Large Introns of 5 to 10 Kilo Base Pairs Can Be Spliced out in Arabidopsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.3. Total RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Distribution of Intron Sizes in the Genome of Arabidopsis thaliana
3.2. Validation and Sequence Analysis of Extremely Large Introns in Arabidopsis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, S.W.; Gilbert, W. The evolution of spliceosomal introns: Patterns, puzzles and progress. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mourier, T.; Jeffares, D.C. Eukaryotic intron loss. Science 2003, 300, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2000, 408, 796–815.
- Schnable, P.S.; Ware, D.; Fulton, R.S.; Stein, J.C.; Wei, F.; Pasternak, S.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fulton, L.; Graves, T.A.; et al. The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 2009, 326, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rensing, S.A.; Lang, D.; Zimmer, A.D.; Terry, A.; Salamov, A.; Shapiro, H.; Nishiyama, T.; Perroud, P.F.; Lindquist, E.A.; Kamisugi, Y.; et al. The Physcomitrella genome reveals evolutionary insights into the conquest of land by plants. Science 2008, 319, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, M.; Long, M. Intron-exon structures of eukaryotic model organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nystedt, B.; Street, N.R.; Wetterbom, A.; Zuccolo, A.; Lin, Y.C.; Scofield, D.G.; Vezzi, F.; Delhomme, N.; Giacomello, S.; Alexeyenko, A.; et al. The Norway spruce genome sequence and conifer genome evolution. Nature 2013, 497, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Calixto, C.P.G.; Marquez, Y.; Venhuizen, P.; Tzioutziou, N.A.; Guo, W.; Spensley, M.; Entizne, J.C.; Lewandowska, D.; Ten Have, S.; et al. A high quality Arabidopsis transcriptome for accurate transcript-level analysis of alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5061–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liu, C.M. A single-nucleotide exon found in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, D.; Carpenter, R.; Sommer, H.; Hartley, N.; Coen, E. Complementary floral homeotic phenotypes result from opposite orientations of a transposon at the plena locus of Antirrhinum. Cell 1993, 72, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.; Shin, J.S.; Chung, C.H.; Ohlrogge, J.B.; Suh, M.C. Seed-specific expression of sesame microsomal oleic acid desaturase is controlled by combinatorial properties between negative cis-regulatory elements in the SeFAD2 promoter and enhancers in the 5’-UTR intron. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2006, 276, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigal, M.; Kevei, Z.; Pélissier, T.; Mathieu, O. DNA methylation in an intron of the IBM1 histone demethylase gene stabilizes chromatin modification patterns. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2981–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, J.M.; Stepanova, A.N.; Leisse, T.J.; Kim, C.J.; Chen, H.; Shinn, P.; Stevenson, D.K.; Zimmerman, J.; Barajas, P.; Cheuk, R.; et al. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 2003, 301, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallaud, C.; Gay, C.; Larmande, P.; Bès, M.; Piffanelli, P.; Piégu, B.; Droc, G.; Regad, F.; Bourgeois, E.; Meynard, D.; et al. High throughput T-DNA insertion mutagenesis in rice: A first step towards in silico reverse genetics. Plant J. 2004, 39, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissier, A.F.; Marillonnet, S.; Klimyuk, V.; Patel, K.; Torres, M.A.; Murphy, G.; Jones, J.D. Multiple independent defective suppressor-mutator transposon insertions in Arabidopsis: A tool for functional genomics. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Long, T.; Wu, C. Effort and contribution of T-DNA Insertion mutant library for rice functional genomics research in China: Review and perspective. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

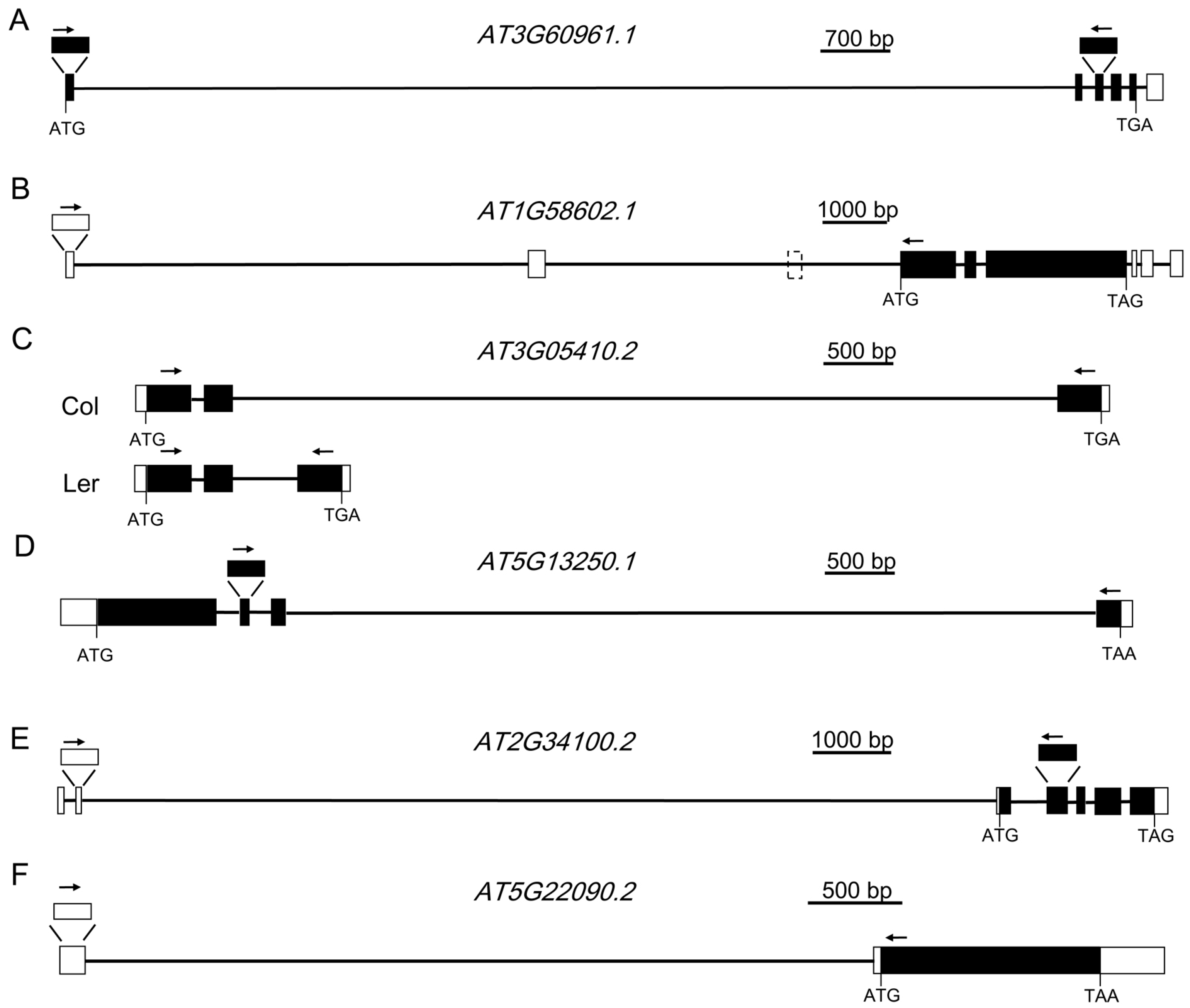
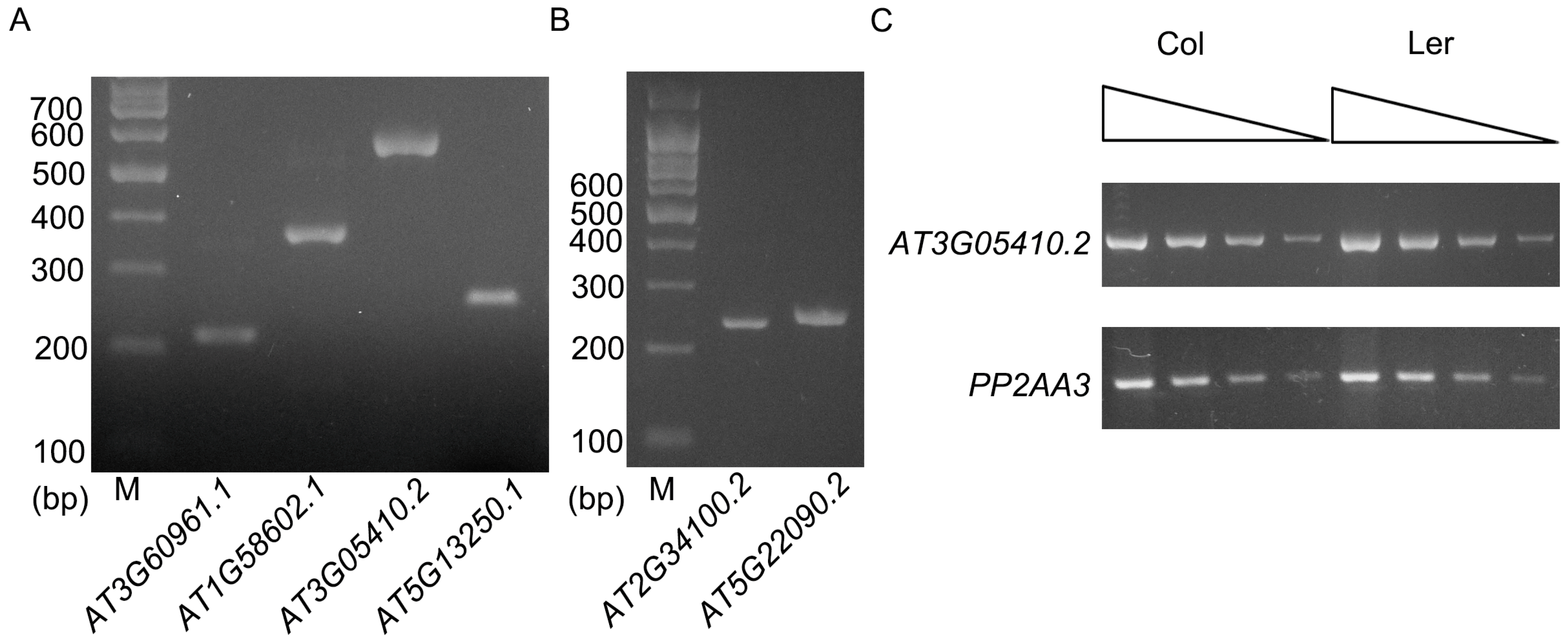
| Gene | Annotated Intron | Length (bp) | Validation Results | Description of Gene | Description of Intron | Total Size of TEs in the Intron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT2G34100.2 | AT2G34100.2-2 | 11,602 | Validated; 11,602 bp | Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay-like protein | This intron contains 13 genes or TEs: AT2TE63770, AT2G34110, AT2TE63775, AT2TE63780, AT2G34120, AT2TE63785, AT2G34123, AT2TE63790, AT2TE63795, AT2TE63800, AT2G34130, AT2TE63805, AT2G34135, with different sizes. | 6325 bp; (54.52%) |
| AT3G60961.1 | AT3G60961.1-1 | 10,234 | Validated; 10,247 bp | P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolases superfamily protein | This intron was also annotated as AT3G60965, a copia-like retrotransposon. | 9903 bp (96.64%) |
| AT2G34110.1 | AT2G34110.1-1 | 9724 | Not validated | hypothetical protein | NA | |
| AT1G58602.1 | AT1G58602.1-1 | 7384 | Validated; 7385 bp | LRR and NB-ARC domains-containing disease resistance protein | This intron contains 4 TEs: AT1TE71765, AT1TE71770, AT1TE71775 and AT1TE71780. | 6164 bp (83.47%) |
