Abstract
The 14-3-3 family of proteins performs key regulatory functions in phosphorylation-dependent signaling pathways including cell survival and proliferation, apoptosis, regulation of chromatin structure and autophagy. In this study, the zeta isoform of 14-3-3 proteins (designated as Tm14-3-3ζ) was identified from the expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) database of the coleopteran pest, Tenebrio molitor. Tm14-3-3ζ messenger RNA (mRNA) is expressed at higher levels in the immune organs of the larval and adult stages of the insect and exhibit almost five-fold induction within 3 h post-infection of the larvae with Escherichia coli and Candida albicans. To investigate the biological function of Tm14-3-3ζ, a peptide-based Tm14-3-3ζ polyclonal antibody was generated in rabbit and the specificity was confirmed using Western blot analysis. Immunostaining and confocal microscopic analyses indicate that Tm14-3-3ζ is mainly expressed in the membranes of midgut epithelial cells, the nuclei of fat body and the cytosol of hemocytes. Gene silencing of Tm14-3-3ζ increases mortality of the larvae at 7 days post-infection with E. coli and C. albicans. Our findings demonstrate that 14-3-3ζ in T. molitor is essential in the host defense mechanisms against bacteria and fungi.
1. Introduction
The 14-3-3 family constitutes a highly conserved group of eukaryotic proteins that play a pivotal role in the regulation of cell survival, apoptosis and signal transduction [1,2,3]. They bind to a functionally wide array of cellular proteins that include kinases, phosphatases, receptors, structural proteins and transcription factors [4,5,6]. In fact, over 200 target ligands of 14-3-3 proteins are known and the binding of 14-3-3 proteins to their ligands is facilitated by the consensus phosphoserine or threonine containing 14-3-3 binding motifs in the amino acid sequence of the protein [7,8]. The binding, in turn, affects interaction of the ligand with other proteins, largely due to the conformational alteration of the ligand [9]. Previous reports show that a deletion of 14-3-3 isoform results in loss of viability in yeast [7,10]. Similarly, loss of Drosophila 14-3-3ζ leads to impaired viability of the embryo even in the presence of a functional 14-3-3ε isoform [11]. Studies in mammalian models of disease have shown the association of 14-3-3ζ proteins with epilepsy development and other neurological conditions such as seizures [12,13].
Since their initial discovery, 14-3-3 family members have been reported from both vertebrates and invertebrates. The number of 14-3-3 encoding genes varies, with only one gene reported from the lower eukaryote, Candida albicans [10], seven genes encoding seven distinct isoforms (β, ε, γ, η, ζ, θ and σ) from most mammals and up to thirteen genes in Arabidopsis thaliana [14]. A pair of 14-3-3 genes (isoforms ζ and ε), have been identified in insects including Drosophila melanogaster [15], Bombyx mori [16] and Anopheles mosquitoes [17,18]. The 14-3-3ζ protein shows a ubiquitous expression pattern in the tissues during the developmental stages of B. mori [19,20]. Recently, a 14-3-3ζ homolog has been characterized from the Indian meal moth, Plodia interpunctella, a very common household pest feeding principally on stored food products [21]. Earlier studies have focused on the role of 14-3-3ζ in the regulation of immune signaling in insects such as Antheraea pernyi, B. mori, Heliothis virescens, Spodoptera litura and D. melanogaster [22,23,24]. It has also been suggested that 14-3-3ζ is required in the regulation of developmental autophagy and diapause processes in insects [25].
The coleopteran insect—Tenebrio molitor—has been extensively studied for immune genes and signaling mechanisms including the extracellular and intracellular components of Toll signaling cascades [26,27,28,29], immune deficiency (imd) pathway [30], other regulatory genes such as CD63 [31], R-type lectin [32], apolipophorin-III [33], 14-3-3 epsilon [34] and autophagy signaling genes [35,36]. In the present study, we identified the ζ isoform of 14-3-3 gene (Tm14-3-3ζ) from T. molitor expressed sequence tag (EST) and RNA sequencing database and characterized the full-length complementary DNA (cDNA) and protein sequence using in silico tools. Furthermore, we generated a peptide-based Tm14-3-3ζ polyclonal antiserum from rabbit and confirmed its specificity with the recombinant Tm14-3-3ζ protein (rTm14-3-3ζ). We used the antiserum to analyze the subcellular localization of Tm14-3-3ζ in T. molitor larvae. We then analyzed the putative role of Tm14-3-3ζ in innate immune response by silencing the Tm14-3-3ζ transcript in the larvae of the host insect by exogenous double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) treatment. Taken together, our results demonstrated the requirement of Tm14-3-3ζ in innate immune response against Escherichia coli and C. albicans in T. molitor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
Tenebrio molitor larvae were collected from Pusan National University, Pusan, South Korea and reared on an artificial diet (4.4 g NeoVita, 0.5 g Chloramphenicol, 0.4 g Ascorbic Acid, 0.5 g Sorbic Acid, 0.5 mL Propionic Acid, 2.2 g Yeast dry powder, 2.2 g Bean powder, 7.6 g Agar, 4.4 g Wheat powder, 73.3 g Wheat bran, in 200 mL of distilled water) sterilized at 121 °C for 15 min. The reared larvae were maintained at 26 ± 1 °C and 60 ± 5% relative humidity in dark conditions.
2.2. Microbial Cultures and Bioassays
The E. coli K12 and C. albicans cultures were used in the infection and bioassay experiments. Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and Sabouraud Dextrose broth (BD Biosciences) were used to culture E. coli and C. albicans, respectively. For all experiments, overnight cultures at 37 °C were harvested, washed twice and re-suspended in phosphate buffered saline medium (1X PBS; 130 mM NaCl, 7 mM Na2HPO4, 3 mM NaH2PO4·H2O; pH 7.2) by centrifugation (Hanil science co., Ltd, Daejeon City, Korea) at 3500 rpm for 10 min. The cultures were serially diluted to attain a final concentration of 109 colony-forming unit (CFU)/ml and 5 × 107 CFU/ml for E. coli and C. albicans, respectively.
