Replicated Risk Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Genes for Nicotine Dependence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Replicated Associations between Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Genes (CHRNs) and Nicotine Dependence/Cigarettes per Day (ND/CPD) and the Expression of Risk Genes in Brain
2.2. Expression Correlation Analysis in Human Brain
2.3. Detection of Chrn mRNA Expression in Mouse Brains
2.4. Cis-Acting Genetic Regulation of Expression Analysis in Human Brain Tissues
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNA) and piRNA Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Replicated Associations between CHRNs and ND/CPD (Table 1)
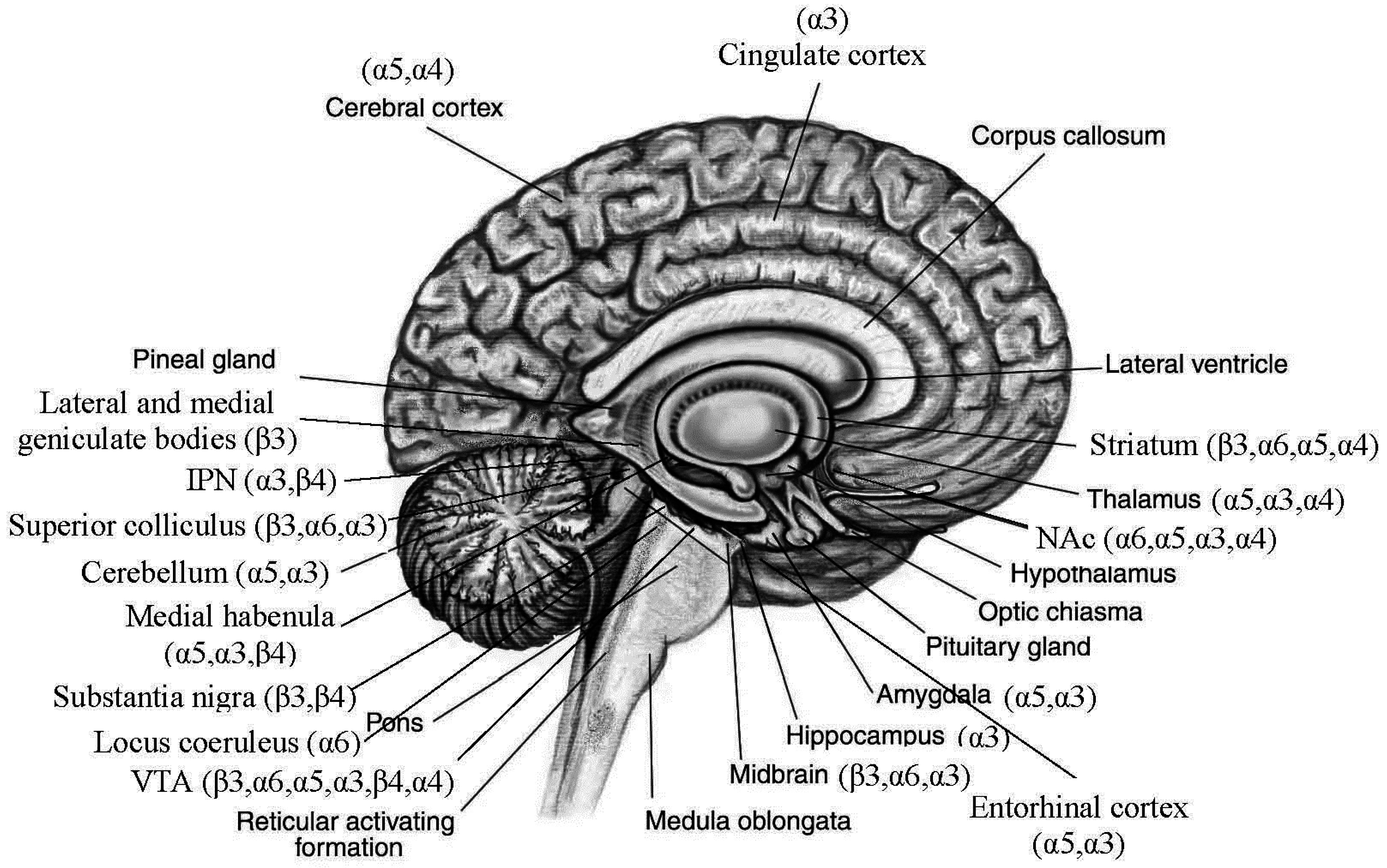
3.2. Distributions of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors (nAChRs) Encoded by the Replicated Risk CHRNs in Brain (Figure 1)
3.3. All Six CHRN Genes Were Expressed in Human Brain and Their Expression Was Correlated with Dopaminergic or GABAergic Expression (Table 2, Tables S1 and S2)
3.4. All Six Chrn Genes Were Expressed in Mouse Brain in Distinct Areas and at Different Levels, a Majority of Which Verified Previous Reports (Table 3)
3.5. The CHRN Variants May Regulate the Expression of CHRN Genes (Table 4)
3.6. Bioinformatics Analysis (Table 5)
3.7. The LncRNAs and piRNAs Related to the Replicated Risk CHRNs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
Abbreviations
| nAChRs | nicotinic acetylcholine receptors |
| CHRNs | nicotinic cholinergic receptor genes |
| ND | nicotine dependence |
| CPD | cigarettes smoked per day |
| FTND | Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence |
| ncRNAs | non-coding RNAs |
| LncRNAs | long non-coding RNAs |
| NAc | nucleus accumbens |
| VTA | ventral tegmental area |
References
- Heatherton, T.F.; Kozlowski, L.T.; Frecker, R.C.; Fagerstrom, K.O. The Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence: A revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. Br. J. Addict. 1991, 86, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessov, C.N.; Martin, N.G.; Statham, D.J.; Todorov, A.A.; Slutske, W.S.; Bucholz, K.K.; Heath, A.C.; Madden, P.A. Defining nicotine dependence for genetic research: Evidence from Australian twins. Psychol. Med. 2004, 34, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, C.R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Chen, X.; Zhong, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Associations of rare nicotinic cholinergic receptor gene variants to nicotine and alcohol dependence. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, P.P.; Dinger, M.E.; Mercer, T.R.; Mattick, J.S. The eukaryotic genome as an RNA machine. Science 2008, 319, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Arai, S.; Song, X.; Reichart, D.; Du, K.; Pascual, G.; Tempst, P.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Glass, C.K.; Kurokawa, R. Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription. Nature 2008, 454, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, G.C.; St Laurent, G., 3rd; Wahlestedt, C. The Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Drug Addiction. Front. Genet. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhu, R.; Deng, Y.; Shao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of long non-coding RNAs of the nucleus accumbens in cocaine-conditioned mice. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, I.A.; Mattick, J.S.; Mehler, M.F. Long non-coding RNAs in nervous system function and disease. Brain Res. 2010, 1338, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, D.; Prasanth, K.V.; Tripathi, V.; Colasse, S.; Nakamura, T.; Xuan, Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Sedel, F.; Jourdren, L.; Coulpier, F.; et al. A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryger, R.; Fan, L.; Wilce, P.A.; Jaquet, V. MALAT-1, a non protein-coding RNA is upregulated in the cerebellum, hippocampus and brain stem of human alcoholics. Alcohol 2012, 46, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelhaugh, S.K.; Lipovich, L.; Blythe, J.; Jia, H.; Kapatos, G.; Bannon, M.J. Mining Affymetrix microarray data for long non-coding RNAs: Altered expression in the nucleus accumbens of heroin abusers. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, R.; Luettich, K.; Heguy, A.; Hackett, N.R.; Harvey, B.G.; Crystal, R.G. Monoallelic up-regulation of the imprinted H19 gene in airway epithelium of phenotypically normal cigarette smokers. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouko, L.A.; Shantikumar, K.; Knezovich, J.; Haycock, P.; Schnugh, D.J.; Ramsay, M. Effect of alcohol consumption on CpG methylation in the differentially methylated regions of H19 and IG-DMR in male gametes: Implications for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivna, S.T.; Beyret, E.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. A novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, G.; Slack, F.J. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, S.R.; Juliano, C.E. Untangling the web: The diverse functions of the PIWI/piRNA pathway. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 632–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.J.; Weiner, M.M.; Lin, H. PIWI proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs in the soma. Nature 2014, 505, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkouche, A.; Grentzinger, T.; Fablet, M.; Armenise, C.; Burlet, N.; Braman, V.; Chambeyron, S.; Vieira, C. Maternally deposited germline piRNAs silence the tirant retrotransposon in somatic cells. