Association of Diurnal Rainfall in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau with the Retreat of the South Asian High
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources
3. Results
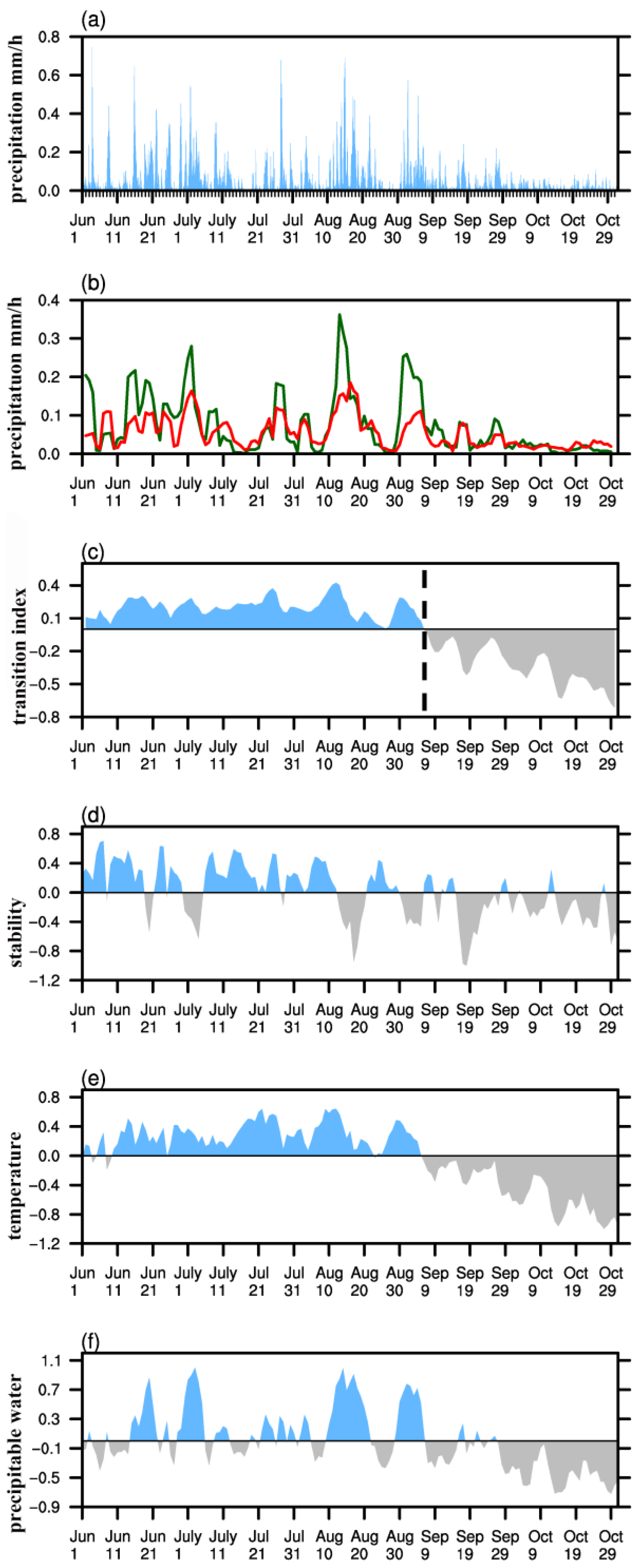
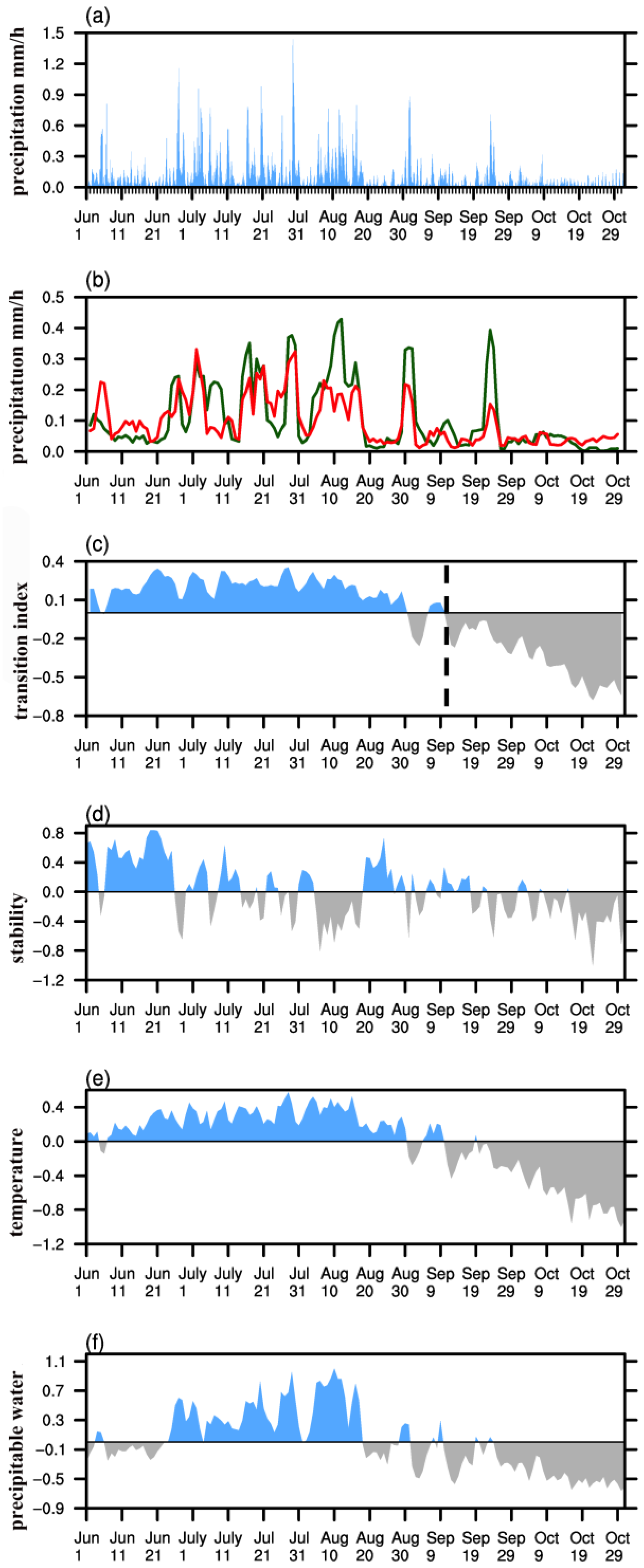
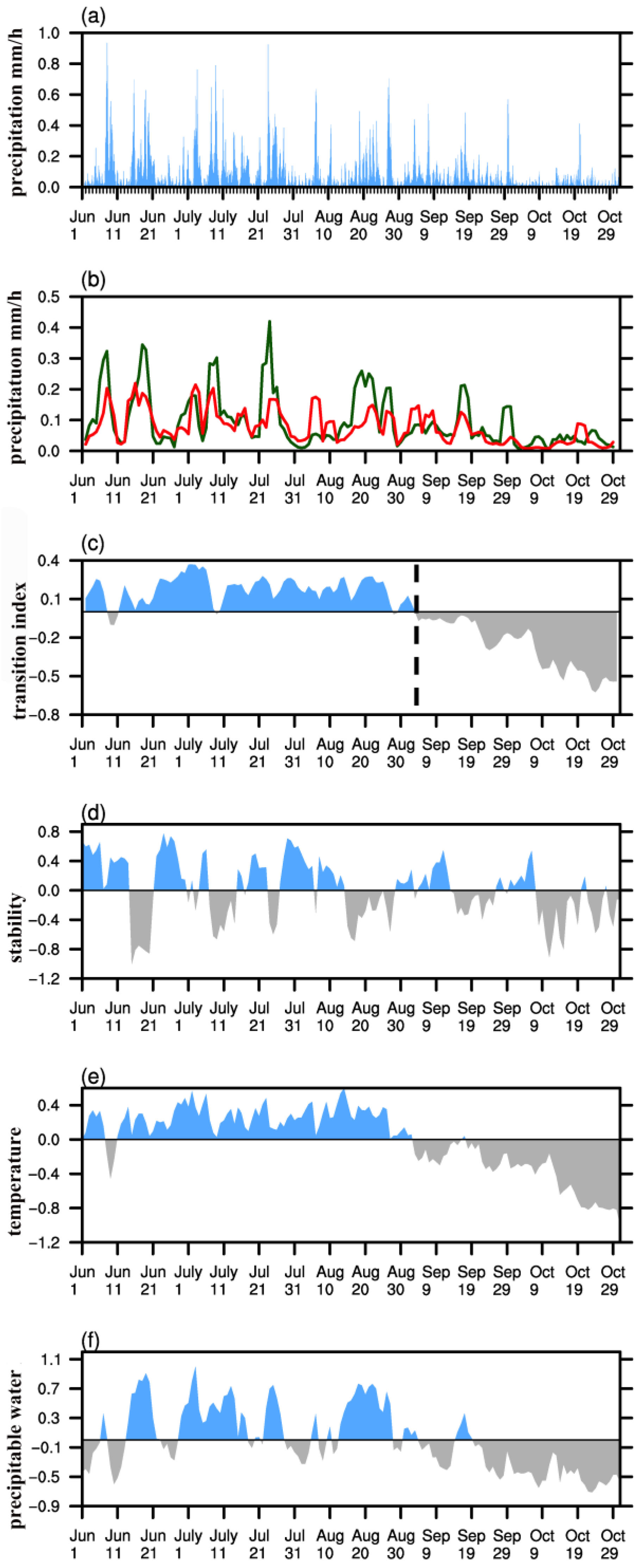
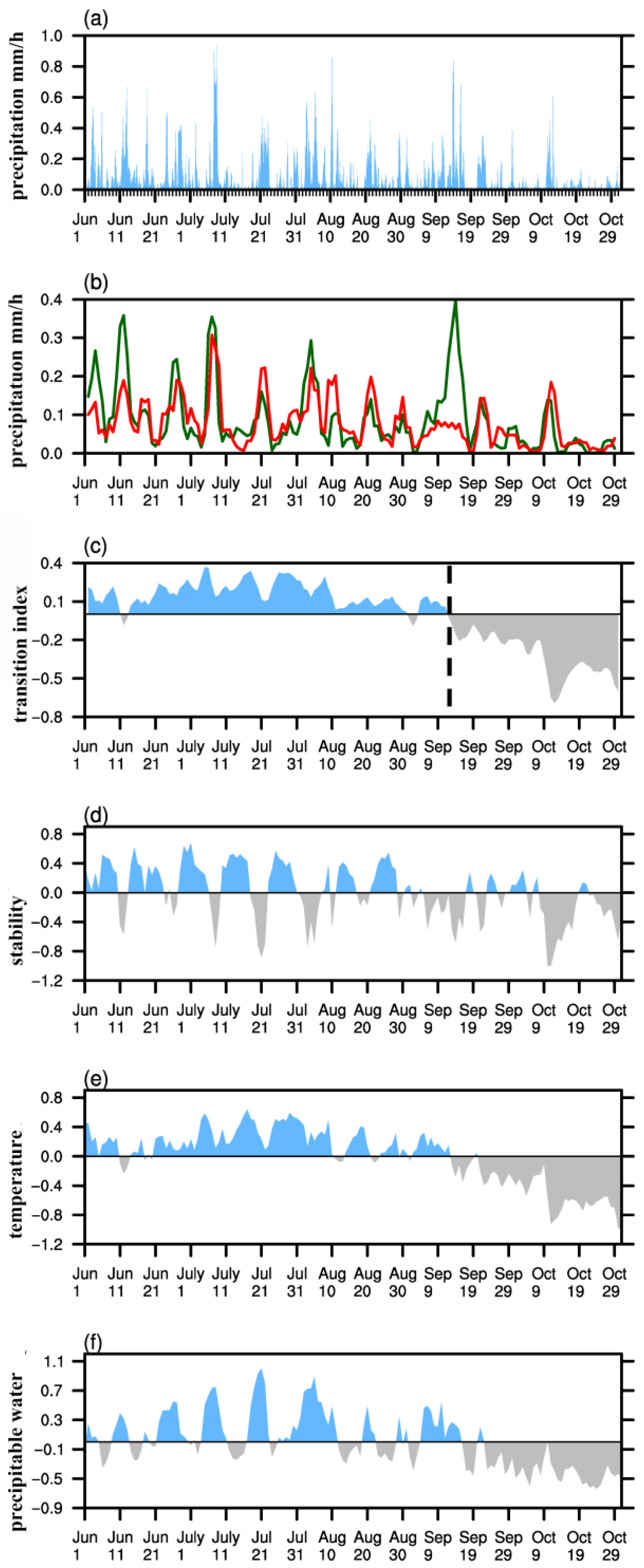
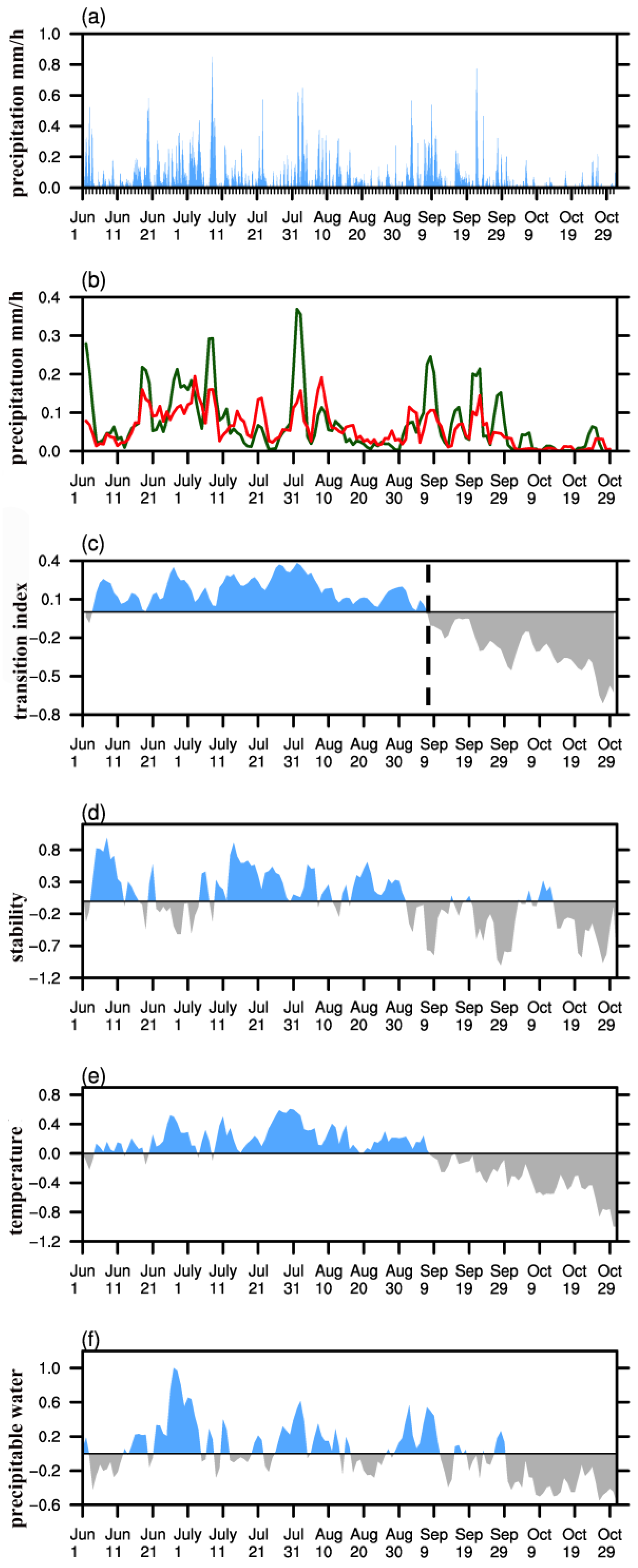
3.1. Warm Season Rainfall Patterns over the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau
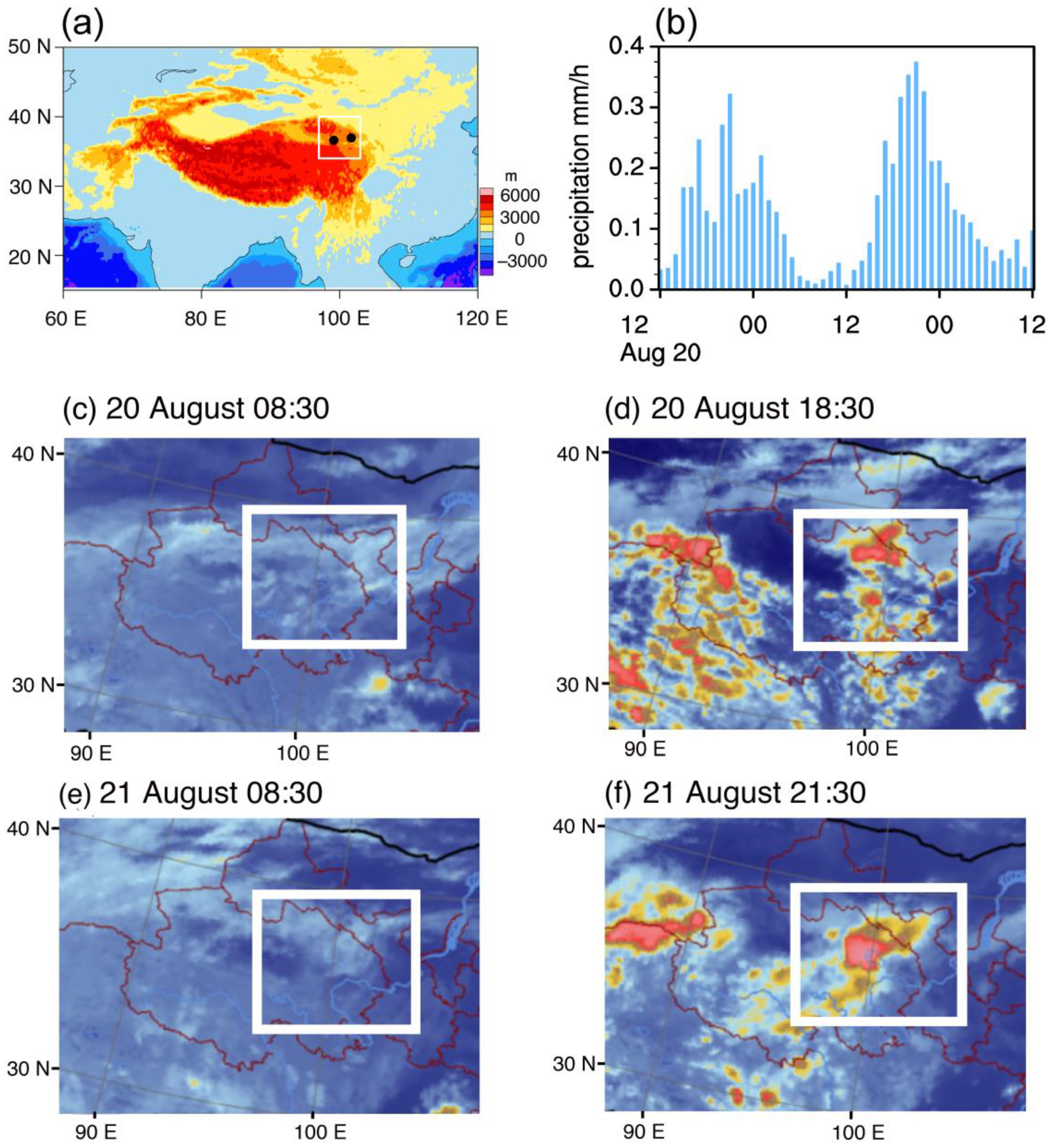
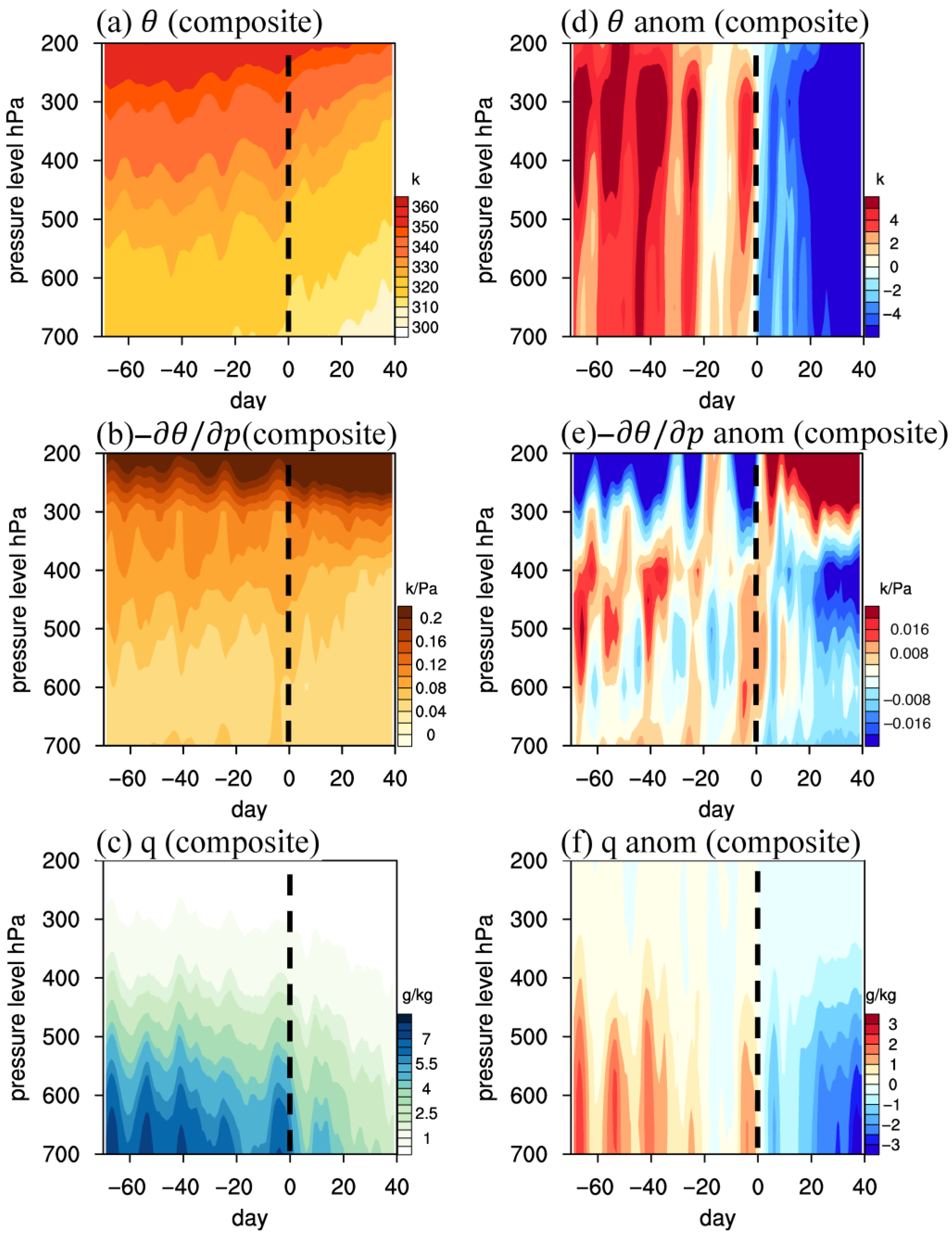
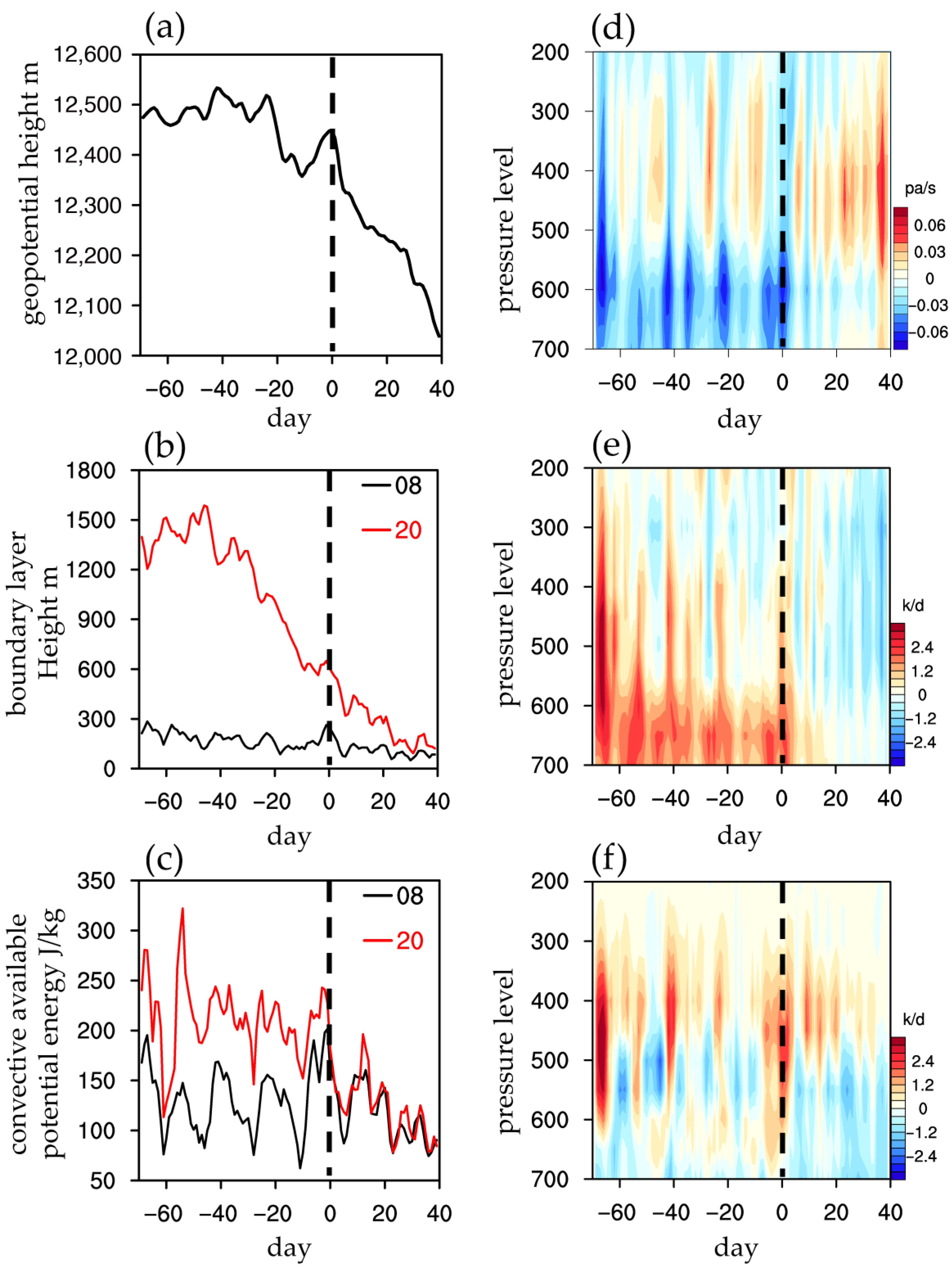
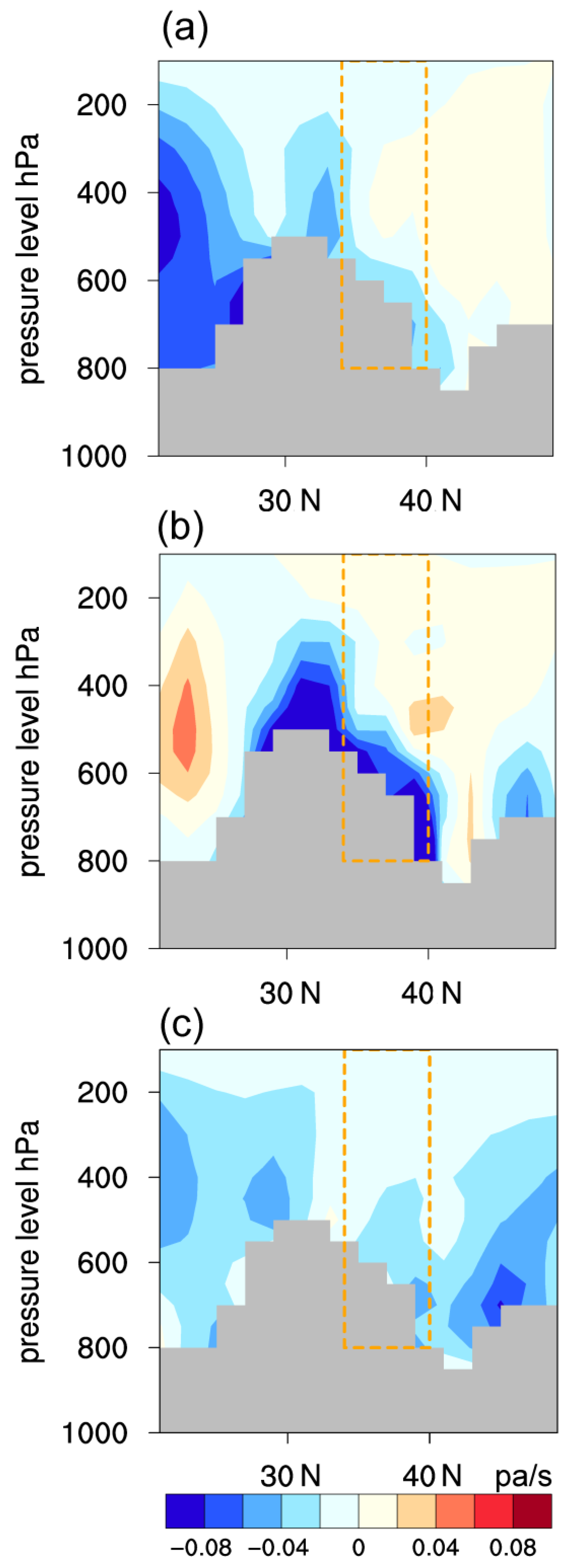
3.2. Atmospheric Circulation Associated with Increased Precipitation
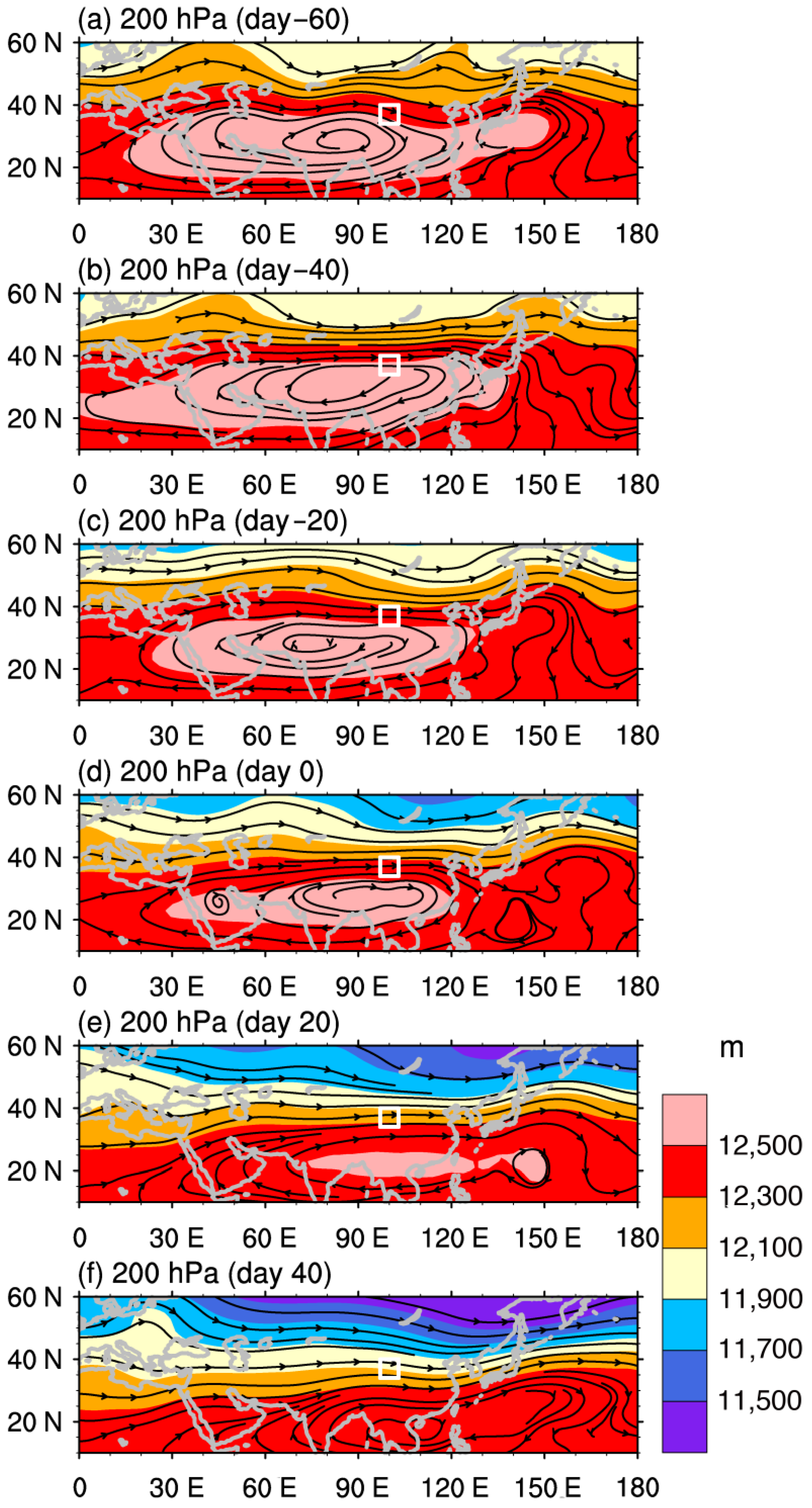
3.3. Relationship with the South Asian High
4. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Carbone, R.; Tuttle, J. Rainfall occurrence in the US warm season: The diurnal cycle. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 4132–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-R.; Wang, S.-Y. Impact of land-sea breezes at different scales on the diurnal rainfall in Taiwan. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, A.; Liu, C. Diurnal variations of summertime precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau in relation to orographically-induced regional circulations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, S.W.; Zipser, E.J. The diurnal cycle of rainfall and convective intensity according to three years of TRMM measurements. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1456–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Chia, H.-H.; Gillies, R.R.; Jiang, X. Quasi-biweekly mode and its modulation on the diurnal rainfall in Taiwan forecasted by the CFS. Weather Forecast. 2013, 28, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zipser, E.J. Diurnal variations of precipitation, deep convection, and lightning over and east of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Smith, E.A. Mechanisms for diurnal variability of global tropical rainfall observed from TRMM. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5190–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, F.; Sun, J. Diurnal variations of warm-season precipitation east of the Tibetan Plateau over China. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 2790–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Chen, G.T.-J.; Carbone, R.E. A climatology of warm-season cloud patterns over East Asia based on GMS infrared brightness temperature observations. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1606–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, S.; Ueno, K. Formation of mesoscale convective systems over the eastern Tibetan Plateau affected by plateau-scale heating contrasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wu, G.; Mao, J.; He, J. Genesis of the South Asian high and its impact on the Asian summer monsoon onset. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2976–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. Remotely modulated tropical-North Pacific ocean–atmosphere interactions by the South Asian high. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, R. Interannual and interdecadal variations of the South Asian and western Pacific subtropical highs and their relationships with Asian-Pacific summer climate. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2011, 113, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiong, Z.; Wu, G. The large area flood and drought over Yangtze River valley and its relation to the south Asia high. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2001, 59, 569–577. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.-Q. Characteristics and mechanisms of the subseasonal eastward extension of the South Asian High. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 6799–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Qian, Z.; Wang, Q. The climatic and synoptical study about the relation between the Qinghai–Xizang high pressure on the 100 mb surface and the flood and drought in East China in summer. Plateau Meteorol. 1982, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M.; Rong, X.; Li, T. Impact of Indian summer monsoon on the South Asian High and its influence on summer rainfall over China. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M.; Kim, B.-J.; Nam, J.-C. Interannual variation of the South Asian High and its relation with Indian and East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.; Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Dokken, D.J.; Ebi, K.L.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Mach, K.J.; Plattner, G.K.; Allen, S.K.; et al. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, A.; Xiao, Z. Does the climate warming hiatus exist over the Tibetan Plateau? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, J.C.; Meehl, G.A.; England, M.H.; Mann, M.E.; Santer, B.D.; Flato, G.M.; Hawkins, E.; Gillett, N.P.; Xie, S.P.; Kosaka, Y.; et al. Making sense of the early-2000s warming slowdown. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Pal, J.S.; Giorgi, F. Projected changes in mean and extreme precipitation over the Mediterranean region from a high resolution double nested RCM simulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L03706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Peng, W.; Kang, H.-S.; Waliser, D. Assessment of dynamic downscaling of the extreme rainfall over East Asia using a regional climate model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1077–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L. Observed trends in extreme precipitation events in China during 1961–2001 and the associated changes in large-scale circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L09707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hao, X.; Shao, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Multi-model ensemble projections in temperature and precipitation extremes of the Tibetan Plateau in the 21st century. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 80, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, Z. Quality assessment of hourly merged precipitation product over China. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 36, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, W.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Xue, J.; Wang, Z. Sensible Heat Driven Air-Pump over the Tibetan Plateau and its Impacts on the Asian Summer Monsoon; Chinese Science Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, A.; Wang, T.; Wan, R.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X. The influence of mechanical and thermal forcing by the Tibetan Plateau on Asian climate. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Yang, M.; Wang, H. Sensible and latent heat flux response to diurnal variation in soil surface temperature and moisture under different freeze/thaw soil conditions in the seasonal frozen soil region of the central Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Fan, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Tsukamoto, O.; Yao, T.; Koike, T.; Zuo, H.; Hu, Z.; Su, Z. Diurnal