For immune challenge experiments, 1 µL of culture suspension equivalent to 106 CFU/Larva for E. coli or 5 × 104 CFU/Larva for C. albicans were microinjected into healthy T. molitor larvae using a Picospritzer III micro-dispense system (Parker, Hollis, NH, USA). PBS (1 µL volume) was injected into a separate group of T. molitor larvae as an injection control.
2.3. Isolation of Tm14-3-3ζ Full-Length Complementary DNA Sequence
A partial cDNA sequence of Tm14-3-3ζ was screened from T. molitor EST and RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) database. For the amplification of full-length cDNA sequence of Tm14-3-3ζ, gene-specific oligonucleotides were designed using Primer 3.0 software (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3-0.4.0/) (Table 1). The 5′- and 3′-RACE-ready cDNAs were synthesized from 1 µg of total RNA using SMARTer rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) amplification kit (Clontech Laboratories, CA, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed at 94 °C for 30 s (denaturation), 55 °C for 30 s (annealing) and 72 °C for 30 s (extension) for 30 cycles. The gene-specific primer and the nested primer sequences have been enlisted in Table 1. The PCR products were purified using the AccuPrep PCR purification kit (Bioneer, Daejeon, Korea), cloned into TOPO TA cloning vector (Invitrogen Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and subsequently transformed into the competent E. coli (DH5α strain) cells.

Table 1.
The primers used in this study.
2.4. Protein Domain and Phylogenetic Analysis
The structural domains of Tm14-3-3ζ were predicted using InterProScan (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence-search) and Simple modular Architecture research tool (SMART) version 7.0) [37]. Using the SMART screen page, protein family (PFAM) domains, signal peptides and internal repeats were validated. The amino acid sequences of 14-3-3ζ proteins from various insect species were retrieved from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) and percentage identity analysis were done using ClustalX software [38]. The distance analysis and the construction of phylogenetic tree were performed using the maximum-likelihood method (JTT matrix model) using the MEGA 6 software [39]. The GenBank accession numbers of 14-3-3ζ amino acid sequences are provided in Table S1.
2.5. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
Relative quantification of mRNA transcripts was conducted by RT-PCR and analyzed by the comparative CT method. Total RNAs were isolated from the different developmental stages and larval/adult tissues of the insect using the TRIZOL reagent method (Favorgen Biotech Corp., Pingtung County, Taiwan). Then cDNAs were synthesized with 2 µg of total RNAs using AccuPower® RT Pre-Mix (Bioneer) and oligo (dT)12–18 primer on a C1000 Touch PCR machine (Bio-Rad, USA). Signals were detected using the gene-specific primers listed in Table 1 and AccuPower® 2X green star quantitative PCR (qPCR) master mix (Bioneer) by Exicycler 96 RT-PCR machine (Bioneer). PCR conditions were as follows: An initial denaturation of 95 °C for 20 s followed by 40 cycles at 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 20 s. 60S ribosomal protein L27a gene from T. molitor (TmL27a) was used as an internal control.
2.6. Generation of Peptide-Based Tm14-3-3ζ Antiserum and Reactivity Studies
A 16-mer peptide (N-SDTQGEADEPQETGDN-C) from the C-terminal part of Tm14-3-3ζ was designed and synthesized (Ab Frontier Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea). A cysteine residue was added to the C-terminus of the peptide for conjugation to carrier protein. The peptide was conjugated to Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) separately, using Maleimidobenzoyl-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (MBS). The peptide-KLH was used for immunization of rabbit and peptide-BSA was used for testing the specificity of the antibody.
The specificity of the peptide-based Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum was examined with the whole-body lysate of last instar T. molitor larvae and the bacterial lysate induced by isopropyl β-D-1- thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) using Western blot analysis. Samples were homogenized in 1X phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 13,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C to remove the cell debris. The total protein concentration in the supernatant fraction was determined using the Bradford dye-binding method. Proteins were separated in 15% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) system and transferred onto a polyvinylidendifluoride (PVDF) membrane. The PVDF membrane was blocked for 1 h in 5% non-fat milk in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) containing 0.1% Tween 20 (TBST; 10 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% Tween 20, pH 7.5), followed by an incubation of 3 h with anti-Tm14-3-3ζ rabbit serum (1:5000 in blocking buffer). The membrane was then washed six times for 10 min each in large volumes of wash buffer (TBST). The washed membrane was incubated in alkaline-phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) for 1 h and visualized using a nitro blue tetrazolium/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-phosphate (NBT/BCIP) solution. Anti-His-monoclonal antibody (Applied Biological Materials Inc., Richmond, British Columbia, Canada) was used as a positive control to detect the His-tagged rTm14-3-3ζ.
2.7. Subcellular Localization of Tm14-3-3ζ by Immunofluorescence
The tissues from the last-instar larvae of T. molitor such as gut, fat body, Malpighian tubules and hemocytes were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 1X PBS, pH 7.4 for 12 h at 4 °C. The fixed tissues were rinsed in 1X PBS, followed by incubation in a sucrose gradient (12–20% sucrose in PBS). Samples were embedded into FSC22 clear resin (Leica Biosystems, Wetzlar, Germany) and cryosectioned with Leica CM1850 cryostat (Leica Biosystems). The cryosections were blocked for 1 h with 2% BSA in 1X PBS containing 0.2% Tween 20 (PBST). Subsequently, the sections were incubated in Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum (diluted 1:300 in blocking buffer) for 3 h. After three washes (5 min each) with PBST, cells were incubated for 1 h with Alexa Flour 488 dye-conjugated secondary antibody (1:300 dilution in PBST). The nucleus and the actin molecules were detected by TO-PRO-3 iodide (1:300 dilution in PBST) and Alexa Flour 568 Phalloidin (1:300 dilution in PBST), respectively. The samples were mounted with Dako Cytomation fluorescent mounting medium (Dako, Carpentaria, CA, USA). Sub-cellular localization of Tm14-3-3ζ was recorded using a Fluoview 500 Confocal microscopic system (Olympus, Ina, Japan).
