Cucumber Metallothionein-Like 2 (CsMTL2) Exhibits Metal-Binding Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gene Cloning and Plasmid Construction
2.2. qRT-PCR Analysis of CsMTL2 Expression under Zn2+ and Cd2+ Stress
- CsActin-Q-F: 5′-GGTGGTGAACATGTAACCTC-3′,
- CsActin-Q-R: 5′-TTCTGGTGATGGTGTGAGTC-3′,
- CsMTL2-Q-F: AATGAGCAGCAGCAGCATCAAGAGC
- CsMTL2-Q-R: AAGACGCAACACAACGGAGAACGAA
2.3. Expression and Purification of CsMTL2, CsMTL2m, HsMTXb, and PCL
2.4. Immunoblot Analysis
2.5. Assay of Heavy Metal Binding Ability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Protein Analysis
3. Results
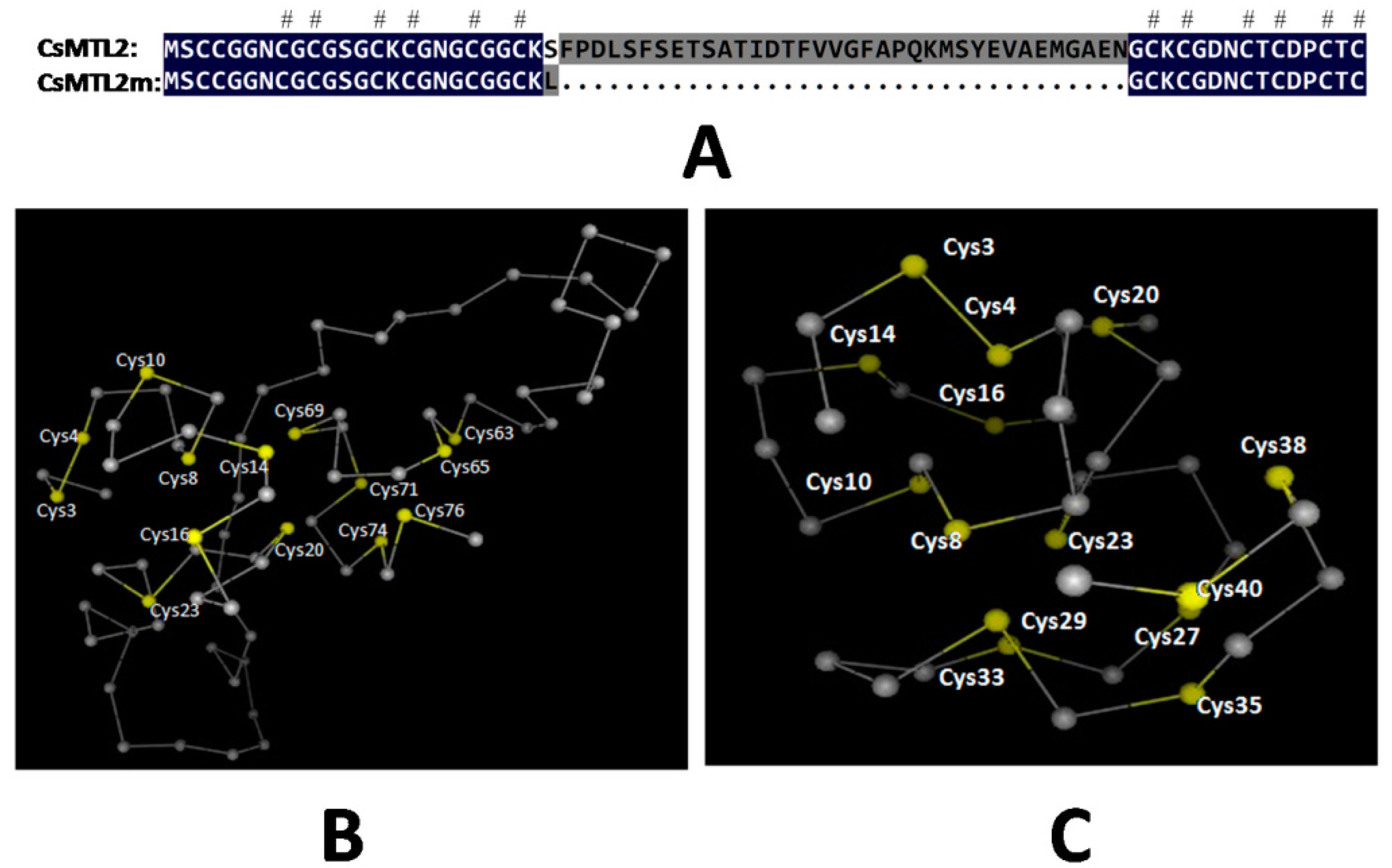
3.1. Isolation of CsMTL2 cDNA and Structural Analysis of the Encoded Gene Product
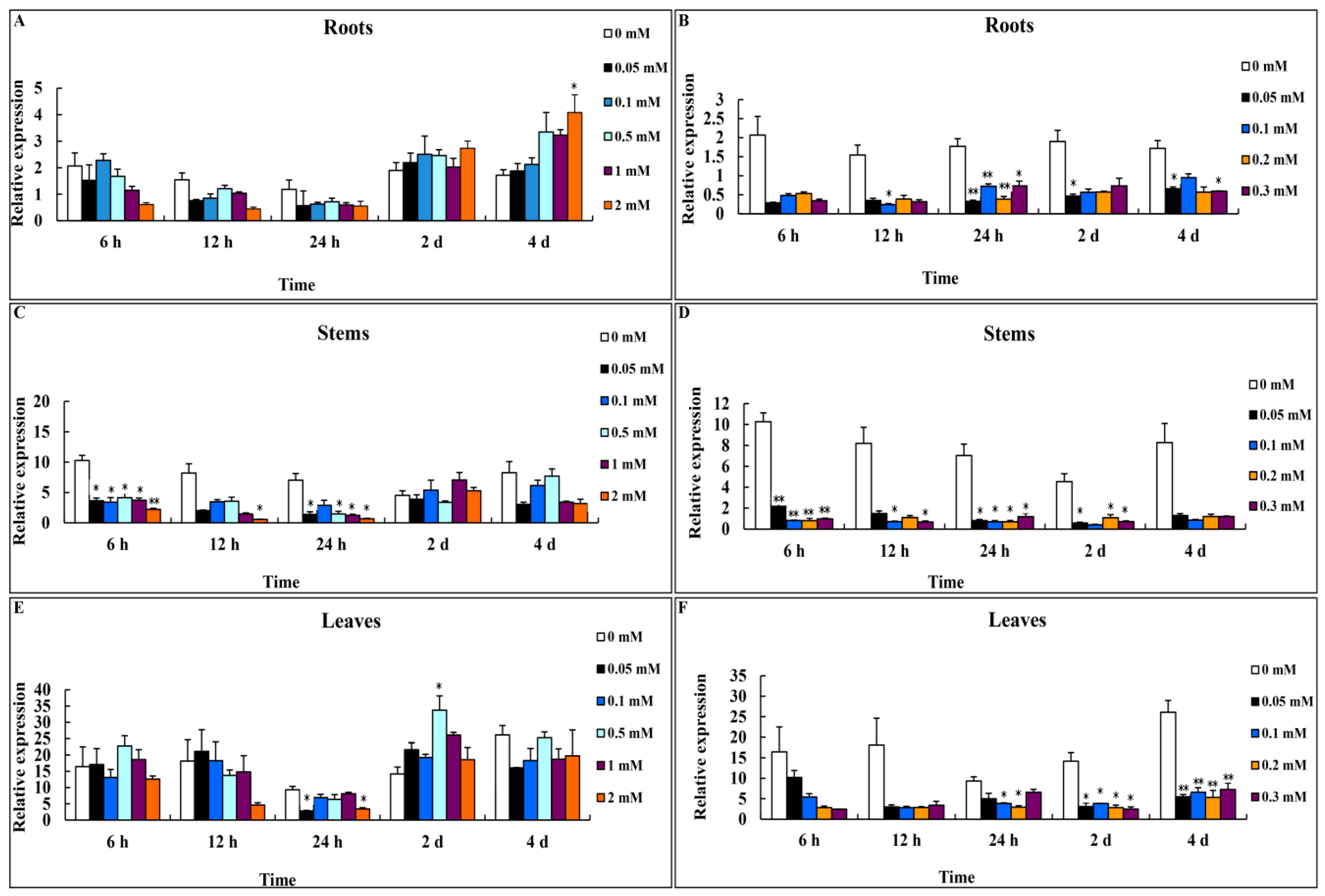
3.2. Expression Profiles of CsMTL2 under Zn2+ and Cd2+ Stress
3.3. Protein Analysis
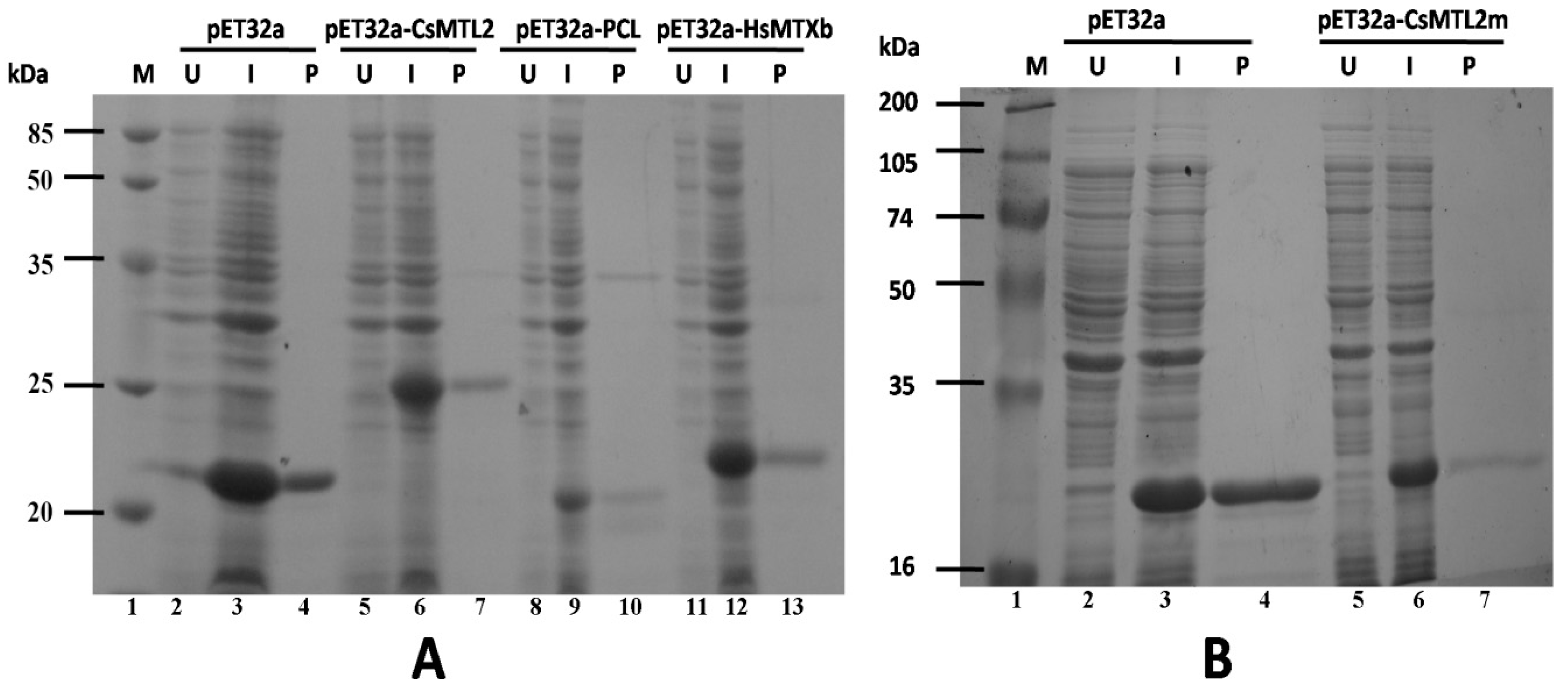
3.4. Expression and Purification of Trx-CsMTL2, Trx-CsMTL2m, Trx-HsMTXb, and Trx-PCL Fusion Proteins
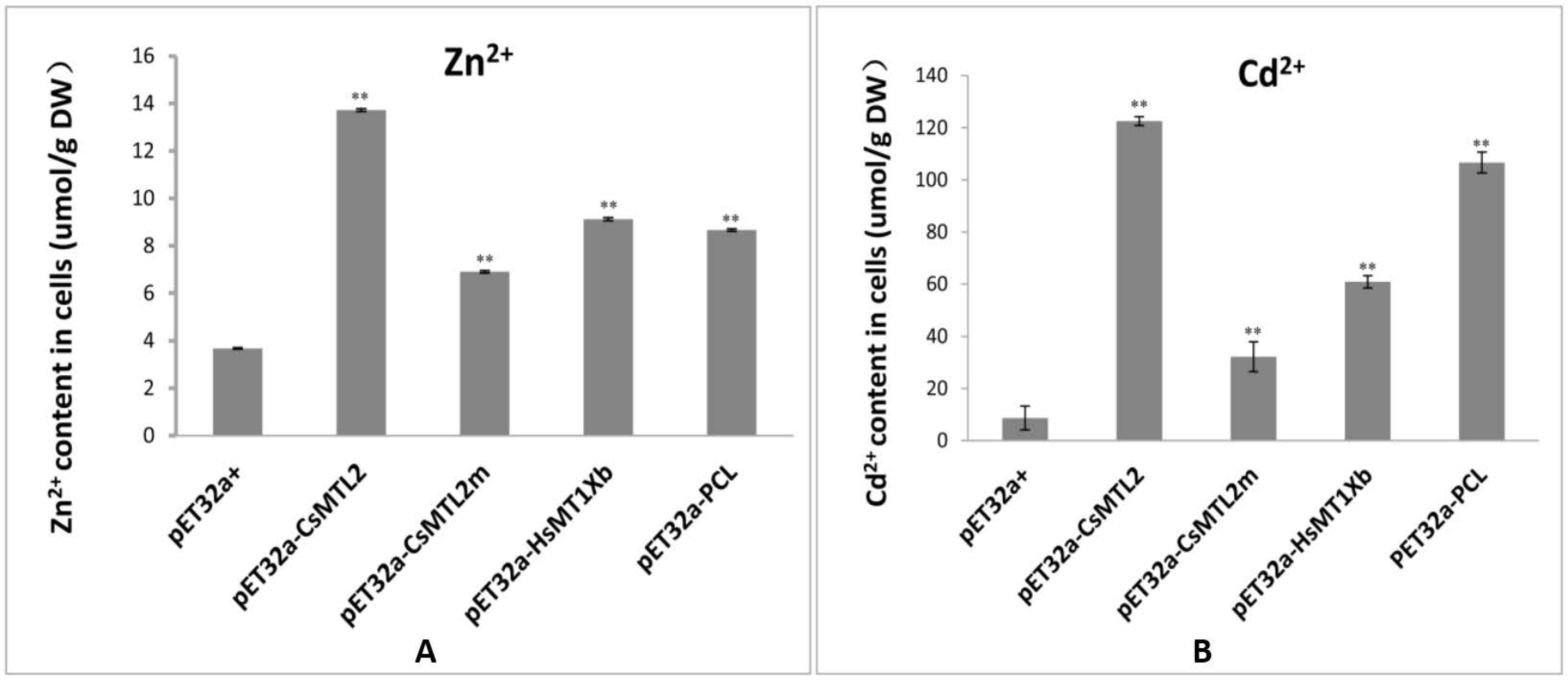
3.5. Metal Tolerance and Ion Accumulation in E. coli Expressing CsMTL2, CsMTL2m, HsMTXb, and PCL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobbett, C.; Goldsbrough, P. Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: Roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdineaud, J.P.; Baudrimont, M.; Gonzalez, P.; Moreau, J.L. Challenging the model for induction of metallothionein gene expression. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassinen, V.H.; Tuomainen, M.; Peraniemi, S.; Schat, H.; Karenlampi, S.O.; Tervahauta, A.I. Metallothioneins 2 and 3 contribute to the metal-adapted phenotype but are not directly linked to Zn accumulation in the metal hyperaccumulator, Thlaspi caerulescens. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.Y.; Wang, Y.S. Expression and characterization analysis of type 2 metallothionein from grey mangrove species (Avicennia marina) in response to metal stress. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, G.; Domenech, J.; Huguet, G.; Guo, W.J.; Goldsbrough, P.; Atrian, S.; Molinas, M. A plant type 2 metallothionein (MT) from cork tissue responds to oxidative stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, G.K. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression by oxidative stress and metal ions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Mishra, A.; Tiwari, V.; Jha, B. Cloning and transcript analysis of type 2 metallothionein gene (SBMT-2) from extreme halophyte Salicornia brachiata and its heterologous expression in E. Coli. Gene 2012, 499, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, M.G.; Kang, Y.J. Metallothionein and liver cell regeneration. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2006, 231, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Anandhan, S.; Singh, S.; Patade, V.Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Pande, V. Metallothionein-like gene from Cicer microphyllum is regulated by multiple abiotic stresses. Protoplasma 2011, 248, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, P.; Philcox, J.; Carey, L.; Rofe, A.M. Metallothionein: The multipurpose protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 627–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freisinger, E. Metallothioneins in plants. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2009, 5, 107–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-O.; Patel, D.H.; Lee, D.-S.; Song, Y.; Bae, H.-J. High cadmium-binding ability of a novel Colocasia esculenta metallothionein increases cadmium tolerance in Escherichia coli and tobacco. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1912–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Sun, D.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, S. Expression of the rgmt gene, encoding for a rice metallothionein-like protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Genet. 