | ||
| Akyüz et al. [28] | Zonguldak, Turkey | Urban | Oct.–Apr. 2006–2007 | M1 | 3.37 ± 2.01 a,b | 2.88 ± 1.63 a | ||
| Freshour et al. [33] | DE, USA | Coastal | July–Aug. 2012 | M2 | 28 | 6 c | 3 | 2 |
| Freshour et al. [33] | OK, USA | Continental | Apr.–May 2013 | M2 | 14 | 35 c | 150 | 20 |
| Hanson et al. [32] | GA, USA | Urban | July–Aug. 2009 | M2 | 0.5–2 | 4–15 c | ~4 | 3–25 |
| Hellén et al. [25] | Helsinki, Finland | Urban | May–Aug. 2011 | M3 | 23.6 | 8.4 c | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Hemmilä et al. [38] | Hyytiälä, Finland | Boreal forest | Mar.–Dec. 2015 d | M4 | <LOD-8.2 b | <LOD-6.1 | ||
| Kieloaho et al. [24] | Hyytiälä, Finland | Boreal forest | May–Oct. 2011 | M3 | 42 ± 30 | 21 ± 23 c | 6.5 ± 5.6 | <3.2 |
| Kürten et al. [35] | Viebrunn, Germany | Agricultural | May–June 2014 | M5 | ~1 | 1–5 c | 1–5 | 1–5 |
| Sellegri et al. [29] | Hyytiälä, Finland | Boreal forest | March 2002 | M6 | <LOD | 34–80 | ||
| Sipilä et al. [34] | Hyytiälä, Finland | Boreal forest | May–June 2013 | M5 | <0.15 b | |||
| VandenBoer et al. [40] | Toronto, Canada | Urban | June–July 2009 | M7 | <2.7 | <2.7 e | <1.0 | |
| VandenBoer et al. [39] | Egbert, Canada | Rural (agricultural) | Oct. 2010 | M7 | 6.5 ± 2.1 | ~1 e | ||
| Van Neste et al. [13] | Oahu, Hawaii | Coastal | July–Aug. 1985 | M8 | <0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | ||
| Yao et al. [37] | Shangai, China | Urban | July–Aug. 2015 | M9 | 40 ± 14.3 | 1.1 ± 0.6 c | 15.4 ± 7.9 | 3.5 ± 2.2 |
| You et al. [30] | AL, USA | Rural forest | June–July 2013 | M6 | <4.8 | 1–10 c | <23.1 | <13.0 |
| You et al. [30] | OH, USA | Μoderated polluted | June–July 2013 | M6 | <4.8 | 5–10 | 10–50 | <13.0 |
| Yu and Lee [31] | OH, USA | Suburban | Nov. 2011 | M6 | 8 ± 3 | 16 ± 7 c | <41 | <8 |
| Zheng et al. [36] | Nanjing, China | Industrialized | Aug.–Sep. 2012 | M9 | 0.1–29.9 | 0.1–9.3 c | ||
| This study | Finokalia, Crete | Coastal | 2013–2016 | M3 | 7.8 ± 12.0 LOD-78.0 | 7.5 ± 12.4 LOD-69.5 | 1.1 ± 3.5 LOD-37.5 | 0.6 ± 0.4 LOD-3.1 |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMA+EA | −0.780 | ||||
| TMA | −0.694 | ||||
| DEA | −0.823 | ||||
| TEA | −0.732 | ||||
| Na+ | −0.883 | ||||
| NH4+ | −0.729 | ||||
| Mg++ | −0.965 | ||||
| Cl− | −0.929 | ||||
| NO3− | |||||
| SO42− | −0.904 | ||||
| NH3 | −0.795 | ||||
| Black Carbon fossil fuel | −0.812 | ||||
| Black Carbon wood burning | 0.972 | ||||
| Variance explained | 26.3 | 16.7 | 13.2 | 11.4 | 8.1 |
| DMA | EA | TMA | DEA | TEA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (K) | 295–298 | 295–298 | 295–298 | 298 | 298 |
| Reaction Rate (cm3/molecules/s) | (6.49–7.10) ×10−11 | (2.38–2.77) ×10−11 | (3.58–6.09) ×10−11 | (7.40–11.9) ×10−11 | 7.70 ×10−11 |
| Lifetime (h) | 4.3 | 10–11.7 | 4.6–7 | 2.3–3.4 | 3.0 |
| Air Mass Origin | n | DMA+EA | TMA | DEA | TEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed | 25 | 4.2 (2.9) | 5.7 (7.4) | 0.8 (1.3) | 0.6 (0.3) |
| N | 33 | 11.2 (17.3) | 8.7 (14.5) | 0.8 (1.1) | 0.6 (0.3) |
| NE | 34 | 7.0 (11.9) | 7.3 (13.2) | 1.6 (6.4) | 0.6 (0.1) |
| NW | 12 | 10.0 (11.8) | 11.3 (18.0) | 1.3 (2.0) | 0.9 (0.8) |
| SW | 10 | 7.9 (9.2) | 5.7 (9.2) | 0.9 (1.1) | 0.8 (0.7) |
| W | 9 | 5.6 (6.5) | 5.6 (6.5) | 1.1 (1.8) | 0.5 (0.0) |
| E | 1 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tzitzikalaki, E.; Kalivitis, N.; Kanakidou, M. Observations of Gas-Phase Alkylamines at a Coastal Site in the East Mediterranean Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111454
Tzitzikalaki E, Kalivitis N, Kanakidou M. Observations of Gas-Phase Alkylamines at a Coastal Site in the East Mediterranean Atmosphere. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(11):1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111454
Chicago/Turabian StyleTzitzikalaki, Evangelia, Nikos Kalivitis, and Maria Kanakidou. 2021. "Observations of Gas-Phase Alkylamines at a Coastal Site in the East Mediterranean Atmosphere" Atmosphere 12, no. 11: 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111454
APA StyleTzitzikalaki, E., Kalivitis, N., & Kanakidou, M. (2021). Observations of Gas-Phase Alkylamines at a Coastal Site in the East Mediterranean Atmosphere. Atmosphere, 12(11), 1454. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111454