2.8. Double Stranded RNA Treatment and Gene Silencing
To synthesize dsRNA for Tm14-3-3ζ, specific primers conjugated with T7 promoter sequences were designed using the Snapdragon dsRNA design software [40,41]. The primer sequences are available in Table 1. Enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) dsRNA was synthesized from pEGFP-C1 plasmid vector (Clontech Laboratories, CA, USA) and injected as the negative control. Template cDNAs for dsTm14-3-3ζ synthesis were amplified by using ExTaq polymerase (Takara, kusatsu, Japan) with specific primers as described in Table 1. PCR products containing the T7 promoter sequences were purified using the AccuPrep PCR purification kit (Bioneer). dsTm14-3-3ζ was synthesized with 1 µg of purified PCR products using the Ampliscribe T7-flash transcription kit (Epicentre Biotechnologies, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). Synthesized dsRNAs were confirmed by electrophoresis on 1% agarose gels. For gene specific silencing, 1 µg of dsTm14-3-3ζ were injected into T. molitor larvae using Picospritzer III micro-dispense system (Parker). dsEGFP was injected as a negative control using the same concentration. Transcript levels of Tm14-3-3ζ were analyzed using real-time PCR.
2.9. Mortality Assay
The E. coli (1 × 106 cells per larva) or C. albicans (5 × 104 cells per larva) were injected into dsTm14-3-3ζ-treated T. molitor larvae. Mortality was monitored for seven days and expressed as percentage of dead larva per day per treatment. dsEGFP injected group for each pathogen was used as a negative control. Each injection group consisted of ten larvae and the experiment was conducted in triplicates.
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Tm14-3-3ζ Gene
The full-length cDNA of Tm14-3-3ζ was obtained using RT-PCR and RACE-PCR. The Tm14-3-3ζ cDNA comprised of 747 bp coding region flanked by 18 bp 5′-untranslated region (UTR) and a 387 bp 3′-UTR including the poly (A) tail. The deduced protein encoded by the coding region was 248 amino acids long (Figure 1). A putative polyadenylation signal (5′-ATTAAA-3′) was found 112 bp upstream of the poly (A) tail. No signal peptide was predicted in the N-terminus of the protein. Analysis of the amino acid sequence showed a 14-3-3 domain that includes the peptide binding residues (Leu-219, Ile-220, Leu-223, Asn-227, Leu-230 and Trp-231) and a nuclear export localization signal sequence (NLS) composed of thirteen amino acids (N-LIMQLLRDNLTLW-C). The full-length Tm14-3-3ζ sequence was deposited in GenBank under accession number KP099938.

Figure 1.
The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of Tm14-3-3ζ. The deduced protein sequence is shown below the nucleotide sequence. The complementary DNA (cDNA) sequence is numbered from the first base of the translation start codon and is shown in the 5′ to 3′ direction; (*) denotes the termination codon. The polyadenylation signal in 3′-Unstransleted region (UTR) is denoted in grey face. The conserved 14-3-3 domain is shaded. The direct peptide binding residues are boxed. The nuclear localization signal sequence (NLS) is shown underlined. The cDNA encodes a gene of 747 nucleotides in length and a protein of 248 amino acids in length. This sequence is submitted to the GenBank Data Bank with accession number KP099938.
3.2. Sequence Homology and Phylogenetic Analysis
The predicted amino acid sequence of Tm14-3-3ζ was found to be highly similar to other known insect 14-3-3ζ protein sequences. This was demonstrated by multiple sequence alignment of Tm14-3-3ζ amino acid sequence with NCBI retrieved sequences of other insect 14-3-3ζ proteins. The 14-3-3ζ homologues showed a high level of sequence conservation within the NLS motif of 14-3-3 domain (Figure S1A). The protein shared sequence identity that is higher than 90% with 14-3-3ζ proteins from other insect species. A sequence identity of 87% and 81% were detected with Ceratitis capitata and Homo sapiens Tm14-3-3ζ sequences, respectively. The percentage distance matrix showed a divergence of 5% to 14% in between Tm14-3-3ζ and other insect 14-3-3ζ proteins (Figure S1B). Furthermore, molecular taxonomical clustering of 14-3-3ζ proteins showed evolutionary relationships between Tm14-3-3ζ and other representative insect 14-3-3ζ proteins (Figure S1C). The phylogenetic tree showed the clustering of insect Tm14-3-3ζ proteins into their respective taxonomical orders. Importantly, Tm14-3-3ζ protein was found in a separate cluster with another coleopteran insect Tribolium castaneum 14-3-3ζ protein (Tc14-3-3ζ). The 14-3-3ζ proteins under the insect orders Coleoptera and Diptera form two major clusters with high bootstrap support. On the other hand, the 14-3-3ζ proteins representing Hemiptera and Lepidoptera orders showed a lower bootstrap strength. Human 14-3-3ζ (Hu14-3-3ζ) was considered as an outgroup and was used to assess the overall phylogenetic classification.