2014, 93, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, B.A.; Hildebrand, C.E.; Kojima, Y.; Webb, M. Nomenclature of metallothionein. In Metallothionein II; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1987; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, N.J.; Tommey, A.M.; Kuske, C.; Jackson, P.J. Plant metallothioneins. Biochem. J. 1993, 295 Pt 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Choudhuri, S. Metallothionein: An intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, P.; Klaassen, C.D. Metallothionein-I and -II knock-out mice are not more sensitive than control mice to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine neurotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 273, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, E.; Winnacker, E.L.; Zenk, M.H. Phytochelatins: The principal heavy-metal complexing peptides of higher plants. Science 1985, 230, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gekeler, W.; Grill, E.; Winnacker, E.L.; Zenk, M.H. Algae sequester heavy metals via synthesis of phytochelatin complexes. Arch. Microbiol. 1988, 150, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbett, C.S. Phytochelatins and their roles in heavy metal detoxification. Plant. Physiol. 2000, 123, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, A.T.; Hawksworth, G.M.; Beattie, J.H.; Rodilla, V. Induction, regulation, degradation, and biological significance of mammalian metallothioneins. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 35, 35–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasak, M.; Meloni, G. Chemistry and biology of mammalian metallothioneins. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freisinger, E. Structural features specific to plant metallothioneins. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Freisinger, E. The plant metallothionein 2 from Cicer arietinum forms a single metal-thiolate cluster. Metallomics 2009, 1, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binz, P.-A.; Kägi, J.H.R. Metallothionein: Molecular evolution and classification. In Metallothionein IV; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Cheng, Y.; Guan, Q.; Liu, D.; Takano, T.; Liu, S. A metallothionein-like protein of rice (rgMT) functions in E. coli and its gene expression is induced by abiotic stresses. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.J.; Bundithya, W.; Goldsbrough, P.B. Characterization of the Arabidopsis metallothionein gene family: Tissue-specific expression and induction during senescence and in response to copper. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, K.; Nishimura, N.; Ishida, Y.; Yokota, A. Potent hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity of drought-induced type-2 metallothionein in wild watermelon. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giritch, A.; Ganal, M.; Stephan, U.W.; Baumlein, H. Structure, expression and chromosomal localisation of the metallothionein-like gene family of tomato. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1998, 37, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilon-Smits, E.; Pilon, M. Breeding mercury-breathing plants for environmental cleanup. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommey, A.M.; Shi, J.; Lindsay, W.P.; Urwin, P.E.; Robinson, N.J. Expression of the pea gene PsMTA in E. Coli. Metal-binding properties of the expressed protein. FEBS Lett. 1991, 292, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Bi, H.; Liu, P.; Ai, X. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the gene encoding sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase from Cucumis sativus. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Dong, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, M.; Ai, X. Decreased TK activity alters growth, yield and tolerance to low temperature and low light intensity in transgenic cucumber plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, C.; Sui, Y.; Malik, A.A.; Chen, J. Selection of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in cucumber. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 399, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple sequence alignment using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Leszczyszyn, O.I. Metallothioneins: Unparalleled diversity in structures and functions for metal ion homeostasis and more. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 720–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwede, T.; Kopp, J.; Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, J.; Tinti, A.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S.; Torreggiani, A. Structural study of the zinc and cadmium complexes of a type 2 plant (Quercus suber) metallothionein: Insights by vibrational spectroscopy. Biopolymers 2007, 86, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowald, G.R.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Blindauer, C.A. Earthworm Lumbricus rubellus MT-2: Metal binding and protein folding of a true cadmium-mt. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Takano, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Abiotic stress response in yeast and metal-binding ability of a type 2 metallothionein-like protein (PutMT2) from Puccinellia tenuiflora. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5839–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenech, J.; Mir, G.; Huguet, G.; Capdevila, M.; Molinas, M.; Atrian, S. Plant metallothionein domains: Functional insight into physiological metal binding and protein folding. Biochimie 2006, 88, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, Z.; Komatsu, S. Contribution of proteomic studies towards understanding plant heavy metal stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 3, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ling, H.-Q.; Chu, C. OsMT1a, a type 1 metallothionein, plays the pivotal role in zinc homeostasis and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 70, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Yadav, S.K.; Pareek, A.; Reddy, M.K.; Sopory, S.K. Transgenic tobacco overexpressing glyoxalase pathway enzymes grow and set viable seeds in zinc-spiked soils. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.; Tarun, A.S.; Weber, S.U.; Jouanin, L.; Terry, N. Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in indian mustard is enhanced by overexpressing γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Ying, G.E. Response of glutathione and glutathione S-transferase in rice seedlings exposed to cadmium stress. Rice Sci. 2008, 15, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczyszyn, O.I.; Imam, H.T.; Blindauer, C.A. Diversity and distribution of plant metallothioneins: A review of structure, properties and functions. Metallomics 2013, 5, 1146–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldron, K.J.; Robinson, N.J. How do bacterial cells ensure that metalloproteins get the correct metal? Nat. Rev. Microb. 2010, 6, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, Ò.; Pagani, A.; Pérez-Rafael, S.; Egg, M.; Höckner, M.; Brandstätter, A.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S.; Dallinger, R. Shaping mechanisms of metal specificity in a family of metazoan metallothioneins: Evolutionary differentiation of mollusc metallothioneins. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blindauer, C.A.; Schmid, R. Cytosolic metal handling in plants: Determinants for zinc specificity in metal transporters and metallothioneins. Metallomics 2010, 2, 510–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhai, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Su, C.; Zhang, X. Cucumber Metallothionein-Like 2 (CsMTL2) Exhibits Metal-Binding Properties. Genes 2016, 7, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7120106
Pan Y, Pan Y, Zhai J, Xiong Y, Li J, Du X, Su C, Zhang X. Cucumber Metallothionein-Like 2 (CsMTL2) Exhibits Metal-Binding Properties. Genes. 2016; 7(12):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7120106
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yu, Yanglu Pan, Junpeng Zhai, Yan Xiong, Jinhua Li, Xiaobing Du, Chenggang Su, and Xingguo Zhang. 2016. "Cucumber Metallothionein-Like 2 (CsMTL2) Exhibits Metal-Binding Properties" Genes 7, no. 12: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7120106
APA StylePan, Y., Pan, Y., Zhai, J., Xiong, Y., Li, J., Du, X., Su, C., & Zhang, X. (2016). Cucumber Metallothionein-Like 2 (CsMTL2) Exhibits Metal-Binding Properties. Genes, 7(12), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7120106