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasethupathy, P.; Antonov, I.; Sheridan, R.; Frey, S.; Sander, C.; Tuschl, T.; Kandel, E.R. A role for neuronal piRNAs in the epigenetic control of memory-related synaptic plasticity. Cell 2012, 149, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Banerjee, S.; Zhou, H.; Jammalamadaka, A.; Arcila, M.; Manjunath, B.S.; Kosik, K.S. Identification of piRNAs in the central nervous system. RNA 2011, 17, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Nelson, M.C.; Brandt, J.E.; Wessman, M.; Mahmud, N.; Weller, K.P.; Hoffman, R. Human CD34(+) stem cells express the hiwi gene, a human homologue of the Drosophila gene piwi. Blood 2001, 97, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrat, P.N.; DasGupta, S.; Wang, J.; Theurkauf, W.; Weng, Z.; Rosbash, M.; Waddell, S. Transposition-driven genomic heterogeneity in the Drosophila brain. Science 2013, 340, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Hu, H.Y.; Jiang, X.; Maierhofer, V.; Neb, E.; He, L.; Hu, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; et al. Widespread expression of piRNA-like molecules in somatic tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 6596–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghildiyal, M.; Seitz, H.; Horwich, M.D.; Li, C.; Du, T.; Lee, S.; Xu, J.; Kittler, E.L.; Zapp, M.L.; Weng, Z.; et al. Endogenous siRNAs derived from transposons and mRNAs in Drosophila somatic cells. Science 2008, 320, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharap, A.; Nakka, V.P.; Vemuganti, R. Altered expression of PIWI RNA in the rat brain after transient focal ischemia. Stroke 2011, 42, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.C.; Lin, H. Beyond transposons: The epigenetic and somatic functions of the Piwi-piRNA mechanism. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.E. Multiple brain pathways and receptors underlying tobacco addiction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, P.; Tolu, S.; Valverde, S.; Naude, J. Role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in regulating dopamine neuron activity. Neuroscience 2014, 282C, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, S.R.; Salminen, O.; Laverty, D.C.; Whiteaker, P.; McIntosh, J.M.; Collins, A.C.; Marks, M.J. The subtypes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on dopaminergic terminals of mouse striatum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champtiaux, N.; Han, Z.Y.; Bessis, A.; Rossi, F.M.; Zoli, M.; Marubio, L.; McIntosh, J.M.; Changeux, J.P. Distribution and pharmacology of alpha 6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors analyzed with mutant mice. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drenan, R.M.; Grady, S.R.; Whiteaker, P.; McClure-Begley, T.; McKinney, S.; Miwa, J.M.; Bupp, S.; Heintz, N.; McIntosh, J.M.; Bencherif, M.; et al. In vivo activation of midbrain dopamine neurons via sensitized, high-affinity alpha 6 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron 2008, 60, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, A.; Schulz, R.; Benfante, R.; Battaglioli, E.; Terzano, S.; Clementi, F.; Fornasari, D. Neuronal and extraneuronal expression and regulation of the human alpha5 nicotinic receptor subunit gene. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, O.; Murphy, K.L.; McIntosh, J.M.; Drago, J.; Marks, M.J.; Collins, A.C.; Grady, S.R. Subunit composition and pharmacology of two classes of striatal presynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors mediating dopamine release in mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoli, M.; Moretti, M.; Zanardi, A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Clementi, F.; Gotti, C. Identification of the nicotinic receptor subtypes expressed on dopaminergic terminals in the rat striatum. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8785–8789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gahring, L.C.; Persiyanov, K.; Dunn, D.; Weiss, R.; Meyer, E.L.; Rogers, S.W. Mouse strain-specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression by inhibitory interneurons and astrocytes in the dorsal hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 468, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, D.C.; Xiao, Y.; Nguyen, H.N.; Musachio, J.L.; Davila-Garcia, M.I.; Kellar, K.J. Measuring nicotinic receptors with characteristics of alpha4beta2, alpha3beta2 and alpha3beta4 subtypes in rat tissues by autoradiography. J. Neurochem. 2002, 82, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R.; Kellar, K.J. Nicotinic cholinergic receptors in the rat cerebellum: Multiple heteromeric subtypes. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9258–9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, C.D.; Lu, Q.; Johnson, P.M.; Marks, M.J.; Kenny, P.J. Habenular alpha5 nicotinic receptor subunit signalling controls nicotine intake. Nature 2011, 471, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klink, R.; de Kerchove d’Exaerde, A.; Zoli, M.; Changeux, J.P. Molecular and physiological diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the midbrain dopaminergic nuclei. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quick, M.W.; Ceballos, R.M.; Kasten, M.; McIntosh, J.M.; Lester, R.A. Alpha3beta4 subunit-containing nicotinic receptors dominate function in rat medial habenula neurons. Neuropharmacology 1999, 38, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, R.; Pieri, F.; De Biasi, M. Decreased signs of nicotine withdrawal in mice null for the beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10035–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, A.L.; Mandelkern, M.A.; London, E.D.; Olmstead, R.E.; Farahi, J.; Scheibal, D.; Jou, J.; Allen, V.; Tiongson, E.; Chefer, S.I.; et al. Cigarette smoking saturates brain alpha 4 beta 2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picciotto, M.R.; Zoli, M.; Rimondini, R.; Lena, C.; Marubio, L.M.; Pich, E.M.; Fuxe, K.; Changeux, J.P. Acetylcholine receptors containing the beta2 subunit are involved in the reinforcing properties of nicotine. Nature 1998, 391, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Champtiaux, N.; Gotti, C.; Cordero-Erausquin, M.; David, D.J.; Przybylski, C.; Lena, C.; Clementi, F.; Moretti, M.; Rossi, F.M.; Le Novere, N.; et al. Subunit composition of functional nicotinic receptors in dopaminergic neurons investigated with knock-out mice. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7820–7829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gotti, C.; Moretti, M.; Gaimarri, A.; Zanardi, A.; Clementi, F.; Zoli, M. Heterogeneity and complexity of native brain nicotinic receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, O.; Drapeau, J.A.; McIntosh, J.M.; Collins, A.C.; Marks, M.J.; Grady, S.R. Pharmacology of alpha-conotoxin MII-sensitive subtypes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors isolated by breeding of null mutant mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exley, R.; Clements, M.A.; Hartung, H.; McIntosh, J.M.; Cragg, S.J. Alpha6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors dominate the nicotine control of dopamine neurotransmission in nucleus accumbens. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 2158–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.L.; Yoshikami, D.; McIntosh, J.M. The neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors alpha 4* and alpha 6* differentially modulate dopamine release in mouse striatal slices. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotti, C.; Moretti, M.; Clementi, F.; Riganti, L.; McIntosh, J.M.; Collins, A.C.; Marks, M.J.; Whiteaker, P. Expression of nigrostriatal alpha 6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is selectively reduced, but not eliminated, by beta 3 subunit gene deletion. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Novere, N.; Zoli, M.; Changeux, J.P. Neuronal nicotinic receptor alpha 6 subunit mRNA is selectively concentrated in catecholaminergic nuclei of the rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2428–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Booker, T.K.; Allen, R.S.; Grady, S.R.; Whiteaker, P.; Marks, M.J.; Salminen, O.; Tritto, T.; Butt, C.M.; Allen, W.R.; et al. The beta3 nicotinic receptor subunit: A component of alpha-conotoxin MII-binding nicotinic acetylcholine receptors that modulate dopamine release and related behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11045–11053. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moretti, M.; Vailati, S.; Zoli, M.; Lippi, G.; Riganti, L.; Longhi, R.; Viegi, A.; Clementi, F.; Gotti, C. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes expression during rat retina development and their regulation by visual experience. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.P.; Hartz, S.M.; Agrawal, A.; Almasy, L.; Bennett, S.; Breslau, N.; Bucholz, K.K.; Doheny, K.F.; Edenberg, H.J.; Goate, A.M.; et al. CHRNB3 is more strongly associated with Fagerstrom test for cigarette dependence-based nicotine dependence than cigarettes per day: Phenotype definition changes genome-wide association studies results. Addiction 2012, 107, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Yi, S.G.; Yoon, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Payne, T.J.; Ma, J.Z.; Park, T.; Li, M.D. Significant association of CHRNB3 variants with nicotine dependence in multiple ethnic populations. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccone, N.L.; Saccone, S.F.; Hinrichs, A.L.; Stitzel, J.A.; Duan, W.; Pergadia, M.L.; Agrawal, A.; Breslau, N.; Grucza, R.A.; Hatsukami, D.; et al. Multiple distinct risk loci for nicotine dependence identified by dense coverage of the complete family of nicotinic receptor subunit (CHRN) genes. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2009, 150B, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccone, N.L.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Wang, J.C.; Grucza, R.A.; Breslau, N.; Hatsukami, D.; Johnson, E.O.; Rice, J.P.; Goate, A.M.; Bierut, L.J. Multiple cholinergic nicotinic receptor genes affect nicotine dependence risk in African and European Americans. Genes Brain Behav. 2010, 9, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culverhouse, R.C.; Johnson, E.O.; Breslau, N.; Hatsukami, D.K.; Sadler, B.; Brooks, A.I.; Hesselbrock, V.M.; Schuckit, M.A.; Tischfield, J.A.; Goate, A.M.; et al. Multiple distinct CHRNB3-CHRNA6 variants are genetic risk factors for nicotine dependence in African Americans and European Americans. Addiction 2014, 109, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.O.; Chen, L.S.; Breslau, N.; Hatsukami, D.; Robbins, T.; Saccone, N.L.; Grucza, R.A.; Bierut, L.J. Peer smoking and the nicotinic receptor genes: An examination of genetic and environmental risks for nicotine dependence. Addiction 2010, 105, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoft, N.R.; Corley, R.P.; McQueen, M.B.; Schlaepfer, I.R.; Huizinga, D.; Ehringer, M.A. Genetic association of the CHRNA6 and CHRNB3 genes with tobacco dependence in a nationally representative sample. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartz, S.M.; Short, S.E.; Saccone, N.L.; Culverhouse, R.; Chen, L.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Coon, H.; Han, Y.; Stephens, S.H.; Sun, J.; et al. Increased genetic vulnerability to smoking at CHRNA5 in early-onset smokers. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Surakka, I.; Vink, J.M.; Amin, N.; Geller, F.; Sulem, P.; Rafnar, T.; Esko, T.; Walter, S.; et al. Sequence variants at CHRNB3-CHRNA6 and CYP2A6 affect smoking behavior. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, D.S.; Mermelstein, R.J.; Hedeker, D.; Coon, H.; Cook, E.H.; McMahon, W.M.; Hamil, C.; Dunn, D.; Weiss, R.B. Effect of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes (CHRN) on longitudinal cigarettes per day in adolescents and young adults. Nicot. Tob. Res. 2014, 16, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Chu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X. Association study of 45 candidate genes in nicotine dependence in Han Chinese. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, W.Y.; Park, B.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, L.; Kwon, M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.U.; Shin, H.D.; Kim, D.J. Genetic Association of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 Gene Polymorphisms with Nicotine Dependence Syndrome Scale in Korean Population. Psychiatry Investig. 2014, 11, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobacco and Genetics Consortium Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 441–447.
- Bierut, L.J.; Agrawal, A.; Bucholz, K.K.; Doheny, K.F.; Laurie, C.; Pugh, E.; Fisher, S.; Fox, L.; Howells, W.; Bertelsen, S.; et al. A genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5082–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Z.; Tozzi, F.; Waterworth, D.M.; Pillai, S.G.; Muglia, P.; Middleton, L.; Berrettini, W.; Knouff, C.W.; Yuan, X.; Waeber, G.; et al. Meta-analysis and imputation refines the association of 15q25 with smoking quantity. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, D.B.; Reginsson, G.W.; Gaddis, N.C.; Chen, X.; Saccone, N.L.; Lutz, S.M.; Qaiser, B.; Sherva, R.; Steinberg, S.; Zink, F.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis reveals common splice site acceptor variant in CHRNA4 associated with nicotine dependence. Transl. Psychiatry 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.S.; Park, J.Y.; Zabaleta, J.; Moody-Thomas, S.; Sothern, M.S.; Chen, T.; Evans, D.E.; Lin, H.Y. Role of nicotine dependence on the relationship between variants in the nicotinic receptor genes and risk of lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Geller, F.; Sulem, P.; Rafnar, T.; Wiste, A.; Magnusson, K.P.; Manolescu, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Stefansson, H.; Ingason, A.; et al. A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature 2008, 452, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrettini, W.; Yuan, X.; Tozzi, F.; Song, K.; Francks, C.; Chilcoat, H.; Waterworth, D.; Muglia, P.; Mooser, V. Alpha-5/alpha-3 nicotinic receptor subunit alleles increase risk for heavy smoking. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etter, J.F.; Hoda, J.C.; Perroud, N.; Munafo, M.; Buresi, C.; Duret, C.; Neidhart, E.; Malafosse, A.; Bertrand, D. Association of genes coding for the alpha-4, alpha-5, beta-2 and beta-3 subunits of nicotinic receptors with cigarette smoking and nicotine dependence. Addict. Behav. 2009, 34, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabzuni, D.; Ryten, M.; Walker, R.; Smith, C.; Imran, S.; Ramasamy, A.; Weale, M.E.; Hardy, J. Quality control parameters on a large dataset of regionally dissected human control brains for whole genome expression studies. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzen, E.L.; Ge, D.; Cronin, K.D.; Maia, J.M.; Shianna, K.V.; Gabriel, W.N.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.A.; Hulette, C.M.; Denny, T.N.; Goldstein, D.B. Tissue-specific genetic control of splicing: Implications for the study of complex traits. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Taylor, J.A. SNPinfo: Integrating GWAS and candidate gene information into functional SNP selection for genetic association studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W600–W605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Pritchard, B.; Rios, D.; Chen, Y.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. Deriving the consequences of genomic variants with the Ensembl API and SNP Effect Predictor. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2069–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc Hum. Genet. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.C.; Taylor, J.; Elnitski, L.; Chiaromonte, F.; Miller, W.; Hardison, R.C. Evaluation of regulatory potential and conservation scores for detecting cis-regulatory modules in aligned mammalian genome sequences. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Cassarino, T.G.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkel, J.M. Visiting “noncodarnia“. Biotechniques 2013, 54, 301, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C.; et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Sunkin, S.M.; Mehler, M.F.; Mattick, J.S. Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Luo, X. Long non-coding RNAs in psychiatric disorders. Psychiatric Genet. 2016, 26, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sai Lakshmi, S.; Agrawal, S. piRNABank: A web resource on classified and clustered Piwi-interacting RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D173–D177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierut, L.J.; Stitzel, J.A.; Wang, J.C.; Hinrichs, A.L.; Grucza, R.A.; Xuei, X.; Saccone, N.L.; Saccone, S.F.; Bertelsen, S.; Fox, L.; et al. Variants in nicotinic receptors and risk for nicotine dependence. Am. J. Psychiatry 2008, 165, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierut, L.J.; Madden, P.A.; Breslau, N.; Johnson, E.O.; Hatsukami, D.; Pomerleau, O.F.; Swan, G.E.; Rutter, J.; Bertelsen, S.; Fox, L.; et al. Novel genes identified in a high-density genome wide association study for nicotine dependence. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.D. Identifying susceptibility loci for nicotine dependence: 2008 update based on recent genome-wide linkage analyses. Hum. Genet. 2008, 123, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, N.; Gu, F.; Chatterjee, N.; Sheng-Chih, J.; Yu, K.; Yeager, M.; Chen, C.; Jacobs, K.; Wheeler, W.; Landi, M.T.; et al. Genome-wide and candidate gene association study of cigarette smoking behaviors. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccone, S.F.; Hinrichs, A.L.; Saccone, N.L.; Chase, G.A.; Konvicka, K.; Madden, P.A.; Breslau, N.; Johnson, E.O.; Hatsukami, D.; Pomerleau, O.; et al. Cholinergic nicotinic receptor genes implicated in a nicotine dependence association study targeting 348 candidate genes with 3713 SNPs. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Cruchaga, C.; Saccone, N.L.; Bertelsen, S.; Liu, P.; Budde, J.P.; Duan, W.; Fox, L.; Grucza, R.A.; Kern, J.; et al. Risk for nicotine dependence and lung cancer is conferred by mRNA expression levels and amino acid change in CHRNA5. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherva, R.; Wilhelmsen, K.; Pomerleau, C.S.; Chasse, S.A.; Rice, J.P.; Snedecor, S.M.; Bierut, L.J.; Neuman, R.J.; Pomerleau, O.F. Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism in neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha 5 (CHRNA5) with smoking status and with ‘pleasurable buzz’ during early experimentation with smoking. Addiction 2008, 103, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskitalo, K.; Broms, U.; Heliovaara, M.; Ripatti, S.; Surakka, I.; Perola, M.; Pitkaniemi, J.; Peltonen, L.; Aromaa, A.; Kaprio, J. Association of serum cotinine level with a cluster of three nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes (CHRNA3/CHRNA5/CHRNB4) on chromosome 15. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4007–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.B.; Baker, T.B.; Cannon, D.S.; von Niederhausern, A.; Dunn, D.M.; Matsunami, N.; Singh, N.A.; Baird, L.; Coon, H.; McMahon, W.M.; et al. A candidate gene approach identifies the CHRNA5-A3-B4 region as a risk factor for age-dependent nicotine addiction. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, I.R.; Hoft, N.R.; Collins, A.C.; Corley, R.P.; Hewitt, J.K.; Hopfer, C.J.; Lessem, J.M.; McQueen, M.B.; Rhee, S.H.; Ehringer, M.A. The CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster variability as an important determinant of early alcohol and tobacco initiation in young adults. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrettini, W.H.; Doyle, G.A. The CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene cluster in nicotine addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freathy, R.M.; Ring, S.M.; Shields, B.; Galobardes, B.; Knight, B.; Weedon, M.N.; Smith, G.D.; Frayling, T.M.; Hattersley, A.T. A common genetic variant in the 15q24 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene cluster (CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4) is associated with a reduced ability of women to quit smoking in pregnancy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2922–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Marchand, L.; Derby, K.S.; Murphy, S.E.; Hecht, S.S.; Hatsukami, D.; Carmella, S.G.; Tiirikainen, M.; Wang, H. Smokers with the CHRNA lung cancer-associated variants are exposed to higher levels of nicotine equivalents and a carcinogenic tobacco-specific nitrosamine. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9137–9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.G.; Ge, D.; Zhu, G.; Kong, X.; Shianna, K.V.; Need, A.C.; Feng, S.; Hersh, C.P.; Bakke, P.; Gulsvik, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Identification of two major susceptibility loci. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, G.; Li, P.; Esch, C.; Hsu, S.; Goate, A.M.; Steinbach, J.H. Functional characterization improves associations between rare non-synonymous variants in CHRNB4 and smoking behavior. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Niu, T.; Xing, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Peng, S.; Wang, L.; Laird, N. A common haplotype of the nicotine acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 subunit gene is associated with vulnerability to nicotine addiction in men. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.D.; Beuten, J.; Ma, J.Z.; Payne, T.J.; Lou, X.Y.; Garcia, V.; Duenes, A.S.; Crews, K.M.; Elston, R.C. Ethnic- and gender-specific association of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha4 subunit gene (CHRNA4) with nicotine dependence. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccone, S.F.; Pergadia, M.L.; Loukola, A.; Broms, U.; Montgomery, G.W.; Wang, J.C.; Agrawal, A.; Dick, D.M.; Heath, A.C.; Todorov, A.A.; et al. Genetic linkage to chromosome 22q12 for a heavy-smoking quantitative trait in two independent samples. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiger, J.S.; Haberstick, B.C.; Schlaepfer, I.; Collins, A.C.; Corley, R.P.; Crowley, T.J.; Hewitt, J.K.; Hopfer, C.J.; Lessem, J.; McQueen, M.B.; et al. The neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit genes (CHRNA6 and CHRNB3) are associated with subjective responses to tobacco. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, S.; Chao, H.H.; Li, C.S. Resting-State Functional Connectivity of the Locus Coeruleus in Humans: In Comparison with the Ventral Tegmental Area/Substantia Nigra Pars Compacta and the Effects of Age. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 3413–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Risch, E.; Deng, Q.; Biglia, N.; Picardo, E.; Katsaros, D.; Yu, H. An insulin-like growth factor-II intronic variant affects local DNA conformation and ovarian cancer survival. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2024–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Q.; Katsaros, D.; Mayne, S.T.; Risch, H.A.; Mu, L.; Canuto, E.M.; Gregori, G.; et al. Association of large noncoding RNA HOTAIR expression and its downstream intergenic CpG island methylation with survival in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Katsaros, D.; Mayne, S.T.; Risch, H.A.; Benedetto, C.; Canuto, E.M.; Yu, H. Functional study of risk loci of stem cell-associated gene lin-28B and associations with disease survival outcomes in epithelial ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.S.; Sinha, R. Inhibitory control and emotional stress regulation: Neuroimaging evidence for frontal-limbic dysfunction in psycho-stimulant addiction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, J.S.; Li, C.S. A cerebellar thalamic cortical circuit for error-related cognitive control. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Ide, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Sinha, R.; Li, C.S. Conflict anticipation in alcohol dependence—A model-based fMRI study of stop signal task. Neuroimage Clin. 2015, 8, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, J.E.; Rhodes, C.H.; Thirtamara-Rajamani, K.; Smith, R.M. Genetic influences on nicotinic alpha5 receptor (CHRNA5) CpG methylation and mRNA expression in brain and adipose tissue. Genes Environ. 2015, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, D.B.; Wang, J.C.; Gaddis, N.C.; Levy, J.L.; Saccone, N.L.; Stitzel, J.A.; Goate, A.; Bierut, L.J.; Johnson, E.O. A multiancestry study identifies novel genetic associations with CHRNA5 methylation in human brain and risk of nicotine dependence. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5940–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Spiegel, N.; Bertelsen, S.; Le, N.; McKenna, N.; Budde, J.P.; Harari, O.; Kapoor, M.; Brooks, A.; Hancock, D.; et al. Cis-regulatory variants affect CHRNA5 mRNA expression in populations of African and European ancestry. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.M.; Guttman, M.; Huarte, M.; Garber, M.; Raj, A.; Rivea Morales, D.; Thomas, K.; Presser, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; van Oudenaarden, A.; et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Wahlestedt, C. Regulatory roles of natural antisense transcripts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas, V.E.; Zaphiropoulos, P.G. Neighboring gene regulation by antisense long non-coding RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3251–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, N.C.; Tomoda, T.; Cooper, M.; Dietz, G.; Hatten, M.E. Mice that lack astrotactin have slowed neuronal migration. Development 2002, 129, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| SNP | Gene | p | Ref. | p | Ref. | p | Ref. | p | Ref. | p | Ref. | p | Ref. | p | Ref. | p | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10958725 | CHRNB3-A6 | 3.1 × 10−8 | [54] | 4.7 × 10−3 | [55] | 3.6 × 10−5 | [55] | ||||||||||
| rs10958726 | CHRNB3-A6 | 1.2 × 10−7 | [54] | 9.6 × 10−5 | [56] | 5.7 × 10−3 | [57] | 1.1 × 10−3 | [57] | 1.1 × 10−2 | [55] | 1.4 × 10−5 | [55] | ||||
| rs13273442 | CHRNB3-A6 | 1.4 × 10−7 | [54] | 2.0 × 10−2 | [58] | 1.4 × 10−3 | [58] | 3.0 × 10−2 | [58] | ||||||||
| rs4736835 | CHRNB3-A6 | 3.0 × 10−8 | [54] | 6.0 × 10−3 | [55] | 6.2 × 10−3 | [57] | ||||||||||
| rs1955186 | CHRNB3-A6 | 8.3 × 10−5 | [56] | 5.4 × 10−3 | [57] | 1.1 × 10−2 | [57] | ||||||||||
| rs1955185 | CHRNB3-A6 | 4.6 × 10−8 | [54] | 1.0 × 10−4 | [56] | 1.1 × 10−5 | [55] | 5.4 × 10−3 | [57] | 1.2 × 10−3 | [57] | ||||||
| rs13277254 | CHRNB3-A6 | 4.0 × 10−3 | [59] | 4.0 × 10−5 | [56] | 7.8 × 10−4 | [57] | 6.3 × 10−4 | [60] | ||||||||
| rs13277524 | CHRNB3-A6 | 6.0 × 10−5 | [56] | 3.8 × 10−3 | [57] | 7.4 × 10−4 | [57] | ||||||||||
| rs6474412 | CHRNB3-A6 | 1.1 × 10−4 | [56] | 5.6 × 10−3 | [57] | 1.0 × 10−3 | [61] | 8.7 × 10−3 | [55] | 2.1 × 10−5 | [55] | * 1.7 × 10−4 | [62] | * 2.6 × 10−5 | [62] | * 8.0 × 10−3 | [63] |
| rs6474413 | CHRNB3-A6 | 3.6 × 10−8 | [54] | 6.3 × 10−5 | [56] | 9.3 × 10−4 | [57] | ||||||||||
| rs7004381 | CHRNB3-A6 | 9.9 × 10−8 | [54] | 3.9 × 10−2 | [60] | 3.1 × 10−3 | [57] | ||||||||||