3.3. Developmental and Tissue Specific Expression Patterns of Tm14-3-3ζ
In order to study the expression pattern of Tm14-3-3ζ transcript in different developmental stages and tissues, qPCR analysis was conducted using specific primers (Table 1). TmL27a gene was used as an internal control for qPCR experiments. The developmental expression patterns of Tm14-3-3ζ was revealed using cDNAs synthesized from last instar larva, pre-pupa, pupa (pupal day 1 to day 7) and adult (day 1 and day 2). The qPCR analysis showed a consistent expression of Tm14-3-3ζ protein in all the developmental stages of the insect (Figure 2A). In addition, the tissue specificity of Tm14-3-3ζ was examined using cDNAs synthesized from gut, integument, fat body, Malpighian tubule and hemocytes isolated from last instar larva and 2-day old adults. The expression pattern of Tm14-3-3ζ was also analyzed in ovary and testis tissues isolated from 2-day old adults. In the last instar larval stage, higher expression of Tm14-3-3ζ was seen in the gut and Malpighian tubules whereas lower expression was found in the integument (Figure 2B). In 2-day old adult tissues, expression was highest in the ovaries followed by Malpighian tubules, hemocytes, gut and fat body (Figure 2C).

Figure 2.
Expression analysis of Tm14-3-3ζ messenger RNA (mRNA) during development and in larval and adult tissues of Tenebrio molitor. The expression patterns were measured using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) having synthesized cDNA samples as template. (A) Developmental expression patterns show the consistent expression of Tm14-3-3ζ in all stages of the life cycle; (B,C) Tissue specific expression patterns indicate higher expression of Tm14-3-3ζ in gut, Malpighian tubule and hemocytes of last instar larva (B) and Malpighian tubule and ovary of 2-day old adult (C). Abbreviations are as follows: T. molitor last instar larva (LL), Prepupa (PP), 1-day to 7-day old pupa (P1–P7) and 1-day and 2-day old adult (A1 and A2), integument (IT), fat body (FB), Malpighian tubule (MT), hemocyte (HC), ovary (OV) and testis (TE). TmL27a mRNA was used as an internal control. The results were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s multiple range tests at 95% confidence levels (p < 0.05). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences among groups.
3.4. Expression Analysis of Tm14-3-3ζ in Response to Microorganisms
In order to identify whether Tm14-3-3ζ transcripts can be induced by microorganisms, the T. molitor last instar larvae were challenged with Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli) and yeast (C. albicans) through systemic circulation using PBS as an injection control. The expression of Tm14-3-3ζ increased in last instar larvae 3 h post-infection with E. coli and C. albicans (Figure 3). After an immediate upregulation of Tm14-3-3ζ transcripts, sudden downregulation was noticed at 6, 9 and 12 h post-infection.

Figure 3.
Temporal expression analysis of Tm14-3-3ζ after Escherichia coli and Candida albicans challenge. E. coli and C. albicans were injected into T. molitor larvae and samples were collected at 3, 6, 9 and 12 h post-infection. Patterns of Tm14-3-3ζ expression was investigated, showing the dramatic increase in Tm14-3-3ζ expression at 3 h post-injection of microorganisms. Results of three biological replications are presented with standard errors.
3.5. Characterization of Polyclonal Antibody and Sub-Cellular Localization of Tm14-3-3ζ
We generated a peptide-based polyclonal antibody against Tm14-3-3ζ protein and studied its specificity with recombinant protein (rTm14-3-3ζ) using Western blot analysis. This was to study the specific immunoreactions of the polyclonal Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum against rTm14-3-3ζ and the endogenous form (Figure 4A). SDS-PAGE analysis of IPTG induced cell fractions showed a potential band corresponding to rTm14-3-3ζ. This band was found slightly higher in the separating gel compared to the endogenous form (Figure 4A-I). The rTm14-3-3ζ expressed by the IPTG-induced cells of E. coli (BL21-DE3 strain) was found reactive to anti-His tagged monoclonal antibody, used as the positive control (Figure 4A-II). Bands corresponding to rTm14-3-3ζ and the endogenous form of Tm14-3-3ζ were not detected in pre-immune blood, acting as the negative control (Figure 4A-III). The specificity of the Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum was validated by its ability to detect rTm14-3-3ζ as well as endogenous Tm14-3-3ζ in the protein extracts of the T. molitor whole body (Figure 4A-IV).

Figure 4.
Subcellular localization of 14-3-3ζ in tissues of late instar T. molitor larva using anti-Tm14-3-3ζ polyclonal antiserum. Production of anti-Tm14-3-3ζ polyclonal antibody and its specificity with recombinant Tm14-3-3ζ (rTm14-3-3ζ). (A-I) Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) characterization of protein profiles in non-induced, isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) induced E. coli homogenate and late instar larval whole-body homogenate; (A-II) The detection of rTm14-3-3ζ using His-Tag monoclonal antibody; (A-III) Western blot with pre-immune blood used as negative control; (A-IV) Western blot for the detection of rTm14-3-3ζ and endogenous Tm14-3-3ζ using anti-Tm14-3-3ζ polyclonal antibody. C, non-induced E. coli homogenate; I, IPTG induced E. coli homogenate; N, native T. molitor late instar larval whole-body homogenate. (B) Immunohistochemical localization of the 14-3-3ζ protein in midgut, fat body, Malpighian tubules and hemocyte of late instar T. molitor larva. Cryosections of the harvested, fixed and washed tissues were blocked for 1 h with 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing Tween-20 and incubated with rabbit anti-Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum (1:300) for 3 h at 4 °C. After washing, the samples were incubated in Alexa Fluor 488 dye-conjugated secondary antibody (1:300). The immunoreactivity (green signals) of Tm14-3-3ζ localization was analyzed by an Fluoview 500 confocal microscopic system (Olympus). TO-PRO-3 Iodide and Alexa fluor 568 phalloidin was used to detect the nuclei (blue signals) and the actin (red signals) molecules.