and inter-monthly variation of land surface heat fluxes over the central Tibetan Plateau area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2005, 80, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, Z.L.; Škerlak, B.; Kim, S.W.; Lauer, A.; Mues, A.; Rupakheti, M.; Kang, S. Atmospheric brown clouds reach the Tibetan Plateau by crossing the Himalayas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6007–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Tang, S.; Xiao, W.; Shi, C.; Ma, Y.; Yu, X.; et al. The Tibetan Plateau Surface-Atmosphere Coupling System and Its Weather and Climate Effects: The Third Tibetan Plateau Atmospheric Science Experiment. J. Meteorol. Res.-Prc. 2019, 33, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhou, L.; Ma, S.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Li, A.; Jia, J.; Gao, D. Local wind system in the Rongbuk Valley on the northern slope of Mt. Everest. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.C.; Chan, J.C. Diurnal variations of circulation and precipitation in the vicinity of the Tibetan Plateau in early summer. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 32, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qian, Z. The comparative analyses of differences between vertical circulation on north side of Tibetan Plateau in wet and dry summer and thermal effects of the plateau. Acta Meteoro. Sin. 1996, 54, 558–568. [Google Scholar]
- Yanai, M.; Esbensen, S.; Chu, J.H. Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large-scale heat and moisture budgets. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, G.; Qian, Y. The bimodality of the 100 hPa South Asia High and its relationship to the climate anomaly over East Asia in summer. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn Ser. II 2002, 80, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; He, B.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Q.; Ren, R. Location and variation of the summertime upper-troposphere temperature maximum over South Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; You, Q.; Zhang, Y. The influence of the Asian summer monsoon onset on the northward movement of the South Asian high towards the Tibetan Plateau and its thermodynamic mechanism. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, R.; Luan, L.; Lyu, S.; Zhang, T.; Ao, Y.; Han, B.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y. Detecting hydrological consistency between soil moisture and precipitation and changes of soil moisture in summer over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 4157–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, C.R.; Wood, E.F. Observed land-atmosphere coupling from satellite remote sensing and reanalysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1221–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Guo, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; La, Z.; Peng, H.; et al. The Third Atmospheric Scientific Experiment for Understanding the Earth-Atmosphere Coupled System over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Effects. Bull. Am. 2018, 99, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Wu, C.-H.; Los, S.; Lyu, S.; Meng, X.; Wen, L.; Luo, S.; Ao, Y.; Li, Z. Association of Diurnal Rainfall in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau with the Retreat of the South Asian High. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010105
Zhao L, Wang S-YS, Wu C-H, Los S, Lyu S, Meng X, Wen L, Luo S, Ao Y, Li Z. Association of Diurnal Rainfall in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau with the Retreat of the South Asian High. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lin, S.-Y. Simon Wang, Chi-Hua Wu, Sebastian Los, Shihua Lyu, Xianhong Meng, Lijuan Wen, Siqiong Luo, Yinhuan Ao, and Zhaoguo Li. 2020. "Association of Diurnal Rainfall in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau with the Retreat of the South Asian High" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010105
APA StyleZhao, L., Wang, S.-Y. S., Wu, C.-H., Los, S., Lyu, S., Meng, X., Wen, L., Luo, S., Ao, Y., & Li, Z. (2020). Association of Diurnal Rainfall in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau with the Retreat of the South Asian High. Atmosphere, 11(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010105