| rs4950 | CHRNB3-A6 | 9.5 × 10−8 | [54] | 1.0 × 10−4 | [56] | 1.4 × 10−3 | [57] | 7.0 × 10−3 | [60] | 1.1 × 10−5 | [55] | ||||||
| rs13280604 | CHRNB3-A6 | 1.0 × 10−7 | [54] | 6.0 × 10−3 | [60] | 1.4 × 10−5 | [55] | * 1.2 × 10−4 | [62] | * 2.7 × 10−5 | [62] | ||||||
| rs4952 | CHRNB3-A6 | 4.1 × 10−3 | [56] | 1.1 × 10−2 | [57] | 1.4 × 10−3 | [57] | 2.0 × 10−2 | [58] | ||||||||
| rs4954 | CHRNB3-A6 | 4.3 × 10−7 | [64] | 6.0 × 10−3 | [65] | 4.1 × 10−3 | [57] | ||||||||||
| rs16969968 | CHRNA5-A3-B4 | 1.0 × 10−2 | [59] | 1.3 × 10−4 | [56] | * 2.4 × 10−69 | [62] | * 5.6 × 10−72 | [66] | * 9.0 × 10−4 | [67] | * 4.3 × 10−65 | [68] | 5.1 × 10−17 | [69] | ||
| rs1051730 | CHRNA5-A3-B4 | 2.0 × 10−4 | [56] | 2.0 × 10−3 | [70] | * 5.8 × 10−44 | [68] | * 2.8 × 10−73 | [66] | * 1.0 × 10−3 | [67] | * 1.7 × 10−66 | [68] | * 6.0 × 10−20 | [71] | 4.3 × 10−17 | [69] |
| rs6495308 | CHRNA5-A3-B4 | 1.9 × 10−3 | [56] | * 6.9 × 10−5 | [72] | 4.8 × 10−3 | [56] | 1.7 × 10−7 | [69] | ||||||||
| rs2236196 | CHRNA4 | 3.1 × 10−7 | [64] | 2.0 × 10−2 | [73] | 5.0 × 10−4 | [57] | 4.4 × 10−4 | [57] | 2.7 × 10−2 | [69] |
| Genes | CHRNB3 | CHRNA6 | CHRNA5 | CHRNA3 | CHRNB4 | CHRNA4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRD1 | SNIG | PUTM,TCTX | FCTX,TCTX | FCTX,THAL | ||
| DRD2 | SNIG,TCTX | PUTM,SNIG,TCTX,THAL | FCTX,HIPP,TCTX,THAL | CRBL,FCTX | CRBL,OCTX,SNIG,TCTX,THAL | |
| DRD3 | FCTX | PUTM | THAL | FCTX | FCTX,OCTX | |
| DRD4 | FCTX | THAL | FCTX,TCTX | FCTX,HIPP,OCTX,PUTM,TCTX | ||
| DRD5 | WHMT | THAL | THAL | FCTX,THAL,WHMT | CRBL,FCTX,HIPP,SNIG,WHMT | THAL |
| TH | SNIG,TCTX,WHMT | SNIG,TCTX | FCTX,TCTX | CRBL,FCTX,OCTX | CRBL,SNIG | |
| GABRA1 | SNIG | SNIG,THAL | SNIG,THAL | CRBL,THAL | FCTX | FCTX,HIPP,MEDU,SNIG,THAL |
| GABRA2 | OCTX | MEDU,OCTX,PUTM,THAL | CRBL,MEDU | FCTX,MEDU,TCTX,THAL | FCTX,MEDU | OCTX,THAL |
| GABRA3 | OCTX,SNIG | MEDU,OCTX,SNIG,THAL | MEDU,SNIG,THAL | CRBL,THAL | CRBL,FCTX,HIPP,OCTX,PUTM,SNIG,TCTX,THAL | |
| GABRA4 | FCTX,OCTX,SNIG,THAL | MEDU,OCTX,PUTM,SNIG,THAL,WHMT | CRBL,MEDU,THAL | FCTX,MEDU,TCTX,THAL,WHMT | FCTX,MEDU,TCTX | CRBL,FCTX,HIPP,SNIG,THAL |
| GABRA5 | OCTX | MEDU,OCTX,THAL | MEDU,THAL | MEDU,THAL | CRBL | CRBL,FCTX,OCTX,THAL |
| GABRA6 | CRBL | |||||
| GABRB1 | FCTX,OCTX,PUTM,SNIG | MEDU,PUTM,SNIG,THAL | CRBL,MEDU,SNIG | FCTX,OCTX,TCTX | FCTX,TCTX | OCTX,SNIG |
| GABRB2 | SNIG | SNIG,THAL | CRBL,THAL | CRBL,FCTX,PUTM,TCTX,THAL | FCTX,TCTX | FCTX,HIPP,MEDU,THAL |
| GABRB3 | OCTX,SNIG | MEDU,OCTX,SNIG,THAL | MEDU,THAL | MEDU,TCTX,THAL | MEDU,TCTX | CRBL,FCTX,OCTX,SNIG,THAL |
| GABRD | WHMT | THAL | THAL | CRBL,PUTM,THAL,WHMT | FCTX,HIPP,MEDU,THAL | |
| GABRE | THAL | MEDU | ||||
| GABRG1 | MEDU | CRBL,MEDU | MEDU,OCTX | |||
| GABRG2 | OCTX,SNIG,WHMT | SNIG,THAL | THAL | CRBL,TCTX,THAL | TCTX | FCTX,HIPP,MEDU,SNIG,THAL |
| GABRG3 | FCTX | MEDU,PUTM | CRBL | TCTX | FCTX,TCTX | CRBL,FCTX,MEDU |
| GABRP | FCTX,PUTM | FCTX | CRBL,FCTX,PUTM | |||
| GABRQ | HIPP | THAL | THAL | HIPP,THAL | CRBL | CRBL,MEDU,PUTM,THAL |
| GABRR2 | THAL |
| Gene | Location (Chr, Mb) | Whole Brain | Cortex | Striatum | NAc | Hippocampus | Amygdala | Midbrain | VTA | Cerebellum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrnb3 | Chr8: 28.504645 | 7.85 | 7.11 | 7.25 | 7.65 | |||||
| Chrna6 | Chr8: 28.513939 | 8.73 | 7.79 | 7.13 | 10.37 | 8.97 | 7.23 | |||
| Chrna5 | Chr9: 54.852890 | 7.22 | 8.44 | 7.45 | ||||||
| Chrna3 | Chr9: 54.860390 | 9.35 | 7.22 | 8.32 | 7.60 | 7.61 | ||||
| Chrnb4 | Chr9: 54.877893 | 7.23 | 7.58 | 8.65 | 8.18 | 8.23 | ||||
| Chrna4 | Chr2: 180.759407 | 9.48 | 10.05 | 9.02 | 8.29 | 9.95 | 10.73 | 9.64 | 8.71 | 8.30 |
| SNPs | Target gene | Cerebellar Cortex | Frontal Cortex | Temporal Cortex | Occipital Cortex | Putamen | Thalamus | Hippo-Campus | Substantia Nigra | Intralobular White Matter | Medulla |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10958725 | CHRNB3 | 0.015 | 0.026 | ||||||||
| rs10958725 | CHRNA6 | 0.042 | 0.027 | ||||||||
| rs10958726 | CHRNB3 | 0.020 | 0.028 | ||||||||
| rs10958726 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.031 | ||||||||
| rs13273442 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs13273442 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs4736835 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs4736835 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs1955186 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs1955186 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs1955185 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs1955185 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs13277254 | CHRNB3 | 0.021 | 0.031 | ||||||||
| rs13277254 | CHRNA6 | 0.042 | 0.033 | ||||||||
| rs13277524 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs13277524 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs6474412 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs6474412 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs6474413 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs6474413 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs7004381 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs7004381 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs4950 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs4950 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs13280604 | CHRNB3 | 0.022 | 0.030 | ||||||||
| rs13280604 | CHRNA6 | 0.043 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| rs16969968 | CHRNA5 | 0.034 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 9.3 × 10−5 | 5.1 × 10−6 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 2.2 × 10−3 | 5.9 × 10−5 | 1.8 × 10−5 | 0.016 | 1.6 × 10−4 |