Subsequently, Tm14-3-3ζ polyclonal antibody and Alexa Flour 488 dye-conjugated secondary antibody were used to examine the localization of Tm14-3-3ζ in the gut, fat body, Malpighian tubules and hemocytes of last instar larva. The immunohistochemical analysis was performed using a confocal microscope (Figure 4B). Tm14-3-3ζ signal was found detected in the membrane and cytosol of gut and fat body. In hemocytes Tm14-3-3ζ signals were distributed in the cytosol and cell’s perimeter.
3.6. Tm14-3-3ζ Silencing Increases Susceptibility to Escherichia coli and Candida albicans Infection in Larvae
To investigate the function of Tm14-3-3ζ in the survival of the larvae against E. coli and C. albicans infection, we injected Tm14-3-3ζ dsRNA to the host larvae thereby setting a gene silencing model. The efficiency of Tm14-3-3ζ silencing was found to be 95-fold as compared with the dsEGFP injected group. The study was conducted in three biological replications and the silencing of Tm14-3-3ζ transcripts was found to be significant (Figure 5A). The dsRNA induced silencing of Tm14-3-3ζ transcript was also noticed at the protein level using Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum (Figure 5B). Subsequent E. coli and C. albicans inoculation to Tm14-3-3ζ silenced larvae showed a compromised immune response with a decrease in the larval survivability to almost 30% (Figure 5C) and 20% (Figure 5D), respectively. The reduced survivability of T. molitor larvae was significant (p < 0.05) at seven days post-infection of the microbes.
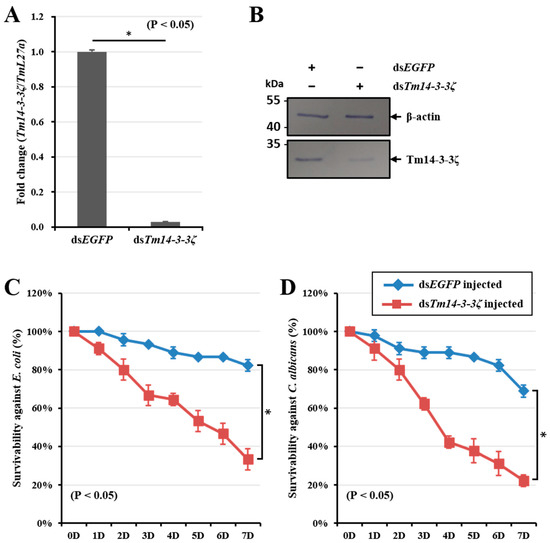
Figure 5.
Silencing of Tm14-3-3ζ transcripts using RNA interference (RNAi) and mortality assay after E. coli and C. albicans injection. About 98% of Tm14-3-3ζ mRNA (A) and protein (B) expression were decreased by injection of 1 μg of dsTm14-3-3ζ RNA. Mortality against injection of pathogenic microorganisms such as E. coli (C) and C. albicans (D) in dsTm14-3-3ζ-treated T. molitor larvae were investigated. The results suggest that silencing of Tm14-3-3ζ induces mortality in the infected larvae.
4. Discussion
The 14-3-3 family of proteins expressed in vertebrates and invertebrates are responsible for interaction with a variety of cytosolic proteins with phosphorylated serine/threonine residues and direct signaling roles [42,43]. In the vertebrate model systems, seven different 14-3-3 isoforms participate in diverse functions, while in insects two isoforms (ε and ζ) have been identified. In the coleopteran pest T. molitor, the functional specificity of 14-3-3 proteins remains unexplored. As previously reported, T. molitor is an efficient model for functional studies involving immunity, defense and physiology [28,29]. The 14-3-3ε isoform identified earlier showed hemocyte antimicrobial activity [34]. In this study, we cloned 14-3-3ζ isoform from T. molitor and provide an indirect evidence for its role in phagocytosis of Gram-negative bacterium E. coli and yeast C. albicans. The putative 14-3-3 domain in 14-3-3ζ protein is responsible for regulating a wide array of cellular processes [44,45,46]. The peptide-binding residues in the 14-3-3 domain may be responsible for cross-talk of Tm14-3-3ζ with other interacting proteins and channelizing regulatory processes [47]. Multiple alignments of Tm14-3-3ζ with 14-3-3ε isoform of T. molitor show 14-3-3 conserved domain and residues including the NLS sequence. In light of high level of sequence similarity of Tm14-3-3ζ to 14-3-3ζ proteins in other species, which have a role in phagocytosis, it is likely that the protein in T. molitor is playing a similar role. In the planarian, Dugesia japonica, the 14-3-3ζ and 14-3-3ε possess conserved domains with a common phosphorylated site [48]. The sequence identity of the 14-3-3 isoforms could reflect functional redundancy and the minor sequence variations might be responsible for their differential binding activity [49]. As reported earlier for the 14-3-3ε/ζ isoforms, the essential serine residues for interactions with different ligands are conserved [50]. These conserved serine residues were found at 187th and 233rd position in Tm14-3-3ζ. Another striking identity in the sequence conservation of 14-3-3ζ proteins is the annexin-like consensus sequence (N-MKGDYYRYLAEVTRNAVV-C) in the 14-3-3 domain, which may have functional importance during the 14-3-3 mediated exocytosis [51]. With regards to immunological functions, it is found that the 14-3-3ε transcript from T. molitor is responsible for a decreased secretion of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) from hemocyte to hemolymph [34], while Tm14-3-3ζ is responsible for phagocytosis function against E. coli and C. albicans. In any case, silencing of both the transcripts leads to reduced survivability of the larvae after microorganism inoculation.