| AT1G58602.1 | AT1G58602.1-2 and AT1G58602.1-3 | 6070 | Validated; 6070 bp | LRR and NB-ARC domains-containing disease resistance protein | These two annotated introns and the exon between them were found to be an intron of 6070 bp. It contains 10 TEs: AT1TE71785, AT1TE71790, AT1TE71795, AT1TE71800, AT1TE71805, AT1TE71810, AT1TE71815, AT1TE71820, AT1TE71825 and AT1TE71830. | 5192 bp (85.54%) |
| AT3G05410.2 | AT3G05410.2-2 | 5748 | Validated; 5748 bp | Photosystem II reaction center OEC23 protein | A major part of the intron is a transposon, AT3TE06550. | 5261 bp (91.53%) |
| AT5G13250.1 | AT5G13250.1-3 | 5670 | Validated; 5673 bp | RING finger protein | This intron contains AT5TE15340, AT5TE15345, AT5TE15350 and AT5G02075, which constitute only a small part of the intron. | 530 bp (9.34%) |
| AT3G52700.1 | AT3G52700.1-1 | 5134 | Not validated | Hypothetical protein | NA | |
| AT5G22090.2 | AT5G22090.2-1 | 5082 | Validated; 5082 bp | FAF-like protein | This intron contains 3 TEs: AT5TE26450, AT5TE26455, AT5TE26460 | 1985 bp (39.06%) |
| Organism | Length (bp) |
|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana (Col-0) | 5748 |
| Arabidopsis thaliana (Ler) | 456 |
| Arabidopsis lyrata | 461 |
| Capsella rubella | 391 |
| Citrus sinensis | 77 |
| Populus euphratica | 83 |
| Vitis vinifera | 18 |
| Oryza sativa | 254 |
| Populus trichocarpa | 130 |
| Sesamum indicum | 2903 |
| Organism | Length (bp) |
|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana (Col-0) | 5670 |
| Arabidopsis lyrata | 8873 |
| Populus euphratica | 6986 |
| Citrus sinensis | 5302 |
| Vitis vinifera | 6587 |
| Oryza sativa (Chromosome 4) | 9945 |
| Oryza sativa (Chromosome 12) | 16,721 |
| Populus trichocarpa (linkage group 1) | 6684 |
| Populus trichocarpa (linkage group 3) | 6244 |
| Sesamum indicum | 5931 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, N.; Sun, Q.; Hu, J.; An, C.; Gao, A.H. Large Introns of 5 to 10 Kilo Base Pairs Can Be Spliced out in Arabidopsis. Genes 2017, 8, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080200
Chang N, Sun Q, Hu J, An C, Gao AH. Large Introns of 5 to 10 Kilo Base Pairs Can Be Spliced out in Arabidopsis. Genes. 2017; 8(8):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080200
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Ning, Qingqing Sun, Jinglei Hu, Chuanjing An, and And Hongbo Gao. 2017. "Large Introns of 5 to 10 Kilo Base Pairs Can Be Spliced out in Arabidopsis" Genes 8, no. 8: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080200
APA StyleChang, N., Sun, Q., Hu, J., An, C., & Gao, A. H. (2017). Large Introns of 5 to 10 Kilo Base Pairs Can Be Spliced out in Arabidopsis. Genes, 8(8), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080200