| rs16969968 | CHRNA3 | 8.9 × 10−4 | |||||||||
| rs1051730 | CHRNA5 | 0.034 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 9.3 × 10−5 | 5.1 × 10−6 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 2.2 × 10−3 | 5.9 × 10−5 | 1.8 × 10−5 | 0.016 | 1.6 × 10−4 |
| rs1051730 | CHRNA3 | 8.9 × 10−4 | |||||||||
| rs6495308 | CHRNA5 | 5.1 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−4 | 4.2 × 10−3 | 8.4 × 10−3 | 2.8 × 10−4 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 7.3 × 10−3 | 3.4 × 10−3 | ||
| rs6495308 | CHRNA3 | 2.7 × 10−3 | 0.013 | ||||||||
| rs6495308 | CHRNB4 | 0.025 | 0.014 | ||||||||
| rs2236196 | CHRNA4 | 0.044 | 0.035 |
| SNP | Chr | Position | Location | Allele Frequency | 2nd RNA Alteration | Bioinformatics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Build 37) | Allele | European | African | Asian | |||||
| rs10958725 | 8 | 42524584 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | G | 0.822 | 0.239 | 0.792 | Highly significant | -- |
| rs10958726 | 8 | 42535909 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | T | 0.807 | 0.328 | 0.816 | no | -- |
| rs13273442 | 8 | 42544017 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | G | 0.825 | 0.35 | 0.826 | Significant | -- |
| rs4736835 | 8 | 42547033 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | C | 0.825 | 0.35 | 0.826 | Significant | LncRNA |
| rs1955186 | 8 | 42549491 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | C | 0.833 | 0.326 | 0.875 | Mild | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs1955185 | 8 | 42549647 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | T | 0.822 | 0.233 | 0.836 | no | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs13277254 | 8 | 42549982 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | A | 0.833 | 0.435 | 0.875 | no | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs13277524 | 8 | 42550057 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | T | 0.833 | 0.326 | 0.875 | Significant | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs6474412 | 8 | 42550498 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | T | 0.81 | 0.309 | 0.824 | Significant | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs6474413 | 8 | 42551064 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | T | 0.833 | 0.235 | 0.875 | no | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs7004381 | 8 | 42551161 | 5′ to CHRNB3 | G | 0.825 | 0.339 | 0.826 | Mild | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs4950 | 8 | 42552633 | 5′UTR of CHRNB3 | A | 0.828 | 0.182 | 0.826 | no | TFBS, LncRNA |
| rs13280604 | 8 | 42559586 | Intron 1 of CHRNB3 | A | 0.825 | 0.178 | 0.826 | no | LncRNA |
| rs4952 | 8 | 42587065 | Exon 6 of CHRNB3 | C | 0.983 | 1 | 1 | Highly significant | -- |
| rs4954 | 8 | 42587796 | Intron 6 of CHRNB3 | A | 0.973 | 0.773 | 0.885 | no | chromatin |
| rs16969968 (Asp398Asn) | 15 | 78882925 | Exon 5 of CHRNA5 | G | 0.587 | 1 | 0.982 | Highly significant | splicing,tolerated, benign,conservative |
| rs1051730 | 15 | 78894339 | Exon 7 of CHRNA3 | G | 0.608 | 0.876 | 0.982 | no | CpG |
| rs6495308 | 15 | 78907656 | Intron 6 of CHRNA3 | T | 0.792 | 0.661 | 0.244 | no | -- |
| rs2236196 | 20 | 61977556 | 3′UTR of CHRNA4 | A | 0.744 | 0.458 | 0.889 | no | chromatin |
| LncRNA name (NCBI Gene) | Alias | Length (nt) | Distance to risk gene | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XR_949716.1 | LOC105379396 | 21,176 | Covering CHRNB3 | antisense LncRNA |
| XR_932509.1 | LOC105370913 | 35,230 | 37,240 bp to CHRNB4 | intergenic sense LincRNA |
| NR_110634.1 | LOC100130587 | 11,190 | Overlap with exon 1 of CHRNA4 | antisense LncRNA |
| Replicable genes | Position (Build 37) | Number of piRNAs | Length (nt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHRNB3 | chr8:42552561–42592208 | 42 | 26–31 |
| CHRNA6 | chr8:42607762–42623618 | 8 | 29–31 |
| CHRNA5 | chr15:78857905–78886459 | 17 | 28–31 |
| CHRNA3 | chr15:78887650:78913321 | 20 | 26–31 |
| CHRNB4 | Chr15:78916635:78933586 | 4 | 27–29 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, L.; Garcia-Milian, R.; Guo, X.; Zhong, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Kang, L.; Lu, L.; et al. Replicated Risk Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Genes for Nicotine Dependence. Genes 2016, 7, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7110095
Zuo L, Garcia-Milian R, Guo X, Zhong C, Tan Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Wang X, Kang L, Lu L, et al. Replicated Risk Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Genes for Nicotine Dependence. Genes. 2016; 7(11):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7110095
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Lingjun, Rolando Garcia-Milian, Xiaoyun Guo, Chunlong Zhong, Yunlong Tan, Zhiren Wang, Jijun Wang, Xiaoping Wang, Longli Kang, Lu Lu, and et al. 2016. "Replicated Risk Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Genes for Nicotine Dependence" Genes 7, no. 11: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7110095
APA StyleZuo, L., Garcia-Milian, R., Guo, X., Zhong, C., Tan, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Wang, X., Kang, L., Lu, L., Chen, X., Li, C.-S. R., & Luo, X. (2016). Replicated Risk Nicotinic Cholinergic Receptor Genes for Nicotine Dependence. Genes, 7(11), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7110095