The Tm14-3-3ζ transcript was found consistently throughout the developmental stages and in different tissues of the insect. In Aedes aegypti the 14-3-3ζ isoforms were identified in the larval and pupal stages during the mosquito development. The transcripts were also expressed in the head, ovary, fat body and midgut tissues of adult female mosquitoes [52]. Among the ε and ζ isoforms of 14-3-3 proteins, the 14-3-3ζ isoform generally shows markedly higher expressions in all stages and tissues in comparison with the 14-3-3ε isoform. This has been found to be true in the B. mori [16] and A. aegypti 14-3-3ε/ζ isoforms [52]. The expression of Tm14-3-3ζ transcripts showed a sudden increase followed by a sharp decline after inoculation of the insect larvae with E. coli and C. albicans. It has been reported that the stimulation by pathogen associated molecular patterns such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycan (PGN), teichoic acids and so forth could lead to expression of Tm14-3-3ζ transcript with immune-related functions [53]. The 14-3-3ζ proteins promote immunity by regulating TLR-3 signaling through TICAM-1 pathway [54] and immune responses through Stat3 signaling in oral cancers [55]. The 14-3-3ζ proteins promote phagocytosis and microbial clearance in Drosophila hemocytes. This has been demonstrated through in vivo phagocytosis assay involving 14-3-3ζ screened from RNA interference (RNAi)-based phenotypic screens [23].
rTm14-3-3ζ was successfully expressed in the E. coli system. The rTm14-3-3ζ and the endogenous Tm14-3-3ζ reacted with the Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum that was synthesized commercially from a 16-mer region at the C-terminal end. Our findings highlight protein bands at ~35 kDa and ~27 kDa corresponding to rTm14-3-3ζ and the endogenous form, respectively. The Tm14-3-3ζ antiserum was then utilized for the immunohistochemical localization of Tm14-3-3ζ proteins in tissues of T. molitor larvae. The subcellular localization of Tm14-3-3ζ protein in all the major tissues including gut, fat body, Malpighian tubules and hemocytes were investigated. The results are consistent to an earlier report of sub-cellular localization of 14-3-3ζ gene in the Indian meal moth, Plodia interpunctella [21]. The immunohistochemical observations in the present study show extensive localization of Tm14-3-3ζ proteins in the cytosolic space of the larval tissues. In the gut and fat body, Tm14-3-3ζ was localized on the membrane and in the cytosol, respectively. Like other members of the 14-3-3 family, Tm14-3-3ζ was found distributed in the cytosol and selectively along the membrane of some cells. 14-3-3ζ has been found in the mitochondria, microsomes and nuclear compartments of the mouse hippocampus [56,57]. The Opisthorchis viverrini 14-3-3ζ isoform were expressed throughout the tissues except in the gut epithelium and expression was highest in the testis, suggesting a potential role in spermatogenesis [58].
RNAi-based functional analysis has been useful for the characterization of several immune-related genes such as MyD88, CD63, apolipophorin-III and PGRP-LE in response to microorganism challenge [28,30,31,33,59]. Recently, the Tm14-3-3ε isoform was found to play a role in secretion of antimicrobial peptide in response to E. coli [34]. Further, 14-3-3ζ isoform is a novel candidate gene that promotes phagocytosis in Drosophila model and is required for the survival of host against the Gram-positive bacterium, Staphylococcus aureus [23]. In the same light, a functional role could be attributed to Tm14-3-3ζ eliciting innate immune responses since silencing of 14-3-3ζ transcripts in the larvae resulted in a reduction in larval survivability against E. coli and C. albicans. An earlier report demonstrated that 14-3-3ε silencing in T. molitor impairs the exocytosis of AMPs from hemocyte to hemolymph and affects the bactericidal action on the microbes [34]. In the context of the present study, Tm14-3-3ζ is critical for larval survivability against normal bacterial and fungal infections. In addition, established studies suggest that 14-3-3ζ play an important regulatory role in apoptosis [1,5], autophagy [2,57,60] and phagocytosis of microbes [23]. Similar experiments would be required to confirm the role of Tm14-3-3ζ more precisely. A better understanding of Tm14-3-3ζ role in innate immunity of T. molitor will be a critical towards its bio-control in agricultural fields and helping in improve the regulation of critical biological processes in the insect.
5. Conclusions
We have screened and characterized a novel isoform of 14-3-3 family from the coleopteran pest T. molitor EST and RNA Sequencing database (Tm14-3-3ζ) and generated a peptide-based polyclonal antibody and validated it against the endogenous and recombinant Tm14-3-3ζ. Finally, we have characterized functional role of Tm14-3-3ζ in larval survivability against E. coli and C. albicans using RNAi technique in T. molitor.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/9/7/330/s1, Figure S1: Molecular phylogenetic and percent identity analysis of 14-3-3ζ isoform in T. molitor, Table S1. Gene information used.
Author Contributions
Y.S.H and Y.H.J. conceived and designed the experiments; J.H.S., G.W.S., S.P., K.B.P., J.H.C., H.J.K. and C.E.K. performed the experiments; Y.H.J. analyzed the data; Y.S.H. and Y.S.L. contributed reagents/ materials/analysis tools; Y.S.H., Y.H.J., B.B.P., S.A.J., Y.S.C., Y.W.K. and I.S.B. wrote the paper.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and future Planning (MSIP) (No. 2015R1A2A2A01005301) and by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through Export Promotion Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (No. 617077-5).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cao, W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.; Teng, Z.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.; Fei, Z. Targeting 14-3-3 protein, difopein induces apoptosis of human glioma cells and suppresses tumor growth in mice. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozuelo-Rubio, M. 14-3-3 proteins are regulators of autophagy. Cells 2012, 1, 754–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Acharya, S.; Sahin, O.; Zhang, Q.; Saito, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Lowery, F.J.; et al. 14-3-3ζ turns TGF-β’s function from tumor suppressor to metastasis promoter in breast cancer by contextual changes of smad partners from p53 to Gli2. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Subramanian, R.R.; Masters, S.C. 14-3-3 proteins: Structure, function, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 617–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, S.C.; Fu, H. 14-3-3 proteins mediate an essential anti-apoptotic signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45193–45200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muda, K.; Bertinetti, D.; Gesellchen, F.; Hermann, J.S.; von Zweydorf, F.; Geerlof, A.; Jacob, A.; Ueffing, M.; Gloeckner, C.J.; Herberg, F.W. Parkinson-related LRRK2 mutation R1441C/G/H impairs PKA phosphorylation of LRRK2 and disrupts its interaction with 14-3-3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E34–E43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Heusden, G.P.; Steensma, H.Y. Yeast 14-3-3 proteins. Yeast 2006, 23, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BoseDasgupta, S.; Moes, S.; Jenoe, P.; Pieters, J. Cytokine-induced macropinocytosis in macrophages is regulated by 14-3-3ζ through its interaction with serine-phosphorylated coronin 1. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.L.; Sehnke, P.C.; Ferl, R.J. Isoform-specific subcellular localization among 14-3-3 proteins in arabidopsis seems to be driven by client interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognetti, D.; Davis, D.; Sturtevant, J. The Candida albicans 14-3-3 gene, BMH1, is essential for growth. Yeast 2002, 19, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, S.F.; Tsigkari, K.K.; Grammenoudi, S.; Skoulakis, E.M.C. In vivo functional specificity and homeostasis of drosophila 14-3-3 proteins. Genetics 2007, 177, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasiuk, K.; Kontula, L.; Pitkanen, A. cDNA profiling of epileptogenesis in the rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, G.P.; Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; McKiernan, R.C.; Engel, T.; Tzivion, G.; Henshall, D.C. Transgenic overexpression of 14-3-3ζ protects hippocampus against endoplasmic reticulum stress and status epilepticus in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLille, J.M.; Sehnke, P.C.; Ferl, R.J. The arabidopsis 14-3-3 family of signaling regulators. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.T.; Parry, D.H.; Donahoe, B.; Chien, C.T.; O’Farrell, P.H.; Purdy, A. Cell cycle roles for two 14-3-3 proteins during drosophila development. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Lv, Z.; Chen, J.; Nie, Z.; Wang, D.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Expression analysis and tissue distribution of two 14-3-3 proteins in silkworm (Bombyx mori). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1770, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.A.; Noh, M.Y.; Jo, Y.H.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, I.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.C.; Seo, S.J.; Bang, I.S.; Han, Y.S. Peptide-based polyclonal antibody against mosquito 14-3-3ζ recognizes 14-3-3 homolog from dipteran and lepidopteran insects. Entomol. Res. 2009, 39, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.H.; Noh, M.Y.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Oh, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Bang, I.S.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, I.; Han, Y.S. Molecular cloning and expression pattern of 14-3-3ζ from the malaria vector, Anopheles sinensis. Entomol. Res. 2009, 39, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabunoki, H.; Shimada, T.; Banno, Y.; Sato, R.; Kajiwara, H.; Mita, K.; Satoh, J. Identification of Bombyx mori 14-3-3 orthologs and the interactor Hsp60. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 61, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Li, R.Q.; Cheng, D.J.; Fan, W.; Zha, X.F.; Cheng, T.C.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; Mita, K.; Xiang, Z.H.; et al. SilkDB v2.0: A platform for silkworm (Bombyx mori) genome biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D453–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.N.; Bian, D.D.; Ge, B.M.; Zhou, C.L.; Tang, B.P. Molecular characterization of a 14-3-3ζ gene from Plodia interpunctella: A potential marker for phylogenetic inference. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 60, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, K.S.; Popham, H.J.R. Analysis of ESTs generated from immune-stimulated hemocytes of larval Heliothis virescens. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 101, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulvila, J.; Vanha-aho, L.M.; Kleino, A.; Vaha-Makila, M.; Vuoksio, M.; Eskelinen, S.; Hultmark, D.; Kocks, C.; Hallman, M.; Parikka, M.; et al. Cofilin regulator 14-3-3ζ is an evolutionarily conserved protein required for phagocytosis and microbial resistance. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, E.Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.K.; Yin, Y.P. Gene cloning, expression, and function analysis of SpL14-3-3ζ in Spodoptera litura and its response to the entomopathogenic fungus Nomuraea rileyi. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2014, 172, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Z.; Ma, W.H.; Wang, X.P.; Niu, C.Y.; Lei, C.L. Analysis of pupal head proteome and its alteration in diapausing pupae of Helicoverpa armigera. J. Insect. Physiol. 2010, 56, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, K.B.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, H.; Kwon, H.M.; Park, J.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Kurokawa, K.; Ha, N.C.; Lee, W.J.; Lemaitre, B.; et al. Proteolytic cascade for the activation of the insect toll pathway induced by the fungal cell wall component. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19474–19481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, H.M.; Hwang, H.O.; Jang, I.H.; Masuda, A.; Kurokawa, K.; Nakayama, H.; Lee, W.J.; Dohmae, N.; et al. Diversity of innate immune recognition mechanism for bacterial polymeric meso-diaminopimelic acid-type peptidoglycan in insects. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 32937–32945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, B.B.; Patnaik, H.H.; Seo, G.W.; Jo, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.L.; Han, Y.S. Gene structure, cDNA characterization and RNAi-based functional analysis of a myeloid differentiation factor 88 homolog in Tenebrio molitor larvae exposed to Staphylococcus aureus infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 46, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, K.B.; Seong, J.H.; Kim, S.G.; Park, S.; Noh, M.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, Y.S. TmCactin plays an important role in Gram-negative and -positive bacterial infection by regulating expression of 7 AMP genes in Tenebrio molitor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindwa, H.; Patnaik, B.B.; Kim, D.H.; Mun, S.; Jo, Y.H.; Lee, B.L.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, N.J.; Han, Y.S. Cloning, characterization and effect of TmPGRP-LE gene silencing on survival of Tenebrio molitor against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22462–22482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, B.B.; Kang, S.M.; Seo, G.W.; Lee, H.J.; Patnaik, H.H.; Jo, Y.H.; Tindwa, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.L.; Kim, N.J.; et al. Molecular cloning, sequence characterization and expression analysis of a CD63 homologue from the coleopteran beetle, Tenebrio molitor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20744–20767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Patnaik, B.B.; Seo, G.W.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.L.; Han, Y.S. Identification and expression analysis of a novel R-type lectin from the coleopteran beetle, Tenebrio molitor. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 114, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.Y.; Patnaik, B.B.; Tindwa, H.; Seo, G.W.; Kim, D.H.; Patnaik, H.H.; Jo, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.L.; Kim, N.J.; et al. Genomic organization, sequence characterization and expression analysis of Tenebrio molitor apolipophorin-III in response to an intracellular pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes. Gene 2014, 534, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, G.W.; Jo, Y.H.; Seong, J.H.; Park, K.B.; Patnaik, B.B.; Tindwa, H.; Kim, S.A.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, Y.S. The silencing of a 14-3-3varepsilon homolog in Tenebrio molitor leads to increased antimicrobial activity in hemocyte and reduces larval survivability. Genes 2016, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindwa, H.; Jo, Y.H.; Patnaik, B.B.; Noh, M.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, I.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.L.; Kim, N.J. Depletion of autophagy-related genes ATG3 and ATG5 in Tenebrio molitor leads to decreased survivability against an intracellular pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2015, 88, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tindwa, H.; Jo, Y.H.; Patnaik, B.B.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, S.S.; Han, Y.S. Molecular cloning and characterization of autophagy-related gene TmATG8 in Listeria-invaded hemocytes of Tenebrio molitor. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 51, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. SMART7: Recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D302–D305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.M.; Booker, M.; Silver, S.J.; Friedman, A.; Hong, P.; Perrimon, N.; Mathey-Prevot, B. Evidence of off-target effects associated with long dsRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster cell-based assays. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Creanga, A.; Lum, L.; Beachy, P.A. Prevalence of off-target effects in Drosophila RNA interference screens. Nature 2006, 443, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, A.K.; Morrison, D.K. 14-3-3 proteins: Diverse functions in cell proliferation and cancer progression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, A.H.; van Kleeff, P.J.; Gao, J. Plant 14-3-3 proteins as spiders in a web of phosphorylation. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, A.; Siu, K.W.M.; Ralhan, R. 14-3-3 zeta as novel molecular target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2012, 16, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.; Saraiva, M.J. Transthyretin regulates lysosomal degradation of hippocampal 14-3-3ζ. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 557. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.J.; Wang, D.J.; Peng, T.; Wang, L.; Wei, G.Q.; Liu, C.L. Characterization and function of a gene Pc 14-3-3 isoform from red crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Pak. J. Zool. 2014, 46, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.K. The 14-3-3 proteins: Integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhen, H.; Deng, H.; Song, Q.; Ma, K.; Cao, Z.; Pang, Q.; Zhao, B. 14-3-3α and 14-3-3ζ contribute to immune responses in planarian Dugesia japonica. Gene 2017, 615, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obsilova, V.; Kopecka, M.; Kosek, D.; Kacirova, M.; Kylarova, S.; Rezabkova, L.; Obsil, T. Mechanisms of the 14-3-3 protein function: Regulation of protein function through conformational modulation. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63, S155–S164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexander, R.D.; Morris, P.C. A proteomic analysis of 14-3-3 binding proteins from developing barley grains. Proteomics 2006, 6, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.; Morgan, A.; Burgoyne, R.D. Identification of a key domain in annexin and 14-3-3 proteins that stimulate calcium-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1993, 320, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Ocampo, A.; Cazares-Raga, F.E.; Celestino-Montes, A.; Cortes-Martinez, L.; Rodriguez, M.H.; Hernandez-Hernandez, F.C. Identification and expression analysis of two 14-3-3 proteins in the mosquito Aedes aegypti, an important arboviruses vector. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 93, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.G.; Ying, S.H.; Wang, J.J.; Sun, W.L.; Tian, C.G.; Feng, M.G. Unveiling equal importance of two 14-3-3 proteins for morphogenesis, conidiation, stress tolerance and virulence of an insect pathogen. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1444–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funami, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Obuse, C.; Seya, T. 14-3-3-zeta participates in TLR3-mediated TICAM-1 signal-platform formation. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 73, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Han, Y.; Jiao, H.; Jie, Y. 14-3-3zeta regulates immune response through Stat3 signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, N.; Bonner, H.P.; Ward, M.W.; Murphy, B.M.; Prehn, J.H.; Henshall, D.C. Depletion of 14-3-3ζ zeta elicits endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell death, and increases vulnerability to kainate-induced injury in mouse hippocampal cultures. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heverin, M.; Brennan, G.P.; Koehler, C.J.; Treumann, A.; Henshall, D.C. Proteomic analysis of 14-3-3ζ binding proteins in the mouse hippocampus. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 4, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kafle, A.; Puchadapirom, P.; Plumworasawat, S.; Dontumprai, R.; Chan-On, W.; Buates, S.; Laha, T.; Sripa, B.; Suttiprapa, S. Identification and characterization of protein 14-3-3 in carcinogenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, B.B.; Patnaik, H.H.; Park, K.B.; Jo, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, Y.S. Silencing of apolipophorin-III causes abnormal adult morphological phenotype and susceptibility to Listeria monocytogenes infection in Tenebrio molitor. Entomol. Res. 2015, 45, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozuelo-Rubio, M. Regulation of autophagic activity by 14-3-3ζ proteins associated with class III phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).